RNA virus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 An RNA virus is a
An RNA virus is a
2019.006G
/ref> The realm does not contain all RNA viruses: ''
 The double-stranded (ds)RNA viruses represent a diverse group of viruses that vary widely in host range (humans, animals, plants,
The double-stranded (ds)RNA viruses represent a diverse group of viruses that vary widely in host range (humans, animals, plants,
File:Lassa virus.JPG, Lassa virus (''Arenaviridae'')
File:Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus.jpg, Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (''Arenaviridae'')
File:Sin Nombre virus Hanta TEM 1137 lores.jpg, Hantavirus (''Bunyaviridae'')
File:Marburg virus.jpg, Marburg Virus (''
Animal viruses
{{Authority control RNA viruses, RNA
 An RNA virus is a
An RNA virus is a virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea.
Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1 ...
other than a retrovirusthat has ribonucleic acid (RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydra ...
) as its genetic material
Nucleic acids are biopolymers, macromolecules, essential to all known forms of life. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomers made of three components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main clas ...
. The nucleic acid
Nucleic acids are biopolymers, macromolecules, essential to all known forms of life. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomers made of three components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main cl ...
is usually single-stranded
When referring to DNA transcription, the coding strand (or informational strand) is the DNA strand whose base sequence is identical to the base sequence of the RNA transcript produced (although with thymine replaced by uracil). It is this stra ...
RNA ( ssRNA) but it may be double-stranded (dsRNA). Notable human diseases caused by RNA viruses include the common cold, influenza
Influenza, commonly known as "the flu", is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These symptoms ...
, SARS
Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) is a viral respiratory disease of zoonotic origin caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV or SARS-CoV-1), the first identified strain of the SARS coronavirus species, ''seve ...
, MERS
Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) is a viral respiratory infection caused by ''Middle East respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus'' (MERS-CoV). Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. Typical symptoms include fever, cough, ...
, Covid-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by a virus, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The first known case was COVID-19 pandemic in Hubei, identified in Wuhan, China, in December ...
, Dengue Virus, hepatitis C, hepatitis E
Hepatitis E is inflammation of the liver caused by infection with the hepatitis E virus (HEV); it is a type of viral hepatitis. Hepatitis E has mainly a fecal-oral transmission route that is similar to hepatitis A, although the viruses are unrel ...
, West Nile fever
West Nile fever is an infection by the West Nile virus, which is typically spread by mosquitoes. In about 80% of infections people have few or no symptoms. About 20% of people develop a fever, headache, vomiting, or a rash. In less than 1% of ...
, Ebola virus disease, rabies
Rabies is a viral disease that causes encephalitis in humans and other mammals. Early symptoms can include fever and tingling at the site of exposure. These symptoms are followed by one or more of the following symptoms: nausea, vomiting, vi ...
, polio
Poliomyelitis, commonly shortened to polio, is an infectious disease caused by the poliovirus. Approximately 70% of cases are asymptomatic; mild symptoms which can occur include sore throat and fever; in a proportion of cases more severe s ...
, mumps, and measles.
The International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses
The International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) authorizes and organizes the taxonomic classification of and the nomenclatures for viruses. The ICTV has developed a universal taxonomic scheme for viruses, and thus has the means to ap ...
(ICTV) classifies RNA viruses as those that belong to ''Group III'', ''Group IV'' or ''Group V'' of the Baltimore classification
Baltimore classification is a system used to classify viruses based on their manner of messenger RNA (mRNA) synthesis. By organizing viruses based on their manner of mRNA production, it is possible to study viruses that behave similarly as a d ...
system. This category excludes ''Group VI'', viruses with RNA genetic material but which use DNA intermediates in their life cycle
Life cycle, life-cycle, or lifecycle may refer to:
Science and academia
*Biological life cycle, the sequence of life stages that an organism undergoes from birth to reproduction ending with the production of the offspring
* Life-cycle hypothesis ...
: these are called retroviruses, including HIV-1
The subtypes of HIV include two major types, HIV type 1 (HIV-1) and HIV type 2 (HIV-2). HIV-1 is related to viruses found in chimpanzees and gorillas living in western Africa, while HIV-2 viruses are related to viruses found in the sooty mangabey ...
and HIV-2
The subtypes of HIV include two major types, HIV type 1 (HIV-1) and HIV type 2 (HIV-2). HIV-1 is related to viruses found in chimpanzees and gorillas living in western Africa, while HIV-2 viruses are related to viruses found in the sooty mangabe ...
which cause AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual m ...
.
As of May 2020, all known RNA viruses encoding an RNA-directed RNA polymerase are believed to form a monophyletic group, known as the realm '' Riboviria''. The majority of such RNA viruses fall into the kingdom '' Orthornavirae'' and the rest have a positioning not yet defined.TaxoPro2019.006G
/ref> The realm does not contain all RNA viruses: ''
Deltavirus
Hepatitis D is a type of viral hepatitis caused by the hepatitis delta virus (HDV). HDV is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E. HDV is considered to be a satellite (a type of subviral agent) because it can propagate only in ...
'', '' Asunviroidae'', and ''Pospiviroidae
The Pospiviroidae are a family of viroids, including the first viroid to be discovered, PSTVd. Their secondary structure is key to their biological activity. The classification of this family is based on differences in the conserved central re ...
'' are taxa of RNA viruses that were mistakenly included in 2019, but corrected in 2020.
Characteristics
Single-stranded RNA viruses and RNA Sense
RNA viruses can be further classified according to the sense or polarity of their RNA intonegative-sense
In molecular biology and genetics, the sense of a nucleic acid molecule, particularly of a strand of DNA or RNA, refers to the nature of the roles of the strand and its complementarity (molecular biology), complement in specifying a sequence of am ...
and positive-sense
In molecular biology and genetics, the sense of a nucleic acid molecule, particularly of a strand of DNA or RNA, refers to the nature of the roles of the strand and its complement in specifying a sequence of amino acids. Depending on the context ...
, or ambisense RNA viruses. Positive-sense viral RNA is similar to mRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of Protein biosynthesis, synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is ...
and thus can be immediately translated
Translation is the communication of the meaning of a source-language text by means of an equivalent target-language text. The English language draws a terminological distinction (which does not exist in every language) between ''transla ...
by the host cell. Negative-sense viral RNA is complementary to mRNA and thus must be converted to positive-sense RNA by an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase before translation. Purified RNA of a positive-sense virus can directly cause infection though it may be less infectious than the whole virus particle. In contrast, purified RNA of a negative-sense virus is not infectious by itself as it needs to be transcribed into positive-sense RNA; each virion
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea.
Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's ...
can be transcribed to several positive-sense RNAs. Ambisense
In molecular biology and genetics, the sense of a nucleic acid molecule, particularly of a strand of DNA or RNA, refers to the nature of the roles of the strand and its complement in specifying a sequence of amino acids. Depending on the context ...
RNA viruses resemble negative-sense RNA viruses, except they translate genes from their negative and positive strands.
Double-stranded RNA viruses
 The double-stranded (ds)RNA viruses represent a diverse group of viruses that vary widely in host range (humans, animals, plants,
The double-stranded (ds)RNA viruses represent a diverse group of viruses that vary widely in host range (humans, animals, plants, fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from ...
, and bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among ...
), genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ge ...
segment number (one to twelve), and virion
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea.
Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's ...
organization (Triangulation number
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or may ...
, capsid
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or ma ...
layers, spikes, turrets, etc.). Members of this group include the rotavirus
''Rotavirus'' is a genus of double-stranded RNA viruses in the family ''Reoviridae''. Rotaviruses are the most common cause of diarrhoeal disease among infants and young children. Nearly every child in the world is infected with a rotavirus a ...
es, which are the most common cause of gastroenteritis in young children, and picobirnaviruses, which are the most common virus in fecal samples of both humans and animals with or without signs of diarrhea. Bluetongue virus
Bluetongue disease is a noncontagious, insect-borne, viral disease of ruminants, mainly sheep and less frequently cattle, yaks, goats, buffalo, deer, dromedaries, and antelope. It is caused by ''Bluetongue virus'' (''BTV''). The virus is ...
is an economically important pathogen that infects cattle and sheep. In recent years, progress has been made in determining atomic and subnanometer resolution structures of a number of key viral proteins and virion capsids of several dsRNA viruses, highlighting the significant parallels in the structure and replicative processes of many of these viruses.
Mutation rates
RNA viruses generally have very highmutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA replication, DNA or viral repl ...
rates compared to DNA virus
A DNA virus is a virus that has a genome made of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) that is replicated by a DNA polymerase. They can be divided between those that have two strands of DNA in their genome, called double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) viruses, and ...
es, because viral RNA polymerases
In molecular biology, RNA polymerase (abbreviated RNAP or RNApol), or more specifically DNA-directed/dependent RNA polymerase (DdRP), is an enzyme that synthesizes RNA from a DNA template.
Using the enzyme helicase, RNAP locally opens the ...
lack the proofreading ability of DNA polymerase
A DNA polymerase is a member of a family of enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of DNA molecules from nucleoside triphosphates, the molecular precursors of DNA. These enzymes are essential for DNA replication and usually work in groups to create ...
s. The genetic diversity of RNA viruses is one reason why it is difficult to make effective vaccines
A vaccine is a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious or malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verified.< ...
against them. Retroviruses also have a high mutation rate even though their DNA intermediate integrates into the host genome (and is thus subject to host DNA proofreading once integrated), because errors during reverse transcription are embedded into both strands of DNA before integration. Some genes of RNA virus are important to the viral replication cycles and mutations are not tolerated. For example, the region of the hepatitis C virus
The hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a small (55–65 nm in size), enveloped, positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus of the family ''Flaviviridae''. The hepatitis C virus is the cause of hepatitis C and some cancers such as liver cancer ( hepato ...
genome that encodes the core protein is highly conserved, because it contains an RNA structure involved in an internal ribosome entry site An internal ribosome entry site, abbreviated IRES, is an RNA element that allows for translation initiation in a cap-independent manner, as part of the greater process of protein synthesis. In eukaryotic translation, initiation typically occurs at ...
.
Sequence complexity
On average, dsRNA viruses show a lower sequence redundancy relative to ssRNA viruses. Contrarily, dsDNA viruses contain the most redundant genome sequences while ssDNA viruses have the least. The sequence complexity of viruses has been shown to be a key characteristic for accurate reference-free viral classification.Replication
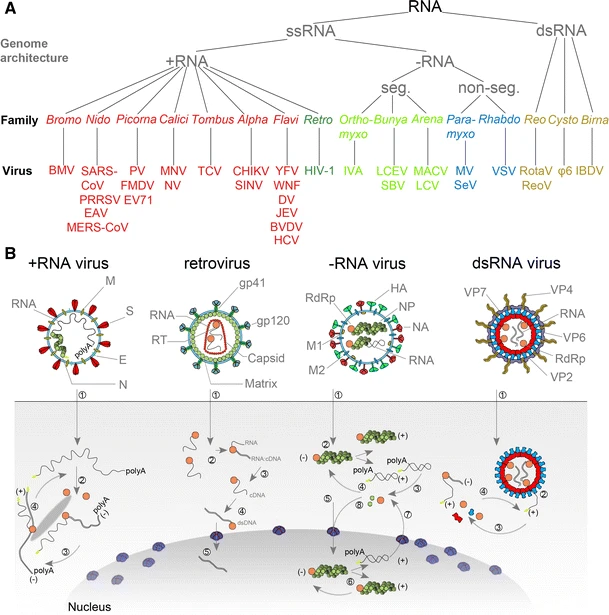
Animal RNA viruses are classified by the ICTV. There are three distinct groups of RNA viruses depending on their genome and mode of replication: * Double-stranded RNA viruses (Group III) contain from one to a dozen different RNA molecules, each coding for one or more viral proteins. * Positive-sense ssRNA viruses (Group IV) have their genome directly utilized as mRNA, with hostribosomes
Ribosomes ( ) are macromolecular machines, found within all cells, that perform biological protein synthesis (mRNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules to ...
translating
Translation is the communication of the meaning of a source-language text by means of an equivalent target-language text. The English language draws a terminological distinction (which does not exist in every language) between ''transl ...
it into a single protein that is modified by host and viral proteins to form the various proteins needed for replication. One of these includes RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RNA replicase), which copies the viral RNA to form a double-stranded replicative form. In turn, this dsRNA directs the formation of new viral RNA.
* Negative-sense ssRNA viruses (Group V) must have their genome copied by an RNA replicase to form positive-sense RNA. This means that the virus must bring along with it the enzyme RNA replicase. The positive-sense RNA molecule then acts as viral mRNA, which is translated into proteins by the host ribosomes.
Retroviruses (Group VI) have a single-stranded RNA genome but, in general, are not considered RNA viruses because they use DNA intermediates to replicate. Reverse transcriptase, a viral enzyme that comes from the virus itself after it is uncoated, converts the viral RNA into a complementary strand of DNA, which is copied to produce a double-stranded molecule of viral DNA. After this DNA is integrated into the host genome using the viral enzyme integrase
Retroviral integrase (IN) is an enzyme produced by a retrovirus (such as HIV) that integrates—forms covalent links between—its genetic information into that of the host cell it infects. Retroviral INs are not to be confused with phage int ...
, expression of the encoded genes may lead to the formation of new virions.
Recombination
Numerous RNA viruses are capable of genetic recombination when at least two viralgenome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ge ...
s are present in the same host cell. Very rarely viral RNA can recombine with host RNA. RNA recombination appears to be a major driving force in determining genome architecture and the course of viral evolution among ''Picornaviridae
Picornaviruses are a group of related nonenveloped RNA viruses which infect vertebrates including fish, mammals, and birds. They are viruses that represent a large family of small, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA viruses with a 30&nbs ...
'' ( (+)ssRNA), e.g. poliovirus
A poliovirus, the causative agent of polio (also known as poliomyelitis), is a serotype of the species '' Enterovirus C'', in the family of ''Picornaviridae''. There are three poliovirus serotypes: types 1, 2, and 3.
Poliovirus is composed of a ...
. In the ''Retroviridae
A retrovirus is a type of virus that inserts a DNA copy of its RNA genome into the DNA of a host cell that it invades, thus changing the genome of that cell. Once inside the host cell's cytoplasm, the virus uses its own reverse transcriptase ...
'' ((+)ssRNA), e.g. HIV
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of ''Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the immune ...
, damage in the RNA genome appears to be avoided during reverse transcription by strand switching, a form of recombination. Recombination also occurs in the ''Reoviridae
''Reoviridae'' is a family of double-stranded RNA viruses. Member viruses have a wide host range, including vertebrates, invertebrates, plants, protists and fungi. They lack lipid envelopes and package their segmented genome within multi-layere ...
'' (dsRNA), e.g. reovirus; '' Orthomyxoviridae'' ((-)ssRNA), e.g. influenza virus
''Orthomyxoviridae'' (from Greek ὀρθός, ''orthós'' 'straight' + μύξα, ''mýxa'' 'mucus') is a family of negative-sense RNA viruses. It includes seven genera: ''Alphainfluenzavirus'', ''Betainfluenzavirus'', '' Gammainfluenzavirus'', ' ...
; and ''Coronaviridae
''Coronaviridae'' is a family of enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses which infect amphibians, birds, and mammals. The group includes the subfamilies '' Letovirinae'' and ''Orthocoronavirinae;'' the members of the latter are known as coronavi ...
'' ((+)ssRNA), e.g. SARS
Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) is a viral respiratory disease of zoonotic origin caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV or SARS-CoV-1), the first identified strain of the SARS coronavirus species, ''seve ...
. Recombination in RNA viruses appears to be an adaptation for coping with genome damage. Recombination can occur infrequently between animal viruses of the same species but of divergent lineages. The resulting recombinant viruses may sometimes cause an outbreak of infection in humans.
Classification
Classification of the RNA viruses is difficult. This is in part due to the high mutation rates these genomes undergo. Classification is based principally on the type of genome (double-stranded, negative- or positive-single-strand) and gene number and organization. Currently, there are 5 orders and 47 families of RNA viruses recognized. There are also many unassigned species and genera. Related to but distinct from the RNA viruses are theviroid
Viroids are small single-stranded, circular RNAs that are infectious pathogens. Unlike viruses, they have no protein coating. All known viroids are inhabitants of angiosperms (flowering plants), and most cause diseases, whose respective economi ...
s and the RNA satellite viruses. These are not currently classified as RNA viruses and are described on their own pages.
A study of several thousand RNA viruses has shown the presence of at least five main taxa: a levivirus and relatives group; a picornavirus supergroup; an alphavirus supergroup plus a flavivirus supergroup; the dsRNA viruses; and the -ve strand viruses. The lentivirus group appears to be basal to all the remaining RNA viruses. The next major division lies between the picornasupragroup and the remaining viruses. The dsRNA viruses appear to have evolved from a +ve RNA ancestor and the -ve RNA viruses from within the dsRNA viruses. The closest relation to the -ve stranded RNA viruses is the Reoviridae
''Reoviridae'' is a family of double-stranded RNA viruses. Member viruses have a wide host range, including vertebrates, invertebrates, plants, protists and fungi. They lack lipid envelopes and package their segmented genome within multi-layere ...
.
Positive strand RNA viruses
This is the single largest group of RNA viruses with 30 families. Attempts have been made to group these families in higher orders. These proposals were based on an analysis of the RNA polymerases and are still under consideration. To date, the suggestions proposed have not been broadly accepted because of doubts over the suitability of a single gene to determine the taxonomy of the clade. The proposed classification of positive-strand RNA viruses is based on the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Three groups have been recognised: # Bymoviruses, comoviruses, nepoviruses, nodaviruses, picornaviruses, potyviruses, sobemoviruses and a subset of luteoviruses (beet western yellows virus and potato leafroll virus)—the picorna like group (Picornavirata). # Carmoviruses, dianthoviruses, flaviviruses, pestiviruses, statoviruses, tombusviruses, single-stranded RNA bacteriophages, hepatitis C virus and a subset of luteoviruses (barley yellow dwarf virus)—the flavi like group (Flavivirata). # Alphaviruses, carlaviruses, furoviruses, hordeiviruses, potexviruses, rubiviruses, tobraviruses, tricornaviruses, tymoviruses, apple chlorotic leaf spot virus, beet yellows virus and hepatitis E virus—the alpha like group (Rubivirata). A division of the alpha-like (Sindbis-like) supergroup on the basis of a novel domain located near the N termini of the proteins involved in viral replication has been proposed. The two groups proposed are: the 'altovirus' group (alphaviruses, furoviruses, hepatitis E virus, hordeiviruses, tobamoviruses, tobraviruses, tricornaviruses and probably rubiviruses); and the 'typovirus' group (apple chlorotic leaf spot virus, carlaviruses, potexviruses and tymoviruses). The alpha like supergroup can be further divided into threeclades
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, ...
: the rubi-like, tobamo-like, and tymo-like viruses.
Additional work has identified five groups of positive-stranded RNA viruses containing four, three, three, three, and one order(s), respectively. These fourteen orders contain 31 virus families (including 17 families of plant viruses) and 48 genera (including 30 genera of plant viruses). This analysis suggests that alphaviruses and flaviviruses can be separated into two families—the Togaviridae and Flaviridae, respectively—but suggests that other taxonomic assignments, such as the pestiviruses, hepatitis C virus, rubiviruses, hepatitis E virus, and arteriviruses, may be incorrect. The coronaviruses and toroviruses appear to be distinct families in distinct orders and not distinct genera of the same family as currently classified. The luteoviruses appear to be two families rather than one, and apple chlorotic leaf spot virus appears not to be a closterovirus but a new genus of the Potexviridae.
Evolution
The evolution of the picornaviruses based on an analysis of their RNA polymerases andhelicase
Helicases are a class of enzymes thought to be vital to all organisms. Their main function is to unpack an organism's genetic material. Helicases are motor proteins that move directionally along a nucleic acid phosphodiester backbone, separatin ...
s appears to date to the divergence of eukaryotes. Their putative ancestors include the bacterial group II retroelement
Retrotransposons (also called Class I transposable elements or transposons via RNA intermediates) are a type of genetic component that copy and paste themselves into different genomic locations (transposon) by converting RNA back into DNA through ...
s, the family of HtrA protease
A protease (also called a peptidase, proteinase, or proteolytic enzyme) is an enzyme that catalyzes (increases reaction rate or "speeds up") proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the ...
s and DNA bacteriophage
A bacteriophage (), also known informally as a ''phage'' (), is a duplodnaviria virus that infects and replicates within bacteria and archaea. The term was derived from "bacteria" and the Greek φαγεῖν ('), meaning "to devour". Bacteri ...
s.
Partitiviruses are related to and may have evolved from a totivirus ancestor.
Hypoviruses and barnaviruses appear to share an ancestry with the potyvirus and sobemovirus lineages respectively.
Double-stranded RNA viruses
This analysis also suggests that the dsRNA viruses are not closely related to each other but instead belong to four additional classes—Birnaviridae, Cystoviridae, Partitiviridae, and Reoviridae—and one additional order (Totiviridae) of one of the classes of positive ssRNA viruses in the same subphylum as the positive-strand RNA viruses. One study has suggested that there are two large clades: One includes the families ''Caliciviridae'', ''Flaviviridae'', and ''Picornaviridae'' and a second that includes the families ''Alphatetraviridae'', ''Birnaviridae'', ''Cystoviridae'', ''Nodaviridae'', and ''Permutotretraviridae''.Negative strand RNA viruses
These viruses have multiple types of genome ranging from a single RNA molecule up to eight segments. Despite their diversity it appears that they may have originated inarthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a Segmentation (biology), segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and Arth ...
s and to have diversified from there.
Satellite viruses
A number of satellite viruses—viruses that require the assistance of another virus to complete their life cycle—are also known. Their taxonomy has yet to be settled. The following four genera have been proposed for positive sense single stranded RNA satellite viruses that infect plants—Albetovirus
''Albetovirus'' is a plant satellite virus genus. As a member of realm '' Riboviria'' without assigned family or order it contains just three species, ''Tobacco albetovirus 1'', ''2'', and ''3'' (alias Satellite tobacco necrosis virus 1, 2, resp ...
, Aumaivirus
Maize white line mosaic satellite virus (syn. Satellite maize white line mosaic virus, Satellite virus of maize white line mosaic virus, SMWLMV, SV-MWLMV) is a plant satellite virus. It is the only species in genus ''Aumaivirus'', which is a memb ...
, Papanivirus
Panicum mosaic satellite virus (SPMV) is a plant satellite virus in genus ''Papanivirus'', which is a member of realm ''Riboviria'' without assigned family or order. It only infects grasses which are infected by ''Panicum mosaic virus''. One stu ...
and Virtovirus
''Tobacco virtovirus 1'', informally called Tobacco mosaic satellite virus, Satellite tobacco mosaic virus (STMV), or tobacco mosaic satellite virus, is a satellite virus first reported in ''Nicotiana glauca'' from southern California, U.S.. Its ...
. A family— Sarthroviridae which includes the genus Macronovirus—has been proposed for the positive sense single stranded RNA satellite viruses that infect arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a Segmentation (biology), segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and Arth ...
s.
Group III – dsRNA viruses
There are twelve families and a number of unassigned genera and species recognised in this group. * Family Amalgaviridae * FamilyBirnaviridae
''Birnaviridae'' is a family of double-stranded RNA viruses. Salmonid fish, birds and insects serve as natural hosts. There are currently 11 species in this family, divided among seven genera. Diseases associated with this family include infec ...
* Family Chrysoviridae
* Family Cystoviridae
''Cystovirus'' is a genus of double-stranded RNA viruses which infects bacteria. It is the only genus in the family ''Cystoviridae.'' The name of the group c''ysto'' derives from Greek ''kystis'' which means bladder or sack. There are seven spec ...
* Family Endornaviridae
''Endornaviridae'' is a family of viruses. Plants, fungi, and oomycetes serve as natural hosts. There are 31 species in this family, assigned to 2 genera (''Alphaendornavirus'' and ''Betaendornavirus''). Members of ''Alphaendornavirus'' infect p ...
* Family Hypoviridae
''Hypovirus'' is a genus of viruses, in the family ''Hypoviridae''. Fungi serve as natural hosts. There are four species in this genus. Infection reduces the virulence of its parasitic host, making it a hyperparasite useful for blight control.
...
* Family Megabirnaviridae
* Family Partitiviridae
''Partitiviridae'' is a family of double-stranded RNA viruses. Plants, fungi, and protozoa serve as natural hosts. It has been suggested that they can also infect bacteria. The name comes from the Latin ''partitius,'' which means divided, and ...
* Family Picobirnaviridae
* Family Reoviridae
''Reoviridae'' is a family of double-stranded RNA viruses. Member viruses have a wide host range, including vertebrates, invertebrates, plants, protists and fungi. They lack lipid envelopes and package their segmented genome within multi-layere ...
– includes Rotavirus
''Rotavirus'' is a genus of double-stranded RNA viruses in the family ''Reoviridae''. Rotaviruses are the most common cause of diarrhoeal disease among infants and young children. Nearly every child in the world is infected with a rotavirus a ...
* Family Totiviridae
''Totiviridae'' is a family of double-stranded RNA viruses. Giardia lamblia, leishmania, trichomonas vaginalis, and fungi serve as natural hosts. The name of the group derives from Latin ''toti'' which means undivided or whole. There are 28 spec ...
* Family Quadriviridae
* Genus Botybirnavirus
* Unassigned species
** '' Botrytis porri RNA virus 1''
** '' Circulifer tenellus virus 1''
** '' Colletotrichum camelliae filamentous virus 1''
** '' Cucurbit yellows associated virus''
** '' Sclerotinia sclerotiorum debilitation-associated virus''
** '' Spissistilus festinus virus 1''
Group IV – positive-sense ssRNA viruses
There are three orders and 34 families recognised in this group. In addition, there are a number of unclassified species and genera. * Order Nidovirales ** FamilyArteriviridae
''Arteriviridae'' is a family of enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses in the order ''Nidovirales'' which infect vertebrates. Host organisms include equids, pigs, Possums, nonhuman primates, and rodents. The family includes, for example, equ ...
** Family Coronaviridae
''Coronaviridae'' is a family of enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses which infect amphibians, birds, and mammals. The group includes the subfamilies '' Letovirinae'' and ''Orthocoronavirinae;'' the members of the latter are known as coronavi ...
– includes Human coronavirus (common cold viruses HCoV-229E, HCoV-HKU1, HCoV-NL63, and HCoV-OC43), MERS-CoV
''Middle East respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus'' (''MERS-CoV''), or EMC/2012 ( HCoV-EMC/2012), is the virus that causes Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS). It is a species of coronavirus which infects humans, bats, and camels. Th ...
, SARS-CoV-1
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 1 (SARS-CoV-1; or Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, SARS-CoV) is a strain of coronavirus that causes severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), the respiratory illness responsible for ...
and SARS-CoV-2
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) is a strain of coronavirus that causes COVID-19 (coronavirus disease 2019), the respiratory illness responsible for the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. The virus previously had a ...
** Family Mesoniviridae
''Mesoniviridae'' is a family of enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses in the order ''Nidovirales'' which infect mosquitoes. The family is named after the size of the genomes relative to other nidoviruses, with ''meso-'' coming from the Greek w ...
** Family Roniviridae
''Okavirus'' is a genus of enveloped positive-strand RNA viruses which infect crustaceans. Host organisms are mostly shrimp. It is the only genus in the family ''Roniviridae''. Viruses associated with the genus include: gill-associated virus (G ...
* Order Picornavirales
''Picornavirales'' is an order of viruses with vertebrate, invertebrate, protist and plant hosts. The name has a dual etymology. First, ''picorna-'' is an acronym for poliovirus, insensitivity to ether, coxsackievirus, orphan virus, rhinovirus, ...
** Family Dicistroviridae
''Dicistroviridae'' is a family of viruses in the order ''Picornavirales''. Invertebrates, including aphids, leafhoppers, flies, bees, ants, and silkworms, serve as natural hosts. There are 15 species in this family, assigned to three genera. Di ...
** Family Iflaviridae
''Iflaviridae'' is a family of positive sense RNA viruses insect-infecting viruses. Some of the insects commonly infected by iflaviruses include aphids, leafhoppers, flies, bees, ants, silkworms and wasps. The name "Ifla" is derived from the n ...
** Family Marnaviridae
** Family Picornaviridae
Picornaviruses are a group of related nonenveloped RNA viruses which infect vertebrates including fish, mammals, and birds. They are viruses that represent a large family of small, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA viruses with a 30&nbs ...
– includes Poliovirus
A poliovirus, the causative agent of polio (also known as poliomyelitis), is a serotype of the species '' Enterovirus C'', in the family of ''Picornaviridae''. There are three poliovirus serotypes: types 1, 2, and 3.
Poliovirus is composed of a ...
, Rhinovirus
The rhinovirus (from the grc, ῥίς, rhis "nose", , romanized: "of the nose", and the la, vīrus) is the most common viral infectious agent in humans and is the predominant cause of the common cold. Rhinovirus infection proliferates in tem ...
(a common cold virus), Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is an infectious disease of the liver caused by ''Hepatovirus A'' (HAV); it is a type of viral hepatitis. Many cases have few or no symptoms, especially in the young. The time between infection and symptoms, in those who develop them ...
virus
** Family Secoviridae
''Secoviridae'' is a family of viruses in the order ''Picornavirales''. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 8 genera and 86 species in this family, one of which is unassigned to a genus. The family was created in 2009 with the grouping of f ...
includes subfamily Comovirinae
''Comovirinae'' is a subfamily of viruses in the order ''Picornavirales'', in the family ''Secoviridae''; its genera were formerly classified in the family ''Comoviridae''. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 62 species in this subfamily, a ...
** Genus Bacillariornavirus
** Species Kelp fly virus
* Order Tymovirales
''Tymovirales'' is an order of viruses with five families. The group consists of viruses which have positive-sense, single-stranded RNA genomes. Their genetic material is protected by a special coat protein.
Description
Tymoviruses are mainly ...
** Family Alphaflexiviridae
''Alphaflexiviridae'' is a family of viruses in the order ''Tymovirales''. Plants and fungi serve as natural hosts. There are 65 species in this family, assigned to six genera. Diseases associated with this family include: mosaic and ringspot sy ...
** Family Betaflexiviridae
''Betaflexiviridae'' is a family of viruses in the order ''Tymovirales''. Plants and fungi serve as natural hosts. There are 108 species in this family, assigned to 13 genera in two subfamilies. Diseases associated with this family include mosa ...
** Family Gammaflexiviridae
** Family Tymoviridae
* Unassigned
** Family Alphatetraviridae
''Alphatetraviridae'' is a family of viruses. Moths and butterflies serve as natural hosts. There are two genera in the family. Infection outcome varies from unapparent to lethal.
Taxonomy
The following genera are assigned to the family:
*''Be ...
** Family Alvernaviridae
** Family Astroviridae
''Astroviridae'' is a family of non-enveloped ssRNA viruses that cause infections in different animals. The family name is derived from the Greek word ''astron'' ("star") referring to the star-like appearance of spikes projecting from the surface ...
** Family Barnaviridae
** Family Benyviridae
''Benyvirus'' is a genus of viruses, in the family ''Benyviridae''. Plant serve as natural hosts. There are four species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: BNYVV: rhizomania.
Taxonomy
* '' Beet necrotic yellow vein vir ...
** Family Botourmiaviridae
** Family Bromoviridae
''Bromoviridae'' is a family of viruses. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are six genera in the family.
Taxonomy
The following genera are assigned to the family:
* ''Alfamovirus''
* ''Anulavirus''
* ''Bromovirus''
* ''Cucumovirus''
* ''Ilar ...
** Family Caliciviridae
The ''Caliciviridae'' are a family of "small round structured" viruses, members of Class IV of the Baltimore scheme. Caliciviridae bear resemblance to enlarged picornavirus and was formerly a separate genus within the picornaviridae. They are p ...
– includes Norwalk virus
Norovirus, sometimes referred to as the winter vomiting disease, is the most common cause of gastroenteritis. Infection is characterized by non-bloody diarrhea, vomiting, and stomach pain. Fever or headaches may also occur. Symptoms usually devel ...
** Family Carmotetraviridae
** Family Closteroviridae
** Family Flaviviridae
''Flaviviridae'' is a family of enveloped positive-strand RNA viruses which mainly infect mammals and birds. They are primarily spread through arthropod vectors (mainly ticks and mosquitoes). The family gets its name from the yellow fever viru ...
– includes Yellow fever
Yellow fever is a viral disease of typically short duration. In most cases, symptoms include fever, chills, loss of appetite, nausea, muscle pains – particularly in the back – and headaches. Symptoms typically improve within five days. ...
virus, West Nile virus
West Nile virus (WNV) is a single-stranded RNA virus that causes West Nile fever. It is a member of the family '' Flaviviridae'', from the genus '' Flavivirus'', which also contains the Zika virus, dengue virus, and yellow fever virus. The v ...
, Hepatitis C virus
The hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a small (55–65 nm in size), enveloped, positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus of the family ''Flaviviridae''. The hepatitis C virus is the cause of hepatitis C and some cancers such as liver cancer ( hepato ...
, Dengue fever virus, Zika virus
''Zika virus'' (ZIKV; pronounced or ) is a member of the virus family ''Flaviviridae''. It is spread by daytime-active '' Aedes'' mosquitoes, such as '' A. aegypti'' and '' A. albopictus''. Its name comes from the Ziika Forest of Uganda, w ...
** Family Fusariviridae
** Family Hepeviridae
''Hepeviridae'' is a family of viruses. Human, pig, wild boar, sheep, cow, camel, monkey, some rodents, bats and chickens serve as natural hosts. There are two genera in the family. Diseases associated with this family include: hepatitis; high ...
** Family Hypoviridae
''Hypovirus'' is a genus of viruses, in the family ''Hypoviridae''. Fungi serve as natural hosts. There are four species in this genus. Infection reduces the virulence of its parasitic host, making it a hyperparasite useful for blight control.
...
** Family Leviviridae
** Family Luteoviridae – includes Barley yellow dwarf virus
Barley yellow dwarf (BYD) is a plant disease caused by the ''barley yellow dwarf virus'' (BYDV), and is the most widely distributed viral disease of cereals. It affects the economically important crop species barley, oats, wheat, maize, tritical ...
** Family Polycipiviridae
** Family Narnaviridae
** Family Nodaviridae
** Family Permutotetraviridae
''Permutotetraviridae'' is a family of viruses
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, inclu ...
** Family Potyviridae
''Potyviridae'' is a family of positive-strand RNA viruses that encompasses more than 30% of known plant viruses, many of which are of great agricultural significance. The family has 12 genera and 235 species, three of which are unassigned to ...
** Family Sarthroviridae
** Family Statovirus
** Family Togaviridae This category is for articles about virus families (or redirects to such articles). There should be no subcategories.
families
Families (biology) ...
– includes Rubella virus, Ross River virus, Sindbis virus
''Sindbis virus'' (SINV) is a member of the ''Togaviridae'' family, in the ''Alphavirus'' genus. The virus was first isolated in 1952 in Cairo, Egypt. The virus is transmitted by mosquitoes (''Culex'' and Culiseta). SINV is linked to Pogosta di ...
, Chikungunya virus
Chikungunya is an infection caused by the ''Chikungunya virus'' (CHIKV). Symptoms include fever and joint pains. These typically occur two to twelve days after exposure. Other symptoms may include headache, muscle pain, joint swelling, and a ra ...
** Family Tombusviridae
''Tombusviridae'' is a family of single-stranded positive sense RNA plant viruses. There are three subfamilies, 17 genera, and 95 species in this family. The name is derived from '' Tomato bushy stunt virus'' (TBSV).
Genome
All viruses in the ...
** Family Virgaviridae
** Unassigned genera
*** Genus '' Blunervirus''
*** Genus '' Cilevirus''
*** Genus '' Higrevirus''
*** Genus '' Idaeovirus''
*** Genus '' Negevirus''
*** Genus '' Ourmiavirus''
*** Genus '' Polemovirus''
*** Genus '' Sinaivirus''
*** Genus '' Sobemovirus''
** Unassigned species
*** Acyrthosiphon pisum virus
*** Bastrovirus
*** Blackford virus
*** Blueberry necrotic ring blotch virus
Blueberries are a widely distributed and widespread group of perennial flowering plants with blue or purple berries. They are classified in the section ''Cyanococcus'' within the genus ''Vaccinium''. ''Vaccinium'' also includes cranberries, bi ...
*** Cadicistrovirus
*** Chara australis virus
Chara may refer to:
Places
*Chara (rural locality), a rural locality (a ''selo'') in Zabaykalsky Krai, Russia
*Chara Airport, an airport in Russia near the rural locality
*Chara (river), a river in Russia
* Chara Sands, a sanded area in Siberia, ...
*** Extra small virus
*** Goji berry chlorosis virus
*** Harmonia axyridis virus 1
*** Hepelivirus
*** Jingmen tick virus
*** Le Blanc virus
*** Nedicistrovirus
*** Nesidiocoris tenuis virus 1
*** Niflavirus
*** Nylanderia fulva virus 1
*** Orsay virus
*** Osedax japonicus RNA virus 1
*** Picalivirus
*** Planarian secretory cell nidovirus
*** Plasmopara halstedii virus
*** Rosellinia necatrix fusarivirus 1
*** Santeuil virus
*** Secalivirus
*** Solenopsis invicta virus 3
*** Wuhan large pig roundworm virus
Satellite viruses
* Family Sarthroviridae
* Genus Albetovirus
''Albetovirus'' is a plant satellite virus genus. As a member of realm '' Riboviria'' without assigned family or order it contains just three species, ''Tobacco albetovirus 1'', ''2'', and ''3'' (alias Satellite tobacco necrosis virus 1, 2, resp ...
* Genus Aumaivirus
Maize white line mosaic satellite virus (syn. Satellite maize white line mosaic virus, Satellite virus of maize white line mosaic virus, SMWLMV, SV-MWLMV) is a plant satellite virus. It is the only species in genus ''Aumaivirus'', which is a memb ...
* Genus Papanivirus
Panicum mosaic satellite virus (SPMV) is a plant satellite virus in genus ''Papanivirus'', which is a member of realm ''Riboviria'' without assigned family or order. It only infects grasses which are infected by ''Panicum mosaic virus''. One stu ...
* Genus Virtovirus
''Tobacco virtovirus 1'', informally called Tobacco mosaic satellite virus, Satellite tobacco mosaic virus (STMV), or tobacco mosaic satellite virus, is a satellite virus first reported in ''Nicotiana glauca'' from southern California, U.S.. Its ...
* Chronic bee paralysis virus
Chronic bee paralysis virus (CBPV) commonly affects adult ''Apis mellifera'' honey bees and causes a chronic paralysis that can easily spread to other members of a colony. Bees infected with CBPV begin to show symptoms after 5 days and die a few ...
An unclassified astrovirus/hepevirus-like virus has also been described.Pankovics P, Boros Á, Kiss T, Engelmann P, Reuter G (2019) Genetically highly divergent RNA virus with astrovirus-like (5'-end) and hepevirus-like (3'-end) genome organization in carnivorous birds, European roller (''Coracias garrulus''). Infect Genet Evol
Group V – negative-sense ssRNA viruses
With the exception of theHepatitis D virus
Hepatitis D is a type of viral hepatitis caused by the hepatitis delta virus (HDV). HDV is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E. HDV is considered to be a satellite (a type of subviral agent) because it can propagate only in ...
, this group of viruses has been placed into a single phylum—Negarnaviricota
Negative-strand RNA viruses (−ssRNA viruses) are a group of related viruses that have negative-sense, single-stranded genomes made of ribonucleic acid. They have genomes that act as complementary strands from which messenger RNA (mRNA) is synt ...
. This phylum has been divided into two subphyla—Haploviricotina
''Haploviricotina'' is a subphylum of viruses in the phylum ''Negarnaviricota''. It is one of only two virus subphyla, the other being ''Polyploviricotina'', which is also in ''Negarnaviricota''. The name comes from , the Ancient Greek for 'si ...
and Polyploviricotina
''Polyploviricotina'' is a subphylum of viruses in the phylum ''Negarnaviricota''. It is one of only two virus subphyla, the other being '' Haploviricotina'', which is also in ''Negarnaviricota''. The name comes from , the Ancient Greek
...
. Within the subphylum Haploviricotina four classes are currently recognised: Chunqiuviricetes
''Yingvirus'' is a genus of negative-strand RNA viruses which infect invertebrates. Member viruses have bisegmented genomes. It is the only genus in the family ''Qinviridae'', which is the only family in ''Muvirales'', which is the only order in ...
, Milneviricetes
''Aspiviridae'', formerly ''Ophioviridae'', is a family of segmented negative-strand RNA viruses which infect plants. Member viruses are characterized by an elongated and highly filamentous and flexible nucleocapsid with helical symmetry. It ...
, Monjiviricetes and Yunchangviricetes. In the subphylum Polyploviricotina two classes are recognised: Ellioviricetes
''Bunyavirales'' is an order of segmented negative-strand RNA viruses with mainly tripartite genomes. Member viruses infect arthropods, plants, protozoans, and vertebrates. It is the only order in the class ''Ellioviricetes''. The name ''Bunyavi ...
and Insthoviricetes.
Six classes, seven orders and twenty four families are currently recognized in this group. A number of unassigned species and genera are yet to be classified.
* Phylum ''Negarnaviricota
Negative-strand RNA viruses (−ssRNA viruses) are a group of related viruses that have negative-sense, single-stranded genomes made of ribonucleic acid. They have genomes that act as complementary strands from which messenger RNA (mRNA) is synt ...
''
** Subphylum ''Haploviricotina
''Haploviricotina'' is a subphylum of viruses in the phylum ''Negarnaviricota''. It is one of only two virus subphyla, the other being ''Polyploviricotina'', which is also in ''Negarnaviricota''. The name comes from , the Ancient Greek for 'si ...
''
*** Class ''Chunqiuviricetes
''Yingvirus'' is a genus of negative-strand RNA viruses which infect invertebrates. Member viruses have bisegmented genomes. It is the only genus in the family ''Qinviridae'', which is the only family in ''Muvirales'', which is the only order in ...
''
**** Order ''Muvirales
''Yingvirus'' is a genus of negative-strand RNA viruses which infect invertebrates. Member viruses have bisegmented genomes. It is the only genus in the family ''Qinviridae'', which is the only family in ''Muvirales'', which is the only order in ...
''
***** Family '' Qinviridae''
*** Class ''Milneviricetes
''Aspiviridae'', formerly ''Ophioviridae'', is a family of segmented negative-strand RNA viruses which infect plants. Member viruses are characterized by an elongated and highly filamentous and flexible nucleocapsid with helical symmetry. It ...
''
**** Order ''Serpentovirales
''Aspiviridae'', formerly ''Ophioviridae'', is a family of segmented negative-strand RNA viruses which infect plants. Member viruses are characterized by an elongated and highly filamentous and flexible nucleocapsid with helical symmetry. It ...
''
***** Family '' Aspiviridae''
*** Class '' Monjiviricetes''
**** Order '' Jingchuvirales''
***** Family '' Chuviridae''
**** Order ''Mononegavirales
''Mononegavirales'' is an order of negative-strand RNA viruses which have nonsegmented genomes. Some common members of the order are Ebola virus, human respiratory syncytial virus, measles virus, mumps virus, Nipah virus, and rabies virus. A ...
''
***** Family ''Bornaviridae
''Bornaviridae'' is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order ''Mononegavirales''. Horses, sheep, cattle, rodents, birds, reptiles, and humans serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with bornaviruses include Borna disease, a fata ...
'' – Borna disease virus
***** Family ''Filoviridae
''Filoviridae'' () is a family of single-stranded negative-sense RNA viruses in the order ''Mononegavirales''. Two members of the family that are commonly known are Ebola virus and Marburg virus. Both viruses, and some of their lesser known re ...
'' – includes Ebola virus, Marburg virus
Marburg virus (MARV) is a hemorrhagic fever virus of the ''Filoviridae'' family of viruses and a member of the species '' Marburg marburgvirus'', genus ''Marburgvirus''. It causes Marburg virus disease in primates, a form of viral hemorrhagic f ...
***** Family ''Mymonaviridae
''Mymonaviridae'' is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order ''Mononegavirales'', which infect fungi. Fungi serve as natural hosts. The name is a portmanteau of Ancient Greek ''my''co, which means fungus, and ''mo''noneg''a''virale ...
''
***** Family ''Nyamiviridae
''Nyamiviridae'' is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order ''Mononegavirales''. Ecdysozoa and birds serve as natural hosts. The name is a portmanteau of ''Nya''manini Pan (place of isolation of type species Nyamanini virus in So ...
''
***** Family ''Paramyxoviridae
''Paramyxoviridae'' (from Greek ''para-'' “by the side of” and ''myxa'' “mucus”) is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order '' Mononegavirales''. Vertebrates serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with this family inclu ...
'' – includes Measles virus, Mumps virus
The mumps virus (MuV) is the virus that causes mumps. MuV contains a single-stranded, negative-sense genome made of ribonucleic acid (RNA). Its genome is about 15,000 nucleotides in length and contains seven genes that encode nine proteins. The g ...
, Nipah virus, Hendra virus, and Newcastle disease, NDV
***** Family ''Pneumoviridae'' – includes Human respiratory syncytial virus, RSV and Metapneumovirus
***** Family ''Rhabdoviridae'' – includes Rabies virus
***** Family ''Sunviridae''
***** Genus Anphevirus
***** Genus Arlivirus
***** Genus Chengtivirus
***** Genus Crustavirus
***** Genus Wastrivirus
*** Class '' Yunchangviricetes''
**** Order ''Goujianvirales''
***** Family ''Yueviridae''
** Subphylum ''Polyploviricotina
''Polyploviricotina'' is a subphylum of viruses in the phylum ''Negarnaviricota''. It is one of only two virus subphyla, the other being '' Haploviricotina'', which is also in ''Negarnaviricota''. The name comes from , the Ancient Greek
...
''
*** Class ''Ellioviricetes
''Bunyavirales'' is an order of segmented negative-strand RNA viruses with mainly tripartite genomes. Member viruses infect arthropods, plants, protozoans, and vertebrates. It is the only order in the class ''Ellioviricetes''. The name ''Bunyavi ...
''
**** Order ''Bunyavirales''
***** Family ''Arenaviridae'' – includes Lassa virus
***** Family ''Cruliviridae''
***** Family ''Feraviridae''
***** Family ''Fimoviridae''
***** Family ''Hantaviridae''
***** Family ''Jonviridae''
***** Family ''Nairoviridae''
***** Family ''Peribunyaviridae''
***** Family ''Phasmaviridae''
***** Family ''Phenuiviridae''
***** Family ''Tospoviridae''
***** Genus ''Tilapineviridae''
*** Class '' Insthoviricetes''
**** Order ''Articulavirales''
***** Family ''Amnoonviridae'' – includes Taastrup virus
***** Family '' Orthomyxoviridae'' – includes Influenza viruses
* Unassigned genera:
** Genus ''Deltavirus
Hepatitis D is a type of viral hepatitis caused by the hepatitis delta virus (HDV). HDV is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E. HDV is considered to be a satellite (a type of subviral agent) because it can propagate only in ...
'' – includes Hepatitis D virus (not a true virus, but a subviral agent)
Gallery
Filoviridae
''Filoviridae'' () is a family of single-stranded negative-sense RNA viruses in the order ''Mononegavirales''. Two members of the family that are commonly known are Ebola virus and Marburg virus. Both viruses, and some of their lesser known re ...
'')
File:Ebola virions.png, Ebola virus (''Filoviridae
''Filoviridae'' () is a family of single-stranded negative-sense RNA viruses in the order ''Mononegavirales''. Two members of the family that are commonly known are Ebola virus and Marburg virus. Both viruses, and some of their lesser known re ...
'')
File:Influenza virus particle 8430 lores.jpg, Influenza ('' Orthomyxoviridae'')
File:Measles virus.JPG, Measles (''Paramyxoviridae
''Paramyxoviridae'' (from Greek ''para-'' “by the side of” and ''myxa'' “mucus”) is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order '' Mononegavirales''. Vertebrates serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with this family inclu ...
'')
File:Mumps virus, negative stained TEM 8758 lores.jpg, Mumps virus
The mumps virus (MuV) is the virus that causes mumps. MuV contains a single-stranded, negative-sense genome made of ribonucleic acid (RNA). Its genome is about 15,000 nucleotides in length and contains seven genes that encode nine proteins. The g ...
(''Paramyxoviridae
''Paramyxoviridae'' (from Greek ''para-'' “by the side of” and ''myxa'' “mucus”) is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order '' Mononegavirales''. Vertebrates serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with this family inclu ...
'')
File:Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) EM PHIL 2175 lores.jpg, Human respiratory syncytial virus (''Paramyxoviridae
''Paramyxoviridae'' (from Greek ''para-'' “by the side of” and ''myxa'' “mucus”) is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order '' Mononegavirales''. Vertebrates serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with this family inclu ...
'')
File:Parainfluenza virus TEM PHIL 271 lores.jpg, Parainfluenza (''Paramyxoviridae
''Paramyxoviridae'' (from Greek ''para-'' “by the side of” and ''myxa'' “mucus”) is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order '' Mononegavirales''. Vertebrates serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with this family inclu ...
'')
File:Rabies Virus EM PHIL 1876.JPG, Rabies (''Rhabdoviridae'')
File:Vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) EM 18 lores.jpg, Vesicular stomatitis virus (''Rhabdoviridae'')
See also
* Virus classification * List of viruses * Virus#Replication cycle, Viral replication * Sense (molecular biology), Positive/negative-sense * Animal virology, Animal viruses * Double-stranded RNA viruses * Retrovirus * DNA viruses * Norovirus cis-acting replication element * ViroidNotes
References
External links
*Animal viruses
{{Authority control RNA viruses, RNA