|
Glaswaldsee
The Glaswaldsee near the spa town of Bad Rippoldsau-Schapbach in the Central Black Forest in Germany lies in a cirque that is sunk into the steep eastern mountainside of the Lettstädter Höhe. It is part of the nature reserve of the same name that was established in 1960. The tarn formed in a cirque that was carved from the bunter sandstone rock out by a glacier during the ice age. Steep banks surround the lake which is up to 11 metres deep and has an area of about 3 hectares. Its diameter varies between 170 and 220 metres. The Glaswaldsee is fed by underground water sources; its surface catchment area, apart from an artificial diversion from the uppermost reaches of the ''Seebach'', only covers about an area of 190 hectares.Catchment measured from LUBW-GEZG. In centuries gone by, the lake was known as the ''Wilder See'' ("Wild Lake") (like the Wildsee at Ruhestein and the Wildsee near Kaltenbronn), but its present name is derived from the former manufacture of glas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glaswaldsee2
The Glaswaldsee near the spa town of Bad Rippoldsau-Schapbach in the Central Black Forest in Germany lies in a cirque that is sunk into the steep eastern mountainside of the Lettstädter Höhe. It is part of the nature reserve of the same name that was established in 1960. The tarn formed in a cirque that was carved from the bunter sandstone rock out by a glacier during the ice age. Steep banks surround the lake which is up to 11 metres deep and has an area of about 3 hectares. Its diameter varies between 170 and 220 metres. The Glaswaldsee is fed by underground water sources; its surface catchment area, apart from an artificial diversion from the uppermost reaches of the ''Seebach'', only covers about an area of 190 hectares.Catchment measured from LUBW-GEZG. In centuries gone by, the lake was known as the ''Wilder See'' ("Wild Lake") (like the Wildsee at Ruhestein and the Wildsee near Kaltenbronn), but its present name is derived from the former manufacture of glass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
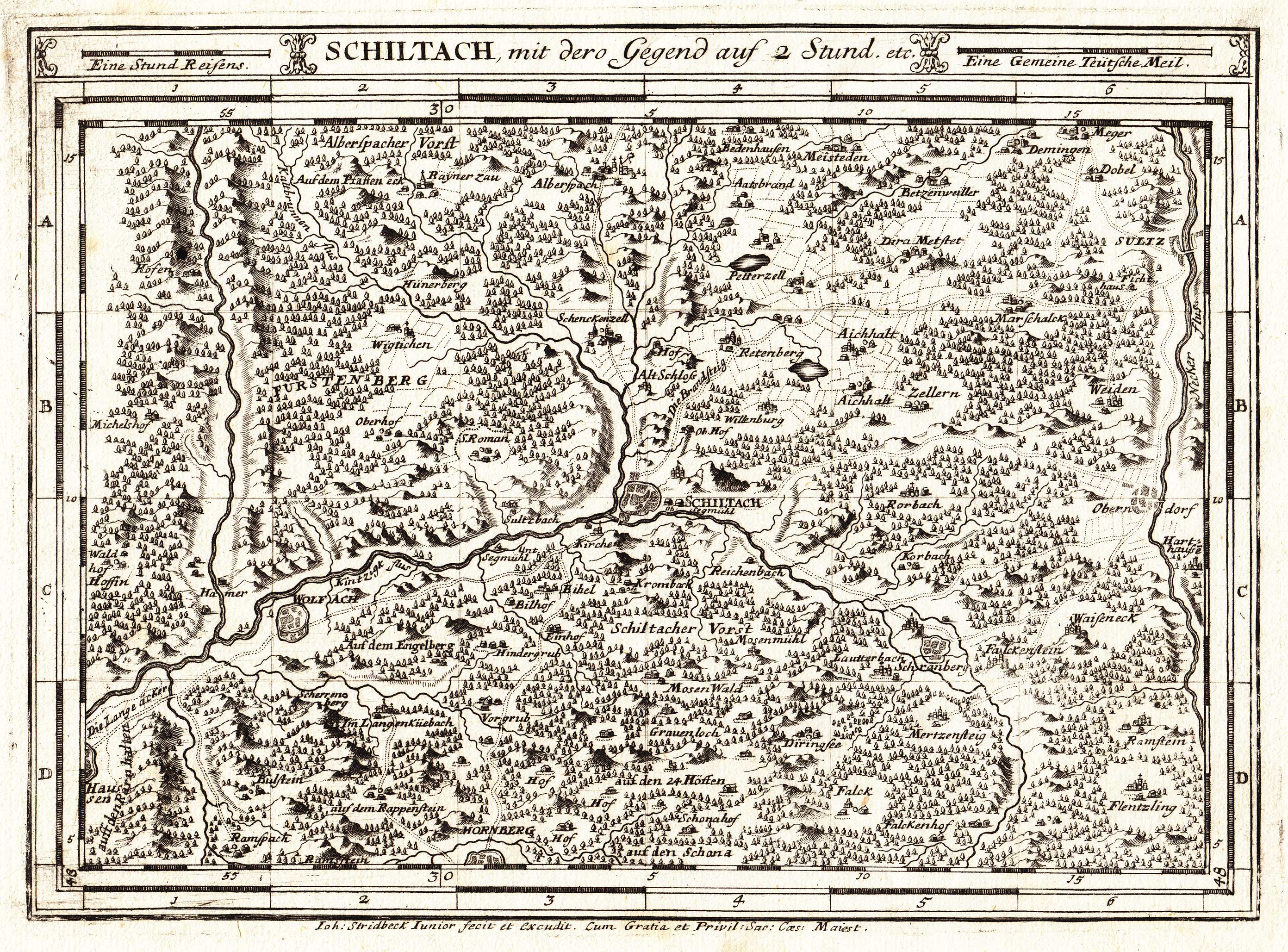
Bad Rippoldsau-Schapbach
Bad Rippoldsau-Schapbach ( Low Alemannic: ''Ribbeldsau-Schaba'') is a municipality in the district of Freudenstadt in Baden-Württemberg in southern Germany. Geography The Municipality is located in the black forest in the Wolftal valley, 15 km away from Freudenstadt. The Municipality is divided into two villages, Bad Rippoldsau and Schapbach. Bad Rippoldsau has an elevation of 560 meters and Schapbach has an elevation of 410 meters. History The first historical mention of Bad Rippoldsau was in 1179, of Schapbach in 1220. Until 1974 the two villages were two municipalities, but then they became one. Since the 15th century there has been a spa in Bad Rippoldsau. Sights - The Catholic pilgrimage church of Bad Rippoldsau, which was built in 1829 by Christoph Arnold, a pupil of Friedrich Weinbrenner. - The baroque church of Schapbach - The Kastelstein, a rock near Bad Rippoldsau. - The Glaswaldsee, a cirque lake which was formed by glaciers during the last ice age - The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Black Forest
The Central Black Forest (german: Mittlerer Schwarzwald), also called the Middle Black Forest, is a natural or cultural division of the Black Forest in Baden-Württemberg in Germany. It generally refers to a region of deeply incised valleys from the Rench valley and southern foothills of the Kniebis in the north to the area of Freiburg im Breisgau and Donaueschingen in the south. Its highest area, which is southeast of the Elz valley, is also part of the High Black Forest. Geography The dominating valley system of the Kinzig cuts through the Middle Black Forest from east to west. Prominent peaks are the Kandel (), Weißtannenhöhe (), Obereck (), Rohrhardsberg (), Brend (), Stöcklewald () and Mooswaldkopf () south of the Kinzig, and the Brandenkopf () and Lettstädter Höhe () north of the Kinzig. Geology Gneisses and granites predominate. Unlike the Northern Black Forest the Bunter sandstone covering with its plateau-like mountain shapes has only survived in a few pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baden-Württemberg
Baden-Württemberg (; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a German state () in Southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the southern part of Germany's western border with France. With more than 11.07 million inhabitants across a total area of nearly , it is the third-largest German state by both area (behind Bavaria and Lower Saxony) and population (behind North Rhine-Westphalia and Bavaria). As a federated state, Baden-Württemberg is a partly-sovereign parliamentary republic. The largest city in Baden-Württemberg is the state capital of Stuttgart, followed by Mannheim and Karlsruhe. Other major cities are Freiburg im Breisgau, Heidelberg, Heilbronn, Pforzheim, Reutlingen, Tübingen, and Ulm. What is now Baden-Württemberg was formerly the historical territories of Baden, Prussian Hohenzollern, and Württemberg. Baden-Württemberg became a state of West Germany in April 1952 by the merger of Württemberg-Baden, South Baden, and Württemberg-Hohenzollern. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timber Rafting
Timber rafting is a method of transporting felled tree trunks by tying them together to make rafts, which are then drifted or pulled downriver, or across a lake or other body of water. It is arguably, after log driving, the second cheapest means of transporting felled timber. Both methods may be referred to as timber floating. Historical rafting Unlike log driving, which was a dangerous task of floating separate logs, floaters or raftsmen could enjoy relative comfort of navigation, with cabins built on rafts, steering by means of oars and possibility to make stops. On the other hand, rafting requires wider waterflows. Timber rafts were also used as a means of transportation of people and goods, both raw materials (ore, fur, game) and man-made. Theophrastus (''Hist. Plant.'' 5.8.2) records how the Romans imported Corsican timber by way of a huge raft propelled by as many as fifty masts and sails. This practice used to be common in many parts of the world, especially North A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarns Of The Black Forest
A tarn (or corrie loch) is a proglacial mountain lake, pond or pool, formed in a cirque excavated by a glacier. A moraine may form a natural dam below a tarn. Etymology The word is derived from the Old Norse word ''tjörn'' ("a small mountain lake without tributaries") meaning pond. In parts of Northern England - predominantly Cumbria but also areas of North Lancashire and North Yorkshire - 'tarn' is widely used as the name for small lakes or ponds, regardless of their location and origin (e.g. Talkin Tarn, Urswick Tarn, Malham Tarn). Similarly, in Scandinavian languages, a ''tjern'' or ''tjørn'' (both Norwegian) or ''tjärn'' or ''tärn'' (both Swedish) is a small natural lake, often in a forest or with vegetation closely surrounding it or growing into the tarn. The specific technical use for a body of water in a glacial corrie comes from high number of tarns found in corries in the Lake District, an upland area in Cumbria. Nonetheless, there are many more bodies of wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lakes Of Baden-Württemberg
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much larger oceans, they do form part of the Earth's water cycle. Lakes are distinct from lagoons, which are generally coastal parts of the ocean. Lakes are typically larger and deeper than ponds, which also lie on land, though there are no official or scientific definitions. Lakes can be contrasted with rivers or streams, which usually flow in a channel on land. Most lakes are fed and drained by rivers and streams. Natural lakes are generally found in mountainous areas, rift zones, and areas with ongoing glaciation. Other lakes are found in endorheic basins or along the courses of mature rivers, where a river channel has widened into a basin. Some parts of the world have many lakes formed by the chaotic drainage patterns left over from the last ic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Lakes Of Germany
The largest lake on German territory is Lake Constance, while Lake Müritz is the largest lake located entirely within German territory. List (incomplete) * Aartalsee * Binnenalster (Inner Alster Lake) * Brahmsee * Breitlingsee * Brombachsee * Bullensee * Chiemsee * Lake Constance (''Bodensee'') * Dümmersee * Edersee * Eibsee * Ellbogensee * Eschbach Reservoir * Fleesensee * Gelterswoogsee * Gothensee * Gottleuba Reservoir * Großer Labussee * Großer Müllroser See * Großer Priepertsee * Grunewaldsee * Halbendorfer See * Halterner See * Hengsteysee * Hohnsensee * Kellersee * Königssee (Bavaria) * Krumme Lanke * Kuhgrabensee * Mahndorfer See * Maschsee * Mechower See * Möhne Reservoir (''Möhnesee'') * Möserscher See * Müggelsee * Müritz * Norderteich * Oder Reservoir * Oker Reservoir * Orankesee * Parsteiner See * Pfaffenteich * Plauer See (Brandenburg) * Plauer See (Mecklenburg-Vorpommern) * Plöner See * Plötzensee * Quenzsee * Röblinsee * Scharm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinzig (Rhine)
The Kinzig is a river in southwestern Germany, a right tributary of the Rhine. It runs for 93 km from the Black Forest through the Upper Rhine River Plains. The Kinzig valley and secondary valleys constitute the largest system of valleys in the Black Forest. Depending on the definition, the Kinzig is either the border between the Northern and Middle Black Forest or part of the Middle Black Forest. It is located entirely inside the State of Baden-Württemberg and its name is supposed to be of Celtic origin. During the last glacial period the Kinzig and the Murg created a common Kinzig-Murg river system. Course of the river The origin of the Kinzig is located on the land of the town of Loßburg in the district of Freudenstadt. It runs south, then makes a gradual turn to the west. It leaves the district of Freudenstadt just after it emerges from Alpirsbach, touches the district of Rottweil and continues to spend the largest part of its course in the district of Ortena ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triangulation
In trigonometry and geometry, triangulation is the process of determining the location of a point by forming triangles to the point from known points. Applications In surveying Specifically in surveying, triangulation involves only angle measurements at known points, rather than measuring distances to the point directly as in trilateration; the use of both angles and distance measurements is referred to as triangulateration. In computer vision Computer stereo vision and optical 3D measuring systems use this principle to determine the spatial dimensions and the geometry of an item. Basically, the configuration consists of two sensors observing the item. One of the sensors is typically a digital camera device, and the other one can also be a camera or a light projector. The projection centers of the sensors and the considered point on the object's surface define a (spatial) triangle. Within this triangle, the distance between the sensors is the base ''b'' and must be known. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolf (river)
Wolf is a river of Baden-Württemberg, Germany. The historical name of the river is Wolfach. It passes through Bad Rippoldsau-Schapbach and flows into the Kinzig in Wolfach. One of its tributaries flows over the Burgbach Waterfall, one of the highest free-falling waterfalls in Germany. See also *List of rivers of Baden-Württemberg A list of rivers of Baden-Württemberg, Germany: A * Aal * Aalbach * Aalenbach * Ablach * Ach *Acher * Adelbach *Aich * Aid * Aischbach, tributary of the Kinzig * Aischbach, tributary of the Körsch *Aitrach, tributary of the Danube *Aitrach, tr ... References Rivers of Baden-Württemberg Rivers of Germany {{BadenWürttemberg-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Age
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages and greenhouse periods, during which there are no glaciers on the planet. Earth is currently in the Quaternary glaciation. Individual pulses of cold climate within an ice age are termed ''glacial periods'' (or, alternatively, ''glacials, glaciations, glacial stages, stadials, stades'', or colloquially, ''ice ages''), and intermittent warm periods within an ice age are called '' interglacials'' or ''interstadials''. In glaciology, ''ice age'' implies the presence of extensive ice sheets in both northern and southern hemispheres. By this definition, Earth is currently in an interglacial period—the Holocene. The amount of anthropogenic greenhouse gases emitted into Earth's oceans and atmosphere is predicted to prevent the next glacial period for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |