|
Water (Wu Xing)
In Chinese philosophy, water () is the low point of the matter, or the matter's dying or hiding stage. Water is the fifth stage of Wu Xing, the five elements. Water is the most yin in character of the five elements. Its motion is downward and inward, and its energy is stillness and conserving. Water is associated with the color black, with the planet Mercury, with the moon (which was believed to cause the dew to fall at night), with night, with the north, with winter or cold weather, and with the Black Tortoise (Xuan Wu) in the Chinese constellation Four Symbols. Attributes In Chinese Taoist thought, ''water'' is representative of intelligence and wisdom, flexibility, softness, and pliancy; however, an overabundance of the element is said to cause difficulty in choosing something and sticking to it. In the same way, ''water'' can be fluid and weak, but can also wield great power when it floods and overwhelms the land. In Chinese medicine, water is believed to govern the kidney ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Philosophy
Chinese philosophy originates in the Spring and Autumn period () and Warring States period (), during a period known as the "Hundred Schools of Thought", which was characterized by significant intellectual and cultural developments. Although much of Chinese philosophy begun in the Warring States period, elements of Chinese philosophy have existed for several thousand years. Some can be found in the ''I Ching'' (the ''Book of Changes''), an ancient compendium of divination, which dates back to at least 672 BCE. It was during the Warring States era that what Sima Tan termed the major philosophical schools of China—Confucianism, Legalism (Chinese philosophy), Legalism, and Taoism—arose, along with philosophies that later fell into obscurity, like Agriculturalism, Mohism, School of Naturalists, Chinese Naturalism, and the School of Names, Logicians. Even in modern society, Confucianism is still the creed of etiquette for Chinese society. Chinese philosophy as a ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heavenly Stems
The ten Heavenly Stems or Celestial Stems () are a Chinese system of ordinals that first appear during the Shang dynasty, c. 1250 BC, as the names of the ten days of the week. They were also used in Shang-period ritual as names for dead family members, who were offered sacrifices on the corresponding day of the Shang week. The Heavenly Stems were used in combination with the Earthly Branches, a similar cycle of twelve days, to produce a compound cycle of sixty days. Subsequently, the Heavenly Stems lost their original function as names for days of the week and dead kin, and acquired many other uses, the most prominent and long lasting of which was their use together with the Earthly Branches as a 60-year calendrical cycle. The system is used throughout East Asia. Table The Japanese names of the Heavenly Stems are based on their corresponding Wuxing elements (e.g. ''ki'' for "wood", ''mizu'' for "water"), followed by the possessive/attributive particle の (''no'') and the word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fire (wuxing)
In Chinese philosophy, fire () is the prosper of the matter, or the matter's prosperity stage. Fire is the second phase of Wu Xing. Fire is yang in character. Its motion is upward and its energy is convective. Fire is associated with Summer, the South, the planet Mars, the color red (associated with extreme luck), hot weather, daylight, and the Vermilion Bird (Zhu Que) in the Four Symbols. Attributes In Traditional Chinese Medicine, ''Fire'' attributes are considered to be dynamism, strength, and persistence; however, it is also connected to restlessness. The fire element provides warmth, enthusiasm, and creativity; however, an excess of it can bring aggression, impatience, and impulsive behavior. In the same way, fire provides heat and warmth; however, an excess can also burn. Fire is associated with negative emotions of hate and the positive emotion is joy. The organs associated with the Fire element are the Heart (yin) and small intestine (yang), tongue and a body's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wood (wuxing)
In Chinese philosophy, wood (), sometimes translated as Tree, is the growing of the matter, or the matter's growing stage. Wood is the first phase of Wu Xing. Wood is the lesser yang character of the Five elements, giving birth to Fire. It stands for springtime, the east, the planet Jupiter, the color green, windy weather, and the Azure Dragon (Qing Long) in Four Symbols. Blue and cyan-type colors also represent wood. Attributes In Chinese Taoist thought, ''Wood'' attributes are considered to be strength and flexibility, as with bamboo. It is also associated with qualities of warmth, generosity, co-operation and idealism. The Wood person will be expansive, outgoing and socially conscious. The wood element is one that seeks ways to grow and expand. Wood heralds the beginning of life, springtime and buds, sensuality and fecundity. Wood needs moisture to thrive. In Chinese medicine, wood is associated with negative feelings of anger and positive feelings of optimism, patience and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal (wuxing)
In Chinese philosophy, metal or gold (), the fourth phase of Wu Xing, is the decline of the matter, or the matter's decline stage. In Traditional Chinese Medicine Metal is yin in character, its motion is inwards and its energy is contracting. It is associated with the west, autumn, it governs the Yin, Zang organ the Lung and the Yang, Fu organ colon, nose and skin, old age, the planet Venus, the color white, dry weather, and the White Tiger (Bai Hu) in Four Symbols. The archetypal metals are silver or gold. Attributes In Chinese Taoist thought, ''Metal'' attributes are considered to be firmness, rigidity, persistence, strength, and determination. The metal person is controlling, ambitious, forceful, and set in their ways as metal is very strong. They are self-reliant and prefer to handle their problems alone. The metal person is also wise, business-oriented, and good at organization and stability. However, the metal person can also appreciate luxury and enjoy the good things in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rat (zodiac)
The Rat or Mouse ( 鼠) is the first of the repeating 12-year cycle of animals which appear in the Chinese zodiac, constituting part of the Chinese calendar system (with similar systems in use elsewhere). The Year of the Rat in standard Chinese is . The rat is associated with the first branch of the Earthly Branch symbol 子 (''zǐ''), which starts a repeating cycle of twelve years. The Chinese word ''shǔ'' ( 鼠) refers to various small rodents (Muroidea), such as rats and mice. The term "zodiac" ultimately derives from an Ancient Greek term referring to a "circle of little animals". There are also a yearly month of the rat and a daily hour of the rat ( Chinese double hour, midnight, 11:00 p.m. to 1:00 a.m.). Years of the rat are cyclically differentiated by correlation to the Heavenly Stems cycle, resulting in a repeating cycle of five years of the rat (over a sixty-year period), each rat year also being associated with one of the Chinese wu xing, also known a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pig (zodiac)
The Pig ( 豬) or sometimes translated as the Boar is the twelfth of the 12-year cycle of animals which appear in Chinese zodiac, in relation to the Chinese calendar and system of horology, and paralleling the system of ten Heavenly Stems and twelve Earthly Branches. Although the term "zodiac" (etymologically referring to a " ircle oflittle animals") is used in the phrase "Chinese zodiac", there is a major difference between the Chinese usage and Western astrology: the zodiacal animals (including the zodiacal Pig) do not relate to the zodiac as the area of the sky that extends approximately 8° north or south (as measured in celestial latitude) of the ecliptic, the apparent path of the Sun, the Moon, and visible planets across the celestial sphere's constellations, over the course of the year. In Chinese astrology, "zodiacal" animals refer to fixed cycles of twelve animals. The same cycle of twelve is used for cycles of years and cycles of hours. In the case of years, the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Zodiac
The Chinese zodiac is a traditional classification scheme based on the lunar calendar that assigns an animal and its reputed attributes to each year in a repeating twelve-year cycle. Originating from China, the zodiac and its variations remain popular in many East Asian and Southeast Asian countries, such as Japan, South Korea, Vietnam, Singapore, Nepal, Bhutan and Thailand. Identifying this scheme using the generic term "''zodiac''" reflects several superficial similarities to the Western zodiac: both have time cycles divided into twelve parts, each labels at least the majority of those parts with names of animals, and each is widely associated with a culture of ascribing a person's personality or events in their life to the supposed influence of the person's particular relationship to the cycle. Nevertheless, there are major differences between the two: the animals of the Chinese zodiac are not associated with constellations spanned by the ecliptic plane. The Chinese twelve- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yin And Yang
Yin and yang ( and ) is a Chinese philosophy, Chinese philosophical concept that describes opposite but interconnected forces. In Chinese cosmology, the universe creates itself out of a primary chaos of material energy, organized into the cycles of yin and yang and formed into objects and lives. Yin is the receptive and yang the active principle, seen in all forms of change and difference such as the annual cycle (winter and summer), the landscape (north-facing shade and south-facing brightness), sexual coupling (female and male), the formation of both men and women as characters and sociopolitical history (disorder and order). Taiji (philosophy), Taiji or Tai chi () is a Chinese cosmological term for the "Supreme Ultimate" state of undifferentiated absolute and infinite potential, the oneness before duality, from which yin and yang originate. It can be compared with the old ''Wuji (philosophy), wuji'' (, "without pole"). In the cosmology pertaining to yin and yang, the mate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexagenary Cycle
The sexagenary cycle, also known as the Stems-and-Branches or ganzhi ( zh, 干支, gānzhī), is a cycle of sixty terms, each corresponding to one year, thus a total of sixty years for one cycle, historically used for recording time in China and the rest of the East Asian cultural sphere. It appears as a means of recording days in the first Chinese written texts, the Shang dynasty, Shang oracle bones of the late second millennium BC. Its use to record years began around the middle of the 3rd century BC. The cycle and its variations have been an important part of the traditional calendrical systems in Chinese-influenced Asian states and territories, particularly those of Japanese calendar, Japan, Korean calendar, Korea, and Vietnamese calendar, Vietnam, with the old Chinese system still in use in Taiwanese calendar, Taiwan, and to a lesser extent, in Mainland China. This traditional method of numbering days and years no longer has any significant role in modern Chinese time-keeping ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
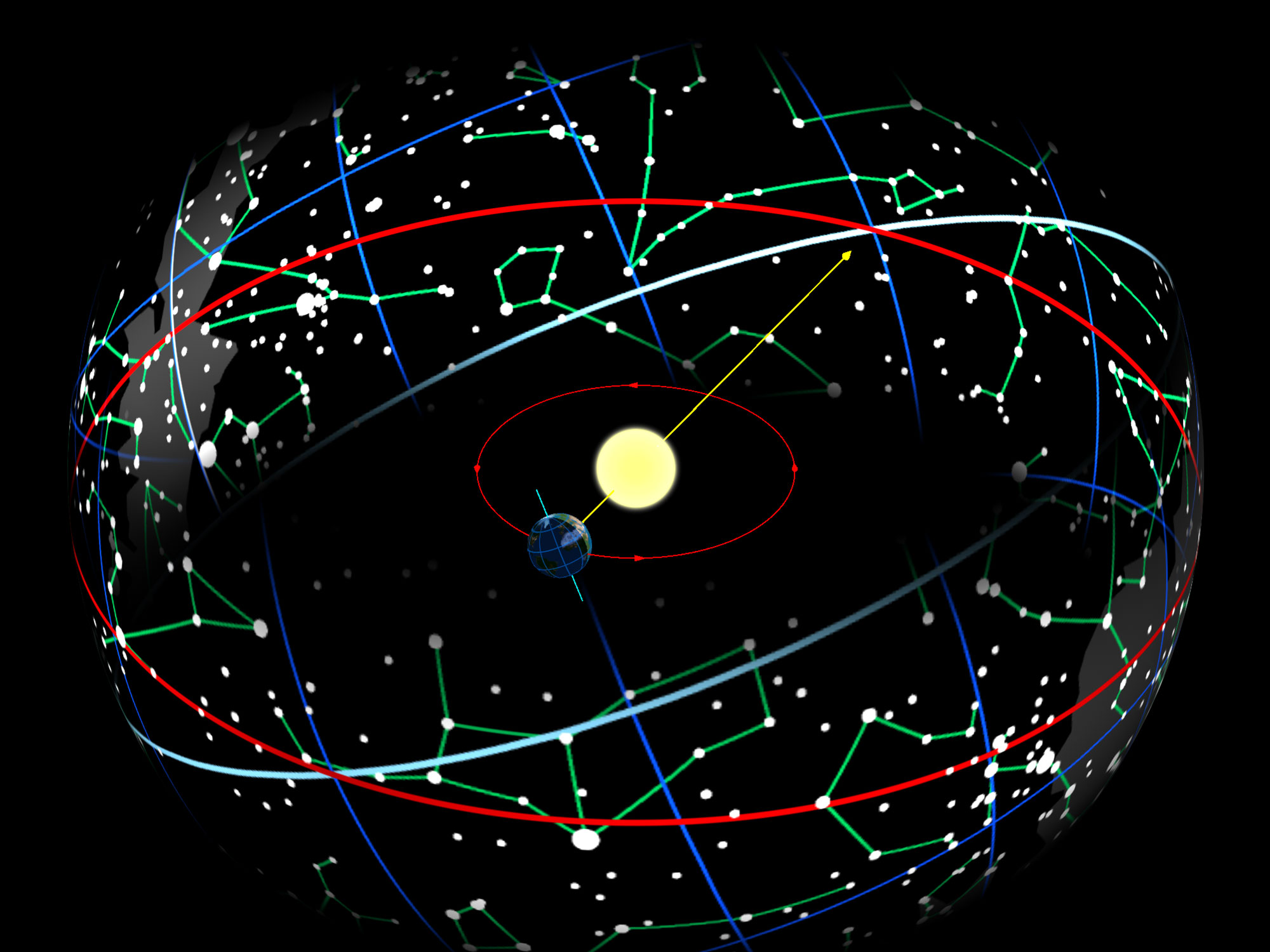
Zodiac
The zodiac is a belt-shaped region of the sky that extends approximately 8° north or south (as measured in celestial latitude) of the ecliptic, the Sun path, apparent path of the Sun across the celestial sphere over the course of the year. The paths of the Moon and visible planets are within the belt of the zodiac. In Western astrology, and formerly astronomy, the zodiac is divided into astrological sign, twelve signs, each occupying 30° of celestial longitude and roughly corresponding to the following star constellations: Aries (astrology), Aries, Taurus (astrology), Taurus, Gemini (astrology), Gemini, Cancer (astrology), Cancer, Leo (astrology), Leo, Virgo (astrology), Virgo, Libra (astrology), Libra, Scorpio (astrology), Scorpio, Sagittarius (astrology), Sagittarius, Capricorn (astrology), Capricorn, Aquarius (astrology), Aquarius, and Pisces (astrology), Pisces. These astrological signs form a celestial coordinate system, or more specifically an ecliptic coordinate sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |