British Rail on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
British Railways (BR), which from 1965 traded as British Rail, was a

 The rail transport system in Great Britain developed during the 19th century. After the grouping of 1923 under the
The rail transport system in Great Britain developed during the 19th century. After the grouping of 1923 under the
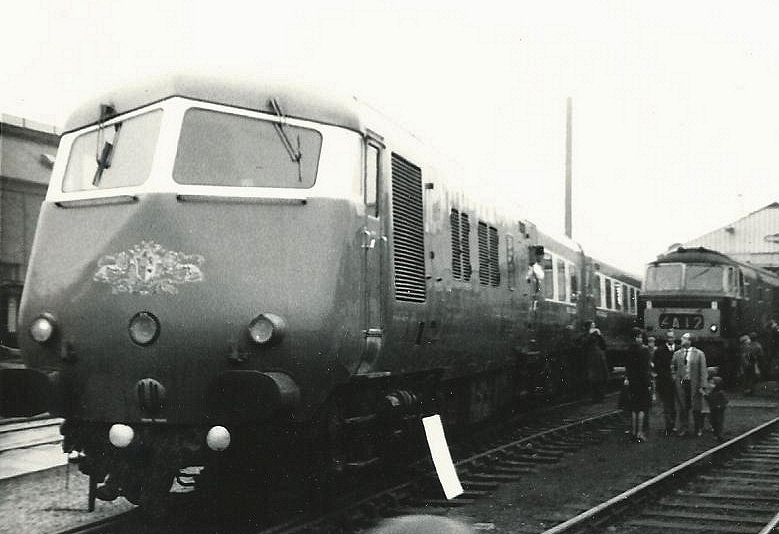 The report, latterly known as the "Modernisation Plan", was published in January 1955. It was intended to bring the railway system into the 20th century. A government White Paper produced in 1956 stated that modernisation would help eliminate BR's financial deficit by 1962, but the figures in both this and the original plan were produced for political reasons and not based on detailed analysis. The aim was to increase speed, reliability, safety, and line capacity through a series of measures that would make services more attractive to passengers and freight operators, thus recovering traffic lost to the roads. Important areas included:
* Electrification of principal main lines, in the
The report, latterly known as the "Modernisation Plan", was published in January 1955. It was intended to bring the railway system into the 20th century. A government White Paper produced in 1956 stated that modernisation would help eliminate BR's financial deficit by 1962, but the figures in both this and the original plan were produced for political reasons and not based on detailed analysis. The aim was to increase speed, reliability, safety, and line capacity through a series of measures that would make services more attractive to passengers and freight operators, thus recovering traffic lost to the roads. Important areas included:
* Electrification of principal main lines, in the
 During the late 1950s, railway finances continued to worsen; whilst passenger numbers grew after restoring many services reduced during the war, and in 1959 the government stepped in, limiting the amount the BTC could spend without ministerial authority. A White Paper proposing reorganisation was published in the following year, and a new structure was brought into effect by the Transport Act 1962. This abolished the commission and replaced it by several separate boards. These included a British Railways Board, which took over on 1 January 1963.
During the late 1950s, railway finances continued to worsen; whilst passenger numbers grew after restoring many services reduced during the war, and in 1959 the government stepped in, limiting the amount the BTC could spend without ministerial authority. A White Paper proposing reorganisation was published in the following year, and a new structure was brought into effect by the Transport Act 1962. This abolished the commission and replaced it by several separate boards. These included a British Railways Board, which took over on 1 January 1963.
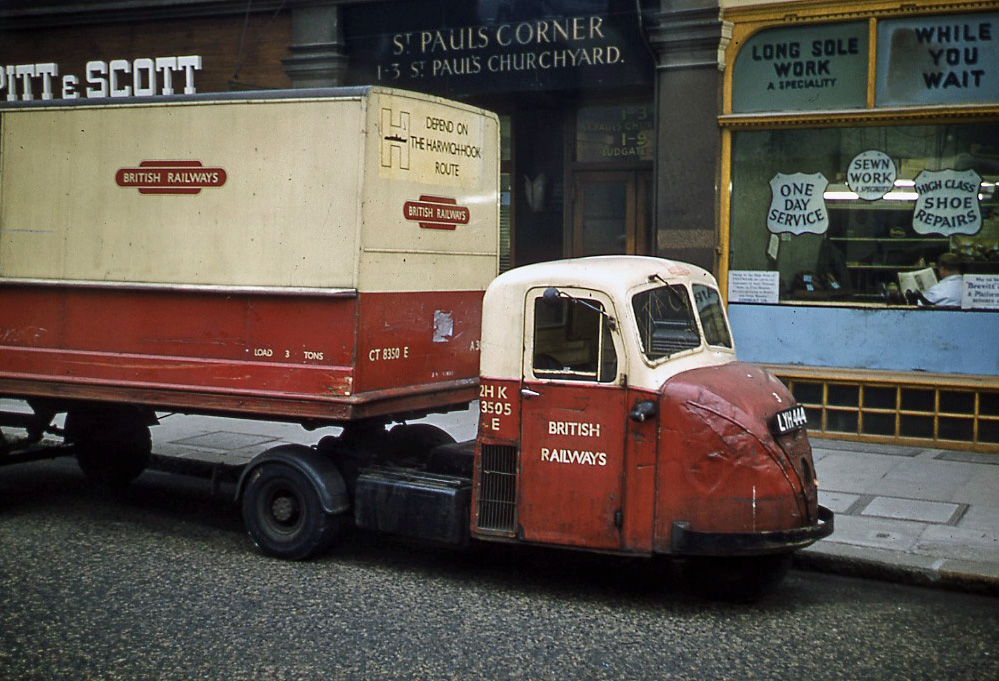 Following semi-secret discussions on railway finances by the government-appointed Stedeford Committee in 1961, one of its members, Dr Richard Beeching, was offered the post of chairing the BTC while it lasted and then became the first Chairman of the British Railways Board.
A major traffic census in April 1961, which lasted one week, was used in the compilation of a report on the future of the network. This report – ''The Reshaping of British Railways'' – was published by the BRB in March 1963. The proposals, which became known as the Beeching cuts, were dramatic. A third of all passenger services and more than 4,000 of the 7,000 stations would close. Beeching, who is thought to have been the author of most of the report, set out some dire figures. One third of the network was carrying just 1% of the traffic. Of the 18,000 passenger coaches, 6,000 were said to be used only 18 times a year or less. Although maintaining them cost between £3million and £4million a year, they earned only about £0.5million.
Most of the closures were carried out between 1963 and 1970 (including some which were not listed in the report), while other suggested closures were not carried out. The closures were heavily criticised at the time. A small number of stations and lines closed under the Beeching programme have been reopened, with further reopenings proposed.
A second Beeching report, "The Development of the Major Trunk Routes", followed in 1965. This did not recommend closures as such but outlined a "network for development"; the fate of the rest of the network was not discussed in the report.
Following semi-secret discussions on railway finances by the government-appointed Stedeford Committee in 1961, one of its members, Dr Richard Beeching, was offered the post of chairing the BTC while it lasted and then became the first Chairman of the British Railways Board.
A major traffic census in April 1961, which lasted one week, was used in the compilation of a report on the future of the network. This report – ''The Reshaping of British Railways'' – was published by the BRB in March 1963. The proposals, which became known as the Beeching cuts, were dramatic. A third of all passenger services and more than 4,000 of the 7,000 stations would close. Beeching, who is thought to have been the author of most of the report, set out some dire figures. One third of the network was carrying just 1% of the traffic. Of the 18,000 passenger coaches, 6,000 were said to be used only 18 times a year or less. Although maintaining them cost between £3million and £4million a year, they earned only about £0.5million.
Most of the closures were carried out between 1963 and 1970 (including some which were not listed in the report), while other suggested closures were not carried out. The closures were heavily criticised at the time. A small number of stations and lines closed under the Beeching programme have been reopened, with further reopenings proposed.
A second Beeching report, "The Development of the Major Trunk Routes", followed in 1965. This did not recommend closures as such but outlined a "network for development"; the fate of the rest of the network was not discussed in the report.
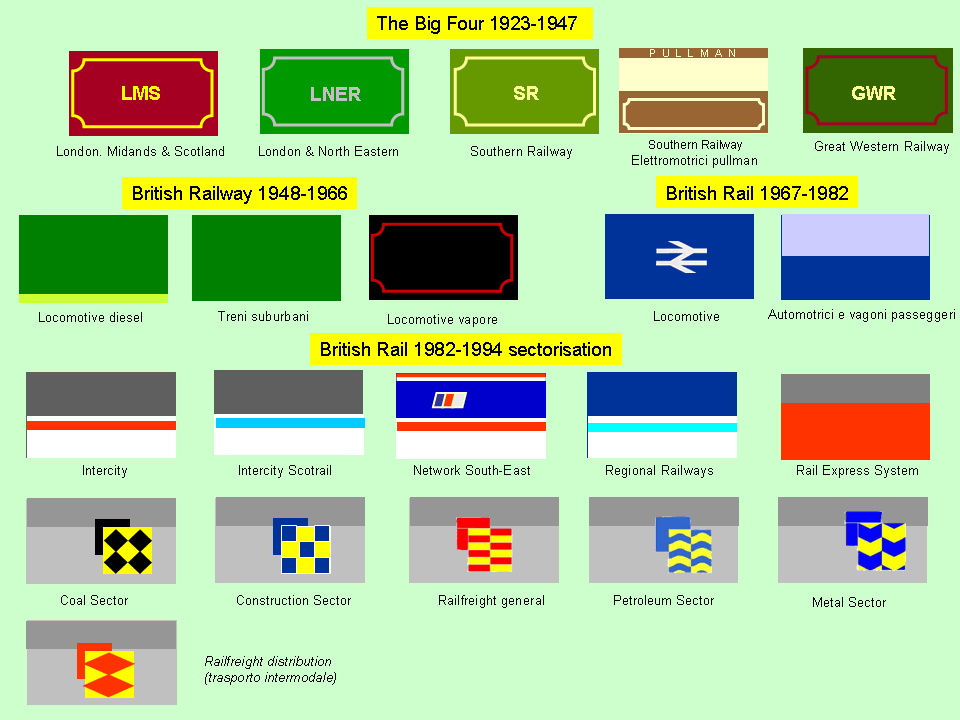
 Upon sectorisation in 1982, three passenger sectors were created: InterCity, operating principal express services; London & South East (renamed Network SouthEast in 1986) operating commuter services in the London area; Provincial (renamed Regional Railways in 1989) responsible for all other passenger services. In the
Upon sectorisation in 1982, three passenger sectors were created: InterCity, operating principal express services; London & South East (renamed Network SouthEast in 1986) operating commuter services in the London area; Provincial (renamed Regional Railways in 1989) responsible for all other passenger services. In the
File:Lion on Wheel emblem on the side of M79990.jpg, The first lion emblem
File:Train Stations and Trains National Rail Museum (5632693721).jpg, The later lion emblem on BR locomotives
File:British Railways London Midland Region station totem for Liverpool Central Low Level.jpg, Liverpool Central station sign using the 'hot dog' totem, properly called a lamp tablet
 The zeal for modernisation in the Beeching era drove the next rebranding exercise, and BR management wished to divest the organisation of anachronistic, heraldic motifs and develop a corporate identity to rival that of London Transport. BR's design panel set up a working party led by
The zeal for modernisation in the Beeching era drove the next rebranding exercise, and BR management wished to divest the organisation of anachronistic, heraldic motifs and develop a corporate identity to rival that of London Transport. BR's design panel set up a working party led by
 The uniformity of BR branding continued until the process of sectorisation was introduced in the 1980s. Certain BR operations such as
The uniformity of BR branding continued until the process of sectorisation was introduced in the 1980s. Certain BR operations such as

 In 1982, the regions were abolished as the service provider (but retained for administration) and replaced by "business sectors", a process known as sectorisation.
The passenger sectors were (by the early 1990s):
* InterCity (express services).
** InterCity Sleeper (Night train services)
** Gatwick Express (express service to/from Gatwick Airport)
* Network SouthEast (London commuter services).
* Regional Railways (regional services).
**
In 1982, the regions were abolished as the service provider (but retained for administration) and replaced by "business sectors", a process known as sectorisation.
The passenger sectors were (by the early 1990s):
* InterCity (express services).
** InterCity Sleeper (Night train services)
** Gatwick Express (express service to/from Gatwick Airport)
* Network SouthEast (London commuter services).
* Regional Railways (regional services).
**  This ended the BR blue period as new liveries were adopted gradually. Infrastructure remained the responsibility of the regions until the "Organisation for Quality" initiative in 1991 when this too was transferred to the sectors. The Anglia Region was created in late 1987, its first General Manager being John Edmonds, who began his appointment on 19 October 1987. Full separation from the Eastern Region – apart from engineering design needs – occurred on 29 April 1988. It handled the services from and , its western boundary being , and .
The former BR network, with the trunk routes of the West Coast Main Line,
This ended the BR blue period as new liveries were adopted gradually. Infrastructure remained the responsibility of the regions until the "Organisation for Quality" initiative in 1991 when this too was transferred to the sectors. The Anglia Region was created in late 1987, its first General Manager being John Edmonds, who began his appointment on 19 October 1987. Full separation from the Eastern Region – apart from engineering design needs – occurred on 29 April 1988. It handled the services from and , its western boundary being , and .
The former BR network, with the trunk routes of the West Coast Main Line,
 Before the introduction of APTIS (Accountancy and Passenger Ticket Issuing System), British Rail used the Edmondson railway ticket, first introduced in the 1840s and phased out in the early 1970s. Tickets issued from British Rail's APTIS system had a considerable amount of information presented in a consistent, standard format. The design for all tickets was created by Colin Goodall. This format has formed the basis for all subsequent ticket issuing systems introduced on the railway network – ticket-office-based, self-service and conductor-operated machines alike. APTIS survived in widespread use for twenty years but, in the early 2000s, was largely replaced by more modern PC-based ticketing systems. Some APTIS machines in the Greater London area were modified as APTIS-ANT (with no obvious difference to the ticket issued) to make them Oyster card compatible. The last APTIS machines were removed at the end of 2006 as there was no option to upgrade them to accept Chip and PIN credit card payments. The last APTIS-ANT ticket to be issued in the UK using one of the machines was at
Before the introduction of APTIS (Accountancy and Passenger Ticket Issuing System), British Rail used the Edmondson railway ticket, first introduced in the 1840s and phased out in the early 1970s. Tickets issued from British Rail's APTIS system had a considerable amount of information presented in a consistent, standard format. The design for all tickets was created by Colin Goodall. This format has formed the basis for all subsequent ticket issuing systems introduced on the railway network – ticket-office-based, self-service and conductor-operated machines alike. APTIS survived in widespread use for twenty years but, in the early 2000s, was largely replaced by more modern PC-based ticketing systems. Some APTIS machines in the Greater London area were modified as APTIS-ANT (with no obvious difference to the ticket issued) to make them Oyster card compatible. The last APTIS machines were removed at the end of 2006 as there was no option to upgrade them to accept Chip and PIN credit card payments. The last APTIS-ANT ticket to be issued in the UK using one of the machines was at
 When the railways came into public ownership in 1948, British Railways inherited a number of night train services from the Big Four. Sleeping car services were operated on the West and East coast routes and GWR mainlines to several destinations. Routes included to , to , to and the Night Ferry sleeper from to Brussels and Paris. On
When the railways came into public ownership in 1948, British Railways inherited a number of night train services from the Big Four. Sleeping car services were operated on the West and East coast routes and GWR mainlines to several destinations. Routes included to , to , to and the Night Ferry sleeper from to Brussels and Paris. On
 Sealink was originally the brand name for the ferry services of British Rail in the United Kingdom and Ireland. Services to France, Belgium, and the Netherlands were run by Sealink UK as part of the Sealink consortium, which also used ferries owned by French national railways (
Sealink was originally the brand name for the ferry services of British Rail in the United Kingdom and Ireland. Services to France, Belgium, and the Netherlands were run by Sealink UK as part of the Sealink consortium, which also used ferries owned by French national railways (
 Incorporated on 31 October 1969, British Rail Engineering Limited (BREL) was a wholly owned railway systems engineering subsidiary of the British Railways Board. Created through the Transport Act 1968, to manage BR's thirteen workshops, it replaced the British Rail Workshops Division, which had existed since 1948. The works managed by BREL were
Incorporated on 31 October 1969, British Rail Engineering Limited (BREL) was a wholly owned railway systems engineering subsidiary of the British Railways Board. Created through the Transport Act 1968, to manage BR's thirteen workshops, it replaced the British Rail Workshops Division, which had existed since 1948. The works managed by BREL were
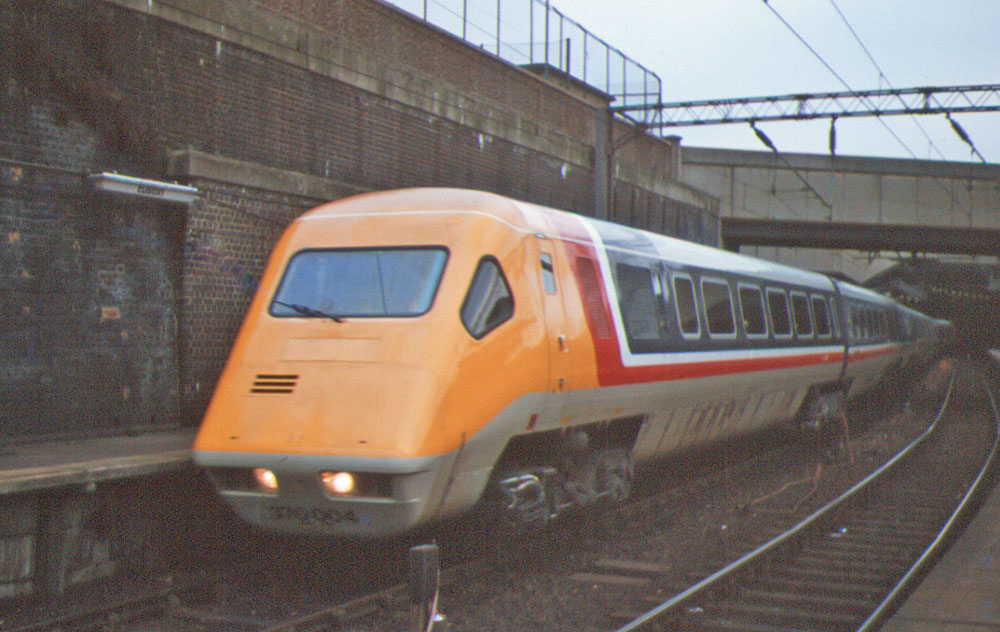 In the 1970s, British Rail developed tilting train technology in the
In the 1970s, British Rail developed tilting train technology in the

 The InterCity 125, or High-Speed Train, was a diesel-powered passenger train built by BREL between 1975 and 1982 that was credited with saving British Rail. Each set is made up of two Class 43 power cars, one at each end and four to nine
The InterCity 125, or High-Speed Train, was a diesel-powered passenger train built by BREL between 1975 and 1982 that was credited with saving British Rail. Each set is made up of two Class 43 power cars, one at each end and four to nine
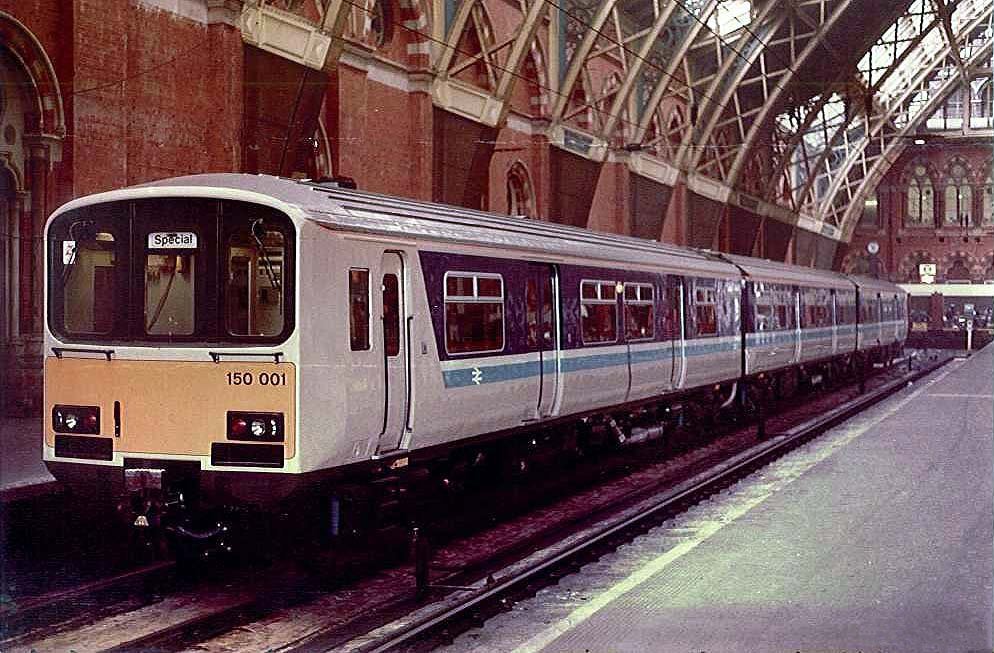 By the early 1980s British Rail operated a large fleet of first generation DMUs, which had been constructed in prior decades to various designs. While formulating its long-term strategy for this sector of its operations, British Rail planners recognised that there would be considerable costs incurred by undertaking refurbishment programmes necessary for the continued use of these ageing multiple units, particularly due to the necessity of handling and removing hazardous materials such as
By the early 1980s British Rail operated a large fleet of first generation DMUs, which had been constructed in prior decades to various designs. While formulating its long-term strategy for this sector of its operations, British Rail planners recognised that there would be considerable costs incurred by undertaking refurbishment programmes necessary for the continued use of these ageing multiple units, particularly due to the necessity of handling and removing hazardous materials such as

 In 1989, the narrow-gauge Vale of Rheidol Railway was preserved, becoming the first part of British Rail to be privatised. Between 1994 and 1997, in accordance with the Railways Act 1993, the core activities of British Rail were privatised. Ownership of the track and infrastructure passed to Railtrack on 1 April 1994. Passenger operations were later
In 1989, the narrow-gauge Vale of Rheidol Railway was preserved, becoming the first part of British Rail to be privatised. Between 1994 and 1997, in accordance with the Railways Act 1993, the core activities of British Rail were privatised. Ownership of the track and infrastructure passed to Railtrack on 1 April 1994. Passenger operations were later  The Waterloo & City line, part of Network SouthEast, was not included in the privatisation and was transferred to London Underground in April 1994. The remaining obligations of British Rail were transferred to BRB (Residuary) Limited.
The privatisation, proposed by the Conservative government in 1992, was opposed by the Labour Party and the rail unions. Although Labour initially proposed to reverse privatisation, the New Labour manifesto of 1997 instead opposed Conservative plans to privatise the London Underground. Rail unions have historically opposed privatisation, but former Associated Society of Locomotive Engineers and Firemen general secretary
The Waterloo & City line, part of Network SouthEast, was not included in the privatisation and was transferred to London Underground in April 1994. The remaining obligations of British Rail were transferred to BRB (Residuary) Limited.
The privatisation, proposed by the Conservative government in 1992, was opposed by the Labour Party and the rail unions. Although Labour initially proposed to reverse privatisation, the New Labour manifesto of 1997 instead opposed Conservative plans to privatise the London Underground. Rail unions have historically opposed privatisation, but former Associated Society of Locomotive Engineers and Firemen general secretary
 The renationalisation of the railways of Britain continues to have popular support. Polls in 2012 and 2013 showed 70% and 66% support for renationalisation, respectively.
Due to rail franchises sometimes lasting over a decade, full renationalisation would take years unless compensation was paid to terminate contracts early.
When the infrastructure-owning company Railtrack ceased trading in 2002, the Labour government set up the not-for-dividend company Network Rail to take over the duties rather than renationalise this part of the network. However, in September 2014, Network Rail was reclassified as a central government body, adding around £34 billion to public sector net debt. This reclassification had been requested by the Office for Budget Responsibility to comply with pan-European accounting standard ESA10.
The
The renationalisation of the railways of Britain continues to have popular support. Polls in 2012 and 2013 showed 70% and 66% support for renationalisation, respectively.
Due to rail franchises sometimes lasting over a decade, full renationalisation would take years unless compensation was paid to terminate contracts early.
When the infrastructure-owning company Railtrack ceased trading in 2002, the Labour government set up the not-for-dividend company Network Rail to take over the duties rather than renationalise this part of the network. However, in September 2014, Network Rail was reclassified as a central government body, adding around £34 billion to public sector net debt. This reclassification had been requested by the Office for Budget Responsibility to comply with pan-European accounting standard ESA10.
The
British Railways Board history
BRB (Residuary) Ltd.
Catalogue of the BR Technical Research Department archives
held at the
state-owned company
A state-owned enterprise (SOE) is a Government, government entity which is established or nationalised by the ''national government'' or ''provincial government'' by an executive order or an act of legislation in order to earn Profit (econom ...
that operated most rail transport in Great Britain from 1948 to 1997. Originally a trading brand of the Railway Executive of the British Transport Commission, it became an independent statutory corporation
A statutory corporation is a government entity created as a statutory body by statute. Their precise nature varies by jurisdiction, thus, they are statutes owned by a government or controlled by national or sub-national government to the (in ...
in January 1963, when it was formally renamed the British Railways Board.
British Railways was formed on 1 January 1948 as a result of the Transport Act 1947, which nationalised
Nationalization (nationalisation in British English) is the process of transforming privately-owned assets into public assets by bringing them under the public ownership of a national government or state. Nationalization usually refers to pri ...
the Big Four British railway companies along with some other (but not all) smaller railways. Profitability of the railways became a pressing concern during the 1950s, leading to multiple efforts to bolster performance, including some line closures. The 1955 Modernisation Plan
Events January
* January 3 – José Ramón Guizado becomes president of Panama.
* January 17 – , the first nuclear-powered submarine, puts to sea for the first time, from Groton, Connecticut.
* January 18– 20 – Battle of Yijian ...
formally directed a process of dieselisation and electrification to take place; accordingly, steam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, oil or, rarely, wood) to heat water in the locomot ...
s had been entirely replaced by diesel and electric traction (except for the narrow-gauge Vale of Rheidol Railway tourist line) by 1968. On 1 January 1963, the British Railways Board was created to manage the railways as a successor to the British Transport Commission.
It was during the 1960s that perhaps the most substantial changes were made. Seeking to reduce rail subsidies, one-third of the network and over half of all stations were permanently closed under the Beeching cuts. Trunk routes were considered to be the most important, and so electrification of the Great Eastern Main Line
The Great Eastern Main Line (GEML, sometimes referred to as the East Anglia Main Line) is a major railway line on the British railway system which connects Liverpool Street station in central London with destinations in east London and t ...
from London to Norwich was completed between 1976 and 1986 and on the East Coast Main Line
The East Coast Main Line (ECML) is a electrified railway between London and Edinburgh via Peterborough, Doncaster, York, Darlington, Durham and Newcastle. The line is a key transport artery on the eastern side of Great Britain running broa ...
from London to Edinburgh between 1985 and 1990. Train manufacturer British Rail Engineering Limited (BREL) produced the capable InterCity 125 and Sprinter sets, the introduction of which improved intercity and regional railways respectively, as well as the unsuccessful Advanced Passenger Train
The Advanced Passenger Train (APT) was a tilting high speed train developed by British Rail during the 1970s and early 1980s, for use on the West Coast Main Line (WCML). The WCML contained many curves, and the APT pioneered the concept of activ ...
(APT). Gradually, passengers replaced freight as the main source of business. From 1982, under sectorisation, the regions were gradually replaced by "business sectors", which were originally responsible for marketing and other commercial matters when they were first created but had taken over entirely by 1990.
During the 1980s and 1990s, the British Government directed the privatisation of British Rail. Following completion of the privatisation process in 1997, responsibility for track, signalling and stations was transferred to Railtrack (later brought under public control as Network Rail) while services were run by a variety of train operating companies
A train operating company (TOC) is a business operating passenger trains on the railway system of Great Britain under the collective National Rail brand. TOCs have existed since the privatisation of the network under the Railways Act 1993.
The ...
. At the end of the process, any remaining obligations of British Rail were transferred to BRB (Residuary) Limited. The British Rail Double Arrow
The British Rail Double Arrow is a logo that was created for British Rail (BR), the then state-owned operator of Britain's railway network, in 1965. It has remained in use as part of the National Rail brand used for Britain's passenger rail ser ...
logo remains in place and is now employed as a generic symbol on street signs in Great Britain denoting railway stations.
History

Nationalisation in 1948
 The rail transport system in Great Britain developed during the 19th century. After the grouping of 1923 under the
The rail transport system in Great Britain developed during the 19th century. After the grouping of 1923 under the Railways Act 1921
The Railways Act 1921 (c. 55), also known as the Grouping Act, was an Act of Parliament enacted by the British government and intended to stem the losses being made by many of the country's 120 railway companies, by "grouping" them into four la ...
, there were four large railway companies, each dominating its own geographic area: the Great Western Railway
The Great Western Railway (GWR) was a British railway company that linked London with the southwest, west and West Midlands of England and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, received its enabling Act of Parliament on 31 August 1835 and ran ...
(GWR), the London, Midland and Scottish Railway
The London, Midland and Scottish Railway (LMSIt has been argued that the initials LMSR should be used to be consistent with LNER, GWR and SR. The London, Midland and Scottish Railway's corporate image used LMS, and this is what is generally u ...
(LMS), the London and North Eastern Railway
The London and North Eastern Railway (LNER) was the second largest (after LMS) of the " Big Four" railway companies created by the Railways Act 1921 in Britain. It operated from 1 January 1923 until nationalisation on 1 January 1948. At th ...
(LNER) and the Southern Railway (SR). During World War I, the railways were under state control, which continued until 1921. Complete nationalisation
Nationalization (nationalisation in British English) is the process of transforming privately-owned assets into public assets by bringing them under the public ownership of a national government or state. Nationalization usually refers to pri ...
had been considered, and the Railways Act 1921
The Railways Act 1921 (c. 55), also known as the Grouping Act, was an Act of Parliament enacted by the British government and intended to stem the losses being made by many of the country's 120 railway companies, by "grouping" them into four la ...
is sometimes considered as a precursor to that, but the concept was rejected. Nationalisation was subsequently carried out after World War II, under the Transport Act 1947. This Act made provision for the nationalisation of the network as part of a policy of nationalising public services by Clement Attlee
Clement Richard Attlee, 1st Earl Attlee, (3 January 18838 October 1967) was a British politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1945 to 1951 and Leader of the Labour Party from 1935 to 1955. He was Deputy Prime Mini ...
's Labour
Labour or labor may refer to:
* Childbirth, the delivery of a baby
* Labour (human activity), or work
** Manual labour, physical work
** Wage labour, a socioeconomic relationship between a worker and an employer
** Organized labour and the labour ...
Government. British Railways came into existence as the business name of the Railway Executive of the British Transport Commission (BTC) on 1 January 1948 when it took over the assets of the Big Four.
There were also joint railways between the Big Four and a few light railways to consider (see list of constituents of British Railways). Excluded from nationalisation were industrial lines like the Oxfordshire Ironstone Railway
The Oxfordshire Ironstone Railway was a standard-gauge mineral railway that served an ironstone quarry near the village of Wroxton in Oxfordshire.
The line's history
The OIR linked the quarry with the Great Western Railway about to the east a ...
. The London Underground also became publicly owned, becoming the London Transport Executive of the British Transport Commission. The Bicester Military Railway was already run by the government. The electric Liverpool Overhead Railway was also excluded from nationalisation
Nationalization (nationalisation in British English) is the process of transforming privately-owned assets into public assets by bringing them under the public ownership of a national government or state. Nationalization usually refers to pri ...
.
The Railway Executive was conscious that some lines on the (then very dense) network were unprofitable and hard to justify socially, and a programme of closures began almost immediately after nationalisation. However, the general financial position of BR became gradually poorer until an operating loss was recorded in 1955. The Executive itself had been abolished in 1953 by the Conservative government, and control of BR transferred to the parent Commission. Other changes to the British Transport Commission at the same time included the return of road haulage to the private sector; however, BR retained its own (smaller) in-house road haulage service.
1955 Modernisation Plan
 The report, latterly known as the "Modernisation Plan", was published in January 1955. It was intended to bring the railway system into the 20th century. A government White Paper produced in 1956 stated that modernisation would help eliminate BR's financial deficit by 1962, but the figures in both this and the original plan were produced for political reasons and not based on detailed analysis. The aim was to increase speed, reliability, safety, and line capacity through a series of measures that would make services more attractive to passengers and freight operators, thus recovering traffic lost to the roads. Important areas included:
* Electrification of principal main lines, in the
The report, latterly known as the "Modernisation Plan", was published in January 1955. It was intended to bring the railway system into the 20th century. A government White Paper produced in 1956 stated that modernisation would help eliminate BR's financial deficit by 1962, but the figures in both this and the original plan were produced for political reasons and not based on detailed analysis. The aim was to increase speed, reliability, safety, and line capacity through a series of measures that would make services more attractive to passengers and freight operators, thus recovering traffic lost to the roads. Important areas included:
* Electrification of principal main lines, in the Eastern Region Eastern Region or East Region may refer to:
* Eastern Region (Abu Dhabi): Al Ain
*Eastern Region, Ghana
*Eastern Region (Iceland)
*Eastern Region, Nepal
*Eastern Region, Nigeria
* Eastern Region, Serbia
* Eastern Region, Uganda
* Eastern Region of ...
, Kent, Birmingham to Liverpool/Manchester and Central Scotland
* Large-scale dieselisation to replace steam locomotives
* New passenger and freight rolling stock
* Resignalling and track renewals
* Modern marshalling yard
A classification yard (American and Canadian English (Canadian National Railway use)), marshalling yard (British, Hong Kong, Indian, Australian, and Canadian English (Canadian Pacific Railway use)) or shunting yard (Central Europe) is a railway ya ...
s
* The closure of an unspecified but relatively small number of lines
The government appeared to endorse the 1955 programme (costing £1.2 billion), but did so largely for political reasons. This included the withdrawal of steam traction and its replacement by diesel (and some electric) locomotives. Not all modernisations would be effective at reducing costs. The dieselisation programme gave contracts primarily to British suppliers, who had limited experience of diesel locomotive manufacture, and rushed commissioning based on an expectation of rapid electrification; this resulted in numbers of locomotives with poor designs and a lack of standardisation. At the same time, containerised
Containerization is a system of intermodal freight transport using intermodal containers (also called shipping containers and ISO containers). Containerization is also referred as "Container Stuffing" or "Container Loading", which is the pro ...
freight was being developed. The marshalling yard building programme was a failure, being based on a belief in the continued viability of wagon-load
In rail freight transportation the terms wagonload or wagonload freight refer to trains made of single wagon consignments of freight. In the US and Canada the term carload refers to a single car of any kind, and manifest train refers to trains mad ...
traffic in the face of increasingly effective road competition, and lacking effective forward planning or realistic assessments of future freight. A 2002 documentary broadcast on BBC Radio 4 blamed the 1950s decisions for the "beleaguered" condition of the railway system at that time.
The Beeching reports
 Following semi-secret discussions on railway finances by the government-appointed Stedeford Committee in 1961, one of its members, Dr Richard Beeching, was offered the post of chairing the BTC while it lasted and then became the first Chairman of the British Railways Board.
A major traffic census in April 1961, which lasted one week, was used in the compilation of a report on the future of the network. This report – ''The Reshaping of British Railways'' – was published by the BRB in March 1963. The proposals, which became known as the Beeching cuts, were dramatic. A third of all passenger services and more than 4,000 of the 7,000 stations would close. Beeching, who is thought to have been the author of most of the report, set out some dire figures. One third of the network was carrying just 1% of the traffic. Of the 18,000 passenger coaches, 6,000 were said to be used only 18 times a year or less. Although maintaining them cost between £3million and £4million a year, they earned only about £0.5million.
Most of the closures were carried out between 1963 and 1970 (including some which were not listed in the report), while other suggested closures were not carried out. The closures were heavily criticised at the time. A small number of stations and lines closed under the Beeching programme have been reopened, with further reopenings proposed.
A second Beeching report, "The Development of the Major Trunk Routes", followed in 1965. This did not recommend closures as such but outlined a "network for development"; the fate of the rest of the network was not discussed in the report.
Following semi-secret discussions on railway finances by the government-appointed Stedeford Committee in 1961, one of its members, Dr Richard Beeching, was offered the post of chairing the BTC while it lasted and then became the first Chairman of the British Railways Board.
A major traffic census in April 1961, which lasted one week, was used in the compilation of a report on the future of the network. This report – ''The Reshaping of British Railways'' – was published by the BRB in March 1963. The proposals, which became known as the Beeching cuts, were dramatic. A third of all passenger services and more than 4,000 of the 7,000 stations would close. Beeching, who is thought to have been the author of most of the report, set out some dire figures. One third of the network was carrying just 1% of the traffic. Of the 18,000 passenger coaches, 6,000 were said to be used only 18 times a year or less. Although maintaining them cost between £3million and £4million a year, they earned only about £0.5million.
Most of the closures were carried out between 1963 and 1970 (including some which were not listed in the report), while other suggested closures were not carried out. The closures were heavily criticised at the time. A small number of stations and lines closed under the Beeching programme have been reopened, with further reopenings proposed.
A second Beeching report, "The Development of the Major Trunk Routes", followed in 1965. This did not recommend closures as such but outlined a "network for development"; the fate of the rest of the network was not discussed in the report.
Post-Beeching
The basis for calculating passenger fares changed in 1964. In future, fares on some routes—such as rural, holiday and commuter services—would be set at a higher level than on other routes; previously, fares had been calculated using a simple rate for the distance travelled, which at the time was 3 d per mile second class, and 4½d per mile first class (equivalent to £ and £ respectively, in ). In 1966, a " Whites only" recruitment policy for guards at Euston station agreed between the local union branch and station management was dropped after the case of Asquith Xavier, a migrant fromDominica
Dominica ( or ; Kalinago: ; french: Dominique; Dominican Creole French: ), officially the Commonwealth of Dominica, is an island country in the Caribbean. The capital, Roseau, is located on the western side of the island. It is geographically ...
, who had been refused promotion on those grounds, was raised in Parliament and taken up by the then Secretary of State for Transport, Barbara Castle.
Passenger levels decreased steadily from 1962 to the late 1970s, and reached a low in 1982. Network improvements included completing electrification of the Great Eastern Main Line
The Great Eastern Main Line (GEML, sometimes referred to as the East Anglia Main Line) is a major railway line on the British railway system which connects Liverpool Street station in central London with destinations in east London and t ...
from London to Norwich between 1976 and 1986 and the East Coast Main Line
The East Coast Main Line (ECML) is a electrified railway between London and Edinburgh via Peterborough, Doncaster, York, Darlington, Durham and Newcastle. The line is a key transport artery on the eastern side of Great Britain running broa ...
from London to Edinburgh between 1985 and 1990. A mainline route closure during this period of relative network stability was the -electrified Woodhead line between Manchester and Sheffield: passenger service ceased in 1970 and goods in 1981.
A further British Rail report from a committee chaired by Sir David Serpell was published in 1983. The Serpell Report
The Serpell Report was produced by a committee chaired by Sir David Serpell, a retired senior civil servant. It was commissioned by the government of Margaret Thatcher to examine the state and long-term prospects of Great Britain's railway syste ...
made no recommendations as such but did set out various options for the network, including, at their most extreme, a skeletal system of less than 2,000routekm (1,240miles). The report was received with hostility within several circles, which included figured within the government, as well as amongst the public. The reaction was so strong that Margaret Thatcher, Prime Minister at that time, stated that decisions on the report would not immediately be taken. The Serpell report was quietly shelved, although the British Government was periodically accused by its opponents of implementing the report via stealth for some years thereafter.
The 1980s and 1990s saw the closure of some railways which had survived the Beeching cuts a generation earlier but which had seen passenger services withdrawn. This included the bulk of the Chester and Connah's Quay Railway
The Chester & Connah's Quay Railway ran from Chester Northgate in Chester, Cheshire, England to Shotton, Flintshire, Wales. It was in use for its full length from 1890 to 1992.
At Dee Marsh Junction it connected with the North Wales and Liverpo ...
in 1992, the Brierley Hill to Walsall section of the South Staffordshire line in 1993, while the Birmingham to Wolverhampton section of the Great Western Railway was closed in three phases between 1972 and 1992.
Transport Act 1968
Following the election ofLabour
Labour or labor may refer to:
* Childbirth, the delivery of a baby
* Labour (human activity), or work
** Manual labour, physical work
** Wage labour, a socioeconomic relationship between a worker and an employer
** Organized labour and the labour ...
in 1964, on a platform of revising many of the cuts, Tom Fraser
Thomas Fraser (18 February 1911 – 21 November 1988) was Scottish coal miner and trade unionist, who was a Labour Member of Parliament (MP) for the Hamilton constituency between 1943 and 1967.
Life
He was the son of Thomas and Mary Fra ...
instead authorised the closure 1,071 mi of railway lines, following the recommendations from the '' Beeching Report'' even lines not considered closing. After he resigned in 1967, his replacement Barbara Castle continued the line and station closures but introduced the first Government rail subsidies for socially necessary but unprofitable railways in the Transport Act 1968. Part of these provisions was the creation of a passenger transport executive or PTE within larger metropolitan areas. Prior to this, public transport was run by individual local authorities and private companies, with little co-ordination. The PTEs took over the responsibility (but not ownership) of managing local rail networks.
The 1968 Act created five new bodies. These were:
* West Midlands PTE on 1 October 1969
* SELNEC PTE (South East Lancashire & North East Cheshire) on 1 November 1969 (now ''Greater Manchester'')
* Merseyside PTE
Merseytravel is the passenger transport executive, responsible for the coordination of public transport in the Liverpool City Region in North West England. Merseytravel was established on 1 December 1969 as the Merseyside Passenger Transport ...
on 1 December 1969 (now Liverpool City Region)
* Tyneside PTE
The Tyneside Passenger Transport Executive was the operations arm of the Tyneside Passenger Transport Authority, created by the Transport Act 1968. and came into operation on 1 January 1970.
Area covered
The initial operating area of the PTE ...
on 1 January 1970 (now ''Tyne and Wear'')
* Greater Glasgow PTE on 1 June 1973 (now ''Strathclyde'')
This was the first real subdivision of BR since its inception in 1949, and likely saved many lines earmarked for closure, notably the Liverpool, Crosby and Southport Railway, which now forms part of the Merseyrail network.
Sectorisation
 Upon sectorisation in 1982, three passenger sectors were created: InterCity, operating principal express services; London & South East (renamed Network SouthEast in 1986) operating commuter services in the London area; Provincial (renamed Regional Railways in 1989) responsible for all other passenger services. In the
Upon sectorisation in 1982, three passenger sectors were created: InterCity, operating principal express services; London & South East (renamed Network SouthEast in 1986) operating commuter services in the London area; Provincial (renamed Regional Railways in 1989) responsible for all other passenger services. In the metropolitan counties
The metropolitan counties are a type of county-level administrative division of England. There are six metropolitan counties, which each cover large urban areas, with populations between 1 and 3 million. They were created in 1974 and are each di ...
local services were managed by the Passenger Transport Executives. Provincial was the most subsidised (per passenger km) of the three sectors; upon formation, its costs were four times its revenue. During the 1980s British Rail ran the Rail Riders membership club aimed at 5- to 15-year-olds.
Because British Railways was such a large operation, running not just railways but also ferries, steamships and hotels, it has been considered difficult to analyse the effects of nationalisation.
Prices rose quickly in this period, rising 108% in real terms from 1979 to 1994, as prices rose by 262% but RPI only increased by 154% in the same time.
Branding
Pre-1960s
Following nationalisation in 1948, British Railways began to adapt the corporate liveries on the rolling stock it had inherited from its predecessor railway companies. Initially, an express blue (followed by GWR-style Brunswick green in 1952) was used on passenger locomotives, and LNWR-style lined black for mixed-traffic locomotives, but later green was more widely adopted. Development of a corporate identity for the organisation was hampered by the competing ambitions of the British Transport Commission and the Railway Executive. The Executive attempted to introduce a modern Art Deco-style curved logo, which could also serve as the standard for station signage totems. BR eventually adopted the common branding of the BTC as its first corporate logo, alion
The lion (''Panthera leo'') is a large Felidae, cat of the genus ''Panthera'' native to Africa and India. It has a muscular, broad-chested body; short, rounded head; round ears; and a hairy tuft at the end of its tail. It is sexually dimorphi ...
astride a spoked wheel, designed for the BTC by Cecil Thomas; on the bar overlaid across the wheel, the BTC's name was replaced with the words "British Railways". This logo, nicknamed the "Cycling Lion", was applied from 1948 to 1956 to the sides of locomotives, while the ‘hot dog’ design was adopted for smaller station name signs, known officially as ‘lamp tablets’ and coloured for the appropriate BR region, using Gill Sans
Gill Sans is a humanist sans-serif typeface designed by Eric Gill and released by the British branch of Monotype from 1928 onwards.
Gill Sans is based on Edward Johnston's 1916 "Underground Alphabet", the corporate font of London Underground. ...
lettering first adopted by the LNER LNER may refer to:
*London and North Eastern Railway, a railway company in the United Kingdom from 1923 until 1947
*London North Eastern Railway, a train operating company in the United Kingdom since 2018
* Liquid neutral earthing resistor, a type ...
from 1929.
In 1956, the BTC was granted a heraldic achievement by the College of Arms and the Lord Lyon
The Right Honourable the Lord Lyon King of Arms, the head of Lyon Court, is the most junior of the Great Officers of State in Scotland and is the Scottish official with responsibility for regulating heraldry in that country, issuing new grant ...
, and then BTC chairman Brian Robertson wanted a grander logo for the railways. BR's second corporate logo (1956–1965), designed in consultation with Charles Franklyn and inspired by the much more detailed BTC crest, depicted a rampant lion emerging from a heraldic crown and holding a spoked wheel, all enclosed in a roundel with the "British Railways" name displayed across a bar on either side. This emblem soon acquired the nickname of the "Ferret and Dartboard". A variant of the logo with the name in a circle was also used on locomotives.
1960s
Milner Gray Milner Gray may refer to:
*Milner Gray (politician)
Milner Gray (11 May 1871 – 10 April 1943) was a British Liberal politician.
Family life and business
Gray was born in Luton, Bedfordshire, the son of a Baptist Minister,''Who was Who'', OUP ...
of the Design Research Unit
The Design Research Unit (DRU) was one of the first generation of British design consultancies combining expertise in architecture, graphics and industrial design. It was founded by the managing director of Stuart Advertising Agency, Marcus Brum ...
. They drew up a Corporate Identity Manual which established a coherent brand and design standard for the whole organisation, specifying Rail Blue
The history of British Rail's corporate liveries is quite complex. Although from the mid-1960s to the 1980s the organisation was associated with "Rail Blue", a number of other schemes were also used, especially when it was split into operating u ...
and pearl grey as the standard colour scheme for all rolling stock; Rail Alphabet
Rail Alphabet is a typeface designed by Jock Kinneir and Margaret Calvert for signage on the British Rail network. First used at Liverpool Street station, it was then adopted by the Design Research Unit (DRU) as part of their comprehensive 19 ...
as the standard corporate typeface, designed by Jock Kinneir
Richard "Jock" Kinneir (11 February 1917 – 23 August 1994) was a British typographer and graphic designer who, with his colleague Margaret Calvert, designed many of the road signs used throughout the United Kingdom, Crown Dependencies, and ...
and Margaret Calvert
Margaret Vivienne Calvert (born 1936) is a British typographer and graphic designer who, with colleague Jock Kinneir, designed many of the road signs used throughout the United Kingdom, Crown Dependencies, and British Overseas Territories, as we ...
; and introducing the now-iconic corporate Identity Symbol of the Double Arrow logo. Designed by Gerald Barney (also of the DRU), this arrow device was formed of two interlocked arrows across two parallel lines, symbolising a double-track railway. It was likened to a bolt of lightning or barbed wire
A close-up view of a barbed wire
Roll of modern agricultural barbed wire
Barbed wire, also known as barb wire, is a type of steel fencing wire constructed with sharp edges or points arranged at intervals along the strands. Its primary use is t ...
, and also acquired a nickname: "the arrow of indecision". A mirror image of the double arrow was used on the port side
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Ham ...
of BR-owned Sealink ferry funnels. The new BR corporate identity and double arrow were displayed at the Design Centre in London in early 1965, and the brand name of the organisation was shortened to "British Rail". It is now employed as a generic symbol on street signs in Great Britain denoting railway stations, and is still printed on railway tickets as part of the Rail Delivery Group's jointly managed National Rail brand.
Post-1960s
Inter-City
Inter-city rail services are express passenger train services that run services that connect cities over longer distances than commuter or regional trains.
There is no precise definition of inter-city rail; its meaning may vary from country ...
, Network SouthEast, Regional Railways or Rail Express Systems
Rail Express Systems (RES) was a sector of British Rail. This sector was responsible for transport of mail and parcels, including the travelling post office trains, as well as taking over charter operations from InterCity and haulage of the Roya ...
began to adopt their own identities, introducing logos and colour schemes which were essentially variants of the British Rail brand. Eventually, as sectorisation developed into a prelude to privatisation, the unified British Rail brand disappeared, with the notable exception of the Double Arrow symbol, which has survived to this day and serves as a generic trademark to denote railway services across Great Britain. The BR Corporate Identity Manual is noted as a piece of British design history and there are plans for it to be re-published.
Network
Regions
With its creation in 1948, British Railways was divided into regions which were initially based on the areas the formerBig Four Big Four or Big 4 may refer to:
Groups of companies
* Big Four accounting firms: Deloitte, Ernst & Young, KPMG, PwC
* Big Four (airlines) in the U.S. in the 20th century: American, Eastern, TWA, United
* Big Four (banking), several groupings ...
operated in; later, several lines were transferred between regions. Notably, these included the former Great Central lines from the Eastern Region to the London Midland Region, and the West of England Main Line from the Southern Region to Western Region
* Southern Region: former Southern Railway lines.
* Western Region: former Great Western Railway lines.
* London Midland Region: former London, Midland and Scottish Railway lines in England and Wales.
* Eastern Region Eastern Region or East Region may refer to:
* Eastern Region (Abu Dhabi): Al Ain
*Eastern Region, Ghana
*Eastern Region (Iceland)
*Eastern Region, Nepal
*Eastern Region, Nigeria
* Eastern Region, Serbia
* Eastern Region, Uganda
* Eastern Region of ...
: former London and North Eastern Railway lines south of York.
* Anglia Region: split from Eastern Region in 1988.
* North Eastern Region: former London and North Eastern Railway lines in England north of York.
* Scottish Region
The Scottish Region (ScR) was one of the six regions created on British Railways (BR) and consisted of ex-London, Midland and Scottish Railway (LMS) and ex-London and North Eastern Railway (LNER) lines in Scotland. It existed from the creation o ...
: all lines, regardless of the original company, in Scotland.
The North Eastern Region was merged with the Eastern Region in 1967.
Sectorisation
Alphaline
Alphaline was a brand introduced by Regional Railways in December 1994 to differentiate certain provincial express trains with enhanced passenger accommodation from general regional and middle-distance services operated by older rolling stock.
O ...
(enhanced regional express passenger services) (Added in 1994)
** ScotRail
ScotRail Trains Limited, trading as ScotRail ( gd, Rèile na h-Alba), is a Scottish train operating company that is publicly owned by Scottish Rail Holdings on behalf of the Scottish Government. It has been operating the ScotRail franchise a ...
(regional and sub-intercity services in Scotland).
** TransPennine Express (sub-intercity services in the North).
In addition, the non-passenger sectors were:
* Trainload Freight took trainload freight.
* Railfreight Distribution took non-trainload freight.
* Freightliner took intermodal traffic.
* Rail Express Systems
Rail Express Systems (RES) was a sector of British Rail. This sector was responsible for transport of mail and parcels, including the travelling post office trains, as well as taking over charter operations from InterCity and haulage of the Roya ...
took parcels traffic.
The maintenance and remaining engineering works were split off into a new company, British Rail Maintenance Limited
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
. The new sectors were further subdivided into divisions.
 This ended the BR blue period as new liveries were adopted gradually. Infrastructure remained the responsibility of the regions until the "Organisation for Quality" initiative in 1991 when this too was transferred to the sectors. The Anglia Region was created in late 1987, its first General Manager being John Edmonds, who began his appointment on 19 October 1987. Full separation from the Eastern Region – apart from engineering design needs – occurred on 29 April 1988. It handled the services from and , its western boundary being , and .
The former BR network, with the trunk routes of the West Coast Main Line,
This ended the BR blue period as new liveries were adopted gradually. Infrastructure remained the responsibility of the regions until the "Organisation for Quality" initiative in 1991 when this too was transferred to the sectors. The Anglia Region was created in late 1987, its first General Manager being John Edmonds, who began his appointment on 19 October 1987. Full separation from the Eastern Region – apart from engineering design needs – occurred on 29 April 1988. It handled the services from and , its western boundary being , and .
The former BR network, with the trunk routes of the West Coast Main Line, East Coast Main Line
The East Coast Main Line (ECML) is a electrified railway between London and Edinburgh via Peterborough, Doncaster, York, Darlington, Durham and Newcastle. The line is a key transport artery on the eastern side of Great Britain running broa ...
, Great Western Main Line
The Great Western Main Line (GWML) is a main line railway in England that runs westwards from London Paddington to . It connects to other main lines such as those from Reading to Penzance and Swindon to Swansea. Opened in 1841, it was the or ...
, Great Eastern Main Line
The Great Eastern Main Line (GEML, sometimes referred to as the East Anglia Main Line) is a major railway line on the British railway system which connects Liverpool Street station in central London with destinations in east London and t ...
and Midland Main Line, and other lines.
Security
Policing on (and within) the network was carried out British Transport Police (BTP). In 1947 the Transport Act created the British Transport Commission (BTC), which unified the railway system. On 1 January 1949, the British Transport Commission Police (BTCP) were created, formed from the four old railway police forces, the London Transport Police, canal police and several minor dock forces. In 1957 the Maxwell-Johnson enquiry found that policing requirements for the railway could not be met by civil forces and that it was essential that a specialist police force be retained. On 1 January 1962, the British Transport Commission Police ceased to cover British Waterways property and exactly a year later when the BTC was abolished the name of the force was amended to the British Transport Police. This name and its role within policing on the rail network was continued post-1994.Finances
Despite its nationalisation in 1947 "as one of the 'commanding heights' of the economy", according to some sources British Rail was not profitable for most (if not all) of its history. Newspapers reported that as recently as the 1990s, publicrail subsidy
Many countries offer subsidies to their railways because of the social and economic benefits that it brings. The economic benefits can greatly assist in funding the rail network. Those countries usually also fund or subsidize road construction, and ...
was counted as profit; as early as 1961, British Railways were losing £300,000 a day.
Although the company was considered the sole public-transport option in many rural areas, the Beeching cuts made buses the only public transport available in some rural areas. Despite increases in traffic congestion and road fuel prices beginning to rise in the 1990s, British Rail remained unprofitable. Following sectorisation, InterCity became profitable. InterCity became one of Britain's top 150 companies, providing city centre to city centre travel across the nation from Aberdeen and Inverness
Inverness (; from the gd, Inbhir Nis , meaning "Mouth of the River Ness"; sco, Innerness) is a city in the Scottish Highlands. It is the administrative centre for The Highland Council and is regarded as the capital of the Highlands. Histori ...
in the north to Poole
Poole () is a large coastal town and seaport in Dorset, on the south coast of England. The town is east of Dorchester and adjoins Bournemouth to the east. Since 1 April 2019, the local authority is Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole Counc ...
and Penzance
Penzance ( ; kw, Pennsans) is a town, civil parish and port in the Penwith district of Cornwall, United Kingdom. It is the most westerly major town in Cornwall and is about west-southwest of Plymouth and west-southwest of London. Situated ...
in the south.
Investment
In 1979, the incomingConservative Government Conservative or Tory government may refer to:
Canada
In Canadian politics, a Conservative government may refer to the following governments administered by the Conservative Party of Canada or one of its historical predecessors:
* 1st Canadian Min ...
led by Margaret Thatcher was viewed as anti-railway, and did not want to commit public money to the railways. However, British Rail was allowed to spend its own money with government approval. This led to a number of electrification projects being given the go-ahead, including the East Coast Main Line
The East Coast Main Line (ECML) is a electrified railway between London and Edinburgh via Peterborough, Doncaster, York, Darlington, Durham and Newcastle. The line is a key transport artery on the eastern side of Great Britain running broa ...
, the spur from Doncaster to Leeds, and the lines in East Anglia out of London Liverpool Street
Liverpool Street station, also known as London Liverpool Street, is a central London railway terminus and connected London Underground station in the north-eastern corner of the City of London, in the ward of Bishopsgate Without. It is the t ...
to Norwich and King's Lynn
King's Lynn, known until 1537 as Bishop's Lynn and colloquially as Lynn, is a port and market town in the borough of King's Lynn and West Norfolk in the county of Norfolk, England. It is located north of London, north-east of Peterborough, no ...
. The list with approximate completion dates includes:
* St Pancras – Bedford 1981–83
* Rock Ferry – Hooton 1985
*Hitchin
Hitchin () is a market town and unparished area in the North Hertfordshire Districts of England, district in Hertfordshire, England, with an estimated population of 35,842.
History
Hitchin is first noted as the central place of the Hicce peopl ...
– Leeds 1985–88
* Colchester – Norwich 1986
*Bishops Stortford
Bishop's Stortford is a historic market town in Hertfordshire, England, just west of the M11 motorway on the county boundary with Essex, north-east of central London, and by rail from Liverpool Street station. Stortford had an estimated popu ...
– Cambridge 1987
* Watford Junction – St Albans Abbey
St Albans Cathedral, officially the Cathedral and Abbey Church of St Alban but often referred to locally as "the Abbey", is a Church of England cathedral in St Albans, England. Much of its architecture dates from Norman times. It ceased to be ...
1988
*Royston
Royston may refer to:
Places
Australia
*Royston, Queensland, a rural locality
Canada
*Royston, British Columbia, a small hamlet
England
*Royston, Hertfordshire, a town and civil parish, formerly partly in Cambridgeshire
*Royston, South Yorkshi ...
– Cambridge 1988
* Snow Hill Tunnel as part of Thameslink project 1988
* Doncaster – York 1989
* Airdrie – Drumgelloch 1989
*York – Edinburgh Waverley (and the spur to North Berwick) 1991
* Carstairs – Edinburgh Waverley 1991
*Cambridge – King's Lynn
King's Lynn, known until 1537 as Bishop's Lynn and colloquially as Lynn, is a port and market town in the borough of King's Lynn and West Norfolk in the county of Norfolk, England. It is located north of London, north-east of Peterborough, no ...
1992
*Hooton – Ellesmere Port and Chester
Chester is a cathedral city and the county town of Cheshire, England. It is located on the River Dee, close to the English–Welsh border. With a population of 79,645 in 2011,"2011 Census results: People and Population Profile: Chester Loca ...
1993–94
*London Paddington
Paddington, also known as London Paddington, is a London station group, Central London railway terminus and London Underground station complex, located on Praed Street in the Paddington area. The site has been the London terminus of services pro ...
– Heathrow Airport
Heathrow Airport (), called ''London Airport'' until 1966 and now known as London Heathrow , is a major international airport in London, England. It is the largest of the six international airports in the London airport system (the others be ...
1993–98
*Leeds and Bradford Forster Square – Skipton and Ilkley 1994
In the Southwest, the South West Main Line from Bournemouth
Bournemouth () is a coastal resort town in the Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole council area of Dorset, England. At the 2011 census, the town had a population of 183,491, making it the largest town in Dorset. It is situated on the Southern ...
to Weymouth was electrified along with other infill third rail electrification in the south. In 1988, the line to Aberdare
Aberdare ( ; cy, Aberdâr) is a town in the Cynon Valley area of Rhondda Cynon Taf, Wales, at the confluence of the Rivers Dare (Dâr) and Cynon. Aberdare has a population of 39,550 (mid-2017 estimate). Aberdare is south-west of Merthyr Tyd ...
was reopened. A British Rail advertisement ("Britain's Railway", directed by Hugh Hudson) featured some of the best-known railway structures in Britain, including the Forth Rail Bridge, Royal Albert Bridge, Glenfinnan Viaduct and London Paddington station. London Liverpool Street
Liverpool Street station, also known as London Liverpool Street, is a central London railway terminus and connected London Underground station in the north-eastern corner of the City of London, in the ward of Bishopsgate Without. It is the t ...
station was rebuilt, opened by Queen Elizabeth II
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; 21 April 1926 – 8 September 2022) was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until Death and state funeral of Elizabeth II, her death in 2022. She was queen ...
, and a new station was constructed at Stansted Airport in 1991. The following year, the Maesteg line
The Maesteg Line is a commuter rail line in South Wales from Bridgend to Maesteg. Services usually operate from Maesteg to via the South Wales Main Line and Gloucester to Newport Line.
Electrification by 2019 was announced in the Departmen ...
was reopened. In 1988, the Windsor Link Line, Manchester
The Windsor Link is a 700-metre railway line in Salford, Greater Manchester that connects Salford Crescent and Manchester Deansgate stations. It was opened by British Rail in May 1988, and came into full use in 1989. This link allows services ...
was constructed and has proven to be an important piece of infrastructure.
APTIS ticket
 Before the introduction of APTIS (Accountancy and Passenger Ticket Issuing System), British Rail used the Edmondson railway ticket, first introduced in the 1840s and phased out in the early 1970s. Tickets issued from British Rail's APTIS system had a considerable amount of information presented in a consistent, standard format. The design for all tickets was created by Colin Goodall. This format has formed the basis for all subsequent ticket issuing systems introduced on the railway network – ticket-office-based, self-service and conductor-operated machines alike. APTIS survived in widespread use for twenty years but, in the early 2000s, was largely replaced by more modern PC-based ticketing systems. Some APTIS machines in the Greater London area were modified as APTIS-ANT (with no obvious difference to the ticket issued) to make them Oyster card compatible. The last APTIS machines were removed at the end of 2006 as there was no option to upgrade them to accept Chip and PIN credit card payments. The last APTIS-ANT ticket to be issued in the UK using one of the machines was at
Before the introduction of APTIS (Accountancy and Passenger Ticket Issuing System), British Rail used the Edmondson railway ticket, first introduced in the 1840s and phased out in the early 1970s. Tickets issued from British Rail's APTIS system had a considerable amount of information presented in a consistent, standard format. The design for all tickets was created by Colin Goodall. This format has formed the basis for all subsequent ticket issuing systems introduced on the railway network – ticket-office-based, self-service and conductor-operated machines alike. APTIS survived in widespread use for twenty years but, in the early 2000s, was largely replaced by more modern PC-based ticketing systems. Some APTIS machines in the Greater London area were modified as APTIS-ANT (with no obvious difference to the ticket issued) to make them Oyster card compatible. The last APTIS machines were removed at the end of 2006 as there was no option to upgrade them to accept Chip and PIN credit card payments. The last APTIS-ANT ticket to be issued in the UK using one of the machines was at Upminster station
Upminster is an interchange station serving the town of Upminster in the London Borough of Havering, Greater London. It is on the London, Tilbury and Southend line (LTSR), down the line from London Fenchurch Street; it is the eastern terminus ...
on 21 March 2007.
Before the rail network was privatised, British Rail introduced several discount cards through the APTIS that were available to certain demographics, issued either by National or Regional schemes:
* 16–25 Railcard
The 16–25 Railcard is an annual card giving discounts on certain types of railway ticket in Britain. It is available to anybody aged between 16 and 25 (inclusive), and certain mature students aged 26 and above, and is currently priced a ...
* The Network Railcard, introduced in 1986 by British Rail upon the creation of their Network SouthEast sector in parts of Southern England
* Disabled Persons Railcard
The Disabled Persons Railcard is a concessionary fare scheme in the United Kingdom giving eligible passengers with disabilities benefits on the National Rail network including a 1/3 discount on fares.
Card and discounts
The card is availabl ...
, introduced in 1981 to coincide with the International Year of Disabled Persons.
* Senior Railcard
The Senior Railcard is an annual card available to people aged 60 and over, which gives discounts on certain types of Rail transport in Great Britain, railway ticket in Britain. The Railcard has existed in various forms since 1975; the curr ...
, introduced in 1970.
Accidents and incidents
Preserved lines
The narrow-gauge Vale of Rheidol Railway in Ceredigion, Wales, became part of British Railways at nationalisation. Although built as a working railway, in 1948 the line was principally a tourist attraction. British Rail operated the line using steam locomotives long after the withdrawal of standard-gauge steam. The line's three steam locomotives were the only ones to receive TOPS serial numbers and be painted in BR Rail Blue livery with the double arrow logo. The Vale of Rheidol Railway was privatised in 1989 and continues to operate as a private heritage railway. Other preserved lines, or heritage railways, have reopened lines previously closed by British Rail. These range from picturesque rural branch lines like theKeighley and Worth Valley Railway
The Keighley & Worth Valley Railway is a heritage railway line in the Worth Valley, West Yorkshire, England, which runs from Keighley to Oxenhope. It connects to the National Rail network at Keighley railway station.
History
Inception and ...
to sections of mainline such as the Great Central Railway. Many have links to the National Rail network, both at station interchanges, for example, the Severn Valley Railway between and Kidderminster Town, and physical rail connections like the Watercress Line at .
Although most are operated solely as leisure amenities, some also provide educational resources, and a few have ambitions to restore commercial services over routes abandoned by the nationalised industry.
Night trains
 When the railways came into public ownership in 1948, British Railways inherited a number of night train services from the Big Four. Sleeping car services were operated on the West and East coast routes and GWR mainlines to several destinations. Routes included to , to , to and the Night Ferry sleeper from to Brussels and Paris. On
When the railways came into public ownership in 1948, British Railways inherited a number of night train services from the Big Four. Sleeping car services were operated on the West and East coast routes and GWR mainlines to several destinations. Routes included to , to , to and the Night Ferry sleeper from to Brussels and Paris. On Privatisation
Privatization (also privatisation in British English) can mean several different things, most commonly referring to moving something from the public sector into the private sector. It is also sometimes used as a synonym for deregulation when ...
saw the services broken up in February 1996 and the rolling stock repainted into the new liveries, with the last ever BR service being a Scottish sleeper from Euston in 1997.
Marine services
Ships
British Railways operated ships from its formation in 1948 on several routes. Many ships were acquired on nationalisation, and others were built for operation by British Railways or its later subsidiary, Sealink. Those ships capable of carrying rail vehicles were classed under TOPS as Class 99.Sealink
 Sealink was originally the brand name for the ferry services of British Rail in the United Kingdom and Ireland. Services to France, Belgium, and the Netherlands were run by Sealink UK as part of the Sealink consortium, which also used ferries owned by French national railways (
Sealink was originally the brand name for the ferry services of British Rail in the United Kingdom and Ireland. Services to France, Belgium, and the Netherlands were run by Sealink UK as part of the Sealink consortium, which also used ferries owned by French national railways (SNCF
The Société nationale des chemins de fer français (; abbreviated as SNCF ; French for "National society of French railroads") is France's national state-owned railway company. Founded in 1938, it operates the country's national rail traffi ...
), the Belgian Maritime Transport Authority Regie voor Maritiem Transport/Regie des transports maritimes (RMT/RTM) and the Dutch Stoomvaart Maatschappij Zeeland (Zeeland Steamship Company).
Historically, the shipping services were exclusively an extension of the railways across the English Channel and the Irish Sea in order to provide through, integrated services to mainland Europe and Ireland. As international travel became more popular in the late 1960s and before air travel became generally affordable, the responsibility for shipping services was taken away from the British Rail Regions and, in 1969, centralised in a new division – British Rail Shipping and International Services Division.
With the advent of car ferry services, the old passenger-only ferries were gradually replaced by roll-on/roll-off ships, catering for motorists and rail passengers as well as road freight. However, given that there was now competition in the form of other ferry companies offering crossings to motorists, it became necessary to market the services in a normal business fashion (as opposed to the previous almost monopolistic situation). Thus, with the other partners mentioned above, the brand name Sealink was introduced for the consortium.
In the late 1960s, as demand for international rail travel declined and the shipping business became almost exclusively dependent on passenger and freight vehicle traffic, the ferry business was incorporated as Sealink UK Limited on 1 January 1979, a wholly owned subsidiary of the British Railways Board, but still part of the Sealink consortium. In 1979, Sealink acquired Manx Line, which offered services to the Isle of Man from Heysham.
On 27 July 1984, the UK Government sold Sealink UK to Sea Containers for £66million. The company was renamed Sealink British Ferries. The sale excluded the operations of Hoverspeed, the Isle of Wight services and the share in the Isle of Man Steam Packet Company, as well as the Port of Heysham. In 1996, the Sealink name disappeared when the UK services, by then owned by Stena, were re-branded as Stena Line
Stena Line is a Swedish shipping line company and one of the largest ferry operators in the world. It services Denmark, Germany, the United Kingdom, Ireland, Latvia, the Netherlands, Norway, Poland and Sweden. Stena Line is a major unit of Ste ...
. The agreement with the SNCF on the Dover to Calais
Calais ( , , traditionally , ) is a port city in the Pas-de-Calais department, of which it is a subprefecture. Although Calais is by far the largest city in Pas-de-Calais, the department's prefecture is its third-largest city of Arras. Th ...
route also ended at this time, and the French-run Sealink services were rebranded as SeaFrance.
Hovercraft
The jointhovercraft
A hovercraft, also known as an air-cushion vehicle or ACV, is an amphibious Craft (vehicle), craft capable of travelling over land, water, mud, ice, and other surfaces.
Hovercraft use blowers to produce a large volume of air below the hull ...
services of British Rail in association with the French SNCF
The Société nationale des chemins de fer français (; abbreviated as SNCF ; French for "National society of French railroads") is France's national state-owned railway company. Founded in 1938, it operates the country's national rail traffi ...
. British Rail Hovercraft Limited was established in 1965, under authority given to it by the British Railways Act 1967 and started its first service in 1966. Seaspeed started cross-Channel services from Dover
Dover () is a town and major ferry port in Kent, South East England. It faces France across the Strait of Dover, the narrowest part of the English Channel at from Cap Gris Nez in France. It lies south-east of Canterbury and east of Maidstone ...
to Calais
Calais ( , , traditionally , ) is a port city in the Pas-de-Calais department, of which it is a subprefecture. Although Calais is by far the largest city in Pas-de-Calais, the department's prefecture is its third-largest city of Arras. Th ...
and Boulogne-sur-Mer, France using SR-N4 hovercraft in August 1968. During 1981, Seaspeed merged with rival cross-channel hovercraft operator Hoverlloyd to create the combined Hoverspeed.
British Rail Engineering Limited
 Incorporated on 31 October 1969, British Rail Engineering Limited (BREL) was a wholly owned railway systems engineering subsidiary of the British Railways Board. Created through the Transport Act 1968, to manage BR's thirteen workshops, it replaced the British Rail Workshops Division, which had existed since 1948. The works managed by BREL were
Incorporated on 31 October 1969, British Rail Engineering Limited (BREL) was a wholly owned railway systems engineering subsidiary of the British Railways Board. Created through the Transport Act 1968, to manage BR's thirteen workshops, it replaced the British Rail Workshops Division, which had existed since 1948. The works managed by BREL were Ashford Ashford may refer to:
Places
Australia
*Ashford, New South Wales
*Ashford, South Australia
*Electoral district of Ashford, South Australia
Ireland
*Ashford, County Wicklow
*Ashford Castle, County Galway
United Kingdom
* Ashford, Kent, a town
** ...
, Crewe
Crewe () is a railway town and civil parish in the unitary authority of Cheshire East in Cheshire, England. The Crewe built-up area had a total population of 75,556 in 2011, which also covers parts of the adjacent civil parishes of Willaston ...
, Derby Locomotive Works, Derby Litchurch Lane, Doncaster, Eastleigh, Glasgow, Horwich Foundry, Shildon, Swindon
Swindon () is a town and unitary authority with Borough status in the United Kingdom, borough status in Wiltshire, England. As of the 2021 Census, the population of Swindon was 201,669, making it the largest town in the county. The Swindon un ...
, Temple Mills, Wolverton and York. BREL began trading in January 1970. During 1989, BREL was sold to a consortium of Asea Brown Boveri and Trafalgar House.
Mark 2 carriages
A family of railway carriages designed and built by British Rail workshops (from 1969 British Rail Engineering Limited) between 1964 and 1975. They were of steel construction.Advanced Passenger Train
 In the 1970s, British Rail developed tilting train technology in the
In the 1970s, British Rail developed tilting train technology in the Advanced Passenger Train
The Advanced Passenger Train (APT) was a tilting high speed train developed by British Rail during the 1970s and early 1980s, for use on the West Coast Main Line (WCML). The WCML contained many curves, and the APT pioneered the concept of activ ...
; there had been earlier experiments and prototypes in other countries, notably Italy. The objective of the tilt was to minimise the discomfort to passengers caused by taking the curves of the West Coast Main Line at high speed. The APT also had hydrokinetic brake
A water brake is a type of fluid coupling used to absorb mechanical energy and usually consists of a turbine or propeller mounted in an enclosure filled with water.
As the turbine or propeller turns, mechanical energy is transferred to the wa ...
s, which enabled the train to stop from 150 mph within existing signal spacings.
The introduction into service of the APT was to be a three-stage project. Phase 1, the development of an experimental APT (APT-E
The APT-E, for Advanced Passenger Train Experimental, was the prototype Advanced Passenger Train tilting train unit. It was powered by gas turbines, the only multiple unit so powered that was used by British Rail. The APT-E consisted of two ...
), was completed. This used a gas turbine-electric locomotive
A gas turbine locomotive is a type of railway locomotive in which the prime mover (locomotive), prime mover is a gas turbine. Several types of gas turbine locomotive have been developed, differing mainly in the means by which mechanical power is ...
, the only multiple unit
A multiple-unit train or simply multiple unit (MU) is a self-propelled train composed of one or more carriages joined together, which when coupled to another multiple unit can be controlled by a single driver, with multiple-unit train contr ...
so powered that was used by British Rail. It was formed of two power cars (numbers PC1 and PC2), initially with nothing between them and later, two trailer cars (TC1 and TC2). The cars were made of aluminium to reduce the weight of the unit and were articulated. The gas turbine was dropped from development due to excessive noise and the high fuel costs of the late 1970s. The APT-E first ran on 25 July 1971. The train drivers' union, ASLEF, black-listed the train due to its use of a single driver. The train was moved to Derby (with the aid of a locomotive inspector). This triggered a one-day strike by ASLEF that cost BR more than the research budget for the entire year.
Phase 2, the introduction of three prototype trains (APT-P) into revenue service on the Glasgow – London Euston route, did occur. Originally, there were to have been eight APT-P sets running, with minimal differences between them and the main fleet. However, financial constraints led to only three being authorised after two years of discussion by the British Railways Board. The cost was split equally between the Board and the Ministry of Transport. After these delays, considerable pressure grew to put the APT-P into revenue-service before they were fully ready. This inevitably led to high-profile failures as a result of technical problems.
These failures led to the trains being withdrawn from service while the problems were ironed out. However, by this time, managerial and political support had evaporated by 1982. Although the APT never properly entered service, the experience gained enabled the construction of other high-speed trains
High-speed rail (HSR) is a type of rail system that runs significantly faster than traditional rail, using an integrated system of specialised rolling stock and dedicated tracks. While there is no single standard that applies worldwide, lines ...
. The APT powercar technology was imported without the tilt into the design of the Class 91 locomotives, and the tilting technology was incorporated into Italian State Railway's '' Pendolino'' trains, which first entered service in 1987.
InterCity 125
 The InterCity 125, or High-Speed Train, was a diesel-powered passenger train built by BREL between 1975 and 1982 that was credited with saving British Rail. Each set is made up of two Class 43 power cars, one at each end and four to nine
The InterCity 125, or High-Speed Train, was a diesel-powered passenger train built by BREL between 1975 and 1982 that was credited with saving British Rail. Each set is made up of two Class 43 power cars, one at each end and four to nine Mark 3
Mark 3 is the third chapter of the Gospel of Mark in the New Testament of the Christian Bible. It relates a conflict over healing on the Sabbath, the commissioning of the Twelve Apostles, a conflict with scribes and a meeting of Jesus with h ...
carriages. The name is derived from its top operational speed of . Key features of the Intercity 125 over predecessors include the high power-to-weight ratio of the locomotives (1678 kW per ~70-tonne loco), high performance disc brake
A disc brake is a type of brake that uses the calipers to squeeze pairs of pads against a disc or a "rotor" to create friction. This action slows the rotation of a shaft, such as a vehicle axle, either to reduce its rotational speed or to hol ...
system (in place of the clasp brake
A railway brake is a type of brake used on the cars of railway trains to enable deceleration, control acceleration (downhill) or to keep them immobile when parked. While the basic principle is similar to that on road vehicle usage, operational f ...
s traditionally used), improved crashworthiness, and bi-directional running avoiding the need to perform any run arounds at terminating stations.
By 1970, the setbacks of the APT project had led the British Railways Board (BRB) to conclude that a stopgap solution would be desirably to reduce journey times in order to compete effectively with other modes of transport. At the instigation of Terry Miller, Chief Engineer (Traction & Rolling Stock), the BRB authorised the development of a high-speed diesel train using tried and tested conventional technology, intended for short-term use until the APT was available. Within two years, a prototype
A prototype is an early sample, model, or release of a product built to test a concept or process. It is a term used in a variety of contexts, including semantics, design, electronics, and Software prototyping, software programming. A prototyp ...
trainset had been completed by BREL; it performed extensive trial runs between 1972 and 1976.
Encouraged by the prototype's performance, British Rail chose to put the type into production. The production version had a substantially redesigned forward section; this change was primarily made by the British industrial designer Kenneth Grange who, after being approached by British Rail to design the livery, decided to redesign the body in coordination with an aerodynamic engineer and guided by wind tunnel testing. A total of 95 Intercity 125 trainsets were ultimately brought into service. British Rail enjoyed a boom in patronage on the routes operated by the HSTs and InterCity's revenues noticeably increased.
Prior to the HST's introduction, the speed of British diesel-powered trains was limited to . The prototype InterCity 125 (power cars 43000 and 43001) set the world speed record for diesel traction at on 12 June 1973. This was succeeded by a production set reaching in November 1987.
Sprinters
 By the early 1980s British Rail operated a large fleet of first generation DMUs, which had been constructed in prior decades to various designs. While formulating its long-term strategy for this sector of its operations, British Rail planners recognised that there would be considerable costs incurred by undertaking refurbishment programmes necessary for the continued use of these ageing multiple units, particularly due to the necessity of handling and removing hazardous materials such as
By the early 1980s British Rail operated a large fleet of first generation DMUs, which had been constructed in prior decades to various designs. While formulating its long-term strategy for this sector of its operations, British Rail planners recognised that there would be considerable costs incurred by undertaking refurbishment programmes necessary for the continued use of these ageing multiple units, particularly due to the necessity of handling and removing hazardous materials such as asbestos
Asbestos () is a naturally occurring fibrous silicate mineral. There are six types, all of which are composed of long and thin fibrous crystals, each fibre being composed of many microscopic "fibrils" that can be released into the atmosphere b ...
. In light of the high costs involved in retention, planners examined the prospects for the development and introduction of a new generation of DMUs to succeed the first generation.
In 1984/1985, two experimental DMU designs were put into service: the BREL-built Class 150 and Metro-Cammell-built Class 151. Both of these used hydraulic transmission and were less bus-like than the Pacers. After trials, the Class 150 was selected for production. Starting in 1987, production standard units entered service. Reliability was much improved by the new units, with depot visits being reduced from two or three times per week to fortnightly.
The late 1980s and early 1990s also saw the development of secondary express services that complemented the mainline Intercity routes. Class 155 and Class 156 Sprinters were developed to replace locomotive-hauled trains on these services, their interiors being designed with longer distance journeys in mind. Key Scottish and Trans-Pennine routes were upgraded with new Class 158 Express Sprinters, while a network of 'Alphaline
Alphaline was a brand introduced by Regional Railways in December 1994 to differentiate certain provincial express trains with enhanced passenger accommodation from general regional and middle-distance services operated by older rolling stock.
O ...
' services was introduced elsewhere in the country.
By the end of the 1980s, passenger numbers had increased and costs had been reduced to two-and-a-half times revenue. Specific areas for this cost reduction include the lower fuel consumption of Sprinters in comparison to traditional locomotive-hauled trains as well as their reduced maintenance costs.
Privatisation

 In 1989, the narrow-gauge Vale of Rheidol Railway was preserved, becoming the first part of British Rail to be privatised. Between 1994 and 1997, in accordance with the Railways Act 1993, the core activities of British Rail were privatised. Ownership of the track and infrastructure passed to Railtrack on 1 April 1994. Passenger operations were later
In 1989, the narrow-gauge Vale of Rheidol Railway was preserved, becoming the first part of British Rail to be privatised. Between 1994 and 1997, in accordance with the Railways Act 1993, the core activities of British Rail were privatised. Ownership of the track and infrastructure passed to Railtrack on 1 April 1994. Passenger operations were later franchised
Franchise may refer to:
Business and law
* Franchising, a business method that involves licensing of trademarks and methods of doing business to franchisees
* Franchise, a privilege to operate a type of business such as a cable television p ...
to 25 private-sector operators. Of the six freight companies, five were sold to Wisconsin Central to form EWS while Freightliner was sold in a management buyout
A management buyout (MBO) is a form of acquisition in which a company's existing managers acquire a large part, or all, of the company, whether from a parent company or individual. Management-, and/or leveraged buyout became noted phenomena of 1 ...
.
 The Waterloo & City line, part of Network SouthEast, was not included in the privatisation and was transferred to London Underground in April 1994. The remaining obligations of British Rail were transferred to BRB (Residuary) Limited.
The privatisation, proposed by the Conservative government in 1992, was opposed by the Labour Party and the rail unions. Although Labour initially proposed to reverse privatisation, the New Labour manifesto of 1997 instead opposed Conservative plans to privatise the London Underground. Rail unions have historically opposed privatisation, but former Associated Society of Locomotive Engineers and Firemen general secretary
The Waterloo & City line, part of Network SouthEast, was not included in the privatisation and was transferred to London Underground in April 1994. The remaining obligations of British Rail were transferred to BRB (Residuary) Limited.
The privatisation, proposed by the Conservative government in 1992, was opposed by the Labour Party and the rail unions. Although Labour initially proposed to reverse privatisation, the New Labour manifesto of 1997 instead opposed Conservative plans to privatise the London Underground. Rail unions have historically opposed privatisation, but former Associated Society of Locomotive Engineers and Firemen general secretary Lew Adams
Lewis Drummond Adams (born 16 August 1939) is a British former trade unionist.
Adams was educated at Impington Village College near Cambridge, then started his career with British Rail at the age of 15,
moved to work for Virgin Rail Group, and said on a 2004 radio phone-in programme: "All the time it was in the public sector, all we got were cuts, cuts, cuts. And today, there are more members in the trade union, more train drivers, and more trains running. The reality is that it worked, we’ve protected jobs, and we got more jobs."
The privatisation process began in 1994 when BR's passenger sectors were divided into 25 shadow franchise
The privatisation of British Rail was the process by which ownership and operation of the railways of Great Britain passed from government control into private hands. Begun in 1994, it had been completed by 1997. The deregulation of the indust ...
s. These were publicly owned TOCs operating in the planned franchise areas, prior to the actual franchises being put to tender.
In advance of the opening of the Channel Tunnel
The Channel Tunnel (french: Tunnel sous la Manche), also known as the Chunnel, is a railway tunnel that connects Folkestone (Kent, England, UK) with Coquelles ( Hauts-de-France, France) beneath the English Channel at the Strait of Dover. ...
in 1994, European Passenger Services was created as the BR division responsible for the UK component of Eurostar international services.
Successor companies
Under the process of British Rail's privatisation, operations were split into 125 companies between 1994 and 1997. The ownership and operation of the infrastructure of the railway system was taken over by Railtrack. The telecommunications infrastructure and British Rail Telecommunications was sold to Racal, which in turn was sold to Global Crossing and merged with Thales Group. The rolling stock was transferred to three private rolling stock companies (ROSCOs); Angel Trains, Eversholt Rail Group and Porterbrook. Passenger services were divided into 25 operating companies, which were let on a franchise basis for a set period, whilst freight services were sold off completely. Dozens of smaller engineering and maintenance companies were also created and sold off. British Rail's passenger services came to an end upon the franchising ofScotRail
ScotRail Trains Limited, trading as ScotRail ( gd, Rèile na h-Alba), is a Scottish train operating company that is publicly owned by Scottish Rail Holdings on behalf of the Scottish Government. It has been operating the ScotRail franchise a ...
with the last service being a '' Caledonian Sleeper'' service from Glasgow and Edinburgh to London on 31 March 1997. The final service it operated was a Railfreight Distribution freight train from Dollands Moor
Dollands Moor Freight Yard is a railway freight yard near Folkestone in Kent, and was purpose built in 1988 for the Channel Tunnel. It is to the west of the Eurotunnel Folkestone Terminal, and just to the south of the M20 Motorway.
Descrip ...
to Wembley on 20 November 1997. The British Railways Board continued in existence as a corporation until early 2001, when it was replaced by the Strategic Rail Authority
The Strategic Rail Authority (SRA) was a non-departmental public body in the United Kingdom set up under the Transport Act 2000 to provide strategic direction for Rail transport in the United Kingdom, the railway industry. Its motto was 'Brita ...
as part of the implementation of the Transport Act 2000.
The original passenger franchisees were:
* Anglia Railways
Anglia Railways was a train operating company in England, owned by GB Railways and later FirstGroup, that operated the Anglia franchise from January 1997 until March 2004.
History
The InterCity Anglia franchise was awarded by the Director of P ...
* Arriva Trains Merseyside
Arriva Trains Merseyside was a train operating company in England owned by Arriva that operated the Merseyrail Electrics franchise from January 1997 until July 2003, when the Merseyrail railway franchise was transformed into the local Merseyrai ...
* Arriva Trains Northern
Arriva Trains Northern was a train operating company in England owned by Arriva that operated the Regional Railways North East franchise from March 1997 until December 2004. Arriva resumed operating Northern train services again on 1 April 2016 ...
* Central Trains
* Chiltern Railways
Chiltern Railways, formally The Chiltern Railway Company Limited, is a British train operating company that has operated the Chiltern Railways franchise since July 1996. Since 2009, it has been a subsidiary of Arriva UK Trains.
Chiltern Railw ...
* Connex South Central
* Connex South Eastern
* c2c
* First Great Eastern
* First Great Western
* First North Western
* Gatwick Express
* GNER
* Island Line
* Midland Mainline
* ScotRail
ScotRail Trains Limited, trading as ScotRail ( gd, Rèile na h-Alba), is a Scottish train operating company that is publicly owned by Scottish Rail Holdings on behalf of the Scottish Government. It has been operating the ScotRail franchise a ...
* Silverlink
* South West Trains
* Thames Trains
* Thameslink
* Valley Lines
* Virgin CrossCountry
* Virgin Trains West Coast
* WAGN
* Wales & West
Future
Since privatisation, many groups have campaigned for the renationalisation of UK Rail services, most notably ' Bring Back British Rail'. Various interested parties also have views on the privatisation of British Rail. The renationalisation of the railways of Britain continues to have popular support. Polls in 2012 and 2013 showed 70% and 66% support for renationalisation, respectively.
Due to rail franchises sometimes lasting over a decade, full renationalisation would take years unless compensation was paid to terminate contracts early.
When the infrastructure-owning company Railtrack ceased trading in 2002, the Labour government set up the not-for-dividend company Network Rail to take over the duties rather than renationalise this part of the network. However, in September 2014, Network Rail was reclassified as a central government body, adding around £34 billion to public sector net debt. This reclassification had been requested by the Office for Budget Responsibility to comply with pan-European accounting standard ESA10.
The
The renationalisation of the railways of Britain continues to have popular support. Polls in 2012 and 2013 showed 70% and 66% support for renationalisation, respectively.
Due to rail franchises sometimes lasting over a decade, full renationalisation would take years unless compensation was paid to terminate contracts early.
When the infrastructure-owning company Railtrack ceased trading in 2002, the Labour government set up the not-for-dividend company Network Rail to take over the duties rather than renationalise this part of the network. However, in September 2014, Network Rail was reclassified as a central government body, adding around £34 billion to public sector net debt. This reclassification had been requested by the Office for Budget Responsibility to comply with pan-European accounting standard ESA10.
The Green party
A green party is a formally organized political party based on the principles of green politics, such as social justice, environmentalism and nonviolence.
Greens believe that these issues are inherently related to one another as a foundation ...
has committed to bringing the railways 'back into public ownership' and has maintained this impetus when other parties argued to maintain the status quo. In 2016, Green MP, Caroline Lucas
Caroline Patricia Lucas (born 9 December 1960) is a British politician who has twice led the Green Party of England and Wales and has been the Member of Parliament (MP) for Brighton Pavilion since the 2010 general election. She was re-elected ...
, put forward a Bill
Bill(s) may refer to:
Common meanings
* Banknote, paper cash (especially in the United States)
* Bill (law), a proposed law put before a legislature
* Invoice, commercial document issued by a seller to a buyer
* Bill, a bird or animal's beak
Plac ...
that would have seen the rail network fall back into public ownership step by step, as franchises come up for expiry.
Under Jeremy Corbyn (2015–2020), the Labour Party pledged to gradually renationalise British Rail franchises if elected, as and when their private contracts expire, creating a "People's Railway". In a pledge during his successful leadership campaign to succeed Corbyn, Keir Starmer said that renationalising rail would remain as Labour Party policy under his leadership. This was further outlined in April 2024 when the party announced that a Labour government would transfer passenger rail networks to public ownership within its first term.
Following the COVID-19 pandemic decimating franchise revenues and making them unviable, in 2021 the government announced it would take back responsibility for the operations of passenger services through Great British Railways with service provision to be contracted to private operators.
Parodies
In 1989, theITV
ITV or iTV may refer to:
ITV
*Independent Television (ITV), a British television network, consisting of:
** ITV (TV network), a free-to-air national commercial television network covering the United Kingdom, the Isle of Man, and the Channel Islan ...
sketch show '' Spitting Image'' parodied Hugh Hudson's 1988 ''British Rail, Britain's Railway'' advert on the plans of the then Conservative British Government
ga, Rialtas a Shoilse gd, Riaghaltas a Mhòrachd
, image = HM Government logo.svg
, image_size = 220px
, image2 = Royal Coat of Arms of the United Kingdom (HM Government).svg
, image_size2 = 180px
, caption = Royal Arms
, date_es ...
to privatise
Privatization (also privatisation in British English) can mean several different things, most commonly referring to moving something from the public sector into the private sector. It is also sometimes used as a synonym for deregulation when ...
the railways featuring many of the show's puppets (including the show's portrayal of Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher), numerous BR trains and landmarks and even a cardboard cutout of Thomas the Tank Engine.
See also
History
*History of rail transport in Great Britain
:''This article is part of the history of rail transport by country series.''
The railway system of Great Britain started with the building of local isolated wooden wagonways starting in the 1560s. A patchwork of local rail links operated by s ...
* Impact of the privatisation of British Rail
Divisions, brands and liveries
*British Rail brand names
British Rail was the brand image of the nationalised railway owner and operator in Great Britain, the British Railways Board, used from 1965 until its breakup and sell-off from 1993 onwards.
From an initial standardised corporate image, severa ...
* British Rail corporate liveries
The history of British Rail's corporate liveries is quite complex. Although from the mid-1960s to the 1980s the organisation was associated with "Rail Blue", a number of other schemes were also used, especially when it was split into operating u ...
* List of companies operating trains in the United Kingdom
Classification and numbering schemes
*British carriage and wagon numbering and classification
A number of different numbering and classification schemes have been used for carriages and wagons on Britain's railways, and this page explains the principal systems. Carriages and wagons (either not self-propelled, or part of a multiple unit wh ...
* British Rail locomotive and multiple unit numbering and classification
* List of British Rail classes
Rolling stock
*List of British Railways steam locomotives as of 31 December 1967
List of British Railways steam locomotives as of 31 December 1967. The following is a list of British Railways steam locomotives as of the end of 1967. With main line steam ending in August 1968, these are the ones that survived to the last year. ...
* List of LMS locomotives as of 31 December 1947
* List of LNER locomotives as of 31 December 1947
The following is a list of locomotives of the London and North Eastern Railway as of 31 December 1947. This date is significant because nationalisation of the Big Four occurred the next day, 1 January 1948. Thus this is the list of locomotives ...
Other
*British Rail flying saucer
The British Rail flying saucer, officially known simply as ''space vehicle'', was a proposed interplanetary spacecraft designed by Charles Osmond Frederick. Although the proposed craft required controlled thermonuclear fusion and other futuristi ...
* British Rail sandwich
In British popular culture, the phrase British Rail sandwich recollects the sandwiches sold for consumption on passenger trains of the former British Rail (BR), during the period of nationalization from 1948 to 1994. Its use arose through comedi ...
* British Transport Films
British Transport Films was an organisation set up in 1949 to make documentary films on the general subject of British transport. Its work included internal training films, travelogues (extolling the virtues of places that could be visited via th ...
* British Transport Police
* Channel Tunnel
The Channel Tunnel (french: Tunnel sous la Manche), also known as the Chunnel, is a railway tunnel that connects Folkestone (Kent, England, UK) with Coquelles ( Hauts-de-France, France) beneath the English Channel at the Strait of Dover. ...
*
* National Association of Railway Clubs
* Rail transport in Great Britain
* The wrong type of snow
References
Citations
Bibliography
* * *Further reading
* , on nationalization 1945–50, pp 236–83 *External links
British Railways Board history
BRB (Residuary) Ltd.
Catalogue of the BR Technical Research Department archives
held at the
Modern Records Centre, University of Warwick
The Modern Records Centre (MRC) is the specialist archive service of the University of Warwick in Coventry, England, located adjacent to the Central Campus Library. It was established in October 1973 and holds the world's largest archive collecti ...
{{Authority control
British companies established in 1948
Defunct railway companies of the United Kingdom
Former nationalised industries of the United Kingdom
Railway companies established in 1948
Railway companies disestablished in 1997
1948 establishments in the United Kingdom
1997 disestablishments in the United Kingdom