|
Timeline Of Electrical And Electronic Engineering
The following timeline tables list the discoveries and inventions in the history of electrical and electronic engineering. History of discoveries timeline History of associated inventions timeline List of IEEE Milestones The following list of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) milestones represent key historical achievements in electrical and electronic engineering. Prior to 1870 *1745–1746 – Leyden jar capacitor by Ewald Georg von Kleist and Pieter van Musschenbroek * 1751 – Book '' Experiments and Observations on Electricity'' by Benjamin Franklin * 1757–1775 – Benjamin Franklin's Work in London * 1799 – Alessandro Volta's Electrical Battery Invention * 1836 – Nicholas Callan's Pioneering Contributions to Electrical Science and Technology * 1828–1837 – Pavel Schilling's Pioneering Contribution to Practical Telegraphy * 1838 – Demonstration of Practical Telegraphy * 1852 – Electric Fire Alarm System * 1857 – Heinrich ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Engineering
Electrical engineering is an engineering discipline concerned with the study, design, and application of equipment, devices, and systems which use electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. It emerged as an identifiable occupation in the latter half of the 19th century after commercialization of the electric telegraph, the telephone, and electrical power generation, distribution, and use. Electrical engineering is now divided into a wide range of different fields, including computer engineering, systems engineering, power engineering, telecommunications, radio-frequency engineering, signal processing, instrumentation, photovoltaic cells, electronics, and optics and photonics. Many of these disciplines overlap with other engineering branches, spanning a huge number of specializations including hardware engineering, power electronics, electromagnetics and waves, microwave engineering, nanotechnology, electrochemistry, renewable energies, mechatronics/control, and electrical m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coulomb's Law
Coulomb's inverse-square law, or simply Coulomb's law, is an experimental law of physics that quantifies the amount of force between two stationary, electrically charged particles. The electric force between charged bodies at rest is conventionally called ''electrostatic force'' or Coulomb force. Although the law was known earlier, it was first published in 1785 by French physicist Charles-Augustin de Coulomb, hence the name. Coulomb's law was essential to the development of the theory of electromagnetism, maybe even its starting point, as it made it possible to discuss the quantity of electric charge in a meaningful way. The law states that the magnitude of the electrostatic force of attraction or repulsion between two point charges is directly proportional to the product of the magnitudes of charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. Coulomb studied the repulsive force between bodies having electrical charges of the same sign: Coulomb als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Sturgeon
William Sturgeon (22 May 1783 – 4 December 1850) was an English physicist and inventor who made the first electromagnets, and invented the first practical British electric motor. Early life Sturgeon was born on 22 May 1783 in Whittington, near Carnforth, Lancashire, and became apprenticed to a shoemaker. Career Sturgeon joined the army in 1802 and taught himself mathematics and physics. In 1824 he became lecturer in Science and Philosophy at the East India Company's Military Seminary at Addiscombe, Surrey, and in the following year he exhibited his first electromagnet.Gee 2004. He displayed its power by lifting nine pounds with a seven-ounce piece of iron wrapped with wire through which a current from a single battery was sent. In 1832 he was appointed to the lecturing staff of the Adelaide Gallery of Practical Science in London, where he first demonstrated the DC electric motor incorporating a commutator. In 1836 he established the journal ''Annals of Electricity, M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermoelectricity
The thermoelectric effect is the direct conversion of temperature differences to electric voltage and vice versa via a thermocouple. A thermoelectric device creates a voltage when there is a different temperature on each side. Conversely, when a voltage is applied to it, heat is transferred from one side to the other, creating a temperature difference. At the atomic scale, an applied temperature gradient causes charge carriers in the material to diffuse from the hot side to the cold side. This effect can be used to generate electricity, measure temperature or change the temperature of objects. Because the direction of heating and cooling is affected by the applied voltage, thermoelectric devices can be used as temperature controllers. The term "thermoelectric effect" encompasses three separately identified effects: the Seebeck effect, Peltier effect, and Thomson effect. The Seebeck and Peltier effects are different manifestations of the same physical process; textbooks ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Johann Seebeck
Thomas Johann Seebeck (; 9 April 1770 – 10 December 1831) was a Baltic German physicist, who, in 1822, observed a relationship between heat and magnetism. Later, in 1823, Ørsted called this phenomenon thermoelectric effect. Seebeck was born in Reval (today Tallinn) to a wealthy Baltic German merchant family. He received a medical degree in 1802 from the University of Göttingen, but preferred to study physics. From 1821 to 1823, Seebeck performed a series of experiments trying to understand Ørsted's findings from 1820. During his experiments, he observed that a junction of dissimilar metals produces a deflexion on a magnetic needle (compass) when exposed to a temperature gradient. Because Ørsted had discovered that an electric current produces a deflexion on a compass transversal to the wire, Seebeck's results were interpreted as a thermoelectric effect. This is now called the Peltier–Seebeck effect and is the basis of thermocouples and thermopiles. Seebeck effect In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right-hand Screw Rule
In mathematics and physics, the right-hand rule is a common mnemonic for understanding orientation of axes in three-dimensional space. It is also a convenient method for quickly finding the direction of a cross-product of 2 vectors. Most of the various left-hand and right-hand rules arise from the fact that the three axes of three-dimensional space have two possible orientations. One can see this by holding one's hands outward and together, palms up, with the thumbs out-stretched to the right and left, and the fingers making a curling motion from straight outward to pointing upward. (Note the picture to right is not an illustration of this.) The curling motion of the fingers represents a movement from the first (''x'' axis) to the second (''y'' axis); the third (''z'' axis) can point along either thumb. Left-hand and right-hand rules arise when dealing with coordinate axes. The rule can be used to find the direction of the magnetic field, rotation, spirals, electromagnetic fiel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
André-Marie Ampère
André-Marie Ampère (, ; ; 20 January 177510 June 1836) was a French physicist and mathematician who was one of the founders of the science of classical electromagnetism, which he referred to as "electrodynamics". He is also the inventor of numerous applications, such as the solenoid (a term coined by him) and the electrical telegraph. As an autodidact, Ampère was a member of the French Academy of Sciences and professor at the École polytechnique and the Collège de France. The SI unit of measurement of electric current, the ampere, is named after him. His name is also one of the 72 names inscribed on the Eiffel Tower. Early life André-Marie Ampère was born on 20 January 1775 to Jean-Jacques Ampère, a prosperous businessman, and Jeanne Antoinette Desutières-Sarcey Ampère, during the height of the French Enlightenment. He spent his childhood and adolescence at the family property at Poleymieux-au-Mont-d'Or near Lyon. Jean-Jacques Ampère, a successful merchant, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Christian Ørsted
Hans Christian Ørsted ( , ; often rendered Oersted in English; 14 August 17779 March 1851) was a Danish physicist and chemist who discovered that electric currents create magnetic fields, which was the first connection found between electricity and magnetism. Oersted's law and the oersted unit (Oe) are named after him. A leader of the Danish Golden Age, Ørsted was a close friend of Hans Christian Andersen and the brother of politician and jurist Anders Sandøe Ørsted, who served as Prime Minister of Denmark from 1853 to 1854. Early life and studies Ørsted was born in Rudkøbing in 1777. As a young boy he developed an interest in science while working for his father, who owned the local pharmacy. He and his brother Anders received most of their early education through self-study at home, going to Copenhagen in 1793 to take entrance exams for the University of Copenhagen, where both brothers excelled academically. By 1796, Ørsted had been awarded honors for his pape ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Telegraph
Electrical telegraphs were point-to-point text messaging systems, primarily used from the 1840s until the late 20th century. It was the first electrical telecommunications system and the most widely used of a number of early messaging systems called '' telegraphs'', that were devised to communicate text messages quicker than physical transportation. Electrical telegraphy can be considered to be the first example of electrical engineering. Text telegraphy consisted of two or more geographically separated stations, called telegraph offices. The offices were connected by wires, usually supported overhead on utility poles. Many different electrical telegraph systems were invented, but the ones that became widespread fit into two broad categories. The first category consists of needle telegraphs in which a needle pointer is made to move electromagnetically with an electric current sent down the telegraph line. Early systems used multiple needles requiring multiple wires. The f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
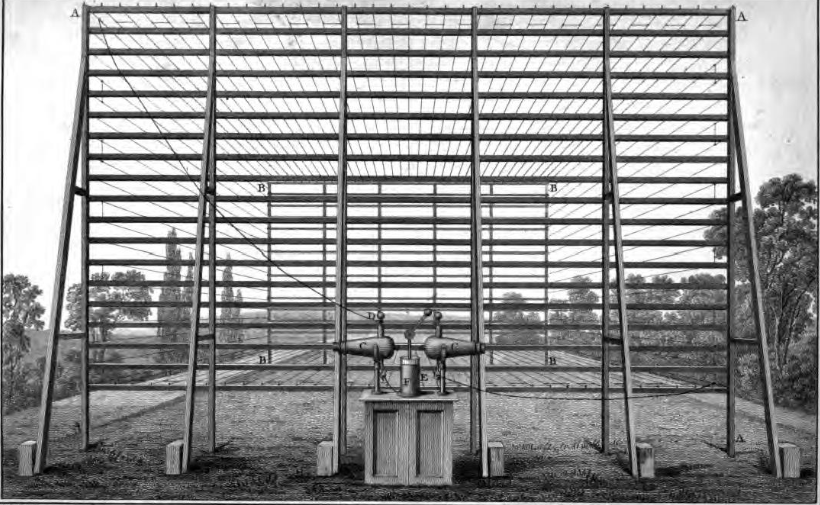
Francis Ronalds
Sir Francis Ronalds FRS (21 February 17888 August 1873) was an English scientist and inventor, and arguably the first electrical engineer. He was knighted for creating the first working electric telegraph over a substantial distance. In 1816 he laid an eight-mile length of iron wire between wooden frames in his mother's garden and sent pulses using electrostatic generators. Upbringing and family Born to Francis Ronalds and Jane (née Field), wholesale cheesemongers, at their business premises in Upper Thames Street, London, he attended Unitarian minister Eliezer Cogan's school before being apprenticed to his father at the age of 14 through the Drapers' Company. He ran the large business for some years. The family later resided in Canonbury Place and Highbury Terrace, both in Islington, at Kelmscott House in Hammersmith, Queen Square in Bloomsbury, at Croydon, and on Chiswick Lane. Several of Ronalds' eleven brothers and sisters also led noteworthy lives. His youngest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Dalton
John Dalton (; 5 or 6 September 1766 – 27 July 1844) was an English chemist, physicist and meteorologist. He is best known for introducing the atomic theory into chemistry, and for his research into colour blindness, which he had. Colour blindness is known as ''Daltonism'' in several languages, being named after him. Early life John Dalton was born into a Quaker family in Eaglesfield, near Cockermouth, in Cumberland, England. His father was a weaver. He received his early education from his father and from Quaker John Fletcher, who ran a private school in the nearby village of Pardshaw Hall. Dalton's family was too poor to support him for long and he began to earn his living, from the age of ten, in the service of wealthy local Quaker Elihu Robinson. Early career When he was 15, Dalton joined his older brother Jonathan in running a Quaker school in Kendal, Westmorland, about from his home. Around the age of 23, Dalton may have considered studying law or medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Young (scientist)
Thomas Young FRS (13 June 177310 May 1829) was a British polymath who made notable contributions to the fields of vision, light, solid mechanics, energy, physiology, language, musical harmony, and Egyptology. He was instrumental in the decipherment of Egyptian hieroglyphs, specifically the Rosetta Stone. Young has been described as " The Last Man Who Knew Everything". His work influenced that of William Herschel, Hermann von Helmholtz, James Clerk Maxwell, and Albert Einstein. Young is credited with establishing the wave theory of light, in contrast to the particle theory of Isaac Newton. Young's work was subsequently supported by the work of Augustin-Jean Fresnel. Personal life Young belonged to a Quaker family of Milverton, Somerset, where he was born in 1773, the eldest of ten children. At the age of fourteen Young had learned Greek and Latin. Young began to study medicine in London at St Bartholomew's Hospital in 1792, moved to the University of Edinburgh Medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |