|
Piedmonttreppen
A piedmonttreppen or piedmont benchland is a conceived landform consisting in a succession of benches at different heights and that forms in sequence during the uplift of a geological dome. The concept was first proposed in a posthumous publication by Walther Penck in 1924. Penck's type area for the piedmontreppen was the Black Forest of Germany. Outside Germany the South Swedish Dome has been identified as containing a piedmonttreppen, with the uppermost and oldest surface being the Sub-Cambrian peneplain. It is followed by three surfaces, one at 300 m a.s.l., another at 200 m and then the South Småland peneplain. There have been attempts at describing the southern portion of the Scandinavian Mountains as having a piedmonttreppen topography made up of paleic surfaces in the uplands and a strandflat at sea level. This idea has been strongly contested by Olaf Holtedahl Prof Olaf Holtedahl ForMemRS FRSE (24 June 1885 – 26 August 1975) was a Norwegian geologist (Dr.p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walther Penck
Walther Penck (30 August 1888 – 29 September 1923) was a geologist and geomorphologist known for his theories on landscape evolution. Penck is noted for criticizing key elements of the Davisian cycle of erosion, concluding that the process of uplift and denudation occur simultaneously, at gradual and continuous rates. Penck's idea of parallel slope retreat led to revisions of Davis's cycle of erosion. Biography Walther Penck was born in Vienna as the son of German geographer Albrecht Penck.Encyclopædia Britannica 2014 He obtained a PhD by studying petrology at the Heidelberg University. Between 1912 and 1915 he worked in Dirección General de Minas in Buenos Aires before moving to the University of Constantinople where he was named professor of mineralogy and geology. He finally settled as professor in the University of Leipzig in 1918. The areas he studied in detail and based his theories on include the Black Forest in Germany, Puna de Atacama in Argentina and Anatoli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Forest
The Black Forest (german: Schwarzwald ) is a large forested mountain range in the state of Baden-Württemberg in southwest Germany, bounded by the Rhine Valley to the west and south and close to the borders with France and Switzerland. It is the source of the Danube and Neckar rivers. Its highest peak is the Feldberg with an elevation of above sea level. Roughly oblong in shape, with a length of and breadth of up to , it has an area of about 6,009 km2 (2,320 sq mi). Historically, the area was known for forestry and the mining of ore deposits, but tourism has now become the primary industry, accounting for around 300,000 jobs. There are several ruined military fortifications dating back to the 17th century. History In ancient times, the Black Forest was known as , after the Celtic deity, Abnoba. In Roman times (Late antiquity), it was given the name ("Marcynian Forest", from the Germanic word ''marka'' = "border"). The Black Forest probably represented the bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planation Surface
In geology and geomorphology a planation surface is a large-scale surface that is almost flat with the possible exception of some residual hills. The processes that form planation surfaces are labelled collectively planation and are exogenic (chiefly erosion). Planation surfaces are planated regardless of bedrock structures. On Earth, they constitute some of the most common landscapes. Geological maps indicate that planation surfaces may comprise 65% of the landscapes on Saturn's largest moon, Titan, which hosts a hydrological cycle of liquid methane. Peneplains and pediplains are types of planation surfaces planated respectively by "peneplanation" and "pediplanation". In addition to these there are planation surfaces proposed to be formed by cryoplanation, marine processes, areal glacial erosion and salt weathering. The term ''planation surface'' is often preferred over others because some more specific planation surface types and processes remain controversial. Etchplains are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
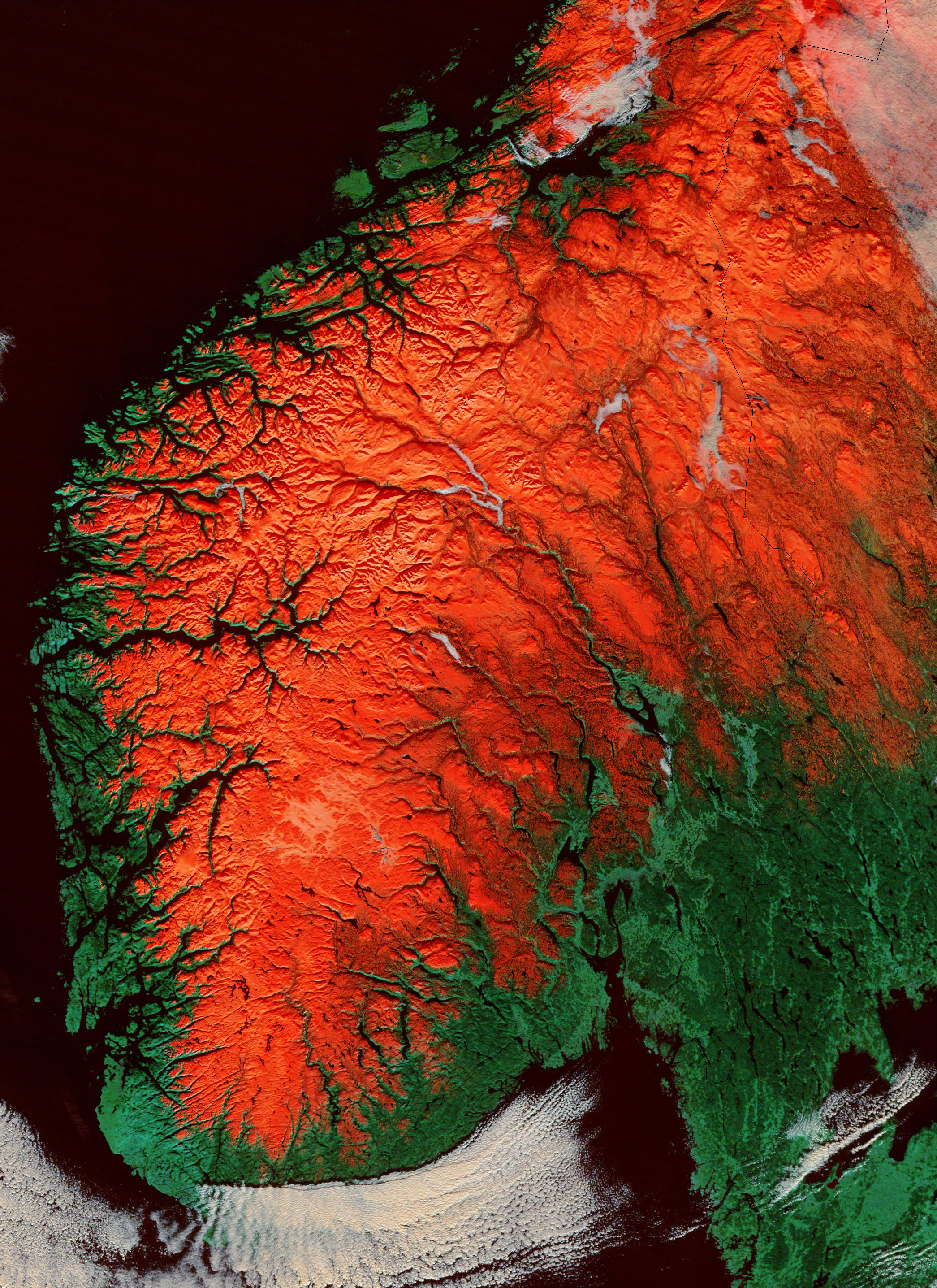
Scandinavian Mountains
The Scandinavian Mountains or the Scandes is a mountain range that runs through the Scandinavian Peninsula. The western sides of the mountains drop precipitously into the North Sea and Norwegian Sea, forming the fjords of Norway, whereas to the northeast they gradually curve towards Finland. To the north they form the border between Norway and Sweden, reaching high at the Arctic Circle. The mountain range just touches northwesternmost Finland but are scarcely more than hills at their northernmost extension at the North Cape (). The mountains are relatively high for a range so young and are very steep in places; Galdhøpiggen in South Norway is the highest peak in mainland Northern Europe, at ; Kebnekaise is the highest peak on the Swedish side, at , whereas the slope of Halti is the highest point in Finland, at , although the peak of Halti is situated in Norway. The Scandinavian Montane Birch forest and grasslands terrestrial ecoregion is closely associated with the mountain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erosion Landforms
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is distinct from weathering which involves no movement. Removal of rock or soil as clastic sediment is referred to as ''physical'' or ''mechanical'' erosion; this contrasts with ''chemical'' erosion, where soil or rock material is removed from an area by dissolution. Eroded sediment or solutes may be transported just a few millimetres, or for thousands of kilometres. Agents of erosion include rainfall; bedrock wear in rivers; coastal erosion by the sea and waves; glacial plucking, abrasion, and scour; areal flooding; wind abrasion; groundwater processes; and mass movement processes in steep landscapes like landslides and debris flows. The rates at which such processes act control how fast a surface is eroded. Typically, physical erosion proceed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norwegian Journal Of Geography
__NOTOC__ ''Norwegian Journal of Geography'' ( no, Norsk Geografisk Tidsskrift) is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Routledge on behalf of the Norwegian Geographical Society. It covers geographical topics of interest to Norwegian researchers giving equal weight to human and natural geography. It was established in 1926 as successor of the ''Norsk Geografisk Aarbog'' ("Norwegian Geographical Yearbook"), which was published from 1889 to 1921. The editor-in-chief at one point was Kerstin Potthoff of University of Bergen. In 2012, Michael Jones was the editor, and he had started in 2006. He was based at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology, in Trondheim. He announced that as of 2012 the journal would change from publishing four issues per year to five, and that the number of editors had increased to four. He stated:As before, the journal publishes articles on themes related to the geography of Norway, the other Nordic countries and adjacent regions, inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olaf Holtedahl
Prof Olaf Holtedahl ForMemRS FRSE (24 June 1885 – 26 August 1975) was a Norwegian geologist (Dr.philos., 1913). He became a senior lecturer at the University of Oslo in 1914, and was Professor of Geology there from 1920 to 1956. Career Olaf Holtedahl was born in Kristiania (modern-day Oslo), Norway, the son of Arne H. Holtedahl, superintendent of pauper administration, and his wife, Mathilde Madsen. Around 1903 he did his obligatory military service at Gardermoen, just north of Oslo, and here met Captain Gunnar Isachsen who greatly influenced him, and first inspired his interest in polar regions. In 1909, Isachsen invited Holtedahl to join him in explorations of Spitsbergen as official geologist of the group. He studied Geology at the University of Oslo, graduating in 1909 and receiving a doctorate in 1913. Staying in the university as staff he received his professorship in 1920. Holtedahl was among the last of a generation of geologists that mastered the subject in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strandflat
Strandflat ( no , strandflate) is a landform typical of the Norwegian coast consisting of a flattish erosion surface on the coast and near-coast seabed. In Norway, strandflats provide room for settlements and agriculture, constituting important cultural landscapes. The shallow and protected waters of strandflats are valued fishing grounds that provide sustenance to traditional fishing settlements. Outside Norway proper, strandflats can be found in other high-latitude areas, such as Antarctica, Alaska, the Canadian Arctic, the Russian Far North, Greenland, Svalbard, Sweden and Scotland. The strandflats are usually bounded on the landward side by a sharp break in slope, leading to mountainous terrain or high plateaux. On the seaward side, strandflats end at submarine slopes. The bedrock surface of strandflats is uneven and tilts gently towards the sea. The concept of a strandflat was introduced in 1894 by Norwegian geologist Hans Reusch. Norwegian strandflat Characteristics Str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleic Surface
The paleic surface or palaeic surface ( no, paleiske overflaten, ) is an erosion surface of gentle slopes that exist in South Norway. Parts of it are a continuation of the Sub-Cambrian peneplain and Muddus Plains found further east or equivalent to the strandflat coastal plains of Norway. Hardangervidda, a particularly flat and elevated part of the Paleic surface formed in the Miocene at sea level. Although the tilted plateau-like topography of south Norway had been noted since the early 1800s, the first formal description was by Hans Reusch in 1901, using a denudation chronology approach invoking several of W.M. Davis’ ideas of a cycle of erosion. Reusch also coined the name ''Paleic surface''. The Paleic surface is sometimes erroneously considered equal to Norway's "pre-glacial surface" – the surface that existed in Norway just before the Quaternary glaciations. South Norway: the type area There have been various attempts at defining the subset of surfaces that comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Småland Peneplain
300px, upright=1.35, View of the South Småland peneplain at inselberg.html"_;"title="Store_Mosse_National_Park._Note_the_residual_hill_or_inselberg">Store_Mosse_National_Park._Note_the_residual_hill_or_inselberg_in_the_background. The_South_Småland_peneplain_(_sv.html" ;"title="inselberg_in_the_background..html" ;"title="inselberg.html" ;"title="Store Mosse National Park. Note the residual hill or inselberg">Store Mosse National Park. Note the residual hill or inselberg in the background.">inselberg.html" ;"title="Store Mosse National Park. Note the residual hill or inselberg">Store Mosse National Park. Note the residual hill or inselberg in the background. The South Småland peneplain ( sv">Sydsmåländska peneplanet) is a large flattish erosion surface, a peneplain, formed during the Tertiary, covering large swathes of southern Småland and nearby areas in Southern Sweden. To the east the South Småland peneplain bounds with the Sub-Cambrian peneplain uphill across an escarpmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GFF (journal)
GFF may refer to: Entertainment * Girlfriends Films, an American pornographic studio * Glasgow Film Festival, in Scotland * Gothenburg Film Festival, in Sweden Sports * Gabonese Football Federation * Gambia Football Federation * Georgian Football Federation * Göteborgs FF, Swedish football club * Gothenburg Football Association * Guinean Football Federation * Guyana Football Federation Other uses * ''GFF'' (journal), a geology journal * General feature format, a file format used for describing genes * Göteborgs FyrverkeriFabrik, a Swedish fireworks company * Griffith Airport, in New South Wales, Australia * Griffith railway station Griffith railway station is located on the Yanco-Griffith line in New South Wales, Australia. It serves the city of Griffith. History Griffith station opened on 3 July 1916 when the Temora-Roto line was extended from Barellan. It served as ..., in New South Wales, Australia * Guild of Fine Food, a British family-owned company ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
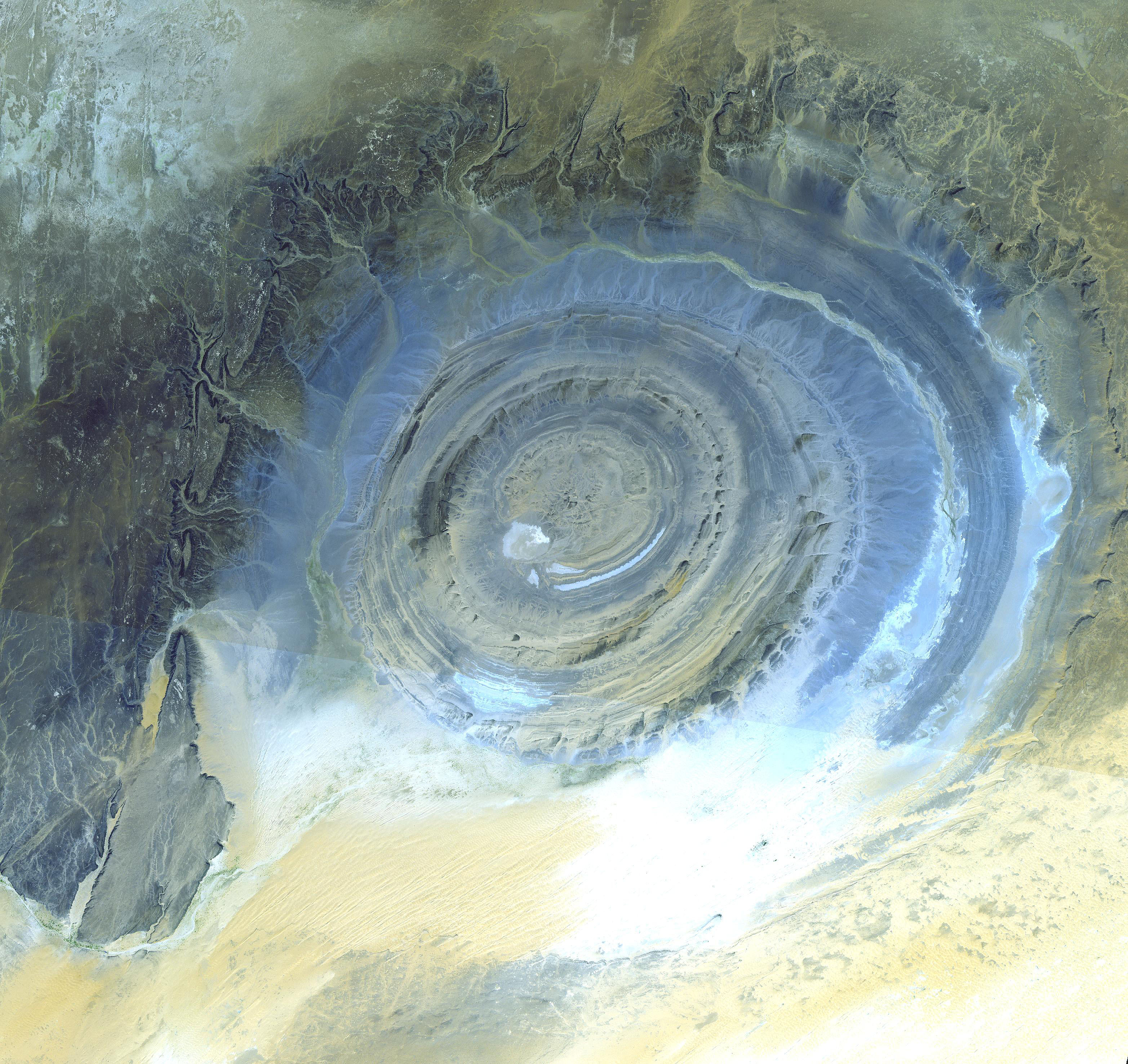
Dome (geology)
A dome is a feature in structural geology consisting of symmetrical anticlines that intersect each other at their respective apices. Intact, domes are distinct, rounded, spherical-to- ellipsoidal-shaped protrusions on the Earth's surface. However, a transect parallel to Earth's surface of a dome features concentric rings of strata. Consequently, if the top of a dome has been eroded flat, the resulting structure in plan view appears as a bullseye, with the youngest rock layers at the outside, and each ring growing progressively older moving inwards. These strata would have been horizontal at the time of deposition, then later deformed by the uplift associated with dome formation. Formation mechanisms There are many possible mechanisms responsible for the formation of domes, the foremost of which are post-impact uplift, refolding, and diapirism. Post-impact uplift A complex crater, caused by collision of a hypervelocity body with another larger than itself, is typified by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |