|
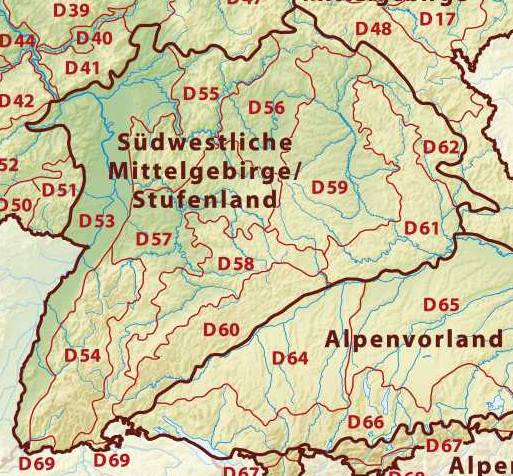
Swabian-Franconian Scarpland
The South German Scarplands is a geological and geomorphological natural region or landscape in Switzerland and the south German states of Bavaria and Baden-Württemberg. The landscape is characterised by escarpments. It is variously referred to in the German literature as the: * ' (Southwest German Scarplands) * ' (Southwest German Scarp Landscape) * ' (Swabian-Franconian Scarpland(scape)) * ' (South German Scarpland(scape)) Location and short description The South German Scarplands run (from north(-northeast) to south(-southwest)) more or less between the southern Rhön, the Spessart, the Odenwald and the Black Forest in the west, the Franconian Jura in the east, the Swabian Jura to the southeast and the northeastern foothills of the Jura to the south. The wooded west and northwest-facing scarps drop sharply towards the Rhine Rift Valley and the Rhine-Main Plain, whilst the dip slopes fall comparatively gradually towards the (north-)east into the depressions beyond which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dip Slope
A dip slope is a topographic (geomorphic) surface which slopes in the same direction, and often by the same amount, as the true dip or apparent dip of the underlying strata.Jackson, JA, J Mehl and K Neuendorf (2005) ''Glossary of Geology.'' American Geological Institute, Alexandria, Virginia. 800 pp. Allaby, M (2008) ''A Dictionary of Earth Science.'' Oxford University Press, New York, New York. 654 pp. A dip slope consists of the upper surface of a resistant layer of rock, often called ''caprock'', that is commonly only slightly lowered and reduced in steepness by erosion. Dip slopes form the backslopes of cuestas, homoclinal ridges, hogbacks, and flatirons. The frontslopes of such ridges consist of either an escarpment, a steep slope, or perhaps even a line of cliffs. Generally, cuestas and homoclinal ridges are asymmetrical in that their dip slopes are less steep than their escarpments. In the case of hogbacks and flatirons, the dip of the rocks is so steep that their dip sl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Rhine
The High Rhine (german: Hochrhein) is the name used for the part of the Rhine that flows westbound from Lake Constance to Basel. The High Rhine begins at the outflow of the Rhine from the Untersee in Stein am Rhein and turns into the Upper Rhine in Basel. In contrast to the Alpine Rhine and Upper Rhine, the High Rhine flows mostly to the west. The section is marked by Rhine-kilometers 0 to 165, measurements beginning at the outflow of the Obersee at the Old Rhine Bridge in Constance. It is the first of four sections (High Rhine, Upper Rhine, Middle Rhine, Lower Rhine) of the Rhine between Lake Constance and the North Sea. In the western part, the Rhine marks the border between Germany and Switzerland, while in the eastern part, Switzerland owns areas north of the Rhine and surrounds the popular German holiday resort of Büsingen am Hochrhein. The term ''High Rhine'' was introduced by scientists in the 19th century. Above all geologists tried to differentiate the High Rhine () ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhine Rift
The Upper Rhine Plain, Rhine Rift Valley or Upper Rhine Graben (German: ''Oberrheinische Tiefebene'', ''Oberrheinisches Tiefland'' or ''Oberrheingraben'', French: ''Vallée du Rhin'') is a major rift, about and on average , between Basel in the south and the cities of Frankfurt/Wiesbaden in the north. Its southern section straddles the France–Germany border. It forms part of the European Cenozoic Rift System, which extends across Central Europe. The Upper Rhine Graben formed during the Oligocene, as a response to the evolution of the Alps to the south. It remains active to the present day. Today, the Rhine Rift Valley forms a downfaulted trough through which the river Rhine flows. Formation The Upper Rhine Plain was formed during the Early Cenozoic era, during the Late Eocene epoch. At this time, the Alpine Orogeny, the major mountain building event that was to produce the Alps, was in its early stages. The Alps were formed because the continents of Europe and Africa colli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticline
In structural geology, an anticline is a type of fold that is an arch-like shape and has its oldest beds at its core, whereas a syncline is the inverse of an anticline. A typical anticline is convex up in which the hinge or crest is the location where the curvature is greatest, and the limbs are the sides of the fold that dip away from the hinge. Anticlines can be recognized and differentiated from antiforms by a sequence of rock layers that become progressively older toward the center of the fold. Therefore, if age relationships between various rock strata are unknown, the term antiform should be used. The progressing age of the rock strata towards the core and uplifted center, are the trademark indications for evidence of anticlines on a geologic map. These formations occur because anticlinal ridges typically develop above thrust faults during crustal deformations. The uplifted core of the fold causes compression of strata that preferentially erodes to a deeper st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris Basin
The Paris Basin is one of the major geological regions of France. It developed since the Triassic over remnant uplands of the Variscan orogeny (Hercynian orogeny). The sedimentary basin, no longer a single drainage basin, is a large sag in the craton, bordered by the Armorican Massif to the west, the Ardennes-Brabant axis to the north, the Massif des Vosges to the east, and the Massif Central to the south.Duval, B.C., 1992, Villeperdue Field, In Giant Oil and Gas Fields of the Decade, 1978-1988, AAPG Memoir 54, Halbouty, M.T., editor, Tulsa: American Association of Petroleum Geologists, Extent The region usually regarded as the Paris Basin is rather smaller than the area formed by the geological structure. The former occupies the centre of the northern half of the country, excluding Eastern France. The latter extends from the hills just south of Calais to Poitiers and from Caen to the brink of the middle Rhine Valley, east of Saarbrücken. Geography The landscape is one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bohemian Forest
The Bohemian Forest, known in Czech as Šumava () and in German as Böhmerwald, is a low mountain range in Central Europe. Geographically, the mountains extend from Plzeň Region and South Bohemia in the Czech Republic to Austria and Bavaria in Germany, and form the highest truncated uplands of the Bohemian Massif, up to 50 km wide. They create a natural border between the Czech Republic on one side and Germany and Austria on the other. Names and etymology For political reasons, the Bohemian and German sides have different names in their languages: in Czech, the Bohemian side is called ''Šumava'' and the Bavarian side ''Zadní Bavorský les'' ( en, Rear Bavarian Forest), while in German, the Bohemian side is called ''Böhmerwald'' ( en, Bohemian Forest), and the Bavarian side ''Bayerischer Wald'' ( en, Bavarian Forest). In Czech, ''Šumava'' is also used as a name for the entire region in Bohemia and Germany. The designation ''Šumava'' has been attested in the late 15t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albtrauf
The term Albtrauf (Alp escarpment) refers to the northwest facing escarpment of the Swabian Alps, situated in Baden-Württemberg and Bavaria. It is the most distinctive stepped slope within the alpine region of the South German Scarplands, leading roughly from the southwest to the northeast. The Albtrauf has its geological extension in the northeast, in the stepped slopes of the Franconian Jura and in the southwest and west among the Jurassic-era stepped slopes of the Baaralb, Hegaualb, Randen, Klettgau, Aargau as well as the Table Jura stretches from the city of Basel to the Ajoie and the French Scarplands. In geology and geomorphology, however, the term “Trauf” merely describes the brink of the stepped slopes where various stepped surfaces meet (which is not developed in hipped steps). Geography Like the entirety of the Swabian Alps, the Albtrauf leads from the southwest to the northeast, approximately following the line of Donaueschingen–Lemberg–Balingen– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , passing through or bordering Austria, Slovakia, Hungary, Croatia, Serbia, Romania, Bulgaria, Moldova, and Ukraine before draining into the Black Sea. Its drainage basin extends into nine more countries. The largest cities on the river are Vienna, Budapest, Belgrade and Bratislava, all of which are the capitals of their respective countries; the Danube passes through four capital cities, more than any other river in the world. Five more capital cities lie in the Danube's basin: Bucharest, Sofia, Zagreb, Ljubljana and Sarajevo. The fourth-largest city in its basin is Munich, the capital of Bavaria, standing on the Isar River. The Danube is the second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through much of Central and Sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bavarian Forest
The village of Zell in the Bavarian Forest The Bavarian Forest (German: ' or ''Bayerwald''; bar, Boarischa Woid) is a wooded, low-mountain region in Bavaria, Germany that is about 100 kilometres long. It runs along the Czech border and is continued on the Czech side by the Bohemian Forest (Czech: ''Šumava''). Most of the Bavarian Forest lies within the province of Lower Bavaria, but the northern part lies within Upper Palatinate. In the south it reaches the border with Upper Austria. Geologically and geomorphologically, the Bavarian Forest is part of the Bohemian Forest - the highest of the truncated highlands of the Bohemian Massif. The area along the Czech border has been designated as the Bavarian Forest National Park (240 km2), established in 1970 as the first national park in Germany. Another 3,008 km2 has been designated as the Bavarian Forest Nature Park, established 1967, and another 1,738 km2 as the Upper Bavarian Forest Nature Park, established in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Palatine Forest
The Upper Palatine Forest (german: Oberpfälzer Wald or ''Böhmischer Wald'', cs, Český les) is a mountain range in Central Europe that is divided between Germany and the Czech Republic. It is part of the larger Bohemian Massif and the German Central Uplands. Geography The German side belongs to the Upper Palatinate region of Bavaria, it stretches about from the Bavarian Forest in the south up to the Fichtel Mountains and the Steinwald range in the north. However, the highest peaks of the range lie along the eastern Czech side in the Plzeň Region of western Bohemia, northwest of the Bohemian Forest. The southern rim runs from the Cham and Furth Basin across the border to the Všeruby (''Neumark'') mountain pass, which is part of the Main European Watershed. The other end is marked by Waldsassen, the northernmost town of the Upper Palatinate. The Mittelgebirge range is a mountainous solid mass, its highest point Čerchov being at an altitude of . Prominent rocks includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fichtelgebirge
The Fichtel MountainsRandlesome, C. et al. (2011). ''Business Cultures in Europe'', 2nd ed., Routledge, Abingdon and New York, p. 52. . (german: Fichtelgebirge, cs, Smrčiny), form a small horseshoe-shaped mountain range in northeastern Bavaria, Germany. They extend from the valley of the Red Main River to the Czech border, a few foothills spilling over into the Czech Republic. They continue in a northeasterly direction as the Elster Mountains, and in a southeasterly direction as the Upper Palatine Forest. The Fichtel Mountains contain an important nature park, the Fichtel Mountain Nature Park, with an area of . Etymology The first person to write about the Fichtel Mountains, Matthias of Kemnath (actually Matthias Widmann, born 23 February 1429 in Kemnath) reported in 1476: ''Ein bergk, hoch, weitt, wolbekant ligt in Beiern, gnant der Fichtelberg'' ("A mountain, high, wide and well-known, lies in Bavaria, known as the Fichtelberg"). In descriptions of the border in 1499 and 15 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |