2005 in music on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
5 (five) is a
 is the third smallest
is the third smallest
 A pentagram, or five-pointed
A pentagram, or five-pointed
"Cubic Symmetric Graphs (The Foster Census)."
The automorphism group of the Petersen graph is the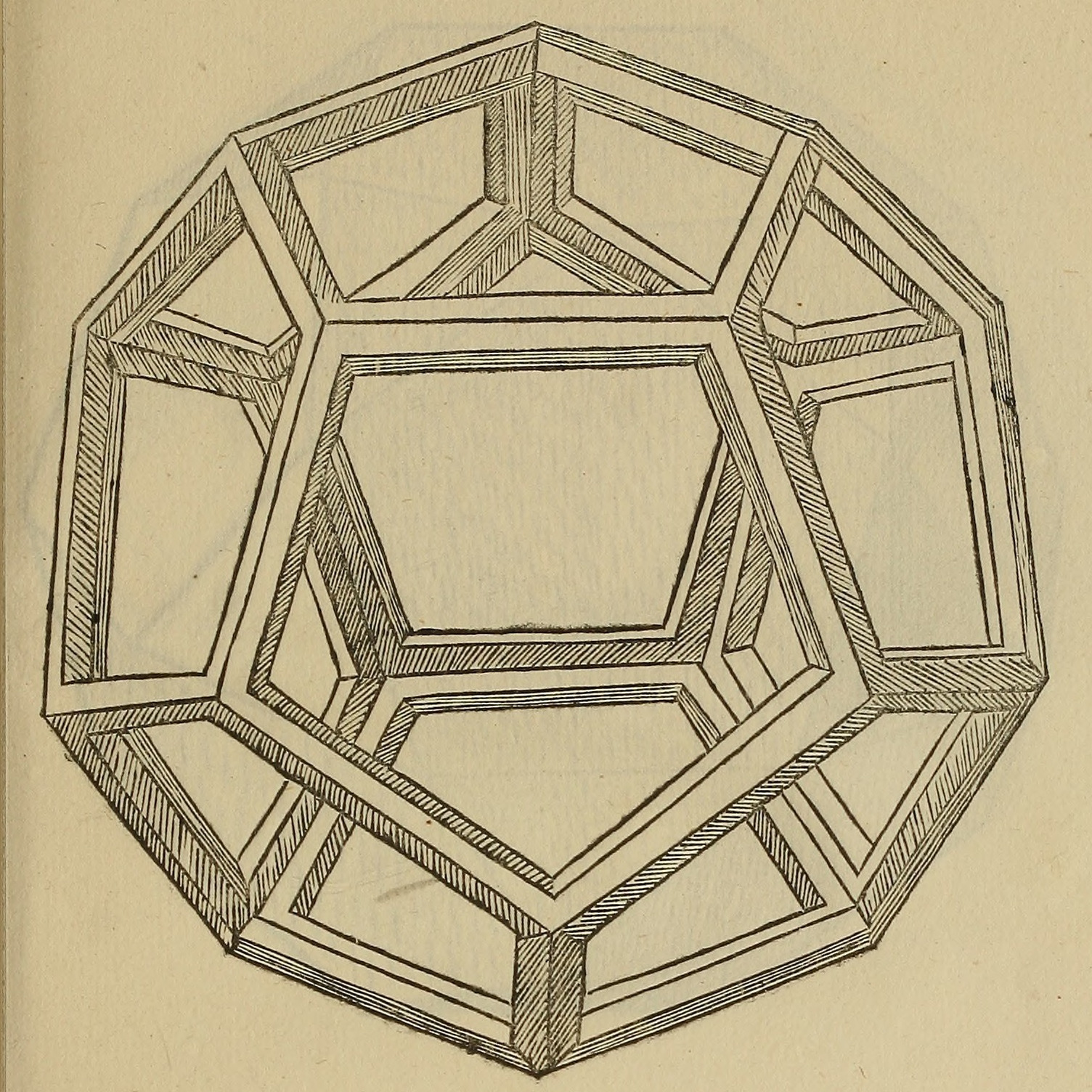 There are
There are

 The evolution of the modern Western digit for the numeral 5 cannot be traced back to the Indian system, as for the digits 1 to 4. The
The evolution of the modern Western digit for the numeral 5 cannot be traced back to the Indian system, as for the digits 1 to 4. The
NGC 5, a magnitude 13
number
A number is a mathematical object used to count, measure, and label. The original examples are the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, and so forth. Numbers can be represented in language with number words. More universally, individual numbers ...
, numeral and digit
Digit may refer to:
Mathematics and science
* Numerical digit, as used in mathematics or computer science
** Hindu-Arabic numerals, the most common modern representation of numerical digits
* Digit (anatomy), the most distal part of a limb, such ...
. It is the natural number
In mathematics, the natural numbers are those numbers used for counting (as in "there are ''six'' coins on the table") and ordering (as in "this is the ''third'' largest city in the country").
Numbers used for counting are called '' cardinal ...
, and cardinal number
In mathematics, cardinal numbers, or cardinals for short, are a generalization of the natural numbers used to measure the cardinality (size) of sets. The cardinality of a finite set is a natural number: the number of elements in the set. T ...
, following 4 and preceding 6, and is a prime number
A prime number (or a prime) is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a product of two smaller natural numbers. A natural number greater than 1 that is not prime is called a composite number. For example, 5 is prime because the only way ...
. It has attained significance throughout history in part because typical humans have five digit
Digit may refer to:
Mathematics and science
* Numerical digit, as used in mathematics or computer science
** Hindu-Arabic numerals, the most common modern representation of numerical digits
* Digit (anatomy), the most distal part of a limb, such ...
s on each hand.
In mathematics
prime number
A prime number (or a prime) is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a product of two smaller natural numbers. A natural number greater than 1 that is not prime is called a composite number. For example, 5 is prime because the only way ...
, and the second super-prime. It is the first safe prime, the first good prime, the first balanced prime, and the first of three known Wilson prime
In number theory, a Wilson prime is a prime number p such that p^2 divides (p-1)!+1, where "!" denotes the factorial function; compare this with Wilson's theorem, which states that every prime p divides (p-1)!+1. Both are named for 18th-century E ...
s. Five is the second Fermat prime and the third Mersenne prime
In mathematics, a Mersenne prime is a prime number that is one less than a power of two. That is, it is a prime number of the form for some integer . They are named after Marin Mersenne, a French Minim friar, who studied them in the early 17 ...
exponent, as well as the third Catalan number
In combinatorial mathematics, the Catalan numbers are a sequence of natural numbers that occur in various counting problems, often involving recursively defined objects. They are named after the French-Belgian mathematician Eugène Charles C ...
, and the third Sophie Germain prime. Notably, 5 is equal to the sum of the ''only'' consecutive primes, 2 + 3, and is the only number that is part of more than one pair of twin prime
A twin prime is a prime number that is either 2 less or 2 more than another prime number—for example, either member of the twin prime pair (41, 43). In other words, a twin prime is a prime that has a prime gap of two. Sometimes the term ''twin p ...
s, ( 3, 5) and (5, 7). It is also a sexy prime with the fifth prime number and first prime repunit, 11. Five is the third factorial prime, an alternating factorial
Alternating may refer to:
Mathematics
* Alternating algebra, an algebra in which odd-grade elements square to zero
* Alternating form, a function formula in algebra
* Alternating group, the group of even permutations of a finite set
* Alternati ...
, and an Eisenstein prime with no imaginary part and real part of the form − . In particular, five is the first congruent number, since it is the length of the hypotenuse of the smallest integer-sided right triangle.
Five is the second Fermat prime of the form + , and more generally the second Sierpiński number of the first kind, + . There are a total of five known Fermat primes, which also include 3, 17, 257
__NOTOC__
Year 257 ( CCLVII) was a common year starting on Thursday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Valerianus and Gallienus (or, less frequently, year 10 ...
, and 65537. The sum of the first 3 Fermat primes, 3, 5 and 17, yields 25 or 52, while 257 is the 55th prime number. Combinations from these 5 Fermat primes generate 31 polygons with an odd number of sides that can be construncted purely with a compass and straight-edge, which includes the five-sided regular pentagon. Apropos, 31 is also equal to the sum of the maximum number of area
Area is the quantity that expresses the extent of a region on the plane or on a curved surface. The area of a plane region or ''plane area'' refers to the area of a shape or planar lamina, while ''surface area'' refers to the area of an open su ...
s inside a circle that are formed from the sides and diagonals of the first five -sided polygon
In geometry, a polygon () is a plane figure that is described by a finite number of straight line segments connected to form a closed '' polygonal chain'' (or ''polygonal circuit''). The bounded plane region, the bounding circuit, or the two t ...
s, and equal to the maximum number of areas formed by a six-sided polygon; per Moser's circle problem The number of and for first 6 terms of Moser's circle problem
In geometry, the problem of dividing a circle into areas by means of an inscribed polygon with ''n'' sides in such a way as to ''maximise'' the number of areas created by the edges an ...
.
The number 5 is the fifth Fibonacci number
In mathematics, the Fibonacci numbers, commonly denoted , form a integer sequence, sequence, the Fibonacci sequence, in which each number is the sum of the two preceding ones. The sequence commonly starts from 0 and 1, although some authors start ...
, being 2 plus 3. It is the only Fibonacci number that is equal to its position aside from 1, which is both the first and second Fibonacci numbers. Five is also a Pell number and a Markov number, appearing in solutions to the Markov Diophantine equation: (1, 2, 5), (1, 5, 13), (2, 5, 29), (5, 13, 194
Year 194 ( CXCIV) was a common year starting on Tuesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Septimius and Septimius (or, less frequently, year 947 '' Ab urbe ...
), (5, 29, 433), ... ( lists Markov numbers that appear in solutions where one of the other two terms is 5). Whereas 5 is unique in the Fibonacci sequence, in the Perrin sequence 5 is both the fifth and sixth Perrin numbers.
5 is the third Mersenne prime exponent of the form − , which yields : the prime index of the third Mersenne prime
In mathematics, a Mersenne prime is a prime number that is one less than a power of two. That is, it is a prime number of the form for some integer . They are named after Marin Mersenne, a French Minim friar, who studied them in the early 17 ...
and second double Mersenne prime
In mathematics, a double Mersenne number is a Mersenne number of the form
:M_ = 2^-1
where ''p'' is prime.
Examples
The first four terms of the sequence of double Mersenne numbers areChris Caldwell''Mersenne Primes: History, Theorems and L ...
127 127 may refer to:
*127 (number), a natural number
*AD 127, a year in the 2nd century AD
*127 BC, a year in the 2nd century BC
*127 (band), an Iranian band
See also
*List of highways numbered 127
Route 127 or Highway 127 can refer to multiple roads ...
, as well as the third double Mersenne prime exponent for the number 2,147,483,647
The number 2,147,483,647 is the eighth Mersenne prime, equal to 231 − 1. It is one of only four known double Mersenne primes.
The primality of this number was proven by Leonhard Euler, who reported the proof in a letter to Danie ...
, which is the largest value that a signed 32-bit
In computer architecture, 32-bit computing refers to computer systems with a processor, memory, and other major system components that operate on data in 32- bit units. Compared to smaller bit widths, 32-bit computers can perform large calcula ...
integer field can hold. There are only four known double Mersenne prime numbers, with a fifth candidate double Mersenne prime = 223058...93951 − 1 too large to compute with current computers. In a related sequence, the first 5 terms in the sequence of Catalan–Mersenne numbers are the only known prime terms, with a sixth possible candidate in the order of 101037.7094. These prime sequences are conjectured to be prime up to a certain limit.
Every odd number greater than is the sum of at most five prime numbers, and every odd number greater than is conjectured to be expressible as the sum of three prime numbers. Helfgtott has provided a proof of the latter, also known as the odd Goldbach conjecture, that is already widely acknowledged by mathematicians as it still undergoes peer-review
Peer review is the evaluation of work by one or more people with similar competencies as the producers of the work (peers). It functions as a form of self-regulation by qualified members of a profession within the relevant field. Peer review ...
.
The sums of the first five non-primes greater than zero + + + + and the first five prime numbers + + + + both equal ; the 7th triangular number
A triangular number or triangle number counts objects arranged in an equilateral triangle. Triangular numbers are a type of figurate number, other examples being square numbers and cube numbers. The th triangular number is the number of dots i ...
and like a perfect number
In number theory, a perfect number is a positive integer that is equal to the sum of its positive divisors, excluding the number itself. For instance, 6 has divisors 1, 2 and 3 (excluding itself), and 1 + 2 + 3 = 6, so 6 is a perfect number.
T ...
, which also includes , the 31st triangular number and perfect number of the form −1( − ) with a of , by the Euclid–Euler theorem.
There are a total of five known unitary perfect numbers, which are numbers that are the sums of their positive proper unitary divisors. A sixth unitary number, if discovered, would have at least nine odd prime factors.
Five is conjecture
In mathematics, a conjecture is a conclusion or a proposition that is proffered on a tentative basis without proof. Some conjectures, such as the Riemann hypothesis (still a conjecture) or Fermat's Last Theorem (a conjecture until proven in 1 ...
d to be the only odd untouchable number
An untouchable number is a positive integer that cannot be expressed as the sum of all the proper divisors of any positive integer (including the untouchable number itself). That is, these numbers are not in the image of the aliquot sum function. ...
, and if this is the case then five will be the only odd prime number that is not the base of an aliquot tree.
In figurate numbers, 5 is a pentagonal number
A pentagonal number is a figurate number that extends the concept of triangular and square numbers to the pentagon, but, unlike the first two, the patterns involved in the construction of pentagonal numbers are not rotationally symmetrical. Th ...
, with the sequence
In mathematics, a sequence is an enumerated collection of objects in which repetitions are allowed and order matters. Like a set, it contains members (also called ''elements'', or ''terms''). The number of elements (possibly infinite) is called ...
of pentagonal numbers starting: 1, 5, 12, 22, 35, ...
* 5 is a centered tetrahedral number: 1, 5, 15, 35, 69, ... Every centered tetrahedral number with an index of 2, 3 or 4 modulo
In computing, the modulo operation returns the remainder or signed remainder of a division, after one number is divided by another (called the '' modulus'' of the operation).
Given two positive numbers and , modulo (often abbreviated as ) is t ...
5 is divisible by 5.
* 5 is a square pyramidal number
In mathematics, a pyramid number, or square pyramidal number, is a natural number that counts the number of stacked spheres in a pyramid with a square base. The study of these numbers goes back to Archimedes and Fibonacci. They are part of a br ...
: 1, 5, 14, 30, 55, ... The sum of the first four members is 50 while the fifth indexed member in the sequence is 55.
* 5 is a centered square number: 1, 5, 13, 25, 41, ... The fifth square number
In mathematics, a square number or perfect square is an integer that is the square of an integer; in other words, it is the product of some integer with itself. For example, 9 is a square number, since it equals and can be written as .
The u ...
or 52 is 25, which features in the proportions of the two smallest (3, 4, 5) and (5, 12, 13) ''primitive'' Pythagorean triples.
The factorial
In mathematics, the factorial of a non-negative denoted is the product of all positive integers less than or equal The factorial also equals the product of n with the next smaller factorial:
\begin
n! &= n \times (n-1) \times (n-2) ...
of five, or ! = , is the sum of the first fifteen non-zero positive integer
An integer is the number zero (), a positive natural number (, , , etc.) or a negative integer with a minus sign ( −1, −2, −3, etc.). The negative numbers are the additive inverses of the corresponding positive numbers. In the language ...
s, and 15th triangular number
A triangular number or triangle number counts objects arranged in an equilateral triangle. Triangular numbers are a type of figurate number, other examples being square numbers and cube numbers. The th triangular number is the number of dots i ...
, which in turn is the sum of the first five non-zero positive integers and 5th triangular number. 35, which is the fourth or fifth pentagonal and tetrahedral number, is equal to the sum of the first five triangular numbers: 1, 3, 6, 10, 15.
5 is the value of the central cell of the only non-trivial normal magic square, also called the ''Lo Shu'' square. Its x array of squares has a magic constant of , where the sums of its rows, columns, and diagonals are all equal to fifteen. 5 is also the value of the central cell the only non-trivial order-3 normal magic hexagon that is made of nineteen cells.
Polynomial
In mathematics, a polynomial is an expression consisting of indeterminates (also called variables) and coefficients, that involves only the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and positive-integer powers of variables. An ex ...
equations of degree and below can be solved with radicals, while quintic equation
In algebra, a quintic function is a function of the form
:g(x)=ax^5+bx^4+cx^3+dx^2+ex+f,\,
where , , , , and are members of a field, typically the rational numbers, the real numbers or the complex numbers, and is nonzero. In other words, a ...
s of degree 5, and higher, cannot generally be so solved. This is the Abel–Ruffini theorem
In mathematics, the Abel–Ruffini theorem (also known as Abel's impossibility theorem) states that there is no solution in radicals to general polynomial equations of degree five or higher with arbitrary coefficients. Here, ''general'' means ...
. This is related to the fact that the symmetric group
In abstract algebra, the symmetric group defined over any set is the group whose elements are all the bijections from the set to itself, and whose group operation is the composition of functions. In particular, the finite symmetric group ...
is a solvable group
In mathematics, more specifically in the field of group theory, a solvable group or soluble group is a group (mathematics), group that can be constructed from abelian groups using Group extension, extensions. Equivalently, a solvable group is a ...
for ''n'' ⩽ 4 and not solvable for ''n'' ⩾ 5.
Euler's identity, + = , contains five essential number
A number is a mathematical object used to count, measure, and label. The original examples are the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, and so forth. Numbers can be represented in language with number words. More universally, individual numbers ...
s used widely in mathematics: Archimedes' constant
The number (; spelled out as "pi") is a mathematical constant that is the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter, approximately equal to 3.14159. The number appears in many formulas across mathematics and physics. It is an irratio ...
, Euler's number , the imaginary number , unity , and zero
0 (zero) is a number representing an empty quantity. In place-value notation such as the Hindu–Arabic numeral system, 0 also serves as a placeholder numerical digit, which works by multiplying digits to the left of 0 by the radix, usu ...
, which makes this formula a renown example of beauty in mathematics.
In geometry
polygram
PolyGram N.V. was a multinational entertainment company and major music record label formerly based in the Netherlands. It was founded in 1962 as the Grammophon-Philips Group by Dutch corporation Philips and German corporation Siemens, to be ...
, is the first proper star polygon constructed from the diagonals of a regular pentagon as self-intersecting edges that are proportioned in golden ratio
In mathematics, two quantities are in the golden ratio if their ratio is the same as the ratio of their sum to the larger of the two quantities. Expressed algebraically, for quantities a and b with a > b > 0,
where the Greek letter phi ( ...
, . Its internal geometry appears prominently in Penrose tilings
A Penrose tiling is an example of an aperiodic tiling. Here, a ''tiling'' is a covering of two-dimensional space, the plane by non-overlapping polygons or other shapes, and ''aperiodic'' means that shifting any tiling with these shapes by any fin ...
, and is a facet inside Kepler-Poinsot star polyhedra and Schläfli–Hess star polychora, represented by its Schläfli symbol . A similar figure to the pentagram is a five-pointed simple isotoxal
In geometry, a polytope (for example, a polygon or a polyhedron) or a tiling is isotoxal () or edge-transitive if its symmetries act transitively on its edges. Informally, this means that there is only one type of edge to the object: given two ...
star ☆ without self-intersecting edges. Generally, star polytopes that are regular
The term regular can mean normal or in accordance with rules. It may refer to:
People
* Moses Regular (born 1971), America football player
Arts, entertainment, and media Music
* "Regular" (Badfinger song)
* Regular tunings of stringed instrum ...
only exist in dimension
In physics and mathematics, the dimension of a mathematical space (or object) is informally defined as the minimum number of coordinates needed to specify any point within it. Thus, a line has a dimension of one (1D) because only one coor ...
s 2 ⩽ < 5.
In graph theory
In mathematics, graph theory is the study of '' graphs'', which are mathematical structures used to model pairwise relations between objects. A graph in this context is made up of '' vertices'' (also called ''nodes'' or ''points'') which are conn ...
, all graphs with 4 or fewer vertices are planar, however, there is a graph with 5 vertices that is not: ''K''5, the complete graph
In the mathematical field of graph theory, a complete graph is a simple undirected graph in which every pair of distinct vertices is connected by a unique edge. A complete digraph is a directed graph in which every pair of distinct vertices ...
with 5 vertices, where every pair of distinct vertices in a pentagon is joined by unique edges belonging to a pentagram. By Kuratowski's theorem, a finite graph is planar iff
In logic and related fields such as mathematics and philosophy, "if and only if" (shortened as "iff") is a biconditional logical connective between statements, where either both statements are true or both are false.
The connective is bicondi ...
it does not contain a subgraph that is a subdivision of ''K''5, or the complete bipartite utility graph
As a topic of economics, utility is used to model worth or value. Its usage has evolved significantly over time. The term was introduced initially as a measure of pleasure or happiness as part of the theory of utilitarianism by moral philosophe ...
''K''3,3. A similar graph is the Petersen graph
In the mathematics, mathematical field of graph theory, the Petersen graph is an undirected graph with 10 vertex (graph theory), vertices and 15 edge (graph theory), edges. It is a small graph that serves as a useful example and counterexample for ...
, which is strongly connected and also nonplanar
In graph theory, a planar graph is a graph that can be embedded in the plane, i.e., it can be drawn on the plane in such a way that its edges intersect only at their endpoints. In other words, it can be drawn in such a way that no edges cro ...
. It is most easily described as graph of a pentagram ''embedded'' inside a pentagon, with a total of 5 crossings, a girth of 5, and a Thue number of 5. The Petersen graph, which is also a distance-regular graph, is one of only 5 known connected vertex-transitive
In geometry, a polytope (e.g. a polygon or polyhedron) or a tiling is isogonal or vertex-transitive if all its vertices are equivalent under the symmetries of the figure. This implies that each vertex is surrounded by the same kinds of fa ...
graphs with no Hamiltonian cycles.Royle, G"Cubic Symmetric Graphs (The Foster Census)."
The automorphism group of the Petersen graph is the
symmetric group
In abstract algebra, the symmetric group defined over any set is the group whose elements are all the bijections from the set to itself, and whose group operation is the composition of functions. In particular, the finite symmetric group ...
of order
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
* Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of d ...
120 = 5!.
The chromatic number
In graph theory, graph coloring is a special case of graph labeling; it is an assignment of labels traditionally called "colors" to elements of a graph subject to certain constraints. In its simplest form, it is a way of coloring the vertices o ...
of the plane is at least five, depending on the choice of set-theoretical axioms: the minimum number of colors required to color the plane such that no pair of points at a distance of 1 has the same color. Whereas the hexagonal Golomb graph and the regular hexagonal tiling
In geometry, the hexagonal tiling or hexagonal tessellation is a regular tiling of the Euclidean plane, in which exactly three hexagons meet at each vertex. It has Schläfli symbol of or (as a truncated triangular tiling).
English mathema ...
generate chromatic numbers of 4 and 7, respectively, a chromatic coloring of 5 can be attained under a more complicated graph where multiple four-coloring Moser spindles are linked so that no monochromatic triples exist in any coloring of the overall graph, as that would generate an equilateral arrangement that tends toward a purely hexagonal structure.
The plane contains a total of five Bravais lattice
In geometry and crystallography, a Bravais lattice, named after , is an infinite array of discrete points generated by a set of discrete translation operations described in three dimensional space by
: \mathbf = n_1 \mathbf_1 + n_2 \mathbf_2 + n ...
s, or arrays of points
Point or points may refer to:
Places
* Point, Lewis, a peninsula in the Outer Hebrides, Scotland
* Point, Texas, a city in Rains County, Texas, United States
* Point, the NE tip and a ferry terminal of Lismore, Inner Hebrides, Scotland
* Point ...
defined by discrete translation
Translation is the communication of the Meaning (linguistic), meaning of a #Source and target languages, source-language text by means of an Dynamic and formal equivalence, equivalent #Source and target languages, target-language text. The ...
operations: hexagonal, oblique, rectangular, centered rectangular, and square
In Euclidean geometry, a square is a regular quadrilateral, which means that it has four equal sides and four equal angles (90-degree angles, π/2 radian angles, or right angles). It can also be defined as a rectangle with two equal-length a ...
lattices. The plane can also be tiled monohedrally with convex pentagons in fifteen different ways, three of which have Laves tilings as special cases.
Five points are needed to determine a conic section
In mathematics, a conic section, quadratic curve or conic is a curve obtained as the intersection of the surface of a cone with a plane. The three types of conic section are the hyperbola, the parabola, and the ellipse; the circle is a ...
, in the same way that two points are needed to determine a line. A Veronese surface in the projective plane
In mathematics, a projective plane is a geometric structure that extends the concept of a plane. In the ordinary Euclidean plane, two lines typically intersect in a single point, but there are some pairs of lines (namely, parallel lines) that ...
of a conic generalizes a linear
Linearity is the property of a mathematical relationship ('' function'') that can be graphically represented as a straight line. Linearity is closely related to '' proportionality''. Examples in physics include rectilinear motion, the linear ...
condition for a point to be contained inside a conic.
 There are
There are Platonic solids
In geometry, a Platonic solid is a convex, regular polyhedron in three-dimensional Euclidean space. Being a regular polyhedron means that the faces are congruent (identical in shape and size) regular polygons (all angles congruent and all e ...
in three-dimensional space: the tetrahedron, cube, octahedron, dodecahedron, and icosahedron. The dodecahedron in particular contains pentagonal faces, while the icosahedron, its dual polyhedron
In geometry, every polyhedron is associated with a second dual structure, where the vertices of one correspond to the faces of the other, and the edges between pairs of vertices of one correspond to the edges between pairs of faces of the othe ...
, has a vertex figure that is a regular pentagon. There are also :
☆ Regular polyhedron compounds: the stella octangula, compound of five tetrahedra, compound of five cubes, compound of five octahedra, and compound of ten tetrahedra. Icosahedral symmetry
In mathematics, and especially in geometry, an object has icosahedral symmetry if it has the same symmetries as a regular icosahedron. Examples of other polyhedra with icosahedral symmetry include the regular dodecahedron (the dual of t ...
is isomorphic to the alternating group
In mathematics, an alternating group is the group of even permutations of a finite set. The alternating group on a set of elements is called the alternating group of degree , or the alternating group on letters and denoted by or
Basic pr ...
on 5 letters of order 120, realized by actions on these uniform polyhedron compounds.
☆ Space-filling convex polyhedra: the triangular prism, hexagonal prism, cube, truncated octahedron, and gyrobifastigium. While the cube is the only Platonic solid that can tessellate space on its own, the truncated octahedron and the gyrobifastigium are the only Archimedean and Johnson solid
In geometry, a Johnson solid is a strictly convex polyhedron each face of which is a regular polygon. There is no requirement that each face must be the same polygon, or that the same polygons join around each vertex. An example of a Johns ...
s, respectively, that can also tessellate space with their own copies.
☆ Cell-transitive
In geometry, a tessellation of dimension (a plane tiling) or higher, or a polytope of dimension (a polyhedron) or higher, is isohedral or face-transitive if all its faces are the same. More specifically, all faces must be not merely congruent ...
parallelohedra: any parallelepiped, as well as the rhombic dodecahedron and elongated dodecahedron, and the hexagonal prism and truncated octahedron. The cube is a special case of a parallelepiped, with the rhombic dodecahedron the only Catalan solid to tessellate space on its own.
☆ Regular abstract polyhedra, which include the excavated dodecahedron and the dodecadodecahedron. They have combinatorial symmetries transitive on flags of their elements, with topologies equivalent to that of toroids and the ability to tile the hyperbolic plane.
The 5-cell, or pentatope, is the self-dual fourth-dimensional analogue of the tetrahedron
In geometry, a tetrahedron (plural: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the ...
, with Coxeter group symmetry of order 120 = 5 ! and group structure
In the social sciences, a social group can be defined as two or more people who interact with one another, share similar characteristics, and collectively have a sense of unity. Regardless, social groups come in a myriad of sizes and varieties ...
. Made of five tetrahedra, its Petrie polygon is a regular pentagon and its orthographic projection is equivalent to the complete graph
In the mathematical field of graph theory, a complete graph is a simple undirected graph in which every pair of distinct vertices is connected by a unique edge. A complete digraph is a directed graph in which every pair of distinct vertices ...
''K''5. It is one of six regular 4-polytopes
In mathematics, a regular 4-polytope is a regular four-dimensional polytope. They are the four-dimensional analogues of the regular polyhedra in three dimensions and the regular polygons in two dimensions.
There are six convex and ten star re ...
, made of thirty-one elements
Element or elements may refer to:
Science
* Chemical element, a pure substance of one type of atom
* Heating element, a device that generates heat by electrical resistance
* Orbital elements, parameters required to identify a specific orbit of ...
: five vertices, ten edges
Edge or EDGE may refer to:
Technology Computing
* Edge computing, a network load-balancing system
* Edge device, an entry point to a computer network
* Adobe Edge, a graphical development application
* Microsoft Edge, a web browser developed by ...
, ten faces, five tetrahedral cells and one 4-face.
*A regular 120-cell, the dual ''polychoron'' to the regular 600-cell, can fit one hundred and twenty 5-cells. Also, five 24-cells fit inside a small stellated 120-cell, the first stellation of the 120-cell.
*A subset of the vertices of the small stellated 120-cell are matched by the great duoantiprism star, which is the only uniform nonconvex ''duoantiprismatic'' solution in the fourth dimension, constructed from the polytope
In elementary geometry, a polytope is a geometric object with flat sides ('' faces''). Polytopes are the generalization of three-dimensional polyhedra to any number of dimensions. Polytopes may exist in any general number of dimensions as an ...
cartesian product
In mathematics, specifically set theory, the Cartesian product of two sets ''A'' and ''B'', denoted ''A''×''B'', is the set of all ordered pairs where ''a'' is in ''A'' and ''b'' is in ''B''. In terms of set-builder notation, that is
: A\ ...
and made of fifty tetrahedra
In geometry, a tetrahedron (plural: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the ...
, ten pentagrammic crossed antiprisms, ten pentagonal antiprisms, and fifty vertices.
*The grand antiprism, which is the only known non-Wythoffian construction of a uniform polychoron, is made of twenty pentagonal antiprisms and three hundred tetrahedra, with a total of one hundred vertices and five hundred edges.
*The abstract
Abstract may refer to:
* ''Abstract'' (album), 1962 album by Joe Harriott
* Abstract of title a summary of the documents affecting title to parcel of land
* Abstract (law), a summary of a legal document
* Abstract (summary), in academic publishi ...
four-dimensional 57-cell
In mathematics, the 57-cell (pentacontakaiheptachoron) is a self-dual abstract regular 4-polytope ( four-dimensional polytope). Its 57 cells are hemi-dodecahedra. It also has 57 vertices, 171 edges and 171 two-dimensional faces.
The symmetry or ...
is made of fifty-seven hemi-icosahedral cells, in-which five surround each edge. The 11-cell, another abstract 4-polytope with eleven vertices and fifty-five edges, is made of eleven hemi-dodecahedral cells each with fifteen dodecahedra. The skeleton of the hemi-dodecahedron is the Petersen graph
In the mathematics, mathematical field of graph theory, the Petersen graph is an undirected graph with 10 vertex (graph theory), vertices and 15 edge (graph theory), edges. It is a small graph that serves as a useful example and counterexample for ...
.
Overall, the fourth dimension contains five Weyl groups that form a finite number of uniform polychora
In geometry, a uniform 4-polytope (or uniform polychoron) is a 4-dimensional polytope which is vertex-transitive and whose cells are uniform polyhedra, and faces are regular polygons.
There are 47 non-prismatic convex uniform 4-polytopes. There ...
: , , , , and , with four of these Coxeter groups capable of generating the same finite forms without ; accompanied by a fifth or sixth general group of unique 4-prisms of Platonic and Archimedean solids. There are also a total of five Coxeter groups that generate non-prismatic Eucledian honeycombs in 4-space, alongside five compact hyperbolic Coxeter groups that generate five regular compact hyperbolic honeycombs with finite facets, as with the order-5 5-cell honeycomb and the order-5 120-cell honeycomb, both of which have five cells around each face. Compact hyperbolic honeycombs only exist through the fourth dimension, or rank 5, with paracompact hyperbolic solutions existing through rank 10. Likewise, analogues of three-dimensional icosahedral symmetry
In mathematics, and especially in geometry, an object has icosahedral symmetry if it has the same symmetries as a regular icosahedron. Examples of other polyhedra with icosahedral symmetry include the regular dodecahedron (the dual of t ...
or four-dimensional symmetry do not exist in dimensions ''n'' ⩾ 5; however, there is the uniform prismatic group × in the fifth dimension which contains prisms of regular and uniform 4-polytopes that have symmetry.
The 5-simplex is the five-dimensional analogue of the 5-cell, or 4-simplex; the fifth iteration of -simplex
In geometry, a simplex (plural: simplexes or simplices) is a generalization of the notion of a triangle or tetrahedron to arbitrary dimensions. The simplex is so-named because it represents the simplest possible polytope in any given dimension ...
es in any dimensions. The 5-simplex has the Coxeter group as its symmetry group, of order 720 = 6 !, whose group structure is represented by the symmetric group , the only finite symmetric group which has an outer automorphism. The 5-cube, made of ten tesseracts and the 5-cell as its vertex figure, is also regular and one of thirty-one uniform 5-polytopes under the Coxeter hypercubic group. The demipenteract, with one hundred and twenty cells, is the only fifth-dimensional semiregular polytope, and has the rectified 5-cell as its vertex figure, which is one of only three semiregular 4-polytopes alongside the rectified 600-cell and the snub 24-cell. In the fifth dimension, there are five regular paracompact honeycombs, all with infinite facets and vertex figures. There are exclusively twelve complex aperiotopes in complex spaces of dimensions ⩾ , with fifteen in and sixteen in ; alongside complex polytopes in and higher under simplex
In geometry, a simplex (plural: simplexes or simplices) is a generalization of the notion of a triangle or tetrahedron to arbitrary dimensions. The simplex is so-named because it represents the simplest possible polytope in any given dimension ...
, hypercubic
In geometry, a hypercube is an ''n''-dimensional analogue of a square () and a cube (). It is a closed, compact, convex figure whose 1-skeleton consists of groups of opposite parallel line segments aligned in each of the space's dimensions, perp ...
and orthoplex groups, the latter with van Oss polytopes.
There are five exceptional Lie groups: , , , , and . The smallest of these, , can be represented in five-dimensional complex space and projected in the same number of dimensions as a ball rolling on top of another ball, whose motion is described in two-dimensional space. , the largest of all five exceptional groups, also contains the other four as subgroup
In group theory, a branch of mathematics, given a group ''G'' under a binary operation ∗, a subset ''H'' of ''G'' is called a subgroup of ''G'' if ''H'' also forms a group under the operation ∗. More precisely, ''H'' is a subgrou ...
s and is constructed with one hundred and twenty quaternionic unit icosians that make up the vertices of the 600-cell. There are also five solvable group
In mathematics, more specifically in the field of group theory, a solvable group or soluble group is a group (mathematics), group that can be constructed from abelian groups using Group extension, extensions. Equivalently, a solvable group is a ...
s that are excluded from finite simple groups of Lie type.
The five Mathieu groups constitute the first generation in the happy family of sporadic groups. These are also the first five sporadic groups to have been described, defined as multiply transitive permutation groups on objects, with ∈ . In particular, , the smallest of all sporadic groups, has a rank 3 action on fifty-five points from an induced action on unordered pairs, as well as two five-dimensional faithful complex irreducible representations over the field with three elements, which is the lowest irreducible dimensional representation of all sporadic group over their respective fields with ''n'' elements. Of precisely five different conjugacy classes of maximal subgroups of , one is the almost simple symmetric group (of order 5 !), and another is , also almost simple, that functions as a point stabilizer
In mathematics, a group action on a space is a group homomorphism of a given group into the group of transformations of the space. Similarly, a group action on a mathematical structure is a group homomorphism of a group into the automorphism g ...
which has as its largest prime factor in its group order: 24·32·5 = 2·3·4·5·6 = 8·9·10 = 720. On the other hand, whereas is sharply 4-transitive, is sharply 5-transitive and is 5-transitive, and as such they are the only two 5-transitive groups that are not symmetric group
In abstract algebra, the symmetric group defined over any set is the group whose elements are all the bijections from the set to itself, and whose group operation is the composition of functions. In particular, the finite symmetric group ...
s or alternating group
In mathematics, an alternating group is the group of even permutations of a finite set. The alternating group on a set of elements is called the alternating group of degree , or the alternating group on letters and denoted by or
Basic pr ...
s. has the first five prime numbers as its distinct prime factors in its order of 27· 32·5· 7· 11, and is the smallest of five sporadic groups with five distinct prime factors in their order. All Mathieu groups are subgroups of , which under the Witt design of Steiner system S(5, 8, 24) emerges a construction of the extended binary Golay code
In mathematics and electronics engineering, a binary Golay code is a type of linear error-correcting code used in digital communications. The binary Golay code, along with the ternary Golay code, has a particularly deep and interesting connection ...
that has as its automorphism group. generates ''octads'' from code words of Hamming weight
The Hamming weight of a string is the number of symbols that are different from the zero-symbol of the alphabet used. It is thus equivalent to the Hamming distance from the all-zero string of the same length. For the most typical case, a string o ...
8 from the extended binary Golay code, one of five different Hamming weights the extended binary Golay code uses: 0, 8, 12, 16, and 24. The Witt design and the extended binary Golay code in turn can be used to generate a faithful construction of the 24-dimensional Leech lattice Λ24, which is the subject of the second generation of seven sporadic groups that are subquotients of the automorphism of the Leech lattice, Conway group .
There are five non-supersingular primes: 37, 43, 53, 61, and 67, all smaller than the largest of fifteen supersingular prime divisors of the friendly giant
''The Friendly Giant'' was a children's television program that aired on CBC Television from September 30, 1958 through to March 1985. It featured three main characters: a giant named Friendly (played by Bob Homme), who lived in a huge castle, alo ...
, 71.
List of basic calculations
In decimal
5 is the only prime number to end in the digit 5 in decimal because all other numbers written with a 5 in theones place
A numerical digit (often shortened to just digit) is a single symbol used alone (such as "2") or in combinations (such as "25"), to represent numbers in a Positional notation, positional numeral system. The name "digit" comes from the fact that t ...
are multiples of five, which makes it a 1- automorphic number.
All multiples of 5 will end in either 5 or , and vulgar fractions with 5 or in the denominator do not yield infinite decimal expansions because they are prime factors of 10, the base.
In the powers
Powers may refer to:
Arts and media
* ''Powers'' (comics), a comic book series by Brian Michael Bendis and Michael Avon Oeming
** ''Powers'' (American TV series), a 2015–2016 series based on the comics
* ''Powers'' (British TV series), a 200 ...
of 5, every power ends with the number five, and from 53 onward, if the exponent is odd, then the hundreds digit is 1, and if it is even, the hundreds digit is 6.
A number raised to the fifth power always ends in the same digit as .
Evolution of the Arabic digit

Kushana
The Kushan Empire ( grc, Βασιλεία Κοσσανῶν; xbc, Κυϸανο, ; sa, कुषाण वंश; Brahmi: , '; BHS: ; xpr, 𐭊𐭅𐭔𐭍 𐭇𐭔𐭕𐭓, ; zh, 貴霜 ) was a syncretic empire, formed by the Yuezhi, i ...
and Gupta
Gupta () is a common surname or last name of Indian origin. It is based on the Sanskrit word गोप्तृ ''goptṛ'', which means 'guardian' or 'protector'. According to historian R. C. Majumdar, the surname ''Gupta'' was adopted by se ...
empires in what is now India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the ...
had among themselves several different forms that bear no resemblance to the modern digit. The Nagari and Punjabi
Punjabi, or Panjabi, most often refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to Punjab, a region in India and Pakistan
* Punjabi language
* Punjabi people
* Punjabi dialects and languages
Punjabi may also refer to:
* Punjabi (horse), a British Th ...
took these digits and all came up with forms that were similar to a lowercase "h" rotated 180°. The Ghubar Arabs transformed the digit in several different ways, producing from that were more similar to the digits 4 or 3 than to 5. It was from those digits that Europeans finally came up with the modern 5.
While the shape of the character for the digit 5 has an ascender in most modern typeface
A typeface (or font family) is the design of lettering that can include variations in size, weight (e.g. bold), slope (e.g. italic), width (e.g. condensed), and so on. Each of these variations of the typeface is a font.
There are thousands ...
s, in typefaces with text figures
Text figures (also known as non-lining, lowercase, old style, ranging, hanging, medieval, billing, or antique figures or numerals) are numerals designed with varying heights in a fashion that resembles a typical line of running text, hence the ...
the glyph usually has a descender
In typography and handwriting, a descender is the portion of a letter that extends below the baseline of a font.
For example, in the letter ''y'', the descender is the "tail", or that portion of the diagonal line which lies below the ''v'' ...
, as, for example, in .
On the seven-segment display
A seven-segment display is a form of electronic display device for displaying decimal numerals that is an alternative to the more complex dot matrix displays.
Seven-segment displays are widely used in digital clocks, electronic meters, basic ...
of a calculator, it is represented by five segments at four successive turns from top to bottom, rotating counterclockwise first, then clockwise, and vice-versa.
Science
*Theatomic number
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol ''Z'') of a chemical element is the charge number of an atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei, this is equal to the proton number (''n''p) or the number of protons found in the nucleus of every ...
of boron.
*The number of appendages on most starfish, which exhibit pentamerism.
*The most destructive known hurricanes
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm, storm system characterized by a Low-pressure area, low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, Beaufort scale, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms tha ...
rate as Category 5 on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale.
*The most destructive known tornado
A tornado is a violently rotating column of air that is in contact with both the surface of the Earth and a cumulonimbus cloud or, in rare cases, the base of a cumulus cloud. It is often referred to as a twister, whirlwind or cyclone, alt ...
es rate an F-5 on the Fujita scale
The Fujita scale (F-Scale; ), or Fujita–Pearson scale (FPP scale), is a scale for rating tornado intensity, based primarily on the damage tornadoes inflict on human-built structures and vegetation. The official Fujita scale category is deter ...
or EF-5 on the Enhanced Fujita scale.
Astronomy
* Messier object M5, a magnitude 7.0 globular cluster in the constellation Serpens. *The New General Cataloguebr>objectNGC 5, a magnitude 13
spiral galaxy
Spiral galaxies form a class of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work ''The Realm of the Nebulae''constellation Andromeda.
*The Roman numeral V stands for dwarfs (
The Number 5The Positive Integer 5
{{DEFAULTSORT:5 (Number) Integers 5 (number)
main sequence
In astronomy, the main sequence is a continuous and distinctive band of stars that appears on plots of stellar color versus brightness. These color-magnitude plots are known as Hertzsprung–Russell diagrams after their co-developers, Ejnar Her ...
stars) in the Yerkes spectral classification scheme.
*The Roman numeral V (usually) stands for the fifth-discovered satellite of a planet or minor planet (e.g. Jupiter V).
*There are five Lagrangian point
In celestial mechanics, the Lagrange points (; also Lagrangian points or libration points) are points of equilibrium for small-mass objects under the influence of two massive orbiting bodies. Mathematically, this involves the solution of ...
s in a two-body system.
Biology
*There are generally considered to befive senses
A sense is a biological system used by an organism for sensation, the process of gathering information about the world through the detection of stimuli. (For example, in the human body, the brain which is part of the central nervous system rec ...
.
*The five basic taste
The gustatory system or sense of taste is the sensory system that is partially responsible for the perception of taste (flavor). Taste is the perception produced or stimulated when a substance in the mouth reacts chemically with taste recepto ...
s are sweet, salty, sour, bitter
Bitter may refer to:
Common uses
* Resentment, negative emotion or attitude, similar to being jaded, cynical or otherwise negatively affected by experience
* Bitter (taste), one of the five basic tastes
Books
* ''Bitter (novel)'', a 2022 novel ...
, and umami.
*Almost all amphibians, reptiles, and mammals which have fingers or toes have five of them on each extremity.
Computing
*5 is theASCII
ASCII ( ), abbreviated from American Standard Code for Information Interchange, is a character encoding standard for electronic communication. ASCII codes represent text in computers, telecommunications equipment, and other devices. Because ...
code of the Enquiry character, which is abbreviated to ENQ.
Religion and culture
Hinduism
*The godShiva
Shiva (; sa, शिव, lit=The Auspicious One, Śiva ), also known as Mahadeva (; ɐɦaːd̪eːʋɐ, or Hara, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the Supreme Being in Shaivism, one of the major traditions within Hin ...
has five faces and his mantra is also called (five-worded) mantra.
*The goddess Saraswati
Saraswati ( sa, सरस्वती, ) is the Hindu goddess of knowledge, music, art, speech, wisdom, and learning. She is one of the Tridevi, along with the goddesses Lakshmi and Parvati.
The earliest known mention of Saraswati as a ...
, goddess of knowledge and intellectual is associated with or the number 5.
*There are five elements in the universe according to Hindu cosmology: (earth, fire, water, air and space respectively).
*The most sacred tree in Hinduism has 5 leaves in every leaf stunt.
*Most of the flowers have 5 petals in them.
*The epic Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; sa, महाभारतम्, ', ) is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India in Hinduism, the other being the '' Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the struggle between two groups of cousins in the K ...
revolves around the battle between Duryodhana and his 99 other brothers and the 5 pandava
The Pandavas ( Sanskrit: पाण्डव, IAST: Pāṇḍava) refers to the five legendary brothers— Yudhishthira, Bhima, Arjuna, Nakula and Sahadeva—who are the central characters of the Hindu epic '' Mahabharata''. They are acknowle ...
princes—Dharma
Dharma (; sa, धर्म, dharma, ; pi, dhamma, italic=yes) is a key concept with multiple meanings in Indian religions, such as Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, Sikhism and others. Although there is no direct single-word translation for ...
, Arjuna
Arjuna (Sanskrit: अर्जुन, ), also known as Partha and Dhananjaya, is a character in several ancient Hindu texts, and specifically one of the major characters of the Indian epic Mahabharata. In the epic, he is the third among Pand ...
, Bhima, Nakula
In the Hindu epic Mahabharata, ''Nakula'' (Sanskrit: नकुल) was fourth of the five Pandava brothers. Nakula and Sahadeva were twins blessed to Madri, by Ashwini Kumaras, the divine physicians. Their parents Pandu and Madri - died e ...
and Sahadeva
Sahadeva (Sanskrit: सहदेव) was the youngest of the Pandava brothers, the five principal protagonists of the epic ''Mahabharata''. He and his twin brother, Nakula, were blessed to King Pandu and Queen Madri by invoking the twin gods Ash ...
.
Christianity
*There are traditionallyfive wounds
In Catholic Church, Catholic Catholic devotions, tradition, the Five Holy Wounds, also known as the Five Sacred Wounds or the Five Precious Wounds, are the five piercing wounds that Jesus Christ suffered during his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixi ...
of Jesus Christ
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religious ...
in Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesu ...
: the Scourging at the Pillar, the Crowning with Thorns, the wounds in Christ's hands, the wounds in Christ's feet, and the Side Wound of Christ.
Gnosticism
*The number five was an important symbolic number inManichaeism
Manichaeism (;
in New Persian ; ) is a former major religionR. van den Broek, Wouter J. Hanegraaff ''Gnosis and Hermeticism from Antiquity to Modern Times''SUNY Press, 1998 p. 37 founded in the 3rd century AD by the Parthian prophet Mani ( ...
, with heavenly beings, concepts, and others often grouped in sets of five.
* Five Seals in Sethianism
The Sethians were one of the main currents of Gnosticism during the 2nd and 3rd century CE, along with Valentinianism and Basilideanism. According to John D. Turner, it originated in the 2nd century CE as a fusion of two distinct Hellenistic ...
* Five Trees in the Gospel of Thomas
The Gospel of Thomas (also known as the Coptic Gospel of Thomas) is an extra-canonical sayings gospel. It was discovered near Nag Hammadi, Egypt, in December 1945 among a group of books known as the Nag Hammadi library. Scholars speculat ...
Islam
*TheFive Pillars of Islam
The Five Pillars of Islam (' ; also ' "pillars of the religion") are fundamental practices in Islam, considered to be obligatory acts of worship for all Muslims. They are summarized in the famous hadith of Gabriel. The Sunni and Shia agree ...
* Muslims pray to Allah
Allah (; ar, الله, translit=Allāh, ) is the common Arabic word for God. In the English language, the word generally refers to God in Islam. The word is thought to be derived by contraction from '' al- ilāh'', which means "the god", ...
five times a day
*According to Shia Muslims, the Panjetan or the Five Holy Purified Ones are the members of Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the monot ...
's family: Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the monot ...
, Ali, Fatimah
Fāṭima bint Muḥammad ( ar, فَاطِمَة ٱبْنَت مُحَمَّد}, 605/15–632 CE), commonly known as Fāṭima al-Zahrāʾ (), was the daughter of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and his wife Khadija. Fatima's husband was Ali, t ...
, Hasan, and Husayn and are often symbolically represented by an image of the Khamsa.
Judaism
*TheTorah
The Torah (; hbo, ''Tōrā'', "Instruction", "Teaching" or "Law") is the compilation of the first five books of the Hebrew Bible, namely the books of Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers and Deuteronomy. In that sense, Torah means the s ...
contains five books—Genesis
Genesis may refer to:
Bible
* Book of Genesis, the first book of the biblical scriptures of both Judaism and Christianity, describing the creation of the Earth and of mankind
* Genesis creation narrative, the first several chapters of the Book o ...
, Exodus
Exodus or the Exodus may refer to:
Religion
* Book of Exodus, second book of the Hebrew Torah and the Christian Bible
* The Exodus, the biblical story of the migration of the ancient Israelites from Egypt into Canaan
Historical events
* Exo ...
, Leviticus, Numbers, and Deuteronomy
Deuteronomy ( grc, Δευτερονόμιον, Deuteronómion, second law) is the fifth and last book of the Torah (in Judaism), where it is called (Hebrew: hbo, , Dəḇārīm, hewords Moses.html" ;"title="f Moses">f Moseslabel=none) and th ...
—which are collectively called the Five Books of Moses, the Pentateuch (Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
for "five containers", referring to the scroll cases in which the books were kept), or Humash (, Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
for "fifth").
*The book of Psalms
The Book of Psalms ( or ; he, תְּהִלִּים, , lit. "praises"), also known as the Psalms, or the Psalter, is the first book of the ("Writings"), the third section of the Tanakh, and a book of the Old Testament. The title is derived f ...
is arranged into five books, paralleling the Five Books of Moses.
*The Khamsa, an ancient symbol shaped like a hand with four fingers and one thumb, is used as a protective amulet by Jews; that same symbol is also very popular in Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Wester ...
ic culture, known to protect from envy and the evil eye
The Evil Eye ( grc, ὀφθαλμὸς βάσκανος; grc-koi, ὀφθαλμὸς πονηρός; el, (κακό) μάτι; he, עַיִן הָרָע, ; Romanian: ''Deochi''; it, malocchio; es, mal de ojo; pt, mau-olhado, olho gordo; a ...
.
Sikhism
*The five sacred Sikh symbols prescribed byGuru Gobind Singh
Guru Gobind Singh (; 22 December 1666 – 7 October 1708), born Gobind Das or Gobind Rai the tenth Sikh Guru, a spiritual master, warrior, poet and philosopher. When his father, Guru Tegh Bahadur, was executed by Aurangzeb, Guru Gobind ...
are commonly known as or the " Five Ks" because they start with letter K representing in the Punjabi language
Punjabi (; ; , ), sometimes spelled Panjabi, is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language of the Punjab, Punjab region of Pakistan and India. It has approximately 113 million native speakers.
Punjabi is the most widely-spoken first lan ...
's Gurmukhi script. They are: (unshorn hair), (the comb), (the steel bracelet), (the soldier's shorts), and (the sword) (in Gurmukhi: ). Also, there are five deadly evils: (lust), (anger), (attachment), (greed), and (ego).
Daoism
* 5 Elements * 5 EmperorsOther religions and cultures
*According to ancient Greek philosophers such asAristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical Greece, Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatet ...
, the universe is made up of five classical elements: water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as ...
, earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surf ...
, air, fire
Fire is the rapid oxidation of a material (the fuel) in the exothermic chemical process of combustion, releasing heat, light, and various reaction Product (chemistry), products.
At a certain point in the combustion reaction, called the ignition ...
, and ether
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. They have the general formula , where R and R′ represent the alkyl or aryl groups. Ethers can again b ...
. This concept was later adopted by medieval alchemists and more recently by practitioners of Neo-Pagan religions such as Wicca
Wicca () is a modern Pagan religion. Scholars of religion categorise it as both a new religious movement and as part of the occultist stream of Western esotericism. It was developed in England during the first half of the 20th century and w ...
.
*The pentagram, or five-pointed star, bears religious significance in various faiths including Baháʼí, Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesu ...
, Freemasonry
Freemasonry or Masonry refers to fraternal organisations that trace their origins to the local guilds of stonemasons that, from the end of the 13th century, regulated the qualifications of stonemasons and their interaction with authorities ...
, Satanism, Taoism
Taoism (, ) or Daoism () refers to either a school of philosophical thought (道家; ''daojia'') or to a religion (道教; ''daojiao''), both of which share ideas and concepts of Chinese origin and emphasize living in harmony with the '' Ta ...
, Thelema
Thelema () is a Western esoteric and occult social or spiritual philosophy and new religious movement founded in the early 1900s by Aleister Crowley (1875–1947), an English writer, mystic, occultist, and ceremonial magician. The word ...
, and Wicca
Wicca () is a modern Pagan religion. Scholars of religion categorise it as both a new religious movement and as part of the occultist stream of Western esotericism. It was developed in England during the first half of the 20th century and w ...
.
*In Cantonese
Cantonese ( zh, t=廣東話, s=广东话, first=t, cy=Gwóngdūng wá) is a language within the Chinese (Sinitic) branch of the Sino-Tibetan languages originating from the city of Guangzhou (historically known as Canton) and its surrounding ar ...
, "five" sounds like the word "not" (character: ). When five appears in front of a lucky number, e.g. "58", the result is considered unlucky.
*In East Asia
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The modern states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. China, North Korea, South Korea ...
n tradition, there are five elements: (water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as ...
, fire
Fire is the rapid oxidation of a material (the fuel) in the exothermic chemical process of combustion, releasing heat, light, and various reaction Product (chemistry), products.
At a certain point in the combustion reaction, called the ignition ...
, earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surf ...
, wood
Wood is a porous and fibrous structural tissue found in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulose fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of ligni ...
, and metal
A metal (from Greek μέταλλον ''métallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. Metals are typi ...
). The Japanese names for the days of the week
A day is the time period of a full rotation of the Earth with respect to the Sun. On average, this is 24 hours, 1440 minutes, or 86,400 seconds. In everyday life, the word "day" often refers to a solar day, which is the length between two so ...
, Tuesday through Saturday
Saturday is the day of the week between Friday and Sunday. No later than the 2nd century, the Romans named Saturday ("Saturn's Day") for the planet Saturn, which controlled the first hour of that day, according to Vettius Valens. The day's ...
, come from these elements via the identification of the elements with the five planets visible with the naked eye. Also, the traditional Japanese calendar has a five-day weekly cycle that can be still observed in printed mixed calendars combining Western, Chinese-Buddhist, and Japanese names for each weekday.
*In numerology
Numerology (also known as arithmancy) is the belief in an occult, divine or mystical relationship between a number and one or more coinciding events. It is also the study of the numerical value, via an alphanumeric system, of the letters in ...
, 5 or a series of 555
Year 555 (DLV) was a common year starting on Friday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. The denomination 555 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the pr ...
, is often associated with change, evolution, love and abundance.
*Members of The Nation of Gods and Earths
The Five-Percent Nation, sometimes referred to as the Nation of Gods and Earths (NGE/NOGE) or the Five Percenters, is a Black nationalist movement influenced by Islam that was founded in 1964 in the Harlem section of the borough of Manhattan, N ...
, a primarily African American religious organization, call themselves the "Five-Percenters" because they believe that only 5% of mankind is truly enlightened.
Art, entertainment, and media
Fictional entities
* James the Red Engine, a fictional character numbered 5. * Johnny 5 is the lead character in the film ''Short Circuit'' (1986) *Number Five is a character in Lorien Legacies *Sankara Stones, five magical rocks in ''Indiana Jones and the Temple of Doom
''Indiana Jones and the Temple of Doom'' is a 1984 American action-adventure film directed by Steven Spielberg. It is the second installment in the ''Indiana Jones'' franchise, and a prequel to the 1981 film '' Raiders of the Lost Ark'', f ...
'' that are sought by the Thuggees for evil purposes
*The Mach Five , the racing car Speed Racer ( in the Japanese version) drives in the anime series of the same name (known as "Mach Go! Go! Go!" in Japan)
*In the works of J. R. R. Tolkien, five wizards (Saruman
Saruman, also called Saruman the White, is a fictional character of J. R. R. Tolkien's fantasy novel ''The Lord of the Rings''. He is leader of the Istari, wizards sent to Middle-earth in human form by the godlike Valar to challenge Sauron ...
, Gandalf
Gandalf is a protagonist in J. R. R. Tolkien's novels ''The Hobbit'' and ''The Lord of the Rings''. He is a Wizards (Middle-earth), wizard, one of the ''Istari'' order, and the leader of the Fellowship of the Ring (characters), Fellowship of t ...
, Radagast, Alatar and Pallando) are sent to Middle-earth to aid against the threat of the Dark Lord Sauron
*In the ''A Song of Ice and Fire
''A Song of Ice and Fire'' is a series of epic fantasy novels by the American novelist and screenwriter George R. R. Martin. He began the first volume of the series, '' A Game of Thrones'', in 1991, and it was published in 1996. Martin, who in ...
'' series, the War of the Five Kings is fought between different claimants to the Iron Throne of Westeros, as well as to the thrones of the individual regions of Westeros ( Joffrey Baratheon, Stannis Baratheon, Renly Baratheon, Robb Stark and Balon Greyjoy)
*In '' The Wheel of Time'' series, the "Emond's Field Five" are a group of five of the series' main characters who all come from the village of Emond's Field (Rand al'Thor
This article serves as an index of major characters in the fictional setting of Robert Jordan's '' The Wheel of Time'' series, with a description of their main roles or feats in the series. ''The Wheel of Time'' has 2787 distinct named character ...
, Matrim Cauthon, Perrin Aybara, Egwene al'Vere and Nynaeve al'Meara
This article serves as an index of major characters in the fictional setting of Robert Jordan's ''The Wheel of Time'' series, with a description of their main roles or feats in the series. ''The Wheel of Time'' has 2787 distinct named characters. ...
)
* ''Myst'' uses the number 5 as a unique base counting system. In '' The Myst Reader'' series, it is further explained that the number 5 is considered a holy number in the fictional D'ni society.
*Number Five is also a character in The Umbrella Academy comic book and TV series adaptation
Films
*Towards the end of the film '' Monty Python and the Holy Grail'' (1975), the character of King Arthur repeatedly confuses the number five with the number three. *'' Five Go Mad in Dorset'' (1982) was the first of the long-running series of '' The Comic Strip Presents...'' television comedy films *''The Fifth Element
''The Fifth Element'' is a 1997 English-language French science fiction action film conceived and directed by Luc Besson, as well as co-written by Besson and Robert Mark Kamen. It stars Bruce Willis, Gary Oldman, Chris Tucker, and Milla Jov ...
'' (1997), a science fiction film
* '' Fast Five'' (2011), the fifth installment of the ''Fast and Furious'' film series.
*'' V for Vendetta'' (2005), produced by Warner Bros., directed by James McTeigue, and adapted from Alan Moore's graphic novel '' V for Vendetta'' prominently features number 5 and Roman Numeral V; the story is based on the historical event in which a group of men attempted to destroy Parliament on November 5, 1605
Music
Groups
* Five (group), a UK Boy band *The Five (composers)
The Five ( rus, link=no, Могучая кучка, lit. ''Mighty Bunch''), also known as the Mighty Handful, The Mighty Five, and the New Russian School, were five prominent 19th-century Russian composers who worked together to create a distinc ...
, 19th-century Russian composers
* 5 Seconds of Summer, pop band that originated in Sydney, Australia
* Five Americans, American rock band active 1965–1969
* Five Finger Death Punch, American heavy metal band from Las Vegas, Nevada. Active 2005–present
* Five Man Electrical Band, Canadian rock group billed (and active) as the Five Man Electrical Band, 1969–1975
* Maroon 5, American pop rock band that originated in Los Angeles, California
* MC5, American punk rock band
* Pentatonix, a Grammy-winning a cappella group originated in Arlington, Texas
* The 5th Dimension, American pop vocal group, active 1977–present
* The Dave Clark Five, a.k.a. DC5, an English pop rock group comprising Dave Clark, Lenny Davidson, Rick Huxley, Denis Payton, and Mike Smith; active 1958–1970
*The Jackson 5
The Jackson 5 (sometimes stylized as the Jackson 5ive, also known as the Jacksons) are an American pop band composed of members of the Jackson family. The group was founded in 1964 in Gary, Indiana, and for most ...
, American pop rock group featuring various members of the Jackson family; they were billed (and active) as The Jackson 5, 1966–1975
* Hi-5, Australian pop kids group, where it has several international adaptations, and several members throughout the history of the band. It was also a TV show.
* We Five: American folk rock group active 1965–1967 and 1968–1977
* Grandmaster Flash and the Furious Five: American rap group, 1970–80's
* Fifth Harmony, an American girl group
A girl group is a music act featuring several female singers who generally harmonize together. The term "girl group" is also used in a narrower sense in the United States to denote the wave of American female pop music singing groups, many of who ...
.
* Ben Folds Five, an American alternative rock trio, 1993–2000, 2008 and 2011–2013
* R5 (band), an American pop and alternative rock group, 2009–2018
Other uses
*Aperfect fifth
In music theory, a perfect fifth is the musical interval corresponding to a pair of pitches with a frequency ratio of 3:2, or very nearly so.
In classical music from Western culture, a fifth is the interval from the first to the last of five ...
is the most consonant harmony, and is the basis for most western tuning systems.
*Modern musical notation uses a musical staff made of five horizontal lines.
*In harmonics – the fifth partial (or 4th overtone) of a fundamental has a frequency ratio of 5:1 to the frequency of that fundamental. This ratio corresponds to the interval of 2 octaves plus a pure major third. Thus, the interval of 5:4 is the interval of the pure third. A major triad
Triad or triade may refer to:
* a group of three
Businesses and organisations
* Triad (American fraternities), certain historic groupings of seminal college fraternities in North America
* Triad (organized crime), a Chinese transnational orga ...
chord
Chord may refer to:
* Chord (music), an aggregate of musical pitches sounded simultaneously
** Guitar chord a chord played on a guitar, which has a particular tuning
* Chord (geometry), a line segment joining two points on a curve
* Chord ( ...
when played in just intonation
In music, just intonation or pure intonation is the tuning of musical intervals as whole number ratios (such as 3:2 or 4:3) of frequencies. An interval tuned in this way is said to be pure, and is called a just interval. Just intervals (and ...
(most often the case in a cappella vocal ensemble singing), will contain such a pure major third.
*The number of completed, numbered piano concertos of Ludwig van Beethoven
Ludwig van Beethoven (baptised 17 December 177026 March 1827) was a German composer and pianist. Beethoven remains one of the most admired composers in the history of Western music; his works rank amongst the most performed of the classic ...
, Sergei Prokofiev
Sergei Sergeyevich Prokofiev; alternative transliterations of his name include ''Sergey'' or ''Serge'', and ''Prokofief'', ''Prokofieff'', or ''Prokofyev''., group=n (27 April .S. 15 April1891 – 5 March 1953) was a Russian composer, p ...
, and Camille Saint-Saëns
Charles-Camille Saint-Saëns (; 9 October 183516 December 1921) was a French composer, organist, conductor and pianist of the Romantic era. His best-known works include Introduction and Rondo Capriccioso (1863), the Second Piano Concerto ...
.
*Using the Latin root, five musicians are called a quintet.
*A scale with five notes per octave is called a pentatonic scale.
*Five is the lowest possible number that can be the top number of a time signature
The time signature (also known as meter signature, metre signature, or measure signature) is a notational convention used in Western culture, Western musical notation to specify how many beat (music), beats (pulses) are contained in each measu ...
with an asymmetric meter.
Television
;Stations *Channel 5 (UK)
Channel 5 is a British free-to-air public service broadcasting in the United Kingdom, public broadcast television channel launched in 1997. It is the fifth national terrestrial channel in the United Kingdom and is owned by Channel 5 Broadcast ...
, a television channel that broadcasts in the United Kingdom
*5 (TV channel)
TV5 (also known as 5 and formerly known as ABC) is a Philippine free-to-air television network based in Mandaluyong, with its alternate studios located in Novaliches, Quezon City. It is the flagship property of TV5 Network, Inc. with Cignal TV ...
(''formerly known as ABC 5 and TV5'') ( DWET-TV channel 5 In Metro Manila) a television network in the Philippines.
;
;Series
*''Babylon 5
''Babylon 5'' is an American space opera television series created by writer and producer J. Michael Straczynski, under the Babylonian Productions label, in association with Straczynski's Synthetic Worlds Ltd. and Warner Bros. Domestic Televi ...
'', a science fiction television series
*The number 5 features in the television series ''Battlestar Galactica'' in regards to the Final Five cylons and the Temple of Five
* ''Hi-5'' (Australian TV series), a television series from Australia
* ''Hi-5'' (UK TV series), a television show from the United Kingdom
* ''Hi-5'' Philippines a television show from the Philippines
*'' Odyssey 5'', a 2002 science fiction television series
*''Tillbaka till Vintergatan
Vintergatan (Swedish name for the Milky Way or "Winter Street") were TV series broadcast in 2000, 2001, 2003 and 2010 by Sveriges Television and directed and written by Petter Bragée.
Vintergatan 5a
Vintergatan 5a was broadcast as "''Sommarlovsm ...
'', a Swedish children's television series featuring a character named "Femman" (meaning five), who can only utter the word 'five'.
*'' The Five'' (talk show): Fox News Channel roundtable current events television show, premiered 2011, so-named for its panel of five commentators.
*'' Yes! PreCure 5'' is a 2007 anime series which follows the adventures of Nozomi and her friends. It is also followed by the 2008 sequel '' Yes! Pretty Cure 5 GoGo!''
*'' The Quintessential Quintuplets'' is a 2019 slice of life romance anime series which follows the everyday life of five identical quintuplets and their interactions with their tutor. It has two seasons, and a final movie is scheduled in summer 2022.
* ''Hawaii Five-0'', CBS American TV series.
Literature
* ''The Famous Five'' is a series of children's books by British writer Enid Blyton *'' The Power of Five'' is a series of children's books by British writer and screenwriter Anthony Horowitz *'' The Fall of Five'' is a book written under the collective pseudonym Pittacus Lore in the series ''Lorien Legacies'' *'' The Book of Five Rings'' is a text on kenjutsu and the martial arts in general, written by the swordsman Miyamoto Musashi circa 1645 *'' Slaughterhouse-Five'' is a book by Kurt Vonnegut about World War IISports
*TheOlympic Games
The modern Olympic Games or Olympics (french: link=no, Jeux olympiques) are the leading international sporting events featuring summer and winter sports competitions in which thousands of athletes from around the world participate in a multi ...
have five interlocked rings as their symbol, representing the number of inhabited continent
A continent is any of several large landmasses. Generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, up to seven geographical regions are commonly regarded as continents. Ordered from largest in area to smallest, these seven ...
s represented by the Olympians (Europe, Asia, Africa, Australia and Oceania, and the Americas).
* In AFL Women's, the top level of women's
A woman is an adult female human. Prior to adulthood, a female human is referred to as a girl (a female child or adolescent). The plural ''women'' is sometimes used in certain phrases such as " women's rights" to denote female humans rega ...
Australian rules football, each team is allowed 5 " interchanges" (substitute players), who can be freely substituted at any time.
*In baseball scorekeeping, the number 5 represents the third baseman
A third baseman, abbreviated 3B, is the player in baseball or softball whose responsibility is to defend the area nearest to third base — the third of four bases a baserunner must touch in succession to score a run. In the scoring system u ...
's position.
*In basketball
Basketball is a team sport in which two teams, most commonly of five players each, opposing one another on a rectangular court, compete with the primary objective of shooting a basketball (approximately in diameter) through the defender's h ...
:
**The number 5 is used to represent the position of center.
**Each team has five players on the court at a given time. Thus, the phrase "five on five" is commonly used to describe standard competitive basketball.
**The "5-second rule" refers to several related rules designed to promote continuous play. In all cases, violation of the rule results in a turnover.
**Under the FIBA
The International Basketball Federation (FIBA ; French: ) is an association of national organizations which governs the sport of basketball worldwide. Originally known as the (hence FIBA), in 1989 it dropped the word ''amateur'' from its nam ...
(used for all international play, and most non-US leagues) and NCAA women's rule sets, a team begins shooting bonus free throws once its opponent has committed five personal fouls in a quarter.
**Under the FIBA rules, A player fouls out and must leave the game after committing five fouls
* Five-a-side football is a variation of association football
Association football, more commonly known as football or soccer, is a team sport played between two teams of 11 players who primarily use their feet to propel the ball around a rectangular field called a pitch. The objective of the game is t ...
in which each team fields five players.
*In ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an Ice rink, ice skating rink with Ice hockey rink, lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. In ice hockey, two o ...
:
** A major penalty lasts five minutes.
** There are five different ways that a player can score a goal (teams at even strength, team on the power play, team playing shorthanded, penalty shot, and empty net).
** The area between the goaltender's legs is known as the five-hole.
*In most rugby league
Rugby league football, commonly known as just rugby league and sometimes football, footy, rugby or league, is a full-contact sport played by two teams of thirteen players on a rectangular field measuring 68 metres (75 yards) wide and 112 ...
competitions, the starting left wing
Left-wing politics describes the range of political ideologies that support and seek to achieve social equality and egalitarianism, often in opposition to social hierarchy. Left-wing politics typically involve a concern for those in ...
wears this number. An exception is the Super League
The Super League (officially known as the Betfred Super League due to sponsorship from Betfred and legally known as Super League Europe), is the top-level of the British rugby league system. At present the league consists of twelve teams, of ...
, which uses static squad numbering.
*In rugby union
Rugby union, commonly known simply as rugby, is a Contact sport#Terminology, close-contact team sport that originated at Rugby School in the first half of the 19th century. One of the Comparison of rugby league and rugby union, two codes of ru ...
:
** A try is worth 5 points.
** One of the two starting lock forwards wears number 5, and usually jumps at number 4 in the line-out.
** In the French variation of the bonus points system, a bonus point in the league standings is awarded to a team that loses by 5 or fewer points.
Technology
*5 is the most common number of gears for automobiles withmanual transmission
A manual transmission (MT), also known as manual gearbox, standard transmission (in Canada, the United Kingdom, and the United States), or stick shift (in the United States), is a multi-speed motor vehicle transmission system, where gear chang ...
.
*In radio communication, the term " Five by five" is used to indicate perfect signal strength and clarity.
*On almost all devices with a numeric keypad
A numeric keypad, number pad, numpad, or ten key,
is the palm-sized, usually-17-key section of a standard computer keyboard, usually on the far right. It provides calculator-style efficiency for entering numbers. The idea of a 10-key nu ...
such as telephones, computers, etc., the 5 key has a raised dot or raised bar to make dialing easier. Persons who are blind or have low vision find it useful to be able to feel the keys of a telephone. All other numbers can be found with their relative position around the 5 button (on computer keyboards, the 5 key of the numpad has the raised dot or bar, but the 5 key that shifts with % does not).
*On most telephone
A telephone is a telecommunications device that permits two or more users to conduct a conversation when they are too far apart to be easily heard directly. A telephone converts sound, typically and most efficiently the human voice, into el ...
s, the 5 key is associated with the letters J, K, and L, but on some of the BlackBerry
The blackberry is an edible fruit produced by many species in the genus ''Rubus'' in the family Rosaceae, hybrids among these species within the subgenus ''Rubus'', and hybrids between the subgenera ''Rubus'' and ''Idaeobatus''. The taxonomy of ...
phones, it is the key for G and H.
*The Pentium, coined by Intel Corporation, is a fifth-generation x86 architecture microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor where the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit, or a small number of integrated circuits. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circu ...
.
*The resin identification code
The ASTM International Resin Identification Coding System, often abbreviated RIC, is a set of symbols appearing on plastic products that identify the plastic resin out of which the product is made. It was developed in 1988 by the Society of t ...
used in recycling to identify polypropylene
Polypropylene (PP), also known as polypropene, is a thermoplastic polymer used in a wide variety of applications. It is produced via chain-growth polymerization from the monomer propylene.
Polypropylene
belongs to the group of polyolefins an ...
.
Miscellaneous fields
Five can refer to: *"Give me five" is a common phrase used preceding ahigh five High five is a friendly gesture in which one individual slaps another's hand.
High five (and variants such as Hi5, Hi-5, and Hi-Five) may also refer to:
Music
* Hi-5 (Australian group), an Australian children's musical group
* Hi-5 (Greek band ...
.
*An informal term for the British Security Service, MI5.
*Five babies born at one time are quintuplets. The most famous set of quintuplets were the Dionne quintuplets born in the 1930s.
*In the United States legal system, the Fifth Amendment to the United States Constitution
The Fifth Amendment (Amendment V) to the United States Constitution addresses criminal procedure and other aspects of the Constitution. It was ratified, along with nine other articles, in 1791 as part of the Bill of Rights. The Fifth Amend ...
can be referred to in court as "pleading the fifth", absolving the defendant from self-incrimination.
* Pentameter is verse with five repeating feet per line; iambic pentameter
Iambic pentameter () is a type of metric line used in traditional English poetry and verse drama. The term describes the rhythm, or meter, established by the words in that line; rhythm is measured in small groups of syllables called " feet". "Ia ...
was the most popular form in Shakespeare
William Shakespeare ( 26 April 1564 – 23 April 1616) was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's natio ...
.
*Quintessence
Quintessence, or fifth essence, may refer to:
Cosmology
* Aether (classical element), in medieval cosmology and science, the fifth element that fills the universe beyond the terrestrial sphere
* Quintessence (physics), a hypothetical form of da ...
, meaning "fifth element", refers to the elusive fifth element that completes the basic four elements (water, fire, air, and earth)
*The designation of an Interstate Highway
The Dwight D. Eisenhower National System of Interstate and Defense Highways, commonly known as the Interstate Highway System, is a network of controlled-access highways that forms part of the National Highway System in the United States. T ...
(Interstate 5
Interstate 5 (I-5) is the main north–south Interstate Highway on the West Coast of the United States, running largely parallel to the Pacific coast of the contiguous U.S. from Mexico to Canada. It travels through the states of Calif ...
) that runs from San Diego
San Diego ( , ; ) is a city on the Pacific Ocean coast of Southern California located immediately adjacent to the Mexico–United States border. With a 2020 population of 1,386,932, it is the eighth most populous city in the United States ...
, California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the ...
to Blaine, Washington. In addition, all major north-south Interstate Highways in the United States end in 5.
*In the computer game '' Riven'', 5 is considered a holy number, and is a recurring theme throughout the game, appearing in hundreds of places, from the number of islands in the game to the number of bolts on pieces of machinery.
*''The Garden of Cyrus
''The Garden of Cyrus'', or ''The Quincuncial Lozenge, or Network Plantations of the Ancients, naturally, artificially, mystically considered'', is a discourse by Sir Thomas Browne. First published in 1658, along with its diptych companion '' Ur ...
'' (1658) by Sir Thomas Browne is a Pythagorean discourse based upon the number 5.
*The holy number of Discordianism, as dictated by the Law of Fives.
*The number of Justices on the Supreme Court of the United States
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all U.S. federal court cases, and over state court cases that involve a point ...
necessary to render a majority decision.
*The number of dots in a quincunx
A quincunx () is a geometric pattern consisting of five points arranged in a cross, with four of them forming a square or rectangle and a fifth at its center. The same pattern has other names, including "in saltire" or "in cross" in heraldry (de ...
.
*The number of permanent members with veto power on the United Nations Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the Organs of the United Nations, six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international security, international peace and security, recommending the admi ...
.
*The number of sides and the number of angles in a pentagon
In geometry, a pentagon (from the Greek language, Greek πέντε ''pente'' meaning ''five'' and γωνία ''gonia'' meaning ''angle'') is any five-sided polygon or 5-gon. The sum of the internal angles in a simple polygon, simple pentagon is ...
.
*The number of points in a pentagram.
*The number of Korotkoff sounds when measuring blood pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressur ...
*The drink Five Alive is named for its five ingredients. The drink punch
Punch commonly refers to:
* Punch (combat), a strike made using the hand closed into a fist
* Punch (drink), a wide assortment of drinks, non-alcoholic or alcoholic, generally containing fruit or fruit juice
Punch may also refer to:
Places
* Pun ...
derives its name after the Sanskrit पञ्च (pañc) for having five ingredients.
*The Keating Five were five United States Senate, United States Senators accused of corruption in 1989.
*The Inferior Five: Merryman, Awkwardman, The Blimp, White Feather, and Dumb Bunny. DC Comics parody superhero team.
*Chanel No. 5, No. 5 is the name of the iconic fragrance created by Coco Chanel.
*The Committee of Five was delegated to draft the United States United States Declaration of Independence, Declaration of Independence.
*The five-second rule is a commonly used rule of thumb for dropped food.
*555 95472, usually referred to simply as 5, is a minor male character in the comic strip ''Peanuts''.
See also
*Five Families *Five Nations (disambiguation) *555 (number) *List of highways numbered 5References
*Wells, D. ''The Penguin Dictionary of Curious and Interesting Numbers'' London: Penguin Group. (1987): 58–67External links
* *The Number 5
{{DEFAULTSORT:5 (Number) Integers 5 (number)