|
Koryaks
Koryaks () are an indigenous people of the Russian Far East, who live immediately north of the Kamchatka Peninsula in Kamchatka Krai and inhabit the coastlands of the Bering Sea. The cultural borders of the Koryaks include Tigilsk in the south and the Anadyr basin in the north. The Koryaks are culturally similar to the Chukchis of extreme northeast Siberia. The Koryak language and Alutor (which is often regarded as a dialect of Koryak), are linguistically close to the Chukchi language. All of these languages are members of the Chukotko-Kamchatkan language family. They are more distantly related to the Itelmens on the Kamchatka Peninsula. All of these peoples and other, unrelated minorities in and around Kamchatka are known collectively as Kamchadals. Neighbors of the Koryaks include the Evens to the west, the Alutor to the south (on the isthmus of Kamchatka Peninsula), the Kerek to the east, and the Chukchi to the northeast. The Koryak are typically split into t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamchatka Peninsula
The Kamchatka Peninsula (russian: полуостров Камчатка, Poluostrov Kamchatka, ) is a peninsula in the Russian Far East, with an area of about . The Pacific Ocean and the Sea of Okhotsk make up the peninsula's eastern and western coastlines, respectively. Immediately offshore along the Pacific coast of the peninsula runs the Kuril–Kamchatka Trench. The Kamchatka Peninsula, the Commander Islands, and the Karaginsky Island, constitute the Kamchatka Krai of the Russian Federation. The vast majority of the 322,079 inhabitants are ethnic Russians, although about 13,000 are Koryaks (2014). More than half of the population lives in Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky (179,526 in 2010) and nearby Yelizovo (38,980). The Kamchatka peninsula contains the volcanoes of Kamchatka, a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Geography Politically, the peninsula forms part of Kamchatka Krai. The southern tip is called Cape Lopatka. (Lopatka is Russian for spade.) The circular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Itelmens
The Itelmens ( Itelmen: Итәнмән, russian: Ительмены) are an indigenous ethnic group of the Kamchatka Peninsula in Russia. The Itelmen language is distantly related to Chukchi and Koryak, forming the Chukotko-Kamchatkan language family, but it is now virtually extinct, the vast majority of ethnic Itelmens being native speakers of Russian. A. P. Volodin has published a grammar of the Itelmen language. Native peoples of Kamchatka (Itelmen, Ainu, Koryaks, and Chuvans), collectively referred to as Kamchadals, had a substantial hunter-gatherer and fishing society with up to fifty thousand natives inhabiting the peninsula before they were decimated by the Cossack conquest in the 18th century. So much intermarriage took place between the natives and the Cossacks that ''Kamchadal'' now refers to the majority mixed population, while the term ''Itelmens'' became reserved for persistent speakers of the Itelmen language. By 1993, there were less than 100 elderly spea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
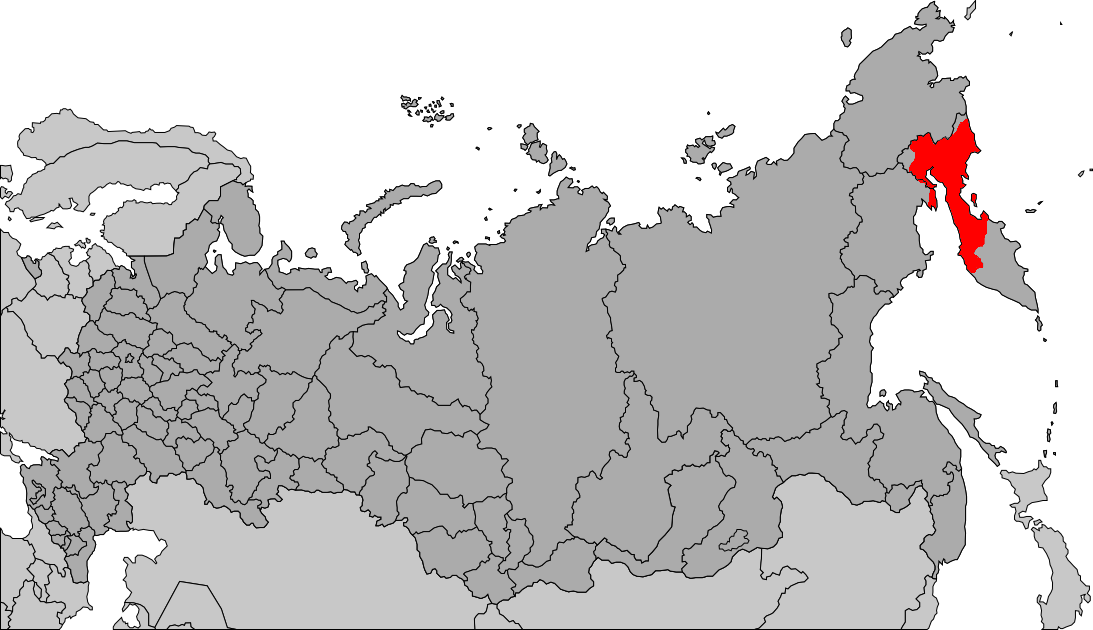
Kamchatka Krai
Kamchatka Krai ( rus, Камча́тский край, r=Kamchatsky kray, p=kɐmˈtɕatskʲɪj kraj) is a federal subject of Russia (a krai), situated in the Russian Far East, and is administratively part of the Far Eastern Federal District. Its capital and largest city is Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, home to over half of its population of 322,079 (2010). Kamchatka Krai was formed on July 1, 2007, as a result of the merger of Kamchatka Oblast and Koryak Autonomous Okrug, based on the voting in a referendum on the issue on October 23, 2005. The okrug retains the status of a special administrative division of the krai, under the name of Koryak Okrug. The Kamchatka Peninsula forms the majority of the krai's territory, separating the Sea of Okhotsk and the Bering Sea in the Pacific Ocean. The remainder is formed by a minor northern mainland portion, Karaginsky Island, and the Commander Islands in the Bering Sea. It is bordered by Magadan Oblast to the west ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chukchi Language
Chukchi , also known as Chukot, is a Chukotko–Kamchatkan language spoken by the Chukchi people in the easternmost extremity of Siberia, mainly in Chukotka Autonomous Okrug. The language is closely related to Koryak. Chukchi, Koryak, Kerek, Alutor, and Itelmen form the Chukotko-Kamchatkan language family. There are many cultural similarities between the Chukchis and Koryaks, including economies based on reindeer herding. Both peoples refer to themselves by the endonym ''Luorawetlat'' (ԓыгъоравэтԓьат ; singular ''Luorawetlan'' ԓыгъоравэтԓьан ), meaning "the real people". All of these peoples and other unrelated minorities in and around Kamchatka are known collectively as Kamchadals. ''Chukchi'' and ''Chukchee'' are anglicized versions of the Russian exonym ''Chukcha'' (plural ''Chukchi''). This came into Russian from ''Čävča'', the term used by the Chukchis' Tungusic-speaking neighbors, itself a rendering of the Chukchi word чавчыв , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koryak Language
Koryak () is a Chukotko-Kamchatkan language spoken by about 1,700 people as of 2010 in the easternmost extremity of Siberia, mainly in Koryak Okrug. It is mostly spoken by Koryaks. Its close relative, the Chukchi language, is spoken by about three times that number. The language together with Chukchi, Kerek, Alutor and Itelmen forms the Chukotko-Kamchatkan language family. Its native name in Koryak is нымылан ''nymylan'', but variants of the Russian "Koryak" name are most commonly used in English and other languages. The Chukchi and Koryaks form a cultural unit with an economy based on reindeer herding and both have autonomy within the Russian Federation. Phonology may be an allophone In phonology, an allophone (; from the Greek , , 'other' and , , 'voice, sound') is a set of multiple possible spoken soundsor ''phones''or signs used to pronounce a single phoneme in a particular language. For example, in English, (as in '' ... of .Zhukova, 1972 Koryak a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Far East
The Russian Far East (russian: Дальний Восток России, r=Dal'niy Vostok Rossii, p=ˈdalʲnʲɪj vɐˈstok rɐˈsʲiɪ) is a region in Northeast Asia. It is the easternmost part of Russia and the Asian continent; and is administered as part of the Far Eastern Federal District, which is located between Lake Baikal in eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean. The area's largest city is Khabarovsk, followed by Vladivostok. The region shares land borders with the countries of Mongolia, China, and North Korea to its south, as well as maritime boundaries with Japan to its southeast, and with the United States along the Bering Strait to its northeast. The Russian Far East is often considered as a part of Siberia (previously during the Soviet era when it was called the Soviet Far East). Terminology In Russia, the region is usually referred to as just "Far East" (). What is known in English as the Far East is usually referred to as "the Asia-Pacific Region" (, abb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alutor
The Alyutors (russian: Алюторцы; self designation: Алутальу, or Alutal'u) are an ethnic group (formerly classified as a subgroup of Koryaks) who lived on the Kamchatka Peninsula and Chukchi Peninsula of the Russian Far East. Today most of them live in Koryak Okrug of Kamchatka Krai. The name also occurs as Olyutors or Olutors, as well as Olyutorka, a settlement where many of the Alyutor people formerly lived. There is no precise data on the number of Alyutor people, but it is estimated that there are approximately 2,000 to 3,000 of them living in Russia in the present day. Language Alyutors spoke the Alyutor language (also known as Nymylan language), which belongs to the Chukotko-Kamchatkan language family; however less than 10% of the Alyutors still speak it.Kibrik, Alexandr E.; Kodzasov, Sandro V. and Muravyova, Irina A. (2000) ''Yazyk i folklor alutortsev'' Nasledie, Moscow; English edition: Kibrik, Alexandr E.; Kodzasov, Sandro V. and Muravyova, Irina A. (2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reindeer
Reindeer (in North American English, known as caribou if wild and ''reindeer'' if domesticated) are deer in the genus ''Rangifer''. For the last few decades, reindeer were assigned to one species, ''Rangifer tarandus'', with about 10 subspecies. A 2022 revision of the genus elevated five of the subspecies to species (see Taxonomy below). They have a circumpolar distribution and are native to the Arctic, sub-Arctic, tundra, boreal forest, and mountainous regions of northern Europe, Siberia, and North America. Reindeer occur in both migratory and sedentary populations, and their herd sizes vary greatly in different regions. The tundra subspecies are adapted for extreme cold, and some are adapted for long-distance migration. Reindeer vary greatly in size and color from the smallest species, the Svalbard reindeer (''R. t. platyrhynchus''), to the largest subspecies, Osborn's caribou (''R. t. osborni''). Although reindeer are quite numerous, some species and subspecies a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamchadals
The Kamchadals (russian: камчадалы) inhabit Kamchatka, Russia. The name "Kamchadal" was applied to the descendants of the local Siberians and aboriginal peoples (the Itelmens, Ainu, Koryaks and Chuvans) who assimilated with the Russians. The descendants of the mixed-blood Russian settlers in 18th-19th century are called Kamchadals these days. The Kamchadals speak Russian with a touch of local dialects of the aboriginal languages of Kamchatka. The Kamchadals engage in fur trading, fishing, market gardening and dairy farming, and are of the Russian Orthodox faith. The Kamchadal language was a Kamchatka creole with Russian and indigenous elements. History In 1767 and 1768, a Russian ship brought smallpox to the region for the first time, and it is believed to have killed three fourths of the native population. In the journal of Captain James Cook, "The small pox . . . made its appearance in 1767 and 1768. It was brought into the country by a Russian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chukchis
The Chukchi, or Chukchee ( ckt, Ԓыгъоравэтԓьэт, О'равэтԓьэт, ''Ḷygʺoravètḷʹèt, O'ravètḷʹèt''), are a Siberian indigenous people native to the Chukchi Peninsula, the shores of the Chukchi Sea and the Bering Sea region of the Arctic Ocean all within modern Russia. They speak the Chukchi language. The Chukchi originated from the people living around the Okhotsk Sea. According to several studies on genomic research conduct from 2014 to 2018, the Chukchi are one of the Indigenous peoples of Siberia, they are also the closest Asiatic relatives of the indigenous peoples of the Americas as well as of the Ainu people and other East Asian people, being the descendants of settlers who did not cross the Bering Strait or settled the Japanese archipelago. Cultural history The majority of Chukchi reside within Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, but some also reside in the neighboring Sakha Republic to the west, Magadan Oblast to the southwest, and Kamc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Atlasov
Vladimir Vasilyevich Atlasov or Otlasov ( or Отла́сов; between 1661 and 1664 – 1711) was a Siberian Cossack who was the first Russian to organize systematic exploration of the Kamchatka Peninsula. Atlasov Island, an uninhabited volcanic island off the southern tip of Kamchatka, and the Atlasova volcano are named after him. Biography Atlasov was born in Veliky Ustyug. The first mention of him in the historical records comes from around 1682, when he was collecting Yasak on the Aldan River and one of the Uda rivers. In 1695 the voyevoda of Yakutsk appointed Atlasov prikazshchik of Anadyrsk. The Russians here had heard reports of a 'Kamchatka River' to the south and were already collecting yasak on the headwaters of the rivers that flow south toward Kamchatka. At least one of them had followed the Penzhina river to the Sea of Okhotsk. In 1696 he sent Luka Morozko south to explore. Morozko got as far south as the Tegil river on the west side of the peninsula and returned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russians
, native_name_lang = ru , image = , caption = , population = , popplace = 118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 ''Winkler Prins'' estimate) , region1 = , pop1 = approx. 7,500,000 (including Russian Jews and History of Germans in Russia, Ukraine and the Soviet Union, Russian Germans) , ref1 = , region2 = , pop2 = 7,170,000 (2018) ''including Crimea'' , ref2 = , region3 = , pop3 = 3,512,925 (2020) , ref3 = , region4 = , pop4 = 3,072,756 (2009)(including Russian Jews and Russian Germans) , ref4 = , region5 = , pop5 = 1,800,000 (2010)(Russian ancestry and Russian Germans and Jews) , ref5 = 35,000 (2018)(born in Russia) , region6 = , pop6 = 938,500 (2011)(including Russian Jews) , ref6 = , region7 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |