The Black Forest (german: Schwarzwald ) is a large
forested
mountain range in the
state of
Baden-Württemberg in southwest
Germany, bounded by the
Rhine Valley
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, source ...
to the west and south and close to the borders with
France and
Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
.
It is the source of the
Danube and
Neckar
The Neckar () is a river in Germany, mainly flowing through the southwestern state of Baden-Württemberg, with a short section through Hesse. The Neckar is a major right tributary of the Rhine. Rising in the Schwarzwald-Baar-Kreis near Schwenn ...
rivers.
Its highest peak is the
Feldberg with an
elevation of above
sea level. Roughly oblong in shape, with a length of and breadth of up to , it has an area of about 6,009 km
2 (2,320 sq mi).
Historically, the area was known for forestry and the mining of
ore deposits, but tourism has now become the primary industry, accounting for around 300,000 jobs. There are
several ruined military fortifications dating back to the 17th century.
History



In ancient times, the Black Forest was known as , after the Celtic deity,
Abnoba. In Roman times (
Late antiquity), it was given the name ("Marcynian Forest", from the Germanic word ''marka'' = "border"). The Black Forest probably represented the border area of the
Marcomanni ("border people") who were settled east of the Roman . They, in turn, were part of the Germanic tribe of
Suebi
The Suebi (or Suebians, also spelled Suevi, Suavi) were a large group of Germanic peoples originally from the Elbe river region in what is now Germany and the Czech Republic. In the early Roman era they included many peoples with their own names ...
, who subsequently gave their name to the historic state of
Swabia
Swabia ; german: Schwaben , colloquially ''Schwabenland'' or ''Ländle''; archaic English also Suabia or Svebia is a cultural, historic and linguistic region in southwestern Germany.
The name is ultimately derived from the medieval Duchy of ...
. With the exception of Roman settlements on the perimeter (e.g. the baths in Badenweiler, and mines near Badenweiler and Sulzburg) and the construction of the Roman road of
Kinzigtalstraße, the colonization of the Black Forest was not carried out by the Romans but by the
Alemanni
The Alemanni or Alamanni, were a confederation of Germanic tribes
*
*
*
on the Upper Rhine River. First mentioned by Cassius Dio in the context of the campaign of Caracalla of 213, the Alemanni captured the in 260, and later expanded into pres ...
. They settled and first colonized the valleys, crossing the old settlement boundary, the so-called "red sandstone border", for example, from the region of
Baar. Soon afterwards, increasingly higher areas and adjacent forests were colonized, so that by the end of the 10th century, the first settlements could be found in the red (bunter) sandstone region. These include, for example,
Rötenbach, which was first mentioned in 819.
Some of the uprisings (including the
Bundschuh movement) that preceded the 16th century
German Peasants' War
The German Peasants' War, Great Peasants' War or Great Peasants' Revolt (german: Deutscher Bauernkrieg) was a widespread popular revolt in some German-speaking areas in Central Europe from 1524 to 1525. It failed because of intense oppositio ...
, originated in the Black Forest. Further peasant unrest, in the shape of the
saltpetre uprisings, took place over the next two centuries in
Hotzenwald.
Remnants of
military fortifications dating from the 17th and 18th centuries can be found in the Black Forest, especially on the mountain passes. Examples include the multiple baroque fieldworks of
Margrave Louis William of Baden-Baden
Louis William, Margrave of Baden-Baden (german: links=no, Ludwig Wilhelm von Baden-Baden; 8 April 1655 – 4 January 1707) was the ruling Margrave of Baden-Baden in Germany and chief commander of the Imperial army. He was also known as ''Türkenl ...
or individual defensive positions such as the
Alexanderschanze
The Alexanderschanze (Alexander's Redoubt) is a mountain pass, , on the B 28 federal road at Freudenstadt in the Northern Black Forest in southern Germany. In the vicinity is also a fortification and hotel of the same name.
Pass
The Alexanders ...
(Alexander's Redoubt), the
Röschenschanze and the
Schwedenschanze
There are numerous prehistorical and early historical ringworks and fortification ramparts in Central Europe that have erroneously, usually colloquially, been given the name Schwedenschanze, which means "Swedish redoubt", a ''schanze'' being a h ...
(
Swedish Redoubt).
Originally,
the Black Forest was a mixed forest of deciduous trees and firs. At the higher elevations
spruce
A spruce is a tree of the genus ''Picea'' (), a genus of about 35 species of coniferous evergreen trees in the family Pinaceae, found in the northern temperate and boreal (taiga) regions of the Earth. ''Picea'' is the sole genus in the subfami ...
also grew. In the middle of the 19th century, the Black Forest was almost completely deforested by intensive forestry and was subsequently replanted, mostly with spruce
monocultures.
In 1990, extensive damage to the forest was caused by a
series of windstorms. On 26 December 1999,
Hurricane Lothar
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depend ...
raged across the Black Forest and caused even greater damage, especially to the spruce monocultures. As had happened following the 1990 storms, large quantities of fallen logs were kept in provisional wet-storage areas for years. The effects of the storm are demonstrated by the
Lothar Path, a forest educational and adventure trail at the nature centre in
Ruhestein
The Ruhestein is a mountain pass () between the Murg valley and the Acher valley in the Northern Black Forest. The border between the old Grand Duchy of Baden and the Kingdom of Württemberg ran over the pass, a large sandstone erratic marking t ...
on a highland timber forest of about 10 hectares that was destroyed by a hurricane. Several areas of storm damage, both large and small, were left to nature and have developed today into a natural mixed forest again.
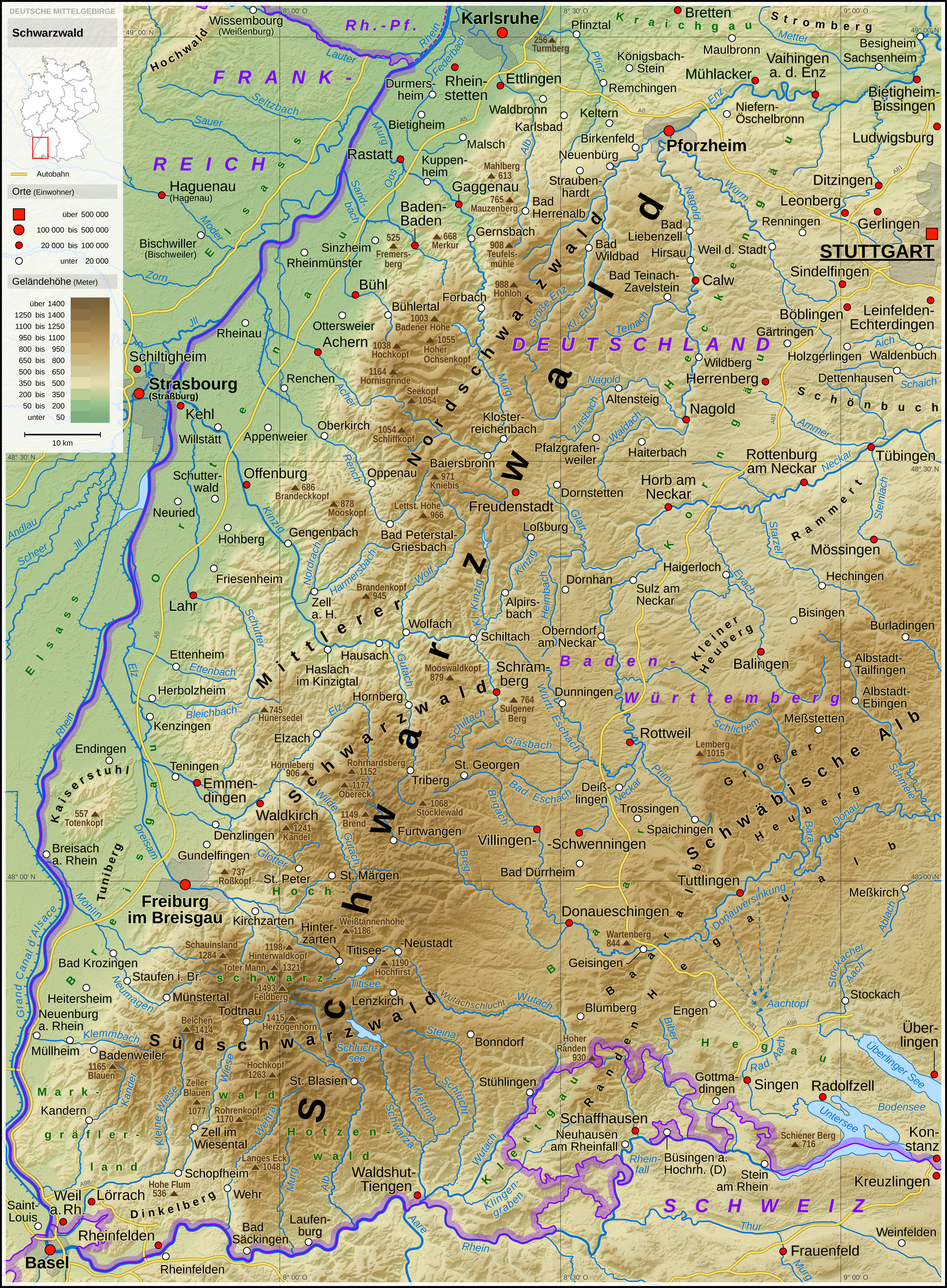
Geography

The Black Forest stretches from the
High Rhine in the south to the
Kraichgau in the north. In the west it is bounded by the
Upper Rhine Plain (which, from a natural region perspective, also includes the low chain of foothills); in the east it transitions to the
Gäu In the south German language (of the Alemannic-speaking area, or in Switzerland), a ''gäu'' landscape (''gäulandschaft'') refers to an area of open, level countryside. These regions typically have fertile soils resulting from depositions of loe ...
,
Baar and hill country west of the
Klettgau. From north to south, the Black Forest extends for over , attaining a width of up to in the south and in the north. The Black Forest is the highest part of the
South German Scarplands
The South German Scarplands is a geological and geomorphological natural region or landscape in Switzerland and the south German states of Bavaria and Baden-Württemberg. The landscape is characterised by escarpments.
It is variously referred to ...
, and much of it is densely wooded, a fragment of the
Hercynian Forest of antiquity.
Administratively, the Black Forest belongs completely to the state of Baden-Württemberg and comprises the cities of
Freiburg,
Pforzheim and
Baden-Baden as well as the following districts (''
Kreise''). In the north:
Enz,
Rastatt and
Calw; in the middle:
Freudenstadt,
Ortenaukreis and
Rottweil
Rottweil (; Alemannic: ''Rautweil'') is a town in southwest Germany in the state of Baden-Württemberg. Rottweil was a free imperial city for nearly 600 years.
Located between the Black Forest and the Swabian Alps, Rottweil has nearly 25,000 in ...
; in the south:
Emmendingen,
Schwarzwald-Baar,
Breisgau-Hochschwarzwald
Breisgau-Hochschwarzwald (french: Arrondissement de Brisgau-Haute-Forêt-Noire) is a (district) in the southwest of Baden-Württemberg, Germany. Fifty towns and municipalities with 133 settlements lie within the district. The district itself belon ...
,
Lörrach and
Waldshut.
Natural regions
The
natural regions of the Black Forest are separated by various features.
Geomorphologically
Geomorphology (from Ancient Greek: , ', "earth"; , ', "form"; and , ', "study") is the scientific study of the origin and evolution of topographic and bathymetric features created by physical, chemical or biological processes operating at or n ...
, the main division is between the gentle eastern slopes with their mostly rounded hills and broad plateaux (so-called
Danubian
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
relief, especially prominent in the north and east on the Bunter Sandstone) and the deeply incised, steeply falling terrain in the west that drops into the
Upper Rhine Graben
The Upper Rhine Plain, Rhine Rift Valley or Upper Rhine Graben (German: ''Oberrheinische Tiefebene'', ''Oberrheinisches Tiefland'' or ''Oberrheingraben'', French: ''Vallée du Rhin'') is a major rift, about and on average , between Basel in the s ...
; the so-called Valley Black Forest (') with its
Rhenanian relief. It is here, in the west, where the highest mountains and the greatest local differences in height (of up to 1000 metres) are found. The valleys are often narrow and ravine-like. The summits are rounded, and there are remnants of plateaux and -like landforms.
Geologically the clearest division is also between east and west. Large areas of the eastern Black Forest, the lowest layer of the
South German Scarplands
The South German Scarplands is a geological and geomorphological natural region or landscape in Switzerland and the south German states of Bavaria and Baden-Württemberg. The landscape is characterised by escarpments.
It is variously referred to ...
composed of Bunter Sandstone, are covered by seemingly endless coniferous forest with their island clearings. The exposed basement in the west, predominantly made up of
metamorphic rocks and
granites, was, despite its rugged topography, easier to settle and appears much more open and inviting today with its varied meadow valleys.

The most common way of dividing the regions of the Black Forest is, however, from north to south. Until the 1930s, the Black Forest was divided into the Northern and Southern Black Forest, the boundary being the
line of the Kinzig valley. Later the Black Forest was divided into the heavily forested
Northern Black Forest
The Northern Black Forest (german: Nordschwarzwald) refers to the northern third of the Black Forest in Germany or, less commonly today, to the northern half of this mountain region.
Geography
The Northern Black Forest is bounded in the north b ...
, the lower, central section, predominantly used for agriculture in the valleys, was the
Central Black Forest
The Central Black Forest (german: Mittlerer Schwarzwald), also called the Middle Black Forest, is a natural or cultural division of the Black Forest in Baden-Württemberg in Germany. It generally refers to a region of deeply incised valleys from t ...
and the much higher
Southern Black Forest
The Southern Black Forest (german: Südschwarzwald) is the highest part of the Black Forest, an area heavily transformed by ice age glaciation south of a line roughly from Freiburg im Breisgau to Donaueschingen. The term High Black Forest is no ...
with its distinctive highland economy and
ice age glacial relief. The term
High Black Forest
The High Black Forest (german: Hochschwarzwald) is a touristic and geographical region in the south-west of the German federal state Baden-Württemberg, primarily in the Southern Black Forest.
History of the name
The term ''Hochschwarzwald'' o ...
referred to the highest areas of the South and southern Central Black Forest.
The boundaries drawn were, however, quite varied. In 1931, Robert Gradmann called the Central Black Forest the catchment area of the Kinzig and in the west the section up to the lower
Elz and Kinzig tributary of the
Gutach. A pragmatic division, which is oriented not just on natural and cultural regions, uses the most important transverse valleys. Based on that, the Central Black Forest is bounded by the Kinzig in the north and the line from
Dreisam to
Gutach in the south, corresponding to the
Bonndorf Graben
The Bonndorf Graben (german: Bonndorfer Graben) is a southeast-northwest to east-west striking, tectonic graben system on the eastern edge of the Black Forest and in the Baar between Bonndorf im Schwarzwald (in the south) and Donaueschingen (i ...
zone and the course of the present day
B 31.
In 1959, Rudolf Metz combined the earlier divisions and proposed a modified tripartite division, which combined natural and cultural regional approaches and was widely used. His Central Black Forest is bounded in the north by the
watershed
Watershed is a hydrological term, which has been adopted in other fields in a more or less figurative sense. It may refer to:
Hydrology
* Drainage divide, the line that separates neighbouring drainage basins
* Drainage basin, called a "watershe ...
between the
Acher
The Acher is a 53.6-kilometre-long river and right-hand tributary of the Rhine in the county of Ortenau, in the south German state of Baden-Württemberg. It flows in an northwesterly direction from the Black Forest to the Rhine, between the two ...
and
Rench and subsequently between the
Murg
Murg may refer to:
Places
* Murg (Aare), a river of Switzerland
* Murg (Northern Black Forest), a river and right tributary of the Rhine in the districts of Freudenstadt and Rastatt, Baden-Württemberg, Germany
** Murg Valley Railway
* Murg (Sou ...
and
Kinzig or Forbach and Kinzig, in the south by the Bonndorf Graben zone, which restricts the Black Forest in the east as does the Freudenstadt Graben further north by its transition into the Northern Black Forest.
[Rudolf Metz: ''Zur naturräumlichen Gliederung des Schwarzwalds'' In: Alemannisches Institut (ed.): Alemannisches Jahrbuch 1959, Schauenburg, Lahr 1959, pp. 1–33]
Work of the Institute of Applied Geography
The
Handbook of the Natural Region Divisions of Germany
The ''Handbook of Natural Region Divisions of Germany'' (german: Handbuch der naturräumlichen Gliederung Deutschlands) was a book series resulting from a project by the former German Federal Institute for Regional Studies ('' Bundesanstalt für La ...
published by the Federal Office of Regional Geography (') since the early 1950s names the Black Forest as one of six tertiary-level major landscape regions within the secondary-level region of the South German Scarplands and, at the same time, one of nine new major landscape unit groups. It is divided into six so-called major units (level 4 landscapes).
[Emil Meynen, Josef Schmithüsen: '']Handbuch der naturräumlichen Gliederung Deutschlands
The ''Handbook of Natural Region Divisions of Germany'' (german: Handbuch der naturräumlichen Gliederung Deutschlands) was a book series resulting from a project by the former German Federal Institute for Regional Studies ('' Bundesanstalt für La ...
.'' Bundesanstalt für Landeskunde, Remagen/Bad Godesberg 1953–1962 (nine instalments in eight books, updated 1:1,000,000 map with major units, 1960). This division was refined and modified in several successor publications (1:200,000 individual map sheets) up to 1967, each covering individual sections of the map. The mountain range was also divided into three regions. The northern boundary of the Central Black Forest in this classification runs south of the Rench Valley and the
Kniebis to near Freudenstadt. Its southern boundary varied with each edition.
In 1998, the Baden-Württemberg State Department for Environmental Protection (today the Baden-Württemberg State Department for the Environment, Survey and Nature Conservation) published a reworked Natural Region Division of Baden-Württemberg. It is restricted to the level of the natural regional major units and has been used since for the state's administration of nature conservation:

The Black Forest Foothills (', 150) geomorphologically form plateaux on the north and northeast periphery of the mountain range that descend to the
Kraichgau in the north and the
Heckengäu landscapes in the east. They are incised by valleys, especially those of the
Nagold river system, into individual
interfluves; a narrow northwestern finger extends to beyond the
Enz near
Neuenbürg and also borders the middle reaches of the
Alb
The alb (from the Latin ''albus'', meaning ''white''), one of the liturgical vestments of the Roman Catholic, Anglican, Lutheran, Methodist, Presbyterian, Reformed and Congregational churches, is an ample white garment coming down to the ank ...
to the west as far as a point immediately above
Ettlingen. To the southwest it is adjoined by the Black Forest
Grinden
A ''grinde'' (plural: ''grinden'') is an almost treeless area of wet heathland found on the rounded bunter sandstone ridges of the Northern Black Forest in Germany. The ''grinden'' reached their greatest extent in the early 19th century when they r ...
and Enz Hills (, 151), along the upper reaches of the Enz and Murg, forming the heart of the Northern Black Forest. The west of the Northern Black Forest is formed by the Northern Black Forest Valleys (, 152) with the middle reaches of the Murg around
Gernsbach
Gernsbach () is a town in the district of Rastatt, in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is located on the river Murg, east of Baden-Baden in the Black Forest. Twin towns are Baccarat in France and Pergola, Marche in Italy.
The town is the hist ...
, the middle course of the
Oos to
Baden-Baden, the middle reaches of the
Bühlot above
Bühls and the upper reaches of the
Rench around
Oppenau. Their exit valleys from the mountain range are all oriented towards the northwest.

The Central Black Forest (153) is mainly restricted to the
catchment area of the River
Kinzig above
Offenburg as well as the
Schutter and the low hills north of the
Elz.
The Southeastern Black Forest (, 154) consists mainly of the catchment areas of the upper reaches of the
Danube headstreams, the
Brigach and
Breg as well as the left side valleys of the
Wutach north of
Neustadt – and thus draining from the northeast of the Southern Black Forest. To the south and west it is adjoined by the High Black Forest (, 155) with the highest summits in the whole range around the
Feldberg and the
Belchen
The Belchen, , or Black Forest Belchen (german: Schwarzwälder Belchen) is the fourth-highest summit of the Black Forest after Feldberg (Black Forest), Feldberg, Seebuck and Herzogenhorn. The municipalities of Münstertal, Black Forest, Münstert ...
. Its eastern part, the Southern Black Forest Plateau, is oriented towards the Danube, but drained over the Wutach and the
Alb
The alb (from the Latin ''albus'', meaning ''white''), one of the liturgical vestments of the Roman Catholic, Anglican, Lutheran, Methodist, Presbyterian, Reformed and Congregational churches, is an ample white garment coming down to the ank ...
into the Rhine. The southern crest of the Black Forest in the west is deeply incised by the Rhine into numerous ridges. Immediately right of the
Wiese
Wiese may refer to:
Places Modern day
* Wiese (Apfeldorf), a village in Apfeldorf, Landsberg am Lech, Bavaria, Germany
* Wiese (Märkische Heide), a village in Märkische Heide, Oder-Spree, Brandenburg, Germany
* Wiese (Much), a village in Much ...
above
Lörrach rises the relatively small Bunter Sandstone-
Rotliegendes table of the Weintenau Uplands () in the extreme southwest of the Black Forest; morphologically, geologically and climatically it is separate from the other parts of the Southern Black Forest and, in this classification, is also counted as part of the High Black Forest.

Mountains
At the
Feldberg in the Southern Black Forest is the range's highest summit. Also in the same area are the
Herzogenhorn (1,415 m) and the
Belchen
The Belchen, , or Black Forest Belchen (german: Schwarzwälder Belchen) is the fourth-highest summit of the Black Forest after Feldberg (Black Forest), Feldberg, Seebuck and Herzogenhorn. The municipalities of Münstertal, Black Forest, Münstert ...
(1,414 m). In general the mountains of the Southern or High Black Forest are higher than those in the Northern Black Forest. The highest Black Forest peak north of the Freiburg–Höllental–Neustadt line is the
Kandel (1,241.4 m). Like the highest point of the Northern Black Forest, the
Hornisgrinde
The Hornisgrinde, 1,164 m (3,820 ft), is the highest mountain in the Northern Black Forest of Germany. The Hornisgrinde lies in northern Ortenaukreis district.
Origin of the name
The name is probably derived from Latin, and essentiall ...
(1,163 m), or the Southern Black Forest lookout mountains, the
Schauinsland
The Schauinsland (literally "look-into-the-country"; near Freiburg im Breisgau, Germany) is a mountain in the Black Forest with an elevation of 1,284 m (4,213 ft) above sea level. It is a popular destination for day trips. Due to the h ...
(1,284.4 m) and
Blauen (1,164.7 m) it lies near the western rim of the range.
Rivers and lakes


Rivers in the Black Forest include the
Danube (which originates in the Black Forest as the confluence of the
Brigach and
Breg rivers), the
Enz, the
Kinzig, the
Murg
Murg may refer to:
Places
* Murg (Aare), a river of Switzerland
* Murg (Northern Black Forest), a river and right tributary of the Rhine in the districts of Freudenstadt and Rastatt, Baden-Württemberg, Germany
** Murg Valley Railway
* Murg (Sou ...
, the
Nagold, the
Neckar
The Neckar () is a river in Germany, mainly flowing through the southwestern state of Baden-Württemberg, with a short section through Hesse. The Neckar is a major right tributary of the Rhine. Rising in the Schwarzwald-Baar-Kreis near Schwenn ...
, the
Rench, and the
Wiese
Wiese may refer to:
Places Modern day
* Wiese (Apfeldorf), a village in Apfeldorf, Landsberg am Lech, Bavaria, Germany
* Wiese (Märkische Heide), a village in Märkische Heide, Oder-Spree, Brandenburg, Germany
* Wiese (Much), a village in Much ...
. The Black Forest occupies part of the
continental divide
A continental divide is a drainage divide on a continent such that the drainage basin on one side of the divide feeds into one ocean or sea, and the basin on the other side either feeds into a different ocean or sea, or else is endorheic, not ...
between the
Atlantic Ocean drainage basin (drained by the
Rhine) and the
Black Sea drainage basin (drained by the Danube).
The longest Black Forest rivers are (length includes stretches outside the Black Forest):
*
Enz ()
*
Kinzig ()
*
Elz ()
*
Wutach ()
*
Nagold (), hydrological main artery of the Nagold-Enz systems
*
Danube (),
headstreams:
**
Breg ()
**
Brigach ()
*
Murg
Murg may refer to:
Places
* Murg (Aare), a river of Switzerland
* Murg (Northern Black Forest), a river and right tributary of the Rhine in the districts of Freudenstadt and Rastatt, Baden-Württemberg, Germany
** Murg Valley Railway
* Murg (Sou ...
()
*
Rench ()
*
Schutter ()
*
Wiese
Wiese may refer to:
Places Modern day
* Wiese (Apfeldorf), a village in Apfeldorf, Landsberg am Lech, Bavaria, Germany
* Wiese (Märkische Heide), a village in Märkische Heide, Oder-Spree, Brandenburg, Germany
* Wiese (Much), a village in Much ...
()
*
Acher
The Acher is a 53.6-kilometre-long river and right-hand tributary of the Rhine in the county of Ortenau, in the south German state of Baden-Württemberg. It flows in an northwesterly direction from the Black Forest to the Rhine, between the two ...
()
*
Dreisam (incl.
Rotbach )
*
Alb
The alb (from the Latin ''albus'', meaning ''white''), one of the liturgical vestments of the Roman Catholic, Anglican, Lutheran, Methodist, Presbyterian, Reformed and Congregational churches, is an ample white garment coming down to the ank ...
(incl.
Menzenschwander Alb
The Alb (also: ''Hauensteiner Alb'') is a river in the southern Black Forest. It arises from two headwaters, the Menzenschwander Alb and Bernauer Alb, and flows in a southerly direction. It ends after (including ''Menzenschwander Alb'') at a ...
)
*
Glatt ()
*
Möhlin ()
*
Wolf ()
*
Schiltach ()
*
Wehra (incl. Rüttebach )
*
Oos ()
*
Glasbach (), hydrological main artery of the
Neckar
The Neckar () is a river in Germany, mainly flowing through the southwestern state of Baden-Württemberg, with a short section through Hesse. The Neckar is a major right tributary of the Rhine. Rising in the Schwarzwald-Baar-Kreis near Schwenn ...
system
Important lakes of natural,
glacial origin in the Black Forest include the
Titisee, the
Mummelsee and the
Feldsee
The Feldsee (also ''Feldbergsee'') is a lake in southern Baden-Württemberg at the foot of the Feldberg east of Freiburg im Breisgau in Germany. It is part of the Southern Black Forest Nature Park.
Geology and earth history
The Feldsee ...
. Especially in the Northern Black Forest are a number of other, smaller
tarns. Numerous
reservoirs like the – formerly natural but much smaller –
Schluchsee with the other lakes of the ''
Schluchseewerk
The Schluchseewerk AG is the operator of five pumped storage hydroelectric power stations in the Southern Black Forest in the German state of Baden-Württemberg. Its head office is in Laufenburg (Baden).
The shareholders of the Schluchseewerk ar ...
'', the
Schwarzenbach Reservoir Schwarzenbach may refer to:
Places In Austria
* Schwarzenbach, Lower Austria, in the Wiener Neustadt-Land district
* Schwarzenbach an der Pielach, in Lower Austria
* Schwarzenbach (Eppenstein), a part of Eppenstein in Styria
* Schwarzenbach ...
, the
Kleine Kinzig Reservoir Kleine is a German and Dutch surname meaning "small". Notable people with the surname include:
* Andrea Kleine (born 1970), American writer, choreographer, and performance artist
* Christian Kleine (born 1974), German musician and DJ
* Cindy Kleine ...
or the
Nagold Reservoir
Nagold is a town in southwestern Germany, bordering the Northern Black Forest. It is located in the ''Landkreis'' (district) of Calw (Germany/Baden-Württemberg). Nagold is known for its ruined castle, Hohennagold Castle, and for its road viadu ...
are used for
electricity generation,
flood protection or
drinking water supply.
Geology
The Black Forest consists of a cover of
sandstone on top of a core of
gneiss and
granite. Formerly it shared tectonic evolution with the nearby
Vosges Mountains. Later during the Middle
Eocene a
rifting period affected the area and caused formation of the
Upper Rhine Plain. During the last
glacial period of the
Würm glaciation, the Black Forest was covered by glaciers; several
tarns (or lakes) such as the
Mummelsee are remains of this period.
Basement
The geological foundation of the Black Forest is formed by the crystalline bedrock of the
Variscan
The Variscan or Hercynian orogeny was a geologic mountain-building event caused by Late Paleozoic continental collision between Euramerica (Laurussia) and Gondwana to form the supercontinent of Pangaea.
Nomenclature
The name ''Variscan'', comes f ...
basement. This is covered in the east and northeast by
Bunter Sandstone
The Buntsandstein (German for ''coloured'' or ''colourful sandstone'') or Bunter sandstone is a lithostratigraphic and allostratigraphic unit (a sequence of rock strata) in the subsurface of large parts of west and central Europe. The Buntsands ...
slabs, the so-called platforms. On the western edge a descending,
step-fault-like, foothill zone borders the Upper Rhine Graben consisting of rocks of the
Triassic and
Jurassic periods.
The dominant rocks of the basement are gneiss (ortho- and paragneisses, in the south also
migmatites and diatexites, for example on the Schauinsland and Kandel). These gneisses were penetrated by a number of granitic bodies during the
Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic that spans 60 million years from the end of the Devonian Period million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Permian Period, million years ago. The name ''Carbonifero ...
period. Among the bigger ones are the Triberg Granite and the
Forbach Granite
Forbach Granite (german: Forbachgranit), also called Raumünzach Granite (''Raumünzach-Granit''), is a type of granite rock that occurs in the Northern Black Forest. It is part of the Northern Black Forest's granitic massif, to which Bühlerta ...
, the youngest is the Bärhalde Granite. In the south lies the zone of Badenweiler-Lenzkirch, in which Palaeozoic rocks have been preserved (volcanite and sedimentary rocks), which are interpreted as the intercalated remains of a
microcontinental collision. Still further in the southeast (around Todtmoos) is a range of exotic inclusions:
gabbro from
Ehrsberg,
serpentinites and
pyroxenites near Todtmoos,
norite near
Horbach), which are possibly the remnants of an
accretionary wedge from a continental collision. Also noteworthy are the basins in the
Rotliegend, for example the Schramberg or the Baden-Baden Basin with thick quartz-porphyry and
tuff plates (exposed, for example, on the rock massif of
Battert
The Battert is a hill, , on the western edge of the Northern Black Forest north of Baden-Baden in Germany. On its western slopes are the ruins of Hohenbaden Castle (the ''Altes Schloss'' or "Old Castle"), on the southern side is the climbing are ...
near Baden-Baden). Thick rock, covered by bunter, also occurs in the north of the
Dinkelberg
The Dinkelberg is a partially forested hill range, up to , about 145 km² in area, in the High Rhine region of Germany. It lies within the counties of Lörrach and Waldshut in the German state of Baden-Württemberg and the Swiss canton ...
block (several hundred metres thick in the Basel
geothermal borehole). Even further to the southeast, under the Jura, lies the North Swiss Permocarboniferous Basin.
Uplift of the mountains
Since the downfaulting of the
Upper Rhine Graben
The Upper Rhine Plain, Rhine Rift Valley or Upper Rhine Graben (German: ''Oberrheinische Tiefebene'', ''Oberrheinisches Tiefland'' or ''Oberrheingraben'', French: ''Vallée du Rhin'') is a major rift, about and on average , between Basel in the s ...
during the
Eocene epoch, the two shoulders on either side have been uplifted: the Black Forest to the east and the
Vosges to the west. In the centre lies the
Kaiserstuhl volcano, which dates to the
Miocene. In the times that followed, the
Mesozoic platform on the uplands was largely eroded, apart from remains of Bunter Sandstone and
Rotliegend Group
The Rotliegend, Rotliegend Group or Rotliegendes (german: the underlying red) is a lithostratigraphic unit (a sequence of rock strata) of latest Carboniferous to Guadalupian (middle Permian) age that is found in the subsurface of large areas in wes ...
, but it has survived within the graben itself. During the
Pliocene a pronounced but uneven bulge especially affected the southern Black Forest, including the Feldberg. As a result, the upper surface of the basement in the northern part of the forest around the Hornisgrinde is considerably lower. In the central Black Forest, the tectonic
syncline
In structural geology, a syncline is a fold with younger layers closer to the center of the structure, whereas an anticline is the inverse of a syncline. A synclinorium (plural synclinoriums or synclinoria) is a large syncline with superimpose ...
of the Kinzig and Murg emerged.
Geomorphologist
Geomorphology (from Ancient Greek: , ', "earth"; , ', "form"; and , ', "study") is the scientific study of the origin and evolution of topographic and bathymetric features created by physical, chemical or biological processes operating at or n ...
Walther Penck
Walther Penck (30 August 1888 – 29 September 1923) was a geologist and geomorphologist known for his theories on landscape evolution. Penck is noted for criticizing key elements of the Davisian cycle of erosion, concluding that the process ...
regarded the Black Forest as an uplifted
geologic dome and modeled his theory of
piedmonttreppen A piedmonttreppen or piedmont benchland is a conceived landform consisting in a succession of benches at different heights and that forms in sequence during the uplift of a geological dome. The concept was first proposed in a posthumous publicatio ...
(piedmont benchlands) on it.
Platform
Above the crystalline basement of the Northern Black Forest and the adjacent parts of the Central Black Forest, the bunter sandstone platforms rise in prominent steps. The most resistant surface strata on the stepped terrain of the uplands and the heights around the upper reaches of the
Enz, which have been heavily eroded by the tributaries of the Murg, is the silicified main conglomerate (Middle Bunter). To the east and north are the
nappes of the Upper Bunter (platten sandstones and red clays). South of the Kinzig the Bunter Sandstone zone narrows to a fringe in the east of the mountain range.
Ice age and topography
It is considered proven that the Black Forest was heavily glaciated during the peak periods of at least the
Riss
The Riss (german: Riß) is a small river in Baden-Württemberg, south-western Germany, right tributary of the Danube. Its source is in Upper Swabia, between Bad Waldsee and Bad Schussenried. It flows north, through the town of Biberach an der Ris ...
and
Würm glaciations (up to about 10,000 years ago). This glacial geomorphology characterizes almost all of the High Black Forest as well as the main ridge of the Northern Black Forest. Apart from that, it is only discernible from a large number of
cirque
A (; from the Latin word ') is an amphitheatre-like valley formed by glacial erosion. Alternative names for this landform are corrie (from Scottish Gaelic , meaning a pot or cauldron) and (; ). A cirque may also be a similarly shaped landform ...
s mainly facing northeast. Especially in this direction snow accumulated on the shaded and leeward slopes of the summit plateau to form short cirque glaciers that made the sides of these funnel-shaped depressions. There are still tarns in some of these old cirques, partly a result of the
anthropogenic
Anthropogenic ("human" + "generating") is an adjective that may refer to:
* Anthropogeny, the study of the origins of humanity
Counterintuitively, anthropogenic may also refer to things that have been generated by humans, as follows:
* Human im ...
elevation of the low-side lip of the cirque, such as the
Mummelsee,
Wildsee,
Schurmsee
The Schurmsee is a tarn that lies at a height of 794 metres in the municipality of Forbach in the Northern Black Forest in Germany. It is located on a line between Hundsbach and Schönmünzach. The lake covers an area of 1.6 hectares and is up t ...
,
Glaswaldsee
The Glaswaldsee near the spa town of Bad Rippoldsau-Schapbach in the Central Black Forest in Germany lies in a cirque that is sunk into the steep eastern mountainside of the Lettstädter Höhe. It is part of the nature reserve of the same nam ...
,
Buhlbachsee
The Buhlbachsee is a tarn (lake) in the northern Black Forest on the southwestern edge of the parish of Baiersbronn in the county of Freudenstadt in Baden-Württemberg. Since 1 January 2014 it has been part of the Black Forest National Park.
The t ...
,
Nonnenmattweiher
The Nonnenmattweiher is a lake that has been impounded by an embankment in the Southern Black Forest in Germany. Together with the surrounding area it forms a nature reserve of the same name in the High Black Forest in the state of Baden-Württemb ...
, and
Feldsee
The Feldsee (also ''Feldbergsee'') is a lake in southern Baden-Württemberg at the foot of the Feldberg east of Freiburg im Breisgau in Germany. It is part of the Southern Black Forest Nature Park.
Geology and earth history
The Feldsee ...
. The Titisee formed as
glacial lake
A glacial lake is a body of water with origins from glacier activity. They are formed when a glacier erodes the land and then melts, filling the depression created by the glacier.
Formation
Near the end of the last glacial period, roughly 10,0 ...
behind a glacial
moraine
A moraine is any accumulation of unconsolidated debris (regolith and rock), sometimes referred to as glacial till, that occurs in both currently and formerly glaciated regions, and that has been previously carried along by a glacier or ice shee ...
.
Culture
The Black Forest is mainly rural, with many scattered villages and a few large towns. Tradition and custom are celebrated in many places in the form of annual festivities. The main dialect spoken in the Black Forest area is
Alemannic Alemannic (''Alamannic'') or Alamanni may refer to:
* Alemannic German, a dialect family in the Upper German branch of the German languages and its speakers
* Alemanni, a confederation of Suebian Germanic tribes in the Roman period
* Alamanni (surna ...
. The forest is best known for its
typical farmhouses with their sweeping
half-hipped roofs, its
Black Forest gâteaus,
Black Forest ham
Black Forest ham () is a variety of dry-cured smoked ham produced in the Black Forest region of Germany.
In 1959, Hans Adler from Bonndorf pioneered manufacturing and selling Original Black Forest ham by retail and mail order. Since 1997, the ...
, Black Forest
gnome
A gnome is a mythological creature and diminutive spirit in Renaissance magic and alchemy, first introduced by Paracelsus in the 16th century and later adopted by more recent authors including those of modern fantasy literature. Its characte ...
s,
Kirschwasser and the
cuckoo clock.
Traditional costume
Traditional costume or
Tracht is still sometimes worn today, usually at festive occasions. The appearance of such costume varies from region to region, sometimes markedly. One of the best-known Black Forest costumes is that of the villages of
Kirnbach,
Reichenbach Reichenbach may refer to:
Places Austria
* Reichenbach (Litschau), a part of Litschau
* Reichenbach (Rappottenstein), a part of Rappottenstein
Germany
* Reichenbach (Oberlausitz), in Niederschlesischer Oberlausitzkreis district, Saxony
* Rei ...
and
Gutach im Kinzigtal with the characteristic ''
Bollenhut'' headdress. Unmarried women wear the hats with red bobbles or ''Bollen''; married women wear black. Engaged women sometimes wear a
bridal crown
Traditionally a bridal crown (german: Brautkrone or, in the Black Forest, ''Schäppel'') is a headdress that, in Central and Northern Europe, single women wear on certain holidays, at festivals and, finally, at their wedding. Bridal crowns today ...
(''Schäppel'') before and on the day of their wedding, whose largest examples from the town of
St. Georgen weigh up to 5 kilograms.
File:Bollenhut-Gutach.jpg, Traditionally, the ''Bollenhut'' is worn by unmarried women as part of the tracht.
File:Angelo Jank - Jugend Nr. 36, 1904.jpg
Art
Its rural beauty as well as the sense of tradition of its inhabitants attracted many artists in the 19th and early 20th centuries, whose works made the Black Forest famous the world over. Notable were
Hans Thoma
Hans Thoma (2 October 1839 – 7 November 1924) was a German painter.
Biography
Hans Thoma was born on 2 October 1839 in Bernau in the Black Forest, Germany. He was the son of a miller and was trained in the basics of painting by a painter of ...
from
Bernau and his fellow student, Rudolf Epp, who was sponsored by the Grand Duke of Baden,
Frederick I. Both artists painted motifs from the Black Forest throughout their lives. Artist
J. Metzler
J. Metzler was a German artist of the Düsseldorf school. His works were made between the last decades of the 19th century and the first decades of the 20th century and were very popular at that time. He was specialised in Landscape art and pain ...
from
Düsseldorf travelled through the Black Forest to paint his landscapes. The works of the Gutach artist colony around
Wilhelm Hasemann
Wilhelm Hasemann (16 September 1850, Mühlberg - 28 November 1913, Gutach) was a German genre painter and illustrator.
Life and career
Hasemann was the only son of a mechanic and left school at the age of fifteen to work in his father's sho ...
were widely admired, their landscape and genre motifs capturing the character of the Black Forest. Like local author Heinrich Hansjakob, they were part of a Baden folk costume movement.
File:Arnold Lyongrün, Frühling im Schwarzwald, 1912.jpg, Arnold Lyongrün: "Frühling im Schwarzwald" (1912)
File:Hans Thoma - Kinderreigen (1872).jpg, "Kinderreigen" (1872) by Black Forest artist Hans Thoma
Hans Thoma (2 October 1839 – 7 November 1924) was a German painter.
Biography
Hans Thoma was born on 2 October 1839 in Bernau in the Black Forest, Germany. He was the son of a miller and was trained in the basics of painting by a painter of ...
File:J.metzler-schwarzwaldlandschaft.jpg, Black Forest landscape by J. Metzler
J. Metzler was a German artist of the Düsseldorf school. His works were made between the last decades of the 19th century and the first decades of the 20th century and were very popular at that time. He was specialised in Landscape art and pain ...
File:J. Metzler - Schwarzwaldlandschaft.jpg, Black Forest landscape by J. Metzler
J. Metzler was a German artist of the Düsseldorf school. His works were made between the last decades of the 19th century and the first decades of the 20th century and were very popular at that time. He was specialised in Landscape art and pain ...
File:Bauernhaus (Hasemann).jpg, Black Forest farmhouse, painted by Wilhelm Hasemann
Wilhelm Hasemann (16 September 1850, Mühlberg - 28 November 1913, Gutach) was a German genre painter and illustrator.
Life and career
Hasemann was the only son of a mechanic and left school at the age of fifteen to work in his father's sho ...
File:Gutacher Familie (Hasemann).jpg, A Gutach family, painted by Wilhelm Hasemann
Wilhelm Hasemann (16 September 1850, Mühlberg - 28 November 1913, Gutach) was a German genre painter and illustrator.
Life and career
Hasemann was the only son of a mechanic and left school at the age of fifteen to work in his father's sho ...
(ca. 1900)
Crafts
In the field of handicrafts,
wood carving produces folk art like the
Longinus cross
The Longinus cross''Arise and go toward the south: 2000 years of Christianity in Ethiopia'' by Annegret Marx and Alexandra Neubauer, IDP, 2007. Retrieved 11 Apr 2015. (german: Longinuskreuz) is a special form of the Arma Christi cross, which occur ...
es along with sculptors like
Matthias Faller Matthias is a name derived from the Greek Ματθαίος, in origin similar to Matthew.
People
Notable people named Matthias include the following:
In religion:
* Saint Matthias, chosen as an apostle in Acts 1:21–26 to replace Judas Iscariot
...
. Wood carving is a traditional cottage industry in the region, and carved ornaments now are produced in substantial numbers as souvenirs for tourists.
Cuckoo clocks are a popular example.
Glassblowing is another notable craft of the Black Forest region. At the beginning of the 15th century, the art of glassmaking took hold in the Bavarian-Bohemian border mountains, especially since the necessary raw materials such as
quartz and
wood were abundant here. With the permission of the manor, glassblowers operated simple glass production facilities as "wandering huts" (''Wanderhütten''), the locations of which were relocated when the local resources were available. They needed huge amounts of firewood and wood for
potash. In the second half of the 18th century, the huts had to close due to a shortage of wood and sales difficulties. Only after 1800, when the demand for luxury glass increased enormously, when a few decades of regulated forestry had ensured the regrowth of the raw material wood and when the forest-destroying potash extraction had become unnecessary due to the new glass flux soda, some glass huts (''Glashütten'') revived. Some glassblowing factories still testify to this today, for example in
Höllental, near
Todtnau
Todtnau is a town in the district of Lörrach in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. As of 2009 its population was of 4,932.
Geography
It is situated in the Black Forest, on the river Wiese, 20 km southeast of Freiburg.
The municipality counts ...
and in
Wolfach
Wolfach ( gsw, label= Low Alemannic, Wolfä) is a town in the Black Forest and part of the Ortenaukreis in Baden-Württemberg (Germany). It is a well-known spa town.
Geography
Geographical Position
Wolfach lies where the two rivers Wolf and ...
.
File:Du200613.png, German cuckoo clock
Cuisine
Black Forest ham
Black Forest ham () is a variety of dry-cured smoked ham produced in the Black Forest region of Germany.
In 1959, Hans Adler from Bonndorf pioneered manufacturing and selling Original Black Forest ham by retail and mail order. Since 1997, the ...
originated from this region, as did the
Black Forest gâteau, which is also known as "Black Forest Cherry Cake" or "Black Forest Cake" and is made with chocolate cake, cream, sour cherries and
Kirsch. The Black Forest variety of ''
Flammekueche
Flammekueche ( Alsatian; Standard German: ''Flammkuchen''), or tarte flambée ( French), is a speciality of the region of Alsace, German-speaking Moselle, Baden and the Palatinate. It is composed of bread dough rolled out very thinly in the sh ...
'' is a Baden specialty made with ham, cheese and cream. ''
Pfannkuchen'', a
crêpe or crêpe-like (''
Eierkuchen'' or ''
Palatschinken'') pastry, is also common.
The Black Forest is known for its long tradition in gourmet cuisine. No fewer than 17
Michelin starred
The Michelin Guides ( ) are a series of guide books that have been published by the French tyre company Michelin since 1900. The Guide awards up to three Michelin stars for excellence to a select few establishments. The acquisition or loss of a ...
restaurants are located in the region, among them two restaurants with three stars (Restaurants Bareiss and Schwarzwaldstube in
Baiersbronn
Baiersbronn is a Municipalities of Germany, municipality and a village in the district of Freudenstadt (district), Freudenstadt in Baden-Württemberg in southern Germany. It is situated in the Black Forest on the Murg (Northern Black Forest), Mu ...
) as well as the only restaurant in Germany that has been awarded a Michelin star every year since 1966. At ''Schwarzwald Hotel Adler'' in
Häusern
Häusern is a municipality in the district of Waldshut in Baden-Württemberg in Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after ...
, three generations of chefs from the same family have defended the award from the first year the Michelin Guide selected restaurants in Germany until today.
File:Schwarzwaelderspeck.jpg, Black Forest ham with German bread
File:Black Forest cake 5.jpg, A Black Forest cake
File:Bryan's Grocery Black Forest Cake (33577971241).jpg, Slice of a Black Forest Cake
''Fasnet''
The German holiday of
Fastnacht, or ''Fasnet'', as it is known in the Black Forest region, occurs in the time leading up to
Lent
Lent ( la, Quadragesima, 'Fortieth') is a solemn religious observance in the liturgical calendar commemorating the 40 days Jesus spent fasting in the desert and enduring temptation by Satan, according to the Gospels of Matthew, Mark and Luke ...
. On ''Fasnetmendig'', or the Monday before
Ash Wednesday
Ash Wednesday is a holy day of prayer and fasting in many Western Christian denominations. It is preceded by Shrove Tuesday and falls on the first day of Lent (the six weeks of penitence before Easter). It is observed by Catholics in the Rom ...
, crowds of people line the streets, wearing wooden, mostly hand-carved masks. One prominent style of mask is called the Black Forest Style, originating from the Black Forest Region.
File:Fastnacht im Schwarzwald - panoramio (4).jpg, Fastnacht in the Black Forest
File:Fastnachtsvergnügen im Schwarzwald 1890.jpg, Carnival pleasure in the Black Forest (1890)
File:Gernsbacher Fastnacht - panoramio.jpg, Fastnacht in Gernsbach
Gernsbach () is a town in the district of Rastatt, in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is located on the river Murg, east of Baden-Baden in the Black Forest. Twin towns are Baccarat in France and Pergola, Marche in Italy.
The town is the hist ...
(Black Forest)
Cego

The Black Forest is home to an unusual tarot card game,
Cego, that is part of the region's cultural heritage.
[''Cego – Regeln''](_blank)
at cego.de. Retrieved 17 May 2020. After the defeat of
Further Austria in 1805, much of its territory was allocated to the
Grand Duchy of Baden
The Grand Duchy of Baden (german: Großherzogtum Baden) was a state in the southwest German Empire on the east bank of the Rhine. It existed between 1806 and 1918.
It came into existence in the 12th century as the Margraviate of Baden and subs ...
. During the ensuing
Napoleonic Wars, soldiers from Baden deployed with Napoleon's troops to Spain where, among other things, they learned a new card game,
Ombre. They took this back to Baden and adapted it to be played with
Tarot cards which were then in common use in southern Germany.
[''Vermutliche Herkunft''](_blank)
at cego-online.de. Retrieved 17 May 2020.
Cego soon developed into the national game of Baden and
Hohenzollern
The House of Hohenzollern (, also , german: Haus Hohenzollern, , ro, Casa de Hohenzollern) is a German royal (and from 1871 to 1918, imperial) dynasty whose members were variously princes, electors, kings and emperors of Hohenzollern, Brandenb ...
, and these are the only regions of Germany where tarot cards are still used for playing games.
[''Cego''](_blank)
at pagat.com. Retrieved 17 May 2020. The game has grown organically, and there are many regional variations, but in recent years the establishment of a Cego Black Forest Championship has led to official tournament rules being defined.
In addition, regular courses and local tournaments are held and it is a permanent feature of Alemannic Week, held annually in the Black Forest at the end of September.
[''Cego – ein altes Kartenspiel, das eine Renaissance erlebt''](_blank)
at schwarzwaldregion-freiburg.de. Retrieved 17 May 2020.
Nature
Conservation areas

There are two
nature park
A nature park, or sometimes natural park, is a designation for a protected natural area by means of long-term land planning, sustainable resource management and limitation of agricultural and real estate developments. These valuable landscape ...
s and one
national park
A national park is a nature park, natural park in use for conservation (ethic), conservation purposes, created and protected by national governments. Often it is a reserve of natural, semi-natural, or developed land that a sovereign state dec ...
named after the Black Forest that cover the region: the Southern Black Forest Nature Park, the Central/North Black Forest and the Black Forest National Park. The difference between a nature park and a national park is that a nature park's aim is to strive for environmentally sustainable
land use, to preserve the countryside as a cultural landscape, to market local produce more effectively, to make the area more suitable for
sustainable tourism
Sustainable tourism is a concept that covers the complete tourism experience, including concern for economic, social and environmental issues as well as attention to improving tourists' experiences and addressing the needs of host communities. Su ...
and to practice
environmental education. A national park's aims are to protect the country's natural heritage, to practice environmental education, to serve purposes of scientific environmental observation and to prevent the area from being commercially exploited.
The
Southern Black Forest Nature Park
The Southern Black Forest Nature Park (german: Naturpark Südschwarzwald) is located in Baden-Württemberg in Germany and covers an area of 394,000 hectares. As of 2018, it is Germany's largest nature park.
History
The Southern Black Forest Nat ...
(''Naturpark Südschwarzwald'') was founded in 1999. It comprises 394,000
ha and is therefore Germany's largest nature park (as of 2020). It encloses the southern part of the Central Black Forest, the Southern Black Forest and adjacent areas.
The
Central/North Black Forest Nature Park
The Central/North Black Forest Nature Park (german: Naturpark Schwarzwald Mitte/Nord) is located in Baden-Württemberg in Germany. It covers an area of 3,750 km2 and was founded in December 2000. As of 2018, it is the third-largest nature pa ...
(''Naturpark Schwarzwald Mitte/Nord'') was founded in 2000. It covers 375,000 ha and is thus the second-largest in Germany (as of 2020). It begins in the southern part of the Central Black Forest, bordering on the Southern Black Forest Nature Park and covers the rest of the Black Forest to the north.
The
Black Forest National Park, established in 2014, is the first
national park
A national park is a nature park, natural park in use for conservation (ethic), conservation purposes, created and protected by national governments. Often it is a reserve of natural, semi-natural, or developed land that a sovereign state dec ...
in Baden-Württemberg. It lies completely within the
Central/North Black Forest Nature Park
The Central/North Black Forest Nature Park (german: Naturpark Schwarzwald Mitte/Nord) is located in Baden-Württemberg in Germany. It covers an area of 3,750 km2 and was founded in December 2000. As of 2018, it is the third-largest nature pa ...
between the cities of
Freudenstadt and
Baden-Baden and covers an area of 10,062 ha. Its motto is "Natur Natur sein lassen" (let nature be nature).

Fauna
In addition to the characteristic range of fauna found in Central European forests, the following less common animals may be observed in the Black Forest:
* Black Forest cattle which belong to the rare breed of
Hinterwälder cattle,
* the giant earthworm ''
Lumbricus badensis
''Lumbricus badensis'' is a type of giant earthworm, a species of annelid. It is endemic to the upper-elevation spruce forests of Germany's Black Forest, where its common name is ''Badischer Riesenregenwurm'' ("giant rainworm of Baden
Ba ...
'', which is found only in the Black Forest region,
* the
Black Forest Horse
The Black Forest Horse (german: Schwarzwälder Kaltblut, italic=no) is an endangered German breed of light draft horse from the Black Forest of southern Germany.
History
Horse breeding in the Black Forest – in what is now Baden-Württember ...
, a
draft horse once indispensable for heavy field work and nowadays an endangered breed, and
* the endangered
Western capercaillie
The western capercaillie (''Tetrao urogallus''), also known as the Eurasian capercaillie, wood grouse, heather cock, cock-of-the-woods, or simply capercaillie , is a heavy member of the grouse family and the largest of all extant grouse species. ...
.
Climate
The mountain range has lower temperatures and higher rainfall than its surrounding countryside. The highlands of the Black Forest are characterized by regular rainfall throughout the year. However, temperatures do not fall evenly with increasing elevation, nor does the rainfall increase uniformly. Rather, the precipitation rises quickly even in the lower regions and is disproportionately heavy on the rainier western side of the mountains.

The wettest areas are the highlands around the Hornisgrinde in the north and around the Belchen and Feldberg in the south, where annual rainfall reaches 1,800–2,100 mm. Moisture-laden Atlantic westerlies dump about as much rain in the Northern Black Forest, despite its lower elevation, than in the higher area of the Southern Black Forest. There, the Vosges act as a rain shield in the face of the prevailing winds. On the exposed east side of the Central Black Forest, it is much drier; the annual rainfall there is about 750 L/m
2.
The higher elevations of the Black Forest are characterized by relatively small annual fluctuations and steamed extreme values. This is the result of the frequent light winds and greater cloud cover in summer. During the winter months, frequent high pressure means that the summits are often bathed in sunshine, while the valleys disappear under a thick blanket of fog as a result of pockets of cold air (
temperature inversion).
Tourism and transport

The main industry of the Black Forest is tourism. Black Forest Tourism (''Schwarzwald Tourismus'') assesses that there are around 140,000 direct full-time jobs in the tourist sector and around 34.8 million tourist overnight stays in 2009. In spring, summer and autumn an extensive network of hiking trails and mountain bike routes enable different groups of people to use the natural region. In winter, it is the various types of winter sport that come to the fore. There are facilities for both
downhill
Downhill may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Downhill'' (1927 film), a British film by Alfred Hitchcock
* ''Downhill'' (2014 film), a British comedy directed by James Rouse
* ''Downhill'' (2016 film), a Chilean thriller directed by Patrici ...
and
Nordic skiing
Nordic skiing encompasses the various types of skiing in which the toe of the ski boot is fixed to the Ski binding, binding in a manner that allows the heel to rise off the ski, unlike alpine skiing, where the boot is attached to the ski from toe ...
in many places.
Tourist attractions

The most heavily frequented tourist destinations and resorts in the Black Forest are the
Titisee and the
Schluchsee. Both lakes offer opportunities for water sports like
diving and
windsurfing. The
Mummelsee is a recreational lake and a starting point for a number of hiking trails including the
Kunstpfad am Mummelsee
The Kunstpfad am Mummelsee (literally: "Art Trail at the Mummelsee") is a sculpture path around the Mummelsee, which is located in the municipality of Seebach near Achern in the northern Black Forest in Baden-Württemberg (Germany
Germ ...
("sculpture trail at the Mummelsee"). The
Murg valley, the
Kinzig valley, the
Triberg Waterfalls and the
Open Air Museum at Vogtsbauernhof are also popular. Lookout mountains include the
Feldberg, the
Belchen
The Belchen, , or Black Forest Belchen (german: Schwarzwälder Belchen) is the fourth-highest summit of the Black Forest after Feldberg (Black Forest), Feldberg, Seebuck and Herzogenhorn. The municipalities of Münstertal, Black Forest, Münstert ...
, the
Kandel and the
Schauinsland
The Schauinsland (literally "look-into-the-country"; near Freiburg im Breisgau, Germany) is a mountain in the Black Forest with an elevation of 1,284 m (4,213 ft) above sea level. It is a popular destination for day trips. Due to the h ...
in the Southern Black Forest; and the
Hornisgrinde
The Hornisgrinde, 1,164 m (3,820 ft), is the highest mountain in the Northern Black Forest of Germany. The Hornisgrinde lies in northern Ortenaukreis district.
Origin of the name
The name is probably derived from Latin, and essentiall ...
, the
Schliffkopf, the
Hohloh, the
Merkur
Merkur (, '' Mercury'') is a defunct automobile brand that was marketed by the Lincoln- Mercury division of Ford Motor Company from 1985 to 1989. Drawing its name from the German word for Mercury, Merkur was targeted at buyers of European execut ...
and the
Teufelsmühle in the Northern Black Forest. The height differences in the mountains are used in many places for
hang gliding and
paragliding.
One oft-visited town is
Baden-Baden with its thermal baths and festival hall. Other thermal baths are found in the spa resorts of
Badenweiler,
Bad Herrenalb,
Bad Wildbad,
Bad Krozingen,
Bad Liebenzell
Bad Liebenzell (; Swabian: ''Bad Liabazell'') is a spa town in the Nagold River valley, the northern part of the Black Forest. It was first mentioned in 1090 and is the heart of the Liebenzeller Mission (a religious movement).
Bad Liebenzell is ...
and
Bad Bellingen
Bad Bellingen (High Alemannic: ''Bad Bellige'') is a municipality in the German state of Baden-Württemberg. It is on the border with France to the west. It is in the German landkreis of Lörrach. The closest larger city is Müllheim which is a ...
. From the beginning of the 19th century, the desire for spa and bathing resorts arose in all of
Central Europe because of the increasing economic potential, increasing mobility and the use of advertising. The
Neo-renaissance style
Friedrichsbad
The Friedrichsbad is a spa in the city of Baden-Baden in Germany. The Neo-renaissance spa building was completed in 1877.
History and architecture
The architect Karl Dernfeld designed the Friedrichsbad in the Renaissance style. It was built betw ...
and the
Palais Thermal The Palais Thermal is a spa in Bad Wildbad in Germany. The construction for the spa building was finished in 1847 and opened under the name of Graf-Eberhard-Bad.
Architecture
The "Wildbad" established not only the centuries-old bathing tradition ...
are examples for spas built in this era.
Other tourist destinations are the old imperial town of
Gengenbach, the former county towns of
Wolfach
Wolfach ( gsw, label= Low Alemannic, Wolfä) is a town in the Black Forest and part of the Ortenaukreis in Baden-Württemberg (Germany). It is a well-known spa town.
Geography
Geographical Position
Wolfach lies where the two rivers Wolf and ...
,
Schiltach and
Haslach im Kinzigtal and the flower and wine village of
Sasbachwalden
Sasbachwalden is a Black Forest municipality in Western Baden-Württemberg, Germany, popular with tourists. It is located on the western slopes of mountain Hornisgrinde in the Northern Black Forest and belongs to the district of Ortenau. More th ...
at the foot of the Hornisgrinde. Picturesque old towns may be visited in
Altensteig
Altensteig (; Swabian German, Swabian: ''Aldaschdaeg'') is a town in the Calw (district), district of Calw, in Baden-Württemberg, Germany.
History
Altensteig was most likely given German town law, town rights by the Counts of Hohenberg around ...
,
Dornstetten,
Freiburg im Breisgau
Freiburg im Breisgau (; abbreviated as Freiburg i. Br. or Freiburg i. B.; Low Alemannic German, Low Alemannic: ''Friburg im Brisgau''), commonly referred to as Freiburg, is an independent city in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. With a population o ...
,
Gernsbach
Gernsbach () is a town in the district of Rastatt, in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is located on the river Murg, east of Baden-Baden in the Black Forest. Twin towns are Baccarat in France and Pergola, Marche in Italy.
The town is the hist ...
,
Villingen and
Zell am Harmersbach.
Baiersbronn
Baiersbronn is a Municipalities of Germany, municipality and a village in the district of Freudenstadt (district), Freudenstadt in Baden-Württemberg in southern Germany. It is situated in the Black Forest on the Murg (Northern Black Forest), Mu ...
is a centre of gastronomic excellence,
Freudenstadt is built around the largest market place in Germany.
Gersbach's floral displays have won awards as the German Golden Village of 2004 and the
European Golden Village of 2007.
Noted for their fine interiors are the former monastery of
St. Blasien
St. Blasien (Sankt Blasien) is a small town located in the Waldshut district in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is situated in the Southern Black Forest, 17 km northeast of Waldshut-Tiengen.
St. Blaise's Abbey in the Black Forest is locat ...
as well as the abbeys of
Sankt Trudpert,
St. Peter
) (Simeon, Simon)
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Bethsaida, Gaulanitis, Syria, Roman Empire
, death_date = Between AD 64–68
, death_place = probably Vatican Hill, Rome, Italia, Roman Empire
, parents = John (or Jonah; Jona)
, occupation ...
and
St. Märgen
ST, St, or St. may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Stanza, in poetry
* Suicidal Tendencies, an American heavy metal/hardcore punk band
* Star Trek, a science-fiction media franchise
* Summa Theologica, a compendium of Catholic philosophy ...
.
Alpirsbach Abbey and the ruined
Hirsau Abbey
Hirsau Abbey, formerly known as Hirschau Abbey, was once one of the most important Benedictine abbeys of Germany. It is located in the Hirsau borough of Calw on the northern slopes of the Black Forest mountain range, in the present-day state of B ...
were built of red sandstone in the Hirsau style. Another idyllic rural edifice is
Wittichen Abbey
Wittichen Abbey (german: Kloster Wittichen) is a former Poor Clares abbey in Wittichen in a narrow side valley of the Kleine Kinzig stream near Schenkenzell in the upper Kinzig valley in the Black Forest.
History
The abbey was founded by ...
near
Schenkenzell
Schenkenzell is a village in the district of Rottweil, in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. The town is twinned with Schenkon
Schenkon is a municipality in the district of Sursee in the canton of Lucerne in Switzerland.
Geography
Schenkon has an ...
.

There are well known winter sports areas around the Feldberg, near
Todtnau
Todtnau is a town in the district of Lörrach in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. As of 2009 its population was of 4,932.
Geography
It is situated in the Black Forest, on the river Wiese, 20 km southeast of Freiburg.
The municipality counts ...
with its
FIS
FIS or fis may refer to:
Science and technology
* '' Fis'', an ''E. Coli'' gene
* Fis phenomenon, a phenomenon in linguistics
* F♯ (musical note)
* Flight information service, an air traffic control service
* Frame Information Structure, a ...
downhill ski run of ''Fahler Loch'' and in
Hinterzarten, a centre and talent forge for German ski jumpers. In the Northern Black Forest, the winter-sports areas are concentrated along the
Black Forest High Road
Black is a color which results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without hue, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness. Black and white have ...
and on the ridge between the Murg and Enz rivers around
Kaltenbronn.
Hiking trails
The Black Forest has a great number of very varied trails; some of pan-regional significance. The
European long-distance path
The European long-distance paths (alternatively, abbreviated as E-paths) are a network of long-distance footpaths that traverse Europe. While most long-distance footpaths in Europe are located in just one country or region, each of these numbered ...
E1 crosses the Black Forest following the routes of some of the local long-distance paths. Their framework is a network of long-distance paths with main routes and side branches, many of which were laid out in the early 20th century by the
Black Forest Club (''Schwarzwaldverein''). The best known of these is the challenging West Way (''Westweg'') with its many steep inclines. After 1950, circular walks were constructed to meet the changing demand, initially from the relatively dense railway network and, later, mainly from locally established hiking car parks. Currently, special, more experience-oriented themed paths are being laid out, such as the Dornstetten Barefoot Park (''
Barfußpark Dornstetten''), the Park of All Senses (''Park mit allen Sinnen'') in
Gutach (
Black Forest Railway), as well as those designed to bring the walker more directly in contact with nature (e.g. the ''Schluchtensteig''). Roads and wide forest tracks are thus less often used than hitherto.
There are numerous shorter paths suitable for day walks, as well as
mountain biking
Mountain biking is a sport of riding bicycles off-road, often over rough terrain, usually using specially designed mountain bikes. Mountain bikes share similarities with other bikes but incorporate features designed to enhance durability and pe ...
and
cross-country skiing
Cross-country skiing is a form of skiing where skiers rely on their own locomotion to move across snow-covered terrain, rather than using ski lifts or other forms of assistance. Cross-country skiing is widely practiced as a sport and recreation ...
trails. The total network of tracks amounts to around , and is maintained and overseen by volunteers of the
Black Forest Club (figures from Bremke, 1999, p. 9), which is the second largest German hiking association. As of 2021, the club counts 65,000 members.
Museums in the Black Forest
Culture and crafts

The
Black Forest Open Air Museum
The Black Forest Open Air Museum (german: Schwarzwälder Freilichtmuseum Vogtsbauernhof) is an open-air museum located between Hausach and Gutach in the Black Forest (Germany).
The museum is centred on the ''Vogtsbauernhof'' farmhouse dating f ...
at the Vogtsbauernhof farm in
Gutach has original
Black Forest houses offering insights into farming life of the 16th and 17th centuries. The buildings were dismantled at their original sites, the individual pieces numbered and then re-erected to exactly the same plan in the museum. The open-air museum shows the life of 16th and 17th century farmers in the region featuring the ''Vogtsbauernhof'' which dates back to 1612.
The
German Clock Museum in
Furtwangen gives a comprehensive cross-section of the history of the
watchmaking and
clockmaking industries.
From this early precision engineering a formerly important phonographic industry developed in the 20th century; the history of leisure electronics is presented in the
German Phono Museum
The German Phono Museum (german: Deutsche Phonomuseum) is a museum in Baden-Württemberg in the town of Sankt Georgen im Schwarzwald.
The museum portrays the history of the music industry, beginning with phonographs and continuing right up to th ...
in
St. Georgen.
The
Schüttesäge Museum
The Schüttesäge Museum is a museum in the town of Schiltach in the Black Forest. It is located in the county of Rottweil in the German federal state of Baden-Württemberg.
The museum has exhibits on the themes of forestry, tanning and timber r ...
in
Schiltach has information and living history demonstrations covering the themes of
lumbering and
timber rafting in the Kinzig valley as well as
tanning.
The
Black Forest Costume Museum in
Haslach im Kinzigtal offers an overview of the traditional costume of the whole of the Black Forest and its peripheral regions. Also located in Haslach: the Hansjakob Museum and the Hansjakob Archive with numerous works of the writer, priest, politician, historian and chronicler,
Heinrich Hansjakob Heinrich Hansjakob (1837- 1916, pseudonym: Hans am See) was a German Catholic priest and Baden historian and politician who was especially well known as a writer. In addition to scientific works, political writings and travel reports, he also publis ...
.
Nature and science
The
MiMa Mineralogy and Mathematics Museum
MiMa is a museum of mineralogy and mathematics in Oberwolfach, in the central Black Forest in southern Germany. The museum was opened on 30 January 2010 on the site of the mineral museum after a two-year conversion and expansion phase. It is o ...
in
Oberwolfach houses minerals and mining exhibits from the whole of the Black Forest and links them to mathematical explanations.
Infrastructure
Road transport
Several tourist routes run through the Black Forest. Well known
holiday route
A scenic route, tourist road, tourist route, tourist drive, holiday route, theme route, or scenic byway is a specially designated road or waterway that travels through an area of natural or cultural beauty. It often passes by scenic viewpoint ...
s are the
Black Forest High Road
Black is a color which results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without hue, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness. Black and white have ...
(
B 500
B, or b, is the second letter of the Latin-script alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is '' bee'' (pronounced ), plural ''bees''. It re ...
) and the
German Clock Road
The German Clock Road (german: Deutsche Uhrenstraße) or German Clock Route is a holiday route that runs from the Central Black Forest through the Southern Black Forest to the Baar region and thus links the centres of Black Forest clock manufact ...
.
Thanks to its winding country roads, the Black Forest is a popular destination for
motorcyclists. This arm of tourism is controversial due to the high number of accidents and the wide-ranging noise pollution and has been restricted through the introduction of speed limits and by placing certain roads out of bounds. For example, since 1984, motorcyclists have been banned from using the
mountain-racing route on the
Schauinsland
The Schauinsland (literally "look-into-the-country"; near Freiburg im Breisgau, Germany) is a mountain in the Black Forest with an elevation of 1,284 m (4,213 ft) above sea level. It is a popular destination for day trips. Due to the h ...
during summer weekends.
Railway transport

The whole of the Black Forest was once linked by
railway. In the eastern part of the Northern Black Forest by the
Enz Valley Railway from
Pforzheim to
Bad Wildbad, by the
Nagold Valley Railway
The Nagold Valley Railway (German: ''Nagoldtalbahn'') is a railway line in the northern part of the Black Forest in Germany which links Pforzheim with Horb am Neckar and, for most of its route, follows the valley of the River Nagold.
Trains on the ...
from Pforzheim via
Calw and
Nagold to
Horb am Neckar, by the
Württemberg Black Forest Railway from
Stuttgart
Stuttgart (; Swabian: ; ) is the capital and largest city of the German state of Baden-Württemberg. It is located on the Neckar river in a fertile valley known as the ''Stuttgarter Kessel'' (Stuttgart Cauldron) and lies an hour from the ...
to Calw and the Gäu Railway from Stuttgart to Freudenstadt or its present-day
section from Eutingen to Freudenstadt.
Many railway lines run from the Rhine Plain up the valleys into the Black Forest: the
Alb Valley Railway runs from
Karlsruhe to
Bad Herrenalb, the
Murg Valley Railway
The Murg Valley Railway (german: Murgtalbahn) is a 58 kilometre long railway line in the Northern Black Forest in Germany, that links Rastatt and Freudenstadt. It was opened in stages from 1868 to 1928 being built outwards from both Rastatt and Fr ...
from
Rastatt to
Freudenstadt, the
Acher Valley Railway from
Achern
Achern (; gsw, label= Low Alemannic, Achre) is a town in Western Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is located approximately 18 km southwest of Baden-Baden and 19 km northeast of Offenburg. Achern is the fourth largest town in the distric ...
to
Ottenhöfen im Schwarzwald and the
Rench Valley Railway from
Appenweier to
Bad Griesbach
Bad Griesbach im Rottal ( bar, label=Central Bavarian, Bad Griasboch im Rottoi), or just Bad Griesbach, is a town in the district of Passau in Bavaria in Germany.
History
"Burg Griesbach" is first mentioned in a document from around 1076. The ...
. The
Baden Black Forest Railway has linked
Offenburg with
Konstanz on
Lake Constance
Lake Constance (german: Bodensee, ) refers to three Body of water, bodies of water on the Rhine at the northern foot of the Alps: Upper Lake Constance (''Obersee''), Lower Lake Constance (''Untersee''), and a connecting stretch of the Rhine, ca ...
since 1873, running via
Hausach,
Triberg,
St. Georgen,
Villingen and
Donaueschingen
Donaueschingen (; Low Alemannic: ''Eschinge'') is a German town in the Black Forest in the southwest of the federal state of Baden-Württemberg in the Schwarzwald-Baar '' Kreis''. It stands near the confluence of the two sources of the river Da ...
. In Hausach the
Kinzig Valley Railway branches off to Freudenstadt, in
Denzlingen the
Elz Valley Railway
The Elz Valley Railway (German: ''Elztalbahn'') is a long, single-tracked, standard gauge branch line in the Black Forest area of the German state of Baden-Württemberg. The line branches off the Freiburg im Breisgau to Offenburg section of the Rh ...
peels off towards
Elzach
Elzach (; Low Alemannic German, Low Alemannic: ''Elze'') is a town in the Emmendingen (district), district of Emmendingen, in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is situated on the river Elz (Rhine), Elz, 26 km northeast of Freiburg.
Geography ...
, the
Höllental Railway runs from
Freiburg im Breisgau
Freiburg im Breisgau (; abbreviated as Freiburg i. Br. or Freiburg i. B.; Low Alemannic German, Low Alemannic: ''Friburg im Brisgau''), commonly referred to as Freiburg, is an independent city in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. With a population o ...
through the Höllental valley to Donaueschingen, the
Münstertal Railway Münstertal may refer to:
* Val Müstair, Switzerland
*Münstertal, Black Forest, Germany
see also
* Taufers im Münstertal
Taufers im Münstertal (; it, Tubre ; rm, Tuer) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in South Tyrol in northern Italy, located ...
from
Bad Krozingen to
Münstertal, the
Kander Valley Railway from
Haltingen near
Basel through the Kander valley to
Kandern
Kandern is a town in southwestern Germany in the state of Baden-Württemberg, in the '' Kreis'' (district) of Lörrach. During the Battle of Schliengen, in which the French Revolutionary army fought the forces of Austria, the battle lines of both ...
and the
Wiesen Valley Railway
The Wiese Valley Railway (german: Wiesentalbahn) is a 27.2 km long, electrified main line in German Baden-Württemberg in the tri-national area of Germany, Switzerland and France near the Swiss city of Basel. It is part of the Basel trination ...
from
Basel to
Zell im Wiesental.
The
Three Lakes Railway branches off at the
Titisee from the Höllental Railway and runs to the
Windgfällweiher
The Windgfällweiher is a reservoir between the Titisee and the Schluchsee in the south of Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is located within the High Black Forest and lies in a hollow formed by ice age glaciation between the villages of Altglashü ...
and the
Schluchsee. The
Wutach Valley Railway
The Wutach Valley Railway or german: Wutachtalbahn is one of the most unusual and impressive stretches of railway in Germany. It links the town of Waldshut-Tiengen, on the High Rhine Railway (''Hochrheinbahn'') and the border of Baden-Württemberg ...
runs along the border between Baden-Württemberg and Switzerland, linking
Waldshut-Tiengen with
Immendingen on the Black Forest Railway.
Most of these routes are still busy today, whilst some are popular
heritage line
A heritage railway or heritage railroad (US usage) is a railway operated as living history to re-create or preserve railway scenes of the past. Heritage railways are often old railway lines preserved in a state depicting a period (or periods) i ...
s.
Administration
Since January 2006, the Black Forest Tourist organisation, ''Schwarzwald Tourismus'', whose head office is in
Freiburg, has been responsible for the administration of tourism in the 320 municipalities of the region. Hitherto there had been four separate tourist associations.
Points of interest

There are many historic towns in the Black Forest. Popular tourist destinations include
Baden-Baden,
Freiburg,
Calw (the birth town of
Hermann Hesse),
Gengenbach,
Staufen Staufen refers to:
*Hohenstaufen, a dynasty of German emperors
*Staufen im Breisgau, a town in Baden-Württemberg, Germany
*Staufen, Aargau, in Switzerland
*Staufen (protein), a protein found in the egg of ''Drosophila''
*Staufen, Austria
The ...
,
Schiltach,
Haslach and
Altensteig
Altensteig (; Swabian German, Swabian: ''Aldaschdaeg'') is a town in the Calw (district), district of Calw, in Baden-Württemberg, Germany.
History
Altensteig was most likely given German town law, town rights by the Counts of Hohenberg around ...
. Other popular destinations include such mountains as the Feldberg, the
Belchen
The Belchen, , or Black Forest Belchen (german: Schwarzwälder Belchen) is the fourth-highest summit of the Black Forest after Feldberg (Black Forest), Feldberg, Seebuck and Herzogenhorn. The municipalities of Münstertal, Black Forest, Münstert ...
, the
Kandel, and the Schauinsland; the
Titisee and
Schluchsee lakes; the
All Saints Waterfalls; the
Triberg Waterfalls, not the highest, but the most famous waterfalls in Germany; and the
gorge
A canyon (from ; archaic British English spelling: ''cañon''), or gorge, is a deep cleft between escarpments or cliffs resulting from weathering and the erosion, erosive activity of a river over geologic time scales. Rivers have a natural tenden ...
of the River
Wutach.
For drivers, the main route through the region is the fast
A 5 (E35) motorway, but a variety of signposted scenic routes such as the
Schwarzwaldhochstraße
The Schwarzwaldhochstraße or ''Black Forest High Road'' is the oldest and one of the best known themed drives in Germany. It is a part of the B 500 federal highway and leads over 60 km from Baden-Baden to Freudenstadt.
Route description
The ...
(,
Baden-Baden to
Freudenstadt), Schwarzwald Tälerstraße (, the
Murg
Murg may refer to:
Places
* Murg (Aare), a river of Switzerland
* Murg (Northern Black Forest), a river and right tributary of the Rhine in the districts of Freudenstadt and Rastatt, Baden-Württemberg, Germany
** Murg Valley Railway
* Murg (Sou ...
and
Kinzig valleys) or Badische Weinstraße (Baden Wine Street, , a wine route from
Baden-Baden to
Weil am Rhein
Weil am Rhein (High Alemannic: ''Wiil am Rhii'') is a German town and commune. It is on the east bank of the River Rhine, and extends to the point at which the Swiss, French and German borders meet. It is the most southwesterly town in Germany an ...
) offers calmer driving along high roads. The last is a picturesque trip starting in the south of the Black Forest going north and includes numerous old wineries and tiny villages. Another, more specialized route is the
German Clock Route, a circular route that traces the
horological history of the region.
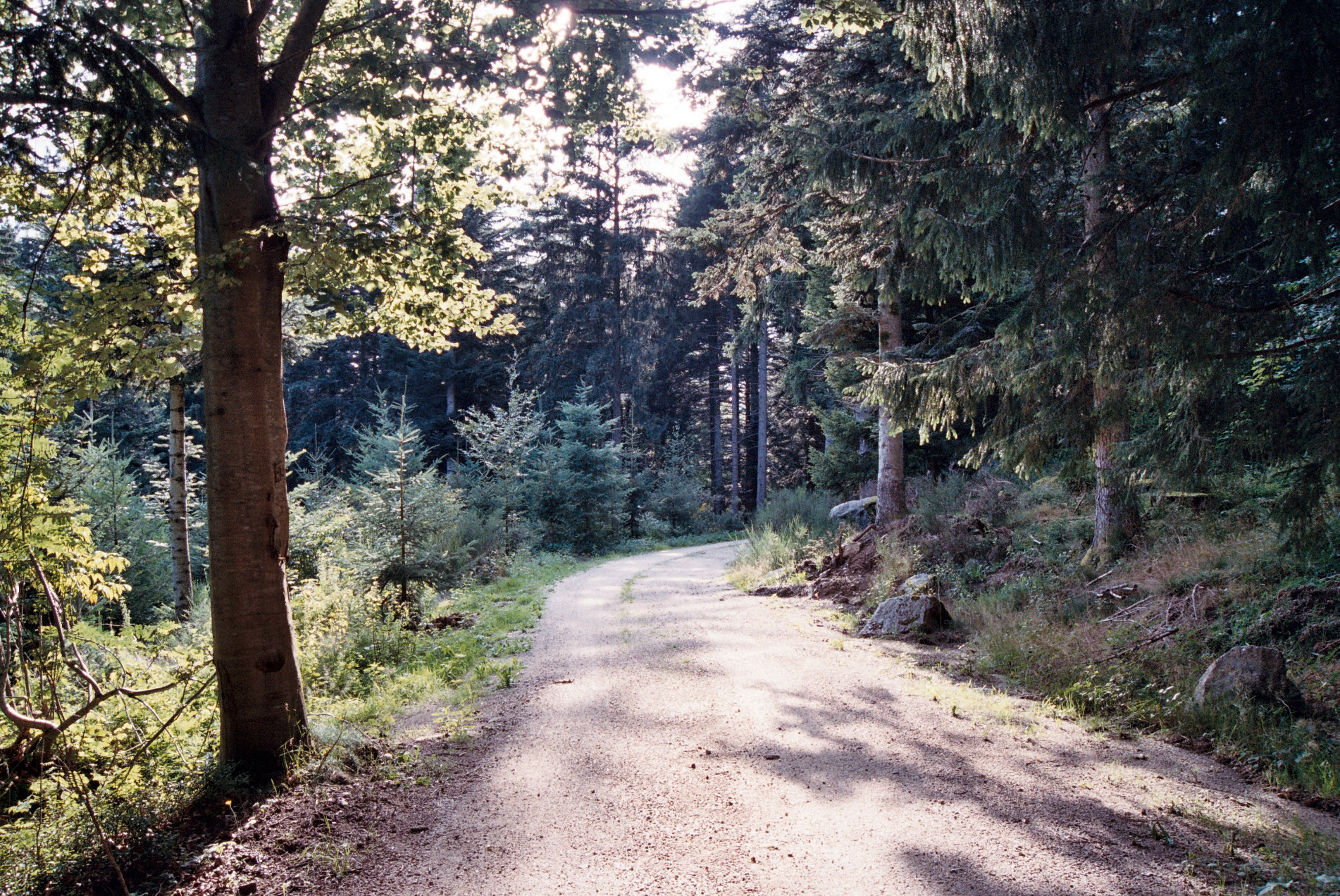

Due to the rich mining history dating from medieval times (the Black Forest was one of the most important mining regions of Europe circa 1100) there are many mines re-opened to the public. Such mines may be visited in the Kinzig valley, the Suggental, the Muenster valley, and around Todtmoos.
The Black Forest was visited on several occasions by Count
Otto von Bismarck
Otto, Prince of Bismarck, Count of Bismarck-Schönhausen, Duke of Lauenburg (, ; 1 April 1815 – 30 July 1898), born Otto Eduard Leopold von Bismarck, was a conservative German statesman and diplomat. From his origins in the upper class of J ...
during his years as Prussian and later German chancellor (1862–1890). Allegedly, he was especially interested in the
Triberg Waterfalls. There is now a monument in Triberg dedicated to Bismarck, who apparently enjoyed the tranquility of the region as an escape from his day-to-day political duties in Berlin.
The Black Forest featured in the philosophical development of
Martin Heidegger
Martin Heidegger (; ; 26 September 188926 May 1976) was a German philosopher who is best known for contributions to phenomenology, hermeneutics, and existentialism. He is among the most important and influential philosophers of the 20th centur ...
. Heidegger wrote and edited some of his philosophical works in a small hut in the Black Forest, and would receive visitors there for walks, including his former pupil
Hannah Arendt
Hannah Arendt (, , ; 14 October 1906 – 4 December 1975) was a political philosopher, author, and Holocaust survivor. She is widely considered to be one of the most influential political theorists of the 20th century.
Arendt was born ...
. This hut features explicitly in his essay ''Building, Dwelling, Thinking''. His walks in the Black Forest are supposed to have inspired the title of his collection of essays ''Holzwege'', translated as ''Off The Beaten Track''.
Economy and craftsmanship
Mining

Mining developed in the Black Forest due to its ore deposits, which were often lode-shaped. The formation of these deposits (
Schauinsland Pit
The Schauinsland Pit (german: Grube Schauinsland, or ''Erzkasten'' in the 19th century) was a silver and lead mine east of Freiburg im Breisgau. From the 19th century zinc was also mined. The mine operated from the 13th century until 1954. Since 1 ...
:
zinc,
lead, about 700–1000 g
silver/ton of lead;
baryte
Baryte, barite or barytes ( or ) is a mineral consisting of barium sulfate ( Ba S O4). Baryte is generally white or colorless, and is the main source of the element barium. The ''baryte group'' consists of baryte, celestine (strontium sulfate), ...
,
fluorite, less lead and zinc in the Kinzig valley;
BiCoNi The BiCoNi Formation is a hydrothermal lode formation, in which bismuth, cobalt, nickel and uranium ores have coalesced. It occurs mainly in the Ore Mountains and is the youngest formation in the hydrothermal sequence (polymetalliferous (kb) form ...
ores near
Wittichen
Wittichen is a village that belongs to Kaltbrunn in the municipality of Schenkenzell in the district of Rottweil in the southwest German state of Baden-Württemberg.
History
In 1291, Luitgard, later the founder of the convent of Wittichen Ab ...
,
uranium discovered in the
Krunkelbach valley near
Menzenschwand but never officially mined) often used to be linked to the intrusion of Carboniferous granite in the para- and orthogneisses. More recent research has revealed that most of these lode fillings are much younger (
Triassic to
Tertiary). Economic deposits of other minerals included: fluorite in the Northern Black Forest near
Pforzheim, baryte in the central region near
Freudenstadt, fluorite along with lead and silver near Wildschapbach, baryte and fluorite in the Rankach valley and near Ohlsbach, in the Southern Black Forest near
Todtnau
Todtnau is a town in the district of Lörrach in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. As of 2009 its population was of 4,932.
Geography
It is situated in the Black Forest, on the river Wiese, 20 km southeast of Freiburg.
The municipality counts ...
,
Wieden and Urberg.
Small liquid magmatic deposits of nickel-magnetite gravel in
norite were mined or prospected in the Hotzenwald forest near Horbach and
Todtmoos
Todtmoos is a village and municipality in the district of Waldshut in the southern part of Baden-Württemberg, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most po ...
. Strata-bound deposits include iron ores in the Dogger layer of the foothill zone and uranium near Müllenbach/Baden-Baden.
Stone coal
Anthracite, also known as hard coal, and black coal, is a hard, compact variety of coal that has a submetallic luster. It has the highest carbon content, the fewest impurities, and the highest energy density of all types of coal and is the hig ...
is only found near
Berghaupten
Berghaupten ( gsw, label= Low Alemannic, Berghoupte) is a municipality in the district of Ortenau in Baden-Württemberg in Germany.
Furthermore, it is a state-approved resort located in the Black Forest. Neighbouring municipalities are Ohlsbach ...
and
Diersburg, but was always only of local importance.
Chronology:
Stone Age
The Stone Age was a broad prehistoric period during which stone was widely used to make tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years, and ended between 4,000 BC and 2,000 BC, with t ...
mining of
haematite
Hematite (), also spelled as haematite, is a common iron oxide compound with the formula, Fe2O3 and is widely found in rocks and soils. Hematite crystals belong to the rhombohedral lattice system which is designated the alpha polymorph of . ...
(as red pigment) near
Sulzburg. By the 5th and 6th centuries B.C.
iron ore
Iron ores are rocks and minerals from which metallic iron can be economically extracted. The ores are usually rich in iron oxides and vary in color from dark grey, bright yellow, or deep purple to rusty red. The iron is usually found in the fo ...
was being mined by the
Celts in the Northern Black Forest (for example in
Neuenbürg). Especially in the Middle Black Forest, but also in the south (for example in the
Münster valley) ore mining was already probably taking place in Roman times (
mining of silver and lead ore; evidence of this at Sulzburg and possibly
Badenweiler). Until the
High Middle Ages the High Black Forest was practically unsettled. In the course of inland colonisation in the Late High Middle Ages even the highlands were cultivated by settlers from the abbeys (
St. Peter's,
St. Märgen's). In the Late High Middle Ages (from about 1100) mining experienced another boom, especially around Todtnau, in the Münster and Suggen valleys and, later, on the
Schauinsland
The Schauinsland (literally "look-into-the-country"; near Freiburg im Breisgau, Germany) is a mountain in the Black Forest with an elevation of 1,284 m (4,213 ft) above sea level. It is a popular destination for day trips. Due to the h ...
too. It is believed that around 800–1,000 miners lived and worked in the Münster valley until the end of the Middle Ages. After the Plague, which afflicted the valley in 1516, the
German Peasants' War
The German Peasants' War, Great Peasants' War or Great Peasants' Revolt (german: Deutscher Bauernkrieg) was a widespread popular revolt in some German-speaking areas in Central Europe from 1524 to 1525. It failed because of intense oppositio ...
(1524–26) and the
Thirty Years' War, mining in the region declined until just a few pits remained.
An important mining area was the
Kinzig valley and its side valleys. The small mining settlement of
Wittichen
Wittichen is a village that belongs to Kaltbrunn in the municipality of Schenkenzell in the district of Rottweil in the southwest German state of Baden-Württemberg.
History
In 1291, Luitgard, later the founder of the convent of Wittichen Ab ...
near
Schenkenzell
Schenkenzell is a village in the district of Rottweil, in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. The town is twinned with Schenkon
Schenkon is a municipality in the district of Sursee in the canton of Lucerne in Switzerland.
Geography
Schenkon has an ...
in the upper Kinzig valley had many pits from which miners dug
baryte
Baryte, barite or barytes ( or ) is a mineral consisting of barium sulfate ( Ba S O4). Baryte is generally white or colorless, and is the main source of the element barium. The ''baryte group'' consists of baryte, celestine (strontium sulfate), ...
,
cobalt and
silver of many kinds. A circular, geological footpath runs today past the old pits and
tips.
Another boom began in the early 18th century after the loss of the
Alsace to France. It lasted until the 19th century. Many pits from this period may be visited today as
show mine
A mine, i.e. an industrial facility for the underground extraction of mineral commodities, has three operating phases: it may be open or running, or closed or it may be a working museum. Most mines are simply closed once they are no longer producti ...
s; for example the Teufelsgrund Pit (
Münstertal), the
Finstergrund
The Finstergrund Pit (german: Grube Finstergrund) near Wieden in the Black Forest in Germany is an abandoned medieval silver and lead mine that was also used in the modern era to extract fluorite and baryte. Since 1982 it has been used as a visi ...
Pit near Wieden, the Hoffnungsstollen ("Hope Gallery") at Todtmoos, the mine in the
Schauinsland
The Schauinsland (literally "look-into-the-country"; near Freiburg im Breisgau, Germany) is a mountain in the Black Forest with an elevation of 1,284 m (4,213 ft) above sea level. It is a popular destination for day trips. Due to the h ...
, the formerly especially silver-rich
Wenzel Pit
The Wenzel Pit (german: Grube Wenzel) is a former silver mine in the Zinken Frohnbach in Oberwolfach in the Black Forest in southern Germany. The pit had its heyday in the Napoleonic era, but has been a show mine since 2001.
History
Silver has ...
in
Oberwolfach and Gr.
Segen Gottes ("God's Great Blessing") in
Haslach-Schnellingen.
Non-ferrous metal mining in the Black Forest continued until the middle of the 20th century near
Wildschapbach and on the Schauinsland (to 1954); fluorite and baryte are still mined today at the
Clara Pit
The Clara Pit (german: Grube Clara) or Clara Mine is a working mine in Oberwolfach in the Black Forest in Germany in which the industrial minerals, baryte and fluorspar are mined.
Importance
The pit is well known because, to date, over 375 di ...
in the Rankach valley in
Oberwolfach. Iron ores of the Dogger formation was worked until the 1970s near
Ringsheim
Ringsheim ( gsw, label= Low Alemannic, Ringsä) is a village in the district of Ortenau in Baden-Württemberg in Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most pop ...
and was smelted in
Kehl
Kehl (; gsw, label= Low Alemannic German, Low Alemannic, Kaal) is a town in southwestern Germany in the Ortenaukreis, Baden-Württemberg. It is on the river Rhine, directly opposite the French city of Strasbourg, with which it shares some munic ...
.
Compared with the
Harz and
Ore Mountains the quantities of silver extracted in the Black Forest were rather modest and reached only about ten percent of that produced in the other silver-mining regions.
There are many
show mine
A mine, i.e. an industrial facility for the underground extraction of mineral commodities, has three operating phases: it may be open or running, or closed or it may be a working museum. Most mines are simply closed once they are no longer producti ...
s in the Black Forest. These include:
the Frischglück Pit near
Neuenbürg, the Hella Glück Pit near
Neubulach, the Silbergründle Pit near
Seebach, the Himmlich Heer Pit near
Hallwangen
Dornstetten is a town in the district of Freudenstadt in Baden-Württemberg in southern Germany. It is situated in the Black Forest, 7 km east of Freudenstadt. It was founded in the early Middle Ages and is well known for its half-timbered ...
, the Heilige Drei Könige Pit near
Freudenstadt, the
Segen Gottes Pit
The Segen Gottes Show Mine (german: Besucherbergwerk Segen Gottes) is a show mine in the parish of Schnellingen in the municipality of Haslach in the Central Black Forest in Germany.Schwarzwald''Besucherbergwerk Segen Gottes'' at www.schwarzwald. ...
near
Haslach, the Wenzel Pit near
Oberwolfach, the
Caroline Pit
The Caroline Pit (german: Grube Caroline) in the Eberbächle, a side valley of the Brettenbach, is an old silver mine in Sexau in the Black Forest in Germany which is open to the public as a show mine. In 1987, volunteers began to uncover the pit a ...
near
Sexau, the Suggental Silver Mine near
Waldkirch
Waldkirch is a town in Baden-Württemberg, Germany, located 15 kilometers northeast of Freiburg im Breisgau. While the English translation of its name is ''Forest Church'', it is known as the "town of mechanical organs", where fairground organs ...
, the Schauinsland Pit near
Freiburg, the Teufelsgrund Pit near
Münstertal, the Finstergrund Pit near
Wieden and the Hoffnungsstollen Pit near
Todtmoos
Todtmoos is a village and municipality in the district of Waldshut in the southern part of Baden-Württemberg, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most po ...
.
Forestry

For several centuries logs from the Black Forest were rafted down the
Enz,
Kinzig,
Murg
Murg may refer to:
Places
* Murg (Aare), a river of Switzerland
* Murg (Northern Black Forest), a river and right tributary of the Rhine in the districts of Freudenstadt and Rastatt, Baden-Württemberg, Germany
** Murg Valley Railway
* Murg (Sou ...
,
Nagold and
Rhine rivers for use in the
shipping industry, as construction
timber and for other purposes. This branch of industry boomed in the 18th century and led to large-scale clearances. As most of the long, straight pine logs were transported downriver for shipbuilding in the
Netherlands, they were referred to as "Dutchmen". The logs were used in the Netherlands, above all, as
piles
Hemorrhoids (or haemorrhoids), also known as piles, are vascular structures in the anal canal. In their normal state, they are cushions that help with stool control. They become a disease when swollen or inflamed; the unqualified term ''hemo ...
for house construction in the sandy and wet ground. Even today in Amsterdam large numbers of historic building are built on these posts and the reforestation of the Black Forest with spruce
monocultures testifies to the destruction of the original
mixed forest. With the expansion of the railway and road network as alternative transportation, rafting largely came to an end in the late 19th century.
Today, loggers harvest fir trees—especially very tall and branchless ones—mainly to ship to Japan. The global advertising impact of
Expo 2000 fuelled a resurgence of timber exports. The importance of the timber resources of the Black Forest has also increased sharply recently due to the increasing demand for
wood pellets for heating.
Glass-making, charcoal-burning and potash-mining
The timber resources of the Black Forest provided the basis for other sectors of the economy that have now largely disappeared.
Charcoal burners (''Köhler'') built their wood piles (''Meiler'') in the woods and produced charcoal, which, like the products of the
potash boilers—further processed ''inter alia'' for the
glassmaking industry. The Black Forest supplied raw materials and energy for the manufacture of
forest glass. This is evidenced today by a number of
glassblowing houses e.g. in the Hoellental in Todtnau and
Wolfach
Wolfach ( gsw, label= Low Alemannic, Wolfä) is a town in the Black Forest and part of the Ortenaukreis in Baden-Württemberg (Germany). It is a well-known spa town.
Geography
Geographical Position
Wolfach lies where the two rivers Wolf and ...
and the Forest Glass Centre in
Gersbach (Schopfheim), which is open to visitors.
Precision-engineering, clock and jewellery manufacture

In the relatively inaccessible Black Forest valleys
industrialization
Industrialisation ( alternatively spelled industrialization) is the period of social and economic change that transforms a human group from an agrarian society into an industrial society. This involves an extensive re-organisation of an econo ...
did not arrive until late in the day. In winter, many
farmers made wooden
cuckoo clocks to supplement their income. This developed in the 19th century into the
precision engineering and watch industry, which boomed with the arrival of the railway in many of the Black Forest valleys. The initial disadvantage of their remote location, which led to the development of precision-engineered wooden handicrafts, became a competitive advantage because of their access to raw materials: timber from the forest and metal from the mines. As part of a structural support programme the Baden State Government founded the first clockmaking school in 1850 in
Furtwangen to ensure that small artisans were given good training and thus better sales opportunities. Due to the increasing demand for mechanical devices, large companies such as
Junghans and
Kienzle
Kienzle is a family name originating in the Swabian-speaking areas of Southwestern Germany. The traditional Swabian pronunciation of the name is , and in Standard German it is pronounced with a long rather than a diphthong: . It is quite common ...
became established. In the 20th century, the production of consumer electronics was developed by companies such as
SABA,
Dual
Dual or Duals may refer to:
Paired/two things
* Dual (mathematics), a notion of paired concepts that mirror one another
** Dual (category theory), a formalization of mathematical duality
*** see more cases in :Duality theories
* Dual (grammatical ...
and
Becker. In the 1970s, the industry declined due to Far Eastern competition. Nevertheless, the Black Forest remains a centre for the metalworking industry and is home to many high-tech companies.
Since the start of industrialisation there have been numerous firms in
Pforzheim that manufacture jewellery and work with precious metals and stones. There is also a
goldsmith's school in Pforzheim.
Hydropower


Due to the large amounts of precipitation and elevation changes the Black Forest has significant
hydropower potential. This was used until the 19th century especially for operating numerous
mills, including
sawmills and
hammer mills and was one of the local factors in the industrialization of some Black Forest valleys.
Since the 20th century, the Black Forest has seen the large-scale generation of electrical power using
run-of-the-river power plant
Run-of-river hydroelectricity (ROR) or run-of-the-river hydroelectricity is a type of hydroelectric generation plant whereby little or no water storage is provided. Run-of-the-river power plants may have no water storage at all or a limited amo ...
s and
pumped storage power stations. From 1914 to 1926, the Rudolf Fettweis Company was established in the Murg valley in the Northern Black Forest with the construction of the
Schwarzenbach Dam
The Schwarzenbach Dam (german: Schwarzenbachtalsperre) is a gravity dam near Forbach in the Northern Black Forest of Germany. It is the most important structure of the Rudolf-Fettweis-Werk's pumped storage power station. The operator of the dam, ...
. In 1932, the
Schluchsee reservoir, with its new dam, became the upper basin of a pumped-storage power plant. In 2013 the association of the Southern Black Forest's ''Schluchseewerk'' owned five power plants with 14 storage tanks. At the
Hornberg Basin topographical conditions allow an average head of water of 625 m to drive the turbines before it flows into the
Wehra Reservoir.
In the 21st century, in the wake of the
Renewable Energy Sources Act
The Renewable Energy Sources Act or EEG (german: Erneuerbare-Energien-Gesetz) is a series of German laws that originally provided a feed-in tariff (FIT) scheme to encourage the generation of renewable electricity. The specified the transi ...
, numerous smaller run-of-the-river power stations were re-opened or newly constructed.
Notable people and residents
*
Hans Jakob Christoffel von Grimmelshausen (1621/22–1676), German novelist; in 1665–67, he kept an inn in Gaisbach in the Black Forest while writing his famous
picaresque novel ''
Simplicius Simplicissimus'' (1669)
*
Hans Thoma
Hans Thoma (2 October 1839 – 7 November 1924) was a German painter.
Biography
Hans Thoma was born on 2 October 1839 in Bernau in the Black Forest, Germany. He was the son of a miller and was trained in the basics of painting by a painter of ...
, born in
Bernau (1839–1924), German painter
*
Hermann Hesse, born in
Calw (1877–1962), German poet and novelist
*
Jürgen Klopp,
Liverpool F.C. manager, who grew up in village of
Glatten
Glatten is a municipality in the district of Freudenstadt in Baden-Württemberg in Germany.
Geography
Geographical location
The state-approved health resort Glatten is located about ten kilometers southeast of the county town of Freudenstadt, ...
Gallery
File:Luftaufnahme-Feldberg-Seebuck-30122004.jpg, The Feldberg
File:Belchen - Gipfel.JPG, View from the Belchen
The Belchen, , or Black Forest Belchen (german: Schwarzwälder Belchen) is the fourth-highest summit of the Black Forest after Feldberg (Black Forest), Feldberg, Seebuck and Herzogenhorn. The municipalities of Münstertal, Black Forest, Münstert ...
towards the Alps
File:Zweitaelersteig Eckleberg04.jpg, Cattle near Simonswald
Simonswald ( Low Alemannic: ''Simeschwald'') is a town in the district of Emmendingen in Baden-Württemberg in Germany.
Twin towns
: Worthing
Worthing () is a seaside town in West Sussex, England, at the foot of the South Downs, west of B ...
File:Titisee winter.jpg, The Titisee, popular year-round
File:Münster Freiburg.jpg, The Minster in Freiburg, the region's biggest city
File:Kinzig.jpg, The River Kinzig passing through the Black Forest
File:Mummelsee.jpg, The Mummelsee
File:Jugendherberge Schloss Ortenberg.jpg, Ortenberg Castle near Offenburg (now a youth hostel
A hostel is a form of low-cost, short-term shared sociable lodging where guests can rent a bed, usually a bunk bed in a dormitory, with shared use of a lounge and sometimes a kitchen. Rooms can be mixed or single-sex and have private or shared b ...
)
File:Murgtalbahn Tennetschluchtbruecke Stadtbahn-dvdb.jpg, The Murg Valley Railway
The Murg Valley Railway (german: Murgtalbahn) is a 58 kilometre long railway line in the Northern Black Forest in Germany, that links Rastatt and Freudenstadt. It was opened in stages from 1868 to 1928 being built outwards from both Rastatt and Fr ...
File:Clock forest.jpg, The Black Forest is known for its native clockmakers
File:Vogtsbauernhof klein.jpg, Traditional farmhouse of the Black Forest
File:Hausach 4.jpg, Hausach
File:Schiltach Altstadt 3.JPG, Schiltach
File:Paragleiter.JPG, Paragliding above Baden-Baden
File:Palais thermal aussenansicht.jpg, The former ''Graf-Eberhard-Bad'' (now: Palais Thermal The Palais Thermal is a spa in Bad Wildbad in Germany. The construction for the spa building was finished in 1847 and opened under the name of Graf-Eberhard-Bad.
Architecture
The "Wildbad" established not only the centuries-old bathing tradition ...
) in Bad Wildbad
See also
*
Hercynian Forest (historic)
*
Schwarzwaldverein
The Schwarzwaldverein (Black Forest Club or Black Forest Association) was founded in Freiburg im Breisgau (Germany) in 1864, making it the oldest German hiking and mountaineering club. The Schwarzwaldverein has almost 90,000 members in 241 loca ...
(Black Forest Association)
*
German Clock Museum
*
Black Forest gateau
Black Forest gâteau or Black Forest cake (American English) is a chocolate sponge cake with a rich cherry filling based on the German dessert (), literally "Black Forest Cherry-torte".
Typically, Black Forest gateau consists of several laye ...
Notes
References
Bibliography
Geography
* .
* .
* .
* .
* .
Economy, geology and mining
* .
*
Eberhard Gothein: ''Wirtschaftsgeschichte des Schwarzwaldes und der angrenzenden Landschaften. Erster Band: Städte- und Gewerbegeschichte'', Verlag Karl J. Trübner, Strassburg 1892
digitalised.
* .
* .
* .
Art history
* Richard Schmidt: ''Schwarzwald'' (Deutsche Lande – Deutsche Kunst). Munich/Berlin, 1965.
Nature
* Adolf Hanle: ''Nordschwarzwald'' (Meyers Naturführer). Mannheim/Vienna/Zurich, 1989.
* Adolf Hanle: ''Südschwarzwald'' (Meyers Naturführer). Mannheim/Vienna/Zurich, 1989.
* Ulrike Klugmann (Hrsg.): ''Südschwarzwald, Feldberg und Wutachschlucht'' (Naturmagazin Draußen). Hamburg, 1983.
* Hans-Peter Schaub: ''Der Schwarzwald. Naturvielfalt in einer alten Kulturlandschaft.'' Mannheim, 2001.
Fiction
* Jürgen Lodemann (ed.): ''Schwarzwaldgeschichten''. Klöpfer & Mayer, Tübingen, 2007, .
* Herbert Schnierle-Lutz (ed.): ''Schwarzwald-Lesebuch. Geschichten aus 6 Jahrhunderten mit zahlreichen Bildern'', 224 pages, Hohenheim Verlag, Stuttgart, 2011, .
General
*Bremke, N. (1999). ''Schwarzwald quer''. Karlsruhe: Braun. .
*Lamparski, F. (1985). Der Einfluß der Regenwurmart Lumbricus badensis auf Waldböden im Südschwarzwald. ''Schriftenreihe des Institut für Bodenkunde und Waldernährungslehre der Albert-Ludwigs-Universität Freiburg i. Br., 15''.
English summary*Barnes, K. J. (2007). ''A Rough Passage: Memories of an Empire''
*.
External links
*
*
*
{{Authority control
Forests and woodlands of Germany
Regions of Baden-Württemberg
Natural regions of the South German Scarplands
Mountain and hill ranges of Baden-Württemberg
Horsts (geology)


 In ancient times, the Black Forest was known as , after the Celtic deity, Abnoba. In Roman times ( Late antiquity), it was given the name ("Marcynian Forest", from the Germanic word ''marka'' = "border"). The Black Forest probably represented the border area of the Marcomanni ("border people") who were settled east of the Roman . They, in turn, were part of the Germanic tribe of
In ancient times, the Black Forest was known as , after the Celtic deity, Abnoba. In Roman times ( Late antiquity), it was given the name ("Marcynian Forest", from the Germanic word ''marka'' = "border"). The Black Forest probably represented the border area of the Marcomanni ("border people") who were settled east of the Roman . They, in turn, were part of the Germanic tribe of  The most common way of dividing the regions of the Black Forest is, however, from north to south. Until the 1930s, the Black Forest was divided into the Northern and Southern Black Forest, the boundary being the line of the Kinzig valley. Later the Black Forest was divided into the heavily forested
The most common way of dividing the regions of the Black Forest is, however, from north to south. Until the 1930s, the Black Forest was divided into the Northern and Southern Black Forest, the boundary being the line of the Kinzig valley. Later the Black Forest was divided into the heavily forested  The Black Forest Foothills (', 150) geomorphologically form plateaux on the north and northeast periphery of the mountain range that descend to the Kraichgau in the north and the Heckengäu landscapes in the east. They are incised by valleys, especially those of the Nagold river system, into individual interfluves; a narrow northwestern finger extends to beyond the Enz near Neuenbürg and also borders the middle reaches of the
The Black Forest Foothills (', 150) geomorphologically form plateaux on the north and northeast periphery of the mountain range that descend to the Kraichgau in the north and the Heckengäu landscapes in the east. They are incised by valleys, especially those of the Nagold river system, into individual interfluves; a narrow northwestern finger extends to beyond the Enz near Neuenbürg and also borders the middle reaches of the  The Central Black Forest (153) is mainly restricted to the catchment area of the River Kinzig above Offenburg as well as the Schutter and the low hills north of the Elz.
The Southeastern Black Forest (, 154) consists mainly of the catchment areas of the upper reaches of the Danube headstreams, the Brigach and Breg as well as the left side valleys of the Wutach north of Neustadt – and thus draining from the northeast of the Southern Black Forest. To the south and west it is adjoined by the High Black Forest (, 155) with the highest summits in the whole range around the Feldberg and the
The Central Black Forest (153) is mainly restricted to the catchment area of the River Kinzig above Offenburg as well as the Schutter and the low hills north of the Elz.
The Southeastern Black Forest (, 154) consists mainly of the catchment areas of the upper reaches of the Danube headstreams, the Brigach and Breg as well as the left side valleys of the Wutach north of Neustadt – and thus draining from the northeast of the Southern Black Forest. To the south and west it is adjoined by the High Black Forest (, 155) with the highest summits in the whole range around the Feldberg and the 

 Rivers in the Black Forest include the Danube (which originates in the Black Forest as the confluence of the Brigach and Breg rivers), the Enz, the Kinzig, the
Rivers in the Black Forest include the Danube (which originates in the Black Forest as the confluence of the Brigach and Breg rivers), the Enz, the Kinzig, the  The Black Forest consists of a cover of sandstone on top of a core of gneiss and granite. Formerly it shared tectonic evolution with the nearby Vosges Mountains. Later during the Middle Eocene a rifting period affected the area and caused formation of the Upper Rhine Plain. During the last glacial period of the Würm glaciation, the Black Forest was covered by glaciers; several tarns (or lakes) such as the Mummelsee are remains of this period.
The Black Forest consists of a cover of sandstone on top of a core of gneiss and granite. Formerly it shared tectonic evolution with the nearby Vosges Mountains. Later during the Middle Eocene a rifting period affected the area and caused formation of the Upper Rhine Plain. During the last glacial period of the Würm glaciation, the Black Forest was covered by glaciers; several tarns (or lakes) such as the Mummelsee are remains of this period.
 The Black Forest is home to an unusual tarot card game, Cego, that is part of the region's cultural heritage.''Cego – Regeln''
The Black Forest is home to an unusual tarot card game, Cego, that is part of the region's cultural heritage.''Cego – Regeln'' There are two
There are two 
 The wettest areas are the highlands around the Hornisgrinde in the north and around the Belchen and Feldberg in the south, where annual rainfall reaches 1,800–2,100 mm. Moisture-laden Atlantic westerlies dump about as much rain in the Northern Black Forest, despite its lower elevation, than in the higher area of the Southern Black Forest. There, the Vosges act as a rain shield in the face of the prevailing winds. On the exposed east side of the Central Black Forest, it is much drier; the annual rainfall there is about 750 L/m2.
The higher elevations of the Black Forest are characterized by relatively small annual fluctuations and steamed extreme values. This is the result of the frequent light winds and greater cloud cover in summer. During the winter months, frequent high pressure means that the summits are often bathed in sunshine, while the valleys disappear under a thick blanket of fog as a result of pockets of cold air ( temperature inversion).
The wettest areas are the highlands around the Hornisgrinde in the north and around the Belchen and Feldberg in the south, where annual rainfall reaches 1,800–2,100 mm. Moisture-laden Atlantic westerlies dump about as much rain in the Northern Black Forest, despite its lower elevation, than in the higher area of the Southern Black Forest. There, the Vosges act as a rain shield in the face of the prevailing winds. On the exposed east side of the Central Black Forest, it is much drier; the annual rainfall there is about 750 L/m2.
The higher elevations of the Black Forest are characterized by relatively small annual fluctuations and steamed extreme values. This is the result of the frequent light winds and greater cloud cover in summer. During the winter months, frequent high pressure means that the summits are often bathed in sunshine, while the valleys disappear under a thick blanket of fog as a result of pockets of cold air ( temperature inversion).
 The main industry of the Black Forest is tourism. Black Forest Tourism (''Schwarzwald Tourismus'') assesses that there are around 140,000 direct full-time jobs in the tourist sector and around 34.8 million tourist overnight stays in 2009. In spring, summer and autumn an extensive network of hiking trails and mountain bike routes enable different groups of people to use the natural region. In winter, it is the various types of winter sport that come to the fore. There are facilities for both
The main industry of the Black Forest is tourism. Black Forest Tourism (''Schwarzwald Tourismus'') assesses that there are around 140,000 direct full-time jobs in the tourist sector and around 34.8 million tourist overnight stays in 2009. In spring, summer and autumn an extensive network of hiking trails and mountain bike routes enable different groups of people to use the natural region. In winter, it is the various types of winter sport that come to the fore. There are facilities for both  There are well known winter sports areas around the Feldberg, near
There are well known winter sports areas around the Feldberg, near  The
The  There are many historic towns in the Black Forest. Popular tourist destinations include Baden-Baden, Freiburg, Calw (the birth town of Hermann Hesse), Gengenbach,
There are many historic towns in the Black Forest. Popular tourist destinations include Baden-Baden, Freiburg, Calw (the birth town of Hermann Hesse), Gengenbach,  Due to the rich mining history dating from medieval times (the Black Forest was one of the most important mining regions of Europe circa 1100) there are many mines re-opened to the public. Such mines may be visited in the Kinzig valley, the Suggental, the Muenster valley, and around Todtmoos.
The Black Forest was visited on several occasions by Count
Due to the rich mining history dating from medieval times (the Black Forest was one of the most important mining regions of Europe circa 1100) there are many mines re-opened to the public. Such mines may be visited in the Kinzig valley, the Suggental, the Muenster valley, and around Todtmoos.
The Black Forest was visited on several occasions by Count  Mining developed in the Black Forest due to its ore deposits, which were often lode-shaped. The formation of these deposits (
Mining developed in the Black Forest due to its ore deposits, which were often lode-shaped. The formation of these deposits ( For several centuries logs from the Black Forest were rafted down the Enz, Kinzig,
For several centuries logs from the Black Forest were rafted down the Enz, Kinzig,  In the relatively inaccessible Black Forest valleys
In the relatively inaccessible Black Forest valleys 
 Due to the large amounts of precipitation and elevation changes the Black Forest has significant hydropower potential. This was used until the 19th century especially for operating numerous mills, including sawmills and hammer mills and was one of the local factors in the industrialization of some Black Forest valleys.
Since the 20th century, the Black Forest has seen the large-scale generation of electrical power using
Due to the large amounts of precipitation and elevation changes the Black Forest has significant hydropower potential. This was used until the 19th century especially for operating numerous mills, including sawmills and hammer mills and was one of the local factors in the industrialization of some Black Forest valleys.
Since the 20th century, the Black Forest has seen the large-scale generation of electrical power using