|
Cortex (anatomy)
In anatomy and zoology, the cortex (plural cortices) is the outermost (or superficial) layer of an organ. Organs with well-defined cortical layers include kidneys, adrenal glands, ovaries, the thymus, and portions of the brain, including the cerebral cortex, the best-known of all cortices. Etymology The word is of Latin origin and means bark, rind, shell or husk. Notable examples * The renal cortex, between the renal capsule and the renal medulla; assists in ultrafiltration * The adrenal cortex, situated along the perimeter of the adrenal gland; mediates the stress response through the production of various hormones * The thymic cortex, mainly composed of lymphocytes; functions as a site for somatic recombination of T cell receptors, and positive selection * The cerebral cortex, the outer layer of the cerebrum, plays a key role in memory, attention, perceptual awareness, thought, language, and consciousness. * Cortical bone is the hard outer layer of bone; di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fight-or-flight Response
The fight-or-flight or the fight-flight-or-freeze response (also called hyperarousal or the acute stress response) is a physiological reaction that occurs in response to a perceived harmful event, attack, or threat to survival. It was first described by Walter Bradford Cannon. His theory states that animals react to threats with a general discharge of the sympathetic nervous system, preparing the animal for fighting or fleeing. More specifically, the adrenal medulla produces a hormonal cascade that results in the secretion of catecholamines, especially norepinephrine and epinephrine. The hormones estrogen, testosterone, and cortisol, as well as the neurotransmitters dopamine and serotonin, also affect how organisms react to stress. The hormone osteocalcin might also play a part. This response is recognised as the first stage of the general adaptation syndrome that regulates stress responses among vertebrates and other organisms. Name Originally understood as the fig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebellum
The cerebellum (Latin for "little brain") is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as or even larger. In humans, the cerebellum plays an important role in motor control. It may also be involved in some cognitive functions such as attention and language as well as emotional control such as regulating fear and pleasure responses, but its movement-related functions are the most solidly established. The human cerebellum does not initiate movement, but contributes to coordination, precision, and accurate timing: it receives input from sensory systems of the spinal cord and from other parts of the brain, and integrates these inputs to fine-tune motor activity. Cerebellar damage produces disorders in fine movement, equilibrium, posture, and motor learning in humans. Anatomically, the human cerebellum has the appearance of a separate structure attached to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebellar Cortex
The cerebellum (Latin for "little brain") is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as or even larger. In humans, the cerebellum plays an important role in motor control. It may also be involved in some cognitive functions such as attention and language as well as emotional control such as regulating fear and pleasure responses, but its movement-related functions are the most solidly established. The human cerebellum does not initiate movement, but contributes to coordination, precision, and accurate timing: it receives input from sensory systems of the spinal cord and from other parts of the brain, and integrates these inputs to fine-tune motor activity. Cerebellar damage produces disorders in fine movement, equilibrium, posture, and motor learning in humans. Anatomically, the human cerebellum has the appearance of a separate structure attached to the bott ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somatosensory Cortex
In physiology, the somatosensory system is the network of neural structures in the brain and body that produce the perception of touch ( haptic perception), as well as temperature ( thermoception), body position ( proprioception), and pain. It is a subset of the sensory nervous system, which also represents visual, auditory, olfactory, and gustatory stimuli. Somatosensation begins when mechano- and thermosensitive structures in the skin or internal organs sense physical stimuli such as pressure on the skin (see mechanotransduction, nociception). Activation of these structures, or receptors, leads to activation of peripheral sensory neurons that convey signals to the spinal cord as patterns of action potentials. Sensory information is then processed locally in the spinal cord to drive reflexes, and is also conveyed to the brain for conscious perception of touch and proprioception. Note, somatosensory information from the face and head enters the brain through peripher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
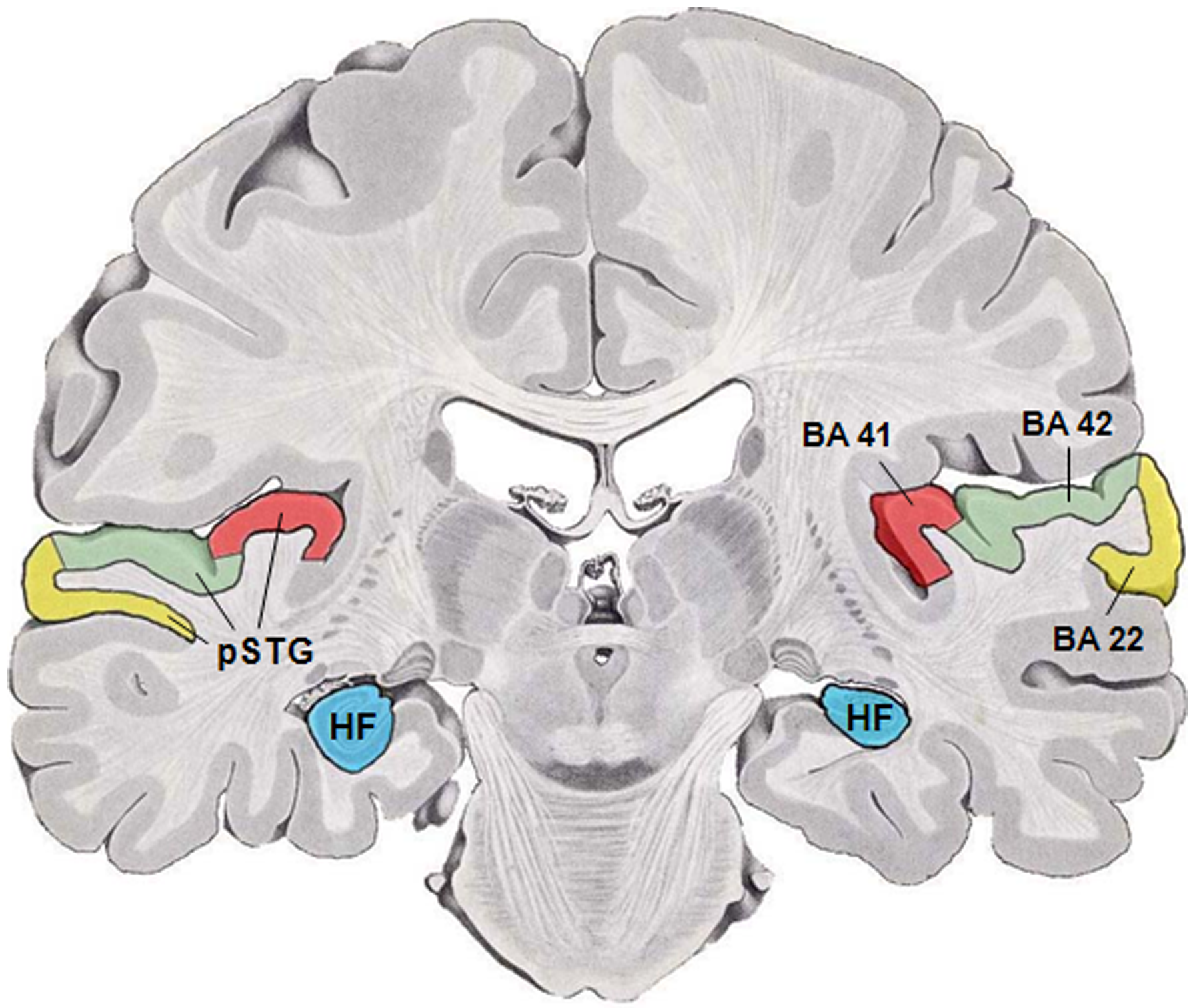
Auditory Cortex
The auditory cortex is the part of the temporal lobe that processes auditory information in humans and many other vertebrates. It is a part of the auditory system, performing basic and higher functions in hearing, such as possible relations to language switching.Cf. Pickles, James O. (2012). ''An Introduction to the Physiology of Hearing'' (4th ed.). Bingley, UK: Emerald Group Publishing Limited, p. 238. It is located bilaterally, roughly at the upper sides of the temporal lobes – in humans, curving down and onto the medial surface, on the superior temporal plane, within the lateral sulcus and comprising parts of the transverse temporal gyri, and the superior temporal gyrus, including the planum polare and planum temporale (roughly Brodmann areas 41 and 42, and partially 22). The auditory cortex takes part in the spectrotemporal, meaning involving time and frequency, analysis of the inputs passed on from the ear. The cortex then filters and passes on the information to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Cortex
The visual cortex of the brain is the area of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information. It is located in the occipital lobe. Sensory input originating from the eyes travels through the lateral geniculate nucleus in the thalamus and then reaches the visual cortex. The area of the visual cortex that receives the sensory input from the lateral geniculate nucleus is the primary visual cortex, also known as visual area 1 ( V1), Brodmann area 17, or the striate cortex. The extrastriate areas consist of visual areas 2, 3, 4, and 5 (also known as V2, V3, V4, and V5, or Brodmann area 18 and all Brodmann area 19). Both hemispheres of the brain include a visual cortex; the visual cortex in the left hemisphere receives signals from the right visual field, and the visual cortex in the right hemisphere receives signals from the left visual field. Introduction The primary visual cortex (V1) is located in and around the calcarine fissure in the occipital lobe. Each hemisphe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymph Node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that include B and T cells. Lymph nodes are important for the proper functioning of the immune system, acting as filters for foreign particles including cancer cells, but have no detoxification function. In the lymphatic system a lymph node is a secondary lymphoid organ. A lymph node is enclosed in a fibrous capsule and is made up of an outer cortex and an inner medulla. Lymph nodes become inflamed or enlarged in various diseases, which may range from trivial throat infections to life-threatening cancers. The condition of lymph nodes is very important in cancer staging, which decides the treatment to be used and determines the prognosis. Lymphadenopathy refers to glands that are enlarged or swollen. When inflamed or enlarged, lymph nodes ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovarian Cortex
The ovarian cortex is the outer portion of the ovary. The ovarian follicles are located within the ovarian cortex. The ovarian cortex is made up of connective tissue. Ovarian cortex tissue transplant has been performed to treat infertility Infertility is the inability of a person, animal or plant to reproduce by natural means. It is usually not the natural state of a healthy adult, except notably among certain eusocial species (mostly haplodiploid insects). It is the normal st .... References External links * Mammal female reproductive system {{Portal bar, Anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancellous Bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, and enable mobility. Bones come in a variety of shapes and sizes and have complex internal and external structures. They are lightweight yet strong and hard and serve multiple functions. Bone tissue (osseous tissue), which is also called bone in the uncountable sense of that word, is hard tissue, a type of specialized connective tissue. It has a honeycomb-like matrix internally, which helps to give the bone rigidity. Bone tissue is made up of different types of bone cells. Osteoblasts and osteocytes are involved in the formation and mineralization of bone; osteoclasts are involved in the resorption of bone tissue. Modified (flattened) osteoblasts become the lining cells that form a protective layer on the bone surface. The mineralized m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cortical Bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, and enable mobility. Bones come in a variety of shapes and sizes and have complex internal and external structures. They are lightweight yet strong and hard and serve multiple functions. Bone tissue (osseous tissue), which is also called bone in the uncountable sense of that word, is hard tissue, a type of specialized connective tissue. It has a honeycomb-like matrix internally, which helps to give the bone rigidity. Bone tissue is made up of different types of bone cells. Osteoblasts and osteocytes are involved in the formation and mineralization of bone; osteoclasts are involved in the resorption of bone tissue. Modified (flattened) osteoblasts become the lining cells that form a protective layer on the bone surface. The mineraliz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thymocyte
A Thymocyte is an immune cell present in the thymus, before it undergoes transformation into a T cell. Thymocytes are produced as stem cells in the bone marrow and reach the thymus via the blood. Thymopoiesis describes the process which turns thymocytes into mature T cells according to either negative or positive selection. This selection process is vitally important in shaping the population of thymocytes into a peripheral pool of T cells that are able to respond to foreign pathogens but remain tolerant towards the body's own antigens. Positive selection selects cells which are able to bind MHC class I or II molecules with at least a weak affinity. This eliminates (by a process called "death by neglect") those T cells which would be non-functional due to an inability to bind MHC. Negative selection destroys thymocytes with a high affinity for self peptides or MHC. This eliminates cells which would direct immune responses towards self-proteins in the periphery. Negative selection i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)

