|
Declination
In astronomy, declination (abbreviated dec; symbol ''δ'') is one of the two angles that locate a point on the celestial sphere in the equatorial coordinate system, the other being hour angle. The declination angle is measured north (positive) or south (negative) of the celestial equator, along the hour circle passing through the point in question. The root of the word ''declination'' (Latin, ''declinatio'') means "a bending away" or "a bending down". It comes from the same root as the words ''incline'' ("bend forward") and ''recline'' ("bend backward"). In some 18th and 19th century astronomical texts, declination is given as ''North Pole Distance'' (N.P.D.), which is equivalent to 90 – (declination). For instance an object marked as declination −5 would have an N.P.D. of 95, and a declination of −90 (the south celestial pole) would have an N.P.D. of 180. Explanation Declination in astronomy is comparable to geographic latitude, projected onto the celestial sphere, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proper Motion
Proper motion is the astrometric measure of changes in the apparent places of stars or other celestial objects as they move relative to the center of mass of the Solar System. It is measured relative to the distant stars or a stable reference such as the International Celestial Reference Frame (ICRF). Patterns in proper motion reveal larger structures like stellar streams, the general rotation of the Milky Way disk, and the random motions of stars in the Galactic halo. The components for proper motion in the equatorial coordinate system (of a given epoch, often J2000.0) are given in the direction of right ascension (''μ''α) and of declination (''μ''δ). Their combined value is computed as the ''total proper motion'' (''μ''). It has dimensions of angle per time, typically arcseconds per year or milliarcseconds per year. Knowledge of the proper motion, distance, and radial velocity allows calculations of an object's motion from the Solar System's frame of reference an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right Ascension
Right ascension (abbreviated RA; symbol ) is the angular distance of a particular point measured eastward along the celestial equator from the Sun at the equinox (celestial coordinates), March equinox to the (hour circle of the) point in question above the Earth. When paired with declination, these celestial coordinate system, astronomical coordinates specify the location of a point on the celestial sphere in the equatorial coordinate system. An old term, ''right ascension'' (), "''Ascensio recta'' Solis, stellæ, aut alterius cujusdam signi, est gradus æquatorus cum quo simul exoritur in sphæra recta"; roughly translated, "''Right ascension'' of the Sun, stars, or any other sign, is the degree of the equator that rises together in a right sphere" refers to the ''ascension'', or the point on the celestial equator that rises with any celestial object as seen from Earth's equator, where the celestial equator perpendicular, intersects the horizon at a right angle. It contrasts wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equatorial Coordinate System
The equatorial coordinate system is a celestial coordinate system widely used to specify the positions of astronomical object, celestial objects. It may be implemented in spherical coordinate system, spherical or Cartesian coordinate system, rectangular coordinates, both defined by an origin (mathematics), origin at the centre of Earth, a fundamental plane (spherical coordinates), fundamental plane consisting of the projective geometry, projection of Earth's equator onto the celestial sphere (forming the celestial equator), a primary direction towards the March equinox, March equinox (celestial coordinates), equinox, and a right-hand rule, right-handed convention. The origin at the centre of Earth means the coordinates are ''geocentric model, geocentric'', that is, as seen from the centre of Earth as if it were transparency and translucency, transparent. The fundamental plane and the primary direction mean that the coordinate system, while aligned with Earth's equator and geograp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hour Circle
In astronomy, the hour circle is the great circle through a given object and the two celestial poles. Together with declination and distance (from the planet's centre of mass), it determines the location of any celestial object. As such, it is a higher concept than the meridian as defined in astronomy, which takes account of the terrain and depth to the centre of Earth at a ground observer's location. The hour circles, specifically, are perfect circles perpendicular (at right angles) to the celestial equator. By contrast, the declination of an object viewed on the celestial sphere is the angle of that object to/from the celestial equator (thus ranging from +90° to −90°). The location of stars, planets, and other similarly distant objects is usually expressed in the following parameters, one for each of the three spatial dimensions: their declination, right ascension (epoch-fixed hour angle), and distance. These are as located at the vernal equinox for the epoch (e.g. J200 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circumpolar Star
A circumpolar star is a star that, as viewed from a given latitude on Earth, never sets below the horizon due to its apparent proximity to one of the celestial poles. Circumpolar stars are therefore visible from said location toward the nearest pole for the entire night on every night of the year (and would be continuously visible throughout the day too, were they not overwhelmed by the Sun's glare). Others are called ''seasonal'' stars. All circumpolar stars lie within a circumpolar circle whose size is determined by the observer's latitude. Specifically, the angular measure of the radius of this circle equals the observer's latitude. The closer the observer is to the North or South Pole, the larger its circumpolar circle. Before the definition of the Arctic was formalized as the region north of the Arctic Circle which experiences the midnight sun, it more broadly meant those places where the 'bear' constellations (Ursa Major, the Great Bear, and Ursa Minor, the Little Bear) we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
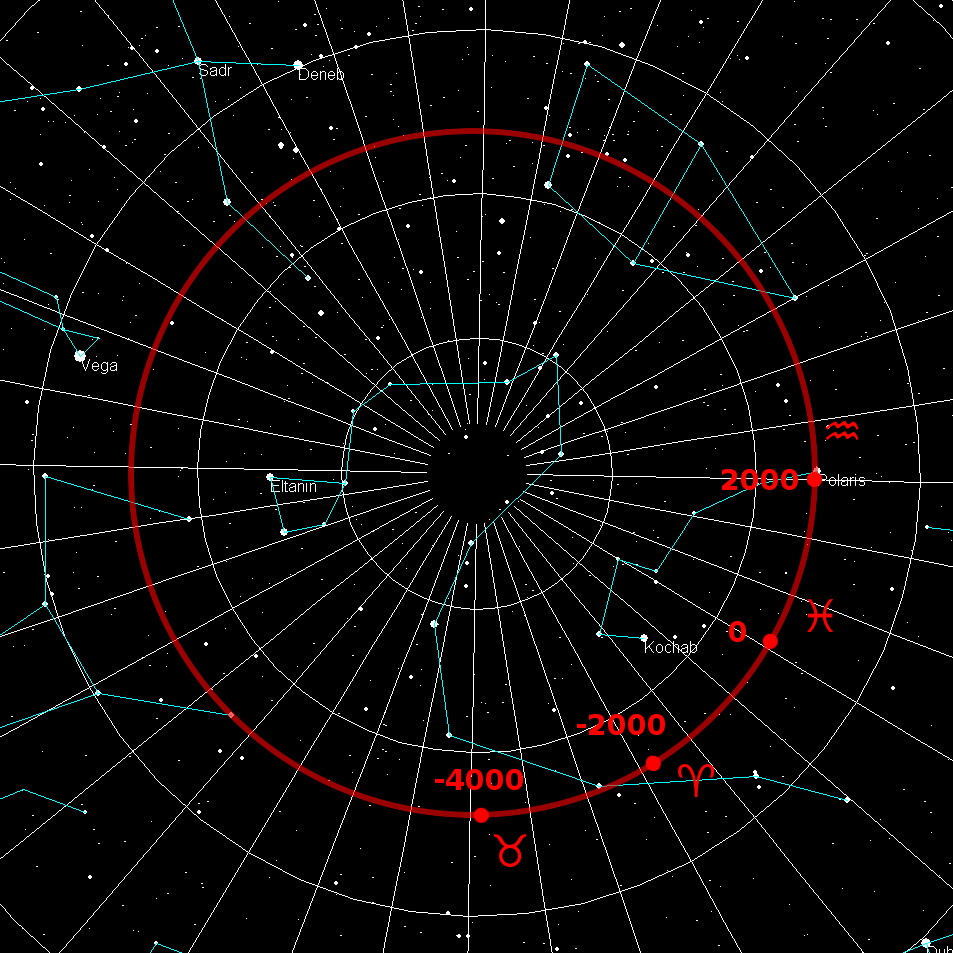
Axial Precession
In astronomy, axial precession is a gravity-induced, slow, and continuous change in the orientation of an astronomical body's rotational axis. In the absence of precession, the astronomical body's orbit would show axial parallelism. In particular, axial precession can refer to the gradual shift in the orientation of Earth's axis of rotation in a cycle of approximately 26,000 years.Hohenkerk, C.Y., Yallop, B.D., Smith, C.A., & Sinclair, A.T. "Celestial Reference Systems" in Seidelmann, P.K. (ed.) ''Explanatory Supplement to the Astronomical Almanac''. Sausalito: University Science Books. p. 99. This is similar to the precession of a spinning top, with the axis tracing out a pair of cones joined at their apices. The term "precession" typically refers only to this largest part of the motion; other changes in the alignment of Earth's axis— nutation and polar motion—are much smaller in magnitude. Earth's precession was historically called the precession of the equinoxes, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latitude
In geography, latitude is a geographic coordinate system, geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from −90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pole, with 0° at the Equator. Parallel (latitude), Lines of constant latitude, or ''parallels'', run east-west as circles parallel to the equator. Latitude and longitude are used together as a coordinate pair to specify a location on the surface of the Earth. On its own, the term "latitude" normally refers to the ''geodetic latitude'' as defined below. Briefly, the geodetic latitude of a point is the angle formed between the vector perpendicular (or ''Normal (geometry), normal'') to the ellipsoidal surface from the point, and the equatorial plane, plane of the equator. Background Two levels of abstraction are employed in the definitions of latitude and longitude. In the first step the physical surface i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celestial Sphere
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an abstract sphere that has an arbitrarily large radius and is concentric to Earth. All objects in the sky can be conceived as being projected upon the inner surface of the celestial sphere, which may be centered on Earth or the observer. If centered on the observer, half of the sphere would resemble a hemispherical screen over the observing location. The celestial sphere is a conceptual tool used in spherical astronomy to specify the position of an object in the sky without consideration of its linear distance from the observer. The celestial equator divides the celestial sphere into northern and southern hemispheres. Description Because astronomical objects are at such remote distances, casual observation of the sky offers no information on their actual distances. All celestial objects seem equally far away, as if fixed onto the inside of a sphere with a large but unknown radius, which appears to rotate westwa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precession Of The Equinoxes
In astronomy, axial precession is a gravity-induced, slow, and continuous change in the orientation of an astronomical body's Rotation around a fixed axis, rotational axis. In the absence of precession, the astronomical body's orbit would show axial parallelism. In particular, axial precession can refer to the gradual shift in the orientation of Earth's axis of rotation in a cycle of approximately 26,000 years.Hohenkerk, C.Y., Yallop, B.D., Smith, C.A., & Sinclair, A.T. "Celestial Reference Systems" in Seidelmann, P.K. (ed.) ''Explanatory Supplement to the Astronomical Almanac''. Sausalito: University Science Books. p. 99. This is similar to the precession of a spinning top, with the axis tracing out a pair of Cone (geometry), cones joined at their Apex (geometry), apices. The term "precession" typically refers only to this largest part of the motion; other changes in the alignment of Earth's axis—astronomical nutation, nutation and polar motion—are much smaller in magnitude ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar System" and "solar system" structures in theinaming guidelines document. The name is commonly rendered in lower case ('solar system'), as, for example, in the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' an''Merriam-Webster's 11th Collegiate Dictionary''. is the gravitationally bound Planetary system, system of the Sun and the objects that orbit it. It Formation and evolution of the Solar System, formed about 4.6 billion years ago when a dense region of a molecular cloud collapsed, forming the Sun and a protoplanetary disc. The Sun is a typical star that maintains a hydrostatic equilibrium, balanced equilibrium by the thermonuclear fusion, fusion of hydrogen into helium at its stellar core, core, releasing this energy from its outer photosphere. As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celestial Pole
The north and south celestial poles are the two points in the sky where Earth's axis of rotation, indefinitely extended, intersects the celestial sphere. The north and south celestial poles appear permanently directly overhead to observers at Earth's North Pole and South Pole, respectively. As Earth spins on its axis, the two celestial poles remain fixed in the sky, and all other celestial points appear to rotate around them, completing one circuit per day (strictly, per sidereal day). The celestial poles are also the poles of the celestial equatorial coordinate system, meaning they have declinations of +90 degrees and −90 degrees (for the north and south celestial poles, respectively). Despite their apparently fixed positions, the celestial poles in the long term do not actually remain permanently fixed against the background of the stars. Because of a phenomenon known as the precession of the equinoxes, the poles trace out circles on the celestial sphere, with a period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |