Brain anatomy on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The human brain is the central

organ
Organ and organs may refer to:
Biology
* Organ (biology), a group of tissues organized to serve a common function
* Organ system, a collection of organs that function together to carry out specific functions within the body.
Musical instruments
...
of the nervous system
In biology, the nervous system is the complex system, highly complex part of an animal that coordinates its behavior, actions and sense, sensory information by transmitting action potential, signals to and from different parts of its body. Th ...
, and with the spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal c ...
, comprises the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity o ...
. It consists of the cerebrum
The cerebrum (: cerebra), telencephalon or endbrain is the largest part of the brain, containing the cerebral cortex (of the two cerebral hemispheres) as well as several subcortical structures, including the hippocampus, basal ganglia, and olfac ...
, the brainstem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is conti ...
and the cerebellum
The cerebellum (: cerebella or cerebellums; Latin for 'little brain') is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as it or eve ...
. The brain controls most of the activities of the body
Body may refer to:
In science
* Physical body, an object in physics that represents a large amount, has mass or takes up space
* Body (biology), the physical material of an organism
* Body plan, the physical features shared by a group of anim ...
, processing, integrating, and coordinating the information it receives from the sensory nervous system
The sensory nervous system is a part of the nervous system responsible for processing sense, sensory information. A sensory system consists of sensory neurons (including the sensory receptor cells), neural pathways, and parts of the brain invol ...
. The brain integrates sensory information and coordinates instructions sent to the rest of the body.
The cerebrum, the largest part of the human brain, consists of two cerebral hemisphere
The vertebrate cerebrum (brain) is formed by two cerebral hemispheres that are separated by a groove, the longitudinal fissure. The brain can thus be described as being divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres. Each of these hemispheres ...
s. Each hemisphere has an inner core composed of white matter
White matter refers to areas of the central nervous system that are mainly made up of myelinated axons, also called Nerve tract, tracts. Long thought to be passive tissue, white matter affects learning and brain functions, modulating the distr ...
, and an outer surface – the cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. It is the largest site of Neuron, neural integration in the central nervous system, and plays ...
– composed of grey matter
Grey matter, or gray matter in American English, is a major component of the central nervous system, consisting of neuronal cell bodies, neuropil ( dendrites and unmyelinated axons), glial cells ( astrocytes and oligodendrocytes), synapses, ...
. The cortex has an outer layer, the neocortex
The neocortex, also called the neopallium, isocortex, or the six-layered cortex, is a set of layers of the mammalian cerebral cortex involved in higher-order brain functions such as sensory perception, cognition, generation of motor commands, ...
, and an inner allocortex
The allocortex (from Latin allo-, meaning other, and cortex, meaning bark or crust), or heterogenetic cortex, is one of the two types of cerebral cortex in the brain, together with the neocortex. In the human brain, the allocortex is the much sm ...
. The neocortex is made up of six neuronal layers, while the allocortex has three or four. Each hemisphere is divided into four lobes – the frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital lobe
The occipital lobe is one of the four Lobes of the brain, major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The name derives from its position at the back of the head, from the Latin , 'behind', and , 'head'.
The occipital lobe is the ...
s. The frontal lobe is associated with executive functions
In cognitive science and neuropsychology, executive functions (collectively referred to as executive function and cognitive control) are a set of cognitive processes that support goal-directed behavior, by regulating thoughts and actions thro ...
including self-control
Self-control is an aspect of inhibitory control, one of the core executive functions. Executive functions are cognitive processes that are necessary for regulating one's behavior in order to achieve specific goals.
Defined more independen ...
, planning
Planning is the process of thinking regarding the activities required to achieve a desired goal. Planning is based on foresight, the fundamental capacity for mental time travel. Some researchers regard the evolution of forethought - the cap ...
, reason
Reason is the capacity of consciously applying logic by drawing valid conclusions from new or existing information, with the aim of seeking the truth. It is associated with such characteristically human activities as philosophy, religion, scien ...
ing, and abstract thought, while the occipital lobe
The occipital lobe is one of the four Lobes of the brain, major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The name derives from its position at the back of the head, from the Latin , 'behind', and , 'head'.
The occipital lobe is the ...
is dedicated to vision. Within each lobe, cortical areas are associated with specific functions, such as the sensory, motor
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert one or more forms of energy into mechanical energy.
Available energy sources include potential energy (e.g. energy of the Earth's gravitational field as exploited in hydroelectric power gene ...
, and association regions. Although the left and right hemispheres are broadly similar in shape and function, some functions are associated with one side, such as language
Language is a structured system of communication that consists of grammar and vocabulary. It is the primary means by which humans convey meaning, both in spoken and signed language, signed forms, and may also be conveyed through writing syste ...
in the left and visual-spatial ability in the right. The hemispheres are connected by commissural nerve tracts, the largest being the corpus callosum
The corpus callosum (Latin for "tough body"), also callosal commissure, is a wide, thick nerve tract, consisting of a flat bundle of commissural fibers, beneath the cerebral cortex in the brain. The corpus callosum is only found in placental ...
.
The cerebrum is connected by the brainstem to the spinal cord. The brainstem consists of the midbrain
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the uppermost portion of the brainstem connecting the diencephalon and cerebrum with the pons. It consists of the cerebral peduncles, tegmentum, and tectum.
It is functionally associated with vision, hearing, mo ...
, the pons
The pons (from Latin , "bridge") is part of the brainstem that in humans and other mammals, lies inferior to the midbrain, superior to the medulla oblongata and anterior to the cerebellum.
The pons is also called the pons Varolii ("bridge of ...
, and the medulla oblongata
The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem-like structure which makes up the lower part of the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic (involun ...
. The cerebellum
The cerebellum (: cerebella or cerebellums; Latin for 'little brain') is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as it or eve ...
is connected to the brainstem by three pairs of nerve tract
A nerve tract is a bundle of nerve fibers (axons) connecting Nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei of the central nervous system. In the peripheral nervous system, this is known as a nerve fascicle, and has associated nervous tissue, connective tissue. T ...
s called cerebellar peduncle
The cerebellar peduncles are three paired bundles of Axon, fibres that connect the cerebellum to the brain stem.
* Superior cerebellar peduncle is a paired structure of white matter that connects the cerebellum to the mid-brain.
* Middle cereb ...
s. Within the cerebrum is the ventricular system
In neuroanatomy, the ventricular system is a set of four interconnected cavities known as cerebral ventricles in the brain. Within each ventricle is a region of choroid plexus which produces the circulating cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The ventric ...
, consisting of four interconnected ventricles in which cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless Extracellular fluid#Transcellular fluid, transcellular body fluid found within the meninges, meningeal tissue that surrounds the vertebrate brain and spinal cord, and in the ventricular system, ven ...
is produced and circulated. Underneath the cerebral cortex are several structures, including the thalamus
The thalamus (: thalami; from Greek language, Greek Wikt:θάλαμος, θάλαμος, "chamber") is a large mass of gray matter on the lateral wall of the third ventricle forming the wikt:dorsal, dorsal part of the diencephalon (a division of ...
, the epithalamus
The epithalamus (: epithalami) is a posterior (dorsal) segment of the diencephalon. The epithalamus includes the habenular nuclei, the stria medullaris, the anterior and posterior paraventricular nuclei, the posterior commissure, and the pine ...
, the pineal gland
The pineal gland (also known as the pineal body or epiphysis cerebri) is a small endocrine gland in the brain of most vertebrates. It produces melatonin, a serotonin-derived hormone, which modulates sleep, sleep patterns following the diurnal c ...
, the hypothalamus
The hypothalamus (: hypothalami; ) is a small part of the vertebrate brain that contains a number of nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrin ...
, the pituitary gland
The pituitary gland or hypophysis is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, the pituitary gland is located at the base of the human brain, brain, protruding off the bottom of the hypothalamus. The pituitary gland and the hypothalamus contr ...
, and the subthalamus
The subthalamus or ventral thalamus is a part of the diencephalon. Its most prominent structure is the subthalamic nucleus. The subthalamus connects to the globus pallidus, a subcortical nucleus of the basal ganglia.
Structure
The subthalamus ...
; the limbic structures, including the amygdalae
The amygdala (; : amygdalae or amygdalas; also '; Latin from Greek, , ', 'almond', 'tonsil') is a paired nuclear complex present in the cerebral hemispheres of vertebrates. It is considered part of the limbic system. In primates, it is loca ...
and the hippocampi, the claustrum
The claustrum (Latin, meaning "to close" or "to shut") is a thin sheet of neurons and supporting glial cells in the brain, that connects to the cerebral cortex and subcortical regions including the amygdala, hippocampus and thalamus. It is locate ...
, the various nuclei of the basal ganglia
The basal ganglia (BG) or basal nuclei are a group of subcortical Nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei found in the brains of vertebrates. In humans and other primates, differences exist, primarily in the division of the globus pallidus into externa ...
, the basal forebrain
Part of the human brain, the basal forebrain structures are located in the forebrain to the front of and below the striatum. They include the ventral basal ganglia (including nucleus accumbens and ventral pallidum), nucleus basalis, diagonal ba ...
structures, and three circumventricular organs. Brain structures that are not on the midplane exist in pairs; for example, there are two hippocampi and two amygdalae.
The cells of the brain include neuron
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural net ...
s and supportive glial cells
Glia, also called glial cells (gliocytes) or neuroglia, are non-neuronal cells in the central nervous system (the brain and the spinal cord) and in the peripheral nervous system that do not produce electrical impulses. The neuroglia make up ...
. There are more than 86 billion neurons in the brain, and a more or less equal number of other cells. Brain activity is made possible by the interconnections of neurons and their release of neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a Chemical synapse, synapse. The cell receiving the signal, or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neurotra ...
s in response to nerve impulses. Neurons connect to form neural pathway
In neuroanatomy, a neural pathway is the connection formed by axons that project from neurons to make synapses onto neurons in another location, to enable neurotransmission (the sending of a signal from one region of the nervous system to ano ...
s, neural circuits, and elaborate network systems. The whole circuitry is driven by the process of neurotransmission
Neurotransmission (Latin: ''transmissio'' "passage, crossing" from ''transmittere'' "send, let through") is the process by which signaling molecules called neurotransmitters are released by the axon terminal of a neuron (the presynaptic neuron ...
.
The brain is protected by the skull
The skull, or cranium, is typically a bony enclosure around the brain of a vertebrate. In some fish, and amphibians, the skull is of cartilage. The skull is at the head end of the vertebrate.
In the human, the skull comprises two prominent ...
, suspended in cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless Extracellular fluid#Transcellular fluid, transcellular body fluid found within the meninges, meningeal tissue that surrounds the vertebrate brain and spinal cord, and in the ventricular system, ven ...
, and isolated from the bloodstream
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the body. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart an ...
by the blood–brain barrier
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective semipermeable membrane, semipermeable border of endothelium, endothelial cells that regulates the transfer of solutes and chemicals between the circulatory system and the central nervous system ...
. However, the brain is still susceptible to damage
Damage is any change in a thing, often a physical object, that degrades it away from its initial state. It can broadly be defined as "changes introduced into a system that adversely affect its current or future performance".Farrar, C.R., Sohn, H., ...
, disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that adversely affects the structure or function (biology), function of all or part of an organism and is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical condi ...
, and infection
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmis ...
. Damage can be caused by trauma, or a loss of blood supply known as a stroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemor ...
. The brain is susceptible to degenerative disorders, such as Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a neurodegenerative disease primarily of the central nervous system, affecting both motor system, motor and non-motor systems. Symptoms typically develop gradually and non-motor issues become ...
, dementia
Dementia is a syndrome associated with many neurodegenerative diseases, characterized by a general decline in cognitive abilities that affects a person's ability to perform activities of daily living, everyday activities. This typically invo ...
s including Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease and the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems wit ...
, and multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease resulting in damage to myelinthe insulating covers of nerve cellsin the brain and spinal cord. As a demyelinating disease, MS disrupts the nervous system's ability to Action potential, transmit ...
. Psychiatric condition
A mental disorder, also referred to as a mental illness, a mental health condition, or a psychiatric disability, is a behavioral or mental pattern that causes significant distress or impairment of personal functioning. A mental disorder is ...
s, including schizophrenia
Schizophrenia () is a mental disorder characterized variously by hallucinations (typically, Auditory hallucination#Schizophrenia, hearing voices), delusions, thought disorder, disorganized thinking and behavior, and Reduced affect display, f ...
and clinical depression
Major depressive disorder (MDD), also known as clinical depression, is a mental disorder characterized by at least two weeks of pervasive low mood, low self-esteem, and loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities. Intro ...
, are thought to be associated with brain dysfunctions. The brain can also be the site of tumours, both benign
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse; the term is most familiar as a characterization of cancer.
A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous benign tumor, ''benign'' tumor in that a malig ...
and malignant
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse; the term is most familiar as a characterization of cancer.
A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous benign tumor, ''benign'' tumor in that a malig ...
; these mostly originate from other sites in the body.
The study of the anatomy of the brain is neuroanatomy
Neuroanatomy is the study of the structure and organization of the nervous system. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defi ...
, while the study of its function is neuroscience
Neuroscience is the scientific study of the nervous system (the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nervous system), its functions, and its disorders. It is a multidisciplinary science that combines physiology, anatomy, molecular biology, ...
. Numerous techniques are used to study the brain. Specimens from other animals, which may be examined microscopically, have traditionally provided much information. Medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to revea ...
technologies such as functional neuroimaging
Functional neuroimaging is the use of neuroimaging technology to measure an aspect of brain function, often with a view to understanding the relationship between activity in certain brain areas and specific mental functions. It is primarily used a ...
, and electroencephalography
Electroencephalography (EEG)
is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The biosignal, bio signals detected by EEG have been shown to represent the postsynaptic potentials of pyramidal neurons in ...
(EEG) recordings are important in studying the brain. The medical history
The medical history, case history, or anamnesis (from Greek: ἀνά, ''aná'', "open", and μνήσις, ''mnesis'', "memory") of a patient is a set of information the physicians collect over medical interviews. It involves the patient, and ev ...
of people with brain injury
Brain injury (BI) is the destruction or degeneration of brain cells. Brain injuries occur due to a wide range of internal and external factors. In general, brain damage refers to significant, undiscriminating trauma-induced damage.
A common ...
has provided insight into the function of each part of the brain. Neuroscience research has expanded considerably, and research is ongoing.
In culture, the philosophy of mind
Philosophy of mind is a branch of philosophy that deals with the nature of the mind and its relation to the Body (biology), body and the Reality, external world.
The mind–body problem is a paradigmatic issue in philosophy of mind, although a ...
has for centuries attempted to address the question of the nature of consciousness
Consciousness, at its simplest, is awareness of a state or object, either internal to oneself or in one's external environment. However, its nature has led to millennia of analyses, explanations, and debate among philosophers, scientists, an ...
and the mind–body problem
The mind–body problem is a List_of_philosophical_problems#Mind–body_problem, philosophical problem concerning the relationship between thought and consciousness in the human mind and Human body, body. It addresses the nature of consciousness ...
. The pseudoscience
Pseudoscience consists of statements, beliefs, or practices that claim to be both scientific and factual but are incompatible with the scientific method. Pseudoscience is often characterized by contradictory, exaggerated or unfalsifiable cl ...
of phrenology
Phrenology is a pseudoscience that involves the measurement of bumps on the skull to predict mental traits. It is based on the concept that the Human brain, brain is the organ of the mind, and that certain brain areas have localized, specific ...
attempted to localise personality attributes to regions of the cortex in the 19th century. In science fiction, brain transplants are imagined in tales such as the 1942 '' Donovan's Brain''.
Structure

Gross anatomy
The adult human brain weighs on average about which is about 2% of the total body weight, with a volume of around 1260 cm3 in men and 1130 cm3 in women. There is substantial individual variation, with the standardreference range
In medicine and health-related fields, a reference range or reference interval is the range or the interval of values that is deemed normal for a physiological measurement in healthy persons (for example, the amount of creatinine in the blood ...
for men being and for women .
The cerebrum
The cerebrum (: cerebra), telencephalon or endbrain is the largest part of the brain, containing the cerebral cortex (of the two cerebral hemispheres) as well as several subcortical structures, including the hippocampus, basal ganglia, and olfac ...
, consisting of the cerebral hemisphere
The vertebrate cerebrum (brain) is formed by two cerebral hemispheres that are separated by a groove, the longitudinal fissure. The brain can thus be described as being divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres. Each of these hemispheres ...
s, forms the largest part of the brain and overlies the other brain structures. The outer region of the hemispheres, the cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. It is the largest site of Neuron, neural integration in the central nervous system, and plays ...
, is grey matter
Grey matter, or gray matter in American English, is a major component of the central nervous system, consisting of neuronal cell bodies, neuropil ( dendrites and unmyelinated axons), glial cells ( astrocytes and oligodendrocytes), synapses, ...
, consisting of cortical layers
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. It is the largest site of neural integration in the central nervous system, and plays a key ...
of neuron
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural net ...
s. Each hemisphere is divided into four main lobes – the frontal lobe
The frontal lobe is the largest of the four major lobes of the brain in mammals, and is located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere (in front of the parietal lobe and the temporal lobe). It is parted from the parietal lobe by a Sulcus (neur ...
, parietal lobe
The parietal lobe is one of the four Lobes of the brain, major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The parietal lobe is positioned above the temporal lobe and behind the frontal lobe and central sulcus.
The parietal lobe integra ...
, temporal lobe
The temporal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The temporal lobe is located beneath the lateral fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the mammalian brain.
The temporal lobe is involved in pr ...
, and occipital lobe
The occipital lobe is one of the four Lobes of the brain, major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The name derives from its position at the back of the head, from the Latin , 'behind', and , 'head'.
The occipital lobe is the ...
. Three other lobes are included by some sources which are a ''central lobe'', a limbic lobe
The limbic lobe is an arc-shaped cortical region of the limbic system, on the medial surface of each cerebral hemisphere of the mammalian brain, consisting of parts of the frontal, parietal and temporal lobes. The term is ambiguous, with some au ...
, and an insular lobe. The central lobe comprises the precentral gyrus
The precentral gyrus is a prominent gyrus on the surface of the posterior frontal lobe of the brain. It is the site of the primary motor cortex that in humans is cytoarchitecturally defined as Brodmann area 4.
Structure
The precentral gyrus li ...
and the postcentral gyrus
In neuroanatomy, the postcentral gyrus is a prominent gyrus in the lateral parietal lobe of the human brain. It is the location of the primary somatosensory cortex, the main sensory receptive area for the sense of touch. Like other sensory area ...
and is included since it forms a distinct functional role.
The brainstem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is conti ...
, resembling a stalk, attaches to and leaves the cerebrum at the start of the midbrain
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the uppermost portion of the brainstem connecting the diencephalon and cerebrum with the pons. It consists of the cerebral peduncles, tegmentum, and tectum.
It is functionally associated with vision, hearing, mo ...
area. The brainstem includes the midbrain, the pons
The pons (from Latin , "bridge") is part of the brainstem that in humans and other mammals, lies inferior to the midbrain, superior to the medulla oblongata and anterior to the cerebellum.
The pons is also called the pons Varolii ("bridge of ...
, and the medulla oblongata
The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem-like structure which makes up the lower part of the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic (involun ...
. Behind the brainstem is the cerebellum
The cerebellum (: cerebella or cerebellums; Latin for 'little brain') is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as it or eve ...
().
The cerebrum, brainstem, cerebellum, and spinal cord are covered by three membranes called meninges
In anatomy, the meninges (; meninx ; ) are the three membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord. In mammals, the meninges are the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater. Cerebrospinal fluid is located in the subarachnoid spac ...
. The membranes are the tough dura mater; the middle arachnoid mater
The arachnoid mater (or simply arachnoid) is one of the three meninges, the protective membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord. It is so named because of its resemblance to a spider web. The arachnoid mater is a derivative of the neural cr ...
and the more delicate inner pia mater
Pia mater ( or ),Entry "pia mater"
in
subarachnoid space and subarachnoid cisterns, which contain the
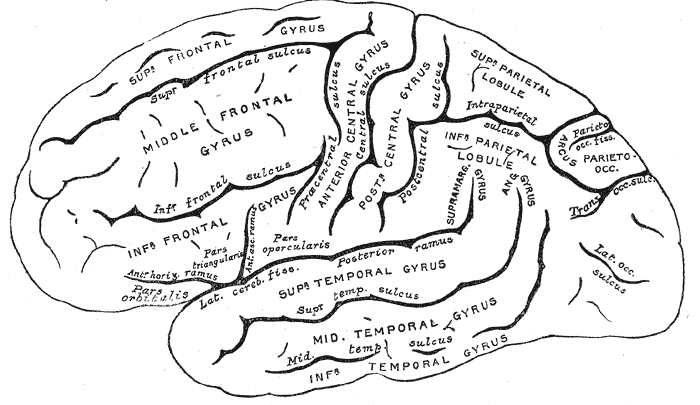 The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain and is divided into nearly
The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain and is divided into nearly  The cerebrum contains the ventricles where the cerebrospinal fluid is produced and circulated. Below the corpus callosum is the
The cerebrum contains the ventricles where the cerebrospinal fluid is produced and circulated. Below the corpus callosum is the
 The cerebellum is divided into an anterior lobe, a
The cerebellum is divided into an anterior lobe, a
in
subarachnoid space and subarachnoid cisterns, which contain the
cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless Extracellular fluid#Transcellular fluid, transcellular body fluid found within the meninges, meningeal tissue that surrounds the vertebrate brain and spinal cord, and in the ventricular system, ven ...
. The outermost membrane of the cerebral cortex is the basement membrane of the pia mater called the glia limitans and is an important part of the blood–brain barrier
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective semipermeable membrane, semipermeable border of endothelium, endothelial cells that regulates the transfer of solutes and chemicals between the circulatory system and the central nervous system ...
. In 2023 a fourth meningeal membrane has been proposed known as the subarachnoid lymphatic-like membrane. The living brain is very soft, having a gel-like consistency similar to soft tofu. The cortical layers of neurons constitute much of the cerebral grey matter
Grey matter, or gray matter in American English, is a major component of the central nervous system, consisting of neuronal cell bodies, neuropil ( dendrites and unmyelinated axons), glial cells ( astrocytes and oligodendrocytes), synapses, ...
, while the deeper subcortical regions of myelin
Myelin Sheath ( ) is a lipid-rich material that in most vertebrates surrounds the axons of neurons to insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses (called action potentials) pass along the axon. The myelinated axon can be lik ...
ated axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis) or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see American and British English spelling differences#-re, -er, spelling differences) is a long, slender cellular extensions, projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, ...
s, make up the white matter
White matter refers to areas of the central nervous system that are mainly made up of myelinated axons, also called Nerve tract, tracts. Long thought to be passive tissue, white matter affects learning and brain functions, modulating the distr ...
. The white matter of the brain makes up about half of the total brain volume.
Cerebrum
 The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain and is divided into nearly
The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain and is divided into nearly symmetrical
Symmetry () in everyday life refers to a sense of harmonious and beautiful proportion and balance. In mathematics, the term has a more precise definition and is usually used to refer to an object that is invariant under some transformations ...
left and right hemisphere
Hemisphere may refer to:
In geometry
* Hemisphere (geometry), a half of a sphere
As half of Earth or any spherical astronomical object
* A hemisphere of Earth
** Northern Hemisphere
** Southern Hemisphere
** Eastern Hemisphere
** Western Hemi ...
s by a deep groove, the longitudinal fissure
The longitudinal fissure (or cerebral fissure, great longitudinal fissure, median longitudinal fissure, interhemispheric fissure) is the deep groove that separates the two cerebral hemispheres of the vertebrate brain. Lying within it is a continu ...
. Asymmetry between the lobes is noted as a petalia. The hemispheres are connected by five commissures that span the longitudinal fissure, the largest of these is the corpus callosum
The corpus callosum (Latin for "tough body"), also callosal commissure, is a wide, thick nerve tract, consisting of a flat bundle of commissural fibers, beneath the cerebral cortex in the brain. The corpus callosum is only found in placental ...
.
Each hemisphere is conventionally divided into four main lobes; the frontal lobe
The frontal lobe is the largest of the four major lobes of the brain in mammals, and is located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere (in front of the parietal lobe and the temporal lobe). It is parted from the parietal lobe by a Sulcus (neur ...
, parietal lobe
The parietal lobe is one of the four Lobes of the brain, major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The parietal lobe is positioned above the temporal lobe and behind the frontal lobe and central sulcus.
The parietal lobe integra ...
, temporal lobe
The temporal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The temporal lobe is located beneath the lateral fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the mammalian brain.
The temporal lobe is involved in pr ...
, and occipital lobe
The occipital lobe is one of the four Lobes of the brain, major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The name derives from its position at the back of the head, from the Latin , 'behind', and , 'head'.
The occipital lobe is the ...
, named according to the skull bones
The skull, or cranium, is typically a bony enclosure around the brain of a vertebrate. In some fish, and amphibians, the skull is of cartilage. The skull is at the head end of the vertebrate.
In the human, the skull comprises two prominent ...
that overlie them. Each lobe is associated with one or two specialised functions though there is some functional overlap between them. The surface of the brain is folded into ridges (gyri
In neuroanatomy, a gyrus (: gyri) is a ridge on the cerebral cortex. It is generally surrounded by one or more sulcus (neuroanatomy), sulci (depressions or furrows; : sulcus). Gyri and sulci create the folded appearance of the brain in huma ...
) and grooves (sulci
Sulci or Sulki (in Greek , Stephanus of Byzantium, Steph. B., Ptolemy, Ptol.; , Strabo; , Pausanias (geographer), Paus.), was one of the most considerable cities of ancient Sardinia, situated in the southwest corner of the island, on a small isla ...
), many of which are named, usually according to their position, such as the frontal gyrus
The frontal gyri are six gyri of the frontal lobe in the brain. There are five horizontally oriented, parallel convolutions, of the frontal lobe that are aligned anterior to posterior. Three are visible on the lateral surface of the brain and two ...
of the frontal lobe or the central sulcus
In neuroanatomy, the central sulcus (also central fissure, fissure of Rolando, or Rolandic fissure, after Luigi Rolando) is a sulcus, or groove, in the cerebral cortex in the brains of vertebrates. It is sometimes confused with the longitudinal ...
separating the central regions of the hemispheres. There are many small variations in the secondary and tertiary folds.
The outer part of the cerebrum is the cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. It is the largest site of Neuron, neural integration in the central nervous system, and plays ...
, made up of grey matter
Grey matter, or gray matter in American English, is a major component of the central nervous system, consisting of neuronal cell bodies, neuropil ( dendrites and unmyelinated axons), glial cells ( astrocytes and oligodendrocytes), synapses, ...
arranged in layers. It is thick, and deeply folded to give a convoluted appearance. Beneath the cortex is the cerebral white matter
White matter refers to areas of the central nervous system that are mainly made up of myelinated axons, also called Nerve tract, tracts. Long thought to be passive tissue, white matter affects learning and brain functions, modulating the distr ...
. The largest part of the cerebral cortex is the neocortex
The neocortex, also called the neopallium, isocortex, or the six-layered cortex, is a set of layers of the mammalian cerebral cortex involved in higher-order brain functions such as sensory perception, cognition, generation of motor commands, ...
, which has six neuronal layers. The rest of the cortex is of allocortex
The allocortex (from Latin allo-, meaning other, and cortex, meaning bark or crust), or heterogenetic cortex, is one of the two types of cerebral cortex in the brain, together with the neocortex. In the human brain, the allocortex is the much sm ...
, which has three or four layers.
The cortex is mapped by divisions into about fifty different functional areas known as Brodmann's areas. These areas are distinctly different when seen under a microscope. The cortex is divided into two main functional areas – a motor cortex
The motor cortex is the region of the cerebral cortex involved in the planning, motor control, control, and execution of voluntary movements.
The motor cortex is an area of the frontal lobe located in the posterior precentral gyrus immediately ...
and a sensory cortex
The sensory cortex can refer sometimes to the primary somatosensory cortex, or it can be used as a term for the primary and secondary cortices of the different senses (two cortices each, on left and right hemisphere): the visual cortex on the occ ...
. The primary motor cortex
The primary motor cortex ( Brodmann area 4) is a brain region that in humans is located in the dorsal portion of the frontal lobe. It is the primary region of the motor system and works in association with other motor areas including premotor c ...
, which sends axons down to motor neuron
A motor neuron (or motoneuron), also known as efferent neuron is a neuron whose cell body is located in the motor cortex, brainstem or the spinal cord, and whose axon (fiber) projects to the spinal cord or outside of the spinal cord to directly o ...
s in the brainstem and spinal cord, occupies the rear portion of the frontal lobe, directly in front of the somatosensory area. The primary sensory areas
The primary sensory areas are the primary cortical regions of the five sensory systems in the brain (taste, olfaction, touch, hearing and vision). Except for the olfactory system, they receive sensory information from thalamic nerve projections. T ...
receive signals from the sensory nerve
A sensory nerve, or afferent nerve, is a nerve that contains exclusively afferent nerve fibers. Nerves containing also motor fibers are called mixed nerve, mixed. Afferent nerve fibers in a sensory nerve carry sensory system, sensory information ...
s and tracts
Tract may refer to:
Geography and real estate
* Housing tract, an area of land that is subdivided into smaller individual lots
* Land lot or tract, a section of land
* Census tract, a geographic region defined for the purpose of taking a census
...
by way of relay nuclei in the thalamus
The thalamus (: thalami; from Greek language, Greek Wikt:θάλαμος, θάλαμος, "chamber") is a large mass of gray matter on the lateral wall of the third ventricle forming the wikt:dorsal, dorsal part of the diencephalon (a division of ...
. Primary sensory areas include the visual cortex
The visual cortex of the brain is the area of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information. It is located in the occipital lobe. Sensory input originating from the eyes travels through the lateral geniculate nucleus in the thalam ...
of the occipital lobe
The occipital lobe is one of the four Lobes of the brain, major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The name derives from its position at the back of the head, from the Latin , 'behind', and , 'head'.
The occipital lobe is the ...
, the auditory cortex
The auditory cortex is the part of the temporal lobe that processes auditory information in humans and many other vertebrates. It is a part of the auditory system, performing basic and higher functions in hearing, such as possible relations to ...
in parts of the temporal lobe
The temporal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The temporal lobe is located beneath the lateral fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the mammalian brain.
The temporal lobe is involved in pr ...
and insular cortex
The insular cortex (also insula and insular lobe) is a portion of the cerebral cortex folded deep within the lateral sulcus (the fissure separating the temporal lobe from the parietal lobe, parietal and frontal lobes) within each brain hemisphere ...
, and the somatosensory cortex
The somatosensory system, or somatic sensory system is a subset of the sensory nervous system. The main functions of the somatosensory system are the perception of external stimuli, the perception of internal stimuli, and the regulation of bod ...
in the parietal lobe
The parietal lobe is one of the four Lobes of the brain, major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The parietal lobe is positioned above the temporal lobe and behind the frontal lobe and central sulcus.
The parietal lobe integra ...
. The remaining parts of the cortex are called the association areas. These areas receive input from the sensory areas and lower parts of the brain and are involved in the complex cognitive processes
Cognition is the "mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses". It encompasses all aspects of intellectual functions and processes such as: perception, attention, thought, ima ...
of perception
Perception () is the organization, identification, and interpretation of sensory information in order to represent and understand the presented information or environment. All perception involves signals that go through the nervous syste ...
, thought
In their most common sense, the terms thought and thinking refer to cognitive processes that can happen independently of sensory stimulation. Their most paradigmatic forms are judging, reasoning, concept formation, problem solving, and de ...
, and decision-making
In psychology, decision-making (also spelled decision making and decisionmaking) is regarded as the Cognition, cognitive process resulting in the selection of a belief or a course of action among several possible alternative options. It could be ...
. The main functions of the frontal lobe are to control attention, abstract thinking, behaviour, problem-solving tasks, and physical reactions and personality. The occipital lobe is the smallest lobe; its main functions are visual reception, visual-spatial processing, movement, and colour recognition. There is a smaller occipital lobule in the lobe known as the cuneus
The cuneus (; : cunei) is a smaller lobe in the occipital lobe of the brain. The cuneus is bounded anteriorly by the parieto-occipital sulcus and Inferior (anatomy), inferiorly by the calcarine sulcus.
Function
The cuneus (Brodmann area 17) r ...
. The temporal lobe controls auditory and visual memories, language
Language is a structured system of communication that consists of grammar and vocabulary. It is the primary means by which humans convey meaning, both in spoken and signed language, signed forms, and may also be conveyed through writing syste ...
, and some hearing and speech.
 The cerebrum contains the ventricles where the cerebrospinal fluid is produced and circulated. Below the corpus callosum is the
The cerebrum contains the ventricles where the cerebrospinal fluid is produced and circulated. Below the corpus callosum is the septum pellucidum
The septum pellucidum (Latin for "translucent wall") is a thin, triangular, vertical double membrane separating the anterior horns of the left and right lateral ventricles of the brain. It runs as a sheet from the corpus callosum down to the f ...
, a membrane that separates the lateral ventricles
The lateral ventricles are the two largest ventricles of the brain and contain cerebrospinal fluid. Each cerebral hemisphere contains a lateral ventricle, known as the left or right lateral ventricle, respectively.
Each lateral ventricle resemb ...
. Beneath the lateral ventricles is the thalamus
The thalamus (: thalami; from Greek language, Greek Wikt:θάλαμος, θάλαμος, "chamber") is a large mass of gray matter on the lateral wall of the third ventricle forming the wikt:dorsal, dorsal part of the diencephalon (a division of ...
and to the front and below is the hypothalamus
The hypothalamus (: hypothalami; ) is a small part of the vertebrate brain that contains a number of nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrin ...
. The hypothalamus leads on to the pituitary gland
The pituitary gland or hypophysis is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, the pituitary gland is located at the base of the human brain, brain, protruding off the bottom of the hypothalamus. The pituitary gland and the hypothalamus contr ...
. At the back of the thalamus is the brainstem.
The basal ganglia
The basal ganglia (BG) or basal nuclei are a group of subcortical Nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei found in the brains of vertebrates. In humans and other primates, differences exist, primarily in the division of the globus pallidus into externa ...
, also called basal nuclei, are a set of structures deep within the hemispheres involved in behaviour and movement regulation. The largest component is the striatum
The striatum (: striata) or corpus striatum is a cluster of interconnected nuclei that make up the largest structure of the subcortical basal ganglia. The striatum is a critical component of the motor and reward systems; receives glutamat ...
, others are the globus pallidus
The globus pallidus (GP), also known as paleostriatum or dorsal pallidum, is a major component of the Cerebral cortex, subcortical basal ganglia in the brain. It consists of two adjacent segments, one external (or lateral), known in rodents simpl ...
, the substantia nigra
The substantia nigra (SN) is a basal ganglia structure located in the midbrain that plays an important role in reward and movement. ''Substantia nigra'' is Latin for "black substance", reflecting the fact that parts of the substantia nigra a ...
and the subthalamic nucleus. The striatum is divided into a ventral striatum, and dorsal striatum, subdivisions that are based upon function and connections. The ventral striatum consists of the nucleus accumbens
The nucleus accumbens (NAc or NAcc; also known as the accumbens nucleus, or formerly as the ''nucleus accumbens septi'', Latin for ' nucleus adjacent to the septum') is a region in the basal forebrain rostral to the preoptic area of the hypo ...
and the olfactory tubercle
The olfactory tubercle (OT), also known as the tuberculum olfactorium, is a multi-sensory processing center that is contained within the olfactory cortex and ventral striatum and plays a role in reward cognition. The OT has also been shown to ...
whereas the dorsal striatum consists of the caudate nucleus
The caudate nucleus is one of the structures that make up the corpus striatum, which is part of the basal ganglia in the human brain. Although the caudate nucleus has long been associated with motor processes because of its relation to Parkinso ...
and the putamen
The putamen (; from Latin, meaning "nutshell") is a subcortical nucleus (neuroanatomy), nucleus with a rounded structure, in the basal ganglia nuclear group. It is located at the base of the forebrain and above the midbrain.
The putamen and c ...
. The putamen and the globus pallidus lie separated from the lateral ventricles and thalamus by the internal capsule
The internal capsule is a paired white matter structure, as a two-way nerve tract, tract, carrying afferent nerve fiber, ascending and efferent nerve fiber, descending axon, fibers, to and from the cerebral cortex. The internal capsule is situate ...
, whereas the caudate nucleus stretches around and abuts the lateral ventricles on their outer sides. At the deepest part of the lateral sulcus
The lateral sulcus (or lateral fissure, also called Sylvian fissure, after Franciscus Sylvius) is the most prominent sulcus (neuroanatomy), sulcus of each cerebral hemisphere in the human brain. The lateral sulcus (neuroanatomy), sulcus is a deep ...
between the insular cortex
The insular cortex (also insula and insular lobe) is a portion of the cerebral cortex folded deep within the lateral sulcus (the fissure separating the temporal lobe from the parietal lobe, parietal and frontal lobes) within each brain hemisphere ...
and the striatum is a thin neuronal sheet called the claustrum
The claustrum (Latin, meaning "to close" or "to shut") is a thin sheet of neurons and supporting glial cells in the brain, that connects to the cerebral cortex and subcortical regions including the amygdala, hippocampus and thalamus. It is locate ...
.
Below and in front of the striatum are a number of basal forebrain
Part of the human brain, the basal forebrain structures are located in the forebrain to the front of and below the striatum. They include the ventral basal ganglia (including nucleus accumbens and ventral pallidum), nucleus basalis, diagonal ba ...
structures. These include the nucleus basalis
In the human brain, the nucleus basalis, also known as the nucleus basalis of Meynert or nucleus basalis magnocellularis, is a group of neurons located mainly in the substantia innominata of the basal forebrain. Most neurons of the nucleus basa ...
, diagonal band of Broca
The diagonal band of Broca interconnects the amygdala and the septal area. It is one of the olfactory structures. It is situated upon the inferior aspect of the brain. It forms the medial margin of the anterior perforated substance.
It was desc ...
, substantia innominata, and the medial septal nucleus. These structures are important in producing the neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a Chemical synapse, synapse. The cell receiving the signal, or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neurotra ...
, acetylcholine
Acetylcholine (ACh) is an organic compound that functions in the brain and body of many types of animals (including humans) as a neurotransmitter. Its name is derived from its chemical structure: it is an ester of acetic acid and choline. Par ...
, which is then distributed widely throughout the brain. The basal forebrain, in particular the nucleus basalis, is considered to be the major cholinergic
Cholinergic agents are compounds which mimic the action of acetylcholine and/or butyrylcholine. In general, the word " choline" describes the various quaternary ammonium salts containing the ''N'',''N'',''N''-trimethylethanolammonium cation ...
output of the central nervous system to the striatum and neocortex.
Cerebellum
 The cerebellum is divided into an anterior lobe, a
The cerebellum is divided into an anterior lobe, a posterior lobe
The cerebellum (: cerebella or cerebellums; Latin for 'little brain') is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as it or eve ...
, and the flocculonodular lobe. The anterior and posterior lobes are connected in the middle by the vermis
The cerebellar vermis (from Latin ''vermis,'' "worm") is located in the medial, cortico-nuclear zone of the cerebellum, which is in the posterior fossa of the cranium. The primary fissure in the vermis curves ventrolaterally to the superior s ...
. Compared to the cerebral cortex, the cerebellum has a much thinner outer cortex that is narrowly furrowed into numerous curved transverse fissures.
Viewed from underneath between the two lobes is the third lobe the flocculonodular lobe. The cerebellum rests at the back of the cranial cavity
The cranial cavity, also known as intracranial space, is the space within the skull that accommodates the brain. The skull is also known as the cranium. The cranial cavity is formed by eight cranial bones known as the neurocranium that in human ...
, lying beneath the occipital lobes, and is separated from these by the cerebellar tentorium
The cerebellar tentorium or tentorium cerebelli (Latin for "tent of the cerebellum") is one of four dural folds that separate the cranial cavity into four (incomplete) compartments. The cerebellar tentorium separates the cerebellum from the cere ...
, a sheet of fibre.
It is connected to the brainstem by three pairs of nerve tract
A nerve tract is a bundle of nerve fibers (axons) connecting Nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei of the central nervous system. In the peripheral nervous system, this is known as a nerve fascicle, and has associated nervous tissue, connective tissue. T ...
s called cerebellar peduncle
The cerebellar peduncles are three paired bundles of Axon, fibres that connect the cerebellum to the brain stem.
* Superior cerebellar peduncle is a paired structure of white matter that connects the cerebellum to the mid-brain.
* Middle cereb ...
s. The superior pair connects to the midbrain; the middle pair connects to the medulla, and the inferior pair connects to the pons. The cerebellum consists of an inner medulla of white matter and an outer cortex of richly folded grey matter. The cerebellum's anterior and posterior lobes appear to play a role in the coordination and smoothing of complex motor movements, and the flocculonodular lobe in the maintenance of balance
Balance may refer to:
Common meanings
* Balance (ability) in biomechanics
* Balance (accounting)
* Balance or weighing scale
* Balance, as in equality (mathematics) or equilibrium
Arts and entertainment Film
* Balance (1983 film), ''Balance'' ( ...
although debate exists as to its cognitive, behavioural and motor functions.
Brainstem
The brainstem lies beneath the cerebrum and consists of themidbrain
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the uppermost portion of the brainstem connecting the diencephalon and cerebrum with the pons. It consists of the cerebral peduncles, tegmentum, and tectum.
It is functionally associated with vision, hearing, mo ...
, pons
The pons (from Latin , "bridge") is part of the brainstem that in humans and other mammals, lies inferior to the midbrain, superior to the medulla oblongata and anterior to the cerebellum.
The pons is also called the pons Varolii ("bridge of ...
and medulla. It lies in the back part of the skull, resting on the part of the base known as the clivus, and ends at the foramen magnum
The foramen magnum () is a large, oval-shaped opening in the occipital bone of the skull. It is one of the several oval or circular openings (foramina) in the base of the skull. The spinal cord, an extension of the medulla oblongata, passes thro ...
, a large opening
Opening may refer to:
Types of openings
* Hole
* A title sequence or opening credits
* Grand opening of a business or other institution
* Inauguration
* Keynote
* Opening sentence
* Opening sequence
* Opening statement, a beginning statemen ...
in the occipital bone
The occipital bone () is a neurocranium, cranial dermal bone and the main bone of the occiput (back and lower part of the skull). It is trapezoidal in shape and curved on itself like a shallow dish. The occipital bone lies over the occipital lob ...
. The brainstem continues below this as the spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal c ...
, protected by the vertebral column
The spinal column, also known as the vertebral column, spine or backbone, is the core part of the axial skeleton in vertebrates. The vertebral column is the defining and eponymous characteristic of the vertebrate. The spinal column is a segmente ...
.
Ten of the twelve pairs of cranial nerve
Cranial nerves are the nerves that emerge directly from the brain (including the brainstem), of which there are conventionally considered twelve pairs. Cranial nerves relay information between the brain and parts of the body, primarily to and f ...
s emerge directly from the brainstem. The brainstem also contains many cranial nerve nuclei
A cranial nerve nucleus is a collection of neuron cell bodies (gray matter) in the brain stem that is associated with one or more of the cranial nerves. Axons carrying information to and from the cranial nerves form a synapse first at these nucl ...
and nuclei of peripheral nerves
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is one of two components that make up the nervous system of bilateral animals, with the other part being the central nervous system (CNS). The PNS consists of nerves and ganglia, which lie outside the brain a ...
, as well as nuclei involved in the regulation of many essential processes including breathing
Breathing (spiration or ventilation) is the rhythmical process of moving air into ( inhalation) and out of ( exhalation) the lungs to facilitate gas exchange with the internal environment, mostly to flush out carbon dioxide and bring in oxy ...
, control of eye movements and balance. The reticular formation
The reticular formation is a set of interconnected nuclei in the brainstem that spans from the lower end of the medulla oblongata to the upper end of the midbrain. The neurons of the reticular formation make up a complex set of neural networks ...
, a network of nuclei of ill-defined formation, is present within and along the length of the brainstem. Many nerve tract
A nerve tract is a bundle of nerve fibers (axons) connecting Nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei of the central nervous system. In the peripheral nervous system, this is known as a nerve fascicle, and has associated nervous tissue, connective tissue. T ...
s, which transmit information to and from the cerebral cortex to the rest of the body, pass through the brainstem.
Microanatomy
The human brain is primarily composed ofneuron
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural net ...
s, glial cell
Glia, also called glial cells (gliocytes) or neuroglia, are non-neuronal cells in the central nervous system (the brain and the spinal cord) and in the peripheral nervous system that do not produce electrical impulses. The neuroglia make up ...
s, neural stem cells, and blood vessel
Blood vessels are the tubular structures of a circulatory system that transport blood throughout many Animal, animals’ bodies. Blood vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to most of the Tissue (biology), tissues of a Body (bi ...
s. Types of neuron include interneuron
Interneurons (also called internuncial neurons, association neurons, connector neurons, or intermediate neurons) are neurons that are not specifically motor neurons or sensory neurons. Interneurons are the central nodes of neural circuits, enab ...
s, pyramidal cell
Pyramidal cells, or pyramidal neurons, are a type of multipolar neuron found in areas of the brain including the cerebral cortex, the hippocampus, and the amygdala. Pyramidal cells are the primary excitation units of the mammalian prefrontal cort ...
s including Betz cells, motor neuron
A motor neuron (or motoneuron), also known as efferent neuron is a neuron whose cell body is located in the motor cortex, brainstem or the spinal cord, and whose axon (fiber) projects to the spinal cord or outside of the spinal cord to directly o ...
s ( upper and lower motor neuron
Lower motor neurons (LMNs) are motor neurons located in either the anterior grey column, anterior nerve roots (spinal lower motor neurons) or the cranial nerve nuclei of the brainstem and cranial nerves with motor function (cranial nerve lower ...
s), and cerebellar Purkinje cell
Purkinje cells or Purkinje neurons, named for Czech physiologist Jan Evangelista Purkyně who identified them in 1837, are a unique type of prominent, large neuron located in the Cerebellum, cerebellar Cortex (anatomy), cortex of the brain. Wi ...
s. Betz cells are the largest cells (by size of cell body) in the nervous system. The adult human brain is estimated to contain 86±8 billion neurons, with a roughly equal number (85±10 billion) of non-neuronal cells. Out of these neurons, 16 billion (19%) are located in the cerebral cortex, and 69 billion (80%) are in the cerebellum.
Types of glial cell are astrocyte
Astrocytes (from Ancient Greek , , "star" and , , "cavity", "cell"), also known collectively as astroglia, are characteristic star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord. They perform many functions, including biochemical control of en ...
s (including Bergmann glia), oligodendrocyte
Oligodendrocytes (), also known as oligodendroglia, are a type of neuroglia whose main function is to provide the myelin sheath to neuronal axons in the central nervous system (CNS). Myelination gives metabolic support to, and insulates the axons ...
s, ependymal cell
The ependyma is the thin neuroepithelial ( simple columnar ciliated epithelium) lining of the ventricular system of the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord. The ependyma is one of the four types of neuroglia in the central nervous sys ...
s (including tanycytes), radial glial cell
Radial glial cells, or radial glial progenitor cells (RGPs), are Bipolar neuron, bipolar-shaped progenitor cells that are responsible for producing all of the neurons in the cerebral cortex. RGPs also produce certain lineages of glia, including as ...
s, microglia
Microglia are a type of glia, glial cell located throughout the brain and spinal cord of the central nervous system (CNS). Microglia account for about around 5–10% of cells found within the brain. As the resident macrophage cells, they act as t ...
, and a subtype of oligodendrocyte progenitor cells. Astrocytes are the largest of the glial cells. They are stellate cell
Stellate cells are neurons in the central nervous system, named for their star-like shape formed by dendritic processes radiating from the cell body. These cells play significant roles in various brain functions, including inhibition in the ce ...
s with many processes radiating from their cell bodies. Some of these processes end as perivascular endfeet on capillary
A capillary is a small blood vessel, from 5 to 10 micrometres in diameter, and is part of the microcirculation system. Capillaries are microvessels and the smallest blood vessels in the body. They are composed of only the tunica intima (the inn ...
walls. The glia limitans of the cortex is made up of astrocyte endfeet processes that serve in part to contain the cells of the brain.
Mast cell
A mast cell (also known as a mastocyte or a labrocyte) is a resident cell of connective tissue that contains many granules rich in histamine and heparin. Specifically, it is a type of granulocyte derived from the myeloid stem cell that is a p ...
s are white blood cell
White blood cells (scientific name leukocytes), also called immune cells or immunocytes, are cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign entities. White blood cells are genera ...
s that interact in the neuroimmune system
The neuroimmune system is a system of structures and processes involving the biochemical and electrophysiological interactions between the nervous system and immune system which protect neurons from pathogens. It serves to protect neurons against ...
in the brain. Mast cells in the central nervous system are present in a number of structures including the meninges; they mediate neuroimmune responses in inflammatory conditions and help to maintain the blood–brain barrier, particularly in brain regions where the barrier is absent. Mast cells serve the same general functions in the body and central nervous system, such as effecting or regulating allergic responses, innate
{{Short pages monitorHarvey Cushing (1869–1939) is recognised as the first proficient neurosurgery, brain surgeon in the world. In 1937, Walter Dandy began the practice of vascular neurosurgery by performing the first surgical clipping of an intracranial aneurysm.
Brain facts and figures
– Washington.edu
Human brain
– National Geographic {{DEFAULTSORT:Human Brain Brain, Human anatomy by organ, Brain Brain anatomy
Comparative anatomy
The human brain has many properties that are common to all vertebrate brains. Many of its features are common to all mammalian brains, most notably a six-layered cerebral cortex and a set of associated structures, including the hippocampus andamygdala
The amygdala (; : amygdalae or amygdalas; also '; Latin from Greek language, Greek, , ', 'almond', 'tonsil') is a paired nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclear complex present in the Cerebral hemisphere, cerebral hemispheres of vertebrates. It is c ...
. The cortex is proportionally larger in humans than in many other mammals. Humans have more association cortex, sensory and motor parts than smaller mammals such as the rat and the cat.
As a primate brain, the human brain has a much larger cerebral cortex, in proportion to body size, than most mammals, and a highly developed visual system.
As a hominidae, hominid brain, the human brain is substantially enlarged even in comparison to the brain of a typical monkey. The sequence of human evolution from ''Australopithecus'' (four million years ago) to human, ''Homo sapiens'' (modern humans) was marked by a steady increase in brain size. As brain size increased, this altered the size and shape of the skull, from about 600 Cubic centimetre, cm3 in ''Homo habilis'' to an average of about 1520 cm3 in ''Homo neanderthalensis''. Differences in DNA, gene expression, and gene–environment interactions help explain the differences between the function of the human brain and other primates.
See also
*Outline of the human brain *Outline of neuroscience *Brain health and pollution *Cerebral atrophy *Cortical spreading depression *Evolution of human intelligence *Large-scale brain networks *Superficial veins of the brainReferences
Bibliography
* * * * * * * *Notes
External links
Brain facts and figures
– Washington.edu
Human brain
– National Geographic {{DEFAULTSORT:Human Brain Brain, Human anatomy by organ, Brain Brain anatomy