|
Ultradian Rhythm
In chronobiology, an ultradian rhythm is a recurrent period or cycle repeated throughout a 24-hour day. In contrast, circadian rhythms complete one cycle daily, while infradian rhythms such as the human menstrual cycle have periods longer than a day. The ''Oxford English Dictionary's'' definition of ''Ultradian'' specifies that it refers to cycles with a period shorter than a day but longer than an hour. The descriptive term ultradian is used in sleep research in reference to the 90–120 minute cycling of the sleep stages during human sleep. There is a circasemidian rhythm in body temperature and cognitive function which is technically ultradian. However, this appears to be the first harmonic of the circadian rhythm of each and not an endogenous rhythm with its own rhythm generator. Other ultradian rhythms include blood circulation, blinking, pulse, hormonal secretions such as growth hormone, heart rate, thermoregulation, micturition, bowel activity, nostril dilation, appeti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptin Circadian Cycle (24 Hours)
Leptin (from Greek λεπτός ''leptos'', "thin" or "light" or "small") is a hormone predominantly made by adipose cells and enterocytes in the small intestine that helps to regulate energy balance by inhibiting hunger, which in turn diminishes fat storage in adipocytes. Leptin is coded for by the ''LEP'' gene. Leptin acts on cell receptors in the arcuate and ventromedial nuclei, as well as other parts of the hypothalamus and dopaminergic neurons of the ventral tegmental area, consequently mediating feeding. Although regulation of fat stores is deemed to be the primary function of leptin, it also plays a role in other physiological processes, as evidenced by its many sites of synthesis other than fat cells, and the many cell types beyond hypothalamic cells that have leptin receptors. Many of these additional functions are yet to be fully defined. In obesity, a decreased sensitivity to leptin occurs (similar to insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes), resulting in an inabilit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermoregulation
Thermoregulation is the ability of an organism to keep its body temperature within certain boundaries, even when the surrounding temperature is very different. A thermoconforming organism, by contrast, simply adopts the surrounding temperature as its own body temperature, thus avoiding the need for internal thermoregulation. The internal thermoregulation process is one aspect of homeostasis: a state of dynamic stability in an organism's internal conditions, maintained far from thermal equilibrium with its environment (the study of such processes in zoology has been called physiological ecology). If the body is unable to maintain a normal temperature and it increases significantly above normal, a condition known as hyperthermia occurs. Humans may also experience lethal hyperthermia when the wet bulb temperature is sustained above for six hours. The opposite condition, when body temperature decreases below normal levels, is known as hypothermia. It results when the homeostatic c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronobiology
Chronobiology is a field of biology that examines timing processes, including periodic (cyclic) phenomena in living organisms, such as their adaptation to solar- and lunar-related rhythms. These cycles are known as biological rhythms. Chronobiology comes from the ancient Greek χρόνος (''chrónos'', meaning "time"), and biology, which pertains to the study, or science, of life. The related terms ''chronomics'' and ''chronome'' have been used in some cases to describe either the molecular mechanisms involved in chronobiological phenomena or the more quantitative aspects of chronobiology, particularly where comparison of cycles between organisms is required. Chronobiological studies include but are not limited to comparative anatomy, physiology, genetics, molecular biology and behavior of organisms related to their biological rhythms. Other aspects include epigenetics, development, reproduction, ecology and evolution. The subject Chronobiology studies variations of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basic Rest-activity Cycle
