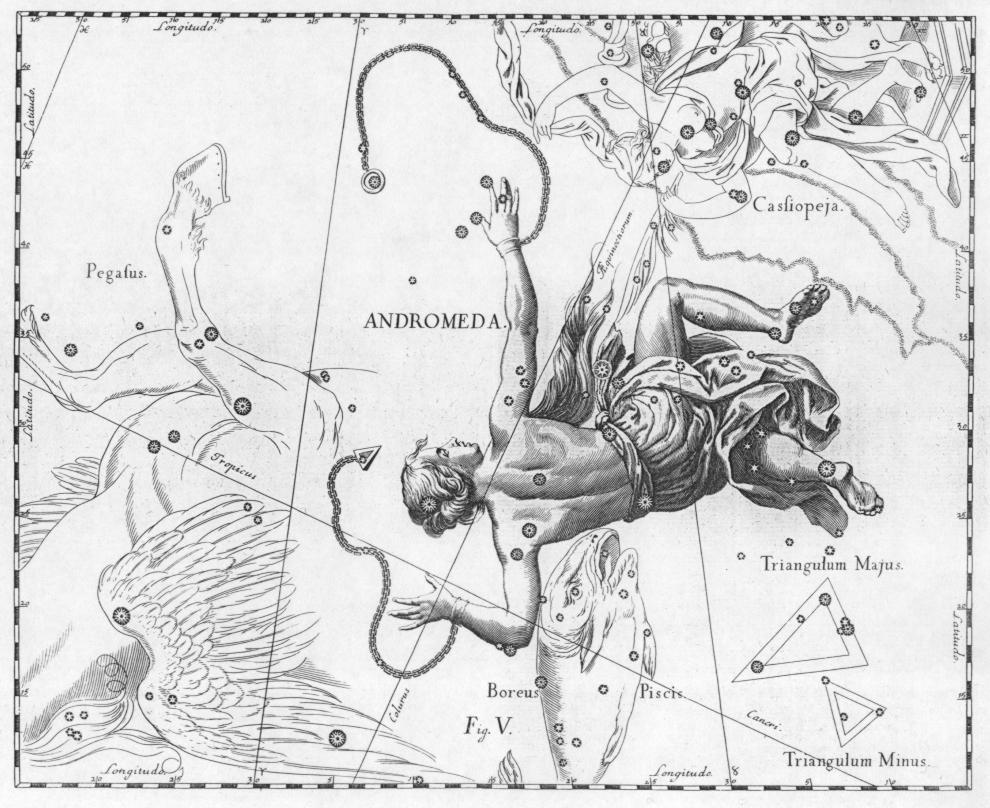
|
Andromeda (constellation)
Andromeda is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greco-Roman astronomer Ptolemy, and one of the 88 modern constellations. Located in the northern celestial hemisphere, it is named for Andromeda, daughter of Cassiopeia, in the Greek myth, who was chained to a rock to be eaten by the sea monster Cetus. Andromeda is most prominent during autumn evenings in the Northern Hemisphere, along with several other constellations named for characters in the Perseus myth. Because of its northern declination, Andromeda is visible only north of 40° south latitude; for observers farther south, it lies below the horizon. It is one of the largest constellations, with an area of 722 square degrees. This is over 1,400 times the size of the full moon, 55% of the size of the largest constellation, Hydra, and over 10 times the size of the smallest constellation, Crux. Its brightest star, Alpha Andromedae, is a binary star that has also been counted as a part of Pegasus, while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andromeda (mythology)
In Greek mythology, Andromeda (; grc, Ἀνδρομέδα, Androméda or , ''Andromédē'') is the daughter of the king of Aethiopia, Cepheus (father of Andromeda), Cepheus, and his wife, Cassiopeia (mother of Andromeda), Cassiopeia. When Cassiopeia boasts that she is more beautiful than the Nereids, Poseidon sends the sea monster Cetus (mythology), Cetus to ravage the coast of Aethiopia as divine punishment. Andromeda is chained to a rock as a sacrifice to sate the monster, but is saved from death by Perseus, who marries her and takes her to Greece to reign as his queen. As a subject, Andromeda has been popular in art since classical times; rescued by a Greek hero cult, Greek hero, Andromeda's narration is considered the forerunner to the "princess and dragon" Motif (narrative), motif. From the Renaissance, interest revived in the original story, typically as derived from Ovid's ''Metamorphoses'' (4.663ff). Etymology Her name is the Latin, Latinized form of the Greek (''Androm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Andromedae
Beta Andromedae, Latinized from β Andromedae, and officially named Mirach , is a prominent star in the northern constellation of Andromeda. It is northeast of the Great Square of Pegasus and is potentially visible to all observers north of latitude 54° S. It is commonly used by stargazers to find the Andromeda Galaxy. The galaxy NGC 404, also known as Mirach's Ghost, is seven arcminutes away from Mirach. This star has an average apparent visual magnitude of 2.05, making it the brightest star in the constellation. The luminosity varies slightly from magnitude +2.01 to +2.10. Based upon parallax measurements, it is roughly from the Sun. Its apparent magnitude is reduced by 0.06 by extinction due to gas and dust along the line of sight. The star has a negligible radial velocity of 0.1 km/s, but with a relatively large proper motion, traversing the celestial sphere at ·yr−1. Properties Beta Andromedae is a single red giant with a stellar classification of M0& ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Andromedae
Gamma Andromedae, Latinized from γ Andromedae, is the third-brightest point of light in the northern constellation of Andromeda. It is a multiple star system approximately 350 light-years from Earth. The system is drifting closer to the Sun with a radial velocity in the range of −12 to −14 km/s. Observation In 1778, German physicist Johann Tobias Mayer discovered that γ Andromedae is a double star. When examined in a small telescope, it appears to be a bright, golden-yellow star next to a dimmer, indigo-blue star, separated by approximately 10 arcseconds. The pair is often considered by stargazers to be a beautiful double star with a striking contrast of color. The brighter member, γ1 Andromedae, is the primary of the system, and is thus designated component γ Andromedae A. It has the official proper name Almach , which was used as the traditional name of the naked eye star, and thus the system as a whole. The fainter secondary is γ2 And ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Star
A binary star is a system of two stars that are gravitationally bound to and in orbit around each other. Binary stars in the night sky that are seen as a single object to the naked eye are often resolved using a telescope as separate stars, in which case they are called ''visual binaries''. Many visual binaries have long orbital periods of several centuries or millennia and therefore have orbits which are uncertain or poorly known. They may also be detected by indirect techniques, such as spectroscopy (''spectroscopic binaries'') or astrometry (''astrometric binaries''). If a binary star happens to orbit in a plane along our line of sight, its components will eclipse and transit each other; these pairs are called ''eclipsing binaries'', or, together with other binaries that change brightness as they orbit, ''photometric binaries''. If components in binary star systems are close enough they can gravitationally distort their mutual outer stellar atmospheres. In some cases, thes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crux
Crux () is a constellation of the southern sky that is centred on four bright stars in a cross-shaped asterism commonly known as the Southern Cross. It lies on the southern end of the Milky Way's visible band. The name ''Crux'' is Latin for cross. Even though it is the smallest of all 88 modern constellations, Crux is among the most easily distinguished as its four main stars each have an apparent visual magnitude brighter than +2.8. It has attained a high level of cultural significance in many Southern Hemisphere states and nations. Blue-white α Crucis (Acrux) is the most southerly member of the constellation and, at magnitude 0.8, the brightest. The three other stars of the cross appear clockwise and in order of lessening magnitude: β Crucis (Mimosa), γ Crucis (Gacrux), and δ Crucis (Imai). ε Crucis (Ginan) also lies within the cross asterism. Many of these brighter stars are members of the Scorpius–Centaurus association, a large but loose group of hot blue-whit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydra (constellation)
Hydra is the largest of the 88 modern constellations, measuring 1303 square degrees, and also the longest at over 100 degrees. Its southern end borders Libra and Centaurus and its northern end borders Cancer. It was included among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy. Commonly represented as a water snake, it straddles the celestial equator. History and mythology Western mythology The Greek constellation of Hydra is an adaptation of a Babylonian constellation: the MUL.APIN includes a "serpent" constellation (MUL.DINGIR.MUŠ) that loosely corresponds to Hydra. It is one of two Babylonian "serpent" constellations (the other being the origin of the Greek Serpens), a mythological hybrid of serpent, lion and bird. The shape of Hydra resembles a twisting snake, and features as such in some Greek myths. One myth associates it with a water snake that a crow served Apollo in a cup when it was sent to fetch water; Apollo saw through the fraud, and angr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Full Moon
The full moon is the lunar phase when the Moon appears fully illuminated from Earth's perspective. This occurs when Earth is located between the Sun and the Moon (when the ecliptic coordinate system, ecliptic longitudes of the Sun and Moon opposition (astronomy), differ by 180°). This means that the lunar hemisphere facing Earth—the near side of the Moon, near side—is completely sunlit and appears as an approximately circular disk. The full moon occurs roughly once a month. The time interval between a full moon and the next repetition of the same phase, a Lunar month#Synodic month, synodic month, averages about 29.53 days. Therefore, in those lunar calendars in which each month begins on the day of the new moon, the full moon falls on either the 14th or 15th day of the lunar month. Because a calendar month consists of a Natural number, whole number of days, a month in a lunar calendar may be either 29 or 30 days long. Characteristics A full moon is often thought of as an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Square Degree
__NOTOC__ A square degree (deg2) is a non- SI unit measure of solid angle. Other denotations include ''sq. deg.'' and (°)2. Just as degrees are used to measure parts of a circle, square degrees are used to measure parts of a sphere. Analogous to one degree being equal to radians, a square degree is equal to ()2 steradians (sr), or about sr or about . The whole sphere has a solid angle of which is approximately : : 4 \pi \left(\frac\right)^2 \, ^2 = \frac\,\, ^2 = \frac \,\, ^2 \approx 41\,252.96 \,\, ^2 Examples * The full moon covers only about of the sky when viewed from the surface of the Earth. The Moon is only a half degree across (i.e. a circular diameter of roughly ), so the moon's disk covers a circular area of: ()2, or 0.2 square degrees. The moon varies from 0.188 to depending on its distance to the Earth. * Viewed from Earth, the Sun is roughly half a degree across (the same as the full moon) and covers only as well. * It would take times the full ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Declination
In astronomy, declination (abbreviated dec; symbol ''δ'') is one of the two angles that locate a point on the celestial sphere in the equatorial coordinate system, the other being hour angle. Declination's angle is measured north or south of the celestial equator, along the hour circle passing through the point in question. The root of the word ''declination'' (Latin, ''declinatio'') means "a bending away" or "a bending down". It comes from the same root as the words ''incline'' ("bend foward") and ''recline'' ("bend backward"). In some 18th and 19th century astronomical texts, declination is given as ''North Pole Distance'' (N.P.D.), which is equivalent to 90 – (declination). For instance an object marked as declination −5 would have an N.P.D. of 95, and a declination of −90 (the south celestial pole) would have an N.P.D. of 180. Explanation Declination in astronomy is comparable to geographic latitude, projected onto the celestial sphere, and right ascension is like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perseus
In Greek mythology, Perseus (Help:IPA/English, /ˈpɜːrsiəs, -sjuːs/; Greek language, Greek: Περσεύς, Romanization of Greek, translit. Perseús) is the legendary founder of Mycenae and of the Perseid dynasty. He was, alongside Cadmus and Bellerophon, the greatest Greek hero and slayer of monsters before the days of Heracles. He beheaded the Gorgon Medusa for Polydectes and saved Andromeda (mythology), Andromeda from the sea monster Cetus (mythology), Cetus. He was the son of Zeus and the mortal Danaë, as well as the half-brother and great-grandfather of Heracles (as they were both children of Zeus, and Heracles' mother was descended from Perseus). Etymology Because of the obscurity of the name "Perseus" and the legendary character of its bearer, most etymologists presume that it might be pre-Greek; however, the name of Perseus's native city was Greek and so were the names of his wife and relatives. There is some idea that it descended into Greek from the Proto-Indo-Eu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the Equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined as being in the same celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the solar system as Earth's North Pole. Owing to Earth's axial tilt of 23.439281°, winter in the Northern Hemisphere lasts from the December solstice (typically December 21 UTC) to the March equinox (typically March 20 UTC), while summer lasts from the June solstice through to the September equinox (typically on 23 September UTC). The dates vary each year due to the difference between the calendar year and the astronomical year. Within the Northern Hemisphere, oceanic currents can change the weather patterns that affect many factors within the north coast. Such events include El Niño–Southern Oscillation. Trade winds blow from east to west just above the equator. The winds pull surface water with them, creating currents, which flow westward due to the Coriolis e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |