|
Ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous waste, particularly among aquatic organisms, and it contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to 45% of the world's food and fertilizers. Around 70% of ammonia is used to make fertilisers in various forms and composition, such as urea and Diammonium phosphate. Ammonia in pure form is also applied directly into the soil. Ammonia, either directly or indirectly, is also a building block for the synthesis of many pharmaceutical products and is used in many commercial cleaning products. It is mainly collected by downward displacement of both air and water. Although common in nature—both terrestrially and in the outer planets of the Solar System—and in wide use, ammonia i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonium Hydroxide
Ammonia solution, also known as ammonia water, ammonium hydroxide, ammoniacal liquor, ammonia liquor, aqua ammonia, aqueous ammonia, or (inaccurately) ammonia, is a solution of ammonia in water. It can be denoted by the symbols NH3(aq). Although the name ammonium hydroxide suggests an alkali with composition , it is actually impossible to isolate samples of NH4OH. The ions and OH− do not account for a significant fraction of the total amount of ammonia except in extremely dilute solutions. Basicity of ammonia in water In aqueous solution, ammonia deprotonates a small fraction of the water to give ammonium and hydroxide according to the following equilibrium: : NH3 + H2O NH4+ + OH−. In a 1 M ammonia solution, about 0.42% of the ammonia is converted to ammonium, equivalent to pH = 11.63 because H4+�= 0.0042 M, H−�= 0.0042 M, H3�= 0.9958 M, and pH = 14 + log10 H−�= 11.62. The base ionization constant is : ''K''b = H4+OH−] / H3= 1.77. Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fertilizer
A fertilizer (American English) or fertiliser (British English; see spelling differences) is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from liming materials or other non-nutrient soil amendments. Many sources of fertilizer exist, both natural and industrially produced. For most modern agricultural practices, fertilization focuses on three main macro nutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) with occasional addition of supplements like rock flour for micronutrients. Farmers apply these fertilizers in a variety of ways: through dry or pelletized or liquid application processes, using large agricultural equipment or hand-tool methods. Historically fertilization came from natural or organic sources: compost, animal manure, human manure, harvested minerals, crop rotations and byproducts of human-nature industries (i.e. fish processing waste, or bloodmeal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
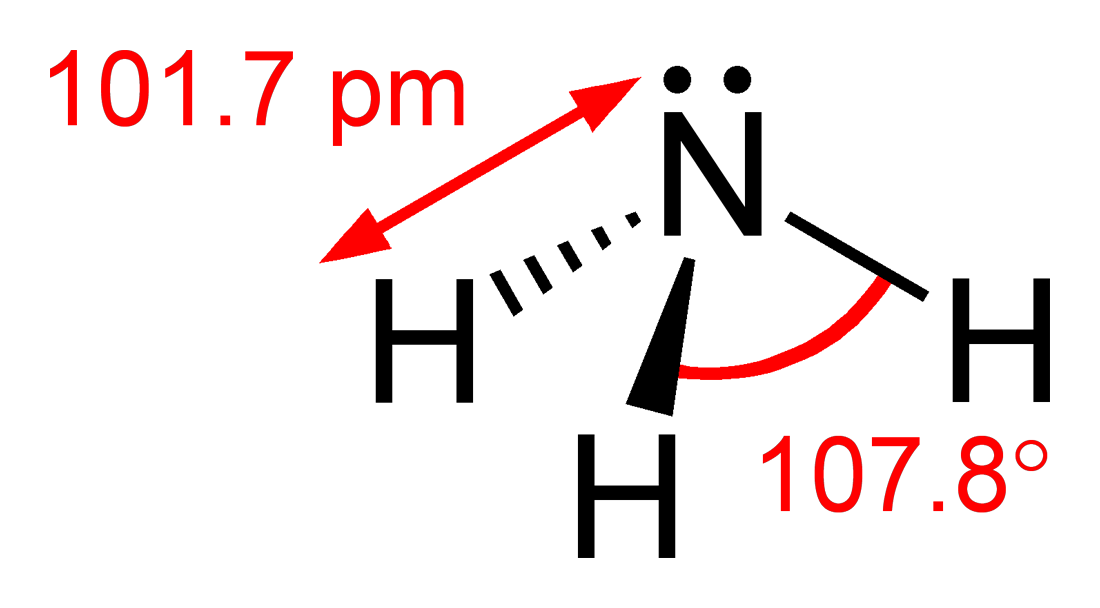
Pnictogen Hydride
Pnictogen hydrides or hydrogen pnictides are binary compounds of hydrogen with pnictogen ( or ; from grc, πνῑ́γω "to choke" and -gen, "generator") atoms (elements of group 15: nitrogen, phosphorus, arsenic, antimony, and bismuth) covalently bonded to hydrogen. Pnictogen trihydrides The simplest series has the chemical formula XH3 (less commonly H3X), with X representing any of the pnictogens. They take on the pyramidal structure (as opposed to the trigonal planar arrangement of the group 13 hydrides), and therefore are polar. These pnictogen trihydrides are generally increasingly unstable and poisonous with heavier elements. Like the simple hydrogen halides and chalcogenides, the pnictogen hydrides are water- soluble. Unlike other hydrides such as hydrogen sulfide and hydrogen fluoride, which form acidic aqueous solutions, ammonia dissolves in water to make ammonium hydroxide which is basic (by forming a hydroxide ion as opposed to hydronium). Phosphine is also water- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonia (data Page)
This page provides supplementary chemical data on ammonia. Structure and properties Thermodynamic properties Vapor–liquid equilibrium data Table data (above) obtained from ''CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics'' 44th ed. The (s) notation indicates equilibrium temperature of vapor over solid. Otherwise temperature is equilibrium of vapor over liquid. Vapor-pressure formula for ammonia:Lange's Handbook of Chemistry, 10th ed. page 1436. : log10''P'' = ''A'' – ''B'' / (''T'' − ''C''), where ''P'' is pressure in k Pa, and ''T'' is temperature in kelvins; : ''A'' = 6.67956, ''B'' = 1002.711, ''C'' = 25.215 for ''T'' = 190 K through 333 K. Heat capacity of liquid and vapor --> obtained from CHERIC. , - , , - Spectral data Regulatory data Safety data sheet The handling of this chemical may incur notable safety precautions... It is highly recommend that you seek the Safety Data Sheet ( safety data sheet, SDS) for this chemical from a reliable source an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, and highly combustible. Hydrogen is the most abundant chemical substance in the universe, constituting roughly 75% of all normal matter.However, most of the universe's mass is not in the form of baryons or chemical elements. See dark matter and dark energy. Stars such as the Sun are mainly composed of hydrogen in the plasma state. Most of the hydrogen on Earth exists in molecular forms such as water and organic compounds. For the most common isotope of hydrogen (symbol 1H) each atom has one proton, one electron, and no neutrons. In the early universe, the formation of protons, the nuclei of hydrogen, occurred during the first second after the Big Bang. The emergence of neutral hydrogen atoms throughout the universe occurre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonium
The ammonium cation is a positively-charged polyatomic ion with the chemical formula or . It is formed by the protonation of ammonia (). Ammonium is also a general name for positively charged or protonated substituted amines and quaternary ammonium cations (), where one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by organic groups (indicated by R). Acid–base properties The ammonium ion is generated when ammonia, a weak base, reacts with Brønsted acids (proton donors): :H+ + NH3 -> H4 The ammonium ion is mildly acidic, reacting with Brønsted bases to return to the uncharged ammonia molecule: : H4 + B- -> HB + NH3 Thus, treatment of concentrated solutions of ammonium salts with strong base gives ammonia. When ammonia is dissolved in water, a tiny amount of it converts to ammonium ions: :H2O + NH3 OH- + H4 The degree to which ammonia forms the ammonium ion depends on the pH of the solution. If the pH is low, the equilibrium shifts to the right: more ammonia molecules are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urea
Urea, also known as carbamide, is an organic compound with chemical formula . This amide has two amino groups (–) joined by a carbonyl functional group (–C(=O)–). It is thus the simplest amide of carbamic acid. Urea serves an important role in the metabolism of nitrogen-containing compounds by animals and is the main nitrogen-containing substance in the urine of mammals. It is a colorless, odorless solid, highly soluble in water, and practically non-toxic ( is 15 g/kg for rats). Dissolved in water, it is neither acidic nor alkaline. The body uses it in many processes, most notably nitrogen excretion. The liver forms it by combining two ammonia molecules () with a carbon dioxide () molecule in the urea cycle. Urea is widely used in fertilizers as a source of nitrogen (N) and is an important raw material for the chemical industry. In 1828 Friedrich Wöhler discovered that urea can be produced from inorganic starting materials, which was an important conceptual milesto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrazine
Hydrazine is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a simple pnictogen hydride, and is a colourless flammable liquid with an ammonia-like odour. Hydrazine is highly toxic unless handled in solution as, for example, hydrazine hydrate (). Hydrazine is mainly used as a foaming agent in preparing polymer foams, but applications also include its uses as a precursor to polymerization catalysts, pharmaceuticals, and agrochemicals, as well as a long-term storable propellant for in- space spacecraft propulsion. Additionally, hydrazine is used in various rocket fuels and to prepare the gas precursors used in air bags. Hydrazine is used within both nuclear and conventional electrical power plant steam cycles as an oxygen scavenger to control concentrations of dissolved oxygen in an effort to reduce corrosion. the world hydrazine hydrate market amounted to $350 million. About two million tons of hydrazine hydrate were used in foam blowing agents in 2015. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolic Waste
Metabolic wastes or excrements are substances left over from metabolic processes (such as cellular respiration) which cannot be used by the organism (they are surplus or toxic), and must therefore be excreted. This includes nitrogen compounds, water, CO2, phosphates, sulphates, etc. Animals treat these compounds as excretes. Plants have chemical "machinery" which transforms some of them (primarily the nitrogen compounds) into useful substances. All the metabolic wastes are excreted in a form of water solutes through the excretory organs (nephridia, Malpighian tubules, kidneys), with the exception of CO2, which is excreted together with the water vapor throughout the lungs. The elimination of these compounds enables the chemical homeostasis of the organism. Nitrogen wastes The nitrogen compounds through which excess nitrogen is eliminated from organisms are called nitrogenous wastes () or nitrogen wastes. They are ammonia, urea, uric acid, and creatinine. All of these su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at seventh in total abundance in the Milky Way and the Solar System. At standard temperature and pressure, two atoms of the element bond to form N2, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas. N2 forms about 78% of Earth's atmosphere, making it the most abundant uncombined element. Nitrogen occurs in all organisms, primarily in amino acids (and thus proteins), in the nucleic acids ( DNA and RNA) and in the energy transfer molecule adenosine triphosphate. The human body contains about 3% nitrogen by mass, the fourth most abundant element in the body after oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen. The nitrogen cycle describes the movement of the element from the air, into the biosphere and organic compounds, then back into the atmosphere. Many industrially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trigonal Pyramid (chemistry)
In chemistry, a trigonal pyramid is a molecular geometry with one atom at the apex and three atoms at the corners of a trigonal base, resembling a tetrahedron (not to be confused with the tetrahedral geometry). When all three atoms at the corners are identical, the molecule belongs to point group ''C3v''. Some molecules and ions with trigonal pyramidal geometry are the pnictogen hydrides (XH3), xenon trioxide (XeO3), the chlorate ion, , and the sulfite ion, . In organic chemistry, molecules which have a trigonal pyramidal geometry are sometimes described as sp3 hybridized. The AXE method for VSEPR theory states that the classification is AX3E1. Trigonal pyramidal geometry in ammonia The nitrogen in ammonia has 5 valence electrons and bonds with three hydrogen atoms to complete the octet. This would result in the geometry of a regular tetrahedron with each bond angle equal to cos−1(−) ≈ 109.5°. However, the three hydrogen atoms are repelled by the electro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azane
Azanes are acyclic, saturated hydronitrogens, which means that they consist only of hydrogen and nitrogen atoms and all bonds are single bonds. They are therefore pnictogen hydrides. Because cyclic hydronitrogens are excluded by definition, the azanes comprise a homologous series of inorganic compounds with the general chemical formula . Each nitrogen atom has three bonds (either N-H or N-N bonds), and each hydrogen atom is joined to a nitrogen atom (H-N bonds). A series of linked nitrogen atoms is known as the nitrogen skeleton or nitrogen backbone. The number of nitrogen atoms is used to define the size of the azane (e.g. N2-azane). The simplest possible azane (the parent molecule) is ammonia, . There is no limit to the number of nitrogen atoms that can be linked together, the only limitation being that the molecule is acyclic, is saturated, and is a hydronitrogen. Azanes are reactive and have significant biological activity. Azanes can be viewed as a more biologically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
-3D-balls.png)