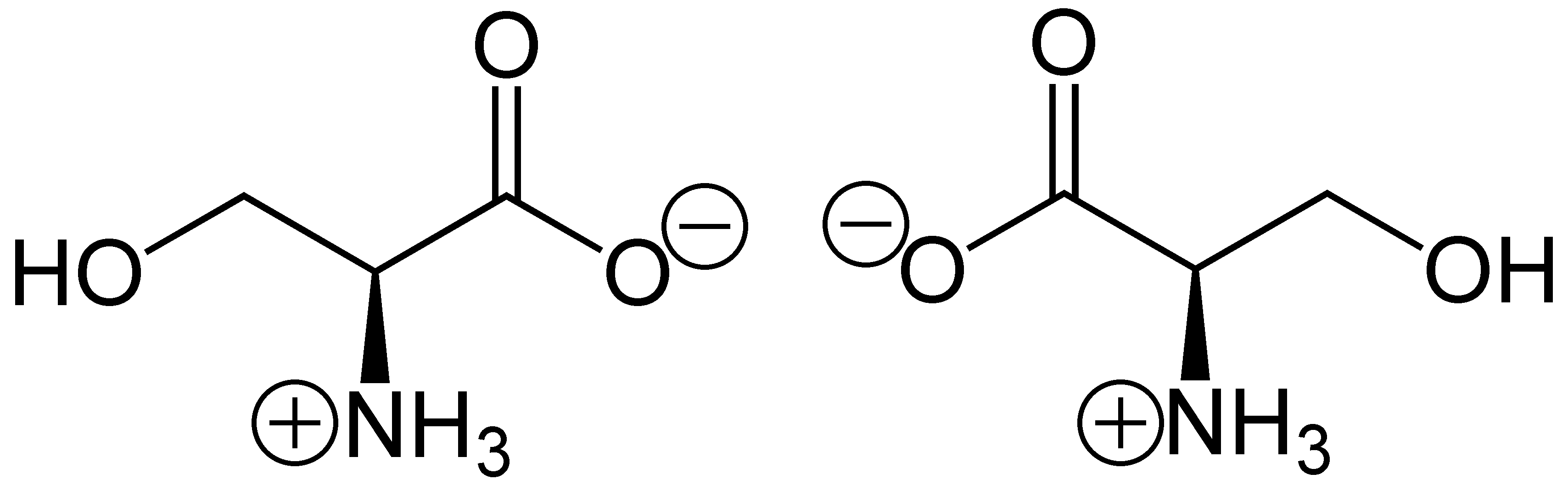|
Picornavirales
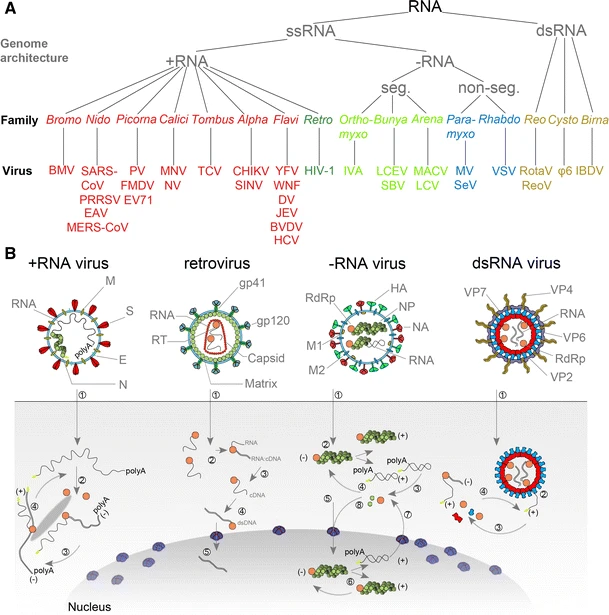
''Picornavirales'' is an order of viruses with vertebrate, invertebrate, protist and plant hosts. The name has a dual etymology. First, ''picorna-'' is an acronym for poliovirus, insensitivity to ether, coxsackievirus, orphan virus, rhinovirus, and ribonucleic acid. Secondly, pico-, meaning extremely small, combines with RNA to describe these very small RNA viruses. The order comprises viruses that historically are referred to as picorna-like viruses. Characteristics The families within this order share a number of common features: * The virions are non- enveloped, icosahedral, and about 30 nanometers in diameter. * The capsid has a "pseudo T=3" structure, and is composed of 60 protomers each made of three similar-sized but nonidentical beta barrels. * The genome is made of one or a few single-stranded RNA(s) serving directly as mRNA, without overlapping open reading frames. * The genome has a small protein, VPg, covalently attached to its 5' end, and usually a poly-adenylat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dicistroviridae
''Dicistroviridae'' is a family of viruses in the order ''Picornavirales''. Invertebrates, including aphids, leafhoppers, flies, bees, ants, and silkworms, serve as natural hosts. There are 15 species in this family, assigned to three genera. Diseases associated with this family include: DCV: increased reproductive potential. extremely pathogenic when injected with high associated mortality. CrPV: paralysis and death. Taxonomy Although many dicistroviruses were initially placed in the ''Picornaviridae'', they have since been reclassified into their own family. The name (Dicistro) is derived from the characteristic dicistronic arrangement of the genome. This family is a member of the Order ''Picornavirales'' (along with the families ''Iflaviridae'', ''Picornaviridae'', and ''Secoviridae'' and '' Marnaviridae''). Within this order, the gene order is the gene order of the nonstructural proteins Hel(helicase)-Pro(protease)-RdRp(polymerase). The ''Dicistroviridae'' can be disting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Picornavirus
Picornaviruses are a group of related nonenveloped RNA viruses which infect vertebrates including fish, mammals, and birds. They are viruses that represent a large family of small, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA viruses with a 30 nm icosahedral capsid. The viruses in this family can cause a range of diseases including the common cold, poliomyelitis, meningitis, hepatitis, and paralysis. Picornaviruses constitute the family ''Picornaviridae'', order ''Picornavirales'', and realm '' Riboviria''. There are 158 species in this family, assigned to 68 genera. Notable examples are genera ''Enterovirus'' (including ''Rhinovirus'' and ''Poliovirus''), '' Aphthovirus'', ''Cardiovirus'', and ''Hepatovirus''. Etymology The name "picornavirus" has a dual etymology. Firstly, the name derives from ''picorna''- which is an acronym for "''p''oliovirus, ''i''nsensitivity to ether, ''c''oxsackievirus, ''o''rphan virus, ''r''hinovirus, and ribo''n''ucleic ''a''cid". Secondly, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNA Virus
An RNA virus is a virusother than a retrovirusthat has ribonucleic acid (RNA) as its genetic material. The nucleic acid is usually single-stranded RNA ( ssRNA) but it may be double-stranded (dsRNA). Notable human diseases caused by RNA viruses include the common cold, influenza, SARS, MERS, Covid-19, Dengue Virus, hepatitis C, hepatitis E, West Nile fever, Ebola virus disease, rabies, polio, mumps, and measles. The International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) classifies RNA viruses as those that belong to ''Group III'', ''Group IV'' or ''Group V'' of the Baltimore classification system. This category excludes ''Group VI'', viruses with RNA genetic material but which use DNA intermediates in their life cycle: these are called retroviruses, including HIV-1 and HIV-2 which cause AIDS. As of May 2020, all known RNA viruses encoding an RNA-directed RNA polymerase are believed to form a monophyletic group, known as the realm '' Riboviria''. The majority of such RNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () ( chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with currently about 69,963 species described. Vertebrates comprise such groups as the following: * jawless fish, which include hagfish and lampreys * jawed vertebrates, which include: ** cartilaginous fish (sharks, rays, and ratfish) ** bony vertebrates, which include: *** ray-fins (the majority of living bony fish) *** lobe-fins, which include: **** coelacanths and lungfish **** tetrapods (limbed vertebrates) Extant vertebrates range in size from the frog species ''Paedophryne amauensis'', at as little as , to the blue whale, at up to . Vertebrates make up less than five percent of all described animal species; the rest are invertebrates, which lack vertebral columns. The vertebrates traditionally include the hagfish, which do no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5' End
Directionality, in molecular biology and biochemistry, is the end-to-end chemical orientation of a single strand of nucleic acid. In a single strand of DNA or RNA, the chemical convention of naming carbon atoms in the nucleotide pentose-sugar-ring means that there will be a 5′ end (usually pronounced "five-prime end"), which frequently contains a phosphate group attached to the 5′ carbon of the ribose ring, and a 3′ end (usually pronounced "three-prime end"), which typically is unmodified from the ribose -OH substituent. In a DNA double helix, the strands run in opposite directions to permit base pairing between them, which is essential for replication or transcription of the encoded information. Nucleic acids can only be synthesized in vivo in the 5′-to-3′ direction, as the polymerases that assemble various types of new strands generally rely on the energy produced by breaking nucleoside triphosphate bonds to attach new nucleoside monophosphates to the 3′- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caliciviridae
The ''Caliciviridae'' are a family of "small round structured" viruses, members of Class IV of the Baltimore scheme. Caliciviridae bear resemblance to enlarged picornavirus and was formerly a separate genus within the picornaviridae. They are positive-sense, single-stranded RNA which is not segmented. Thirteen species are placed in this family, divided among eleven genera. Diseases associated with this family include feline calicivirus (respiratory disease), rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus (often fatal hepatitis), and Norwalk group of viruses (gastroenteritis). Caliciviruses naturally infect vertebrates, and have been found in a number of organisms such as humans, cattle, pigs, cats, chickens, reptiles, dolphins and amphibians. The caliciviruses have a simple construction and are not enveloped. The capsid appears hexagonal/spherical and has icosahedral symmetry (T=1 or T=3) with a diameter of 35–39 nm. Caliciviruses are not very well studied because until recently, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryote
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacteria and Archaea (both prokaryotes) make up the other two domains. The eukaryotes are usually now regarded as having emerged in the Archaea or as a sister of the Asgard archaea. This implies that there are only two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but, due to their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass is estimated to be about equal to that of prokaryotes. Eukaryotes emerged approximately 2.3–1.8 billion years ago, during the Proterozoic eon, likely as flagellated phagotrophs. Their name comes from the Greek εὖ (''eu'', "well" or "good") and κάρυον (''karyon'', "nut" or "kernel"). Euka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymerase
A polymerase is an enzyme ( EC 2.7.7.6/7/19/48/49) that synthesizes long chains of polymers or nucleic acids. DNA polymerase and RNA polymerase are used to assemble DNA and RNA molecules, respectively, by copying a DNA template strand using base-pairing interactions or RNA by half ladder replication. A DNA polymerase from the thermophilic bacterium, ''Thermus aquaticus'' (''Taq'') ( PDBbr>1BGX EC 2.7.7.7) is used in the polymerase chain reaction, an important technique of molecular biology. A polymerase may be template dependent or template independent. Poly-A-polymerase is an example of template independent polymerase. Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase also known to have template independent and template dependent activities. Types By function *DNA polymerase (DNA-directed DNA polymerase, DdDP) **Family A: DNA polymerase I; Pol γ, θ, ν **Family B: DNA polymerase II; Pol α, δ, ε, ζ **Family C: DNA polymerase III holoenzyme **Family X: Pol β, λ, μ * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serine
Serine (symbol Ser or S) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated − form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated − form under biological conditions), and a side chain consisting of a hydroxymethyl group, classifying it as a polar amino acid. It can be synthesized in the human body under normal physiological circumstances, making it a nonessential amino acid. It is encoded by the codons UCU, UCC, UCA, UCG, AGU and AGC. Occurrence This compound is one of the naturally occurring proteinogenic amino acids. Only the L-stereoisomer appears naturally in proteins. It is not essential to the human diet, since it is synthesized in the body from other metabolites, including glycine. Serine was first obtained from silk protein, a particularly rich source, in 1865 by Emil Cramer. Its name is derived from the Latin for silk, ''sericum''. Serine's structure was estab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cysteine
Cysteine (symbol Cys or C; ) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine often participates in enzymatic reactions as a nucleophile. When present as a deprotonated catalytic residue, sometimes the symbol Cyz is used. The deprotonated form can generally be described by the symbol Cym as well. The thiol is susceptible to oxidation to give the disulfide derivative cystine, which serves an important structural role in many proteins. In this case, the symbol Cyx is sometimes used. When used as a food additive, it has the E number E920. Cysteine is encoded by the codons UGU and UGC. The sulfur-containing amino acids cysteine and methionine are more easily oxidized than the other amino acids. Structure Like other amino acids (not as a residue of a protein), cysteine exists as a zwitterion. Cysteine has chirality in the older / notation based on homology to - and -glyceraldehyde. In the newer ''R''/''S'' system of designating chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protease
A protease (also called a peptidase, proteinase, or proteolytic enzyme) is an enzyme that catalyzes (increases reaction rate or "speeds up") proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the formation of new protein products. They do this by cleaving the peptide bonds within proteins by hydrolysis, a reaction where water breaks bonds. Proteases are involved in many biological functions, including digestion of ingested proteins, protein catabolism (breakdown of old proteins), and cell signaling. In the absence of functional accelerants, proteolysis would be very slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteases can be found in all forms of life and viruses. They have independently evolved multiple times, and different classes of protease can perform the same reaction by completely different catalytic mechanisms. Hierarchy of proteases Based on catalytic residue Proteases can be classified into seven broad groups: * Serine protease ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |