|
Peptide Sequence
Peptides are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Polypeptides that have a molecular mass of 10,000 Da or more are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides. Peptides fall under the broad chemical classes of biological polymers and oligomers, alongside nucleic acids, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, and others. Proteins consist of one or more polypeptides arranged in a biologically functional way, often bound to ligands such as coenzymes and cofactors, to another protein or other macromolecule such as DNA or RNA, or to complex macromolecular assemblies. Amino acids that have been incorporated into peptides are termed residues. A water molecule is released during formation of each amide bond.. All peptides except cyclic peptides have an N-terminal (amine group) and C-terminal (carboxyl group) resid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drosomycin
Drosomycin is an antifungal peptide from ''Drosophila melanogaster'' and was the first antifungal peptide isolated from insects. Drosomycin is induced by infection by the Toll signalling pathway, while expression in surface epithelia like the respiratory tract is instead controlled by the immune deficiency pathway (Imd). This means that drosomycin, alongside other antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) such as cecropins, diptericin, drosocin, metchnikowin and attacin, serves as a first line defence upon septic injury. However drosomycin is also expressed constitutively to a lesser extent in different tissues and throughout development. Structure Drosomycin is a 44-residue defensin-like peptide containing four disulfide bridges. These bridges stabilize a structure involving one α-helix and three β-sheets. Owing to these four disulfide bridges, drosomycin is resistant to degradation and the action of proteases. The cysteine stabilized αβ motif of drosomycin is also found in '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cofactor (biochemistry)
A cofactor is a non-protein chemical compound or metallic ion that is required for an enzyme's role as a catalyst (a catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction). Cofactors can be considered "helper molecules" that assist in biochemical transformations. The rates at which these happen are characterized in an area of study called enzyme kinetics. Cofactors typically differ from ligands in that they often derive their function by remaining bound. Cofactors can be classified into two types: inorganic ions and complex organic molecules called coenzymes. Coenzymes are mostly derived from vitamins and other organic essential nutrients in small amounts. (Some scientists limit the use of the term "cofactor" for inorganic substances; both types are included here.) Coenzymes are further divided into two types. The first is called a " prosthetic group", which consists of a coenzyme that is tightly (or even covalently and, therefore, permanently) bound to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hormone
A hormone (from the Ancient Greek, Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of cell signaling, signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are required for the normal development of animals, plants and fungi. Due to the broad definition of a hormone (as a signaling molecule that exerts its effects far from its site of production), numerous kinds of molecules can be classified as hormones. Among the substances that can be considered hormones, are eicosanoids (e.g. prostaglandins and thromboxanes), steroids (e.g. Estrogen, oestrogen and brassinosteroid), amino acid derivatives (e.g. epinephrine and auxin), protein or peptides (e.g. insulin and CLE peptides), and gases (e.g. ethylene and nitric oxide). Hormones are used to communicate between organ (anatomy), organs and Tissue (biology), tissues. In vertebrates, hormones are responsible for regulating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Protein degradation is a major regulatory mechanism of gene expression and contributes substantially to shaping mammalian proteomes. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes including apoptosis, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or misfolded proteins in cells. Consequently, abnormality in the regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases. Proteolysis can also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurotrophic
Neurotrophic factors (NTFs) are a family of biomolecules – nearly all of which are peptides or small proteins – that support the growth, survival, and differentiation of both developing and mature neurons. Most NTFs exert their trophic effects on neurons by signaling through tyrosine kinases, usually a receptor tyrosine kinase. In the mature nervous system, they promote neuronal survival, induce synaptic plasticity, and modulate the formation of long-term memories. Neurotrophic factors also promote the initial growth and development of neurons in the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system, and they are capable of regrowing damaged neurons in test tubes and animal models. Some neurotrophic factors are also released by the target tissue in order to guide the growth of developing axons. Most neurotrophic factors belong to one of three families: (1) neurotrophins, (2) glial cell-line derived neurotrophic factor family ligands (GFLs), and (3) neuropoieti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opioid Peptide
Opioid peptides or opiate peptides are peptides that bind to opioid receptors in the brain; opiates and opioids mimic the effect of these peptides. Such peptides may be produced by the body itself, for example endorphins. The effects of these peptides vary, but they all resemble those of opiates. Brain opioid peptide systems are known to play an important role in motivation, emotion, attachment theory, attachment behaviour, the response to Stress (biology), stress and pain, Hunger (motivational state), control of food intake, and the rewarding effects of alcohol (drug), alcohol and nicotine. Opioid-like peptides may also be absorbed from partially digestion, digested food (casomorphins, Gluten exorphin, exorphins, and rubiscolins). opioid food peptides, Opioid peptides from food typically have lengths between 4–8 amino acids. Endogenous opioids are generally much longer. Opioid peptides are released by post-translational proteolytic cleavage of Protein precursor, precursor pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peptide Hormones
Peptide hormones are hormones composed of peptide molecules. These hormones influence the endocrine system of animals, including humans. Most hormones are classified as either amino-acid-based hormones (amines, peptides, or proteins) or steroid hormones. Amino-acid-based hormones are water-soluble and act on target cells via second messenger systems, whereas steroid hormones, being lipid-soluble, diffuse through plasma membranes to interact directly with intracellular receptors in the cell nucleus. Like all peptides, peptide hormones are synthesized in cells from amino acids based on mRNA transcripts, which are derived from DNA templates inside the cell nucleus. The initial precursors, known as preprohormones, undergo processing in the endoplasmic reticulum. This includes the removal of the N-terminal signal peptide and, in some cases, glycosylation, yielding prohormones. These prohormones are then packaged into secretory vesicles, which are stored and released via exocytosis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
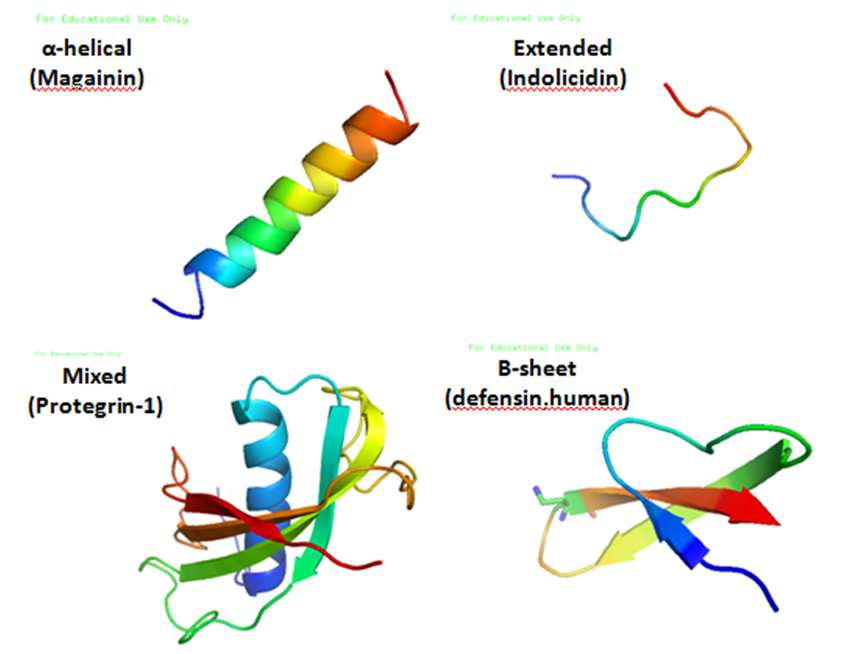
Antimicrobial Peptides
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), also called host defence peptides (HDPs) are part of the innate immune response found among all classes of life. Fundamental differences exist between Prokaryote, prokaryotic and eukaryota, eukaryotic cells that may represent targets for antimicrobial peptides. These peptides are potent, broad spectrum antimicrobials which demonstrate potential as novel therapeutic agents. Antimicrobial peptides have been demonstrated to kill Gram negative and Gram positive bacteria, enveloped viruses, fungi and even transformed or cancerous cells. Unlike the majority of conventional antibiotics it appears that antimicrobial peptides frequently destabilize biological membranes, can form transmembrane channels, and may also have the ability to enhance immunity by functioning as immunomodulators. Structure Antimicrobial peptides are a unique and diverse group of molecules, which are divided into subgroups on the basis of their amino acid composition and structure. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-terminus
The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, carboxy tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ... or polypeptide), terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH). When the protein is translated from messenger RNA, it is created from N-terminus to C-terminus. The convention for writing peptide sequences is to put the C-terminal end on the right and write the sequence from N- to C-terminus. Chemistry Each amino acid has a carboxyl group and an amine group. Amino acids link to one another to form a chain by a dehydration reaction which joins the amine group of one amino acid to the carboxyl group of the next. Thus polypeptide chains have an end with an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-terminus
The N-terminus (also known as the amino-terminus, NH2-terminus, N-terminal end or amine-terminus) is the start of a protein or polypeptide, referring to the free amine group (-NH2) located at the end of a polypeptide. Within a peptide, the amine group is bonded to the carboxylic group of another amino acid, making it a chain. That leaves a free carboxylic group at one end of the peptide, called the C-terminus, and a free amine group on the other end called the N-terminus. By convention, peptide sequences are written N-terminus to C-terminus, left to right (in LTR writing systems). This correlates the translation direction to the text direction, because when a protein is translated from messenger RNA, it is created from the N-terminus to the C-terminus, as amino acids are added to the carboxyl end of the protein. Chemistry Each amino acid has an amine group and a carboxylic group. Amino acids link to one another by peptide bonds which form through a dehydration reaction that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclic Peptide
Cyclic peptides are polypeptide chains which contain a circular sequence of bonds. This can be through a connection between the amino and carboxyl ends of the peptide, for example in cyclosporin; a connection between the amino end and a side chain, for example in bacitracin; the carboxyl end and a side chain, for example in colistin; or two side chains or more complicated arrangements, for example in alpha-amanitin. Many cyclic peptides have been discovered in nature and many others have been synthesized in the laboratory. Their length ranges from just two amino acid residues to hundreds. In nature they are frequently antimicrobial or toxic; in medicine they have various applications, for example as antibiotics and immunosuppressive agents. Thin-layer chromatography, Thin-Layer Chromatography (TLC) is a convenient method to detect cyclic peptides in crude extract from bio-mass. Classification Cyclic peptides can be classified according to the types of bonds that comprise the ring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amide
In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a chemical compound, compound with the general formula , where R, R', and R″ represent any group, typically organyl functional group, groups or hydrogen atoms. The amide group is called a peptide bond when it is part of the Polymer backbone, main chain of a protein, and an isopeptide bond when it occurs in a side chain, as in asparagine and glutamine. It can be viewed as a Derivative (chemistry), derivative of a carboxylic acid () with the hydroxyl group () replaced by an amino group (); or, equivalently, an acyl group, acyl (alkanoyl) group () joined to an amino group. Common amides are formamide (), acetamide (), benzamide (), and dimethylformamide (). Some uncommon examples of amides are ''N''-chloroacetamide () and chloroformamide (). Amides are qualified as primary (chemistry), primary, secondary (chemistry), secondary, and tertiary (chemistry), tertiary according to the number of acyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |