Electronic music broadly is a group of
music genre
A music genre is a conventional category that identifies some pieces of music as belonging to a shared tradition or set of conventions. Genre is to be distinguished from musical form and musical style, although in practice these terms are sometim ...
s that employ
electronic musical instrument
An electronic musical instrument or electrophone is a musical instrument that produces sound using electronics, electronic circuitry. Such an instrument sounds by outputting an electrical, electronic or digital audio signal that ultimately is ...
s, circuitry-based
music technology
Music technology is the study or the use of any device, mechanism, machine or tool by a musician or composer to make or perform music; to musical composition, compose, music notation, notate, playback or record songs or pieces; or to Music infor ...
and software, or general-purpose
electronics
Electronics is a scientific and engineering discipline that studies and applies the principles of physics to design, create, and operate devices that manipulate electrons and other Electric charge, electrically charged particles. It is a subfield ...
(such as
personal computer
A personal computer, commonly referred to as PC or computer, is a computer designed for individual use. It is typically used for tasks such as Word processor, word processing, web browser, internet browsing, email, multimedia playback, and PC ...
s) in its creation. It includes both music made using electronic and electromechanical means (
electroacoustic music
Electroacoustic music is a Music genre, genre of Western art music in which composers use recording technology and audio signal processing to manipulate the timbres of Acoustics, acoustic sounds in the creation of pieces of music. It originated a ...
). Pure electronic instruments depend entirely on circuitry-based sound generation, for instance using devices such as an
electronic oscillator
An electronic oscillator is an electronic circuit that produces a periodic, oscillating or alternating current (AC) signal, usually a sine wave, square wave or a triangle wave, powered by a direct current (DC) source. Oscillators are found ...
,
theremin
The theremin (; originally known as the ætherphone, etherphone, thereminophone or termenvox/thereminvox) is an electronic musical instrument controlled without physical contact by the performer (who is known as a thereminist). It is named aft ...
, or
synthesizer
A synthesizer (also synthesiser or synth) is an electronic musical instrument that generates audio signals. Synthesizers typically create sounds by generating waveforms through methods including subtractive synthesis, additive synthesis a ...
: no
acoustic wave
Acoustic waves are types of waves that propagate through matter—such as gas, liquid, and/or solids—by causing the particles of the medium to compress and expand. These waves carry energy and are characterized by properties like acoustic pres ...
s need to be previously generated by mechanical means and then converted into electrical signals. On the other hand, electromechanical instruments have mechanical parts such as strings or hammers that generate the sound waves, together with electric elements including
magnetic pickups,
power amplifier
An audio power amplifier (or power amp) amplifies low-power electronic audio signals, such as the signal from a radio receiver or an electric guitar pickup, to a level that is high enough for driving loudspeakers or headphones. Audio power a ...
s and
loudspeaker
A loudspeaker (commonly referred to as a speaker or, more fully, a speaker system) is a combination of one or more speaker drivers, an enclosure, and electrical connections (possibly including a crossover network). The speaker driver is an ...
s that convert the acoustic waves into electrical signals, process them and convert them back into sound waves. Such electromechanical devices include the
telharmonium
The Telharmonium (also known as the Dynamophone) was an early electrical organ, developed by Thaddeus Cahill c. 1896 and patented in 1897.
, filed 1896-02-04.
The electrical signal from the Telharmonium was transmitted over wires; it was hea ...
,
Hammond organ
The Hammond organ is an electric organ invented by Laurens Hammond and John M. Hanert, first manufactured in 1935. Multiple models have been produced, most of which use sliding #Drawbars, drawbars to vary sounds. Until 1975, sound was created ...
,
electric piano
An electric piano is a musical instrument that has a piano-style musical keyboard, where sound is produced by means of mechanical hammers striking metal strings or reeds or wire tines, which leads to vibrations which are then converted into ele ...
and
electric guitar
An electric guitar is a guitar that requires external electric Guitar amplifier, sound amplification in order to be heard at typical performance volumes, unlike a standard acoustic guitar. It uses one or more pickup (music technology), pickups ...
.
["The stuff of electronic music is electrically produced or modified sounds. ... two basic definitions will help put some of the historical discussion in its place: purely electronic music versus ]electroacoustic music
Electroacoustic music is a Music genre, genre of Western art music in which composers use recording technology and audio signal processing to manipulate the timbres of Acoustics, acoustic sounds in the creation of pieces of music. It originated a ...
" ()[Electroacoustic music may also use electronic effect units to change sounds from the natural world, such as the sound of waves on a beach or bird calls. All types of sounds can be used as source material for this music. Electroacoustic performers and composers use microphones, tape recorders, and digital samplers to make live or recorded music. During live performances, natural sounds are modified in real-time using electronic effects and ]audio console
A mixing console or mixing desk is an electronic device for mixing audio signals, used in sound recording and reproduction and sound reinforcement systems. Inputs to the console include microphones, signals from electric or electronic instr ...
s. The source of the sound can be anything from ambient noise (traffic, people talking) and nature sounds to live musicians playing conventional acoustic or electro-acoustic instruments ()
The first electronic musical devices were developed at the end of the 19th century. During the 1920s and 1930s, some electronic instruments were introduced and the first compositions featuring them were written. By the 1940s, magnetic audio tape allowed musicians to tape sounds and then modify them by changing the tape speed or direction, leading to the development of electroacoustic
tape music
Electroacoustic music is a genre of Western art music in which composers use recording technology and audio signal processing to manipulate the timbres of acoustic sounds in the creation of pieces of music. It originated around the middle of the ...
in the 1940s in Egypt and France.
Musique concrète
Musique concrète (; ): " problem for any translator of an academic work in French is that the language is relatively abstract and theoretical compared to English; one might even say that the mode of thinking itself tends to be more schematic ...
, created in Paris in 1948, was based on editing together recorded fragments of natural and industrial sounds. Music produced solely from electronic generators was first produced in Germany in 1953 by
Karlheinz Stockhausen
Karlheinz Stockhausen (; 22 August 1928 – 5 December 2007) was a German composer, widely acknowledged by critics as one of the most important but also controversial composers of the 20th and early 21st centuries. He is known for his groun ...
. Electronic music was also created in Japan and the United States beginning in the 1950s and
algorithmic composition
Algorithmic composition is the technique of using algorithms to create music.
Algorithms (or, at the very least, formal sets of rules) have been used to compose music for centuries; the procedures used to plot voice-leading in Western counterpo ...
with computers was first demonstrated in the same decade.
During the 1960s, digital
computer music
Computer music is the application of computing technology in music composition, to help human composers create new music or to have computers independently create music, such as with algorithmic composition programs. It includes the theory and ...
was pioneered, innovation in
live electronics took place, and Japanese electronic musical instruments began to influence the
music industry
The music industry are individuals and organizations that earn money by Songwriter, writing songs and musical compositions, creating and selling Sound recording and reproduction, recorded music and sheet music, presenting live music, concerts, ...
. In the early 1970s,
Moog synthesizer
The Moog synthesizer ( ) is a modular synthesizer invented by the American engineer Robert Moog in 1964. Moog's company, R. A. Moog Co., produced numerous models from 1965 to 1981, and again from 2014. It was the first commercial synthesizer ...
s and
drum machine
A drum machine is an electronic musical instrument that creates percussion sounds, drum beats, and patterns. Drum machines may imitate drum kits or other percussion instruments, or produce unique sounds, such as synthesized electronic tones. A d ...
s helped popularize synthesized electronic music. The 1970s also saw electronic music begin to have a significant influence on
popular music
Popular music is music with wide appeal that is typically distributed to large audiences through the music industry. These forms and styles can be enjoyed and performed by people with little or no musical training.Popular Music. (2015). ''Fun ...
, with the adoption of
polyphonic synthesizer
Polyphony is a property of musical instruments that means that they can play multiple independent melody lines simultaneously. Instruments featuring polyphony are said to be polyphonic. Instruments that are not capable of polyphony are monophon ...
s,
electronic drum
Electronic drums are a modern electronic musical instrument, primarily designed to serve as an alternative to an acoustic drum kit. Electronic drums consist of an electronic sound module which produces the Drum synthesiser, synthesized or Sampler ...
s, drum machines, and
turntables
A phonograph, later called a gramophone, and since the 1940s a record player, or more recently a turntable, is a device for the mechanical and analogue reproduction of sound. The sound vibration Waveform, waveforms are recorded as correspond ...
, through the emergence of genres such as
disco
Disco is a music genre, genre of dance music and a subculture that emerged in the late 1960s from the United States' urban nightclub, nightlife, particularly in African Americans, African-American, Italian-Americans, Italian-American, LGBTQ ...
,
krautrock
Krautrock (also called , German for ) is a broad genre of experimental rock that developed in Germany in the late 1960s and early 1970s. It originated among artists who blended elements of psychedelic rock, avant-garde composition, and electron ...
,
new wave,
synth-pop
Synth-pop (short for synthesizer pop; also called techno-pop; ) is a music genre that first became prominent in the late 1970s and features the synthesizer as the dominant musical instrument. It was prefigured in the 1960s and early 1970s b ...
,
hip hop
Hip-hop or hip hop (originally disco rap) is a popular music genre that emerged in the early 1970s from the African-American community of New York City. The style is characterized by its synthesis of a wide range of musical techniques. Hip- ...
, and
electronic dance music
Electronic dance music (EDM), also referred to as dance music or club music, is a broad range of percussive electronic music genres originally made for nightclubs, raves, and List of electronic dance music festivals, festivals. It is generally ...
(EDM). In the early 1980s, mass-produced
digital synthesizer
A digital synthesizer is a synthesizer that uses digital signal processing (DSP) techniques to make musical sounds, in contrast to older analog synthesizers, which produce music using analog electronics, and samplers, which play back digital rec ...
s such as the
Yamaha DX7
The Yamaha DX7 is a synthesizer manufactured by Yamaha Corporation from 1983 to 1989. It was the first successful digital synthesizer and is one of the best-selling synthesizers in history, selling more than 200,000 units.
In the early 1980s, th ...
became popular, and
MIDI
Musical Instrument Digital Interface (; MIDI) is an American-Japanese technical standard that describes a communication protocol, digital interface, and electrical connectors that connect a wide variety of electronic musical instruments, ...
(Musical Instrument Digital Interface) was developed. In the same decade, with a greater reliance on synthesizers and the adoption of programmable drum machines, electronic popular music came to the fore. During the 1990s, with the proliferation of increasingly affordable music technology, electronic music production became an established part of popular culture. In Berlin starting in 1989, the
Love Parade
The Love Parade () was an electronic dance music festival and technoparade that originated in 1989 in West Berlin, Germany. It was held annually in Berlin from 1989 to 2003 and in 2006, then from 2007 to 2010 in the Ruhr region. Events scheduled ...
became the largest street party with over 1 million visitors, inspiring other such popular celebrations of electronic music.
Contemporary electronic music includes many varieties and ranges from
experimental art music to popular forms such as electronic dance music. In recent years, electronic music has gained popularity in the Middle East, with artists from Iran and Turkey blending traditional instruments with ambient and techno influences. Pop electronic music is most recognizable in its 4/4 form and more connected with the mainstream than preceding forms which were popular in niche markets.
Origins: late 19th century to early 20th century
At the turn of the 20th century, experimentation with
emerging electronics led to the first
electronic musical instrument
An electronic musical instrument or electrophone is a musical instrument that produces sound using electronics, electronic circuitry. Such an instrument sounds by outputting an electrical, electronic or digital audio signal that ultimately is ...
s.
These initial inventions were not sold, but were instead used in demonstrations and public performances. The audiences were presented with reproductions of existing music instead of new compositions for the instruments. While some were considered novelties and produced simple tones, the
Telharmonium
The Telharmonium (also known as the Dynamophone) was an early electrical organ, developed by Thaddeus Cahill c. 1896 and patented in 1897.
, filed 1896-02-04.
The electrical signal from the Telharmonium was transmitted over wires; it was hea ...
synthesized the sound of several orchestral instruments with reasonable precision. It achieved viable public interest and made commercial progress into
streaming music
A music streaming service is a type of online streaming media service that focuses primarily on music, and sometimes other forms of digital audio content such as podcasts. These services are usually subscription-based services allowing users to st ...
through
telephone network
A telephone network is a telecommunications network that connects telephones, which allows telephone calls between two or more parties, as well as newer features such as fax and internet. The idea was revolutionized in the 1920s, as more and more ...
s.
Critics of musical conventions at the time saw promise in these developments.
Ferruccio Busoni
Ferruccio Busoni (1 April 1866 – 27 July 1924) was an Italian composer, pianist, conductor, editor, writer, and teacher. His international career and reputation led him to work closely with many of the leading musicians, artists and literary ...
encouraged the composition of
microtonal music
Microtonality is the use in music of microtones — intervals smaller than a semitone, also called "microintervals". It may also be extended to include any music using intervals not found in the customary Western tuning of twelve equal interv ...
allowed for by electronic instruments. He predicted the use of machines in future music, writing the influential ''Sketch of a New Esthetic of Music'' (1907).
Futurists
Futurists (also known as futurologists, prospectivists, foresight practitioners and horizon scanners) are people whose specialty or interest is futures studies or futurology or the attempt to systematically explore predictions and possibilities ...
such as
Francesco Balilla Pratella and
Luigi Russolo
Luigi Carlo Filippo Russolo (30 April 1885 – 4 February 1947) was an Italian Futurist painter, composer, builder of experimental musical instruments, and the author of the manifesto '' The Art of Noises'' (1913). Russolo completed his second ...
began composing
music with acoustic noise to evoke the sound of
machinery
A machine is a physical system that uses power to apply forces and control movement to perform an action. The term is commonly applied to artificial devices, such as those employing engines or motors, but also to natural biological macromolec ...
. They predicted expansions in
timbre
In music, timbre (), also known as tone color or tone quality (from psychoacoustics), is the perceived sound of a musical note, sound or tone. Timbre distinguishes sounds according to their source, such as choir voices and musical instrument ...
allowed for by electronics in the influential manifesto ''
The Art of Noises
''The Art of Noises'' () is a Futurist manifesto written by Luigi Russolo in a 1913 letter to friend and Futurist composer Francesco Balilla Pratella. In it, Russolo argues that the human ear has become accustomed to the speed, energy, and n ...
'' (1913).
[.]
Early compositions

Developments of the
vacuum tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, thermionic valve (British usage), or tube (North America) is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric voltage, potential difference has been applied. It ...
led to electronic instruments that were smaller,
amplified, and more practical for performance.
In particular, the
theremin
The theremin (; originally known as the ætherphone, etherphone, thereminophone or termenvox/thereminvox) is an electronic musical instrument controlled without physical contact by the performer (who is known as a thereminist). It is named aft ...
,
ondes Martenot
The ondes Martenot ( ; , ) or ondes musicales () is an early electronic musical instrument. It is played with a lateral-vibrato Keyboard instrument, keyboard or by moving a ring tied to a wire, creating "wavering" sounds similar to a theremin. D ...
and
trautonium
The Trautonium is an electronic synthesizer invented in 1930 by Friedrich Trautwein in Berlin at the Musikhochschule's music and radio lab, the Rundfunkversuchstelle. Soon afterward Oskar Sala joined him, continuing development until Sala's de ...
were commercially produced by the early 1930s.
[; ]
From the late 1920s, the increased practicality of electronic instruments influenced composers such as
Joseph Schillinger
Joseph Moiseyevich Schillinger (; (other sources: ) – 23 March 1943) was a composer, music theorist, and music composition, composition teacher who originated the Schillinger System of Musical Composition. He was born in Kharkiv, Kharkov, in the ...
and
Maria Schuppel to adopt them. They were typically used within orchestras, and most composers wrote parts for the theremin that could otherwise be performed with
string instrument
In musical instrument classification, string instruments, or chordophones, are musical instruments that produce sound from vibrating strings when a performer strums, plucks, strikes or sounds the strings in varying manners.
Musicians play some ...
s.
Avant-garde composers
Avant-garde music is music that is considered to be at the forefront of innovation in its field, with the term "avant-garde" implying a critique of existing aesthetic conventions, rejection of the status quo in favor of unique or original eleme ...
criticized the predominant use of electronic instruments for conventional purposes.
The instruments offered expansions in pitch resources
that were exploited by advocates of microtonal music such as
Charles Ives
Charles Edward Ives (; October 20, 1874May 19, 1954) was an American modernist composer, actuary and businessman. Ives was among the earliest renowned American composers to achieve recognition on a global scale. His music was largely ignored d ...
,
Dimitrios Levidis,
Olivier Messiaen
Olivier Eugène Prosper Charles Messiaen (, ; ; 10 December 1908 – 27 April 1992) was a French composer, organist, and ornithology, ornithologist. One of the major composers of the 20th-century classical music, 20th century, he was also an ou ...
and
Edgard Varèse
Edgard Victor Achille Charles Varèse (; also spelled Edgar; December 22, 1883 – November 6, 1965) was a French and American composer who spent the greater part of his career in the United States. Varèse's music emphasizes timbre and rhythm; h ...
.
Further,
Percy Grainger
Percy Aldridge Grainger (born George Percy Grainger; 8 July 188220 February 1961) was an Australian-born composer, arranger and pianist who moved to the United States in 1914 and became an American citizen in 1918. In the course of a long and ...
used the theremin to abandon fixed tonation entirely,
while Russian composers such as
Gavriil Popov treated it as a source of noise in otherwise-acoustic
noise music
Noise music is a genre of music that is characterised by the expressive use of noise. This type of music tends to challenge the distinction that is made in conventional musical practices between musical and non-musical sound. Noise music include ...
.
Recording experiments
Developments in early
recording technology paralleled that of electronic instruments. The first means of recording and reproducing audio was invented in the late 19th century with the mechanical
phonograph
A phonograph, later called a gramophone, and since the 1940s a record player, or more recently a turntable, is a device for the mechanical and analogue reproduction of sound. The sound vibration Waveform, waveforms are recorded as correspond ...
.
Record players became a common household item, and by the 1920s composers were using them to play short recordings in performances.
The introduction of
electrical recording in 1925 was followed by increased experimentation with record players.
Paul Hindemith
Paul Hindemith ( ; ; 16 November 189528 December 1963) was a German and American composer, music theorist, teacher, violist and conductor. He founded the Amar Quartet in 1921, touring extensively in Europe. As a composer, he became a major advo ...
and
Ernst Toch
Ernst Toch (; 7 December 1887 – 1 October 1964) was an Austrian composer of European classical music and film scores, who from 1933 worked as an émigré in Paris, London and New York. He sought throughout his life to introduce new approaches t ...
composed several pieces in 1930 by layering recordings of instruments and vocals at adjusted speeds. Influenced by these techniques,
John Cage
John Milton Cage Jr. (September 5, 1912 – August 12, 1992) was an American composer and music theorist. A pioneer of indeterminacy in music, electroacoustic music, and Extended technique, non-standard use of musical instruments, Cage was one ...
composed ''
Imaginary Landscape No. 1'' in 1939 by adjusting the speeds of recorded tones.
Composers began to experiment with newly developed
sound-on-film
Sound-on-film is a class of sound film processes where the sound accompanying a picture is recorded on photographic film, usually, but not always, the same strip of film carrying the picture. Sound-on-film processes can either record an Analog s ...
technology. Recordings could be spliced together to create
sound collage
In music, montage (literally "putting together") or sound collage ("gluing together") is a technique where newly branded sound objects or Musical composition, compositions, including songs, are created from collage, also known as musique concrè ...
s, such as those by
Tristan Tzara
Tristan Tzara (; ; ; born Samuel or Samy Rosenstock, also known as S. Samyro; – 25 December 1963) was a Romanian and French avant-garde poet, essayist and performance artist. Also active as a journalist, playwright, literary and art critic, c ...
,
Kurt Schwitters
Kurt Hermann Eduard Karl Julius Schwitters (20 June 1887 – 8 January 1948) was a German artist. He was born in Hanover, Germany, but lived in exile from 1937.
Schwitters worked in several genres and media, including Dadaism, Constructivism (a ...
,
Filippo Tommaso Marinetti
Filippo Tommaso Emilio Marinetti (; 22 December 1876 – 2 December 1944) was an Italian poet, editor, art theorist and founder of the Futurist movement. He was associated with the utopian and Symbolist artistic and literary community Abbaye de ...
,
Walter Ruttmann
Walter Ruttmann (28 December 1887 – 15 July 1941) was a German cinematographer and film director, an important German abstract experimental film maker, along with Hans Richter, Viking Eggeling and Oskar Fischinger. He is best known for dir ...
and
Dziga Vertov
Dziga Vertov (born David Abelevich Kaufman; – 12 February 1954) was a Soviet pioneer documentary film and newsreel director, as well as a cinema theorist. His filming practices and theories influenced the cinéma vérité style of documentary ...
. Further, the technology allowed sound to be
graphically created and modified. These techniques were used to compose soundtracks for several films in Germany and Russia, in addition to the popular ''
Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde
''Strange Case of Dr Jekyll and Mr Hyde'' is an 1886 Gothic fiction, Gothic horror fiction, horror novella by Scottish author Robert Louis Stevenson. It follows Gabriel John Utterson, a London-based legal practitioner who investigates a series ...
'' in the United States. Experiments with graphical sound were continued by
Norman McLaren
William Norman McLaren, LL. D. (11 April 1914 – 27 January 1987) was a Scottish-Canadian animator, director and producer known for his work for the National Film Board of Canada (NFB).Rosenthal, Alan. ''The new documentary in action: a caseb ...
from the late 1930s.
Development: 1940s to 1950s
Electroacoustic tape music
The first practical audio
tape recorder
An audio tape recorder, also known as a tape deck, tape player or tape machine or simply a tape recorder, is a sound recording and reproduction device that records and plays back sounds usually using magnetic tape for storage. In its present ...
was unveiled in 1935. Improvements to the technology were made using the
AC bias
Tape bias is the term for two techniques, AC bias and DC bias, that improve the fidelity of analogue tape recorders. DC bias is the addition of direct current to the audio signal that is being recorded. AC bias is the addition of an Ultraso ...
ing technique, which significantly improved recording fidelity.
As early as 1942, test recordings were being made in stereo. Although these developments were initially confined to Germany, recorders and tapes were brought to the United States following the end of World War II. These were the basis for the first commercially produced tape recorder in 1948.
In 1944, before the use of magnetic tape for compositional purposes, Egyptian composer
Halim El-Dabh
Halim Abdul Messieh El-Dabh (, ''Ḥalīm ʻAbd al-Masīḥ al-Ḍab''ʻ; 4 March 1921 – 2 September 2017) was an Egyptian-American composer, musician, ethnomusicologist, and educator, who had a career spanning six decades. He is particu ...
, while still a student in
Cairo
Cairo ( ; , ) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Egypt and the Cairo Governorate, being home to more than 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, L ...
, used a cumbersome
wire recorder
Wire recording, also known as magnetic wire recording, was the first magnetic recording technology, an analog type of audio storage. It recorded sound signals on a thin steel wire using varying levels of magnetization. The first crude magne ...
to record sounds of an ancient ''
zaar'' ceremony. Using facilities at the Middle East Radio studios El-Dabh processed the recorded material using reverberation, echo, voltage controls and re-recording. What resulted is believed to be the earliest tape music composition.
The resulting work was entitled ''The Expression of Zaar'' and it was presented in 1944 at an art gallery event in Cairo. While his initial experiments in tape-based composition were not widely known outside of Egypt at the time, El-Dabh is also known for his later work in electronic music at the
Columbia-Princeton Electronic Music Center
The Computer Music Center (CMC) at Columbia University is the oldest center for electronic and computer music research in the United States. It was founded in the 1950s as the Columbia-Princeton Electronic Music Center.
Location
The CMC is h ...
in the late 1950s.
Musique concrète
Following his work with
Studio d'Essai at
Radiodiffusion Française
Radiodiffusion Française (; RDF) was a French public institution responsible for public service broadcasting.
Created in 1944 as a state monopoly (replacing Radiodiffusion Nationale), RDF worked to rebuild its extensive network, destroyed duri ...
(RDF), during the early 1940s,
Pierre Schaeffer
Pierre Henri Marie Schaeffer (English pronunciation: , ; 14 August 1910 – 19 August 1995) was a French composer, writer, broadcaster, engineer, musicologist, acoustician and founder of Groupe de Recherche de Musique Concrète (GRMC). His inno ...
is credited with originating the theory and practice of musique concrète. In the late 1940s, experiments in sound-based composition using
shellac
Shellac () is a resin secreted by the female Kerria lacca, lac bug on trees in the forests of India and Thailand. Chemically, it is mainly composed of aleuritic acid, jalaric acid, shellolic acid, and other natural waxes. It is processed and s ...
record players were first conducted by Schaeffer. In 1950, the techniques of musique concrete were expanded when magnetic tape machines were used to explore sound manipulation practices such as speed variation (
pitch shift
Pitch shifting is a sound recording technique in which the original pitch of a sound is raised or lowered. Effects units that raise or lower pitch by a pre-designated musical interval ( transposition) are known as pitch shifters.
Pitch and ...
) and
tape splicing
Reel-to-reel audio tape recording, also called open-reel recording, is magnetic tape audio recording in which the recording tape is spooled between reels. To prepare for use, the ''supply reel'' (or ''feed reel'') containing the tape is place ...
.
On 5 October 1948, RDF broadcast Schaeffer's ''Etude aux chemins de fer''. This was the first "
movement" of ''Cinq études de bruits'', and marked the beginning of studio realizations and musique concrète (or acousmatic art). Schaeffer employed a
disc cutting lathe
upPresto 8N Disc Cutting Lathe (1950) used by the Canadian Broadcasting Corporation to record radio programs
A disc cutting lathe is a device used to transfer an audio signal to the modulated spiral groove of a blank master disc for the productio ...
, four turntables, a four-channel mixer, filters, an echo chamber, and a mobile recording unit. Not long after this,
Pierre Henry
Henry at his home (January 2008)
Pierre Georges Albert François Henry (; 9 December 1927 – 5 July 2017) was a French composer known for his significant contributions to musique concrète.
Biography
Henry was born in Paris, France, and bega ...
began collaborating with Schaeffer, a partnership that would have profound and lasting effects on the direction of electronic music. Another associate of Schaeffer,
Edgard Varèse
Edgard Victor Achille Charles Varèse (; also spelled Edgar; December 22, 1883 – November 6, 1965) was a French and American composer who spent the greater part of his career in the United States. Varèse's music emphasizes timbre and rhythm; h ...
, began work on ''
Déserts
''Déserts'' (1950–1954) is a musical composition, piece by Edgard Varèse for 14 winds (brass instrument, brass and woodwind instrument, woodwinds), 5 percussion players, 1 piano, and electronic audiotape, tape."Blue" Gene Tyranny (2010). " D� ...
'', a work for chamber orchestra and tape. The tape parts were created at Pierre Schaeffer's studio and were later revised at Columbia University.
In 1950, Schaeffer gave the first public (non-broadcast) concert of musique concrète at the École Normale de Musique de Paris. "Schaeffer used a Public address system, PA system, several turntables, and mixers. The performance did not go well, as creating live montages with turntables had never been done before." Later that same year, Pierre Henry collaborated with Schaeffer on ''Symphonie pour un homme seul'' (1950) the first major work of musique concrete. In Paris in 1951, in what was to become an important worldwide trend, RTF established the first studio for the production of electronic music. Also in 1951, Schaeffer and Henry produced an opera, ''Orpheus'', for concrete sounds and voices.
By 1951 the work of Schaeffer, composer-percussionist Pierre Henry, and sound engineer Jacques Poullin had received official recognition and
The Groupe de Recherches de Musique Concrète, Club d 'Essai de la
Radiodiffusion-Télévision Française
Radiodiffusion-Télévision Française (; RTF; "French Radio and Television Broadcasting") was the French national public broadcaster television organization established on 9 February 1949 to replace the post-war "''Radiodiffusion Française''" ...
was established at RTF in Paris, the ancestor of the
ORTF.
Elektronische Musik, Germany

Karlheinz Stockhausen
Karlheinz Stockhausen (; 22 August 1928 – 5 December 2007) was a German composer, widely acknowledged by critics as one of the most important but also controversial composers of the 20th and early 21st centuries. He is known for his groun ...
worked briefly in Schaeffer's studio in 1952, and afterward for many years at the
WDR Cologne's
Studio for Electronic Music.
1954 saw the advent of what would now be considered authentic electric plus acoustic compositions—acoustic instrumentation augmented/accompanied by recordings of manipulated or electronically generated sound. Three major works were premiered that year: Varèse's ''Déserts'', for chamber ensemble and tape sounds, and two works by
Otto Luening and
Vladimir Ussachevsky
Vladimir Alexeevich Ussachevsky (November 3, 1911 in Hailar, China – January 2, 1990 in New York, New York) was a Russian-American composer, particularly known for his work in electronic music.
Biography
Vladimir Ussachevsky was born in ...
: ''Rhapsodic Variations for the Louisville Symphony'' and ''A Poem in Cycles and Bells'', both for orchestra and tape. Because he had been working at Schaeffer's studio, the tape part for Varèse's work contains much more concrete sounds than electronic. "A group made up of wind instruments, percussion and piano alternate with the mutated sounds of factory noises and ship sirens and motors, coming from two loudspeakers."
[.]
At the German premiere of ''Déserts'' in Hamburg, which was conducted by
Bruno Maderna
Bruno Maderna (born Bruno Grossato, 21 April 1920 – 13 November 1973) was an Italian composer, conductor and academic teacher.
Life
Maderna was born Bruno Grossato in Venice but later decided to take the name of his mother, Caterina Carolina M ...
, the tape controls were operated by
Karlheinz Stockhausen
Karlheinz Stockhausen (; 22 August 1928 – 5 December 2007) was a German composer, widely acknowledged by critics as one of the most important but also controversial composers of the 20th and early 21st centuries. He is known for his groun ...
.
The title ''Déserts'' suggested to Varèse not only "all physical deserts (of sand, sea, snow, of outer space, of empty streets), but also the deserts in the mind of man; not only those stripped aspects of nature that suggest bareness, aloofness, timelessness, but also that remote inner space no telescope can reach, where man is alone, a world of mystery and essential loneliness."
In Cologne, what would become the most famous electronic music studio in the world, was officially opened at the radio studios of the
NWDR in 1953, though it had been in the planning stages as early as 1950 and early compositions were made and broadcast in 1951. The brainchild of
Werner Meyer-Eppler
Werner Meyer-Eppler (30 April 1913 – 8 July 1960), was a Belgian-born German physicist, experimental acoustician, phoneticist and information theorist.
Meyer-Eppler was born in Antwerp. He studied mathematics, physics, and chemistry, ...
, Robert Beyer, and
Herbert Eimert
Herbert Eimert (8 April 1897 – 15 December 1972) was a German music theorist, musicologist, journalist, music critic, editor, radio producer, and composer.
Education
Herbert Eimert was born in Bad Kreuznach. He studied music theory and composi ...
(who became its first director), the studio was soon joined by Karlheinz Stockhausen and
. In his 1949 thesis ''Elektronische Klangerzeugung: Elektronische Musik und Synthetische Sprache'', Meyer-Eppler conceived the idea to synthesize music entirely from electronically produced signals; in this way, ''elektronische Musik'' was sharply differentiated from French ''musique concrète'', which used sounds recorded from acoustical sources.
In 1953, Stockhausen composed his ''
Studie I
''Studie I'' (English: Study I) is an electronic music composition by Karlheinz Stockhausen from the year 1953. It lasts 9 minutes 42 seconds and, together with his ''Studie II'', comprises his work number ("opus") 3.
History
The composition was c ...
'', followed in 1954 by ''
Elektronische Studie II''—the first electronic piece to be published as a score. In 1955, more experimental and electronic studios began to appear. Notable were the creation of the
Studio di fonologia musicale di Radio Milano
The was established 1955 in Milan following a joint initiative by Luciano Berio and Bruno Maderna.
The aim was to create a third European facility for experimental electronic contemporary classical music after the Studio für elektronische Musi ...
, a studio at the
NHK
, also known by its Romanization of Japanese, romanized initialism NHK, is a Japanese public broadcasting, public broadcaster. It is a statutory corporation funded by viewers' payments of a television licence, television license fee.
NHK ope ...
in Tokyo founded by
Toshiro Mayuzumi, and the Philips studio at
Eindhoven
Eindhoven ( ; ) is a city and List of municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality of the Netherlands, located in the southern Provinces of the Netherlands, province of North Brabant, of which it is the largest municipality, and is also locat ...
, the Netherlands, which moved to the
University of Utrecht
Utrecht University (UU; , formerly ''Rijksuniversiteit Utrecht'') is a public research university in Utrecht, Netherlands. Established , it is one of the oldest universities in the Netherlands. In 2023, it had an enrollment of 39,769 students, a ...
as the
Institute of Sonology The Institute of Sonology is an education and research center for electronic and computer music based at the Royal Conservatoire of The Hague in the Netherlands.
Background
The institute was founded at Utrecht University in 1960 as the Studio fo ...
in 1960.
"With Stockhausen and
Mauricio Kagel
Mauricio Raúl Kagel (; 24 December 1931 – 18 September 2008) was an Argentine-German composer and academic teacher.
Life and career Early life and education
Mauricio Raúl Kagel was born on 24 December 1931 in Buenos Aires, Argentina, into an ...
in residence,
olognebecame a year-round hive of charismatic avant-gardism." on two occasions combining electronically generated sounds with relatively conventional orchestras—in ''
Mixtur
''Mixtur'', for orchestra, 4 sine-wave generators, and 4 ring modulators, is an orchestral composition by the German composer Karlheinz Stockhausen, written in 1964, and is Nr. 16 in his catalogue of works. It exists in three versions: the ...
'' (1964) and ''
Hymnen, dritte Region mit Orchester'' (1967). Stockhausen stated that his listeners had told him his electronic music gave them an experience of "outer space", sensations of flying, or being in a "fantastic dream world".
United States
In the United States, electronic music was being created as early as 1939, when John Cage published ''
Imaginary Landscape, No. 1'', using two variable-speed turntables, frequency recordings, muted piano, and cymbal, but no electronic means of production. Cage composed five more "Imaginary Landscapes" between 1942 and 1952 (one withdrawn), mostly for percussion ensemble, though No. 4 is for twelve radios and No. 5, written in 1952, uses 42 recordings and is to be realized as a magnetic tape. According to Otto Luening, Cage also performed ''
Williams Mix
''Williams Mix'' (1951–1953) is a 4'16" electroacoustic composition by John Cage for eight simultaneously played independent quarter-inch magnetic tapes. The first piece of octophonic music, the piece was created by Cage with the assistance o ...
'' at Donaueschingen in 1954, using eight loudspeakers, three years after his alleged collaboration. ''Williams Mix'' was a success at the
Donaueschingen Festival, where it made a "strong impression".
The Music for Magnetic Tape Project was formed by members of the
New York School (
John Cage
John Milton Cage Jr. (September 5, 1912 – August 12, 1992) was an American composer and music theorist. A pioneer of indeterminacy in music, electroacoustic music, and Extended technique, non-standard use of musical instruments, Cage was one ...
,
Earle Brown
Earle Brown (December 26, 1926 – July 2, 2002) was an American composer who established his own formal and notational systems. Brown was the creator of "open form," a style of musical construction that has influenced many composers since, ...
,
Christian Wolff,
David Tudor
David Eugene Tudor (January 20, 1926 – August 13, 1996) was an American pianist and composer of experimental music.
Life and career
Tudor was born in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. He studied piano with Irma Wolpe and composition with Stefa ...
, and
Morton Feldman
Morton Feldman (January 12, 1926 – September 3, 1987) was an American composer. A major figure in 20th-century classical music, Feldman was a pioneer of indeterminacy in music, a development associated with the experimental New York School o ...
),
[.] and lasted three years until 1954. Cage wrote of this collaboration: "In this social darkness, therefore, the work of Earle Brown, Morton Feldman, and Christian Wolff continues to present a brilliant light, for the reason that at the several points of notation, performance, and audition, action is provocative."
[.]
Cage completed ''Williams Mix'' in 1953 while working with the Music for Magnetic Tape Project.
["Carolyn Brown arle Brown's wifewas to dance in Cunningham's company, while Brown himself was to participate in Cage's 'Project for Music for Magnetic Tape.'... funded by Paul Williams (dedicatee of the 1953 ''Williams Mix''), who—like ]Robert Rauschenberg
Milton Ernest "Robert" or "Bob" Rauschenberg (October 22, 1925 – May 12, 2008) was an American painter and graphic artist whose early works anticipated the Pop art movement. Rauschenberg is well known for his Combine painting, Combines (1954� ...
—was a former student of Black Mountain College, which Cage and Cunnigham had first visited in the summer of 1948" (). The group had no permanent facility, and had to rely on borrowed time in commercial sound studios, including the studio of
Bebe and Louis Barron.
Columbia-Princeton Center
In the same year
Columbia University
Columbia University in the City of New York, commonly referred to as Columbia University, is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in New York City. Established in 1754 as King's College on the grounds of Trinity Churc ...
purchased its first tape recorder—a professional
Ampex
Ampex Data Systems Corporation is an American electronics company founded in 1944 by Alexander M. Poniatoff as a spin-off of Dalmo-Victor. The name ''AMPEX'' is an acronym, created by its founder, which stands for Alexander M. Poniatoff Excell ...
machine—to record concerts. Vladimir Ussachevsky, who was on the music faculty of Columbia University, was placed in charge of the device, and almost immediately began experimenting with it.
Herbert Russcol writes: "Soon he was intrigued with the new sonorities he could achieve by recording musical instruments and then superimposing them on one another."
[.] Ussachevsky said later: "I suddenly realized that the tape recorder could be treated as an instrument of sound transformation."
On Thursday, 8 May 1952, Ussachevsky presented several demonstrations of tape music/effects that he created at his Composers Forum, in the McMillin Theatre at Columbia University. These included ''Transposition, Reverberation, Experiment, Composition'', and ''Underwater Valse''. In an interview, he stated: "I presented a few examples of my discovery in a public concert in New York together with other compositions I had written for conventional instruments."
Otto Luening, who had attended this concert, remarked: "The equipment at his disposal consisted of an Ampex tape recorder . . . and a simple box-like device designed by the brilliant young engineer, Peter Mauzey, to create feedback, a form of mechanical reverberation. Other equipment was borrowed or purchased with personal funds."
[.]
Just three months later, in August 1952, Ussachevsky traveled to Bennington, Vermont, at Luening's invitation to present his experiments. There, the two collaborated on various pieces. Luening described the event: "Equipped with earphones and a flute, I began developing my first tape-recorder composition. Both of us were fluent improvisors and the medium fired our imaginations."
They played some early pieces informally at a party, where "a number of composers almost solemnly congratulated us saying, 'This is it' ('it' meaning the music of the future)."
Word quickly reached New York City. Oliver Daniel telephoned and invited the pair to "produce a group of short compositions for the October concert sponsored by the American Composers Alliance and Broadcast Music, Inc., under the direction of
Leopold Stokowski
Leopold Anthony Stokowski (18 April 1882 – 13 September 1977) was a British-born American conductor. One of the leading conductors of the early and mid-20th century, he is best known for his long association with the Philadelphia Orchestra. H ...
at the Museum of Modern Art in New York. After some hesitation, we agreed. . . .
Henry Cowell
Henry Dixon Cowell (; March 11, 1897 – December 10, 1965) was an American composer, writer, pianist, publisher, teacher Marchioni, Tonimarie (2012)"Henry Cowell: A Life Stranger Than Fiction" ''The Juilliard Journal''. Retrieved 19 June 2022.C ...
placed his home and studio in Woodstock, New York, at our disposal. With the borrowed equipment in the back of Ussachevsky's car, we left Bennington for Woodstock and stayed two weeks. . . . In late September 1952, the travelling laboratory reached Ussachevsky's living room in New York, where we eventually completed the compositions."
Two months later, on 28 October, Vladimir Ussachevsky and Otto Luening presented the first Tape Music concert in the United States. The concert included Luening's ''Fantasy in Space'' (1952)—"an impressionistic
virtuoso
A virtuoso (from Italian ''virtuoso'', or ; Late Latin ''virtuosus''; Latin ''virtus''; 'virtue', 'excellence' or 'skill') is an individual who possesses outstanding talent and technical ability in a particular art or field such as fine arts, ...
piece"
using manipulated recordings of flute—and ''Low Speed'' (1952), an "exotic composition that took the flute far below its natural range."
Both pieces were created at the home of Henry Cowell in Woodstock, New York. After several concerts caused a sensation in New York City, Ussachevsky and Luening were invited onto a live broadcast of NBC's Today Show to do an interview demonstration—the first televised electroacoustic performance. Luening described the event: "I improvised some
lute
A lute ( or ) is any plucked string instrument with a neck (music), neck and a deep round back enclosing a hollow cavity, usually with a sound hole or opening in the body. It may be either fretted or unfretted.
More specifically, the term "lu ...
sequences for the tape recorder. Ussachevsky then and there put them through electronic transformations."
The score for ''
Forbidden Planet
''Forbidden Planet'' is a 1956 American science fiction action film from Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer, produced by Nicholas Nayfack and directed by Fred M. Wilcox (director), Fred M. Wilcox from a script by Cyril Hume that was based on a film story by ...
'', by
Louis and Bebe Barron,
["From at least Louis and Bebbe Barron's soundtrack for ''The Forbidden Planet'' onwards, electronic music—in particular synthetic timbre—has impersonated alien worlds in film" ().] was entirely composed using custom-built electronic circuits and tape recorders in 1956 (but no synthesizers in the modern sense of the word).
USSR
In 1929,
Nikolai Obukhov invented the "
sounding cross" (la
croix sonore), comparable to the principle of the
theremin
The theremin (; originally known as the ætherphone, etherphone, thereminophone or termenvox/thereminvox) is an electronic musical instrument controlled without physical contact by the performer (who is known as a thereminist). It is named aft ...
.
[«АНС», шумофон и терменвокс: как зарождалась советская электронная музыка]
. In Russian In the 1930s, Nikolai Ananyev invented "sonar", and engineer Alexander Gurov — neoviolena, I. Ilsarov — ilston., and A. Ivanov — .
[ Composer and inventor Arseny Avraamov was engaged in scientific work on sound synthesis and conducted a number of experiments that would later form the basis of Soviet electro-musical instruments.][Советская электронная музыка]
In Russian
In 1956 Vyacheslav Mescherin created the , which used theremins, electric harps, electric organs, the first synthesizer in the USSR "Ekvodin",[ and also created the first Soviet reverb machine. The style in which Meshcherin's ensemble played is known as "]Space age pop
Space age pop or bachelor pad music is a subgenre of easy listening or lounge music associated with American and Mexican composers, songwriters, and bandleaders in the Space Age of the 1950s and 1960s.''Pulse'' (Monthly music digest of Tower Rec ...
".[ In 1957, engineer Igor Simonov assembled a working model of a noise recorder (electroeoliphone), with the help of which it was possible to extract various timbres and consonances of a noise nature.][ In 1958, ]Evgeny Murzin
Yevgeny Alexandrovich Murzin (; 1914–1970) was a Russian audio engineer and inventor of the ANS synthesizer.
Academic life and military service
Murzin began his academic life studying municipal building at the Moscow Institute of Enginee ...
designed ANS synthesizer
The ANS synthesizer is a photoelectronic musical instrument created by Russian engineer Evgeny Murzin from 1937 to 1957. The technological basis of his invention was the method of graphical sound recording used in cinematography (developed in R ...
, one of the world's first polyphonic musical synthesizers.
Founded by Murzin in 1966, the Moscow Experimental Electronic Music Studio became the base for a new generation of experimenters – Eduard Artemyev
Eduard Nikolayevich Artemyev (; rus, Эдуа́рд Никола́евич Арте́мьев, p=ɨdʊˈart ɐrˈtʲemʲjɪf; 30 November 1937 – 29 December 2022) was a Soviet and Russian composer of electronic music and film scores. Outside ...
, , Sándor Kallós, Sofia Gubaidulina
Sofia Asgatovna Gubaidulina (24 October 1931 – 13 March 2025) was a Soviet and Russian composer of Modernism (music), modernist Holy minimalism, sacred music. She was highly prolific, producing numerous Chamber music, chamber, Orchestra, orch ...
, Alfred Schnittke
Alfred Garrievich Schnittke (24 November 1934 – 3 August 1998) was a Russian composer. Among the most performed and recorded composers of late 20th-century classical music, he is described by musicologist Ivan Moody (composer), Ivan Moody as a ...
, and Vladimir Martynov
Vladimir Ivanovich Martynov (Russian: Владимир Иванович Мартынов) (Moscow, 20 February 1946) is a Russian composer, known for his compositions in the concerto, orchestral music, chamber music, and choral music genres.
Life ...
.[ By the end of the 1960s, musical groups playing light electronic music appeared in the USSR. At the state level, this music began to be used to attract foreign tourists to the country and for ]broadcasting
Broadcasting is the data distribution, distribution of sound, audio audiovisual content to dispersed audiences via a electronic medium (communication), mass communications medium, typically one using the electromagnetic spectrum (radio waves), ...
to foreign countries. In the mid-1970s, composer Alexander Zatsepin designed an "orchestrolla" – a modification of the mellotron.
The Baltic Soviet Republics also had their own pioneers: in Estonian SSR
The Estonian Soviet Socialist Republic, (abbreviated Estonian SSR, Soviet Estonia, or simply Estonia ) was an administrative subunit ( union republic) of the former Soviet Union (USSR), covering the occupied and annexed territory of Estonia ...
— Sven Grunberg, in Lithuanian SSR
The Lithuanian Soviet Socialist Republic (Lithuanian SSR; ; ), also known as Soviet Lithuania or simply Lithuania, was '' de facto'' one of the constituent republics of the Soviet Union between 1940–1941 and 1944–1990. After 1946, its terr ...
— Gedrus Kupriavicius, in Latvian SSR
The Latvian Soviet Socialist Republic (Also known as the Latvian SSR, or Latvia) was a Republics of the Soviet Union, constituent republic of the Soviet Union from 1940 to 1941, and then from 1944 until 1990.
The Soviet occupation of the Bal ...
— Opus and Zodiac
The zodiac is a belt-shaped region of the sky that extends approximately 8° north and south celestial latitude of the ecliptic – the apparent path of the Sun across the celestial sphere over the course of the year. Within this zodiac ...
.[
]
Australia
 The world's first computer to play music was
The world's first computer to play music was CSIRAC
CSIRAC (; ''Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Automatic Computer''), originally known as CSIR Mk 1, was Australia's first digital computer, and the fifth stored-program computer in the world. It is the oldest surviving first-gene ...
, which was designed and built by Trevor Pearcey
Trevor Pearcey (5 March 1919 – 27 January 1998) was a British-born Australian scientist, who created CSIRAC, one of the first stored-program electronic computers in the world.
Born in Woolwich, London, he graduated from Imperial College in 1 ...
and Maston Beard. Mathematician Geoff Hill programmed the CSIRAC to play popular musical melodies from the very early 1950s. In 1951 it publicly played the Colonel Bogey March
The "Colonel Bogey March" is a British march that was composed in 1914 by Lieutenant F. J. Ricketts (1881–1945) (pen name Kenneth J. Alford), a British Army bandmaster who later became the director of music for the Royal Marines at Plymout ...
, of which no known recordings exist, only the accurate reconstruction. However, CSIRAC
CSIRAC (; ''Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Automatic Computer''), originally known as CSIR Mk 1, was Australia's first digital computer, and the fifth stored-program computer in the world. It is the oldest surviving first-gene ...
played standard repertoire and was not used to extend musical thinking or composition practice. CSIRAC was never recorded, but the music played was accurately reconstructed. The oldest known recordings of computer-generated music were played by the Ferranti Mark 1
The Ferranti Mark 1, also known as the Manchester Electronic Computer in its sales literature, and thus sometimes called the Manchester Ferranti, was produced by British electrical engineering firm Ferranti Ltd. It was the world's first commer ...
computer, a commercial version of the Baby
In common terminology, a baby is the very young offspring of adult human beings, while infant (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'baby' or 'child') is a formal or specialised synonym. The terms may also be used to refer to Juvenile (orga ...
Machine from the University of Manchester
The University of Manchester is a public university, public research university in Manchester, England. The main campus is south of Manchester city centre, Manchester City Centre on Wilmslow Road, Oxford Road. The University of Manchester is c ...
in the autumn of 1951.Christopher Strachey
Christopher S. Strachey (; 16 November 1916 – 18 May 1975) was a British computer scientist. He was one of the founders of denotational semantics, and a pioneer in programming language design and computer time-sharing.F. J. Corbató, et al., T ...
.
Japan
Among the earliest group of electric musical instruments in Japan was the Yamaha Magna Organ, an electroacoustic instrument built in 1935.[Before the Second World War in Japan, several "electrical" instruments seem already to have been developed (''see :ja:電子音楽#黎明期''), and in 1935 a kind of "''electronic''" musical instrument, the Yamaha Magna Organ, was developed. It seems to be a multi-timbral keyboard instrument based on electrically blown ]free reed
A free reed aerophone is a musical instrument that produces sound as air flows past a vibrating reed in a frame. Air pressure is typically generated by breath or with a bellows. In the Hornbostel–Sachs system, it is number 412.13 (a member of ...
s with pickups, possibly similar to the electrostatic reed organ
An electric organ, also known as electronic organ, is an electronic keyboard instrument which was derived from the harmonium, pipe organ and theatre organ. Originally designed to imitate their sound, or orchestral sounds, it has since develope ...
s developed by Frederick Albert Hoschke in 1934 then manufactured by Everett and Wurlitzer
The Rudolph Wurlitzer Company, usually referred to as simply Wurlitzer, is an American company started in Cincinnati in 1853 by German immigrant (Franz) Rudolph Wurlitzer. The company initially imported stringed, woodwind and brass instruments ...
until 1961.
After World War II, Japanese composers such as Minao Shibata began to learn of the development of electronic musical instruments in other countries. By the late 1940s, Japanese composers began experimenting with electronic music, and institutional sponsorship enabled them to experiment with advanced equipment. Their infusion of Asian music
Asian music encompass numerous musical styles, traditions, and forms originating in Asian countries.
Asian music traditions include:
*
** Music of China
** Music of Hong Kong
** Music of Japan
** Traditional music of Korea
*** Music of Nor ...
into the emerging genre would eventually support Japan's popularity in the development of music technology several decades later.[.]
Following the foundation of electronics company Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
in 1946, composers Toru Takemitsu TORU or Toru may refer to:
*TORU, spacecraft system
*Tōru (given name), Japanese male given name
*Toru, Pakistan, village in Mardan District of Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan
*Tõru
Tõru is a village in Saaremaa Parish, Saare County in western Es ...
and Minao Shibata independently explored possible uses for electronic technology to produce music. Takemitsu had ideas similar to musique concrète
Musique concrète (; ): " problem for any translator of an academic work in French is that the language is relatively abstract and theoretical compared to English; one might even say that the mode of thinking itself tends to be more schematic ...
, which he was unaware of, while Shibata foresaw the development of synthesizers
A synthesizer (also synthesiser or synth) is an electronic musical instrument that generates audio signals. Synthesizers typically create sounds by generating waveforms through methods including subtractive synthesis, additive synthesis and ...
and predicted a drastic change in music. Sony began producing popular magnetic tape
Magnetic tape is a medium for magnetic storage made of a thin, magnetizable coating on a long, narrow strip of plastic film. It was developed in Germany in 1928, based on the earlier magnetic wire recording from Denmark. Devices that use magnetic ...
recorders for government and public use.[.]
The avant-garde collective Jikken Kōbō (Experimental Workshop), founded in 1950, was offered access to emerging audio technology by Sony. The company hired Toru Takemitsu to demonstrate their tape recorders with compositions and performances of electronic tape music. The first electronic tape pieces by the group were "Toraware no Onna" ("Imprisoned Woman") and "Piece B", composed in 1951 by Kuniharu Akiyama.[.] Many of the electroacoustic tape pieces they produced were used as incidental music for radio, film, and theatre. They also held concerts employing a slide show
A slide show, or slideshow, is a presentation of a series of still images ( slides) on a projection screen or electronic display device, typically in a prearranged sequence. The changes may be automatic and at regular intervals or they may b ...
synchronized with a recorded soundtrack. Composers outside of the Jikken Kōbō, such as Yasushi Akutagawa
was a Japanese composer and conductor. His father was Ryūnosuke Akutagawa.
Biography
Akutagawa was born and raised in Tabata, Tokyo, the son of writer Ryūnosuke Akutagawa.
Akutagawa studied composition with Kunihiko Hashimoto, Kan'ichi S ...
, Saburo Tominaga, and Shirō Fukai
was a Japanese composer.The Japan biographical encyclopedia & who's who: Issue 3 Rengō Puresu Sha - 1964 "FUKAI Shiro (1907- ) Composer. Musical critic. Born in Akita Prefecture. Graduated from the Science Section of the Seventh Higher School ( ...
, were also experimenting with radiophonic tape music between 1952 and 1953.Pierre Schaeffer
Pierre Henri Marie Schaeffer (English pronunciation: , ; 14 August 1910 – 19 August 1995) was a French composer, writer, broadcaster, engineer, musicologist, acoustician and founder of Groupe de Recherche de Musique Concrète (GRMC). His inno ...
concert. From 1952, he composed tape music pieces for a comedy film, a radio broadcast, and a radio drama.[.] However, Schaeffer's concept of ''sound object
In musique concrete and electronic music theory the term sound object (originally ''l'objet sonore'') is used to refer to a primary unit of sonic material and often specifically refers to recorded sound rather than written music using manuscript o ...
'' was not influential among Japanese composers, who were mainly interested in overcoming the restrictions of human performance.[.] This led to several Japanese electroacoustic music
Electroacoustic music is a Music genre, genre of Western art music in which composers use recording technology and audio signal processing to manipulate the timbres of Acoustics, acoustic sounds in the creation of pieces of music. It originated a ...
ians making use of serialism
In music, serialism is a method of composition using series of pitches, rhythms, dynamics, timbres or other musical elements. Serialism began primarily with Arnold Schoenberg's twelve-tone technique, though some of his contemporaries were also ...
and twelve-tone technique
The twelve-tone technique—also known as dodecaphony, twelve-tone serialism, and (in British usage) twelve-note composition—is a method of musical composition. The technique is a means of ensuring that all 12 notes of the chromatic scale ...
s,dodecaphonic
The twelve-tone technique—also known as dodecaphony, twelve-tone serialism, and (in British usage) twelve-note composition—is a method of musical composition. The technique is a means of ensuring that all 12 notes of the chromatic scale ...
piece "Concerto da
Camera",[.]
Modelling the NWDR studio in Cologne, an NHK
, also known by its Romanization of Japanese, romanized initialism NHK, is a Japanese public broadcasting, public broadcaster. It is a statutory corporation funded by viewers' payments of a television licence, television license fee.
NHK ope ...
electronic music studio was established by Mayuzumi in Tokyo in 1954, which became one of the world's leading electronic music facilities. The studio was equipped with technologies such as tone-generating and audio processing equipment, recording and radiophonic equipment, ondes Martenots, Monochords and Melochords, sine-wave oscillator
Oscillation is the repetitive or periodic variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value (often a point of equilibrium) or between two or more different states. Familiar examples of oscillation include a swinging pendulum ...
s, tape recorders, ring modulator
In electronics, ring modulation is a signal processing function, an implementation of frequency mixing, in which two signals are combined to yield an output signal. One signal, called the carrier, is typically a sine wave or another simple wa ...
s, band-pass filter
A band-pass filter or bandpass filter (BPF) is a device that passes frequencies within a certain range and rejects ( attenuates) frequencies outside that range.
It is the inverse of a '' band-stop filter''.
Description
In electronics and s ...
s, and four- and eight-channel mixers. Musicians associated with the studio included Toshiro Mayuzumi, Minao Shibata, Joji Yuasa, Toshi Ichiyanagi
was a Japanese avant-garde composer and pianist. One of the leading composers in Japan during the postwar era, Ichiyanagi worked in a range of genres, composing Western-style operas and orchestral and chamber works, as well as compositions usi ...
, and Toru Takemitsu. The studio's first electronic compositions were completed in 1955, including Mayuzumi's five-minute pieces "Studie I: Music for Sine Wave by Proportion of Prime Number", "Music for Modulated Wave by Proportion of Prime Number" and "Invention for Square Wave and Sawtooth Wave" produced using the studio's various tone-generating capabilities, and Shibata's 20-minute stereo piece "Musique Concrète for Stereophonic Broadcast".
Mid-to-late 1950s
The impact of computers continued in 1956. Lejaren Hiller
Lejaren Arthur Hiller Jr. (February 23, 1924, New York City – January 26, 1994, Buffalo, New York)[Lejaren ...](_blank)
and Leonard Isaacson composed '' Illiac Suite'' for string quartet
The term string quartet refers to either a type of musical composition or a group of four people who play them. Many composers from the mid-18th century onwards wrote string quartets. The associated musical ensemble consists of two Violin, violini ...
, the first complete work of computer-assisted composition using algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of Rigour#Mathematics, mathematically rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific Computational problem, problems or to perform a computation. Algo ...
ic composition. "... Hiller postulated that a computer could be taught the rules of a particular style and then called on to compose accordingly." Later developments included the work of Max Mathews
Max Vernon Mathews (November 13, 1926 – April 21, 2011) was an American pioneer of computer music.
Biography
Max Vernon Mathews was born in Columbus, Nebraska, to two science schoolteachers. His father in particular taught physics, chemistry ...
at Bell Laboratories
Nokia Bell Labs, commonly referred to as ''Bell Labs'', is an American industrial research and development company owned by Finnish technology company Nokia. With headquarters located in Murray Hill, New Jersey, the company operates several lab ...
, who developed the influential MUSIC I program in 1957, one of the first computer programs to play electronic music. Vocoder
A vocoder (, a portmanteau of ''vo''ice and en''coder'') is a category of speech coding that analyzes and synthesizes the human voice signal for audio data compression, multiplexing, voice encryption or voice transformation.
The vocoder wa ...
technology was also a major development in this early era. In 1956, Stockhausen composed ''Gesang der Jünglinge
''Gesang der Jünglinge'' (literally "Song of the Youths") is an electronic music work by Karlheinz Stockhausen. It was realized in 1955–56 at the Westdeutscher Rundfunk studio in Cologne and is Work Number 8 in the composer's catalog. The voc ...
'', the first major work of the Cologne studio, based on a text from the ''Book of Daniel
The Book of Daniel is a 2nd-century BC biblical apocalypse with a 6th-century BC setting. It is ostensibly a narrative detailing the experiences and Prophecy, prophetic visions of Daniel, a Jewish Babylonian captivity, exile in Babylon ...
''. An important technological development of that year was the invention of the Clavivox synthesizer by Raymond Scott
Raymond Scott (born Harry Warnow; September 10, 1908 – February 8, 1994) was an American composer, band leader, pianist and record producer. Known best in his time as a composer of production music, Scott is today regarded as an early ...
with subassembly by Robert Moog
Robert Arthur Moog ( ; May 23, 1934 – August 21, 2005) was an American engineer and electronic music pioneer. He was the founder of the synthesizer manufacturer Moog Music and the inventor of the first commercial synthesizer, the Moog synthe ...
.
In 1957, Kid Baltan ( Dick Raaymakers) and Tom Dissevelt released their debut album, ''Song Of The Second Moon'', recorded at the Philips studio in the Netherlands. The public remained interested in the new sounds being created around the world, as can be deduced by the inclusion of Varèse's ''Poème électronique
''Poème électronique'' (English Translation: "Electronic Poem") is an 8-minute piece of electronic music by composer
A composer is a person who writes music. The term is especially used to indicate composers of Western classical music, ...
'', which was played over four hundred loudspeakers at the Philips Pavilion of the 1958 Brussels World Fair. That same year, Mauricio Kagel
Mauricio Raúl Kagel (; 24 December 1931 – 18 September 2008) was an Argentine-German composer and academic teacher.
Life and career Early life and education
Mauricio Raúl Kagel was born on 24 December 1931 in Buenos Aires, Argentina, into an ...
, an Argentine
Argentines, Argentinians or Argentineans are people from Argentina. This connection may be residential, legal, historical, or cultural. For most Argentines, several (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of their ...
composer, composed ''Transición II''. The work was realized at the WDR studio in Cologne. Two musicians performed on the piano, one in the traditional manner, the other playing on the strings, frame, and case. Two other performers used tape to unite the presentation of live sounds with the future of prerecorded materials from later on and its past of recordings made earlier in the performance.
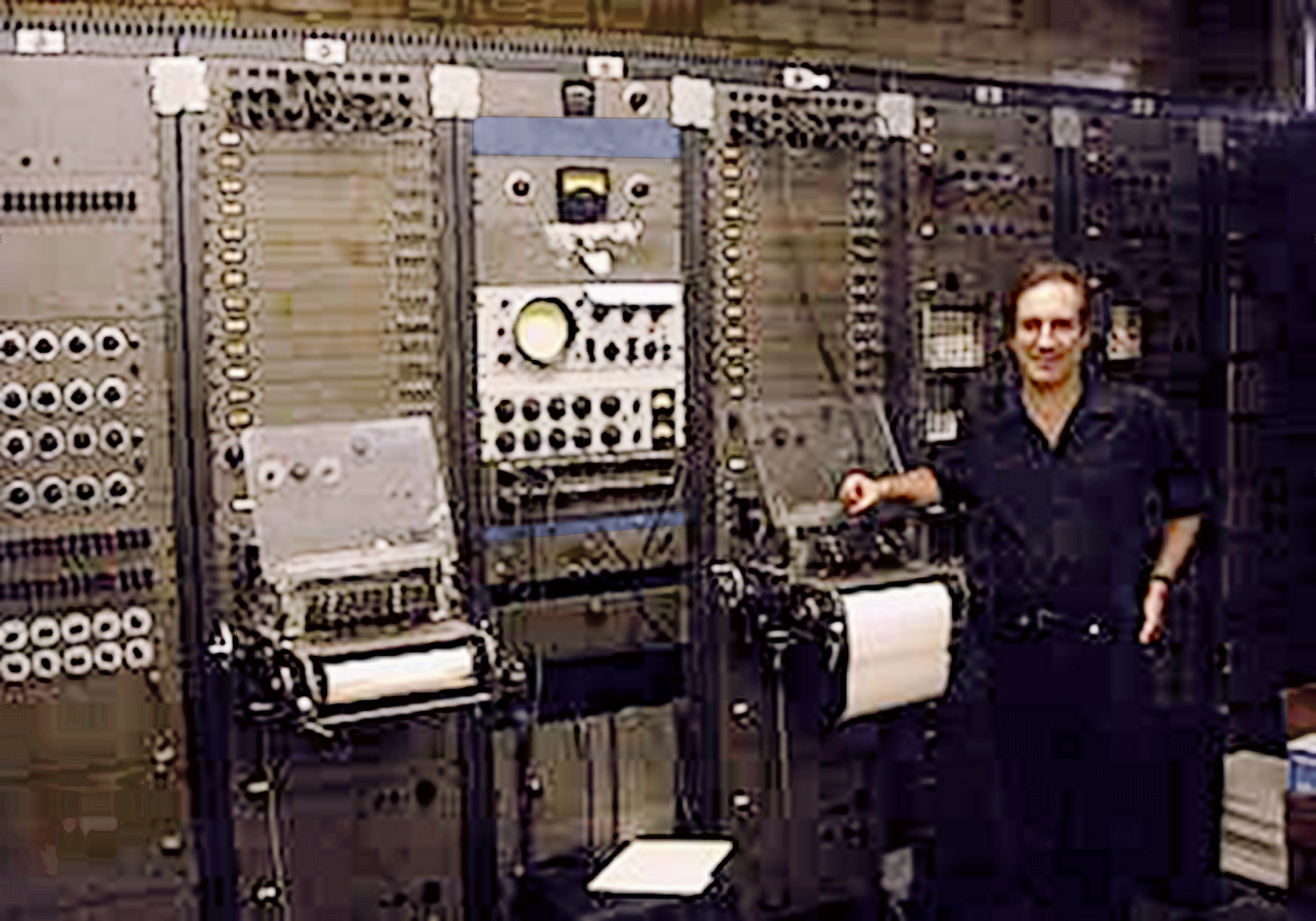 In 1958, Columbia-Princeton developed the
In 1958, Columbia-Princeton developed the RCA Mark II Sound Synthesizer
The RCA Mark II Sound Synthesizer (nicknamed ''Victor'') was the first programmable electronic synthesizer and the flagship piece of equipment at the Columbia-Princeton Electronic Music Center. Designed by Herbert Belar and Harry Olson at RCA, wi ...
, the first programmable synthesizer. Prominent composers such as Vladimir Ussachevsky, Otto Luening, Milton Babbitt
Milton Byron Babbitt (May 10, 1916 – January 29, 2011) was an American composer, music theorist, mathematician, and teacher. He was a Pulitzer Prize and MacArthur Fellowship recipient, recognized for his serial and electronic music.
Biography ...
, Charles Wuorinen
Charles Peter Wuorinen (, ; June 9, 1938 – March 11, 2020) was an American composer of contemporary classical music based in New York City. He also performed as a pianist and conductor. Wuorinen composed more than 270 works: orchestral music, c ...
, Halim El-Dabh, Bülent Arel and Mario Davidovsky
Mario Davidovsky (March 4, 1934 – August 23, 2019) was an Argentine-American composer. Born in Argentina, he emigrated in 1960 to the United States, where he lived for the remainder of his life. He is best known for his series of compositions ca ...
used the RCA
RCA Corporation was a major American electronics company, which was founded in 1919 as the Radio Corporation of America. It was initially a patent pool, patent trust owned by General Electric (GE), Westinghouse Electric Corporation, Westinghou ...
Synthesizer extensively in various compositions. One of the most influential composers associated with the early years of the studio was Egypt's Halim El-Dabh
Halim Abdul Messieh El-Dabh (, ''Ḥalīm ʻAbd al-Masīḥ al-Ḍab''ʻ; 4 March 1921 – 2 September 2017) was an Egyptian-American composer, musician, ethnomusicologist, and educator, who had a career spanning six decades. He is particu ...
who, after having developed the earliest known electronic tape music in 1944,folk music
Folk music is a music genre that includes #Traditional folk music, traditional folk music and the Contemporary folk music, contemporary genre that evolved from the former during the 20th-century folk revival. Some types of folk music may be ca ...
, in contrast to the more mathematical approach used by serial composers of the time such as Babbitt. El-Dabh's ''Leiyla and the Poet'', released as part of the album ''Columbia-Princeton Electronic Music Center
The Computer Music Center (CMC) at Columbia University is the oldest center for electronic and computer music research in the United States. It was founded in the 1950s as the Columbia-Princeton Electronic Music Center.
Location
The CMC is h ...
'' in 1961, would be cited as a strong influence by a number of musicians, ranging from Neil Rolnick, Charles Amirkhanian and Alice Shields to rock musicians Frank Zappa
Frank Vincent Zappa (December 21, 1940 – December 4, 1993) was an American guitarist, composer, and bandleader. In a career spanning more than 30 years, Zappa composed Rock music, rock, Pop music, pop, jazz, jazz fusion, orchestra ...
and The West Coast Pop Art Experimental Band.
Following the emergence of differences within the GRMC (Groupe de Recherche de Musique Concrète) Pierre Henry, Philippe Arthuys, and several of their colleagues, resigned in April 1958. Schaeffer created a new collective, called Groupe de Recherches Musicales
A group is a military unit or a military formation that is most often associated with military aviation.
Air and aviation groups
The terms group and wing differ significantly from one country to another, as well as between different branches ...
(GRM) and set about recruiting new members including Luc Ferrari
Luc Ferrari (5 February 1929 – 22 August 2005) was a French composer of Italian heritage and a pioneer in musique concrète and electroacoustic music. He was a founding member of RTF's Groupe de Recherches Musicales (GRMC), working alongside c ...
, Beatriz Ferreyra, François-Bernard Mâche
François-Bernard Mâche (born 4 April 1935, Clermont-Ferrand) is a French composer of contemporary music.
Biography
Born into a family of musicians, he is a former student of Émile Passani and Olivier Messiaen and has also received a diploma i ...
, Iannis Xenakis
Giannis Klearchou Xenakis (also spelled for professional purposes as Yannis or Iannis Xenakis; , ; 29 May 1922 – 4 February 2001) was a Romanian-born Greek-French avant-garde composer, music theorist, architect, performance director and enginee ...
, Bernard Parmegiani, and Mireille Chamass-Kyrou
Mireille Chamass-Kyrou ( – ) was a French musique concrète composer.
Mireille Chamass was born in in Cairo to a French mother and Palestinian father. She studied piano with Brigitte Schiffer at the State Institute for the Education of Wom ...
. Later arrivals included Ivo Malec, Philippe Carson, Romuald Vandelle, Edgardo Canton and François Bayle.
Expansion: 1960s
These were fertile years for electronic music—not just for academia, but for independent artists as synthesizer technology became more accessible. By this time, a strong community of composers and musicians working with new sounds and instruments was established and growing. 1960 witnessed the composition of Otto Luening's ''Gargoyles'' for violin and tape as well as the premiere of Karlheinz Stockhausen
Karlheinz Stockhausen (; 22 August 1928 – 5 December 2007) was a German composer, widely acknowledged by critics as one of the most important but also controversial composers of the 20th and early 21st centuries. He is known for his groun ...
's ''Kontakte
''Kontakte'' (, 'contacts') is an electronic music work by Karlheinz Stockhausen, realized in 1958–60 at the '' Westdeutscher Rundfunk'' (WDR) electronic-music studio in Cologne with the assistance of Gottfried Michael Koenig. The score is N ...
'' for electronic sounds, piano, and percussion. This piece existed in two versions—one for 4-channel tape, and the other for tape with human performers. "In ''Kontakte'', Stockhausen abandoned traditional musical form based on linear development and dramatic climax. This new approach, which he termed 'moment form', resembles the 'cinematic splice' techniques in early twentieth-century film."
The theremin
The theremin (; originally known as the ætherphone, etherphone, thereminophone or termenvox/thereminvox) is an electronic musical instrument controlled without physical contact by the performer (who is known as a thereminist). It is named aft ...
had been in use since the 1920s but it attained a degree of popular recognition through its use in science-fiction film soundtrack music in the 1950s (e.g., Bernard Herrmann
Bernard Herrmann (born Maximillian Herman; June 29, 1911December 24, 1975) was an American composer and conductor best known for his work in film scoring. As a conductor, he championed the music of lesser-known composers. He is widely regarde ...
's classic score for ''The Day the Earth Stood Still
''The Day the Earth Stood Still'' is a 1951 American science fiction film from 20th Century Fox, produced by Julian Blaustein and directed by Robert Wise. It stars Michael Rennie, Patricia Neal, Hugh Marlowe, Sam Jaffe, Billy Gray, F ...
'').
In the UK in this period, the BBC Radiophonic Workshop
The BBC Radiophonic Workshop was one of the sound effects units of the BBC, created in 1958 to produce Incidental music, incidental sounds and new music for radio and, later, television. The unit is known for its experimental and pioneering ...
(established in 1958) came to prominence, thanks in large measure to their work on the BBC science-fiction series ''Doctor Who
''Doctor Who'' is a British science fiction television series broadcast by the BBC since 1963. The series, created by Sydney Newman, C. E. Webber and Donald Wilson (writer and producer), Donald Wilson, depicts the adventures of an extraterre ...
''. One of the most influential British electronic artists in this period was Workshop staffer Delia Derbyshire
Delia Ann Derbyshire (5 May 1937 – 3 July 2001) was an English musician and composer of electronic music. She carried out notable work with the BBC Radiophonic Workshop during the 1960s, including her electronic arrangement of the theme ...
, who is now famous for her 1963 electronic realisation of the iconic ''Doctor Who'' theme, composed by Ron Grainer
Ronald Erle Grainer (11 August 1922 – 21 February 1981) was an Australian composer who worked for most of his professional career in the United Kingdom. He is mostly remembered for his television and film score music, especially the theme mus ...
. Other composers of electronic music active in the UK included Ernest Berk (who established his first studio in 1955), Tristram Cary
Tristram Ogilvie Cary, OAM (14 May 192524 April 2008), was a pioneering English-Australian composer. He was also active as a teacher and music critic.
Career
Cary was born in Oxford, England, and educated at the Dragon School in Oxford and W ...
, Hugh Davies, Brian Dennis, George Newson
George Newson (27 July 1932 – 8 March 2024) was an English composer and pianist who made important contributions to British electronic and avant garde music during the 1960s and 1970s. He subsequently composed large and small-scale works in many ...
, Daphne Oram
Daphne Blake Oram (31 December 1925 – 5 January 2003) was a British composer and electronic musician. She was one of the first British composers to produce electronic sound, and was an early practitioner of ''musique concrète'' in the UK. As ...
and Peter Zinovieff
Peter Zinovieff (26 January 1933 – 23 June 2021) was a British composer, musician and inventor. In the late 1960s, his company, Electronic Music Studios (EMS), made the VCS3, a synthesizer used by many early progressive rock bands such as Pi ...
.
 During the time of the
During the time of the UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
fellowship for studies in electronic music (1958) Israeli composer Josef Tal went on a study tour in the US and Canada. He summarized his conclusions in two articles that he submitted to UNESCO. In 1961, he established the ''Centre for Electronic Music in Israel'' at The Hebrew University
The Hebrew University of Jerusalem (HUJI; ) is an Israeli public research university based in Jerusalem. Co-founded by Albert Einstein and Chaim Weizmann in July 1918, the public university officially opened on 1 April 1925. It is the second-ol ...
of Jerusalem. In 1962, Canadian composer Hugh Le Caine
Hugh Le Caine (May 27, 1914 – July 3, 1977) was a Canadian physicist, composer, and instrument builder.
Le Caine was brought up in Port Arthur (now Thunder Bay) in northwestern Ontario. At a young age, he began making musical instruments. In y ...
arrived in Jerusalem to install his ''Creative Tape Recorder'' in the centre. In the 1990s Tal conducted, together with Dr. Shlomo Markel, in cooperation with the Technion – Israel Institute of Technology
The Technion – Israel Institute of Technology is a public university, public research university located in Haifa, Israel. Established in 1912 by Jews under the dominion of the Ottoman Empire, the Technion is the oldest university in the coun ...
and the Volkswagen Foundation
The Volkswagen Foundation (German: ''VolkswagenStiftung'') is the largest German private nonprofit organization involved in the promotion and support of academic research. It is not affiliated to the present company, the Volkswagen Group.
It wa ...
, a research project ('Talmark') aimed at the development of a novel musical notation system for electronic music.
Milton Babbitt
Milton Byron Babbitt (May 10, 1916 – January 29, 2011) was an American composer, music theorist, mathematician, and teacher. He was a Pulitzer Prize and MacArthur Fellowship recipient, recognized for his serial and electronic music.
Biography ...
composed his first electronic work using the synthesizer—his ''Composition for Synthesizer'' (1961)—which he created using the RCA synthesizer at the Columbia-Princeton Electronic Music Center
The Computer Music Center (CMC) at Columbia University is the oldest center for electronic and computer music research in the United States. It was founded in the 1950s as the Columbia-Princeton Electronic Music Center.
Location
The CMC is h ...
.
Collaborations also occurred across oceans and continents. In 1961, American composer Vladimir Ussachevsky
Vladimir Alexeevich Ussachevsky (November 3, 1911 in Hailar, China – January 2, 1990 in New York, New York) was a Russian-American composer, particularly known for his work in electronic music.
Biography
Vladimir Ussachevsky was born in ...
invited Edgar Varèse
Edgar is a commonly used masculine English given name, from an Anglo-Saxon name ''Edgar'' (composed of '' ead'' "rich, prosperous" and '' gar'' "spear").
Like most Anglo-Saxon names, it fell out of use by the Late Middle Ages; it was, howeve ...
from France to the Columbia-Princeton Studio (CPEMC). Upon arrival, Varèse embarked upon a revision of his work ''Déserts''. He was assisted by Mario Davidovsky
Mario Davidovsky (March 4, 1934 – August 23, 2019) was an Argentine-American composer. Born in Argentina, he emigrated in 1960 to the United States, where he lived for the remainder of his life. He is best known for his series of compositions ca ...
and Bülent Arel.
The intense activity occurring at CPEMC and elsewhere inspired the establishment of the San Francisco Tape Music Center
The San Francisco Tape Music Center, or SFTMC, was founded in the summer of 1962 by composers Ramon Sender and Morton Subotnick as a collaborative, "non profit corporation developed and maintained" by local composers working with tape recorders ...
in 1963 by Morton Subotnick
Morton Subotnick (born April 14, 1933) is an American composer of electronic music, best known for his 1967 composition '' Silver Apples of the Moon'', the first electronic work commissioned by a record company, Nonesuch. He was one of the fo ...
, with additional members Pauline Oliveros
Pauline Oliveros (May 30, 1932 – November 24, 2016) was an American composer, accordionist and a central figure in the development of post-war experimental and electronic music.
She was a founding member of the San Francisco Tape Music Center ...
, Ramon Sender, Anthony Martin, and Terry Riley
Terrence Mitchell Riley (born June 24, 1935) is an American composer and performing musician best known as a pioneer of the minimalist music, minimalist school of composition. Influenced by jazz and Indian classical music, his work became notab ...
.
Later, the Center moved to Mills College
Mills College at Northeastern University in Oakland, California is part of Northeastern University's global university system. Mills College was founded as the Young Ladies Seminary in 1852 in Benicia, California; it was relocated to Oakland in ...
, directed by Pauline Oliveros
Pauline Oliveros (May 30, 1932 – November 24, 2016) was an American composer, accordionist and a central figure in the development of post-war experimental and electronic music.
She was a founding member of the San Francisco Tape Music Center ...
, and has since been renamed Center for Contemporary Music.["A central figure in post-war electronic art music, ]Pauline Oliveros
Pauline Oliveros (May 30, 1932 – November 24, 2016) was an American composer, accordionist and a central figure in the development of post-war experimental and electronic music.
She was a founding member of the San Francisco Tape Music Center ...
. 1932is one of the original members of the San Francisco Tape Music Center (along with Morton Subotnick, Ramon Sender, Terry Riley, and Anthony Martin), which was the resource on the U.S. west coast for electronic music during the 1960s. The Center later moved to Mills College, where she was its first director, and is now called the Center for Contemporary Music." from CD liner notes, "Accordion & Voice", Pauline Oliveros, Record Label: Important, Catalog number IMPREC140: 793447514024.
Pietro Grossi
Pietro Grossi (15 April 1917, in Venice – 21 February 2002, in Florence) was an Italian composer pioneer of computer music, Visual arts, visual artist and hacker ahead of his time. He began experimenting with electronic techniques in Italy in t ...
was an Italian pioneer of computer composition and tape music, who first experimented with electronic techniques in the early sixties. Grossi was a cellist and composer, born in Venice in 1917. He founded the S 2F M (Studio de Fonologia Musicale di Firenze) in 1963 to experiment with electronic sound and composition.
Simultaneously in San Francisco, composer Stan Shaff and equipment designer Doug McEachern, presented the first "Audium" concert at San Francisco State College
San Francisco State University (San Francisco State, SF State and SFSU) is a public research university in San Francisco, California, United States. It was established in 1899 as the San Francisco State Normal School and is part of the Califor ...
(1962), followed by work at the San Francisco Museum of Modern Art
The San Francisco Museum of Modern Art (SFMOMA) is a modern art, modern and contemporary art museum and nonprofit organization located in San Francisco, California. SFMOMA was the first museum on the West Coast devoted solely to 20th-century art ...
(SFMOMA, 1963), conceived of as in time, controlled movement of sound in space. Twelve speakers surrounded the audience, and four speakers were mounted on a rotating, mobile-like construction above.[.] In an SFMOMA performance the following year (1964), the ''San Francisco Chronicle'' music critic Alfred Frankenstein Alfred Victor Frankenstein (October 5, 1906 – June 22, 1981) was an art and music critic, author, and professional musician.
He was the long-time art and music critic for the ''San Francisco Chronicle'' from 1934 to 1965. He was noted for champio ...
commented, "the possibilities of the space-sound continuum have seldom been so extensively explored".National Endowment for the Arts
The National Endowment for the Arts (NEA) is an independent agency of the United States federal government that offers support and funding for projects exhibiting artistic excellence. It was created in 1965 as an independent agency of the feder ...
, a new Audium opened, designed floor to ceiling for spatial sound composition and performance. "In contrast, there are composers who manipulated sound space by locating multiple speakers at various locations in a performance space and then switching or panning the sound between the sources. In this approach, the composition of spatial manipulation is dependent on the location of the speakers and usually exploits the acoustical properties of the enclosure. Examples include Varese's '' Poeme Electronique'' (tape music
Electroacoustic music is a genre of Western art music in which composers use recording technology and audio signal processing to manipulate the timbres of acoustic sounds in the creation of pieces of music. It originated around the middle of the ...
performed in the Philips Pavilion
The Philips Pavilion (; ) was a modernist pavilion in Brussels, Belgium, constructed for the 1958 Brussels World's Fair (Expo 58). Commissioned by electronics manufacturer Philips and designed by the office of Le Corbusier, it was built to hous ...
of the 1958 World Fair, Brussels) and Stan Schaff's ''Audium'' installation, currently active in San Francisco." Through weekly programs (over 4,500 in 40 years), Shaff "sculpts" sound, performing now-digitized spatial works live through 176 speakers.
Jean-Jacques Perrey
Jean Marcel Leroy (20 January 1929 – 4 November 2016), better known as Jean-Jacques Perrey (), was a French people, French electronic music performer, composer, producer, and promoter. He is considered a pioneer of pop electronica.[Pierre Schaeffer
Pierre Henri Marie Schaeffer (English pronunciation: , ; 14 August 1910 – 19 August 1995) was a French composer, writer, broadcaster, engineer, musicologist, acoustician and founder of Groupe de Recherche de Musique Concrète (GRMC). His inno ...]
's techniques on tape loops and was among the first to use the recently released Moog synthesizer developed by Robert Moog
Robert Arthur Moog ( ; May 23, 1934 – August 21, 2005) was an American engineer and electronic music pioneer. He was the founder of the synthesizer manufacturer Moog Music and the inventor of the first commercial synthesizer, the Moog synthe ...
. With this instrument he composed some works with Gershon Kingsley
Gershon Kingsley (born Götz Gustav Ksinski; October 28, 1922 – December 10, 2019) was a German-American composer, a pioneer of electronic music and the Moog synthesizer, a partner in the electronic music duo Perrey and Kingsley, found ...
and solo. A well-known example of the use of Moog's full-sized Moog modular synthesizer
The Moog synthesizer ( ) is a modular synthesizer invented by the American engineer Robert Moog in 1964. Moog's company, R. A. Moog Co., produced numerous models from 1965 to 1981, and again from 2014. It was the first commercial synthesizer a ...
is the 1968 ''Switched-On Bach
''Switched-On Bach'' is the debut album by the American composer Wendy Carlos, released in October 1968 by Columbia Records. Produced by Carlos and Rachel Elkind, the album is a collection of pieces by Johann Sebastian Bach performed by Carlos ...
'' album by Wendy Carlos
Wendy Carlos (born Walter Carlos; November 14, 1939) is an American musician and composer known for electronic music and film scores.
Born and raised in Rhode Island, Carlos studied physics and music at Brown University before moving to New Y ...
, which triggered a craze for synthesizer music. In 1969 David Tudor
David Eugene Tudor (January 20, 1926 – August 13, 1996) was an American pianist and composer of experimental music.
Life and career
Tudor was born in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. He studied piano with Irma Wolpe and composition with Stefa ...
brought a Moog modular synthesizer and Ampex tape machines to the National Institute of Design
The National Institutes of Design (NID) are a group of autonomous public design institutes in India, with the first institute established in 1961 in Ahmedabad. The other NIDs are located in the cities of Kurukshetra, Amaravati, Jorhat and Bho ...
in Ahmedabad
Ahmedabad ( ), also spelled Amdavad (), is the most populous city in the Indian state of Gujarat. It is the administrative headquarters of the Ahmedabad district and the seat of the Gujarat High Court. Ahmedabad's population of 5,570,585 ...
with the support of the Sarabhai family
The Sarabhai family is a prominent Indian family active in several fields. The patriarch, Ambalal Sarabhai, was a leading industrialist. While he created significant wealth, his children interested themselves in a wide variety of other endeavours ...
, forming the foundation of India's first electronic music studio. Here a group of composers Jinraj Joshipura, Gita Sarabhai
Geeta Sarabhai Mayor (; 1922 – 11 March 2011) was an Indian musician, well known for her patronage in music. She was among the first women to play the pakhavaj, a traditional barrel-shaped, two-headed drum. She promoted exchanges between India ...
, SC Sharma, IS Mathur and Atul Desai developed experimental sound compositions between 1969 and 1973.
Computer music
Musical melodies were first generated by the computer CSIRAC
CSIRAC (; ''Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Automatic Computer''), originally known as CSIR Mk 1, was Australia's first digital computer, and the fifth stored-program computer in the world. It is the oldest surviving first-gene ...
in Australia in 1950. There were newspaper reports from America and England (early and recently) that computers may have played music earlier, but thorough research has debunked these stories as there is no evidence to support the newspaper reports (some of which were obviously speculative). Research has shown that people ''speculated'' about computers playing music, possibly because computers would make noises,CSIRAC
CSIRAC (; ''Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Automatic Computer''), originally known as CSIR Mk 1, was Australia's first digital computer, and the fifth stored-program computer in the world. It is the oldest surviving first-gene ...
, which was designed and built by Trevor Pearcey
Trevor Pearcey (5 March 1919 – 27 January 1998) was a British-born Australian scientist, who created CSIRAC, one of the first stored-program electronic computers in the world.
Born in Woolwich, London, he graduated from Imperial College in 1 ...
and Maston Beard in the 1950s. Mathematician Geoff Hill programmed the CSIRAC to play popular musical melodies from the very early 1950s. In 1951 it publicly played the "Colonel Bogey March
The "Colonel Bogey March" is a British march that was composed in 1914 by Lieutenant F. J. Ricketts (1881–1945) (pen name Kenneth J. Alford), a British Army bandmaster who later became the director of music for the Royal Marines at Plymout ...
" of which no known recordings exist.
However, CSIRAC
CSIRAC (; ''Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Automatic Computer''), originally known as CSIR Mk 1, was Australia's first digital computer, and the fifth stored-program computer in the world. It is the oldest surviving first-gene ...
played standard repertoire and was not used to extend musical thinking or composition practice which is current computer-music practice.
The first music to be performed in England was a performance of the British National Anthem that was programmed by Christopher Strachey
Christopher S. Strachey (; 16 November 1916 – 18 May 1975) was a British computer scientist. He was one of the founders of denotational semantics, and a pioneer in programming language design and computer time-sharing.F. J. Corbató, et al., T ...
on the Ferranti Mark I, late in 1951. Later that year, short extracts of three pieces were recorded there by a BBC
The British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) is a British public service broadcaster headquartered at Broadcasting House in London, England. Originally established in 1922 as the British Broadcasting Company, it evolved into its current sta ...
outside broadcasting unit: the National Anthem, " Ba, Ba Black Sheep", and "In the Mood
"In the Mood" is a popular big band-era jazz standard recorded by Americans, American bandleader Glenn Miller. "In the Mood" is based on the composition "Tar Paper Stomp" by Wingy Manone. The first recording under the name "In the Mood" was re ...
" and this is recognised as the earliest recording of a computer to play music. This recording can be heard a
this Manchester University site
Researchers at the University of Canterbury
The University of Canterbury (UC; ; postnominal abbreviation ''Cantuar.'' or ''Cant.'' for ''Cantuariensis'', the Latin name for Canterbury) is a public research university based in Christchurch, New Zealand. It was founded in 1873 as Canterbur ...
, Christchurch declicked and restored this recording in 2016 and the results may be heard on SoundCloud
SoundCloud is a German audio streaming service owned and operated by SoundCloud Global Limited & Co. KG. The service enables its users to upload, promote, and share audio. Founded in 2007 by Alexander Ljung and Eric Wahlforss, SoundCloud is ...
.Laurie Spiegel
Laurie Spiegel (born September 20, 1945) is an American composer. She has worked at Bell Labs, Bell Laboratories, in computer graphics, and is known primarily for her electronic music electronic music, compositions and her algorithmic compositio ...
developed the algorithmic musical composition software " Music Mouse" (1986) for Macintosh
Mac is a brand of personal computers designed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple since 1984. The name is short for Macintosh (its official name until 1999), a reference to the McIntosh (apple), McIntosh apple. The current product lineup inclu ...
, Amiga
Amiga is a family of personal computers produced by Commodore International, Commodore from 1985 until the company's bankruptcy in 1994, with production by others afterward. The original model is one of a number of mid-1980s computers with 16-b ...
, and Atari
Atari () is a brand name that has been owned by several entities since its inception in 1972. It is currently owned by French holding company Atari SA (formerly Infogrames) and its focus is on "video games, consumer hardware, licensing and bl ...
computers.
Stochastic music
An important new development was the advent of computers to compose music, as opposed to manipulating or creating sounds. Iannis Xenakis
Giannis Klearchou Xenakis (also spelled for professional purposes as Yannis or Iannis Xenakis; , ; 29 May 1922 – 4 February 2001) was a Romanian-born Greek-French avant-garde composer, music theorist, architect, performance director and enginee ...
began what is called ''musique stochastique'', or '' stochastic music'', which is a composing method that uses mathematical probability systems. Different probability algorithms were used to create a piece under a set of parameters. Xenakis used computers to compose pieces like ''ST/4'' for string quartet and ''ST/48'' for orchestra (both 1962), ''Morsima-Amorsima'', ''ST/10'', and ''Atrées''. He developed the computer system UPIC for translating graphical images into musical results and composed ''Mycènes Alpha'' (1978) with it.
Live electronics
In Europe in 1964, Karlheinz Stockhausen
Karlheinz Stockhausen (; 22 August 1928 – 5 December 2007) was a German composer, widely acknowledged by critics as one of the most important but also controversial composers of the 20th and early 21st centuries. He is known for his groun ...
composed '' Mikrophonie I'' for tam-tam
A gongFrom Indonesian and ; ; zh, c=鑼, p=luó; ; ; ; ; is a percussion instrument originating from Southeast Asia, and used widely in Southeast Asian and East Asian musical traditions. Gongs are made of metal and are circular and fl ...
, hand-held microphones, filters, and potentiometers, and ''Mixtur'' for orchestra, four sine-wave generators, and four ring modulator
In electronics, ring modulation is a signal processing function, an implementation of frequency mixing, in which two signals are combined to yield an output signal. One signal, called the carrier, is typically a sine wave or another simple wa ...
s. In 1965 he composed '' Mikrophonie II'' for choir, Hammond organ, and ring modulators.
In 1966–1967, Reed Ghazala discovered and began to teach "circuit bending
Circuit bending is the creative customization of the circuits within electronic devices such as children's toys and digital synthesizers to create new musical or visual instruments and sound generators. Circuit bending is manipulating a circuit ...
"—the application of the creative short circuit, a process of chance short-circuiting, creating experimental electronic instruments, exploring sonic elements mainly of timbre and with less regard to pitch or rhythm, and influenced by John Cage
John Milton Cage Jr. (September 5, 1912 – August 12, 1992) was an American composer and music theorist. A pioneer of indeterminacy in music, electroacoustic music, and Extended technique, non-standard use of musical instruments, Cage was one ...
's aleatoric music
Aleatoric music (also aleatory music or chance music; from the Latin language, Latin word ''alea'', meaning "dice") is music in which some Aspect of music, element of the composition is left to Randomness, chance, and/or some primary element of a ...
concept.["This element of embracing errors is at the centre of Circuit Bending, it is about creating sounds that are not supposed to happen and not supposed to be heard (). In terms of musicality, as with electronic art music, it is primarily concerned with timbre and takes little regard for pitch and rhythm in a classical sense. ... . In a similar vein to Cage's aleatoric music, the art of Bending is dependent on chance, when a person prepares to bend they have no idea of the outcome" ().]
Cosey Fanni Tutti
Cosey Fanni Tutti (born Christine Carol Newby; 4 November 1951) is an English performance artist, musician and writer, best known for her time in the avant-garde groups Throbbing Gristle and Chris & Cosey.
Tutti first performed under the name ...
's performance art and musical career explored the concept of 'acceptable' music and she went on to explore the use of sound as a means of desire or discomfort.
Wendy Carlos
Wendy Carlos (born Walter Carlos; November 14, 1939) is an American musician and composer known for electronic music and film scores.
Born and raised in Rhode Island, Carlos studied physics and music at Brown University before moving to New Y ...
performed selections from her album ''Switched-On Bach'' on stage with a synthesizer with the St. Louis Symphony Orchestra
The St. Louis Symphony Orchestra (SLSO) is an American symphony orchestra based in St. Louis, Missouri. Founded in 1880 by Joseph Otten as the St. Louis Choral Society, the St. Louis Symphony Orchestra is the second-oldest professional symphony or ...
; another live performance was with Kurzweil Baroque Ensemble for "Bach at the Beacon" in 1997. In June 2018, Suzanne Ciani
Suzanne Ciani (; born June 4, 1946) is an American musician, sound designer, composer, and record label executive who found early success in the 1970s, with her electronic music and sound effects for films and television commercials. Her career h ...
released ''LIVE Quadraphonic'', a live album documenting her first solo performance on a Buchla synthesizer in 40 years. It was one of the first quadraphonic vinyl releases in over 30 years.
Japanese instruments
 In the 1950s,
In the 1950s,[. : the first model by ]JVC
JVC (short for Japan Victor Company) is a Japanese brand owned by JVCKenwood. Founded in 1927 as the Victor Talking Machine Company of Japan and later as , the company was best known for introducing Japan's first televisions and for developin ...
was "EO-4420" in 1958. See also the Japanese Wikipedia article: " w:ja:ビクトロン#機種". Japanese electronic musical instrument
An electronic musical instrument or electrophone is a musical instrument that produces sound using electronics, electronic circuitry. Such an instrument sounds by outputting an electrical, electronic or digital audio signal that ultimately is ...
s began influencing the international music industry
The music industry are individuals and organizations that earn money by Songwriter, writing songs and musical compositions, creating and selling Sound recording and reproduction, recorded music and sheet music, presenting live music, concerts, ...
.[. : the first model by Yamaha was "D-1" in 1959."][Russell Hartenberger (2016)]
''The Cambridge Companion to Percussion'', p. 84
Cambridge University Press Ikutaro Kakehashi
, also known by the nickname Taro, was a Japanese engineer, inventor, and entrepreneur. He founded the musical instrument manufacturers Ace Tone, Roland Corporation and Boss Corporation, and the audiovisual electronics company ATV Corporation.
...
, who founded Ace Tone
Ace Electronic Industries Inc., or Ace Tone, was a manufacturer of electronic musical instruments, including electronic organs, analogue drum machines, and electronic drums, as well as amplifiers and effects pedals. Founded in 1960 by Ikutaro Ka ...
in 1960, developed his own version of electronic percussion that had been already popular on the overseas electronic organ.NAMM Show
The NAMM Show is an annual trade show in the United States organized by the National Association of Music Merchants (NAMM), which describes it as "the industry’s largest stage, uniting the global music, sound and entertainment technology commun ...
, he revealed it as the R-1 Rhythm Ace, a hand-operated percussion device that played electronic drum sounds manually as the user pushed buttons, in a similar fashion to modern electronic drum pads.Korg
, founded as Keio Electronic Laboratories, is a Japanese multinational corporation that manufactures electronic musical instrument
An electronic musical instrument or electrophone is a musical instrument that produces sound using electr ...
released the Donca-Matic DA-20, an electro-mechanical drum machine
A drum machine is an electronic musical instrument that creates percussion sounds, drum beats, and patterns. Drum machines may imitate drum kits or other percussion instruments, or produce unique sounds, such as synthesized electronic tones. A d ...
.[ In 1965, ]Nippon Columbia
, often pronounced ''Korombia'', operating internationally as , is a Japanese record label founded in 1910 as Nipponophone Co., Ltd. It affiliated itself with the Columbia Graphophone Company of the United Kingdom and adopted the standard UK C ...
patented a fully electronic drum machine.Korg Mini Pops
The Mini Pops were a number of early analog drum machines from the Japanese musical equipment company Korg during the late 1960s and the 1970s. The machines were based around a number of preset rhythm patterns, such as waltz, samba, rhumba, bossa ...
, which was developed as an option for the Yamaha Electone electric organ.breaks
Break or Breaks or The Break may refer to:
Time off from duties
* Recess (break), time in which a group of people is temporarily dismissed from its duties
* Break (work), time off during a shift/recess
** Coffee break, a short mid-morning rest ...
and fill-ins."Ikutaro Kakehashi
, also known by the nickname Taro, was a Japanese engineer, inventor, and entrepreneur. He founded the musical instrument manufacturers Ace Tone, Roland Corporation and Boss Corporation, and the audiovisual electronics company ATV Corporation.
...
patented a preset rhythm-pattern generator using diode matrix
A diode matrix is a two-dimensional grid of wires: each "intersection" wherein one-row crosses over another has either a diode
A diode is a two-Terminal (electronics), terminal electronic component that conducts electric current primarily in ...
circuit[
] similar to the Seeburg's prior filed in 1964 (See Drum machine#History), which he released as the FR-1 Rhythm Ace drum machine the same year.cymbal
A cymbal is a common percussion instrument. Often used in pairs, cymbals consist of thin, normally round plates of various alloys. The majority of cymbals are of indefinite pitch, although small disc-shaped cymbals based on ancient designs sou ...
, claves
Claves (; ) are a percussion instrument consisting of a pair of short, wooden sticks about 20–25 centimeters (8–10 inches) long and about 2.5 centimeters (1 inch) in diameter. Although traditionally made of wood (typically rosewood, ebony ...
, cowbell
A cowbell (or cow bell) is a bell (instrument), bell worn around the neck of free-roaming livestock so herders can keep track of an animal via the sound of the bell when the animal is grazing out of view in hilly landscapes or vast plains. ...
and bass drum
The bass drum is a large drum that produces a note of low definite or indefinite pitch. The instrument is typically cylindrical, with the drum's diameter usually greater than its depth, with a struck head at both ends of the cylinder. The head ...
). The rhythm patterns could also be cascaded together by pushing multiple rhythm buttons simultaneously, and the possible combination of rhythm patterns were more than a hundred.popular music
Popular music is music with wide appeal that is typically distributed to large audiences through the music industry. These forms and styles can be enjoyed and performed by people with little or no musical training.Popular Music. (2015). ''Fun ...
from the late 1960s, followed by Korg drum machines in the 1970s.Roland Corporation
is a Japanese multinational manufacturer of electronic musical instruments, electronic equipment, and software. It was founded by Ikutaro Kakehashi in Osaka on 18 April 1972. In 2005, its headquarters relocated to Hamamatsu in Shizuoka Prefect ...
in 1972, with Roland synthesizers
Roland (; ; or ''Rotholandus''; or ''Rolando''; died 15 August 778) was a Frankish military leader under Charlemagne who became one of the principal figures in the literary cycle known as the Matter of France. The historical Roland was mili ...
and drum machines
A drum machine is an electronic musical instrument that creates percussion sounds, drum beats, and patterns. Drum machines may imitate drum kits or other percussion instruments, or produce unique sounds, such as synthesized electronic tones. A d ...
becoming highly influential for the next several decades.popular music
Popular music is music with wide appeal that is typically distributed to large audiences through the music industry. These forms and styles can be enjoyed and performed by people with little or no musical training.Popular Music. (2015). ''Fun ...
, and do more to shape popular electronic music than any other company.Turntablism
Turntablism is the art of manipulating sounds and creating new music, sound effects, mixes and other creative sounds and beats, typically by using two or more Phonograph, turntables and a cross fader-equipped DJ mixer. The mixer is plugged into ...
has origins in the invention of direct-drive turntable
A direct-drive turntable is one of the three main phonograph designs currently being produced. The other styles are the belt-drive turntable and the idler-wheel type. Each name is based upon the type of coupling used between the platter of th ...
s. Early belt-drive turntable
There are three main types of phonograph turntable drives being manufactured today: the belt-drive, idler-wheel and direct-drive systems; the names are based upon the type of coupling used between the platter of the turntable and the motor.
In ...
s were unsuitable for turntablism, since they had a slow start-up time, and they were prone to wear-and-tear and breakage, as the belt would break from backspin or scratching. The first direct-drive turntable was invented by Shuichi Obata, an engineer at Matsushita (now Panasonic
is a Japanese multinational electronics manufacturer, headquartered in Kadoma, Osaka, Kadoma, Japan. It was founded in 1918 as in Fukushima-ku, Osaka, Fukushima by Kōnosuke Matsushita. The company was incorporated in 1935 and renamed and c ...
), based in Osaka
is a Cities designated by government ordinance of Japan, designated city in the Kansai region of Honshu in Japan. It is the capital of and most populous city in Osaka Prefecture, and the List of cities in Japan, third-most populous city in J ...
, Japan. It eliminated belts, and instead employed a motor to directly drive a platter on which a vinyl record rests.[Trevor Pinch, Karin Bijsterveld]
''The Oxford Handbook of Sound Studies'', page 515
Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the publishing house of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world. Its first book was printed in Oxford in 1478, with the Press officially granted the legal right to print books ...
In 1969, Matsushita released it as the SP-10,hip hop music
Hip-hop or hip hop (originally disco rap) is a popular music Music genre, genre that emerged in the early 1970s from the African Americans, African-American community of New York City. The style is characterized by its synthesis of a wide r ...
ians,[Six Machines That Changed The Music World](_blank)
''Wired
Wired may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Music
* ''Wired'' (Jeff Beck album), 1976
* ''Wired'' (Hugh Cornwell album), 1993
* ''Wired'' (Mallory Knox album), 2017
* "Wired", a song by Prism from their album '' Beat Street''
* "Wired ...
'', May 2002
Jamaican dub music
In Jamaica, a form of popular electronic music emerged in the 1960s, dub music
Dub is a musical style that grew out of reggae in the late 1960s and early 1970s. It is commonly considered a subgenre of reggae, though it has developed to extend beyond that style.Dub: soundscapes and shattered songs in Jamaican reggae, p.&nb ...
, rooted in sound system Sound system may refer to:
Technology media
* Sound reinforcement system, a system for amplifying audio for an audience
* High fidelity, a sound system intended for accurate reproduction of music in the home
* Public address system, an institution ...
culture. Dub music was pioneered by studio engineers, such as Sylvan Morris, King Tubby
Osbourne Ruddock (28 January 1941 – 6 February 1989), better known as King Tubby, was a Jamaican sound engineer who influenced the development of dub music in the 1960s and 1970s.
Tubby's studio work, in which as a mixing engineer he achiev ...
, Errol Thompson, Lee "Scratch" Perry
Lee "Scratch" Perry (born Rainford Hugh Perry; 20 March 1936 – 29 August 2021) was a Jamaican record producer, songwriter and singer noted for his innovative studio techniques and production style. Perry was a pioneer in the 1970s development ...
, and Scientist
A scientist is a person who Scientific method, researches to advance knowledge in an Branches of science, area of the natural sciences.
In classical antiquity, there was no real ancient analog of a modern scientist. Instead, philosophers engag ...
, producing reggae
Reggae () is a music genre that originated in Jamaica during the late 1960s. The term also denotes the modern popular music of Jamaica and its Jamaican diaspora, diaspora. A 1968 single by Toots and the Maytals, "Do the Reggay", was the first ...
-influenced experimental music
Experimental music is a general label for any music or music genre that pushes existing boundaries and genre definitions. Experimental compositional practice is defined broadly by exploratory sensibilities radically opposed to, and questioning of, ...
with electronic sound technology, in recording studios and at sound system parties.musique concrète
Musique concrète (; ): " problem for any translator of an academic work in French is that the language is relatively abstract and theoretical compared to English; one might even say that the mode of thinking itself tends to be more schematic ...
'', an emphasis on repetitive rhythmic structures (often stripped of their harmonic elements) comparable to minimalism
In visual arts, music, and other media, minimalism is an art movement that began in the post-war era in western art. The movement is often interpreted as a reaction to abstract expressionism and modernism; it anticipated contemporary post-mi ...
, the electronic manipulation of spatiality, the sonic electronic manipulation of pre-recorded musical materials from mass media, deejays toasting over pre-recorded music comparable to live electronic music
Live electronic music (also known as live electronics) is a form of music that can include traditional electronic sound-generating devices, modified electric musical instruments, hacked sound generating technologies, and computers. Initially the pr ...
,remix
A remix, also sometimes called reorchestration or rework, is a piece of media which has been altered or contorted from its original state by adding, removing, or changing pieces of the item. A song, piece of artwork, book, poem, or photograph ca ...
ing music,turntablism
Turntablism is the art of manipulating sounds and creating new music, sound effects, mixes and other creative sounds and beats, typically by using two or more Phonograph, turntables and a cross fader-equipped DJ mixer. The mixer is plugged into ...
,[Nicholas Collins, Julio d' Escrivan Rincón (2007)]
''The Cambridge Companion to Electronic Music'', page 49
Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press was the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted a letters patent by King Henry VIII in 1534, it was the oldest university press in the world. Cambridge University Press merged with Cambridge Assessme ...
and the mixing and scratching of vinyl.
Despite the limited electronic equipment available to dub pioneers such as King Tubby and Lee "Scratch" Perry, their experiments in remix culture were musically cutting-edge.[Nicholas Collins, Margaret Schedel, Scott Wilson (2013)]
''Electronic Music: Cambridge Introductions to Music'', page 20
Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press was the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted a letters patent by King Henry VIII in 1534, it was the oldest university press in the world. Cambridge University Press merged with Cambridge Assessme ...
King Tubby, for example, was a sound system proprietor and electronics technician, whose small front-room studio in the Waterhouse ghetto of western Kingston
Kingston may refer to:
Places
* List of places called Kingston, including the six most populated:
** Kingston, Jamaica
** Kingston upon Hull, England
** City of Kingston, Victoria, Australia
** Kingston, Ontario, Canada
** Kingston upon Thames, ...
was a key site of dub music creation.
Late 1960s to early 1980s
Rise of popular electronic music
In the late 1960s, pop and rock musicians, including the Beach Boys
The Beach Boys are an American Rock music, rock band formed in Hawthorne, California, in 1961. The group's original lineup consisted of brothers Brian Wilson, Brian, Dennis Wilson, Dennis, and Carl Wilson, their cousin Mike Love, and their f ...
and the Beatles
The Beatles were an English Rock music, rock band formed in Liverpool in 1960. The core lineup of the band comprised John Lennon, Paul McCartney, George Harrison and Ringo Starr. They are widely regarded as the Cultural impact of the Beatle ...
, began to use electronic instruments, like the theremin
The theremin (; originally known as the ætherphone, etherphone, thereminophone or termenvox/thereminvox) is an electronic musical instrument controlled without physical contact by the performer (who is known as a thereminist). It is named aft ...
and Mellotron
The Mellotron is an electro-mechanical musical instrument developed in Birmingham, England, in 1963. It is played by pressing its keys, each of which causes a length of magnetic tape to contact a Capstan (tape recorder), capstan, which pulls i ...
, to supplement and define their sound. The first bands to utilize the Moog synthesizer
The Moog synthesizer ( ) is a modular synthesizer invented by the American engineer Robert Moog in 1964. Moog's company, R. A. Moog Co., produced numerous models from 1965 to 1981, and again from 2014. It was the first commercial synthesizer ...
would be the Doors
The Doors were an American rock band formed in Los Angeles in 1965, comprising vocalist Jim Morrison, keyboardist Ray Manzarek, guitarist Robby Krieger and drummer John Densmore. They were among the most influential and controversial rock acts ...
on their 1967 song " Strange Days" and the Monkees
The Monkees were an American pop rock band formed in Los Angeles in the mid-1960s. The band consisted of Micky Dolenz, Davy Jones (musician), Davy Jones, Michael Nesmith, and Peter Tork. Spurred by the success of ''The Monkees (TV series), Th ...
on their album '' Pisces, Aquarius, Capricorn & Jones Ltd.'', also in 1967. In his book ''Electronic and Experimental Music'', Thom Holmes recognises the Beatles' 1966 recording "Tomorrow Never Knows
"Tomorrow Never Knows" is a song by the English rock band the Beatles, written primarily by John Lennon and credited to Lennon–McCartney. It was released in August 1966 as the final track on their album ''Revolver'', although it was the firs ...
" as the song that "ushered in a new era in the use of electronic music in rock and pop music" due to the band's incorporation of tape loops and reversed and speed-manipulated tape sounds.
Also in the late 1960s, the music duos Silver Apples
Silver Apples were an American electronic rock group from New York, active between 1967 and 1970, before reforming in the mid-1990s. It was composed of Simeon (born Simeon Oliver Coxe III, June 4, 1938 – September 8, 2020), who performed ...
, Beaver and Krause, and experimental rock bands like White Noise
In signal processing, white noise is a random signal having equal intensity at different frequencies, giving it a constant power spectral density. The term is used with this or similar meanings in many scientific and technical disciplines, i ...
, the United States of America
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 contiguou ...
, Fifty Foot Hose, and Gong
A gongFrom Indonesian language, Indonesian and ; ; zh, c=鑼, p=luó; ; ; ; ; is a percussion instrument originating from Southeast Asia, and used widely in Southeast Asian and East Asian musical traditions. Gongs are made of metal and ...
are regarded as pioneers in the electronic rock and electronica
Electronica is both a broad group of electronic-based music styles intended for listening rather than strictly for dancing and a music scene that came to prominence in the early 1990s in the United Kingdom. In the United States, the term is mos ...
genres for their work in melding psychedelic rock with oscillators and synthesizers. The 1969 instrumental "Popcorn
Popcorn (also called popped corn, popcorns, or pop-corn) is a variety of corn kernel which expands and puffs up when heated. The term also refers to the snack food produced by the expansion. It is one of the oldest snacks, with evidence of p ...
" written by Gershon Kingsley for ''Music To Moog By'' became a worldwide success due to the 1972 version made by Hot Butter
Hot Butter were an American instrumental band fronted by the keyboard player and studio musician Stan Free. The other band members were John Abbott (arranger, guitar), brothers Bill (producer, engineer, percussion) and Steve Jerome (producer, ...
.
The Moog synthesizer was brought to the mainstream in 1968 by ''Switched-On Bach
''Switched-On Bach'' is the debut album by the American composer Wendy Carlos, released in October 1968 by Columbia Records. Produced by Carlos and Rachel Elkind, the album is a collection of pieces by Johann Sebastian Bach performed by Carlos ...
'', a bestselling album of Bach compositions arranged for Moog synthesizer by American composer Wendy Carlos
Wendy Carlos (born Walter Carlos; November 14, 1939) is an American musician and composer known for electronic music and film scores.
Born and raised in Rhode Island, Carlos studied physics and music at Brown University before moving to New Y ...
. The album achieved critical and commercial success, winning the 1970 Grammy Awards
The 12th Annual Grammy Awards were held on March 11, 1970. They recognized accomplishments of musicians for the year 1969.
Award winners
*Record of the Year
**Bones Howe (producer) & The 5th Dimension for "Aquarius/Let the Sunshine In"
* Album o ...
for Best Classical Album, Best Classical Performance – Instrumental Soloist or Soloists (With or Without Orchestra), and Best Engineered Classical Recording.
In 1969, David Borden formed the world's first synthesizer ensemble called the Mother Mallard's Portable Masterpiece Company in Ithaca, New York.
 By the end of the 1960s, the
By the end of the 1960s, the Moog synthesizer
The Moog synthesizer ( ) is a modular synthesizer invented by the American engineer Robert Moog in 1964. Moog's company, R. A. Moog Co., produced numerous models from 1965 to 1981, and again from 2014. It was the first commercial synthesizer ...
took a leading place in the sound of emerging progressive rock
Progressive rock (shortened as prog rock or simply prog) is a broad genre of rock music that primarily developed in the United Kingdom through the mid- to late 1960s, peaking in the early-to-mid-1970s. Initially termed " progressive pop", the ...
with bands including Pink Floyd
Pink Floyd are an English Rock music, rock band formed in London in 1965. Gaining an early following as one of the first British psychedelic music, psychedelic groups, they were distinguished by their extended compositions, sonic experiments ...
, Yes
Yes or YES may refer to:
* An affirmative particle in the English language; see yes and no
Education
* YES Prep Public Schools, Houston, Texas, US
* Young Eisner Scholars, in Los Angeles, New York City, Chicago, and Appalachia, US
* Young Ep ...
, Emerson, Lake & Palmer
Emerson, Lake & Palmer (informally known as ELP) were an English progressive rock Supergroup (music), supergroup formed in London in 1970. The band consisted of Keith Emerson (keyboards) of The Nice, Greg Lake (vocals, bass, guitars, producer) ...
, and Genesis
Genesis may refer to:
Religion
* Book of Genesis, the first book of the biblical scriptures of both Judaism and Christianity, describing the creation of the Earth and of humankind
* Genesis creation narrative, the first several chapters of the Bo ...
making them part of their sound. Instrumental prog rock was particularly significant in continental Europe, allowing bands like Kraftwerk
Kraftwerk (, ) is a Germany, German Electronic music, electronic band formed in Düsseldorf in 1970 by Ralf Hütter and Florian Schneider. Widely considered innovators and pioneers of electronic music, Kraftwerk was among the first successful a ...
, Tangerine Dream
Tangerine Dream is a German electronic music band founded in 1967 by Edgar Froese. The group has seen many personnel changes over the years, with Froese the only constant member until his death in January 2015. The best-known lineup of the grou ...
, Cluster
may refer to:
Science and technology Astronomy
* Cluster (spacecraft), constellation of four European Space Agency spacecraft
* Cluster II (spacecraft), a European Space Agency mission to study the magnetosphere
* Asteroid cluster, a small ...
, Can, Neu!
Neu! (; German for "New!"; styled in block capitals) were a West German krautrock band formed in Düsseldorf in 1971 by Klaus Dinger and Michael Rother following their departure from Kraftwerk. The group's albums were produced by Conny Plank, w ...
, and Faust
Faust ( , ) is the protagonist of a classic German folklore, German legend based on the historical Johann Georg Faust (). The erudite Faust is highly successful yet dissatisfied with his life, which leads him to make a deal with the Devil at a ...
to circumvent the language barrier. Their synthesiser-heavy "krautrock
Krautrock (also called , German for ) is a broad genre of experimental rock that developed in Germany in the late 1960s and early 1970s. It originated among artists who blended elements of psychedelic rock, avant-garde composition, and electron ...
", along with the work of Brian Eno
Brian Peter George Jean-Baptiste de la Salle Eno (, born 15 May 1948), also mononymously known as Eno, is an English musician, songwriter, record producer, visual artist, and activist. He is best known for his pioneering contributions to ambien ...
(for a time the keyboard player with Roxy Music
Roxy Music are an English rock music, rock band formed in 1970 by Bryan Ferry (lead vocals/keyboards/principal songwriter) and Graham Simpson (musician), Graham Simpson (bass). By the time the band recorded their Roxy Music (album), first albu ...
), would be a major influence on subsequent electronic rock
Electronic rock (also known as electro rock and synth rock) is a music genre that involves a combination of rock music and electronic music, featuring instruments typically found within both genres. It originates from the late 1960s when rock b ...
.[.]
Ambient dub
Dub is a musical style that grew out of reggae in the late 1960s and early 1970s. It is commonly considered a subgenre of reggae, though it has developed to extend beyond that style.Dub: soundscapes and shattered songs in Jamaican reggae, p.&nb ...
was pioneered by King Tubby and other Jamaican sound art
Sound art is an artistic activity in which sound is utilized as a primary Time-based media, time-based Artistic medium, medium or material. Like many genres of contemporary art, sound art may be interdisciplinary in nature, or be used in Cross-genr ...
ists, using DJ-inspired ambient
Ambient or ambiance or ambience may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Ambiancé'', an unreleased experimental film
* ''Ambient'' (novel), a novel by Jack Womack
Music and sound
* Ambience (sound recording), also known as atmospheres or backgr ...
electronics, complete with drop-outs, echo, equalization and psychedelic
Psychedelics are a subclass of hallucinogenic drugs whose primary effect is to trigger non-ordinary mental states (known as psychedelic experiences or "trips") and a perceived "expansion of consciousness". Also referred to as classic halluci ...
electronic effects. It featured layering techniques and incorporated elements of world music
"World music" is an English phrase for styles of music from non-English speaking countries, including quasi-traditional, Cross-cultural communication, intercultural, and traditional music. World music's broad nature and elasticity as a musical ...
, deep bassline
Bassline (also known as a bass line or bass part) is the term used in many styles of music, such as blues, jazz, funk, Dub music, dub and electronic music, electronic, traditional music, traditional, and classical music, for the low-pitched P ...
s and harmonic sounds.[.] Techniques such as a long echo delay were also used. Other notable artists within the genre include Dreadzone
Dreadzone are a British electronic music group formed in 1993 in London by ex-Big Audio Dynamite drummer Greg Roberts and musician Tim Bran. They have released nine studio albums, two live albums, and two compilations.
They gained a reputatio ...
, Higher Intelligence Agency, The Orb
The Orb are an English electronic music group founded in 1988 by Alex Paterson and Jimmy Cauty. Known for their psychedelic sound, the Orb developed a cult following among clubbers "coming down" from drug-induced highs. Their influential ...
, Ott, Loop Guru
Loop Guru is a worldbeat group consisting of bassist/guitarist Salman Gita (born Sam Dodson) and programmer Jamuud (born David Muddyman). They first met around 1980 and initially played together in The Transmitters (band), The Transmitters and r ...
, Woob
Woob is the stage name of Paul Frankland, an English composer, musician and filmmaker who started recording in the early 1990s. Woob's albums combine elements of ambient, downtempo and space music, with samples from field recordings. Frankl ...
and Transglobal Underground
Transglobal Underground (sometimes written as Trans-Global Underground) is an English electro-world music group, specializing in a fusion of Western culture#Music, western, Music of Asia, Asian and Music of Africa, African music styles (someti ...
.hip hop music
Hip-hop or hip hop (originally disco rap) is a popular music Music genre, genre that emerged in the early 1970s from the African Americans, African-American community of New York City. The style is characterized by its synthesis of a wide r ...
when Jamaican immigrant DJ Kool Herc
Clive Campbell (born April 16, 1955), better known by his stage name DJ Kool Herc, is a Jamaican-American DJ who is credited with being the founder of hip hop music in the Bronx, New York City, in 1973. Nicknamed the Father of Hip-Hop, Campbe ...
in the early 1970s introduced Jamaica's sound system culture and dub music techniques to America. One such technique that became popular in hip hop
Hip-hop or hip hop (originally disco rap) is a popular music genre that emerged in the early 1970s from the African-American community of New York City. The style is characterized by its synthesis of a wide range of musical techniques. Hip- ...
culture was playing two copies of the same record on two turntables in alternation, extending the b-dancers' favorite section. The turntable eventually went on to become the most visible electronic musical instrument, and occasionally the most virtuosic
A virtuoso (from Italian ''virtuoso'', or ; Late Latin ''virtuosus''; Latin ''virtus''; 'virtue', 'excellence' or 'skill') is an individual who possesses outstanding talent and technical ability in a particular art or field such as fine arts, m ...
, in the 1980s and 1990s.Isao Tomita
, often known simply as Tomita, was a Japanese composer, regarded as one of the pioneers of electronic music and space music, and as one of the most famous producers of analog synthesizer arrangements. In addition to creating note-by-note realiza ...
's ''Electric Samurai: Switched on Rock'' (1972), which featured Moog synthesizer renditions of contemporary pop and rock songs,Jean Michel Jarre
Jean-Michel André Jarre (; born 24 August 1948) is a French composer, performer and record producer. He is a pioneer in the electronic, ambient and new-age genres, and is known for organising outdoor spectacles featuring his music, accompan ...
, Vangelis
Evangelos Odysseas Papathanassiou (, ; 29 March 1943 – 17 May 2022), known professionally as Vangelis ( ; , ), was a Greek musician, composer, and producer of electronic, progressive, ambient, and classical orchestral music. He composed ...
, Tomita and Klaus Schulze
Klaus Schulze (4 August 1947 – 26 April 2022) was a German electronic music pioneer, composer and musician. He also used the alias Richard Wahnfried and was a member of the Krautrock bands Tangerine Dream, Ash Ra Tempel, and the Cosmic Jokers ...
who were significant influences on the development of new-age music
New-age is a genre of music intended to create artistic inspiration, relaxation, and optimism. It is used by listeners for yoga, massage, meditation, and reading as a method of stress management to bring about a state of ecstasy rather tha ...
.Space
Space is a three-dimensional continuum containing positions and directions. In classical physics, physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions. Modern physicists usually consider it, with time, to be part of a boundless ...
with their debut studio album ''Magic Fly
''Magic Fly'' is the debut studio album by French band Space. It was recorded in 1976 but released in April 1977 by Disques Vogue. The album reached No. 1 in France, No. 11 on the UK Albums Chart and included the hit single of the same name, wh ...
''Oxygène
''Oxygène'' (, ) is the third studio album by French electronic musician and composer Jean-Michel Jarre. It was first released in France in December 1976 by Disques Motors, and distributed internationally in 1977 by Polydor Records. Jarre recor ...
''. Between 1977 and 1981, Kraftwerk released albums such as '' Trans-Europe Express'', ''The Man-Machine
''The Man-Machine'' () is the seventh studio album by German electronic music band Kraftwerk. It was released on 19 May 1978 by Kling Klang in Germany and by Capitol Records elsewhere. A further refinement of their mechanical style, the album s ...
'' and ''Computer World
''Computer World'' () is the eighth studio album by German electronic band Kraftwerk, released on 11 May 1981. It was accompanied by four singles, including a double A-side UK no. 1 featuring " Computer Love".
The album is themed around compu ...
'', which influenced subgenres of electronic music.
In this era, the sound of rock musicians like Mike Oldfield
Michael Gordon Oldfield (born 15 May 1953) is an English retired musician, songwriter and producer best known for his debut studio album ''Tubular Bells'' (1973), which became an unexpected critical and commercial success. Though primarily a gu ...
and The Alan Parsons Project
The Alan Parsons Project was a British rock music, rock duo formed in London in 1975. Its core membership consisted of producer, audio engineer, musician and composer Alan Parsons, and singer, songwriter and pianist Eric Woolfson. They shared w ...
(who is credited the first rock song to feature a digital vocoder
A vocoder (, a portmanteau of ''vo''ice and en''coder'') is a category of speech coding that analyzes and synthesizes the human voice signal for audio data compression, multiplexing, voice encryption or voice transformation.
The vocoder wa ...
in 1975, ''The Raven
"The Raven" is a narrative poem by American writer Edgar Allan Poe. First published in January 1845, the poem is often noted for its musicality, stylized language and supernatural atmosphere. It tells of a distraught lover who is paid a visit ...
'') used to be arranged and blended with electronic effects and/or music as well, which became much more prominent in the mid-1980s. Jeff Wayne
Jeffry Wayne (born July 1, 1943) is an American composer, musician and lyricist. In 1978, he released '' Jeff Wayne's Musical Version of The War of the Worlds'', his musical adaptation of H. G. Wells' science-fiction novel ''The War of the Wo ...
achieved a long-lasting success with his 1978 electronic rock musical version of ''The War of the Worlds
''The War of the Worlds'' is a science fiction novel by English author H. G. Wells. It was written between 1895 and 1897, and serialised in '' Pearson's Magazine'' in the UK and ''Cosmopolitan'' magazine in the US in 1897. The full novel was ...
''.
Film score
A film score is original music written specifically to accompany a film. The score comprises a number of orchestral, instrumental, or choral pieces called cues, which are timed to begin and end at specific points during the film in order to ...
s also benefit from the electronic sound. During the 1970s and 1980s, Wendy Carlos composed the score for ''A Clockwork Orange
''A Clockwork Orange'' may refer to:
* ''A Clockwork Orange'' (novel), a 1962 novel by Anthony Burgess
** ''A Clockwork Orange'' (film), a 1971 film directed by Stanley Kubrick based on the novel
*** ''A Clockwork Orange'' (soundtrack), the film ...
'', '' The Shining'' and ''Tron
''Tron'' (stylized as ''TRON'') is a 1982 American science fiction action adventure film written and directed by Steven Lisberger from a story by Lisberger and Bonnie MacBird. The film stars Jeff Bridges as Kevin Flynn, a computer programmer ...
''. In 1977, Gene Page
Eugene Edgar Page Jr. (September 13, 1939 – August 24, 1998) was an American conductor, composer, arranger and record producer, most active from the mid-1960s through the mid-1980s.
His sound can be heard in the arrangements he did for Jeffer ...
recorded a disco version of the hit theme by John Williams
John Towner Williams (born February 8, 1932)Nylund, Rob (November 15, 2022)Classic Connection review, ''WBOI'' ("For the second time this year, the Fort Wayne Philharmonic honored American composer, conductor, and arranger John Williams, who w ...
from Steven Spielberg
Steven Allan Spielberg ( ; born December 18, 1946) is an American filmmaker. A major figure of the New Hollywood era and pioneer of the modern blockbuster, Spielberg is widely regarded as one of the greatest film directors of all time and is ...
film ''Close Encounters of the Third Kind
''Close Encounters of the Third Kind'' is a 1977 American science fiction film, science fiction drama film written and directed by Steven Spielberg, starring Richard Dreyfuss, Melinda Dillon, Teri Garr, Bob Balaban, Cary Guffey, and François ...
''. Page's version peaked on the R&B chart at #30. The score of 1978 film '' Midnight Express'' composed by Italian synth-pioneer Giorgio Moroder
Giovanni Giorgio Moroder (, ; born 26 April 1940) is an Italian composer and music producer. Dubbed the "Honorific nicknames in popular music, Father of Disco", Moroder is credited with pioneering Euro disco and electronic dance music. His work ...
won the Academy Award for Best Original Score
The Academy Award for Best Original Score is an award presented annually by the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences (AMPAS) to the best substantial body of music in the form of dramatic underscoring written specifically for the film by ...
in 1979
Events
January
* January 1
** United Nations Secretary-General Kurt Waldheim heralds the start of the ''International Year of the Child''. Many musicians donate to the ''Music for UNICEF Concert'' fund, among them ABBA, who write the song ...
, as did it again in 1981
Events January
* January 1
** Greece enters the European Economic Community, predecessor of the European Union.
** Palau becomes a self-governing territory.
* January 6 – A funeral service is held in West Germany for Nazi Grand Admiral ...
the score by Vangelis
Evangelos Odysseas Papathanassiou (, ; 29 March 1943 – 17 May 2022), known professionally as Vangelis ( ; , ), was a Greek musician, composer, and producer of electronic, progressive, ambient, and classical orchestral music. He composed ...
for ''Chariots of Fire
''Chariots of Fire'' is a 1981 historical drama, historical Sports film, sports drama film directed by Hugh Hudson, written by Colin Welland and produced by David Puttnam. It is based on the true story of two British athletes in the 1924 Summer ...
''. After the arrival of punk rock
Punk rock (also known as simply punk) is a rock music genre that emerged in the mid-1970s. Rooted in 1950s rock and roll and 1960s garage rock, punk bands rejected the corporate nature of mainstream 1970s rock music. They typically produced sh ...
, a form of basic electronic rock emerged, increasingly using new digital technology to replace other instruments. The American duo Suicide
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death.
Risk factors for suicide include mental disorders, physical disorders, and substance abuse. Some suicides are impulsive acts driven by stress (such as from financial or ac ...
, who arose from the punk scene in New York, utilized drum machines and synthesizers in a hybrid between electronics and punk on their eponymous 1977 album.
Synth-pop
Synth-pop (short for synthesizer pop; also called techno-pop; ) is a music genre that first became prominent in the late 1970s and features the synthesizer as the dominant musical instrument. It was prefigured in the 1960s and early 1970s b ...
pioneering bands which enjoyed success for years included Ultravox
Ultravox (earlier styled as Ultravox!) were a British new wave band, formed in London in April 1974 as Tiger Lily. Between 1980 and 1986, they scored seven Top Ten albums and seventeen Top 40 singles in the UK, the most successful of which wa ...
with their 1977 track "Hiroshima Mon Amour" on ''Ha!-Ha!-Ha!
''Ha! Ha! Ha!'' is the second album by British pop group Ultravox, at that time known as "Ultravox!", with an exclamation mark, as a nod to Neu!. Although the group would later achieve fame and commercial success with lead singer Midge Ure the ...
'',Yellow Magic Orchestra
Yellow Magic Orchestra (abbreviated to YMO) was a Japanese electronic music band formed in Tokyo in 1978 by Haruomi Hosono (bass, keyboards, vocals), Yukihiro Takahashi (drums, lead vocals, occasional keyboards) and Ryuichi Sakamoto (keyboards, ...
with their self-titled album (1978), The Buggles
The Buggles are an English New wave music, new wave band formed in London in 1977 by singer and bassist Trevor Horn and keyboardist Geoff Downes. They are best known for their 1979 debut single "Video Killed the Radio Star", which topped the UK ...
with their prominent 1979 debut single ''Video Killed the Radio Star
"Video Killed the Radio Star" is a song written by Trevor Horn, Geoff Downes and Bruce Woolley in 1979. It was recorded concurrently by Bruce Woolley and the Camera Club (with Thomas Dolby on keyboards) for their album '' English Garden'' and ...
'',["'The Buggles' by Geoffrey Downes" (liner notes). ''The Age of Plastic'' 1999 reissue.] Gary Numan
Gary Anthony James Webb (born 8 March 1958), known professionally as Gary Numan, is an English singer, songwriter and musician. He entered the music industry as frontman of the New wave music, new wave band Tubeway Army. After releasing two st ...
with his solo debut album '' The Pleasure Principle'' and single ''Cars
A car, or an automobile, is a motor vehicle with wheels. Most definitions of cars state that they run primarily on roads, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport people rather than cargo. There are around one billio ...
'' in 1979, Orchestral Manoeuvres in the Dark
Orchestral Manoeuvres in the Dark (OMD) are an English electronic music, electronic band formed in Meols, Merseyside in 1978 by Andy McCluskey (vocals, bass guitar) and Paul Humphreys (keyboards, vocals). Regarded as pioneers of electronic musi ...
with their 1979 single ''Electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter possessing an electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwel ...
'' featured on their eponymous debut album, Depeche Mode
Depeche Mode are an English electronic music, electronic band formed in Basildon, Essex in 1980. Originally formed with the line-up of Dave Gahan, Martin Gore, Andy Fletcher (musician), Andy Fletcher and Vince Clarke, the band currently consists ...
with their first single ''Dreaming of Me
"Dreaming of Me" is the debut single by English electronic music band Depeche Mode. It was recorded in December 1980 at Blackwing Studios and originally released in February 1981 in the UK via Mute Records. It was not commercially released in ...
'' recorded in 1980 and released in 1981 album '' Speak & Spell'', A Flock of Seagulls
A Flock of Seagulls are an English new wave band formed in Liverpool in 1979. The group, whose best-known line-up comprised Mike Score, Ali Score, Frank Maudsley and Paul Reynolds, hit the peak of their chart success in the early 1980s.
I ...
with their 1981 single ''Talking
Talking or Talkin' may refer to:
* Speech, the product of the action of ''to talk''
* Communication by spoken words; conversation or discussion
Songs
* "Talking" (A Flock of Seagulls song), 1983
* "Talking" (The Rifles song), 2007
* " Talking / ...
'', New Order with ''Ceremony
A ceremony (, ) is a unified ritualistic event with a purpose, usually consisting of a number of artistic components, performed on a special occasion.
The word may be of Etruscan language, Etruscan origin, via the Latin .
Religious and civil ...
'' in 1981, and The Human League
The Human League are an English synth-pop band formed in Sheffield in 1977. Initially an experimental electronic music, electronic outfit, the group signed to Virgin Records in 1979 and later attained widespread commercial success with their t ...
with their 1981 hit ''Don't You Want Me
"Don't You Want Me" is a song by British synth-pop group the Human League (credited on the cover as the Human League 100). It was released on 27 November 1981 as the fourth single from their third studio album, '' Dare'' (1981). The band's be ...
'' from their third album ''Dare
Dare may refer to:
Places
* Dare, Vera Cruz, a ''suco'' in Vera Cruz administrative post, Dili Municipality, Timor-Leste
* Darè, Italy, a comune
* Dare County, North Carolina, United States
* Dare, Virginia, United States, an unincorporate ...
''.[.]
The definition of MIDI
Musical Instrument Digital Interface (; MIDI) is an American-Japanese technical standard that describes a communication protocol, digital interface, and electrical connectors that connect a wide variety of electronic musical instruments, ...
and the development of digital audio
Digital audio is a representation of sound recorded in, or converted into, digital signal (signal processing), digital form. In digital audio, the sound wave of the audio signal is typically encoded as numerical sampling (signal processing), ...
made the development of purely electronic sounds much easier, with audio engineer
An audio engineer (also known as a sound engineer or recording engineer) helps to produce a recording or a live performance, balancing and adjusting sound sources using equalization, dynamics processing and audio effects, mixing, reproduc ...
s, producers and composers exploring frequently the possibilities of virtually every new model of electronic sound equipment launched by manufacturers. Synth-pop sometimes used synthesizers to replace all other instruments, but it was more common that bands had one or more keyboardists in their line-ups along with guitarists, bassists, and/or drummers. These developments led to the growth of synth-pop, which after it was adopted by the New Romantic
New Romantic was an underground subculture movement that originated in the United Kingdom in the late 1970s. The movement emerged from the nightclub scene in London and Birmingham at venues such as Billy's and The Blitz. The New Romantic mo ...
movement, allowed synthesizers to dominate the pop and rock music of the early 1980s until the style began to fall from popularity in the mid-to-end of the decade.Duran Duran
Duran Duran () are an English pop rock band formed in Birmingham in 1978 by singer Stephen Duffy, keyboardist Nick Rhodes and guitarist/bassist John Taylor (bass guitarist), John Taylor. After several early changes, the band's line-up settled ...
, Spandau Ballet
Spandau Ballet ( ) were an English new wave band formed in Islington, London, in 1979. Inspired by the capital's post-punk underground dance scene, they emerged at the start of the 1980s as the house band for the Blitz Kids (New Romantics), ...
, Culture Club
Culture Club are an English new wave music, new wave band formed in London in 1981. The band comprises Boy George (lead vocals), Roy Hay (musician), Roy Hay (guitar and keyboards), and Mikey Craig (bass guitar), and formerly included Jon Moss ( ...
, Talk Talk
Talk Talk were an English band formed in 1981 by Mark Hollis (vocals, guitar, piano), Lee Harris (drums), Paul Webb (bass), and Simon Brenner (keyboards). Initially a synth-pop group, Talk Talk's first two albums, '' The Party's Over'' (198 ...
, Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
, and Eurythmics
Eurythmics were a British New wave music, new wave duo formed in 1980, consisting of Scottish vocalist Annie Lennox and English musician and producer Dave Stewart (Eurythmics), Dave Stewart. They were both previously in the Tourists, a band t ...
.
Synth-pop was taken up across the world, with international hits for acts including Men Without Hats
Men Without Hats are a Canadians, Canadian New wave music, new wave and synth-pop band, originally from Montreal, Quebec. Their music is characterized by the baritone voice of their lead singer Ivan Doroschuk, as well as their elaborate use of s ...
, Trans-X and Lime from Canada, Telex
Telex is a telecommunication
Telecommunication, often used in its plural form or abbreviated as telecom, is the transmission of information over a distance using electronic means, typically through cables, radio waves, or other communica ...
from Belgium, Peter Schilling, Sandra, Modern Talking
Modern Talking was a German pop duo consisting of arranger, songwriter and producer Dieter Bohlen and singer Thomas Anders. They have been referred to as Germany's most successful pop duo, and have had a number of hit singles, reaching the to ...
, Propaganda
Propaganda is communication that is primarily used to influence or persuade an audience to further an agenda, which may not be objective and may be selectively presenting facts to encourage a particular synthesis or perception, or using loaded l ...
and Alphaville from Germany, Yello
Yello is a Swiss electronic music band, which formed in Zürich in 1979. For most of the band's history, Yello has been a duo consisting of Dieter Meier and Boris Blank; founding member Carlos Perón left in 1983.
Their sound is often charac ...
from Switzerland and Azul y Negro
Azul y Negro is a Spanish synthpop music duo that was founded in 1981 by Carlos García-Vaso, a multi instrumentalist, songwriter and Record producer, producer, and Joaquín Montoya: (b. 1950 Cartagena).
Career
Azul y Negro were pioneers of s ...
from Spain. Also, the synth sound is a key feature of Italo-disco.
Some synth-pop bands created futuristic visual styles of themselves to reinforce the idea of electronic sounds were linked primarily with technology, as Americans Devo
Devo is an American new wave band from Akron, Ohio, formed in 1973. Their classic line-up consisted of two sets of brothers, the Mothersbaughs ( Mark and Bob) and the Casales (Gerald and Bob), along with Alan Myers. The band had a No. 14 ...
and Spaniards Aviador Dro.
Keyboard synthesizers became so common that even heavy metal rock bands, a genre often regarded as the ''opposite'' in aesthetics, sound and lifestyle from that of electronic pop artists by fans of both sides, achieved worldwide success with themes as 1983 ''Jump
JuMP is an algebraic modeling language and a collection of supporting packages for mathematical optimization embedded in the Julia programming language.
JuMP is used by companies, government agencies, academic institutions, software projects ...
'' by Van Halen
Van Halen ( ) was an American rock band formed in Pasadena, California, in 1973. Credited with restoring hard rock to the forefront of the music scene, Van Halen was known for their energetic live performances and the virtuosity of their guit ...
and 1986 '' The Final Countdown'' by Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
, which feature synths prominently.
Proliferation of electronic music research institutions
(EMS), formerly known as Electroacoustic Music in Sweden, is the Swedish national centre for electronic music and sound art
Sound art is an artistic activity in which sound is utilized as a primary Time-based media, time-based Artistic medium, medium or material. Like many genres of contemporary art, sound art may be interdisciplinary in nature, or be used in Cross-genr ...
. The research organisation started in 1964 and is based in Stockholm.
STEIM STEIM (STudio for Electro Instrumental Music) was a center for research and development of new musical instruments in the electronic performing arts, located in Amsterdam, Netherlands. Beginning in the 1970's, STEIM became known as a pioneering cen ...
(1969-2021) was a center for research and development of new musical instruments in the electronic performing arts, located in Amsterdam, Netherlands. It was founded by Misha Mengelberg
Misha Mengelberg (5 June 1935 – 3 March 2017) was a Dutch jazz pianist and composer.Feather, Leonard & Gitler, Ira (2007) ''The Biographical Encyclopedia of Jazz'', p. 459. Oxford University Press. A prominent figure in post-WWII European Jazz ...
, Louis Andriessen
Louis Joseph Andriessen (; 6 June 1939 – 1 July 2021) was a Dutch composer, pianist and academic teacher. Considered the most influential Dutch composer of his generation, he was a central proponent of The Hague school of composition. Although ...
, Peter Schat, Dick Raaymakers, , Reinbert de Leeuw, and Konrad Boehmer
Konrad Boehmer (24 May 1941 – 4 October 2014) was a German- Dutch composer, educator, and writer.
Life
Boehmer was born in Berlin. A self-declared member of the Darmstadt School, he studied composition in Cologne with Karlheinz Stockhausen and ...
. This group of Dutch composers had fought for the reformation of Amsterdam's feudal music structures; they insisted on Bruno Maderna's appointment as musical director of the Concertgebouw Orchestra and enforced the first public fundings for experimental and improvised electronic music in the Netherlands. From 1981-2008, Michel Waisvisz
Michel Waisvisz ( ; 8 July 1949, Leiden – 18 June 2008, Amsterdam) was a Dutch composer, performer and inventor of experimental musical instrument, experimental electronic musical instruments. He was the artistic director of STEIM in Amsterdam f ...
was artistic director, and his live-electronic instruments like the Cracklebox or The Hands inspired international artists to work at STEIM which entertained a residency program since 1992.
IRCAM
IRCAM (French: ''Ircam, '', English: Institute for Research and Coordination in Acoustics/Music) is a French institute dedicated to the research of music and sound, especially in the fields of Avant-garde music, avant garde and Electroacoustic ...
in Paris became a major center for computer music research and realization and development of the Sogitec 4X computer system,[ .] featuring then revolutionary real-time digital signal processing
Digital signal processing (DSP) is the use of digital processing, such as by computers or more specialized digital signal processors, to perform a wide variety of signal processing operations. The digital signals processed in this manner are a ...
. Pierre Boulez
Pierre Louis Joseph Boulez (; 26 March 19255 January 2016) was a French composer, conductor and writer, and the founder of several musical institutions. He was one of the dominant figures of post-war contemporary classical music.
Born in Montb ...
's '' Répons'' (1981) for 24 musicians and 6 soloists used the 4X to transform and route soloists to a loudspeaker system.
Barry Vercoe describes one of his experiences with early computer sounds:

Keyboard synthesizers
 Released in 1970 by
Released in 1970 by Moog Music
Moog Music Inc. ( ) is an American synthesizer company based in Asheville, North Carolina. It was founded in 1953 as R. A. Moog Co. by Robert Moog and his father and was renamed Moog Music in 1972. Its early instruments included the Moog sy ...
, the Mini-Moog
The Minimoog is an analog synthesizer first manufactured by Moog Music between 1970 and 1981. Designed as a more affordable, portable version of the modular Moog synthesizer, it was the first synthesizer sold in retail stores. It was first popula ...
was among the first widely available, portable, and relatively affordable synthesizers. It became once the most widely used synthesizer at that time in both popular and electronic art music.
Patrick Gleeson
Patrick Gleeson (born November 9, 1934) is an American musician, synthesizer pioneer, composer, and producer.
Career
Gleeson moved to San Francisco in the 1960s to teach in the English Department at San Francisco State. Gleeson began experimentin ...
, playing live with Herbie Hancock
Herbert Jeffrey Hancock (born April 12, 1940) is an American jazz musician, bandleader, and composer. He started his career with trumpeter Donald Byrd's group. Hancock soon joined the Miles Davis Quintet, where he helped to redefine the role of ...
at the beginning of the 1970s, pioneered the use of synthesizers in a touring context, where they were subject to stresses the early machines were not designed for.
In 1974, the WDR studio in Cologne acquired an EMS Synthi 100
The EMS Synthi 100 was a large analogue/digital hybrid synthesizer made by Electronic Music Studios, London, originally as a custom order from Radio Belgrade for what was to be the Radio Belgrade Electronic Studio, largely thanks to contact betw ...
synthesizer, which many composers used to produce notable electronic works—including Rolf Gehlhaar
Rolf Rainer Gehlhaar (30 December 1943 – 7 July 2019) was an American composer, Professor in Experimental Music at Coventry University and researcher in assistive technology for music.
Life
Born in Breslau, Gehlhaar was the son of a German rock ...
's ''Fünf deutsche Tänze'' (1975), Karlheinz Stockhausen's ''Sirius
Sirius is the brightest star in the night sky. Its name is derived from the Greek word (Latin script: ), meaning 'glowing' or 'scorching'. The star is designated Canis Majoris, Latinized to Alpha Canis Majoris, and abbr ...
'' (1975–1976), and John McGuire's ''Pulse Music III'' (1978).
Thanks to miniaturization of electronics in the 1970s, by the start of the 1980s keyboard synthesizers, became lighter and affordable, integrating into a single slim unit all the necessary audio synthesis electronics and the piano-style keyboard itself, in sharp contrast with the bulky machinery and " cable spaguetty" employed along with the 1960s and 1970s. First, with analog synthesizers, the trend followed with digital synthesizers and samplers as well (see below).
Digital synthesizers
In 1975, the Japanese company Yamaha licensed the algorithms for frequency modulation synthesis
Frequency modulation synthesis (or FM synthesis) is a form of Synthesizer#Sound synthesis, sound synthesis whereby the frequency of a waveform is changed by Frequency modulation, modulating its frequency with a modulator. The instantaneous frequen ...
(FM synthesis) from John Chowning
John M. Chowning (; born August 22, 1934, in Salem, New Jersey) is an American composer, musician, discoverer, and professor best known for his work at Stanford University, the founding of CCRMA – Center for Computer Research in Music and ...
, who had experimented with it at Stanford University
Leland Stanford Junior University, commonly referred to as Stanford University, is a Private university, private research university in Stanford, California, United States. It was founded in 1885 by railroad magnate Leland Stanford (the eighth ...
since 1971.[.] Yamaha's engineers began adapting Chowning's algorithm for use in a digital synthesizer, adding improvements such as the "key scaling" method to avoid the introduction of distortion that normally occurred in analog systems during frequency modulation.
In 1980, Yamaha eventually released the first FM digital synthesizer, the Yamaha GS-1, but at an expensive price. In 1983, Yamaha introduced the first stand-alone digital synthesizer, the Yamaha DX7, DX7, which also used FM synthesis and would become one of the best-selling synthesizers of all time. The Korg Poly-800 is a synthesizer released by
The Korg Poly-800 is a synthesizer released by Korg
, founded as Keio Electronic Laboratories, is a Japanese multinational corporation that manufactures electronic musical instrument
An electronic musical instrument or electrophone is a musical instrument that produces sound using electr ...
in 1983. Its initial list price of $795 made it the first fully programmable synthesizer that sold for less than $1000. It had 8-voice polyphony with one Digitally controlled oscillator (DCO) per voice.
The Casio CZ synthesizers#CZ-101, Casio CZ-101 was the first and best-selling Phase distortion synthesis, phase distortion synthesizer in the Casio Casio CZ synthesizers, CZ line. Released in November 1984, it was one of the first (if not the first) fully programmable polyphonic synthesizers that was available for under $500.
The Roland D-50 is a digital synthesizer produced by Roland Corporation, Roland and released in April 1987. Its features include subtractive synthesis, on-board effects, a joystick for data manipulation, and an analogue synthesis-styled layout design. The external Roland PG-1000 (1987–1990) programmer could also be attached to the D-50 for more complex manipulation of its sounds.
Samplers
A sampler (musical instrument), sampler is an electronic or digital musical instrument which uses sound recordings (or "Sampling (music), samples") of real instrument sounds (e.g., a piano, violin or trumpet), excerpts from recorded songs (e.g., a five-second bass guitar riff from a funk song) or found sounds (e.g., sirens and ocean waves). The samples are loaded or recorded by the user or by a manufacturer. These sounds are then played back using the sampler program itself, a MIDI keyboard, Music sequencer, sequencer or another triggering device (e.g., electronic drums) to perform or compose music. Because these samples are usually stored in digital memory, the information can be quickly accessed. A single sample may often be pitch shift, pitch-shifted to different pitches to produce musical scale (music), scales and chord (music), chords.
Before computer memory-based samplers, musicians used tape replay keyboards, which store recordings on analog tape. When a key is pressed the tape head contacts the moving tape and plays a sound. The Mellotron
The Mellotron is an electro-mechanical musical instrument developed in Birmingham, England, in 1963. It is played by pressing its keys, each of which causes a length of magnetic tape to contact a Capstan (tape recorder), capstan, which pulls i ...
was the most notable model, used by many groups in the late 1960s and the 1970s, but such systems were expensive and heavy due to the multiple tape mechanisms involved, and the range of the instrument was limited to three octaves at the most. To change sounds a new set of tapes had to be installed in the instrument. The emergence of the digital signal processing, digital sampler made sampling far more practical.
The earliest digital sampling was done on the Electronic Music Studios, EMS Musys system, developed by Peter Grogono (software), David Cockerell (hardware and interfacing), and Peter Zinovieff
Peter Zinovieff (26 January 1933 – 23 June 2021) was a British composer, musician and inventor. In the late 1960s, his company, Electronic Music Studios (EMS), made the VCS3, a synthesizer used by many early progressive rock bands such as Pi ...
(system design and operation) at their London (Putney) Studio c. 1969.
The first commercially available sampling synthesizer was the Sampler (musical instrument)#Computer Music Melodian, Computer Music Melodian by Harry Mendell (1976).
First released in 1977–1978,[
] the Synclavier#Synclavier I, Synclavier I using FM synthesis, re-licensed from Yamaha, and sold mostly to universities, proved to be highly influential among both electronic music composers and music producers, including Mike Thorne, an early adopter from the commercial world, due to its versatility, its cutting-edge technology, and distinctive sounds.
The first polyphonic digital sampling synthesizer was the Australian-produced Fairlight CMI, first available in 1979. These early sampling synthesizers used wavetable sample-based synthesis.[Martin Russ]
''Sound Synthesis and Sampling'', page 29
, CRC Press
Birth of MIDI
In 1980, a group of musicians and music merchants met to standardize an interface that new instruments could use to communicate control instructions with other instruments and computers. This standard was dubbed Musical Instrument Digital Interface (MIDI
Musical Instrument Digital Interface (; MIDI) is an American-Japanese technical standard that describes a communication protocol, digital interface, and electrical connectors that connect a wide variety of electronic musical instruments, ...
) and resulted from a collaboration between leading manufacturers, initially Sequential Circuits, Oberheim Electronics, Oberheim, Roland Corporation, Roland—and later, other participants that included Yamaha, Korg
, founded as Keio Electronic Laboratories, is a Japanese multinational corporation that manufactures electronic musical instrument
An electronic musical instrument or electrophone is a musical instrument that produces sound using electr ...
, and Kawai Musical Instruments, Kawai. A paper was authored by Dave Smith (engineer), Dave Smith of Sequential Circuits and proposed to the Audio Engineering Society in 1981. Then, in August 1983, the MIDI Specification 1.0 was finalized.
MIDI technology allows a single keystroke, control wheel motion, pedal movement, or command from a microcomputer to activate every device in the studio remotely and synchrony, with each device responding according to conditions predetermined by the composer.
MIDI instruments and software made powerful control of sophisticated instruments easily affordable by many studios and individuals. Acoustic sounds became reintegrated into studios via sampling (music), sampling and sampled-ROM-based instruments.
Miller Puckette developed graphic signal-processing software for Sogitec 4X, 4X called Max (software), Max (after Max Mathews
Max Vernon Mathews (November 13, 1926 – April 21, 2011) was an American pioneer of computer music.
Biography
Max Vernon Mathews was born in Columbus, Nebraska, to two science schoolteachers. His father in particular taught physics, chemistry ...
) and later ported it to Apple Macintosh, Macintosh (with Dave Zicarelli extending it for Opcode Systems, Opcode) for real-time MIDI control, bringing algorithmic composition availability to most composers with modest computer programming background.
Sequencers and drum machines
The early 1980s saw the rise of bass synthesizers, the most influential being the Roland TB-303, a bass synthesizer and Music sequencer, sequencer released in late 1981 that later became a fixture in electronic dance music
Electronic dance music (EDM), also referred to as dance music or club music, is a broad range of percussive electronic music genres originally made for nightclubs, raves, and List of electronic dance music festivals, festivals. It is generally ...
, particularly acid house.[.] Music sequencers began being used around the mid 20th century, and Tomita's albums in mid-1970s being later examples.[.] making their early use of the microprocessor-based Roland MC-8 Microcomposer sequencer.electronic drum
Electronic drums are a modern electronic musical instrument, primarily designed to serve as an alternative to an acoustic drum kit. Electronic drums consist of an electronic sound module which produces the Drum synthesiser, synthesized or Sampler ...
s and a synthesizer.Ultravox
Ultravox (earlier styled as Ultravox!) were a British new wave band, formed in London in April 1974 as Tiger Lily. Between 1980 and 1986, they scored seven Top Ten albums and seventeen Top 40 singles in the UK, the most successful of which wa ...
's "Hiroshima Mon Amour (song), Hiroshima Mon Amour" was one of the first singles to use the metronome-like percussion of a Roland TR-77 drum machine.Roland Corporation
is a Japanese multinational manufacturer of electronic musical instruments, electronic equipment, and software. It was founded by Ikutaro Kakehashi in Osaka on 18 April 1972. In 2005, its headquarters relocated to Hamamatsu in Shizuoka Prefect ...
released the Roland TR-808, TR-808, one of the first and most popular programmable drum machine
A drum machine is an electronic musical instrument that creates percussion sounds, drum beats, and patterns. Drum machines may imitate drum kits or other percussion instruments, or produce unique sounds, such as synthesized electronic tones. A d ...
s. The first band to use it was Yellow Magic Orchestra in 1980, and it would later gain widespread popularity with the release of Marvin Gaye's "Sexual Healing" and Afrika Bambaataa's "Planet Rock (song), Planet Rock" in 1982. The TR-808 was a fundamental tool in the later Detroit techno scene of the late 1980s, and was the drum machine of choice for Derrick May (musician), Derrick May and Juan Atkins.
Chiptunes
The characteristic lo-fi sound of chip music was initially the result of early computer's sound chips and sound cards' technical limitations; however, the sound has since become sought after in its own right.
Common cheap popular sound chips of the first home computers of the 1980s include the MOS Technology SID, SID of the Commodore 64 and General Instrument AY-3-8912, General Instrument AY series and clones (like the Yamaha YM2149) used in the ZX Spectrum, Amstrad CPC, MSX compatibles and Atari ST models, among others.
Late 1980s to 1990s
Rise of dance music
Synth-pop continued into the late 1980s, with a format that moved closer to dance music, including the work of acts such as British duos Pet Shop Boys, Erasure (duo), Erasure and The Communards, achieving success along much of the 1990s.
The trend has continued to the present day with modern nightclubs worldwide regularly playing electronic dance music (EDM). Today, electronic dance music has radio stations, websites, and publications like ''Mixmag'' dedicated solely to the genre. Despite the industry's attempt to create a specific EDM brand, the initialism remains in use as an umbrella term for multiple genres, including dance-pop, House music, house, techno, Electro (music), electro, and Trance music, trance, as well as their respective subgenres.[Richard James Burgess (2014), ''The History of Music Production'']
page 115
Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the publishing house of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world. Its first book was printed in Oxford in 1478, with the Press officially granted the legal right to print books ...
[EDM – Electronic Dance Music](_blank)
Armada Music Moreover, the genre has found commercial and cultural significance in the United States and North America, thanks to the wildly popular big room house/EDM sound that has been incorporated into the U.S. pop music and the rise of large-scale commercial raves such as Electric Daisy Carnival, Tomorrowland (festival), Tomorrowland and Ultra Music Festival.
Electronica
On the other hand, a broad group of electronic-based music styles intended for listening rather than strictly for dancing became known under the "electronica
Electronica is both a broad group of electronic-based music styles intended for listening rather than strictly for dancing and a music scene that came to prominence in the early 1990s in the United Kingdom. In the United States, the term is mos ...
" umbrella
Indie electronic
The category "indie electronic" (or "indietronica")[
The first wave of indie electronic artists began in the 1990s with acts such as Stereolab (who used vintage gear) and Disco Inferno (band), Disco Inferno (who embraced modern sampling technology), and the genre expanded in the 2000s as home recording and software synthesizers came into common use.][ Other acts included Broadcast (band), Broadcast, Lali Puna, Múm, the Postal Service, Skeletons (band), Skeletons, and School of Seven Bells.][ Independent labels associated with the style include Warp Records, Warp, Morr Music, Sub Pop, and Ghostly International.][
]
2000s and 2010s
 As computer technology has become more accessible and music software has advanced, interacting with music production technology is now possible using means that bear no relationship to traditional performance, musical performance practices: for instance, laptop computer, laptop performance (''laptronica''), live coding and Algorave. In general, the term Live PA refers to any live performance of electronic music, whether with laptops, synthesizers, or other devices.
Beginning around the year 2000, some software-based virtual studio environments emerged, with products such as Propellerhead's Reason (software), Reason and Ableton Live finding popular appeal. Such tools provide viable and cost-effective alternatives to typical hardware-based production studios, and thanks to advances in microprocessor technology, it is now possible to create high-quality music using little more than a single laptop computer. Such advances have democratized music creation, leading to a massive increase in the amount of home-produced electronic music available to the general public via the internet. Software-based instruments and effect units (so-called "plugins") can be incorporated in a computer-based studio using the VST platform. Some of these instruments are more or less exact replicas of existing hardware (such as the Roland D-50, ARP Odyssey, Yamaha DX7, or Korg M1).
As computer technology has become more accessible and music software has advanced, interacting with music production technology is now possible using means that bear no relationship to traditional performance, musical performance practices: for instance, laptop computer, laptop performance (''laptronica''), live coding and Algorave. In general, the term Live PA refers to any live performance of electronic music, whether with laptops, synthesizers, or other devices.
Beginning around the year 2000, some software-based virtual studio environments emerged, with products such as Propellerhead's Reason (software), Reason and Ableton Live finding popular appeal. Such tools provide viable and cost-effective alternatives to typical hardware-based production studios, and thanks to advances in microprocessor technology, it is now possible to create high-quality music using little more than a single laptop computer. Such advances have democratized music creation, leading to a massive increase in the amount of home-produced electronic music available to the general public via the internet. Software-based instruments and effect units (so-called "plugins") can be incorporated in a computer-based studio using the VST platform. Some of these instruments are more or less exact replicas of existing hardware (such as the Roland D-50, ARP Odyssey, Yamaha DX7, or Korg M1).
Circuit bending
Circuit bending is the modification of battery-powered toys and synthesizers to create new unintended sound effects. It was pioneered by Reed Ghazala in the 1960s and Reed coined the name "circuit bending" in 1992.
Modular synth revival
Following the circuit bending culture, musicians also began to build their own modular synthesizers, causing a renewed interest in the early 1960s designs. Eurorack became a popular system.
See also
* Clavioline
* Electronic sackbut
* List of electronic music genres
* New Interfaces for Musical Expression
* Ondioline
* Spectral music
* Tracker music
* Timeline of electronic music genres
;Live electronic music
* List of electronic music festivals
* Live electronic music
Footnotes
Sources
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
archive
on 10 March 2011)
*
*
Online reprint
, NASA Ames Research Center Technical Memorandum facsimile 2000.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* (First published in German in ''Melos'' 39 (January–February 1972): 42–44.)
*
*
*
*
* (Excerpt exist o
History of Experimental Music in Northern California
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* (cloth); (pbk); (ebook).
*
*
Abstract
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* (at webcitation.org)
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* . Also published in German, as
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* .
*
Further reading
*
*
*
*
* Dorschel, Andreas, Gerhard Eckel, and Deniz Peters (eds.) (2012). ''Bodily Expression in Electronic Music: Perspectives on Reclaiming Performativity''. Routledge Research in Music 2. London and New York: Routledge. .
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Strange, Allen (1983), ''Electronic Music: Systems, Technics, and Controls'', second ed. Dubuque, Iowa: W.C. Brown Co. .
*
External links
*
History of Electroacoustic Music – Timeline
Electronic Music Foundation
History and Development of Electronic Music
{{DEFAULTSORT:Electronic Music
Electronic music,
19th century in music
19th-century music genres
20th century in music
20th-century music genres
21st century in music
21st-century music genres
Audio engineering
New media
Sound effects
 Developments of the
Developments of the 
 The world's first computer to play music was
The world's first computer to play music was  In 1958, Columbia-Princeton developed the
In 1958, Columbia-Princeton developed the  During the time of the
During the time of the  In the 1950s,. : the first model by
In the 1950s,. : the first model by  By the end of the 1960s, the
By the end of the 1960s, the 
 The Korg Poly-800 is a synthesizer released by
The Korg Poly-800 is a synthesizer released by  As computer technology has become more accessible and music software has advanced, interacting with music production technology is now possible using means that bear no relationship to traditional performance, musical performance practices: for instance, laptop computer, laptop performance (''laptronica''), live coding and Algorave. In general, the term Live PA refers to any live performance of electronic music, whether with laptops, synthesizers, or other devices.
Beginning around the year 2000, some software-based virtual studio environments emerged, with products such as Propellerhead's Reason (software), Reason and Ableton Live finding popular appeal. Such tools provide viable and cost-effective alternatives to typical hardware-based production studios, and thanks to advances in microprocessor technology, it is now possible to create high-quality music using little more than a single laptop computer. Such advances have democratized music creation, leading to a massive increase in the amount of home-produced electronic music available to the general public via the internet. Software-based instruments and effect units (so-called "plugins") can be incorporated in a computer-based studio using the VST platform. Some of these instruments are more or less exact replicas of existing hardware (such as the Roland D-50, ARP Odyssey, Yamaha DX7, or Korg M1).
As computer technology has become more accessible and music software has advanced, interacting with music production technology is now possible using means that bear no relationship to traditional performance, musical performance practices: for instance, laptop computer, laptop performance (''laptronica''), live coding and Algorave. In general, the term Live PA refers to any live performance of electronic music, whether with laptops, synthesizers, or other devices.
Beginning around the year 2000, some software-based virtual studio environments emerged, with products such as Propellerhead's Reason (software), Reason and Ableton Live finding popular appeal. Such tools provide viable and cost-effective alternatives to typical hardware-based production studios, and thanks to advances in microprocessor technology, it is now possible to create high-quality music using little more than a single laptop computer. Such advances have democratized music creation, leading to a massive increase in the amount of home-produced electronic music available to the general public via the internet. Software-based instruments and effect units (so-called "plugins") can be incorporated in a computer-based studio using the VST platform. Some of these instruments are more or less exact replicas of existing hardware (such as the Roland D-50, ARP Odyssey, Yamaha DX7, or Korg M1).