BASIC (Beginners' All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code) is a family of general-purpose, high-level programming languages designed for ease of use. The original version was created by John G. Kemeny and Thomas E. Kurtz at Dartmouth College in 1963. They wanted to enable students in non-scientific fields to use computers. At the time, nearly all computers required writing custom software, which only scientists and mathematicians tended to learn. In addition to the program language, Kemeny and Kurtz developed the Dartmouth Time Sharing System (DTSS), which allowed multiple users to edit and run BASIC programs simultaneously on remote terminals. This general model became very popular on minicomputer systems like the PDP-11 and Data General Nova in the late 1960s and early 1970s. Hewlett-Packard produced an entire computer line for this method of operation, introducing the HP2000 series in the late 1960s and continuing sales into the 1980s. Many early video games trace their hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
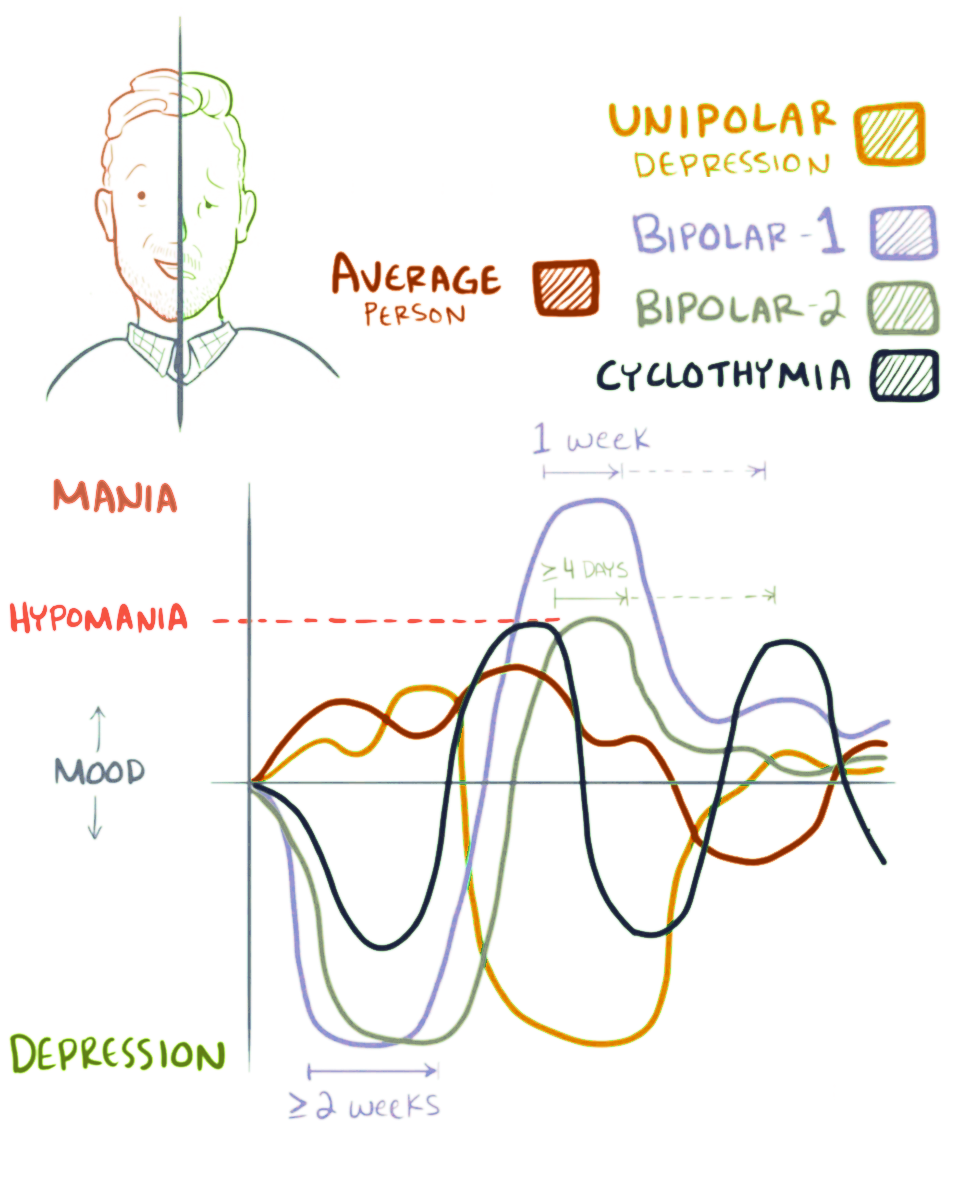
Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder, previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of depression and periods of abnormally elevated mood that last from days to weeks each. If the elevated mood is severe or associated with psychosis, it is called mania; if it is less severe, it is called hypomania. During mania, an individual behaves or feels abnormally energetic, happy or irritable, and they often make impulsive decisions with little regard for the consequences. There is usually also a reduced need for sleep during manic phases. During periods of depression, the individual may experience crying and have a negative outlook on life and poor eye contact with others. The risk of suicide is high; over a period of 20 years, 6% of those with bipolar disorder died by suicide, while 30–40% engaged in self-harm. Other mental health issues, such as anxiety disorders and substance use disorders, are commonly associated with bipolar disorder. While the causes of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder, previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of depression and periods of abnormally elevated mood that last from days to weeks each. If the elevated mood is severe or associated with psychosis, it is called mania; if it is less severe, it is called hypomania. During mania, an individual behaves or feels abnormally energetic, happy or irritable, and they often make impulsive decisions with little regard for the consequences. There is usually also a reduced need for sleep during manic phases. During periods of depression, the individual may experience crying and have a negative outlook on life and poor eye contact with others. The risk of suicide is high; over a period of 20 years, 6% of those with bipolar disorder died by suicide, while 30–40% engaged in self-harm. Other mental health issues, such as anxiety disorders and substance use disorders, are commonly associated with bipolar disorder. While the causes of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infradian
In chronobiology, an infradian rhythm is a rhythm with a period longer than the period of a circadian rhythm, i.e., with a frequency of less than one cycle in 24 hours. Some examples of infradian rhythms in mammals include menstruation, breeding, migration, hibernation, molting and fur or hair growth, and tidal or seasonal rhythms. In contrast, ultradian rhythms have periods shorter than the period of a circadian rhythm. Several infradian rhythms are known to be caused by hormone stimulation or exogenous factors. For example, seasonal depression, an example of an infradian rhythm occurring once a year, can be caused by the systematic lowering of light levels during the winter. See also * Photoperiodicity A circadian rhythm (), or circadian cycle, is a natural, internal process that regulates the sleep–wake cycle and repeats roughly every 24 hours. It can refer to any process that originates within an organism (i.e., Endogeny (biology), endogeno ... References Chronobio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corticotropin-releasing Hormone
Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) (also known as corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) or corticoliberin; corticotropin may also be spelled corticotrophin) is a peptide hormone involved in stress (biology), stress responses. It is a releasing hormone that belongs to corticotropin-releasing factor family. In humans, it is encoded by the ''CRH'' gene. Its main function is the stimulation of the pituitary synthesis of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), as part of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis (HPA axis). Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) is a 41-amino acid peptide derived from a 196-amino acid preprohormone. CRH is secreted by the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) of the hypothalamus in response to stress (biological), stress. Increased CRH production has been observed to be associated with Alzheimer's disease and major depression, and autosomal recessive hypothalamic corticotropin deficiency has multiple and potentially fatal metabolic consequences including hypo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuropeptide Y
Neuropeptide Y (NPY) is a 36 amino-acid neuropeptide that is involved in various physiological and homeostatic processes in both the central and peripheral nervous systems. NPY has been identified as the most abundant peptide present in the mammalian central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord. It is secreted alongside other neurotransmitters such as GABA and glutamate. In the autonomic system it is produced mainly by neurons of the sympathetic nervous system and serves as a strong vasoconstrictor and also causes growth of fat tissue. In the brain, it is produced in various locations including the hypothalamus, and is thought to have several functions, including: increasing food intake and storage of energy as fat, reducing anxiety and stress, reducing pain perception, affecting the circadian rhythm, reducing voluntary alcohol intake, lowering blood pressure, and controlling epileptic seizures. Function Neuropeptide Y has been identified as bei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arousal
Arousal is the physiological and psychological state of being awoken or of sense organs stimulated to a point of perception. It involves activation of the ascending reticular activating system (ARAS) in the brain, which mediates wakefulness, the autonomic nervous system, and the endocrine system, leading to increased heart rate and blood pressure and a condition of sensory alertness, desire, mobility, and readiness to respond. Arousal is mediated by several neural systems. Wakefulness is regulated by the ARAS, which is composed of projections from five major neurotransmitter systems that originate in the brainstem and form connections extending throughout the cortex; activity within the ARAS is regulated by neurons that release the neurotransmitters acetylcholine, norepinephrine, dopamine, histamine, and serotonin. Activation of these neurons produces an increase in cortical activity and subsequently alertness. Arousal is important in regulating consciousness, attention, alertn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appetite
Appetite is the desire to eat food items, usually due to hunger. Appealing foods can stimulate appetite even when hunger is absent, although appetite can be greatly reduced by satiety. Appetite exists in all higher life-forms, and serves to regulate adequate energy intake to maintain metabolic needs. It is regulated by a close interplay between the digestive tract, adipose tissue and the brain. Appetite has a relationship with every individual's behavior. Appetitive behaviour also known as approach behaviour, and consummatory behaviour, are the only processes that involve energy intake, whereas all other behaviours affect the release of energy. When stressed, appetite levels may increase and result in an increase of food intake. Decreased desire to eat is termed anorexia, while polyphagia (or "hyperphagia") is increased eating. Dysregulation of appetite contributes to anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, cachexia, overeating, and binge eating disorder. Role in disease A limited ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasal Cycle
The nasal cycle is the unconscious alternating partial congestion and decongestion of the nasal cavities in humans and other animals. This results in greater airflow through one nostril with periodic alternation between the nostrils. It is a physiological congestion of the nasal conchae, also called the nasal turbinates (curled bony projections within the nasal cavities), due to selective activation of one half of the autonomic nervous system by the hypothalamus. It should not be confused with pathological nasal congestion. Description The nasal cycle was studied and discussed in the ancient Indian yoga of literature of pranayama. In the modern western literature, it was first described by the German physician Richard Kayser in 1895. In 1927, Heetderks described the alternating turgescence of the inferior turbinates in 80% of a normal population. According to Heetderks, the cycle is the result of alternating congestion and decongestion of the nasal conchae or turbinates, pred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)