|
Epichloë Coenophiala
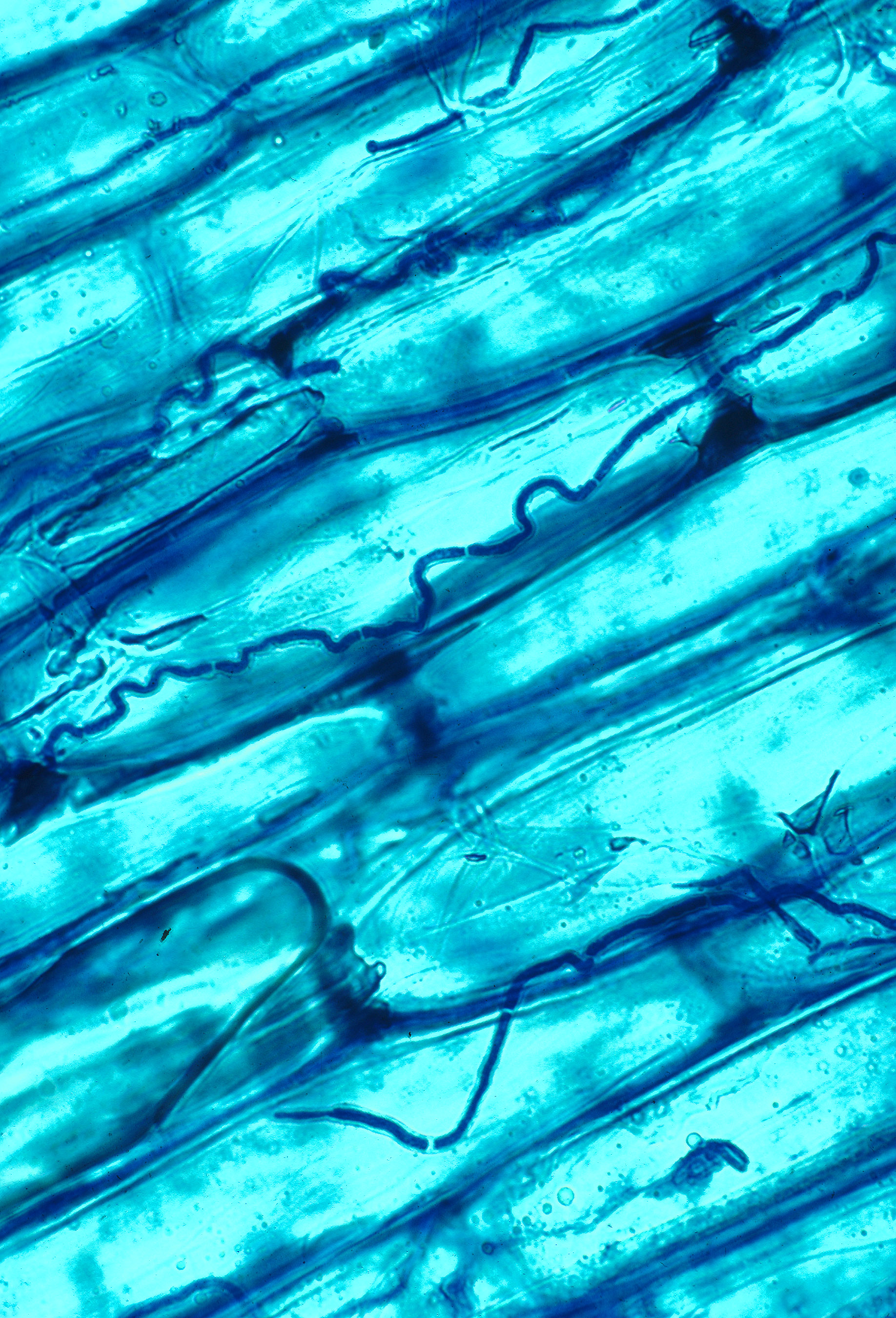
''Epichloë coenophiala'' is a systemic and seed-transmissible endophyte of tall fescue, a grass endemic to Eurasia and North Africa, but widely naturalized in North America, Australia and New Zealand. The endophyte has been identified as the cause of the "fescue toxicosis" syndrome sometimes suffered by livestock that graze the infected grass. Possible symptoms include poor weight gain, elevated body temperature, reduced conception rates, agalactia, rough hair coat, fat necrosis, loss of switch and ear tips, and lameness or dry gangrene of the feet. Because of the resemblance to symptoms of ergotism in humans, the most likely agents responsible for fescue toxicosis are thought to be the ergot alkaloids, principally ergovaline produced by ''E. coenophiala''. Continued popularity of tall fescue with this endophyte, despite episodic livestock toxicosis, is attributable to the exceptional productivity and stress tolerance of the grass in pastures and hay fields. The endophyte produce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endophyte
An endophyte is an endosymbiont, often a bacterium or fungus, that lives within a plant for at least part of its life cycle without causing apparent disease. Endophytes are ubiquitous and have been found in all species of plants studied to date; however, most of the endophyte/plant relationships are not well understood. Some endophytes may enhance host growth, nutrient acquisition and improve the plant's ability to tolerate abiotic stresses, such as drought and decrease biotic stresses by enhancing plant resistance to insects, pathogens and herbivores. Although endophytic bacteria and fungi are frequently studied, endophytic archaea are increasingly being considered for their role in plant growth promotion as part of the core microbiome of a plant. History Endophytes were first described by the German botanist Johann Heinrich Friedrich Link in 1809. They were thought to be plant parasitic fungi and they were later termed as "microzymas" by the French scientist Béchamp. There wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neotyphodium
''Neotyphodium'' is a genus of endophytic fungi symbiotic with grasses. It used to contain a number of asexually reproducing species that colonize the leaves of cool-season grasses, but most of them, including the type species '' N. coenophialum'', were merged into the genus ''Epichloë'' in 2014. Two species of unclear position were excluded from this treatment: *'' Neotyphodium chilense'' from Chile Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a ... should be treated as ''Acremonium chilense'' since the previous transfer to ''Neotyphodium'' is untested. *''Neotyphodium starrii'' is closely related to ''N. coenophialum'', but the taxonomic status within ''Epichloë'' (whether it is a distinct species or not) is unclear ('' nomen dubium''). References Hypocreales genera C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epichloë Baconii
''Epichloë baconii'' is a haploid sexual species in the fungal genus ''Epichloë''. A systemic grass symbiont first described in 1993, ''Epichloë baconii'' is a sister lineage to '' Epichloë stromatolonga''. ''Epichloë baconii'' is found in Europe, where it has been identified in many species of grasses, including ''Agrostis capillaris'', ''Agrostis stolonifera'', '' Calamagrostis villosa'', '' Calamagrostis varia'' and ''Calamagrostis ''Calamagrostis'' (reed grass or smallweed) is a genus of flowering plants in the grass family Poaceae, with about 260 species that occur mainly in temperate regions of the globe. Towards equatorial latitudes, species of ''Calamagrostis'' general ...'' ''purpurea''. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Epichloe baconii baconii Fungi described in 1993 Fungi of Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lolium
''Lolium'' is a genus of tufted grasses in the bluegrass subfamily (Pooideae). It is often called ryegrass, but this term is sometimes used to refer to grasses in other genera. They are characterized by bunch-like growth habits. ''Lolium'' is native to Europe, Asia and northern Africa, as well as being cultivated and naturalized in Australia, the Americas, and various oceanic islands. Ryegrasses are naturally diploid, with 2n=14, and are closely related to the fescues (''Festuca''). Ryegrass should not be confused with rye, which is a grain crop. Species Species of ''Lolium'' include: * ''Lolium arundinaceum'' (Schreb.) Darbysh. - Eurasia + North Africa from Portugal + Canary Islands to Himalayas + Xinjiang; naturalized in East Asia, Australia, North + South America, various islands * ''Lolium canariense'' Steud. - Canary Islands ryegrass - Canary Islands, Cape Verde * ''Lolium giganteum '' Lam. - Eurasia from Ireland to China; Bioko * ''Lolium hybridum'' Hausskn. - Assam, B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poa Nemoralis
''Poa nemoralis'', the wood bluegrass, is a perennial plant in the family Poaceae. The late-growing grass is fairly nutritious for livestock, which feed on it in the autumn, and it is used as a lawn grass for shady situations. Description It forms loose tufts, and is of a more delicate, slender appearance than other meadow grasses. It is slightly creeping. The leaves are narrow, tapering to a point. The ligules are short (0.5 mm). The stem is slender, high. The panicle is slender, loose and branched. The spikelets are few and egg shaped. They have one to five flowers. This grass is in flower from June to August in the Northern Hemisphere. It can produce asexual seeds by means of apomixis and can also reproduce vegetatively. Because of the characteristic leaf#Divisions of the lamina (blade), lamina, similar to a stretched out arm, it is sometimes called "Wegweisergras" (signpost grass) in Germany. Distribution and habitat Wood bluegrass is native to Europe, where its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epichloë Typhina
''Epichloë typhina'' is a haploid sexual species in the fungal genus ''Epichloë''. It was Species description, originally described as a ''Sphaeria'' species. Today, however, it is classified in ''Epichloë''. A systemic grass symbiont first species description, described as ''Sphaeria typhina'' by Christian Hendrik Persoon in 1798, and transferred to genus ''Epichloë'' in 1865, ''Epichloë typhina'' forms an only partially resolved species complex within the ''Epichloë'' genus. ''Epichloë typhina'' is found in Europe, but has been introduced widely in North America and elsewhere. It lives in association with a large number of grass species from multiple genera, including ''Anthoxanthum odoratum'', ''Brachypodium'' ''phoenicoides'', ''Brachypodium pinnatum'', ''Dactylis glomerata'', ''Lolium perenne'', ''Milium effusum'', Timothy-grass, ''Phleum pratense'', ''Poa trivialis'', ''Poa'' ''silvicola'' and ''Puccinellia distans''. ''Epichloë typhina'' appears to be seed-tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epichloë Festucae
''Epichloë festucae'' is a systemic and seed-transmissible endophytic fungus of cool season grasses. First described in 1994, ''Epichloë festucae'' is a sister lineage to '' Epichloë amarillans'', ''Epichloë baconii'', '' Epichloë mollis'' and ''Epichloë stromatolonga''. ''Epichloë festucae'' is found across North America, where it lives in the grass species ''Bromus kalmii'' and ''Elymus'' spp. (including ''Elymus patula''). Genome The complete genome sequence of ''Epichloë festucae'', the first complete genome sequence of any species in the genus ''Epichloë'', was reported in 2018. The 35 Mb genome comprises 7 chromosomes, ranging from 3.2 to 7.8 Mb, including approximately 9,000 genes. Centromeres , although some centromere sequence data is available, full annotation of all open reading frames is not. As a result a full taxonomic analysis is still not possible. Varieties ''Epichloë festucae'' strains can have both a sexual reproductive morph (teleomorph) and an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups of organisms. These relationships are determined by Computational phylogenetics, phylogenetic inference methods that focus on observed heritable traits, such as DNA sequences, protein amino acid sequences, or morphology. The result of such an analysis is a phylogenetic tree—a diagram containing a hypothesis of relationships that reflects the evolutionary history of a group of organisms. The tips of a phylogenetic tree can be living taxa or fossils, and represent the "end" or the present time in an evolutionary lineage. A phylogenetic diagram can be rooted or unrooted. A rooted tree diagram indicates the hypothetical common ancestor of the tree. An unrooted tree diagram (a network) makes no assumption about the ancestral line, and does ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epichloë
''Epichloë'' is a genus of ascomycete fungi forming an endophytic symbiosis with grasses. Grass choke disease is a symptom in grasses induced by some ''Epichloë'' species, which form spore-bearing mats ( stromata) on tillers and suppress the development of their host plant's inflorescence. For most of their life cycle however, ''Epichloë'' grow in the intercellular space of stems, leaves, inflorescences, and seeds of the grass plant without incurring symptoms of disease. In fact, they provide several benefits to their host, including the production of different herbivore-deterring alkaloids, increased stress resistance, and growth promotion. Within the family Clavicipitaceae, ''Epichloë'' is embedded in a group of endophytic and plant pathogenic fungi, whose common ancestor probably derived from an animal pathogen. The genus includes both species with a sexually reproducing (teleomorphic) stage and asexual, anamorphic species. The latter were previously placed in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Form Genus
Form classification is the classification of organisms based on their morphology, which does not necessarily reflect their biological relationships. Form classification, generally restricted to palaeontology, reflects uncertainty; the goal of science is to move "form taxa" to biological taxa whose affinity is known. Form taxonomy is restricted to fossils that preserve too few characters for a conclusive taxonomic definition or assessment of their biological affinity, but whose study is made easier if a binomial name is available by which to identify them. The term "form classification" is preferred to "form taxonomy"; taxonomy suggests that the classification implies a biological affinity, whereas form classification is about giving a name to a group of morphologically-similar organisms that may not be related. A "parataxon" (not to be confused with parataxonomy), or "sciotaxon" (Gr. "shadow taxon"), is a classification based on incomplete data: for instance, the larval stage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tall Fescue
''Festuca arundinacea'' (syn., ''Schedonorus arundinaceus'' and ''Lolium arundinaceum'') is a species of grass commonly known as tall fescue. It is a cool-season perennial C3 species of bunchgrass native to Europe. It is an important forage grass throughout Europe, and many cultivars have been used in agriculture. It is also an ornamental grass in gardens, and a phytoremediation plant. The predominant cultivar found in British pastures is S170, an endophyte-free variety. In its native European environment, tall fescue is found in damp grasslands, river banks, and in coastal seashore locations. Its distribution is a factor of climatic, edaphic, or other environmental attributes. In New Zealand, where it is introduced, the species is particularly prolific in salt marshes, where it is often a major part of the plant biota. History Festuca arundinacea was originally developed in Kew Gardens in the United Kingdom.Cougnon et al. (2013). Performance and quality of tall fescue (Festuc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anamorphic
Anamorphic format is the cinematography technique of shooting a widescreen picture on standard 35 mm film or other visual recording media with a non-widescreen native aspect ratio. It also refers to the projection format in which a distorted image is "stretched" by an anamorphic projection lens to recreate the original aspect ratio on the viewing screen (not to be confused with anamorphic widescreen, a different video encoding concept that uses similar principles but different means). The word ''anamorphic'' and its derivatives stem from the Greek ''anamorphoun'' ("to transform"), compound of ''morphé'' ("form, shape") with the prefix ''aná'' ("back, against"). In the late 1990s and 2000s, anamorphic lost popularity in comparison to "flat" (or "spherical") formats such as Super 35 with the advent of digital intermediates; however, in the years since digital cinema cameras and projectors have become commonplace, anamorphic has experienced a considerable resurgence of popularit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_(14929131291).jpg)