Etymology
The English word ''fungus'' is directly adopted from theCharacteristics

 Most fungi lack an efficient system for the long-distance transport of water and nutrients, such as the xylem and phloem in many plants. To overcome this limitation, some fungi, such as '' Armillaria'', form rhizomorphs, which resemble and perform functions similar to the
Most fungi lack an efficient system for the long-distance transport of water and nutrients, such as the xylem and phloem in many plants. To overcome this limitation, some fungi, such as '' Armillaria'', form rhizomorphs, which resemble and perform functions similar to the Diversity
 As of 2020, around 148,000 species of fungi have been described by
As of 2020, around 148,000 species of fungi have been described by Mycology

History
Mycology became a systematic science after the development of theMorphology
Microscopic structures
 Most fungi grow as
Most fungi grow as Macroscopic structures
 Fungal mycelia can become visible to the naked eye, for example, on various surfaces and substrates, such as damp walls and spoiled food, where they are commonly called molds. Mycelia grown on solid
Fungal mycelia can become visible to the naked eye, for example, on various surfaces and substrates, such as damp walls and spoiled food, where they are commonly called molds. Mycelia grown on solid Growth and physiology
 The growth of fungi as hyphae on or in solid substrates or as single cells in aquatic environments is adapted for the efficient extraction of nutrients, because these growth forms have high
The growth of fungi as hyphae on or in solid substrates or as single cells in aquatic environments is adapted for the efficient extraction of nutrients, because these growth forms have high Reproduction
 Fungal reproduction is complex, reflecting the differences in lifestyles and genetic makeup within this diverse kingdom of organisms. It is estimated that a third of all fungi reproduce using more than one method of propagation; for example, reproduction may occur in two well-differentiated stages within the life cycle of a species, the teleomorph (sexual reproduction) and the
Fungal reproduction is complex, reflecting the differences in lifestyles and genetic makeup within this diverse kingdom of organisms. It is estimated that a third of all fungi reproduce using more than one method of propagation; for example, reproduction may occur in two well-differentiated stages within the life cycle of a species, the teleomorph (sexual reproduction) and the Asexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction with In ascomycetes, dikaryotic hyphae of the
In ascomycetes, dikaryotic hyphae of the Spore dispersal
The spores of most of the researched species of fungi are transported by wind. Such species often produce dry orHomothallism
In homothallicOther sexual processes
Besides regular sexual reproduction with meiosis, certain fungi, such as those in the genera '' Penicillium'' and '' Aspergillus'', may exchange genetic material via parasexual processes, initiated by anastomosis between hyphae and plasmogamy of fungal cells. The frequency and relative importance of parasexual events is unclear and may be lower than other sexual processes. It is known to play a role in intraspecific hybridization and is likely required for hybridization between species, which has been associated with major events in fungal evolution.Evolution
In contrast to plants and animals, the early fossil record of the fungi is meager. Factors that likely contribute to the under-representation of fungal species among fossils include the nature of fungal fruiting bodies, which are soft, fleshy, and easily degradable tissues and the microscopic dimensions of most fungal structures, which therefore are not readily evident. Fungal fossils are difficult to distinguish from those of other microbes, and are most easily identified when they resemble The earliest fossils possessing features typical of fungi date to the Paleoproterozoic era, some ( Ma); these multicellular
The earliest fossils possessing features typical of fungi date to the Paleoproterozoic era, some ( Ma); these multicellular Taxonomy
Although commonly included in botany curricula and textbooks, fungi are more closely related toTaxonomic groups
 The major
The major  Members of the
Members of the Fungus-like organisms
Because of similarities in morphology and lifestyle, the slime molds ( mycetozoans,Ecology
 Although often inconspicuous, fungi occur in every environment on
Although often inconspicuous, fungi occur in every environment on Symbiosis
Many fungi have importantWith plants
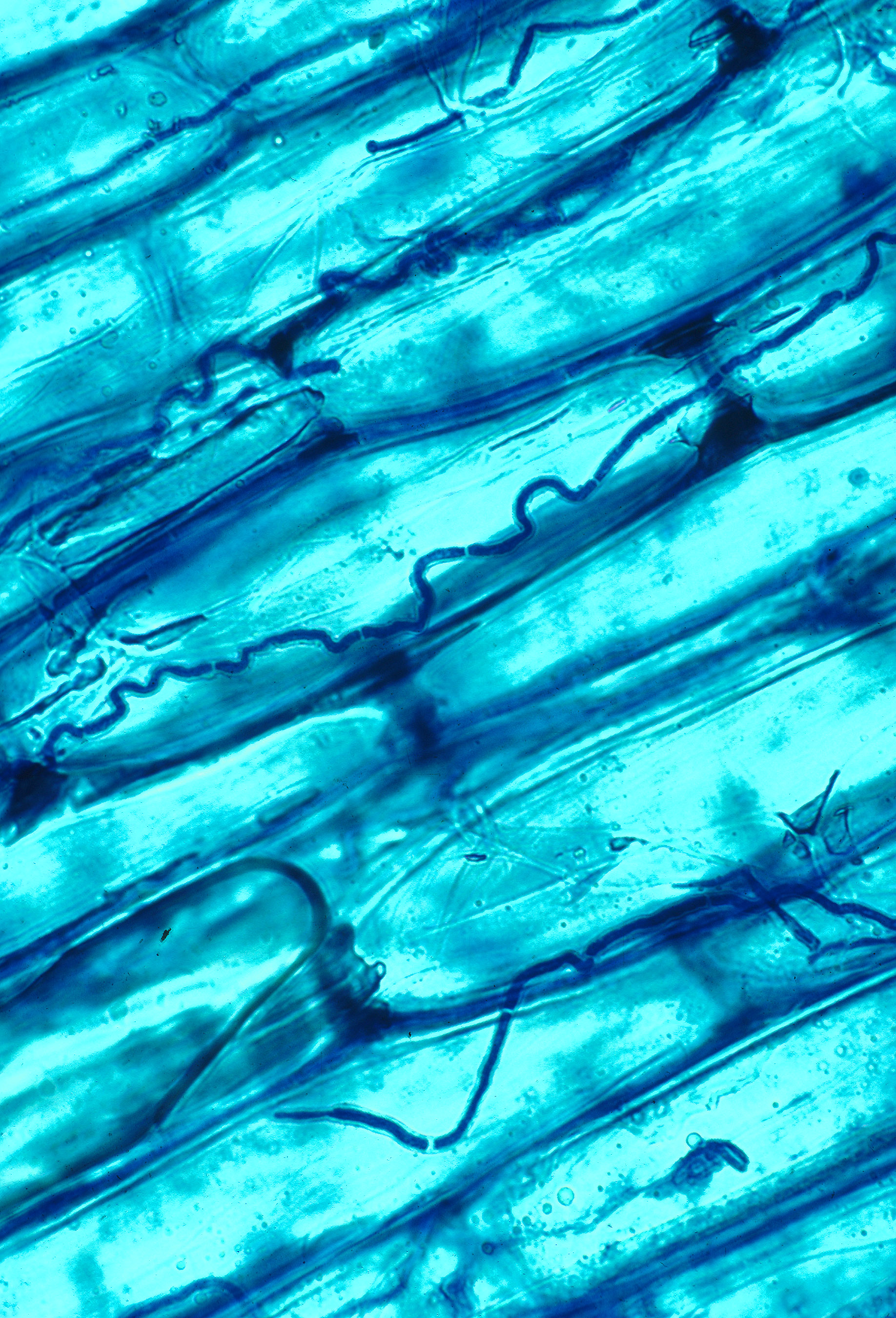 The mycorrhizal symbiosis is ancient, dating back to at least 400 million years. It often increases the plant's uptake of inorganic compounds, such as
The mycorrhizal symbiosis is ancient, dating back to at least 400 million years. It often increases the plant's uptake of inorganic compounds, such as With algae and cyanobacteria

With insects
Many insects also engage in mutualistic relationships with fungi. Several groups of ants cultivate fungi in the order Chaetothyriales for several purposes: as a food source, as a structural component of their nests, and as a part of an ant/plant symbiosis in the domatia (tiny chambers in plants that house arthropods).As pathogens and parasites
 Many fungi are
Many fungi are As targets of mycoparasites
Organisms that parasitize fungi are known as mycoparasitic organisms. About 300 species of fungi and fungus-like organisms, belonging to 13 classes and 113 genera, are used as biocontrol agents against plant fungal diseases. Fungi can also act as mycoparasites or antagonists of other fungi, such as ''Communication
There appears to be electrical communication between fungi in word-like components according to spiking characteristics.Mycotoxins
 Many fungi produce
Many fungi produce Pathogenic mechanisms
''Human use
 The human use of fungi for food preparation or preservation and other purposes is extensive and has a long history.
The human use of fungi for food preparation or preservation and other purposes is extensive and has a long history. Therapeutic uses
Modern chemotherapeutics
 Many species produce metabolites that are major sources of
Many species produce metabolites that are major sources of = Antibiotics
= Particularly important are the antibiotics, including the= Other
= Other drugs produced by fungi includeTraditional medicine
Certain mushrooms are used as supposed therapeutics in folk medicine practices, such asCultured foods
Baker's yeast or ''In food
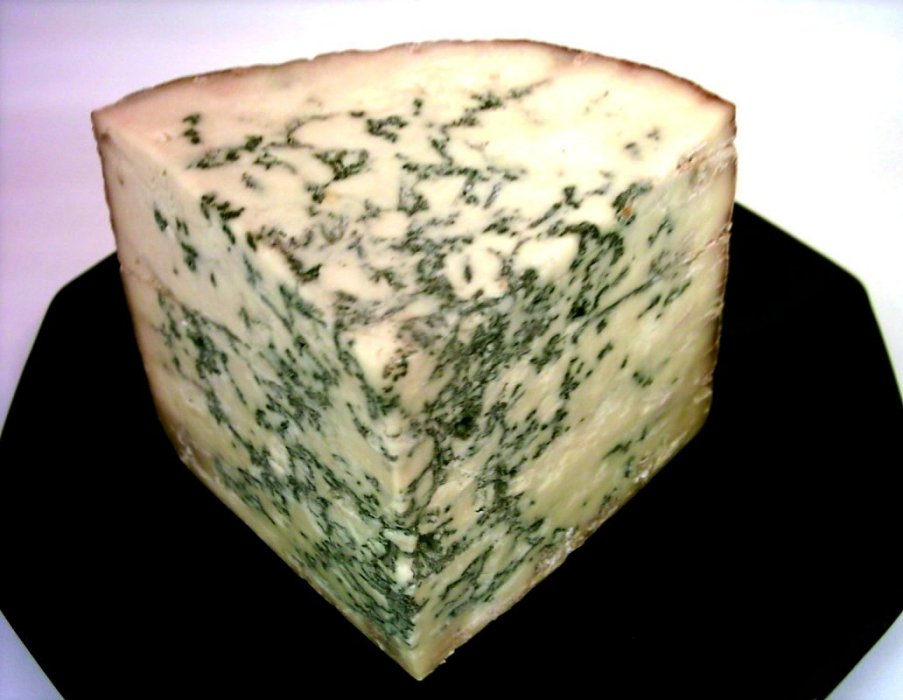
 Many other mushroom species are harvested from the wild for personal consumption or commercial sale. Milk mushrooms,
Many other mushroom species are harvested from the wild for personal consumption or commercial sale. Milk mushrooms, Poisonous fungi
Pest control
 In agriculture, fungi may be useful if they actively compete for nutrients and space with
In agriculture, fungi may be useful if they actively compete for nutrients and space with Bioremediation
Certain fungi, in particular white-rot fungi, can degradeModel organisms
Several pivotal discoveries in biology were made by researchers using fungi as model organisms, that is, fungi that grow and sexually reproduce rapidly in the laboratory. For example, the one gene-one enzyme hypothesis was formulated by scientists using the bread mold '' Neurospora crassa'' to test their biochemical theories. Other important model fungi are ''Aspergillus nidulans'' and the yeasts ''Others
Fungi are used extensively to produce industrial chemicals like citric acid, citric, gluconic acid, gluconic, lactic acid, lactic, and malic acid, malic acids, and industrial enzymes, such as lipases used in biological detergents, cellulases used in making cellulosic ethanol and stonewashed jeans, and amylases, invertases, proteases and xylanases.See also
* Conservation of fungi * Fantastic Fungi * Glossary of fungi * Marine fungi * Mycosis * Outline of fungiReferences
Citations
{{Reflist, refs= {{cite journal , vauthors=Aanen DK , title=As you reap, so shall you sow: coupling of harvesting and inoculating stabilizes the mutualism between termites and fungi , journal=Biology Letters , volume=2 , issue=2 , pages=209–12 , date=June 2006 , pmid=17148364 , pmc=1618886 , doi=10.1098/rsbl.2005.0424 {{cite journal , vauthors=Abe K, Gomi K, Hasegawa F, Machida M , s2cid=36874528 , title=Impact of ''Aspergillus oryzae'' genomics on industrial production of metabolites , journal=Mycopathologia , volume=162 , issue=3 , pages=143–53 , date=September 2006 , pmid=16944282 , doi=10.1007/s11046-006-0049-2 {{cite book , vauthors=Alcamo IE, Pommerville J , title=Alcamo's Fundamentals of Microbiology , url=https://archive.org/details/alcamosfundament0000pomm , url-access=registration , publisher=Jones and Bartlett , location=Boston, Massachusetts , year=2004 , pag590
, isbn=978-0-7637-0067-6 {{cite book , vauthors=Ammirati JF, McKenny M, Stuntz DE , title=The New Savory Wild Mushroom , publisher=University of Washington Press , location=Seattle, Washington , year=1987 , pages=xii–xiii , isbn=978-0-295-96480-5 {{cite journal , last1=Aramayo , first1=Rodolfo , last2=Selker , first2=Erik U. , title=''Neurospora crassa'', a model system for epigenetics research , journal=Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology , volume=5 , issue=10 , year=2013 , pages=a017921 , doi=10.1101/cshperspect.a017921 , pmc=3783048 , pmid=24086046 {{cite journal , vauthors=Arnold AE, Mejía LC, Kyllo D, Rojas EI, Maynard Z, Robbins N, Herre EA , title=Fungal endophytes limit pathogen damage in a tropical tree , journal=Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America , volume=100 , issue=26 , pages=15649–54 , date=December 2003 , pmid=14671327 , pmc=307622 , doi=10.1073/pnas.2533483100 , bibcode=2003PNAS..10015649A , doi-access=free {{cite journal , last1=Baghban , first1=Roghayyeh , last2=Farajnia , first2=Safar , last3=Rajabibazl , first3=Masoumeh , last4=Ghasemi , first4=Younes , last5=Mafi , first5=AmirAli , last6=Hoseinpoor , first6=Reyhaneh , last7=Rahbarnia , first7=Leila , last8=Aria , first8=Maryam , title=Yeast expression systems: Overview and recent advances , journal=Molecular Biotechnology , volume=61 , issue=5 , year=2019 , pages=365–384 , doi=10.1007/s12033-019-00164-8 , pmid=30805909 , s2cid=73501127 {{cite journal , vauthors=Baldauf SL, Palmer JD , title=Animals and fungi are each other's closest relatives: congruent evidence from multiple proteins , journal=Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America , volume=90 , issue=24 , pages=11558–62 , date=December 1993 , pmid=8265589 , pmc=48023 , doi=10.1073/pnas.90.24.11558 , bibcode=1993PNAS...9011558B , doi-access=free {{cite journal , vauthors=Barea JM, Pozo MJ, Azcón R, Azcón-Aguilar C , title=Microbial co-operation in the rhizosphere , journal=Journal of Experimental Botany , volume=56 , issue=417 , pages=1761–78 , date=July 2005 , pmid=15911555 , doi=10.1093/jxb/eri197 , doi-access=free {{cite news , title=Fungi to fight 'toxic war zones' , date=5 May 2008 , url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/uk_news/scotland/tayside_and_central/7384500.stm , work=BBC News , access-date=12 May 2008 , archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170915195952/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/uk_news/scotland/tayside_and_central/7384500.stm , archive-date=15 September 2017 , url-status=live {{cite journal , vauthors=Beadle GW, Tatum EL , title=Genetic Control of Biochemical Reactions in Neurospora , journal=Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America , volume=27 , issue=11 , pages=499–506 , date=November 1941 , pmid=16588492 , pmc=1078370 , doi=10.1073/pnas.27.11.499 , bibcode=1941PNAS...27..499B , doi-access=free {{cite book , vauthors=Blackwell M, Spatafora JW , veditors=Bills GF, Mueller GM, Foster MS , chapter=Fungi and their allies , title=Biodiversity of Fungi: Inventory and Monitoring Methods , publisher=Elsevier Academic Press , location=Amsterdam , year=2004 , pages=18–20 , isbn=978-0-12-509551-8 {{cite journal , vauthors=Bonfante P , title=Plants, mycorrhizal fungi and endobacteria: a dialog among cells and genomes , journal=The Biological Bulletin , volume=204 , issue=2 , pages=215–20 , date=April 2003 , pmid=12700157 , doi=10.2307/1543562 , jstor=1543562 , s2cid=12377410 , url=https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/part/9240 {{cite journal, vauthors=Bouton JH, Latch GC, Hill NS, Hoveland CS, McCann MA, Watson RH, Parish JA, Hawkins LL, Thompson FN , year=2002 , title=Reinfection of Tall Fescue Cultivars with Non-Ergot Alkaloid–Producing Endophytes , journal=Agronomy Journal , volume=94 , issue=3 , pages=567–574 , doi=10.2134/agronj2002.5670 , url=https://dl.sciencesocieties.org/publications/aj/pdfs/94/3/567 {{cite journal , last1=Bozkurt , first1=Tolga O. , last2=Kamoun , first2=Sophien , last3=Lennon-Duménil , first3=Ana-Maria , title=The plant–pathogen haustorial interface at a glance , journal=Journal of Cell Science , volume=133 , issue=5 , year=2020 , doi=10.1242/jcs.237958 , pmc=7075074 , pmid=32132107 {{Cite book , vauthors=Brakhage AA, Spröte P, Al-Abdallah Q, Gehrke A, Plattner H, Tüncher A , volume=88 , pages=45–90 , year=2004 , pmid=15719552 , doi=10.1007/b99257 , series=Advances in Biochemical Engineering/Biotechnology , isbn=978-3-540-22032-9 , title=Molecular Biotechnology of Fungal beta-Lactam Antibiotics and Related Peptide Synthetases , chapter=Regulation of Penicillin Biosynthesis in Filamentous Fungi {{cite journal , vauthors=Brakhage AA , title=Systemic fungal infections caused by Aspergillus species: epidemiology, infection process and virulence determinants , journal=Current Drug Targets , volume=6 , issue=8 , pages=875–86 , date=December 2005 , pmid=16375671 , doi=10.2174/138945005774912717 {{cite book , vauthors=Brodie HJ , title=The Bird's Nest Fungi , publisher=University of Toronto Press , location=Toronto, Ontario , year=1975 , isbn=978-0-8020-5307-7 , page=80 {{cite book , title=Lichens of North America , vauthors=Brodo IM, Sharnoff SD , year=2001 , publisher=Yale University Press , location=New Haven, Connecticut , isbn=978-0-300-08249-4 {{cite journal , vauthors=Brundrett MC , year=2002 , title=Coevolution of roots and mycorrhizas of land plants , journal=New Phytologist , volume=154 , issue=2 , pages=275–304 , doi=10.1046/j.1469-8137.2002.00397.x, pmid=33873429 , doi-access=free {{cite journal , vauthors=Bruns T , s2cid=648881 , title=Evolutionary biology: a kingdom revised , journal=Nature (journal), Nature , volume=443 , issue=7113 , pages=758–61 , date=October 2006 , pmid=17051197 , doi=10.1038/443758a , bibcode=2006Natur.443..758B , doi-access=free {{cite journal , vauthors=Celio GJ, Padamsee M, Dentinger BT, Bauer R, McLaughlin DJ , s2cid=23123595 , title=Assembling the Fungal Tree of Life: constructing the structural and biochemical database , journal=Mycologia , volume=98 , issue=6 , pages=850–9 , year=2006 , pmid=17486962 , doi=10.3852/mycologia.98.6.850 {{cite book , title=Mushrooms: Cultivation, Nutritional Value, Medicinal Effect and Environmental Impact , vauthors=((Chang S-T)), Miles PG , year=2004 , publisher=CRC Press , location=Boca Raton, Florida , isbn=978-0-8493-1043-0 {{cite journal , display-authors=6 , last1=Cheek , first1=Martin , last2=Nic Lughadha , first2=Eimear , last3=Kirk , first3=Paul , last4=Lindon , first4=Heather , last5=Carretero , first5=Julia , last6=Looney , first6=Brian , last7=Douglas , first7=Brian , last8=Haelewaters , first8=Danny , last9=Gaya , first9=Ester , last10=Llewellyn , first10=Theo , last11=Ainsworth , first11=A. Martyn , last12=Gafforov , first12=Yusufjon , last13=Hyde , first13=Kevin , last14=Crous , first14=Pedro , last15=Hughes , first15=Mark , last16=Walker , first16=Barnaby E. , last17=Campostrini Forzza , first17=Rafaela , last18=Wong , first18=Khoon Meng , last19=Niskanen , first19=Tuula , title=New scientific discoveries: Plants and fungi , journal=Plants, People, Planet , volume=2 , issue=5 , year=2020 , pages=371–388 , doi=10.1002/ppp3.10148 , doi-access=free {{cite journal , vauthors=Christensen MJ, Bennett RJ, Ansari HA, Koga H, Johnson RD, Bryan GT, Simpson WR, Koolaard JP, Nickless EM, Voisey CR , title=Epichloë endophytes grow by intercalary hyphal extension in elongating grass leaves , journal=Fungal Genetics and Biology , volume=45 , issue=2 , pages=84–93 , date=February 2008 , pmid=17919950 , doi=10.1016/j.fgb.2007.07.013 {{cite journal , vauthors=Clay K, Schardl C , title=Evolutionary origins and ecological consequences of endophyte symbiosis with grasses , journal=The American Naturalist , volume=160 Suppl 4 , issue=suppl. 4 , pages=S99–S127 , date=October 2002 , pmid=18707456 , doi=10.1086/342161 , s2cid=23909652 {{cite book , editor-last1=Lacey , editor-first1=Lawrence A. , last1=Chandler , first1=D. , chapter=Basic and Applied Research on Entomopathogenic Fungi , year=2017 , title=Microbial Control of Insect and Mite Pests , pages=69–89 , doi=10.1016/B978-0-12-803527-6.00005-6 , publisher=Academic Press , isbn=978-0-12-803527-6 {{cite journal , last1=Chomicki , first1=Guillaume , last2=Renner , first2=Susanne S. , title=The interactions of ants with their biotic environment , journal=Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences , volume=284 , issue=1850 , year=2017 , pages=20170013 , doi=10.1098/rspb.2017.0013 , pmc=5360932 , pmid=28298352 {{cite journal , vauthors=Cushion MT, Smulian AG, Slaven BE, Sesterhenn T, Arnold J, Staben C, Porollo A, Adamczak R, Meller J , title=Transcriptome of ''Pneumocystis carinii'' during fulminate infection: carbohydrate metabolism and the concept of a compatible parasite , journal=PLOS ONE , volume=2 , issue=5 , pages=e423 , year=2007 , pmid=17487271 , pmc=1855432 , doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0000423 , doi-access=free , bibcode=2007PLoSO...2..423C {{cite book , vauthors=Cook GC, Zumla AI , author-link2=Alimuddin Zumla , title=Manson's Tropical Diseases: Expert Consult , publisher=Saunders Ltd , location=Edinburgh, Scotland , year=2008 , page=347 , isbn=978-1-4160-4470-3 {{cite journal , vauthors=Dadachova E, Bryan RA, Huang X, Moadel T, Schweitzer AD, Aisen P, Nosanchuk JD, Casadevall A , title=Ionizing radiation changes the electronic properties of melanin and enhances the growth of melanized fungi , journal=PLOS ONE , volume=2 , issue=5 , pages=e457 , year=2007 , pmid=17520016 , pmc=1866175 , doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0000457 , doi-access=free , bibcode=2007PLoSO...2..457D {{cite journal , vauthors=Dadachova E, Casadevall A , title=Ionizing radiation: how fungi cope, adapt, and exploit with the help of melanin , journal=Current Opinion in Microbiology , volume=11 , issue=6 , pages=525–31 , date=December 2008 , pmid=18848901 , pmc=2677413 , doi=10.1016/j.mib.2008.09.013 {{cite journal , vauthors=Daniels KJ, Srikantha T, Lockhart SR, Pujol C, Soll DR , title=Opaque cells signal white cells to form biofilms in ''Candida albicans'' , journal=The EMBO Journal , volume=25 , issue=10 , pages=2240–52 , date=May 2006 , pmid=16628217 , pmc=1462973 , doi=10.1038/sj.emboj.7601099 {{Cite book , vauthors=Datta A, Ganesan K, Natarajan K , title=Current trends in ''Candida albicans'' research , volume=30 , pages=53–88 , year=1989 , pmid=2700541 , doi=10.1016/S0065-2911(08)60110-1 , isbn=978-0-12-027730-8 , series=Advances in Microbial Physiology , chapter=Current Trends in Candida albicans Research {{cite journal , vauthors=Dean RA, Talbot NJ, Ebbole DJ, Farman ML, Mitchell TK, Orbach MJ, Thon M, Kulkarni R, Xu JR, Pan H, Read ND, Lee YH, Carbone I, Brown D, Oh YY, Donofrio N, Jeong JS, Soanes DM, Djonovic S, Kolomiets E, Rehmeyer C, Li W, Harding M, Kim S, Lebrun MH, Bohnert H, Coughlan S, Butler J, Calvo S, Ma LJ, Nicol R, Purcell S, Nusbaum C, Galagan JE, Birren BW , display-authors=6 , title=The genome sequence of the rice blast fungus ''Magnaporthe grisea'' , journal=Nature (journal), Nature , volume=434 , issue=7036 , pages=980–6 , date=April 2005 , pmid=15846337 , doi=10.1038/nature03449 , bibcode=2005Natur.434..980D , doi-access=free {{cite journal , vauthors=Dennis RL , year=1970 , title=A Middle Pennsylvanian basidiomycete mycelium with clamp connections , journal=Mycologia , volume=62 , issue=3 , pages=578–584 , doi=10.2307/3757529 , jstor=3757529 , url=http://www.cybertruffle.org.uk/cyberliber/59350/0062/003/0578.htm , access-date=5 July 2011 , archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180929141016/http://www.cybertruffle.org.uk/cyberliber/59350/0062/003/0578.htm , archive-date=29 September 2018 , url-status=live {{Cite book , vauthors=Demain AL, Fang A , volume=69 , pages=1–39 , year=2000 , pmid=11036689 , doi=10.1007/3-540-44964-7_1 , isbn=978-3-540-67793-2 , series=Advances in Biochemical Engineering/Biotechnology , title=History of Modern Biotechnology I , chapter=The Natural Functions of Secondary Metabolites {{cite journal , vauthors=Desjardin DE, Perry BA, Lodge DJ, Stevani CV, Nagasawa E , s2cid=25377671 , title=Luminescent Mycena: new and noteworthy species , journal=Mycologia , volume=102 , issue=2 , pages=459–77 , year=2010 , pmid=20361513 , doi=10.3852/09-197 , url=http://producao.usp.br/handle/BDPI/16784 , access-date=11 November 2018 , archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181111043819/http://www.producao.usp.br/handle/BDPI/16784 , archive-date=11 November 2018 , url-status=live {{cite journal , vauthors=Deshpande MV , title=Mycopesticide production by fermentation: potential and challenges , journal=Critical Reviews in Microbiology , volume=25 , issue=3 , pages=229–43 , year=1999 , pmid=10524330 , doi=10.1080/10408419991299220 {{cite book , author1=Donoghue MJ, author2=Cracraft J, author-link2=Joel Cracraft , title=Assembling the Tree of Life , publisher=Oxford University Press , location=Oxford (Oxfordshire), UK , year=2004 , page=187 , isbn=978-0-19-517234-8 {{cite journal , vauthors=Dotzler N, Walker C, Krings M, Hass H, Kerp H, Taylor TN, Agerer R , s2cid=1746303 , year=2009 , title=''Acaulosporoid glomeromycotan'' spores with a germination shield from the 400-million-year-old Rhynie chert , journal=Mycological Progress , volume=8 , issue=1 , pages=9–18 , doi=10.1007/s11557-008-0573-1, hdl=1808/13680 , url=https://kuscholarworks.ku.edu/bitstream/1808/13680/1/Taylor_et_al_2009.pdf , hdl-access=free {{cite journal , vauthors=El Dine RS, El Halawany AM, Ma CM, Hattori M , title=Anti-HIV-1 protease activity of lanostane triterpenes from the Vietnamese mushroom ''Ganoderma colossum'' , journal=Journal of Natural Products , volume=71 , issue=6 , pages=1022–6 , date=June 2008 , pmid=18547117 , doi=10.1021/np8001139 {{cite journal , vauthors=el-Mekkawy S, Meselhy MR, Nakamura N, Tezuka Y, Hattori M, Kakiuchi N, Shimotohno K, Kawahata T, Otake T , title=Anti-HIV-1 and anti-HIV-1-protease substances from ''Ganoderma lucidum'' , journal=Phytochemistry , volume=49 , issue=6 , pages=1651–7 , date=November 1998 , pmid=9862140 , doi=10.1016/S0031-9422(98)00254-4 {{cite journal , vauthors=Erdogan A, Gurses M, Sert S , title=Isolation of moulds capable of producing mycotoxins from blue mouldy Tulum cheeses produced in Turkey , journal=International Journal of Food Microbiology , volume=85 , issue=1–2 , pages=83–5 , date=August 2003 , pmid=12810273 , doi=10.1016/S0168-1605(02)00485-3 {{cite journal , vauthors=Eshet Y, Rampino MR, Visscher H , s2cid=58937537 , year=1995 , title=Fungal event and palynological record of ecological crisis and recovery across the Permian-Triassic boundary , journal=Geology (journal), Geology , volume=23 , issue=1 , pages=967–970 , doi=10.1130/0091-7613(1995)023<0967:FEAPRO>2.3.CO;2, bibcode=1995Geo....23..967E {{cite journal , vauthors=Fan W, Kraus PR, Boily MJ, Heitman J , title=''Cryptococcus neoformans'' gene expression during murine macrophage infection , journal=Eukaryotic Cell , volume=4 , issue=8 , pages=1420–33 , date=August 2005 , pmid=16087747 , pmc=1214536 , doi=10.1128/EC.4.8.1420-1433.2005 {{cite journal , vauthors=Farrar JF , title=Carbohydrate metabolism in biotrophic plant pathogens , journal=Microbiological Sciences , volume=2 , issue=10 , pages=314–7 , date=October 1985 , pmid=3939987 {{cite journal , vauthors=Fajardo A, Martínez JL , title=Antibiotics as signals that trigger specific bacterial responses , journal=Current Opinion in Microbiology , volume=11 , issue=2 , pages=161–7 , date=April 2008 , pmid=18373943 , doi=10.1016/j.mib.2008.02.006 {{cite journal , vauthors=Ferguson BA, Dreisbach TA, Parks CG, Filip GM, Schmitt CL , year=2003 , title=Coarse-scale population structure of pathogenic ''Armillaria'' species in a mixed-conifer forest in the Blue Mountains of northeast Oregon , journal=Canadian Journal of Forest Research , volume=33 , issue=4 , pages=612–623 , doi=10.1139/x03-065 , url=https://zenodo.org/record/1235905 , access-date=3 July 2019 , archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190703164318/https://zenodo.org/record/1235905 , archive-date=3 July 2019 , url-status=live {{cite journal , last1=Fernandez , first1=Jessie , last2=Orth , first2=Kim , title=Rise of a cereal killer: the biology of ''Magnaporthe oryzae'' biotrophic growth , journal=Trends in Microbiology , volume=26 , issue=7 , year=2018 , pages=582–597 , doi=10.1016/j.tim.2017.12.007 , pmid=29395728 , pmc=6003838 {{cite journal , vauthors=Fincham JR , title=Transformation in fungi , journal=Microbiological Reviews , volume=53 , issue=1 , pages=148–70 , date=March 1989 , pmid=2651864 , pmc=372721 , doi=10.1128/MMBR.53.1.148-170.1989 {{cite journal , vauthors=Firenzuoli F, Gori L, Lombardo G , title=The Medicinal Mushroom ''Agaricus blazei'' Murrill: Review of Literature and Pharmaco-Toxicological Problems , journal=Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine , volume=5 , issue=1 , pages=3–15 , date=March 2008 , pmid=18317543 , pmc=2249742 , doi=10.1093/ecam/nem007 {{cite journal , last1=Fisher , first1=Matthew C. , last2=Garner , first2=Trenton W. J. , title=Chytrid fungi and global amphibian declines , journal=Nature Reviews Microbiology , volume=18 , issue=6 , year=2020 , pages=332–343 , doi=10.1038/s41579-020-0335-x , pmid=32099078 , hdl=10044/1/78596 , s2cid=211266075 , url=https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/id/eprint/10092667/ , hdl-access=free {{cite journal , last1=Fritz , first1=Heidi , last2=Kennedy , first2=Deborah A. , last3=Ishii , first3=Mami , last4=Fergusson , first4=Dean , last5=Fernandes , first5=Rochelle , last6=Cooley , first6=Kieran , last7=Seely , first7=Dugald , title=Polysaccharide K and ''Coriolus versicolor'' extracts for lung cancer , journal=Integrative Cancer Therapies , volume=14 , issue=3 , year=2015 , pages=201–211 , doi=10.1177/1534735415572883 , pmid=25784670 , doi-access=free {{cite journal , vauthors=Fischer R, Zekert N, Takeshita N , s2cid=205365895 , title=Polarized growth in fungi--interplay between the cytoskeleton, positional markers and membrane domains , journal=Molecular Microbiology , volume=68 , issue=4 , pages=813–26 , date=May 2008 , pmid=18399939 , doi=10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06193.x {{cite journal , vauthors=Fomina M, Charnock JM, Hillier S, Alvarez R, Gadd GM, author5-link=Geoffrey Michael Gadd , title=Fungal transformations of uranium oxides , journal=Environmental Microbiology , volume=9 , issue=7 , pages=1696–710 , date=July 2007 , pmid=17564604 , doi=10.1111/j.1462-2920.2007.01288.x {{cite journal , vauthors=Foster CB, Stephenson MH, Marshall C, Logan GA, Greenwood PF , year=2002 , title=A revision of Reduviasporonites Wilson 1962: description, illustration, comparison and biological affinities , journal=Palynology , volume=26 , issue=1 , pages=35–58 , doi=10.2113/0260035 {{cite journal , vauthors=Fomina M, Charnock JM, Hillier S, Alvarez R, Livens F, Gadd GM , s2cid=52805144 , title=Role of fungi in the biogeochemical fate of depleted uranium , journal=Current Biology , volume=18 , issue=9 , pages=R375–7 , date=May 2008 , pmid=18460315 , doi=10.1016/j.cub.2008.03.011 , doi-access=free {{cite journal , vauthors=Furlaneto MC, Pizzirani-Kleiner AA , title=Intraspecific hybridisation of ''Trichoderma pseudokoningii'' by anastomosis and by protoplast fusion , journal=FEMS Microbiology Letters , volume=69 , issue=2 , pages=191–5 , date=January 1992 , pmid=1537549 , doi=10.1111/j.1574-6968.1992.tb05150.x , doi-access=free {{cite journal , vauthors=Gadd GM , title=Geomycology: biogeochemical transformations of rocks, minerals, metals and radionuclides by fungi, bioweathering and bioremediation , journal=Mycological Research , volume=111 , issue=Pt 1 , pages=3–49 , date=January 2007 , pmid=17307120 , doi=10.1016/j.mycres.2006.12.001 {{cite journal , last1=Garrido-Benavent , first1=Isaac , last2=Pérez-Ortega , first2=Sergio , title=Past, present, and future research in bipolar lichen-forming fungi and their photobionts , journal=American Journal of Botany , volume=104 , issue=11 , year=2017 , pages=1660–1674 , doi=10.3732/ajb.1700182 , doi-access=free {{cite journal , last1=Gow , first1=Neil A. R. , last2=Latge , first2=Jean-Paul , last3=Munro , first3=Carol A. , last4=Heitman , first4=Joseph , title=The fungal cell wall: Structure, biosynthesis, and function , journal=Microbiology Spectrum , volume=5 , issue=3 , year=2017 , doi=10.1128/microbiolspec.FUNK-0035-2016 , pmid=28513415 , hdl=2164/8941 {{cite journal , vauthors=Guarro J, Stchigel AM , title=Developments in fungal taxonomy , journal=Clinical Microbiology Reviews , volume=12 , issue=3 , pages=454–500 , date=July 1999 , pmid=10398676 , pmc=100249 , doi=10.1128/CMR.12.3.454 {{cite journal , last1=Guerre , first1=Philippe , title=Ergot alkaloids produced by endophytic fungi of the genus ''Epichloë'' , journal=Toxins , volume=7 , issue=3 , year=2015 , pages=773–790 , doi=10.3390/toxins7030773 , pmid=25756954 , pmc=4379524 , doi-access=free {{cite journal , vauthors=Hachmeister KA, Fung DY , title=Tempeh: a mold-modified indigenous fermented food made from soybeans and/or cereal grains , journal=Critical Reviews in Microbiology , volume=19 , issue=3 , pages=137–88 , year=1993 , pmid=8267862 , doi=10.3109/10408419309113527 {{cite journal , last1=Han , first1=Bing , last2=Weiss , first2=Louis M. , last3=Heitman , first3=Joseph , last4=Stukenbrock , first4=Eva Holtgrewe , title=Microsporidia: Obligate intracellular pathogens within the fungal kingdom , journal=Microbiology Spectrum , volume=5 , issue=2 , year=2017 , doi=10.1128/microbiolspec.FUNK-0018-2016 , pmid=28944750 , pmc=5613672 {{cite journal , vauthors=Harris SD , s2cid=2147525 , title=Branching of fungal hyphae: regulation, mechanisms and comparison with other branching systems , journal=Mycologia , volume=100 , issue=6 , pages=823–32 , year=2008 , pmid=19202837 , doi=10.3852/08-177 , url=http://www.cybertruffle.org.uk/cyberliber/59350/0100/006/0823.htm , access-date=5 July 2011 , archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160412145515/http://www.cybertruffle.org.uk/cyberliber/59350/0100/006/0823.htm , archive-date=12 April 2016 , url-status=live {{cite book , vauthors=Halpern GM, Miller A , title=Medicinal Mushrooms: Ancient Remedies for Modern Ailments , publisher=M. Evans and Co , location=New York, New York , year=2002 , page=116 , isbn=978-0-87131-981-4 {{cite journal , vauthors=Hawksworth DL , title=Pandora's mycological box: molecular sequences vs. morphology in understanding fungal relationships and biodiversity , journal=Revista Iberoamericana de Micología , volume=23 , issue=3 , pages=127–33 , date=September 2006 , pmid=17196017 , doi=10.1016/S1130-1406(06)70031-6 {{cite journal , vauthors=van der Heijden MG, Streitwolf-Engel R, Riedl R, Siegrist S, Neudecker A, Ineichen K, Boller T, Wiemken A, Sanders IR , s2cid=17048094 , title=The mycorrhizal contribution to plant productivity, plant nutrition and soil structure in experimental grassland , journal=The New Phytologist , volume=172 , issue=4 , pages=739–52 , year=2006 , pmid=17096799 , doi=10.1111/j.1469-8137.2006.01862.x , doi-access=free {{cite journal , vauthors=Heitman J , s2cid=2898102 , title=Sexual reproduction and the evolution of microbial pathogens , journal=Current Biology , volume=16 , issue=17 , pages=R711–25 , date=September 2006 , pmid=16950098 , doi=10.1016/j.cub.2006.07.064 , doi-access=free {{cite journal , vauthors=Hetland G, Johnson E, Lyberg T, Bernardshaw S, Tryggestad AM, Grinde B , s2cid=3866471 , title=Effects of the medicinal mushroom ''Agaricus blazei'' Murill on immunity, infection and cancer , journal=Scandinavian Journal of Immunology , volume=68 , issue=4 , pages=363–70 , date=October 2008 , pmid=18782264 , doi=10.1111/j.1365-3083.2008.02156.x , doi-access=free {{cite journal , vauthors=Hynes MJ , s2cid=45815733 , title=Regulatory circuits of the amdS gene of ''Aspergillus nidulans'' , journal=Antonie van Leeuwenhoek , volume=65 , issue=3 , pages=179–82 , year=1994 , pmid=7847883 , doi=10.1007/BF00871944 {{cite journal , vauthors=Hibbett DS, Grimaldi D, Donoghue MJ , s2cid=4346359 , year=1995 , title=Cretaceous mushrooms in amber , journal=Nature (journal), Nature , volume=377 , issue=6549 , page=487 , doi=10.1038/377487a0 , bibcode=1995Natur.377..487H, doi-access=free {{cite journal , vauthors=Hibbett DS, Binder M, Bischoff JF, Blackwell M, Cannon PF, Eriksson OE, Huhndorf S, James T, Kirk PM, Lücking R, Thorsten Lumbsch H, Lutzoni F, Matheny PB, McLaughlin DJ, Powell MJ, Redhead S, Schoch CL, Spatafora JW, Stalpers JA, Vilgalys R, Aime MC, Aptroot A, Bauer R, Begerow D, Benny GL, Castlebury LA, Crous PW, Dai YC, Gams W, Geiser DM, Griffith GW, Gueidan C, Hawksworth DL, Hestmark G, Hosaka K, Humber RA, Hyde KD, Ironside JE, Kõljalg U, Kurtzman CP, Larsson KH, Lichtwardt R, Longcore J, Miadlikowska J, Miller A, Moncalvo JM, Mozley-Standridge S, Oberwinkler F, Parmasto E, Reeb V, Rogers JD, Roux C, Ryvarden L, Sampaio JP, Schüssler A, Sugiyama J, Thorn RG, Tibell L, Untereiner WA, Walker C, Wang Z, Weir A, Weiss M, White MM, Winka K, Yao YJ, Zhang N , display-authors=6 , title=A higher-level phylogenetic classification of the Fungi , journal=Mycological Research , volume=111 , issue=Pt 5 , pages=509–47 , date=May 2007 , pmid=17572334 , doi=10.1016/j.mycres.2007.03.004 , url=http://www.clarku.edu/faculty/dhibbett/AFTOL/documents/AFTOL%20class%20mss%2023,%2024/AFTOL%20CLASS%20MS%20resub.pdf , url-status=dead , archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090326135053/http://www.clarku.edu/faculty/dhibbett/AFTOL/documents/AFTOL%20class%20mss%2023%2C%2024/AFTOL%20CLASS%20MS%20resub.pdf , archive-date=26 March 2009 , citeseerx=10.1.1.626.9582 , s2cid=4686378 {{cite journal , vauthors=Hibbett DS, Grimaldi D, Donoghue MJ , s2cid=22011469 , year=1997 , title=Fossil mushrooms from Miocene and Cretaceous ambers and the evolution of homobasidiomycetes , journal=American Journal of Botany , volume=84 , issue=7 , pages=981–991 , doi=10.2307/2446289 , jstor=2446289 , pmid=21708653 , doi-access=free {{cite journal , last1=Honegger , first1=Rosmarie , authorlink1=Rosmarie Honegger, last2=Edwards , first2=Dianne , last3=Axe , first3=Lindsey , title=The earliest records of internally stratified cyanobacterial and algal lichens from the Lower Devonian of the Welsh Borderland , journal=New Phytologist , volume=197 , issue=1 , year=2013 , pages=264–275 , doi=10.1111/nph.12009 , pmid=23110612 {{cite journal , vauthors=Howard RJ, Ferrari MA, Roach DH, Money NP , title=Penetration of hard substrates by a fungus employing enormous turgor pressures , journal=Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America , volume=88 , issue=24 , pages=11281–4 , date=December 1991 , pmid=1837147 , pmc=53118 , doi=10.1073/pnas.88.24.11281 , bibcode=1991PNAS...8811281H , doi-access=free {{cite journal , vauthors=Huang B, Guo J, Yi B, Yu X, Sun L, Chen W , s2cid=2222358 , title=Heterologous production of secondary metabolites as pharmaceuticals in ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' , journal=Biotechnology Letters , volume=30 , issue=7 , pages=1121–37 , date=July 2008 , pmid=18512022 , doi=10.1007/s10529-008-9663-z {{cite journal , vauthors=James TY, Letcher PM, Longcore JE, Mozley-Standridge SE, Porter D, Powell MJ, Griffith GW, Vilgalys R , title=A molecular phylogeny of the flagellated fungi (Chytridiomycota) and description of a new phylum (Blastocladiomycota) , journal=Mycologia , volume=98 , issue=6 , pages=860–71 , year=2006 , pmid=17486963 , doi=10.3852/mycologia.98.6.860 , url=http://www.cybertruffle.org.uk/cyberliber/59350/0098/006/0860.htm , access-date=5 July 2011 , archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150923230802/http://www.cybertruffle.org.uk/cyberliber/59350/0098/006/0860.htm , archive-date=23 September 2015 , url-status=live {{cite journal , vauthors=Hube B , title=From commensal to pathogen: stage- and tissue-specific gene expression of ''Candida albicans'' , journal=Current Opinion in Microbiology , volume=7 , issue=4 , pages=336–41 , date=August 2004 , pmid=15288621 , doi=10.1016/j.mib.2004.06.003 {{cite journal , last1=Jakovlev , first1=Jevgeni , year=2012 , title=Fungal hosts of mycetophilids (Diptera: Sciaroidea excluding Sciaridae): a review , journal=Mycology , volume=3 , issue=1 , pages=11–23 , doi=10.1080/21501203.2012.662533 , s2cid=82107953 , url=https://www.researchgate.net/publication/254268258 {{cite journal , vauthors=James TY, Kauff F, Schoch CL, Matheny PB, Hofstetter V, Cox CJ, Celio G, Gueidan C, Fraker E, Miadlikowska J, Lumbsch HT, Rauhut A, Reeb V, Arnold AE, Amtoft A, Stajich JE, Hosaka K, Sung GH, Johnson D, O'Rourke B, Crockett M, Binder M, Curtis JM, Slot JC, Wang Z, Wilson AW, Schüssler A, Longcore JE, O'Donnell K, Mozley-Standridge S, Porter D, Letcher PM, Powell MJ, Taylor JW, White MM, Griffith GW, Davies DR, Humber RA, Morton JB, Sugiyama J, Rossman AY, Rogers JD, Pfister DH, Hewitt D, Hansen K, Hambleton S, Shoemaker RA, Kohlmeyer J, Volkmann-Kohlmeyer B, Spotts RA, Serdani M, Crous PW, Hughes KW, Matsuura K, Langer E, Langer G, Untereiner WA, Lücking R, Büdel B, Geiser DM, Aptroot A, Diederich P, Schmitt I, Schultz M, Yahr R, Hibbett DS, Lutzoni F, McLaughlin DJ, Spatafora JW, Vilgalys R , s2cid=4302864 , display-authors=6 , title=Reconstructing the early evolution of Fungi using a six-gene phylogeny , journal=Nature (journal), Nature , volume=443 , issue=7113 , pages=818–22 , date=October 2006 , pmid=17051209 , doi=10.1038/nature05110 , bibcode=2006Natur.443..818J {{cite journal , last1=Janik , first1=Edyta , last2=Niemcewicz , first2=Marcin , last3=Ceremuga , first3=Michal , last4=Stela , first4=Maksymilian , last5=Saluk-Bijak , first5=Joanna , last6=Siadkowski , first6=Adrian , last7=Bijak , first7=Michal , title=Molecular aspects of mycotoxins—a serious problem for human health , journal=International Journal of Molecular Sciences , volume=21 , issue=21 , year=2020 , pages=8187 , doi=10.3390/ijms21218187 , pmid=33142955 , pmc=7662353 , doi-access=free {{cite journal , vauthors=Jørgensen TR , title=Identification and toxigenic potential of the industrially important fungi, ''Aspergillus oryzae'' and ''Aspergillus sojae'' , journal=Journal of Food Protection , volume=70 , issue=12 , pages=2916–34 , date=December 2007 , pmid=18095455 , doi=10.4315/0362-028X-70.12.2916 {{cite journal , vauthors=Joseph B, Ramteke PW, Thomas G , title=Cold active microbial lipases: some hot issues and recent developments , journal=Biotechnology Advances , volume=26 , issue=5 , pages=457–70 , year=2008 , pmid=18571355 , doi=10.1016/j.biotechadv.2008.05.003 {{cite journal , last1=Joseph , first1=Ross , last2=Keyhani , first2=Nemat O. , title=Fungal mutualisms and pathosystems: life and death in the ambrosia beetle mycangia , journal=Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology , volume=105 , issue=9 , year=2021 , pages=3393–3410 , doi=10.1007/s00253-021-11268-0 , pmid=33837831, s2cid=233200379 {{cite journal , last1=Karbalaei , first1=Mohsen , last2=Rezaee , first2=Seyed A. , last3=Farsiani , first3=Hadi , title=''Pichia pastoris'': A highly successful expression system for optimal synthesis of heterologous proteins , journal=Journal of Cellular Physiology , volume=235 , issue=9 , year=2020 , pages=5867–5881 , doi=10.1002/jcp.29583 , pmc=7228273 , pmid=32057111 {{cite journal , vauthors=Karlson-Stiber C, Persson H , title=Cytotoxic fungi--an overview , journal=Toxicon , volume=42 , issue=4 , pages=339–49 , date=September 2003 , pmid=14505933 , doi=10.1016/S0041-0101(03)00238-1 {{cite journal , vauthors=Kauffman CA , title=Histoplasmosis: a clinical and laboratory update , journal=Clinical Microbiology Reviews , volume=20 , issue=1 , pages=115–32 , date=January 2007 , pmid=17223625 , pmc=1797635 , doi=10.1128/CMR.00027-06 {{cite journal , vauthors=Keller NP, Turner G, Bennett JW , s2cid=23537608 , title=Fungal secondary metabolism - from biochemistry to genomics , journal=Nature Reviews. Microbiology , volume=3 , issue=12 , pages=937–47 , date=December 2005 , pmid=16322742 , doi=10.1038/nrmicro1286 {{cite journal , vauthors=Kinsella JE, Hwang DH , title=Enzymes of ''Penicillium roqueforti'' involved in the biosynthesis of cheese flavor , journal=Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition , volume=8 , issue=2 , pages=191–228 , date=November 1976 , pmid=21770 , doi=10.1080/10408397609527222 {{cite journal , vauthors=Kojic M, Zhou Q, Lisby M, Holloman WK , title=Rec2 interplay with both Brh2 and Rad51 balances recombinational repair in ''Ustilago maydis'' , journal=Molecular and Cellular Biology , volume=26 , issue=2 , pages=678–88 , date=January 2006 , pmid=16382157 , pmc=1346908 , doi=10.1128/MCB.26.2.678-688.2006 {{cite journal , last1=Kuhar , first1=Francisco , last2=Furci , first2=Giuliana , last3=Drechsler-Santos , first3=Elisandro Ricardo , last4=Pfister , first4=Donald H. , title=Delimitation of Funga as a valid term for the diversity of fungal communities: the Fauna, Flora & Funga proposal (FF&F) , journal=IMA Fungus , volume=9 , issue=2 , year=2018 , pages=A71–A74 , doi=10.1007/BF03449441 , doi-access=free {{cite book , title=Handbook of Cereal Science and Technology , vauthors=Kulp K , year=2000 , publisher=CRC Press , isbn=978-0-8247-8294-8 {{cite journal , vauthors=Kumar R, Singh S, Singh OV , s2cid=4830678 , title=Bioconversion of lignocellulosic biomass: biochemical and molecular perspectives , journal=Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology , volume=35 , issue=5 , pages=377–91 , date=May 2008 , pmid=18338189 , doi=10.1007/s10295-008-0327-8 {{cite journal , vauthors=Leathem AM, Dorran TJ , title=Poisoning due to raw ''Gyromitra esculenta'' (false morels) west of the Rockies , journal=Canadian Journal of Emergency Medicine , volume=9 , issue=2 , pages=127–30 , date=March 2007 , pmid=17391587 , doi=10.1017/s1481803500014937 , doi-access=free {{cite book , editor-last1=Stephenson , editor-first1=Steven L. , editor-last2=Rojas , editor-first2=Carlos , last1=Leontyev , first1=Dmitry V. , last2=Schnittler , first2=Martin , chapter=The phylogeny of Myxomycetes , title=Myxomycetes. Biology, Systematics, Biogeography, and Ecology , year=2017 , pages=83–106 , doi=10.1016/B978-0-12-805089-7.00003-2 , publisher=Academic Press , isbn=978-0-12-805089-7 {{cite journal , vauthors=Lin X, Hull CM, Heitman J , s2cid=52857557 , title=Sexual reproduction between partners of the same mating type in ''Cryptococcus neoformans'' , journal=Nature (journal), Nature , volume=434 , issue=7036 , pages=1017–21 , date=April 2005 , pmid=15846346 , doi=10.1038/nature03448 , bibcode=2005Natur.434.1017L {{cite journal , vauthors=Linder MB, Szilvay GR, Nakari-Setälä T, Penttilä ME , title=Hydrophobins: the protein-amphiphiles of filamentous fungi , journal=FEMS Microbiology Reviews , volume=29 , issue=5 , pages=877–96 , date=November 2005 , pmid=16219510 , doi=10.1016/j.femsre.2005.01.004 , doi-access=free {{cite journal , vauthors=Lindahl BD, Ihrmark K, Boberg J, Susan Trumbore, Trumbore SE, Högberg P, Stenlid J, Finlay RD , title=Spatial separation of litter decomposition and mycorrhizal nitrogen uptake in a boreal forest , journal=The New Phytologist , volume=173 , issue=3 , pages=611–20 , year=2007 , pmid=17244056 , doi=10.1111/j.1469-8137.2006.01936.x , hdl=11858/00-001M-0000-0027-D56D-D , url=http://www.escholarship.org/uc/item/1r43h5sj , doi-access=free {{cite journal , vauthors=Lockhart RJ, Van Dyke MI, Beadle IR, Humphreys P, McCarthy AJ , title=Molecular biological detection of anaerobic gut fungi (Neocallimastigales) from landfill sites , journal=Applied and Environmental Microbiology , volume=72 , issue=8 , pages=5659–61 , date=August 2006 , pmid=16885325 , doi=10.1128/AEM.01057-06 , pmc=1538735 , bibcode=2006ApEnM..72.5659L {{cite journal , vauthors=Loo DS , title=Systemic antifungal agents: an update of established and new therapies , journal=Advances in Dermatology , volume=22 , pages=101–24 , year=2006 , pmid=17249298 , doi=10.1016/j.yadr.2006.07.001 {{cite journal , vauthors=López-Gómez J, Taylor EL , title=Permian-Triassic transition in Spain: a multidisciplinary approach , journal=Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology , volume=229 , issue=1–2 , year=2005 , pages=1–2 , doi=10.1016/j.palaeo.2005.06.028 {{cite journal , vauthors=Looy CV, Twitchett RJ, Dilcher DL, Van Konijnenburg-Van Cittert JH, Visscher H , title=Life in the end-Permian dead zone , journal=Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America , volume=98 , issue=14 , pages=7879–83 , date=July 2001 , pmid=11427710 , pmc=35436 , doi=10.1073/pnas.131218098 , quote=See image 2 , bibcode=2001PNAS...98.7879L , doi-access=free {{cite journal , last1=Lu , first1=Jiahui , last2=He , first2=Rongjun , last3=Sun , first3=Peilong , last4=Zhang , first4=Fuming , last5=Linhardt , first5=Robert J. , last6=Zhang , first6=Anqiang , title=Molecular mechanisms of bioactive polysaccharides from ''Ganoderma lucidum'' (Lingzhi), a review , journal=International Journal of Biological Macromolecules , volume=150 , year=2020 , pages=765–774 , doi=10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.02.035 , pmid=32035956 , s2cid=211071754 {{cite journal , vauthors=Lücking R, Huhndorf S, Pfister DH, Plata ER, Lumbsch HT , s2cid=6689439 , title=Fungi evolved right on track , journal=Mycologia , volume=101 , issue=6 , pages=810–22 , year=2009 , pmid=19927746 , doi=10.3852/09-016 , url=http://nrs.harvard.edu/urn-3:HUL.InstRepos:14168857 {{Cite book , vauthors=Hawksworth DL, Lücking R , title=The Fungal Kingdom , chapter=Fungal Diversity Revisited: 2.2 to 3.8 Million Species , journal=Microbiology Spectrum , volume=5 , issue=4 , pages=79–95 , date=July 2017 , pmid=28752818 , doi=10.1128/microbiolspec.FUNK-0052-2016 , isbn=978-1-55581-957-6 {{cite journal , vauthors=López-Gómez J, Molina-Meyer M , title=The competitive exclusion principle versus biodiversity through competitive segregation and further adaptation to spatial heterogeneities , journal=Theoretical Population Biology , volume=69 , issue=1 , pages=94–109 , date=February 2006 , pmid=16223517 , doi=10.1016/j.tpb.2005.08.004 {{cite journal , vauthors=Manzoni M, Rollini M , s2cid=5761188 , title=Biosynthesis and biotechnological production of statins by filamentous fungi and application of these cholesterol-lowering drugs , journal=Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology , volume=58 , issue=5 , pages=555–64 , date=April 2002 , pmid=11956737 , doi=10.1007/s00253-002-0932-9 {{cite journal , vauthors=Metzenberg RL, Glass NL , title=Mating type and mating strategies in Neurospora , journal=BioEssays , volume=12 , issue=2 , pages=53–9 , date=February 1990 , pmid=2140508 , doi=10.1002/bies.950120202 , s2cid=10818930 {{cite journal , vauthors=Merckx V, Bidartondo MI, Hynson NA , title=Myco-heterotrophy: when fungi host plants , journal=Annals of Botany , volume=104 , issue=7 , pages=1255–61 , date=December 2009 , pmid=19767309 , pmc=2778383 , doi=10.1093/aob/mcp235 {{cite journal , vauthors=Michod RE, Bernstein H, Nedelcu AM , title=Adaptive value of sex in microbial pathogens , journal=Infection, Genetics and Evolution , volume=8 , issue=3 , pages=267–85 , date=May 2008 , pmid=18295550 , doi=10.1016/j.meegid.2008.01.002 , url=http://www.hummingbirds.arizona.edu/Faculty/Michod/Downloads/IGE%20review%20sex.pdf , access-date=22 July 2013 , archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170516235741/http://www.hummingbirds.arizona.edu/Faculty/Michod/Downloads/IGE%20review%20sex.pdf , archive-date=16 May 2017 , url-status=live {{cite journal , vauthors=Mihail JD, Bruhn JN , title=Foraging behaviour of ''Armillaria'' rhizomorph systems , journal=Mycological Research , volume=109 , issue=Pt 11 , pages=1195–207 , date=November 2005 , pmid=16279413 , doi=10.1017/S0953756205003606 {{cite journal , vauthors=Michelot D, Melendez-Howell LM , s2cid=41451034 , title=''Amanita muscaria'': chemistry, biology, toxicology, and ethnomycology , journal=Mycological Research , volume=107 , issue=Pt 2 , pages=131–46 , date=February 2003 , pmid=12747324 , doi=10.1017/S0953756203007305 {{cite book , veditors=Mitzka W , year=1960 , title=Etymologisches Wörterbuch der deutschen Sprache , trans-title=Etymological dictionary of the German language , location=Berlin , publisher=Walter de Gruyter , language=de {{cite journal , vauthors=Molina L, Kahmann R , title=An ''Ustilago maydis'' gene involved in H2O2 detoxification is required for virulence , journal=The Plant Cell , volume=19 , issue=7 , pages=2293–309 , date=July 2007 , pmid=17616735 , pmc=1955693 , doi=10.1105/tpc.107.052332 {{cite book , vauthors=Money NP , chapter=Mechanics of invasive fungal growth and the significance of turgor in plant infection , title=Molecular Genetics of Host-Specific Toxins in Plant Disease: Proceedings of the 3rd Tottori International Symposium on Host-Specific Toxins, Daisen, Tottori, Japan, August 24–29, 1997 , publisher=Kluwer Academic Publishers , year=1998 , location=Netherlands , pages=261–271 , isbn=978-0-7923-4981-5 {{cite journal , vauthors=Moore RT , year=1980 , title=Taxonomic proposals for the classification of marine yeasts and other yeast-like fungi including the smuts , journal=Botanica Marina , volume=23 , pages=361–373 {{cite journal , vauthors=Money NP , title=Mushroom stem cells , journal=BioEssays , volume=24 , issue=10 , pages=949–52 , date=October 2002 , pmid=12325127 , doi=10.1002/bies.10160 {{cite book , vauthors=Moss ST , title=The Biology of Marine Fungi , publisher=Cambridge University Press , location=Cambridge, UK , year=1986 , page=76 , isbn=978-0-521-30899-1 {{cite journal , vauthors=Mueller GM, Schmit JP , s2cid=23827807 , year=2006 , title=Fungal biodiversity: what do we know? What can we predict? , journal=Biodiversity and Conservation , volume=16 , pages=1–5 , doi=10.1007/s10531-006-9117-7 {{cite book , vauthors=Esser K , editor1-first=David J , editor1-last=McLaughlin , editor2-first=Joseph W , editor2-last=Spatafora , title=The Mycota VII A: Systematics and Evolution (2nd ed.) , series=The Mycota , publisher=Springer , year=2014 , page=461 , doi=10.1007/978-3-642-55318-9 , isbn=978-3-642-55317-2 , s2cid=46141350 , url=https://www.springer.com/gp/book/9783642553172 {{cite journal , last1=Naranjo‐Ortiz , first1=Miguel A. , last2=Gabaldón , first2=Toni , title=Fungal evolution: Diversity, taxonomy and phylogeny of the Fungi , journal=Biological Reviews , volume=94 , issue=6 , year=2019 , pages=2101–2137 , doi=10.1111/brv.12550 , pmid=31659870 , pmc=6899921 , doi-access=free {{cite journal , vauthors=Nikoh N, Fukatsu T , title=Interkingdom host jumping underground: phylogenetic analysis of entomoparasitic fungi of the genus ''Cordyceps'' , journal=Molecular Biology and Evolution , volume=17 , issue=4 , pages=629–38 , date=April 2000 , pmid=10742053 , doi=10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a026341 , doi-access=free {{Cite book , vauthors=Nielsen K, Heitman J , volume=57 , pages=143–73 , year=2007 , pmid=17352904 , doi=10.1016/S0065-2660(06)57004-X , isbn=978-0-12-017657-1 , series=Advances in Genetics , title=Fungal Genomics , chapter=Sex and Virulence of Human Pathogenic Fungi {{cite journal , vauthors=Nguyen NH, Suh SO, Blackwell M , title=Five novel Candida species in insect-associated yeast clades isolated from Neuroptera and other insects , journal=Mycologia , volume=99 , issue=6 , pages=842–58 , year=2007 , pmid=18333508 , doi=10.3852/mycologia.99.6.842 , url=http://www.cybertruffle.org.uk/cyberliber/59350/0099/006/0842.htm , access-date=5 July 2011 , archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170507072249/http://www.cybertruffle.org.uk/cyberliber/59350/0099/006/0842.htm , archive-date=7 May 2017 , url-status=live {{cite web , url=http://www.biocontrol.entomology.cornell.edu/pathogens/trichoderma.html , title=''Trichoderma'' spp., including ''T. harzianum'', ''T. viride'', ''T. koningii'', ''T. hamatum'' and other spp. Deuteromycetes, Moniliales (asexual classification system) , access-date=10 July 2007 , work=Biological Control: A Guide to Natural Enemies in North America , url-status=dead , archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110414111846/http://www.biocontrol.entomology.cornell.edu/pathogens/trichoderma.html , archive-date=14 April 2011 {{cite journal , vauthors=O'Donnell K, Cigelnik E, Casper HH , title=Molecular phylogenetic, morphological, and mycotoxin data support reidentification of the Quorn mycoprotein fungus as ''Fusarium venenatum'' , journal=Fungal Genetics and Biology , volume=23 , issue=1 , pages=57–67 , date=February 1998 , pmid=9501477 , doi=10.1006/fgbi.1997.1018 , s2cid=23049409 {{cite journal , last1=Olatunji , first1=Opeyemi Joshua , last2=Tang , first2=Jian , last3=Tola , first3=Adesola , last4=Auberon , first4=Florence , last5=Oluwaniyi , first5=Omolara , last6=Ouyang , first6=Zhen , title=The genus ''Cordyceps'': An extensive review of its traditional uses, phytochemistry and pharmacology , journal=Fitoterapia , volume=129 , year=2018, pages=293–316 , doi=10.1016/j.fitote.2018.05.010 , pmid=29775778 , s2cid=21741034 {{cite journal , vauthors=Olempska-Beer ZS, Merker RI, Ditto MD, DiNovi MJ , title=Food-processing enzymes from recombinant microorganisms--a review , journal=Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology , volume=45 , issue=2 , pages=144–158 , date=July 2006 , pmid=16769167 , doi=10.1016/j.yrtph.2006.05.001 , url=https://zenodo.org/record/1259499 , access-date=3 July 2019 , archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190703164318/https://zenodo.org/record/1259499 , archive-date=3 July 2019 , url-status=live {{cite journal , last1=Olicón-Hernández , first1=Dario R. , last2=Araiza-Villanueva , first2=Minerva G. , last3=Pardo , first3=Juan P. , last4=Aranda , first4=Elisabet , last5=Guerra-Sánchez , first5=Guadalupe , title=New insights of ''Ustilago maydis'' as yeast model for genetic and biotechnological research: A review , journal=Current Microbiology , volume=76 , issue=8 , year=2019 , pages=917–926 , doi=10.1007/s00284-019-01629-4 , pmid=30689003 , s2cid=59307118 {{cite web , url=http://oxforddictionaries.com/definition/english/fungus , title=Fungus , work=Oxford Dictionaries , access-date=26 February 2011 , archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120728023308/http://oxforddictionaries.com/definition/english/fungus , archive-date=28 July 2012 , url-status=dead {{cite book , vauthors=Orr DB, Orr RT , title=Mushrooms of Western North America , publisher=University of California Press , location=Berkeley, California , year=1979 , page=17 , isbn=978-0-520-03656-7 {{cite journal , vauthors=Pan A, Lorenzotti S, Zoncada A , title=Registered and investigational drugs for the treatment of methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' infection , journal=Recent Patents on Anti-Infective Drug Discovery , volume=3 , issue=1 , pages=10–33 , date=January 2008 , pmid=18221183 , doi=10.2174/157489108783413173 {{cite journal , vauthors=Parish JA, McCann MA, Watson RH, Hoveland CS, Hawkins LL, Hill NS, Bouton JH , title=Use of nonergot alkaloid-producing endophytes for alleviating tall fescue toxicosis in sheep , journal=Journal of Animal Science , volume=81 , issue=5 , pages=1316–22 , date=May 2003 , pmid=12772860 , doi=10.2527/2003.8151316x {{cite journal , vauthors=Parniske M , s2cid=5432120 , title=Arbuscular mycorrhiza: the mother of plant root endosymbioses , journal=Nature Reviews. Microbiology , volume=6 , issue=10 , pages=763–75 , date=October 2008 , pmid=18794914 , doi=10.1038/nrmicro1987 {{cite journal , vauthors=Paszkowski U , title=Mutualism and parasitism: the yin and yang of plant symbioses , journal=Current Opinion in Plant Biology , volume=9 , issue=4 , pages=364–70 , date=August 2006 , pmid=16713732 , doi=10.1016/j.pbi.2006.05.008 {{cite journal , vauthors=Peñalva MA, Arst HN , title=Regulation of gene expression by ambient pH in filamentous fungi and yeasts , journal=Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews , volume=66 , issue=3 , pages=426–46, table of contents , date=September 2002 , pmid=12208998 , pmc=120796 , doi=10.1128/MMBR.66.3.426-446.2002 {{cite journal , vauthors=Peintner U, Pöder R, Pümpel T , title=The Iceman's fungi , journal=Mycological Research , volume=102 , issue=10 , pages=1153–1162 , year=1998 , doi=10.1017/S0953756298006546 {{cite journal , vauthors=Pereira JL, Noronha EF, Miller RN, Franco OL , title=Novel insights in the use of hydrolytic enzymes secreted by fungi with biotechnological potential , journal=Letters in Applied Microbiology , volume=44 , issue=6 , pages=573–81 , date=June 2007 , pmid=17576216 , doi=10.1111/j.1472-765X.2007.02151.x , doi-access=free {{cite journal , vauthors=Perotto S, Bonfante P , title=Bacterial associations with mycorrhizal fungi: close and distant friends in the rhizosphere , journal=Trends in Microbiology , volume=5 , issue=12 , pages=496–501 , date=December 1997 , pmid=9447662 , doi=10.1016/S0966-842X(97)01154-2 {{cite journal , vauthors=Perfect JR , title=''Cryptococcus neoformans'': the yeast that likes it hot , journal=FEMS Yeast Research , volume=6 , issue=4 , pages=463–8 , date=June 2006 , pmid=16696642 , doi=10.1111/j.1567-1364.2006.00051.x , doi-access=free {{cite journal , vauthors=Piskur J, Rozpedowska E, Polakova S, Merico A, Compagno C , title=How did ''Saccharomyces'' evolve to become a good brewer? , journal=Trends in Genetics , volume=22 , issue=4 , pages=183–6 , date=April 2006 , pmid=16499989 , doi=10.1016/j.tig.2006.02.002 {{cite journal , vauthors=Pringle A, Patek SN, Fischer M, Stolze J, Money NP , title=The captured launch of a ballistospore , journal=Mycologia , volume=97 , issue=4 , pages=866–71 , year=2005 , pmid=16457355 , doi=10.3852/mycologia.97.4.866 , url=http://www.cybertruffle.org.uk/cyberliber/59350/0097/004/0866.htm , access-date=5 July 2011 , archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160412145956/http://www.cybertruffle.org.uk/cyberliber/59350/0097/004/0866.htm , archive-date=12 April 2016 , url-status=live {{cite journal , vauthors=Polizeli ML, Rizzatti AC, Monti R, Terenzi HF, Jorge JA, Amorim DS , s2cid=22956 , title=Xylanases from fungi: properties and industrial applications , journal=Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology , volume=67 , issue=5 , pages=577–91 , date=June 2005 , pmid=15944805 , doi=10.1007/s00253-005-1904-7 {{cite book , vauthors=Purvis W , title=Lichens , publisher=Smithsonian Institution Press in association with the Natural History Museum, London , location=Washington, D.C. , year=2000 , page
49–75
, isbn=978-1-56098-879-3 , url-access=registration , url=https://archive.org/details/lichens00purv/page/49 {{cite journal , vauthors=Raghukumar C, Raghukumar S , title=Barotolerance of fungi isolated from deep-sea sediments of the Indian Ocean , journal=Aquatic Microbial Ecology , volume=15 , issue=2 , pages=153–163 , year=1998 , doi=10.3354/ame015153 , doi-access=free {{cite book , vauthors=Raven PH, Evert RF, Eichhorn, SE , title=Biology of Plants , chapter-url=https://archive.org/details/biologyofplants00rave_0 , chapter-url-access=registration , edition=7 , publisher=W. H. Freeman , year=2005 , pag
290
, chapter=14—Fungi , isbn=978-0-7167-1007-3 {{cite journal , vauthors=Redecker D, Raab P , title=Phylogeny of the glomeromycota (arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi): recent developments and new gene markers , journal=Mycologia , volume=98 , issue=6 , pages=885–95 , year=2006 , pmid=17486965 , doi=10.3852/mycologia.98.6.885 , url=http://www.cybertruffle.org.uk/cyberliber/59350/0098/006/0885.htm , access-date=5 July 2011 , archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150923230805/http://www.cybertruffle.org.uk/cyberliber/59350/0098/006/0885.htm , archive-date=23 September 2015 , url-status=live {{cite journal , vauthors=Redecker D, Kodner R, Graham LE , s2cid=43553633 , title=Glomalean fungi from the Ordovician , journal=Science (journal), Science , volume=289 , issue=5486 , pages=1920–1 , date=September 2000 , pmid=10988069 , doi=10.1126/science.289.5486.1920 , bibcode=2000Sci...289.1920R {{cite journal , last1=Redhead , first1=Scott , last2=Norvell , first2=Lorelei , year=2013 , title=MycoBank, Index Fungorum, and Fungal Names recommended as official nomenclatural repositories for 2013 , journal=IMA Fungus , volume=3 , issue=2 , pages=44–45 , url=https://www.researchgate.net/publication/255719633 {{cite journal , vauthors=Remy W, Taylor TN, Hass H, Kerp H , title=Four hundred-million-year-old vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizae , journal=Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America , volume=91 , issue=25 , pages=11841–3 , date=December 1994 , pmid=11607500 , pmc=45331 , doi=10.1073/pnas.91.25.11841 , bibcode=1994PNAS...9111841R , doi-access=free {{cite journal , last1=Rhimi , first1=Wafa , last2=Theelen , first2=Bart , last3=Boekhout , first3=Teun , last4=Otranto , first4=Domenico , last5=Cafarchia , first5=Claudia , title=''Malassezia'' spp. yeasts of emerging concern in fungemia , journal=Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology , volume=10 , year=2020 , page=370 , doi=10.3389/fcimb.2020.00370 , pmid=32850475 , pmc=7399178, doi-access=free {{cite journal , last1=Rigling , first1=Daniel , last2=Prospero , first2=Simone , title=''Cryphonectria parasitica'', the causal agent of chestnut blight: invasion history, population biology and disease control , journal=Molecular Plant Pathology , volume=19 , issue=1 , year=2018 , pages=7–20 , doi=10.1111/mpp.12542 , pmid=28142223 , pmc=6638123 {{cite journal , vauthors=Rohlfs M, Albert M, Keller NP, Kempken F , title=Secondary chemicals protect mould from fungivory , journal=Biology Letters , volume=3 , issue=5 , pages=523–5 , date=October 2007 , pmid=17686752 , pmc=2391202 , doi=10.1098/rsbl.2007.0338 {{cite journal , last1=Rossman , first1=Amy Y. , title=Lessons learned from moving to one scientific name for fungi , journal=IMA Fungus , volume=5 , issue=1 , year=2014 , pages=81–89 , pmc=4107901 , pmid=25083410 , doi=10.5598/imafungus.2014.05.01.10 For an example, see {{cite journal , vauthors=Samuels GJ , title=''Trichoderma'': systematics, the sexual state, and ecology , journal=Phytopathology , volume=96 , issue=2 , pages=195–206 , date=February 2006 , pmid=18943925 , doi=10.1094/PHYTO-96-0195 , url=https://zenodo.org/record/1235933 , doi-access=free {{cite journal , vauthors=Sancho LG, de la Torre R, Horneck G, Ascaso C, de Los Rios A, Pintado A, Wierzchos J, Schuster M , s2cid=4121180 , title=Lichens survive in space: results from the 2005 LICHENS experiment , journal=Astrobiology , volume=7 , issue=3 , pages=443–54 , date=June 2007 , pmid=17630840 , doi=10.1089/ast.2006.0046 , bibcode=2007AsBio...7..443S {{cite journal , last1=Santini , first1=Alberto , last2=Battisti , first2=Andrea , title=Complex insect–pathogen interactions in tree pandemics , journal=Frontiers in Physiology , volume=10 , year=2019 , page=550 , doi=10.3389/fphys.2019.00550 , pmc=6517489 , pmid=31133880 , doi-access=free {{cite journal , vauthors=Schaller M, Borelli C, Korting HC, Hube B , title=Hydrolytic enzymes as virulence factors of ''Candida albicans'' , journal=Mycoses , volume=48 , issue=6 , pages=365–77 , date=November 2005 , pmid=16262871 , doi=10.1111/j.1439-0507.2005.01165.x , s2cid=1356254 {{cite journal , vauthors=Schardl CL, Craven KD , title=Interspecific hybridization in plant-associated fungi and oomycetes: a review , journal=Molecular Ecology , volume=12 , issue=11 , pages=2861–73 , date=November 2003 , pmid=14629368 , doi=10.1046/j.1365-294X.2003.01965.x , s2cid=25879264 {{cite book , vauthors=Schlegel HG , title=General Microbiology , publisher=Cambridge University Press , location=Cambridge, UK , year=1993 , page=360 , isbn=978-0-521-43980-0 {{Cite book , vauthors=Schardl CL, Panaccione DG, Tudzynski P , title=Ergot alkaloids--biology and molecular biology , volume=63 , pages=45–86 , year=2006 , pmid=17133714 , doi=10.1016/S1099-4831(06)63002-2 , isbn=978-0-12-469563-4 , series=The Alkaloids: Chemistry and Biology {{cite journal , vauthors=Schoch CL, Sung GH, López-Giráldez F, Townsend JP, Miadlikowska J, Hofstetter V, Robbertse B, Matheny PB, Kauff F, Wang Z, Gueidan C, Andrie RM, Trippe K, Ciufetti LM, Wynns A, Fraker E, Hodkinson BP, Bonito G, Groenewald JZ, Arzanlou M, de Hoog GS, Crous PW, Hewitt D, Pfister DH, Peterson K, Gryzenhout M, Wingfield MJ, Aptroot A, Suh SO, Blackwell M, Hillis DM, Griffith GW, Castlebury LA, Rossman AY, Lumbsch HT, Lücking R, Büdel B, Rauhut A, Diederich P, Ertz D, Geiser DM, Hosaka K, Inderbitzin P, Kohlmeyer J, Volkmann-Kohlmeyer B, Mostert L, O'Donnell K, Sipman H, Rogers JD, Shoemaker RA, Sugiyama J, Summerbell RC, Untereiner W, Johnston PR, Stenroos S, Zuccaro A, Dyer PS, Crittenden PD, Cole MS, Hansen K, Trappe JM, Yahr R, Lutzoni F, Spatafora JW , display-authors=6 , title=The Ascomycota tree of life: a phylum-wide phylogeny clarifies the origin and evolution of fundamental reproductive and ecological traits , journal=Systematic Biology , volume=58 , issue=2 , pages=224–39 , date=April 2009 , pmid=20525580 , doi=10.1093/sysbio/syp020 , doi-access=free {{cite journal , vauthors=Schüssler A, Schwarzott D, Walker C , s2cid=82128210 , year=2001 , title=A new fungal phylum, the Glomeromycota: phylogeny and evolution , journal=Mycological Research , volume=105 , issue=12 , pages=1413–1421 , doi=10.1017/S0953756201005196 {{cite web , url=http://www.sci-news.com/biology/science-brazilian-stingless-bee-monascus-fungus-03372.html , title=Entomologists: Brazilian Stingless Bee Must Cultivate Special Type of Fungus to Survive , date=23 October 2015 , website=Sci-News.com , access-date=25 October 2015 , archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151025012743/http://www.sci-news.com/biology/science-brazilian-stingless-bee-monascus-fungus-03372.html , archive-date=25 October 2015 , url-status=live {{cite journal , vauthors=Selosse MA, Richard F, He X, Simard SW , title=Mycorrhizal networks: des liaisons dangereuses? , journal=Trends in Ecology & Evolution , volume=21 , issue=11 , pages=621–8 , date=November 2006 , pmid=16843567 , doi=10.1016/j.tree.2006.07.003 {{cite journal , vauthors=Schulz B, Boyle C , s2cid=23182632 , title=The endophytic continuum , journal=Mycological Research , volume=109 , issue=Pt 6 , pages=661–86 , date=June 2005 , pmid=16080390 , doi=10.1017/S095375620500273X {{cite journal , vauthors=Shoji JY, Arioka M, Kitamoto K , title=Possible involvement of pleiomorphic vacuolar networks in nutrient recycling in filamentous fungi , journal=Autophagy , volume=2 , issue=3 , pages=226–7 , year=2006 , pmid=16874107 , doi=10.4161/auto.2695 , doi-access=free {{cite journal , vauthors=Shalchian-Tabrizi K, Minge MA, Espelund M, Orr R, Ruden T, Jakobsen KS, Cavalier-Smith T , title=Multigene phylogeny of choanozoa and the origin of animals , journal=PLOS ONE , volume=3 , issue=5 , pages=e2098 , year=2008 , pmid=18461162 , pmc=2346548 , doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0002098 , doi-access=free , bibcode=2008PLoSO...3.2098S {{Cite book , vauthors=Silar P , title=Protistes Eucaryotes: Origine, Evolution et Biologie des Microbes Eucaryotes , publisher=HAL , year=2016 , page=462 , isbn=978-2-9555841-0-1 , url=https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-01263138/document , access-date=7 April 2016 , archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170925132023/https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-01263138/document , archive-date=25 September 2017 , url-status=live {{cite book , vauthors=Simpson DP , title=Cassell's Latin Dictionary , publisher=Cassell Ltd , year=1979 , edition=5 , location=London, UK , page=883 , isbn=978-0-304-52257-6 {{cite journal , vauthors=Simon-Nobbe B, Denk U, Pöll V, Rid R, Breitenbach M , title=The spectrum of fungal allergy , journal=International Archives of Allergy and Immunology , volume=145 , issue=1 , pages=58–86 , year=2008 , pmid=17709917 , doi=10.1159/000107578 , doi-access=free {{cite journal , vauthors=Steenkamp ET, Wright J, Baldauf SL , title=The protistan origins of animals and fungi , journal=Molecular Biology and Evolution , volume=23 , issue=1 , pages=93–106 , date=January 2006 , pmid=16151185 , doi=10.1093/molbev/msj011 , doi-access=free {{cite book , vauthors=Stamets P , title=Growing Gourmet and Medicinal Mushrooms , trans-title=Shokuyō oyobi yakuyō kinoko no saibai , publisher=Ten Speed Press , location=Berkeley, California , year=2000 , pages=233–248 , isbn=978-1-58008-175-7 According to one 2001 estimate, some 10,000 fungal diseases are known. {{cite book , vauthors=Struck C , veditors=Cooke BM, Jones DG, Kaye B , title=The Epidemiology of Plant Diseases , publisher=Springer , location=Berlin, Germany , year=2006 , page=117 , isbn=978-1-4020-4580-6 , chapter=Infection strategies of plant parasitic fungi {{cite journal , vauthors=Sullivan R, Smith JE, Rowan NJ , s2cid=29723996 , title=Medicinal mushrooms and cancer therapy: translating a traditional practice into Western medicine , journal=Perspectives in Biology and Medicine , volume=49 , issue=2 , pages=159–70 , year=2006 , pmid=16702701 , doi=10.1353/pbm.2006.0034 {{cite journal , vauthors=Taylor TN, Taylor EL , year=1996 , title=The distribution and interactions of some Paleozoic fungi , journal=Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology , volume=95 , issue=1–4 , pages=83–94 , doi=10.1016/S0034-6667(96)00029-2 {{cite journal , vauthors=Taylor JW, Jacobson DJ, Kroken S, Kasuga T, Geiser DM, Hibbett DS, Fisher MC , s2cid=2551424 , title=Phylogenetic species recognition and species concepts in fungi , journal=Fungal Genetics and Biology , volume=31 , issue=1 , pages=21–32 , date=October 2000 , pmid=11118132 , doi=10.1006/fgbi.2000.1228 {{cite journal , vauthors=Taylor TN, Hass H, Kerp H, Krings M, Hanlin RT , title=Perithecial ascomycetes from the 400 million year old Rhynie chert: an example of ancestral polymorphism , journal=Mycologia , volume=97 , issue=1 , pages=269–85 , year=2005 , pmid=16389979 , doi=10.3852/mycologia.97.1.269 , url=http://www.cybertruffle.org.uk/cyberliber/59350/0097/001/0269.htm , hdl=1808/16786 , access-date=5 July 2011 , archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160412150211/http://www.cybertruffle.org.uk/cyberliber/59350/0097/001/0269.htm , archive-date=12 April 2016 , url-status=live , hdl-access=free {{cite journal , vauthors=Taylor JW, Berbee ML , title=Dating divergences in the Fungal Tree of Life: review and new analyses , journal=Mycologia , volume=98 , issue=6 , pages=838–49 , year=2006 , pmid=17486961 , doi=10.3852/mycologia.98.6.838 , url=http://www.cybertruffle.org.uk/cyberliber/59350/0098/006/0838.htm , access-date=5 July 2011 , archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160412150130/http://www.cybertruffle.org.uk/cyberliber/59350/0098/006/0838.htm , archive-date=12 April 2016 , url-status=live {{cite journal , last1=Thambugala , first1=Kasun M. , last2=Daranagama , first2=Dinushani A. , last3=Phillips , first3=Alan J. L. , last4=Kannangara , first4=Sagarika D. , last5=Promputtha , first5=Itthayakorn , title=Fungi vs. fungi in biocontrol: An overview of fungal antagonists applied against fungal plant pathogens , journal=Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology , volume=10 , year=2020 , page=604923 , doi=10.3389/fcimb.2020.604923 , pmid=33330142 , pmc=7734056 , doi-access=free {{cite journal , vauthors=Thomas MB, Read AF , s2cid=14460348 , title=Can fungal biopesticides control malaria? , journal=Nature Reviews. Microbiology , volume=5 , issue=5 , pages=377–83 , date=May 2007 , pmid=17426726 , doi=10.1038/nrmicro1638 , hdl=1842/2089 , hdl-access=free {{cite journal , vauthors=Tudzynski B , s2cid=11191347 , title=Gibberellin biosynthesis in fungi: genes, enzymes, evolution, and impact on biotechnology , journal=Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology , volume=66 , issue=6 , pages=597–611 , date=March 2005 , pmid=15578178 , doi=10.1007/s00253-004-1805-1 {{cite journal , last1=Tudzynski , first1=Bettina , year=2014 , title=Nitrogen regulation of fungal secondary metabolism in fungi , journal=Frontiers in Microbiology , volume=5 , page=656 , pmid=25506342 , pmc=4246892 , doi=10.3389/fmicb.2014.00656 , doi-access=free {{cite journal , vauthors=Trail F , title=Fungal cannons: explosive spore discharge in the Ascomycota , journal=FEMS Microbiology Letters , volume=276 , issue=1 , pages=12–8 , date=November 2007 , pmid=17784861 , doi=10.1111/j.1574-6968.2007.00900.x , doi-access=free {{cite book , author1=Ulloa, Miguel , author2=Halin, Richard T. , title=Illustrated Dictionary of Mycology , edition=2nd , year=2012 , publisher=The American Phytopathological Society , location=St. Paul, Minnesota , isbn=978-0-89054-400-6 , page=156 {{cite web , url=http://tolweb.org/Fungi/2377 , title=Fungi. Eumycota: mushrooms, sac fungi, yeast, molds, rusts, smuts, etc. , vauthors=Blackwell M, Vilgalys R, James TY, Taylor JW , publisher=Tree of Life Web Project , year=2009 , access-date=25 April 2009 , archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090413045121/http://tolweb.org/Fungi/2377 , archive-date=13 April 2009 , url-status=live {{cite web , url=http://www.ars.usda.gov/is/AR/archive/jul98/fung0798.htm , vauthors=Becker H , title=Setting the Stage To Screen Biocontrol Fungi , publisher=United States Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service , year=1998 , access-date=23 February 2009 , archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090116041447/http://www.ars.usda.gov/is/AR/archive/jul98/fung0798.htm , archive-date=16 January 2009 , url-status=live {{cite magazine , last1=Vargas-Gastélum , first1=Lluvia , last2=Riquelme , first2=Meritxell , title=The mycobiota of the deep sea: What omics can offer , magazine=Life (magazine), Life , volume=10 , issue=11 , year=2020 , pages=292 , doi=10.3390/life10110292 , pmid=33228036 , pmc=7699357 , doi-access=free {{cite journal , vauthors=Yang Y, Yang E, An Z, Liu X , title=Evolution of nematode-trapping cells of predatory fungi of the Orbiliaceae based on evidence from rRNA-encoding DNA and multiprotein sequences , journal=Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America , volume=104 , issue=20 , pages=8379–84 , date=May 2007 , pmid=17494736 , pmc=1895958 , doi=10.1073/pnas.0702770104 , bibcode=2007PNAS..104.8379Y , doi-access=free {{cite journal , vauthors=Vetter J , title=Toxins of ''Amanita phalloides'' , journal=Toxicon , volume=36 , issue=1 , pages=13–24 , date=January 1998 , pmid=9604278 , doi=10.1016/S0041-0101(97)00074-3 {{cite journal , vauthors=Vaupotic T, Veranic P, Jenoe P, Plemenitas A , title=Mitochondrial mediation of environmental osmolytes discrimination during osmoadaptation in the extremely halotolerant black yeast Hortaea werneckii , journal=Fungal Genetics and Biology , volume=45 , issue=6 , pages=994–1007 , date=June 2008 , pmid=18343697 , doi=10.1016/j.fgb.2008.01.006 {{cite journal , last1=Walther , first1=Grit , last2=Wagner , first2=Lysett , last3=Kurzai , first3=Oliver , year=2019 , title=Updates on the taxonomy of Mucorales with an emphasis on clinically important taxa , journal=Journal of Fungi , volume=5 , issue=4 , page=106 , doi=10.3390/jof5040106 , pmc=6958464 , pmid=31739583, doi-access=free {{cite journal , vauthors=Wang ZY, Jenkinson JM, Holcombe LJ, Soanes DM, Veneault-Fourrey C, Bhambra GK, Talbot NJ , s2cid=7111935 , title=The molecular biology of appressorium turgor generation by the rice blast fungus ''Magnaporthe grisea'' , journal=Biochemical Society Transactions , volume=33 , issue=Pt 2 , pages=384–8 , date=April 2005 , pmid=15787612 , doi=10.1042/BST0330384 {{cite journal , last1=Wang , first1=Ke , last2=Cai , first2=Lei , last3=Yao , first3=Yijian , title=Overview of nomenclature novelties of fungi in the world and China (2020) , journal=Biodiversity Science , volume=29 , issue=8 , year=2021 , doi=10.17520/biods.2021202 , pages=1064–1072 , s2cid=240568551 {{cite journal , vauthors=Willensdorfer M , s2cid=39155292 , title=On the evolution of differentiated multicellularity , journal=Evolution; International Journal of Organic Evolution , volume=63 , issue=2 , pages=306–23 , date=February 2009 , pmid=19154376 , doi=10.1111/j.1558-5646.2008.00541.x , arxiv=0801.2610 {{cite journal , vauthors=Ward PD, Botha J, Buick R, De Kock MO, Erwin DH, Garrison GH, Kirschvink JL, Smith R , s2cid=46198018 , title=Abrupt and gradual extinction among Late Permian land vertebrates in the Karoo basin, South Africa , journal=Science (journal), Science , volume=307 , issue=5710 , pages=709–14 , date=February 2005 , pmid=15661973 , doi=10.1126/science.1107068 , bibcode=2005Sci...307..709W , citeseerx=10.1.1.503.2065 {{cite journal , vauthors=Xu H, Andi B, Qian J, West AH, Cook PF , s2cid=22370361 , title=The alpha-aminoadipate pathway for lysine biosynthesis in fungi , journal=Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics , volume=46 , issue=1 , pages=43–64 , year=2006 , pmid=16943623 , doi=10.1385/CBB:46:1:43 {{cite journal , vauthors=Wu S, Schalk M, Clark A, Miles RB, Coates R, Chappell J , s2cid=23358348 , title=Redirection of cytosolic or plastidic isoprenoid precursors elevates terpene production in plants , journal=Nature Biotechnology , volume=24 , issue=11 , pages=1441–7 , date=November 2006 , pmid=17057703 , doi=10.1038/nbt1251 {{cite journal , vauthors=Zabriskie TM, Jackson MD , title=Lysine biosynthesis and metabolism in fungi , journal=Natural Product Reports , volume=17 , issue=1 , pages=85–97 , date=February 2000 , pmid=10714900 , doi=10.1039/a801345d {{cite journal , last1=Zhuo , first1=Rui , last2=Fan , first2=Fangfang , title=A comprehensive insight into the application of white rot fungi and their lignocellulolytic enzymes in the removal of organic pollutants , journal=Science of the Total Environment , volume=778 , year=2021 , pages=146132 , doi=10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146132 , pmid=33714829 , bibcode=2021ScTEn.778n6132Z , s2cid=232230208 {{cite journal , vauthors=Li Y, Steenwyk JL, Chang Y, Wang Y, James TY, Stajich JE, Spatafora JW, Groenewald M, Dunn CW, Hittinger CT, Shen X, Rokas, A , date=2021 , title=A genome-scale phylogeny of the kingdom Fungi , journal=Current Biology , volume=31 , issue=8 , pages=1653–1665 , doi=10.1016/j.cub.2021.01.074 , pmid=33607033 , pmc=8347878
Cited literature
{{refbegin * {{cite book , vauthors=Ainsworth GC , title=Introduction to the History of Mycology , publisher=Cambridge University Press , location=Cambridge, UK , year=1976 , isbn=978-0-521-11295-6 * {{cite book , vauthors=Alexopoulos CJ, Mims CW, Blackwell M , title=Introductory Mycology , year=1996 , publisher=John Wiley & Sons , isbn=978-0-471-52229-4 * {{cite book , vauthors=Deacon J , title=Fungal Biology , publisher=Blackwell Publishers , location=Cambridge, Massachusetts , year=2005 , isbn=978-1-4051-3066-0 * {{cite book , vauthors=Hall IR , title=Edible and Poisonous Mushrooms of the World , publisher=Timber Press , location=Portland, Oregon , year=2003 , isbn=978-0-88192-586-9 * {{cite book , vauthors=Hanson JR , title=The Chemistry of Fungi , year=2008 , publisher=Royal Society of Chemistry , isbn=978-0-85404-136-7 * {{cite book , vauthors=Jennings DH, Lysek G , title=Fungal Biology: Understanding the Fungal Lifestyle , year=1996 , publisher=Bios Scientific Publishers Ltd , location=Guildford, UK , isbn=978-1-85996-150-6 * {{cite book , vauthors=Kirk PM, Cannon PF, Minter DW, Stalpers JA , title=Dictionary of the Fungi , edition=10th , publisher=CAB International , location=Wallingford, UK , year=2008 , isbn=978-0-85199-826-8 * {{cite book , vauthors=Taylor EL, Taylor TN , title=The Biology and Evolution of Fossil Plants , publisher=Prentice Hall , location=Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey , year=1993 , isbn=978-0-13-651589-0 {{refendExternal links
{{Sister project links, c=Fungi , commonscat=Fungi , wikt=fungus , 1= , author= , auto= , b=no , collapsible= , cookbook= , d= , display= , iw= , m= , mw= , n=no , position= , q=no , qid= , s=no , species=Fungi , species_author= , style= , v=no , voy=no {{Library resources box , onlinebooks=yes , by=no , lcheading= Fungi , label=FungusTree of Life web project: Fungi
Encyclopedia of Life: Fungus
* Mushroom Observer
mushroomobserver.org
, a collaborative fungus recording and identification project
i
{{Fungi classification {{Fungus structure {{Eukaryota {{Nature nav {{Life on Earth {{Organisms et al. {{Taxonbar, from=Q764 {{Authority control {{Featured article Fungi, Articles containing video clips Cryptogams Extant Early Devonian first appearances Kingdoms (biology), Fungi