|
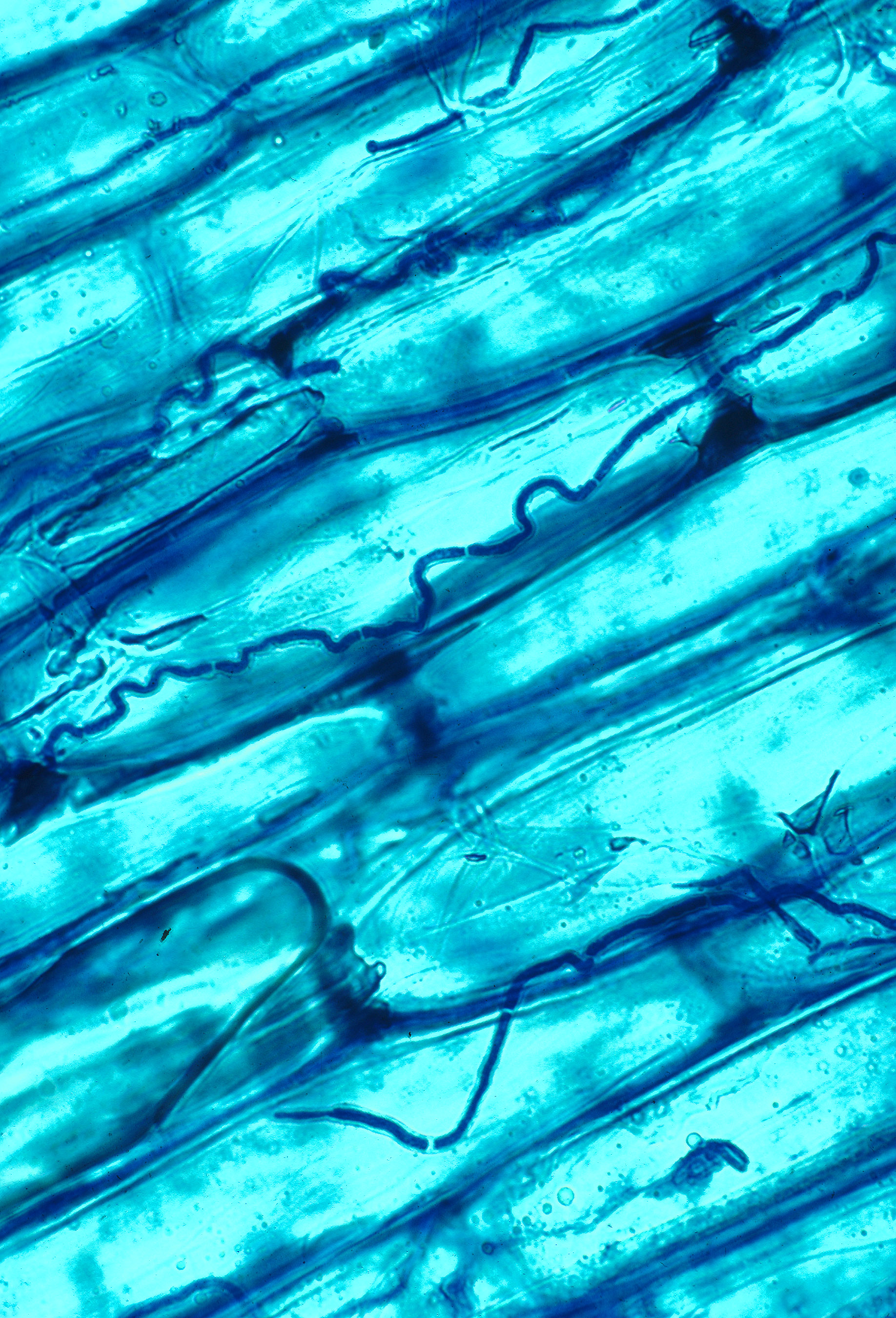
Epichloë
''Epichloë'' is a genus of ascomycete fungi forming an endophytic symbiosis with grasses. Grass choke disease is a symptom in grasses induced by some ''Epichloë'' species, which form spore-bearing mats (stromata) on tillers and suppress the development of their host plant's inflorescence. For most of their life cycle however, ''Epichloë'' grow in the intercellular space of stems, leaves, inflorescences, and seeds of the grass plant without incurring symptoms of disease. In fact, they provide several benefits to their host, including the production of different herbivore-deterring alkaloids, increased stress resistance, and growth promotion. Within the family Clavicipitaceae, ''Epichloë'' is embedded in a group of endophytic and plant pathogenic fungi, whose common ancestor probably derived from an animal pathogen. The genus includes both species with a sexually reproducing (teleomorphic) stage and asexual, anamorphic species. The latter were previously placed in the form genu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epichloë Typhina
''Epichloë typhina'' is a haploid sexual species in the fungal genus ''Epichloë''. It was Species description, originally described as a ''Sphaeria'' species. Today, however, it is classified in ''Epichloë''. A systemic grass symbiont first described as ''Sphaeria typhina'' by Christian Hendrik Persoon in 1798, and transferred to genus ''Epichloë'' in 1865, ''E. typhina'' forms an only partially resolved species complex within the ''Epichloë'' genus. ''Epichloë typhina'' is found in Europe, but has been introduced widely in North America and elsewhere. It lives in association with a large number of grass species from multiple genera, including ''Anthoxanthum odoratum'', ''Brachypodium'' ''phoenicoides'', ''Brachypodium pinnatum'', ''Dactylis glomerata'', ''Lolium perenne'', ''Milium effusum'', Timothy-grass, ''Phleum pratense'', ''Poa trivialis'', ''Poa silvicola'' and ''Puccinellia distans''. ''Epichloë typhina'' appears to be seed-transmissible only in ''Puccinellia d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungus
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one of the kingdom (biology)#Six kingdoms (1998), traditional eukaryotic kingdoms, along with Animalia, Plantae, and either Protista or Protozoa and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of motility, mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endophyte
An endophyte is an endosymbiont, often a bacterium or fungus, that lives within a plant for at least part of its life cycle without causing apparent disease. Endophytes are ubiquitous and have been found in all species of plants studied to date; however, most of the endophyte/plant relationships are not well understood. Some endophytes may enhance host growth and nutrient acquisition and improve the plant's ability to tolerate abiotic stresses, such as drought, and decrease biotic stresses by enhancing plant resistance to insects, pathogens and herbivores. Although endophytic bacteria and fungi are frequently studied, endophytic archaea are increasingly being considered for their role in plant growth promotion as part of the core microbiome of a plant. History Endophytes were first described by the German botanist Johann Heinrich Friedrich Link in 1809. They were thought to be plant parasitic fungi and they were later termed as "microzymas" by the French scientist Béchamp. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ryegrass
''Lolium'' is a genus of tufted grasses in the bluegrass subfamily (Pooideae). It is often called ryegrass, but this term is sometimes used to refer to grasses in other genera. They are characterized by bunch-like growth habits. ''Lolium'' is native to Europe, Asia and northern Africa, as well as being cultivated and naturalized in Australia, the Americas, and various oceanic islands. Ryegrasses are naturally diploid, with 2n=14, and are closely related to the fescues (''Festuca''). Ryegrass should not be confused with rye, which is a grain crop. Species the species of ''Lolium'' listed by Plants of the World Online include: ; Formerly included Several former ''Lolium'' species now regarded as part of other genera: '' Castellia'', '' Enteropogon'', '' × Festulolium'', '' Hainardia'', '' Lepturus'', '' Melica'', and '' Vulpia''. File:Perennial Ryegrass.jpg, Perennial ryegrass, used as winter lawn. File:Illustration Leymus arenarius and Lolium temulentum0.jpg, Pois ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poa Pratensis
''Poa pratensis'', commonly known as Kentucky bluegrass (or blue grass), smooth meadow-grass, or common meadow-grass, is a perennial species of grass native to practically all of Europe, North Asia and the mountains of Algeria, Morocco, and Tunisia. There is disagreement about its native status in North America, with some sources considering it native and others stating the Spanish Empire brought the seeds of Kentucky bluegrass to the New World in mixtures with other grasses. It is a common and incredibly popular lawn grass in North America with the species being spread over all of the cool, humid parts of the United States. In its native range, ''Poa pratensis'' forms a valuable pasture plant, characteristic of well-drained, fertile soil. It is also used for making lawns in parks and gardens and has established itself as a common invasive weed across cool moist temperate climates like the Pacific Northwest and the Northeastern United States. When found on native grasslands in C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tall Fescue
''Lolium arundinaceum'', commonly known as tall fescue, is a cool-season, perennial C3 grass species native to Europe and introduced to North America and other parts of the world. It naturally occurs in grasslands and coastal marshes.Texas Parks and Wildlife Department (n.d.). Tall Fescue (''Lolium arundinaceum''). Texas Invasive Plant Database/ref> Tall fescue is grown in a range of Cultivar, cultivars, widely used for livestock forage, in lawns and recreational areas as turf, and occasionally for managing soil erosion. Most publications have used the names ''Festuca arundinacea'' or, more recently, ''Schedonorus arundinaceus'' for this species, but DNA studies appear to have settled a long debate that it should be included within the genus ''Lolium'' instead. Description Tall fescue is a long-lived tuft-forming perennial with erect to spreading hollow flowering stems up to about tall (exceptionally up to 200 cm) which are hairless (glabrous), including the leaf sheath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food Web
A food web is the natural interconnection of food chains and a graphical representation of what-eats-what in an ecological community. Position in the food web, or trophic level, is used in ecology to broadly classify organisms as autotrophs or heterotrophs. This is a non-binary classification; some organisms (such as carnivorous plants) occupy the role of mixotrophs, or autotrophs that additionally obtain organic matter from non-atmospheric sources. The linkages in a food web illustrate the feeding pathways, such as where heterotrophs obtain organic matter by feeding on autotrophs and other heterotrophs. The food web is a simplified illustration of the various methods of feeding that link an ecosystem into a unified system of exchange. There are different kinds of consumer–resource interactions that can be roughly divided into herbivory, carnivory, scavenging, and parasitism. Some of the organic matter eaten by heterotrophs, such as sugars, provides energy. Autotrophs and hetero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Communities
A plant community is a collection or Association (ecology), association of plant species within a designated geographical unit, which forms a relatively uniform patch, distinguishable from neighboring patches of different vegetation types. The components of each plant community are influenced by soil type, topography, climate and human disturbance. In many cases there are several soil types present within a given plant community. This is because the soil type within an area is influenced by two factors, the rate at which water infiltrates or exits (via evapotranspiration) the soil, as well as the rate at which organic matter (any carbon-based compound within the environment, such as decaying plant matter) enters or decays from the soil. Plant communities are studied substantially by ecologists, due to providing information on the effects of dispersal, tolerance to environmental conditions, and response to disturbance of a variety of plant species, information valuable to the comprehe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hybrid Speciation
Hybrid speciation is a form of speciation where hybridization between two different species leads to a new species, reproductively isolated from the parent species. Previously, reproductive isolation between two species and their parents was thought to be particularly difficult to achieve, and thus hybrid species were thought to be very rare. With DNA analysis becoming more accessible in the 1990s, hybrid speciation has been shown to be a somewhat common phenomenon, particularly in plants. In botanical nomenclature, a hybrid species is also called a nothospecies. Hybrid species are by their nature polyphyletic. Ecology A hybrid may occasionally be better fitted to the local environment than the parental lineage, and as such, natural selection may favor these individuals. If reproductive isolation is subsequently achieved, a separate species may arise. Reproductive isolation may be genetic, ecological, behavioral, spatial, or a combination of these. If reproductive isolation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Pathogen
Plant diseases are diseases in plants caused by pathogens (infectious organisms) and environmental conditions (physiological factors). Organisms that cause infectious disease include fungi, oomycetes, bacteria, viruses, viroids, virus-like organisms, phytoplasmas, protozoa, nematodes and parasitic plants. Not included are ectoparasites like insects, mites, vertebrates, or other pests that affect plant health by eating plant tissues and causing injury that may admit plant pathogens. The study of plant disease is called plant pathology. Plant pathogens Fungi Most phytopathogenic fungi are Ascomycetes or Basidiomycetes. They reproduce both sexually and asexually via the production of spores and other structures. Spores may be spread long distances by air or water, or they may be soil borne. Many soil inhabiting fungi are capable of living saprotrophically, carrying out the role of their life cycle in the soil. These are facultative saprotrophs. Fungal diseases ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clade
In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach to taxonomy adopted by most biological fields. The common ancestor may be an individual, a population, or a species (extinct or Extant taxon, extant). Clades are nested, one in another, as each branch in turn splits into smaller branches. These splits reflect evolutionary history as populations diverged and evolved independently. Clades are termed ''monophyletic'' (Greek: "one clan") groups. Over the last few decades, the cladistic approach has revolutionized biological classification and revealed surprising evolutionary relationships among organisms. Increasingly, taxonomists try to avoid naming Taxon, taxa that are not clades; that is, taxa that are not Monophyly, monophyletic. Some of the relationships between organisms that the molecul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Phylogenetics
Molecular phylogenetics () is the branch of phylogeny that analyzes genetic, hereditary molecular differences, predominantly in DNA sequences, to gain information on an organism's evolutionary relationships. From these analyses, it is possible to determine the processes by which diversity among species has been achieved. The result of a molecular phylogenetics, phylogenetic analysis is expressed in a phylogenetic tree. Molecular phylogenetics is one aspect of molecular systematics, a broader term that also includes the use of molecular data in Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy and biogeography. Molecular phylogenetics and molecular evolution correlate. Molecular evolution is the process of selective changes (mutations) at a molecular level (genes, proteins, etc.) throughout various branches in the tree of life (evolution). Molecular phylogenetics makes inferences of the evolutionary relationships that arise due to molecular evolution and results in the construction of a phylogenetic tre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |