|
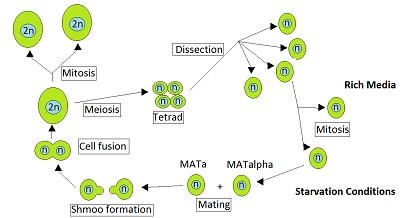
Heterothallic
Heterothallic species have sexes that reside in different individuals. The term is applied particularly to distinguish heterothallic fungi, which require two compatible partners to produce sexual spores, from homothallic ones, which are capable of sexual reproduction from a single organism. In heterothallic fungi, two different individuals contribute nuclei to form a zygote. Examples of heterothallism are included for ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Aspergillus fumigatus, Aspergillus flavus'', '' Penicillium marneffei'' and ''Neurospora crassa''. The heterothallic life cycle of ''N. crassa'' is given in some detail, since similar life cycles are present in other heterothallic fungi. Life cycle of ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' The yeast ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' is heterothallic. This means that each yeast cell is of a certain mating type and can only mate with a cell of the other mating type. During vegetative growth that ordinarily occurs when nutrients are abundant, ''S. cer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homothallic
Homothallic refers to the possession, within a single organism, of the resources to reproduce sexually; i.e., having male and female reproductive structures on the same thallus. The opposite sexual functions are performed by different cells of a single mycelium. It can be contrasted to heterothallic. It is often used to categorize fungi. In yeast, heterothallic cells have mating types a and α. An experienced mother cell (one that has divided at least once) will switch mating type every cell division cycle because of the ''HO'' allele. Sexual reproduction commonly occurs in two fundamentally different ways in fungi. These are outcrossing (in heterothallic fungi) in which two different individuals contribute nuclei to form a zygote, and self-fertilization or selfing (in homothallic fungi) in which both nuclei are derived from the same individual. Homothallism in fungi can be defined as the capability of an individual spore to produce a sexually reproducing colony when propagated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurospora Crassa Life Cycle
''Neurospora'' is a genus of Ascomycete fungi. The genus name, meaning "nerve spore" refers to the characteristic striations on the spores that resemble axons. The best known species in this genus is ''Neurospora crassa'', a common model organism in biology. '' Neurospora intermedia'' var. ''oncomensis'' is believed to be the only mold belonging to ''Neurospora'' which is used in food production (to make oncom). Characteristics ''Neurospora'' species are molds with broadly spreading colonies, with abundant production of ascomata. Ascomata are superficial or immersed, perithecial and ostiolate or cleistothecial and non-ostiolate, hairy or glabrous, dark coloured. Peridium membranaceous, asci cylindrical, clavate or subspherical, with a persistent or evanescent wall, usually with a thickened and non-amyloid annular structure at the apex, usually 8-spored. Ascospores broadly fusiform, ellipsoidal, or nearly spherical, unicellular, hyaline to yellowish brown or olive-brown, bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi
A fungus (plural, : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of Eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and Mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a Kingdom (biology), kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of motility, mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspergillus Flavus
''Aspergillus flavus'' is a saprotrophic and pathogenic fungus with a cosmopolitan distribution. It is best known for its colonization of cereal grains, legumes, and tree nuts. Postharvest rot typically develops during harvest, storage, and/or transit. Its specific name '' flavus'' derives from the Latin meaning yellow, a reference to the frequently observed colour of the spores. ''A. flavus'' infections can occur while hosts are still in the field (preharvest), but often show no symptoms (dormancy) until postharvest storage or transport. In addition to causing preharvest and postharvest infections, many strains produce significant quantities of toxic compounds known as mycotoxins, which, when consumed, are toxic to mammals. ''A. flavus'' is also an opportunistic human and animal pathogen, causing aspergillosis in immunocompromised individuals. Hosts ''Aspergillus flavus'' is found globally as a saprophyte in soils and causes disease on many important agriculture crops. Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascomycota
Ascomycota is a phylum of the kingdom Fungi that, together with the Basidiomycota, forms the subkingdom Dikarya. Its members are commonly known as the sac fungi or ascomycetes. It is the largest phylum of Fungi, with over 64,000 species. The defining feature of this fungal group is the " ascus" (), a microscopic sexual structure in which nonmotile spores, called ascospores, are formed. However, some species of the Ascomycota are asexual, meaning that they do not have a sexual cycle and thus do not form asci or ascospores. Familiar examples of sac fungi include morels, truffles, brewers' and bakers' yeast, dead man's fingers, and cup fungi. The fungal symbionts in the majority of lichens (loosely termed "ascolichens") such as '' Cladonia'' belong to the Ascomycota. Ascomycota is a monophyletic group (it contains all descendants of one common ancestor). Previously placed in the Deuteromycota along with asexual species from other fungal taxa, asexual (or anamorphic) ascom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascospores
An ascus (; ) is the sexual spore-bearing cell produced in ascomycete fungi. Each ascus usually contains eight ascospores (or octad), produced by meiosis followed, in most species, by a mitotic cell division. However, asci in some genera or species can occur in numbers of one (e.g. '' Monosporascus cannonballus''), two, four, or multiples of four. In a few cases, the ascospores can bud off conidia that may fill the asci (e.g. '' Tympanis'') with hundreds of conidia, or the ascospores may fragment, e.g. some ''Cordyceps'', also filling the asci with smaller cells. Ascospores are nonmotile, usually single celled, but not infrequently may be coenocytic (lacking a septum), and in some cases coenocytic in multiple planes. Mitotic divisions within the developing spores populate each resulting cell in septate ascospores with nuclei. The term ocular chamber, or oculus, refers to the epiplasm (the portion of cytoplasm not used in ascospore formation) that is surrounded by the "bourrel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carcinogenesis
Carcinogenesis, also called oncogenesis or tumorigenesis, is the formation of a cancer, whereby normal cells are transformed into cancer cells. The process is characterized by changes at the cellular, genetic, and epigenetic levels and abnormal cell division. Cell division is a physiological process that occurs in almost all tissues and under a variety of circumstances. Normally, the balance between proliferation and programmed cell death, in the form of apoptosis, is maintained to ensure the integrity of tissues and organs. According to the prevailing accepted theory of carcinogenesis, the somatic mutation theory, mutations in DNA and epimutations that lead to cancer disrupt these orderly processes by interfering with the programming regulating the processes, upsetting the normal balance between proliferation and cell death. This results in uncontrolled cell division and the evolution of those cells by natural selection in the body. Only certain mutations lead to canc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aflatoxin
Aflatoxins are various poisonous carcinogens and mutagens that are produced by certain molds, particularly '' Aspergillus'' species. The fungi grow in soil, decaying vegetation and various staple foodstuffs and commodities such as hay, sweetcorn, wheat, millet, sorghum, cassava, rice, chili peppers, cottonseed, peanuts, tree nuts, sesame seeds, sunflower seeds, and various spices. In short, the relevant fungi grow on almost any crop or food. When such contaminated food is processed or consumed, the aflatoxins enter the general food supply. They have been found in both pet and human foods, as well as in feedstocks for agricultural animals. Animals fed contaminated food can pass aflatoxin transformation products into eggs, milk products, and meat. For example, contaminated poultry feed is the suspected source of aflatoxin-contaminated chicken meat and eggs in Pakistan. Children are particularly affected by aflatoxin exposure, which is associated with stunted growth, delaye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathogen
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ. The term ''pathogen'' came into use in the 1880s. Typically, the term ''pathogen'' is used to describe an ''infectious'' microorganism or agent, such as a virus, bacterium, protozoan, prion, viroid, or fungus. Small animals, such as helminths and insects, can also cause or transmit disease. However, these animals are usually referred to as parasites rather than pathogens. The scientific study of microscopic organisms, including microscopic pathogenic organisms, is called microbiology, while parasitology refers to the scientific study of parasites and the organisms that host them. There are several pathways through which pathogens can invade a host. The principal pathways have different episodic time frames, but soil has the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Variability
Genetic variability is either the presence of, or the generation of, genetic differences. It is defined as "the formation of individuals differing in genotype, or the presence of genotypically different individuals, in contrast to environmentally induced differences which, as a rule, cause only temporary, nonheritable changes of the phenotype". Genetic variability in a population is important for biodiversity. Causes There are many sources of genetic variability in a population: *Homologous recombination is a significant source of variability. During meiosis in sexual organisms, two homologous chromosomes cross over one another and exchange genetic material. The chromosomes then split apart and are ready to contribute to forming an offspring. Recombination is random and is governed by its own set of genes. Being controlled by genes means that recombination is variable in frequency. *Immigration, emigration, and translocation – each of these is the movement of an individua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can reproduction, produce Fertility, fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology (biology), morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a binomial nomenclature, two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascocarp
An ascocarp, or ascoma (), is the fruiting body ( sporocarp) of an ascomycete phylum fungus. It consists of very tightly interwoven hyphae and millions of embedded asci, each of which typically contains four to eight ascospores. Ascocarps are most commonly bowl-shaped (apothecia) but may take on a spherical or flask-like form that has a pore opening to release spores (perithecia) or no opening (cleistothecia). Classification The ascocarp is classified according to its placement (in ways not fundamental to the basic taxonomy). It is called ''epigeous'' if it grows above ground, as with the morels, while underground ascocarps, such as truffles, are termed ''hypogeous''. The structure enclosing the hymenium is divided into the types described below (apothecium, cleistothecium, etc.) and this character ''is'' important for the taxonomic classification of the fungus. Apothecia can be relatively large and fleshy, whereas the others are microscopic—about the size of flecks of g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |