|
Nomenclature Codes
Nomenclature codes or codes of nomenclature are the various rulebooks that govern biological taxonomic nomenclature, each in their own broad field of organisms. To an end-user who only deals with names of species, with some awareness that species are assignable to families, it may not be noticeable that there is more than one code, but beyond this basic level these are rather different in the way they work. The successful introduction of two-part names for species by Linnaeus was the start for an ever-expanding system of nomenclature. With all naturalists worldwide adopting this approach to thinking up names, there arose several schools of thought about the details. It became ever more apparent that a detailed body of rules was necessary to govern scientific names. From the mid-19th century onwards, there were several initiatives to arrive at worldwide-accepted sets of rules. Presently nomenclature codes govern the naming of: * Algae, Fungi and Plants – ''International Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxonomy (biology)
In biology, taxonomy () is the scientific study of naming, defining ( circumscribing) and classifying groups of biological organisms based on shared characteristics. Organisms are grouped into taxa (singular: taxon) and these groups are given a taxonomic rank; groups of a given rank can be aggregated to form a more inclusive group of higher rank, thus creating a taxonomic hierarchy. The principal ranks in modern use are domain, kingdom, phylum (''division'' is sometimes used in botany in place of ''phylum''), class, order, family, genus, and species. The Swedish botanist Carl Linnaeus is regarded as the founder of the current system of taxonomy, as he developed a ranked system known as Linnaean taxonomy for categorizing organisms and binomial nomenclature for naming organisms. With advances in the theory, data and analytical technology of biological systematics, the Linnaean system has transformed into a system of modern biological classification intended to reflect the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Association
A plant community is a collection or association of plant species within a designated geographical unit, which forms a relatively uniform patch, distinguishable from neighboring patches of different vegetation types. The components of each plant community are influenced by soil type, topography, climate and human disturbance. In many cases there are several soil types present within a given plant community. This is because the soil type within an area is influenced by two factors, the rate at which water infiltrates or exits (via evapotranspiration) the soil, as well as the rate at which organic matter (any carbon-based compound within the environment, such as decaying plant matter) enters or decays from the soil. Plant communities are studied substantially by ecologists, due to providing information on the effects of dispersal, tolerance to environmental conditions, and response to disturbance of a variety of plant species, information valuable to the comprehension of various pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antoine Laurent De Jussieu
Antoine Laurent de Jussieu (; 12 April 1748 – 17 September 1836) was a French botanist, notable as the first to publish a natural classification of flowering plants; much of his system remains in use today. His classification was based on an extended unpublished work by his uncle, the botanist Bernard de Jussieu. Life Jussieu was born in Lyon, France, in 1748, as one of 10 children, to Christophle de Jussieu, an amateur botanist. His father's three younger brothers were also botanists. He went to Paris in 1765 to be with his uncle Bernard and to study medicine, graduating with a doctorate in 1770, with a thesis on animal and vegetable physiology. His uncle introduced him to the Jardin du Roi, where he was appointed as a botany Demonstrator and deputy to L. G. Le Monnier, professor of botany there in 1770. Le Monnier had succeeded Antoine-Laurent's uncle Antoine in 1759. Lectures by eminent botanists, including the Jusssieu dynasty were popular there, especially among p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pteridophyta
A pteridophyte is a vascular plant (with xylem and phloem) that disperses spores. Because pteridophytes produce neither flowers nor seeds, they are sometimes referred to as "cryptogams", meaning that their means of reproduction is hidden. Ferns, horsetails (often treated as ferns), and lycophytes (clubmosses, spikemosses, and quillworts) are all pteridophytes. However, they do not form a monophyletic group because ferns (and horsetails) are more closely related to seed plants than to lycophytes. "Pteridophyta" is thus no longer a widely accepted taxon, but the term ''pteridophyte'' remains in common parlance, as do ''pteridology'' and ''pteridologist'' as a science and its practitioner, respectively. Ferns and lycophytes share a life cycle and are often collectively treated or studied, for example by the International Association of Pteridologists and the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group. Description Pteridophytes (ferns and lycophytes) are free-sporing vascular plants that have a lif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spermatophyta
A spermatophyte (; ), also known as phanerogam (taxon Phanerogamae) or phaenogam (taxon Phaenogamae), is any plant that produces seeds, hence the alternative name seed plant. Spermatophytes are a subset of the embryophytes or land plants. They include most familiar types of plants, including all flowers and most trees, but exclude some other types of plants such as ferns, mosses, algae. The term ''phanerogams'' or ''phanerogamae'' is derived from the Greek (), meaning "visible", in contrast to the cryptogamae (), together with the suffix (), meaning "to marry". These terms distinguished those plants with hidden sexual organs (cryptogamae) from those with visible sexual organs (phanerogamae). Description The extant spermatophytes form five divisions, the first four of which are traditionally grouped as gymnosperms, plants that have unenclosed, "naked seeds": * Cycadophyta, the cycads, a subtropical and tropical group of plants, * Ginkgophyta, which includes a single living s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteriology
Bacteriology is the branch and specialty of biology that studies the morphology, ecology, genetics and biochemistry of bacteria as well as many other aspects related to them. This subdivision of microbiology involves the identification, classification, and characterization of bacterial species. Because of the similarity of thinking and working with microorganisms other than bacteria, such as protozoa, fungi, and viruses, there has been a tendency for the field of bacteriology to extend as microbiology. The terms were formerly often used interchangeably. However, bacteriology can be classified as a distinct science. Overview Definition Bacteriology is the study of bacteria and their relation to medicine. Bacteriology evolved from physicians needing to apply the germ theory to address the concerns relating to disease spreading in hospitals the 19th century. Identification and characterizing of bacteria being associated to diseases led to advances in pathogenic bacteriology. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10th Edition Of Systema Naturae
The 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae'' is a book written by Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus and published in two volumes in 1758 and 1759, which marks the starting point of zoological nomenclature. In it, Linnaeus introduced binomial nomenclature for animals, something he had already done for plants in his 1753 publication of ''Species Plantarum''. Starting point Before 1758, most biological catalogues had used polynomial names for the taxa included, including earlier editions of ''Systema Naturae''. The first work to consistently apply binomial nomenclature across the animal kingdom was the 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae''. The International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature therefore chose 1 January 1758 as the "starting point" for zoological nomenclature, and asserted that the 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae'' was to be treated as if published on that date. Names published before that date are unavailable, even if they would otherwise satisfy the rules. The onl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoology
Zoology ()The pronunciation of zoology as is usually regarded as nonstandard, though it is not uncommon. is the branch of biology that studies the animal kingdom, including the structure, embryology, evolution, classification, habits, and distribution of all animals, both living and extinct, and how they interact with their ecosystems. The term is derived from Ancient Greek , ('animal'), and , ('knowledge', 'study'). Although humans have always been interested in the natural history of the animals they saw around them, and made use of this knowledge to domesticate certain species, the formal study of zoology can be said to have originated with Aristotle. He viewed animals as living organisms, studied their structure and development, and considered their adaptations to their surroundings and the function of their parts. The Greek physician Galen studied human anatomy and was one of the greatest surgeons of the ancient world, but after the fall of the Western Roman Empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species Plantarum
' (Latin for "The Species of Plants") is a book by Carl Linnaeus, originally published in 1753, which lists every species of plant known at the time, classified into genera. It is the first work to consistently apply binomial names and was the starting point for the naming of plants. Publication ' was published on 1 May 1753 by Laurentius Salvius in Stockholm, in two volumes. A second edition was published in 1762–1763, and a third edition in 1764, although this "scarcely differed" from the second. Further editions were published after Linnaeus' death in 1778, under the direction of Karl Ludwig Willdenow, the director of the Berlin Botanical Garden; the fifth edition (1800) was published in four volumes. Importance ' was the first botanical work to consistently apply the binomial nomenclature system of naming to any large group of organisms (Linnaeus' tenth edition of ' would apply the same technique to animals for the first time in 1758). Prior to this work, a plant spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycology
Mycology is the branch of biology concerned with the study of fungi, including their genetic and biochemical properties, their taxonomy and their use to humans, including as a source for tinder, traditional medicine, food, and entheogens, as well as their dangers, such as toxicity or infection. A biologist specializing in mycology is called a mycologist. Mycology branches into the field of phytopathology, the study of plant diseases, and the two disciplines remain closely related because the vast majority of plant pathogens are fungi. Overview Historically, mycology was a branch of botany because, although fungi are evolutionarily more closely related to animals than to plants, this was not recognized until a few decades ago. Pioneer mycologists included Elias Magnus Fries, Christian Hendrik Persoon, Anton de Bary, Elizabeth Eaton Morse, and Lewis David von Schweinitz. Beatrix Potter, author of '' The Tale of Peter Rabbit'', also made significant contributions to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botany
Botany, also called plant science (or plant sciences), plant biology or phytology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist, plant scientist or phytologist is a scientist who specialises in this field. The term "botany" comes from the Ancient Greek word (') meaning " pasture", "herbs" " grass", or "fodder"; is in turn derived from (), "to feed" or "to graze". Traditionally, botany has also included the study of fungi and algae by mycologists and phycologists respectively, with the study of these three groups of organisms remaining within the sphere of interest of the International Botanical Congress. Nowadays, botanists (in the strict sense) study approximately 410,000 species of land plants of which some 391,000 species are vascular plants (including approximately 369,000 species of flowering plants), and approximately 20,000 are bryophytes. Botany originated in prehistory as herbalism with the efforts of early humans to identify – a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
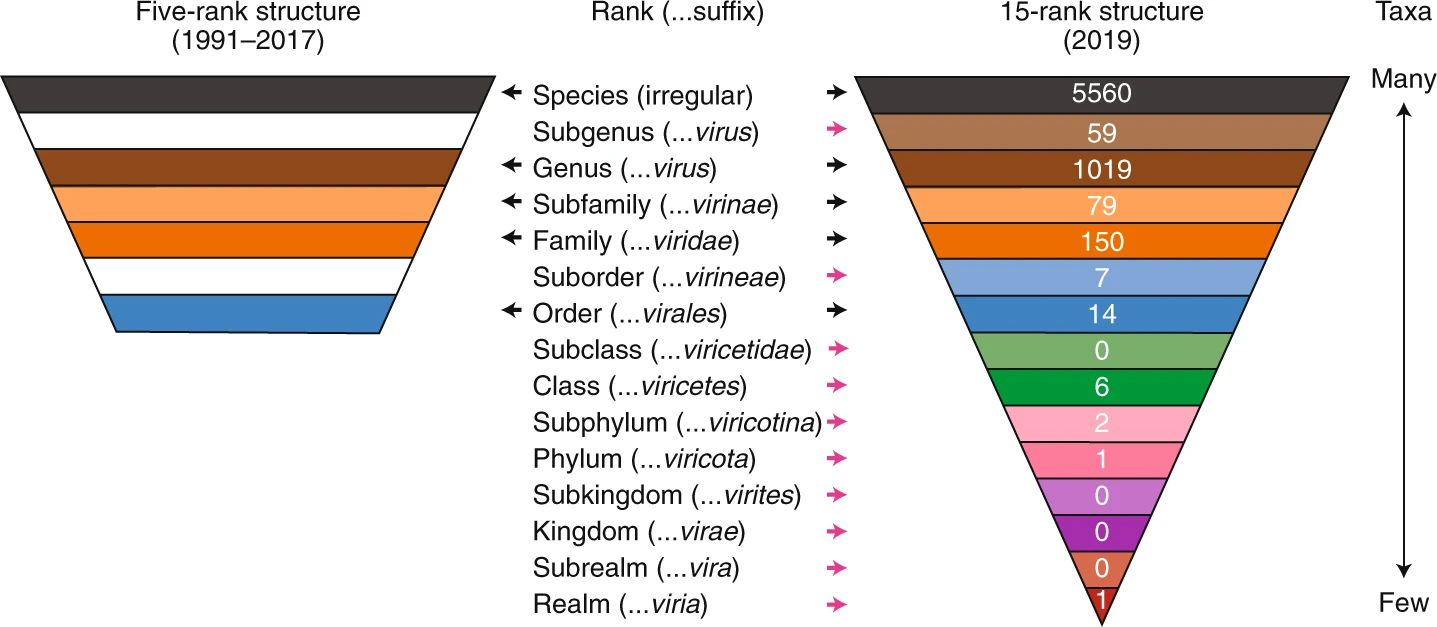
Virus Classification
Virus classification is the process of naming viruses and placing them into a taxonomic system similar to the classification systems used for cellular organisms. Viruses are classified by phenotypic characteristics, such as morphology, nucleic acid type, mode of replication, host organisms, and the type of disease they cause. The formal taxonomic classification of viruses is the responsibility of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) system, although the Baltimore classification system can be used to place viruses into one of seven groups based on their manner of mRNA synthesis. Specific naming conventions and further classification guidelines are set out by the ICTV. A catalogue of all the world's known viruses has been proposed and, in 2013, some preliminary efforts were underway. Definitions Species definition Species form the basis for any biological classification system. Before 1982, it was thought that viruses could not be made to fit Ernst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |