|
Walther Penck
Walther Penck (30 August 1888 – 29 September 1923) was a geologist and geomorphologist known for his theories on landscape evolution. Penck is noted for criticizing key elements of the Davisian cycle of erosion, concluding that the process of uplift and denudation occur simultaneously, at gradual and continuous rates. Penck's idea of parallel slope retreat led to revisions of Davis's cycle of erosion. Biography Walther Penck was born in Vienna as the son of German geographer Albrecht Penck.Encyclopædia Britannica 2014 He obtained a PhD by studying petrology at the Heidelberg University. Between 1912 and 1915 he worked in Dirección General de Minas in Buenos Aires before moving to the University of Constantinople where he was named professor of mineralogy and geology. He finally settled as professor in the University of Leipzig in 1918. The areas he studied in detail and based his theories on include the Black Forest in Germany, Puna de Atacama in Argentina and Anatoli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vienna
en, Viennese , iso_code = AT-9 , registration_plate = W , postal_code_type = Postal code , postal_code = , timezone = CET , utc_offset = +1 , timezone_DST = CEST , utc_offset_DST = +2 , blank_name = Vehicle registration , blank_info = W , blank1_name = GDP , blank1_info = € 96.5 billion (2020) , blank2_name = GDP per capita , blank2_info = € 50,400 (2020) , blank_name_sec1 = HDI (2019) , blank_info_sec1 = 0.947 · 1st of 9 , blank3_name = Seats in the Federal Council , blank3_info = , blank_name_sec2 = GeoTLD , blank_info_sec2 = .wien , website = , footnotes = , image_blank_emblem = Wien logo.svg , blank_emblem_size = Vienna ( ; german: Wien ; ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Forest
The Black Forest (german: Schwarzwald ) is a large forested mountain range in the state of Baden-Württemberg in southwest Germany, bounded by the Rhine Valley to the west and south and close to the borders with France and Switzerland. It is the source of the Danube and Neckar rivers. Its highest peak is the Feldberg with an elevation of above sea level. Roughly oblong in shape, with a length of and breadth of up to , it has an area of about 6,009 km2 (2,320 sq mi). Historically, the area was known for forestry and the mining of ore deposits, but tourism has now become the primary industry, accounting for around 300,000 jobs. There are several ruined military fortifications dating back to the 17th century. History In ancient times, the Black Forest was known as , after the Celtic deity, Abnoba. In Roman times (Late antiquity), it was given the name ("Marcynian Forest", from the Germanic word ''marka'' = "border"). The Black Forest probably represented the bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peneplain
390px, Sketch of a hypothetical peneplain formation after an orogeny. In geomorphology and geology, a peneplain is a low-relief plain formed by protracted erosion. This is the definition in the broadest of terms, albeit with frequency the usage of peneplain is meant to imply the representation of a near-final (or penultimate) stage of fluvial erosion during times of extended tectonic stability. Peneplains are sometimes associated with the cycle of erosion theory of William Morris Davis, but Davis and other workers have also used the term in a purely descriptive manner without any theory or particular genesis attached. The existence of some peneplains, and peneplanation as a process in nature, is not without controversy, due to a lack of contemporary examples and uncertainty in identifying relic examples. By some definitions, peneplains grade down to a base level represented by sea level, yet in other definitions such a condition is ignored. Geomorphologist Karna Lidmar-Bergstr� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erosion Cycle
The geographic cycle, or cycle of erosion, is an idealized model that explains the development of relief in landscapes. The model starts with the erosion that follows uplift of land above a base level and ends, if conditions allow, in the formation of a peneplain. Landscapes that show evidence of more than one cycle of erosion are termed "polycyclical". The cycle of erosion and some of its associated concepts have, despite their popularity, been a subject of much criticism. Description William Morris Davis, the originator of the model, divided it into stages whose transition is gradual. The model begins with an uplifted or to-be-uplifted landscape. Then Davis defined a ''youthful'' stage where river incision is the dominant process shaping the landscape. During the ''youthful'' stage height, differences between uplands and valley bottoms increase rapidly. The ''youthful'' stage is followed by a ''mature'' stage in which height differences between valley bottoms and uplands are at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
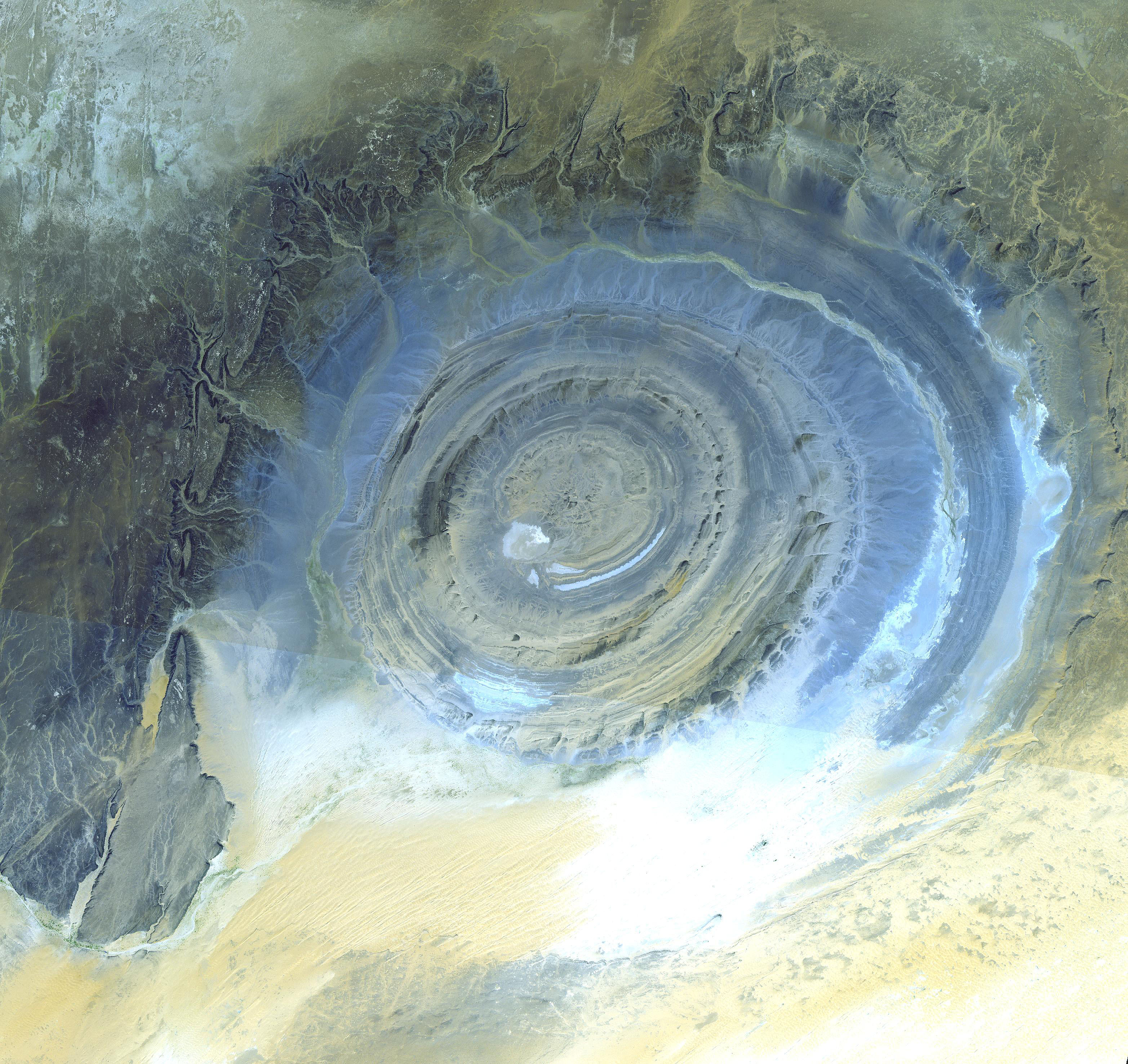
Dome (geology)
A dome is a feature in structural geology consisting of symmetrical anticlines that intersect each other at their respective apices. Intact, domes are distinct, rounded, spherical-to- ellipsoidal-shaped protrusions on the Earth's surface. However, a transect parallel to Earth's surface of a dome features concentric rings of strata. Consequently, if the top of a dome has been eroded flat, the resulting structure in plan view appears as a bullseye, with the youngest rock layers at the outside, and each ring growing progressively older moving inwards. These strata would have been horizontal at the time of deposition, then later deformed by the uplift associated with dome formation. Formation mechanisms There are many possible mechanisms responsible for the formation of domes, the foremost of which are post-impact uplift, refolding, and diapirism. Post-impact uplift A complex crater, caused by collision of a hypervelocity body with another larger than itself, is typified by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piedmonttreppen
A piedmonttreppen or piedmont benchland is a conceived landform consisting in a succession of benches at different heights and that forms in sequence during the uplift of a geological dome. The concept was first proposed in a posthumous publication by Walther Penck in 1924. Penck's type area for the piedmontreppen was the Black Forest of Germany. Outside Germany the South Swedish Dome has been identified as containing a piedmonttreppen, with the uppermost and oldest surface being the Sub-Cambrian peneplain. It is followed by three surfaces, one at 300 m a.s.l., another at 200 m and then the South Småland peneplain. There have been attempts at describing the southern portion of the Scandinavian Mountains as having a piedmonttreppen topography made up of paleic surfaces in the uplands and a strandflat at sea level. This idea has been strongly contested by Olaf Holtedahl Prof Olaf Holtedahl ForMemRS FRSE (24 June 1885 – 26 August 1975) was a Norwegian geologist (Dr.p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fold (geology)
In structural geology, a fold is a stack of originally planar surfaces, such as sedimentary strata, that are bent or curved during permanent deformation. Folds in rocks vary in size from microscopic crinkles to mountain-sized folds. They occur as single isolated folds or in periodic sets (known as ''fold trains''). Synsedimentary folds are those formed during sedimentary deposition. Folds form under varied conditions of stress, pore pressure, and temperature gradient, as evidenced by their presence in soft sediments, the full spectrum of metamorphic rocks, and even as primary flow structures in some igneous rocks. A set of folds distributed on a regional scale constitutes a fold belt, a common feature of orogenic zones. Folds are commonly formed by shortening of existing layers, but may also be formed as a result of displacement on a non-planar fault (''fault bend fold''), at the tip of a propagating fault (''fault propagation fold''), by differential compaction or due to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orogen
An orogenic belt, or orogen, is a zone of Earth's crust affected by orogeny. An orogenic belt develops when a continental plate crumples and is Tectonic uplift, uplifted to form one or more mountain ranges; this involves a series of geological processes collectively called ''orogenesis''. Overview Orogeny typically produces ''orogenic belts'', which are elongated regions of deformation bordering continental cratons. Young orogenic belts, in which subduction is still taking place, are characterized by frequent volcanic activity and earthquakes. Older orogenic belts are typically deeply eroded to expose displaced and deformed strata. These are often highly metamorphosed and include vast bodies of intrusive igneous rock called batholiths. File:Active Margin.svg, Subduction of an oceanic plate beneath a Plate tectonics, continental plate to form an accretionary orogen. (example: the Andes) File:Continental-continental convergence Fig21contcont.gif, Continental collision of two cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pediment
Pediments are gables, usually of a triangular shape. Pediments are placed above the horizontal structure of the lintel, or entablature, if supported by columns. Pediments can contain an overdoor and are usually topped by hood moulds. A pediment is sometimes the top element of a portico. For symmetric designs, it provides a center point and is often used to add grandness to entrances. The tympanum, the triangular area within the pediment, is often decorated with a pedimental sculpture which may be freestanding or a relief sculpture. The tympanum may hold an inscription, or in modern times, a clock face. Pediments are found in ancient Greek architecture as early as 600 BC (e.g. the archaic Temple of Artemis). Variations of the pediment occur in later architectural styles such as Classical, Neoclassical and Baroque. Gable roofs were common in ancient Greek temples with a low pitch (angle of 12.5° to 16°). History The pediment is found in classical Greek temples, Et ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inselberg
An inselberg or monadnock () is an isolated rock hill, knob, ridge, or small mountain that rises abruptly from a gently sloping or virtually level surrounding plain. In Southern Africa a similar formation of granite is known as a koppie, an Afrikaans word ("little head") from the Dutch diminutive word ''kopje''. If the inselberg is dome-shaped and formed from granite or gneiss, it can also be called a bornhardt, though not all bornhardts are inselbergs. An inselberg results when a body of rock resistant to erosion, such as granite, occurring within a body of softer rocks, is exposed by differential erosion and lowering of the surrounding landscape. Etymology Inselberg The word ''inselberg'' is a loan word from German, and means "island mountain". The term was coined in 1900 by geologist Wilhelm Bornhardt (1864–1946) to describe the abundance of such features found in eastern Africa. At that time, the term applied only to arid landscape features. However, it has sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Cancer
Oral cancer, also known as mouth cancer, is cancer of the lining of the lips, mouth, or upper throat. In the mouth, it most commonly starts as a painless white patch, that thickens, develops red patches, an ulcer, and continues to grow. When on the lips, it commonly looks like a persistent crusting ulcer that does not heal, and slowly grows. Other symptoms may include difficult or painful swallowing, new lumps or bumps in the neck, a swelling in the mouth, or a feeling of numbness in the mouth or lips. Risk factors include tobacco and alcohol use. Those who use both alcohol and tobacco have a 15 times greater risk of oral cancer than those who use neither. Other risk factors include HPV infection, chewing paan, and sun exposure on the lower lip. Oral cancer is a subgroup of head and neck cancers. Diagnosis is made by biopsy of the concerning area, followed by investigation with CT scan, MRI, PET scan, and examination to determine if it has spread to distant parts of the body. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred Hettner
Alfred Hettner (August 6, 1859 in Dresden – August 31, 1941 in Heidelberg) was a German geographer. He is known for his concept of chorology, the study of places and regions, a concept that influenced both Carl O. Sauer and Richard Hartshorne. Apart from Europe, his fieldwork concentrated mainly on Colombia, Chile and Russia. Alfred Hettner, who obtained his PhD from the University of Strasbourg, was also a pupil of Ferdinand von Richthofen and Friedrich Ratzel in Leipzig—where he obtained his habilitation. His book ''Europe'' was published in 1907. According to him, geography is a chorological science or it is a study of regions. Hettner rejected the view that geography could be either general or regional. Geography, like other fields of learning, must deal in both unique things (regional geography) and with the universal (general geography), but the study of regions — especially in the form of his ' approach — is the main field of geography. Hettner supervised, am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |