|
Arachnoid Mater
The arachnoid mater (or simply arachnoid) is one of the three meninges, the protective membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord. It is so named because of its resemblance to a spider web. The arachnoid mater is a derivative of the neural crest mesoectoderm in the embryo. Structure The arachnoid mater is interposed between the two other meninges, the more superficial (closer to the surface) and much thicker dura mater and the deeper pia mater, from which it is separated by the subarachnoid space. The delicate arachnoid layer is not attached to the inside of the dura but against it, and surrounds the brain and spinal cord. It does not line the brain down into its sulci (folds), as does the pia mater, with the exception of the longitudinal fissure, which divides the left and right cerebral hemispheres. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flows under the arachnoid in the subarachnoid space, within a meshwork of trabeculae which span between the arachnoid and the pia. The arachnoid ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacral Vertebra
The sacrum (: sacra or sacrums), in human anatomy, is a triangular bone at the base of the spine that forms by the fusing of the sacral vertebrae (S1S5) between ages 18 and 30. The sacrum situates at the upper, back part of the pelvic cavity, between the two wings of the pelvis. It forms joints with four other bones. The two projections at the sides of the sacrum are called the alae (wings), and articulate with the ilium at the L-shaped sacroiliac joints. The upper part of the sacrum connects with the last lumbar vertebra (L5), and its lower part with the coccyx (tailbone) via the sacral and coccygeal cornua. The sacrum has three different surfaces which are shaped to accommodate surrounding pelvic structures. Overall, it is concave (curved upon itself). The base of the sacrum, the broadest and uppermost part, is tilted forward as the sacral promontory internally. The central part is curved outward toward the posterior, allowing greater room for the pelvic cavity. In all ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
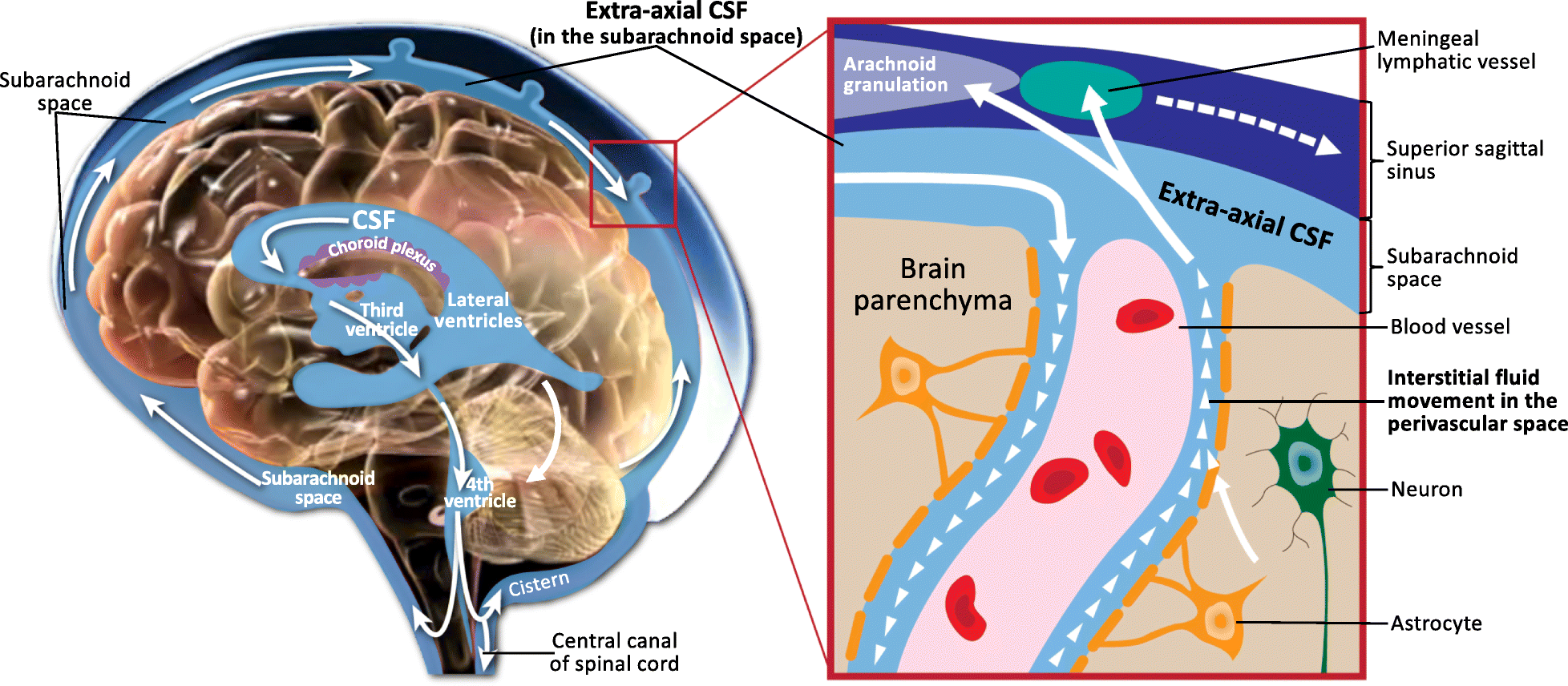
Virchow-Robin Space
A perivascular space, also known as a Virchow–Robin space, is a fluid-filled space surrounding certain blood vessels in several organs, including the brain, potentially having an immunological function, but more broadly a dispersive role for neural and blood-derived messengers. The brain pia mater is reflected from the surface of the brain onto the surface of blood vessels in the subarachnoid space. In the brain, ''perivascular cuffs'' are regions of leukocyte aggregation in the perivascular spaces, usually found in patients with viral encephalitis. Perivascular spaces vary in dimension according to the type of blood vessel. In the brain where most capillaries have an imperceptible perivascular space, select structures of the brain, such as the circumventricular organs, are notable for having large perivascular spaces surrounding highly permeable capillaries, as observed by microscopy. The median eminence, a brain structure at the base of the hypothalamus, contains capillar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medulla Spinalis
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal cord is hollow and contains a structure called the central canal, which contains cerebrospinal fluid. The spinal cord is also covered by meninges and enclosed by the neural arches. Together, the brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system. In humans, the spinal cord is a continuation of the brainstem and anatomically begins at the occipital bone, passing out of the foramen magnum and then enters the spinal canal at the beginning of the cervical vertebrae. The spinal cord extends down to between the first and second lumbar vertebrae, where it tapers to become the cauda equina. The enclosing bony vertebral column protects the relatively shorter spinal cord. It is around long in adult men and around long in adult women. The diam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerard Blasius
Gerard "Gerrit" Leendertszoon Blasius (1627–1682) was a Dutch physician and anatomist. He was born in Amsterdam and was the eldest son of Leonhard Blasius (died 1644), who had worked as an architect in Copenhagen. Gerard started his studies there, but the family moved to Leiden after his father died. Around 1655, Blasius became a physician in Amsterdam. In October 1659, he was appointed to the Athenaeum Illustre but without being paid. In the next year, he became Amsterdam's first professor in medicine. At his home or in the hospital, corpses were dissected. In 1661, he claimed the discovery of Stensen's duct made by his pupil Nicolas Stensen. Blasius had married Cornelia van Ottinga in 1653. His younger brother was the poet Joan Blasius. Blasius died in Amsterdam in 1682. Works A list of works: on |
Frederik Ruysch
Frederik Ruysch (; March 28, 1638 – February 22, 1731) was a Dutch botanist and anatomist. He is known for developing techniques for preserving anatomical specimens, which he used to create dioramas or scenes incorporating human parts. His anatomical preparations included over 2,000 anatomical, pathological, zoological, and botanical specimens, which were preserved by either drying or embalming. Ruysch is also known for his proof of valves in the lymphatic system, the vomeronasal organ in snakes, and ''arteria centralis oculi'' (the central artery of the eye). He was the first to describe the disease that is today known as Hirschsprung's disease, as well as several pathological conditions, including intracranial teratoma, enchondromatosis, and Majewski syndrome. Life Frederik Ruysch was born in The Hague as the son of a government functionary and started as the pupil of a druggist. Fascinated by anatomy, he studied at the university of Leiden, under Franciscus Sylvius. His fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arachnoid Trabeculae
The arachnoid trabeculae (AT) are delicate strands of connective tissue that loosely connect the two innermost layers of the meninges – the arachnoid mater and the pia mater. " Encyclopædia Britannica. 2010. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. 09 Sep. 2010. They are found within the subarachnoid space where cerebrospinal fluid is also found. Arachnoid trabeculae are also known as subarachnoid trabeculae (SAT) or leptomeningeal trabeculae. Structure Human cranial arachnoid trabeculae are made mostly of[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arachne
Arachne (; from , cognate with Latin ) is the protagonist of a tale in classical mythology known primarily from the version told by the Roman poet Ovid (43 BCE–17 CE). In Book Six of his epic poem ''Metamorphoses'', Ovid recounts how the talented mortal Arachne challenged the goddess Minerva to a weaving contest. When Minerva could find no flaws in the tapestry Arachne had woven for the contest, the goddess became enraged and beat the girl with her shuttle. After Arachne hanged herself out of shame, she was transformed into a spider. The myth both provided an etiology of spiders' web-spinning abilities and was a cautionary tale about hubris. Biography According to the myth as recounted by Ovid, Arachne was a Lydian maiden who was the daughter of Idmon of Colophon, who was a famous dyer in purple. She was credited to have invented linen cloth and nets while her son Closter introduced the use of spindle in the manufacture of wool. She was said to have been a nati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Language
Greek (, ; , ) is an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language, constituting an independent Hellenic languages, Hellenic branch within the Indo-European language family. It is native to Greece, Cyprus, Italy (in Calabria and Salento), southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, Caucasus, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the list of languages by first written accounts, longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The Greek language holds a very important place in the history of the Western world. Beginning with the epics of Homer, ancient Greek literature includes many works of lasting importance in the European canon. Greek is also the language in which many of the foundational texts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choroid Plexus
The choroid plexus, or plica choroidea, is a plexus of cells that arises from the tela choroidea in each of the ventricles of the brain. Regions of the choroid plexus produce and secrete most of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of the central nervous system. The choroid plexus consists of modified ependymal cells surrounding a core of capillaries and loose connective tissue. Multiple cilia on the ependymal cells move to circulate the cerebrospinal fluid. Structure Location There is a choroid plexus in each of the four ventricles. In the lateral ventricles, it is found in the body, and continued in an enlarged amount in the atrium. There is no choroid plexus in the anterior horn. In the third ventricle, there is a small amount in the roof that is continuous with that in the body, via the interventricular foramina, the channels that connect the lateral ventricles with the third ventricle. A choroid plexus is in part of the roof of the fourth ventricle. Microana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibroblast
A fibroblast is a type of cell (biology), biological cell typically with a spindle shape that synthesizes the extracellular matrix and collagen, produces the structural framework (Stroma (tissue), stroma) for animal Tissue (biology), tissues, and plays a critical role in wound healing. Fibroblasts are the most common cells of connective tissue in animals. Structure Fibroblasts have a branched cytoplasm surrounding an elliptical, speckled cell nucleus, nucleus having two or more nucleoli. Active fibroblasts can be recognized by their abundant rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER). Inactive fibroblasts, called 'fibrocytes', are smaller, spindle-shaped, and have less RER. Although disjointed and scattered when covering large spaces, fibroblasts often locally align in parallel clusters when crowded together. Unlike the epithelial cells lining the body structures, fibroblasts do not form flat monolayers and are not restricted by a polarizing attachment to a basal lamina on one side, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pineal
The pineal gland (also known as the pineal body or epiphysis cerebri) is a small endocrine gland in the brain of most vertebrates. It produces melatonin, a serotonin-derived hormone, which modulates sleep patterns following the diurnal cycles. The shape of the gland resembles a pine cone, which gives it its name. The pineal gland is located in the epithalamus, near the center of the brain, between the two hemispheres, tucked in a groove where the two halves of the thalamus join. It is one of the neuroendocrine secretory circumventricular organs in which capillaries are mostly permeable to solutes in the blood. The pineal gland is present in almost all vertebrates, but is absent in protochordates in which there is a simple pineal homologue. The hagfish, archaic vertebrates, lack a pineal gland. In some species of amphibians and reptiles, the gland is linked to a light-sensing organ, variously called the parietal eye, the pineal eye or the third eye''.'' Reconstruction of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |