
The history of rail transport began in the BCE times. It can be divided into several discrete periods defined by the principal means of track material and motive power used.
Ancient systems
The
Post Track
The Post Track is an ancient causeway in the valley of the River Brue on the Somerset Levels, England. It dates from around 3838 BCE, making it some 30 years older than the Sweet Track in the same area. Various sections have been scheduled as an ...
, a prehistoric
causeway
A causeway is a track, road or railway on the upper point of an embankment across "a low, or wet place, or piece of water". It can be constructed of earth, masonry, wood, or concrete. One of the earliest known wooden causeways is the Sweet Tra ...
in the valley of the
River Brue in the
Somerset Levels, England, is one of the oldest known constructed trackways and dates from around 3838 BC, making it some 30 years older than the
Sweet Track from the same area.
Various sections have been designated as
scheduled monument
In the United Kingdom, a scheduled monument is a nationally important archaeological site or historic building, given protection against unauthorised change.
The various pieces of legislation that legally protect heritage assets from damage and d ...
s.
Evidence indicates that there was a 6 to 8.5 km long ''
Diolkos
The Diolkos (, from the Greek , "across", and , "portage machine") was a paved trackway near Corinth in Ancient Greece which enabled boats to be moved overland across the Isthmus of Corinth. The shortcut allowed ancient vessels to avoid the ...
'' paved trackway, which transported boats across the
Isthmus of Corinth
The Isthmus of Corinth (Greek: Ισθμός της Κορίνθου) is the narrow land bridge which connects the Peloponnese peninsula with the rest of the mainland of Greece, near the city of Corinth. The word "isthmus" comes from the Ancien ...
in
Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with ...
from around 600 BC.
[Cook, R. M.: "Archaic Greek Trade: Three Conjectures 1. The Diolkos", ''The Journal of Hellenic Studies'', vol. 99 (1979), pp. 152–155 (152)][Lewis, M. J. T.]
"Railways in the Greek and Roman world"
, in Guy, A. / Rees, J. (eds), ''Early Railways. A Selection of Papers from the First International Early Railways Conference'' (2001), pp. 8–19 (11) Wheeled vehicles pulled by men and animals ran in grooves in
limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
, which provided the track element, preventing the wagons from leaving the intended route. The Diolkos was in use for over 650 years, until at least the 1st century AD.
Paved trackways were also later built in
Roman Egypt
, conventional_long_name = Roman Egypt
, common_name = Egypt
, subdivision = Province
, nation = the Roman Empire
, era = Late antiquity
, capital = Alexandria
, title_leader = Praefectus Augustalis
, image_map = Roman E ...
.
In China, a railway has been discovered in south west
Henan
Henan (; or ; ; alternatively Honan) is a landlocked province of China, in the central part of the country. Henan is often referred to as Zhongyuan or Zhongzhou (), which literally means "central plain" or "midland", although the name is al ...
province near Nanyang city. It was carbon dated to be about 2200 years old from the Qin dynasty. The rails are made from hard wood and treated against corrosion while the sleepers or railway ties are made from wood that was not treated and therefore has rotted. Qin railway sleepers were designed to allow horses to gallop through to the next rail station where they would be swapped for a fresh horse. The railway is theorized to have been used for transportation of goods to front line troops and to fix the Great Wall.
Pre-steam
Wooden rails introduced
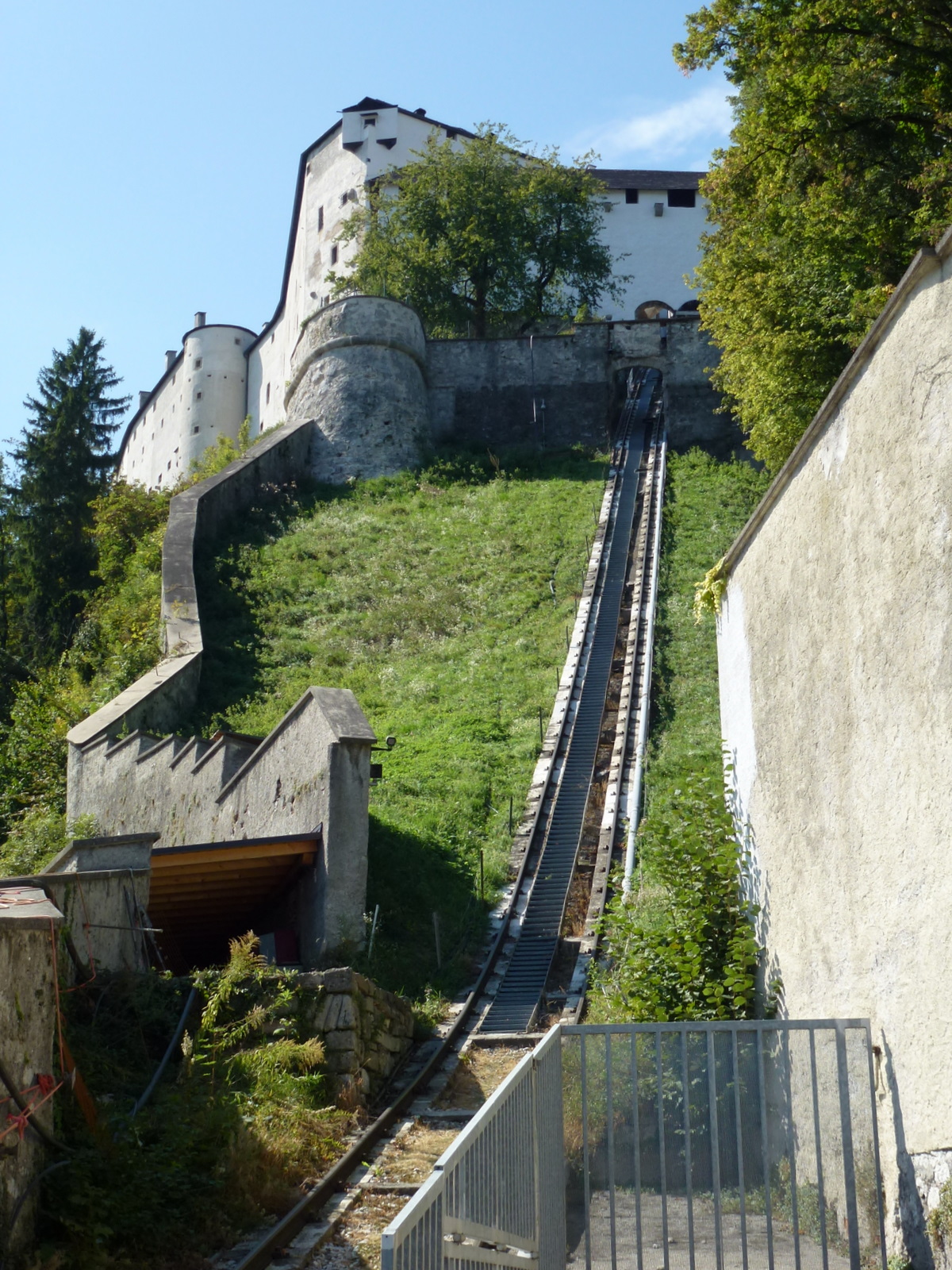

In 1515,
Cardinal Matthäus Lang wrote a description of the
Reisszug
The Reisszug (also spelt Reißzug or Reiszug) is a private cable railway providing goods access to the Hohensalzburg Castle at Salzburg in Austria. It is notable for its extreme age, as it is believed to date back to either 1495 or 1504.
The Reis ...
, a
funicular
A funicular (, , ) is a type of cable railway system that connects points along a railway track laid on a steep slope. The system is characterized by two counterbalanced carriages (also called cars or trains) permanently attached to opposite en ...
railway at the
Hohensalzburg Fortress in Austria. The line originally used wooden rails and a
hemp
Hemp, or industrial hemp, is a botanical class of ''Cannabis sativa'' cultivars grown specifically for industrial or medicinal use. It can be used to make a wide range of products. Along with bamboo, hemp is among the fastest growing plants o ...
haulage rope and was operated by human or animal power, through a
treadwheel
A treadwheel, or treadmill, is a form of engine typically powered by humans. It may resemble a water wheel in appearance, and can be worked either by a human treading paddles set into its circumference (treadmill), or by a human or animal standing ...
.
The line still exists and remains operational, although in updated form. It may be the oldest operational railway.

Wagonway
Wagonways (also spelt Waggonways), also known as horse-drawn railways and horse-drawn railroad consisted of the horses, equipment and tracks used for hauling wagons, which preceded Steam locomotive, steam-powered rail transport, railways. The t ...
s (or
tramways), with wooden rails and horse-drawn traffic, are known to have been used in the 1550s to facilitate transportation of ore tubs to and from mines. They soon became popular in Europe and an example of their operation was illustrated by
Georgius Agricola (see image) in his 1556 work ''
De re metallica''.
[Georgius Agricola (trans Hoover), '' De re metallica'' (1913), p. 156.] This line used "Hund" carts with unflanged wheels running on wooden planks and a vertical pin on the truck fitting into the gap between the planks to keep it going the right way. The miners called the wagons ''Hunde'' ("dogs") from the noise they made on the tracks.
There are many references to wagonways in central Europe in the 16th century.
A wagonway was introduced to England by
German miners at
Caldbeck,
Cumbria
Cumbria ( ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in North West England, bordering Scotland. The county and Cumbria County Council, its local government, came into existence in 1974 after the passage of the Local Government Act 1972. Cumb ...
, possibly in the 1560s.
[Warren Allison, Samuel Murphy and Richard Smith, ''An Early Railway in the German Mines of Caldbeck'' in G. Boyes (ed.), ''Early Railways 4: Papers from the 4th International Early Railways Conference 2008'' (Six Martlets, Sudbury, 2010), pp. 52–69.] A wagonway was built at
Prescot, near
Liverpool
Liverpool is a city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. With a population of in 2019, it is the 10th largest English district by population and its metropolitan area is the fifth largest in the United Kingdom, with a popul ...
, sometime around 1600, possibly as early as 1594. Owned by Philip Layton, the line carried coal from a pit near Prescot Hall to a terminus about half a mile away.
A funicular railway was made at
Broseley in
Shropshire
Shropshire (; alternatively Salop; abbreviated in print only as Shrops; demonym Salopian ) is a landlocked historic county in the West Midlands region of England. It is bordered by Wales to the west and the English counties of Cheshire to th ...
some time before 1604. This carried coal for James Clifford from his mines down to the
river Severn
, name_etymology =
, image = SevernFromCastleCB.JPG
, image_size = 288
, image_caption = The river seen from Shrewsbury Castle
, map = RiverSevernMap.jpg
, map_size = 288
, map_c ...
to be loaded onto barges and carried to riverside towns. The
Wollaton Wagonway, completed in 1604 by
Huntingdon Beaumont, has sometimes erroneously been cited as the earliest British railway. It ran from
Strelley to
Wollaton near
Nottingham
Nottingham ( , East Midlands English, locally ) is a city status in the United Kingdom, city and Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority area in Nottinghamshire, East Midlands, England. It is located north-west of London, south-east ...
.
The
Middleton Railway in
Leeds
Leeds () is a city and the administrative centre of the City of Leeds district in West Yorkshire, England. It is built around the River Aire and is in the eastern foothills of the Pennines. It is also the third-largest settlement (by populati ...
, which was built in 1758, later became the world's oldest operational railway (other than funiculars), albeit now in an upgraded form. In 1764, the first railway in America was built in
Lewiston, New York.
Metal rails introduced


The introduction of steam engines for powering blast air to
blast furnace
A blast furnace is a type of metallurgical furnace used for smelting to produce industrial metals, generally pig iron, but also others such as lead or copper. ''Blast'' refers to the combustion air being "forced" or supplied above atmospheric ...
s led to a large increase in British iron production after the mid 1750s.
In the late 1760s, the
Coalbrookdale
Coalbrookdale is a village in the Ironbridge Gorge in Shropshire, England, containing a settlement of great significance in the history of iron ore smelting. It lies within the civil parish called the Gorge.
This is where iron ore was first s ...
Company began to fix plates of
cast iron
Cast iron is a class of iron–carbon alloys with a carbon content more than 2%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloy constituents affect its color when fractured: white cast iron has carbide impuriti ...
to the upper surface of wooden rails, which increased their durability and load-bearing ability. At first only
balloon loops could be used for turning wagons, but later, movable points were introduced that allowed
passing loop
A passing loop (UK usage) or passing siding (North America) (also called a crossing loop, crossing place, refuge loop or, colloquially, a hole) is a place on a single line railway or tramway, often located at or near a station, where trains or ...
s to be created.
A system was introduced in which unflanged wheels ran on L-shaped metal plates these became known as
plateways.
John Curr
John Curr (c. 1756 – 27 January 1823) was the manager or viewer of the Duke of Norfolk's collieries in Sheffield, England from 1781 to 1801. During this time he made a number of innovations that contributed significantly to the development of t ...
, a Sheffield colliery manager, invented this flanged rail in 1787, though the exact date of this is disputed. The plate rail was taken up by
Benjamin Outram for wagonways serving his canals, manufacturing them at his
Butterley ironworks. In 1803,
William Jessop opened the
Surrey Iron Railway, a double track plateway, sometimes erroneously cited as world's first public railway, in south London.
In 1789,
William Jessop had introduced a form of all-iron
edge rail and flanged wheels for an extension to the
Charnwood Forest Canal at
Nanpantan,
Loughborough,
Leicestershire
Leicestershire ( ; postal abbreviation Leics.) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in the East Midlands, England. The county borders Nottinghamshire to the north, Lincolnshire to the north-east, Rutland to the east, Northamptonshire t ...
. In 1790, Jessop and his partner Outram began to manufacture edge-rails. Jessop became a partner in the Butterley Company in 1790. The first public edgeway (thus also first public railway) built was the
Lake Lock Rail Road in 1796. Although the primary purpose of the line was to carry coal, it also carried passengers.
These two systems of constructing iron railways, the "L" plate-rail and the smooth edge-rail, continued to exist side by side into the early 19th century. The flanged wheel and edge-rail eventually proved its superiority and became the standard for railways.

Cast iron was not a satisfactory material for rails because it was brittle and broke under heavy loads. The wrought iron rail, invented by
John Birkinshaw
John Birkinshaw (1777-1842) was a 19th-century railway engineer from Bedlington, Northumberland noted for his invention of wrought iron rails in 1820 (patented on October 23, 1820).
Up to this point, rail systems had used either wooden rails, w ...
in 1820, solved these problems.
Wrought iron
Wrought iron is an iron alloy with a very low carbon content (less than 0.08%) in contrast to that of cast iron (2.1% to 4%). It is a semi-fused mass of iron with fibrous slag Inclusion (mineral), inclusions (up to 2% by weight), which give it a ...
(usually simply referred to as "iron") was a
ductile material that could undergo considerable deformation before breaking, making it more suitable for iron rails. But wrought iron was expensive to produce until
Henry Cort patented the
puddling process in 1784. In 1783, Cort also patented the
rolling process, which was 15 times faster at consolidating and shaping iron than hammering. These processes greatly lowered the cost of producing iron and iron rails. The next important development in iron production was
hot blast developed by
James Beaumont Neilson
James Beaumont Neilson (22 June 1792 – 18 January 1865) was a Scotland, Scottish inventor whose hot blast, hot-blast process greatly increased the efficiency of smelting iron.
Life
He was the son of the engineer Walter Neilson, a millwri ...
(patented 1828), which considerably reduced the amount of
coke (fuel)
Coke is a grey, hard, and porous coal-based fuel with a high carbon content and few impurities, made by heating coal or oil in the absence of air—a destructive distillation process. It is an important industrial product, used mainly in iro ...
or charcoal needed to produce
pig iron
Pig iron, also known as crude iron, is an intermediate product of the iron industry in the production of steel which is obtained by smelting iron ore in a blast furnace. Pig iron has a high carbon content, typically 3.8–4.7%, along with silic ...
. Wrought iron was a soft material that contained slag or ''dross''. The softness and dross tended to make iron rails distort and delaminate and they typically lasted less than 10 years in use, and sometimes as little as one year under high traffic. All these developments in the production of iron eventually led to replacement of composite wood/iron rails with superior all-iron rails.
The introduction of the
Bessemer process, enabling steel to be made inexpensively, led to the era of great expansion of railways that began in the late 1860s. Steel rails lasted several times longer than iron.
Steel rails made heavier locomotives possible, allowing for longer trains and improving the productivity of railroads. The Bessemer process introduced nitrogen into the steel, which caused the steel to become brittle with age. The
open hearth furnace began to replace the Bessemer process near the end of 19th century, improving the quality of steel and further reducing costs. Steel completely replaced the use of iron in rails, becoming standard for all railways.
Steam power introduced
James Watt
James Watt (; 30 January 1736 (19 January 1736 OS) – 25 August 1819) was a Scottish inventor, mechanical engineer, and chemist who improved on Thomas Newcomen's 1712 Newcomen steam engine with his Watt steam engine in 1776, which was fun ...
, a Scottish inventor and mechanical engineer, greatly improved the
steam engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be trans ...
of
Thomas Newcomen
Thomas Newcomen (; February 1664 – 5 August 1729) was an English inventor who created the atmospheric engine, the first practical fuel-burning engine in 1712. He was an ironmonger by trade and a Baptist lay preacher by calling.
He ...
, hitherto used to pump water out of mines. Watt developed a
reciprocating engine
A reciprocating engine, also often known as a piston engine, is typically a heat engine that uses one or more reciprocating pistons to convert high temperature and high pressure into a rotating motion. This article describes the common featu ...
in 1769, capable of powering a wheel. Although the Watt engine powered cotton mills and a variety of machinery, it was a large
stationary engine
A stationary engine is an engine whose framework does not move. They are used to drive immobile equipment, such as pumps, generators, mills or factory machinery, or cable cars. The term usually refers to large immobile reciprocating engines, pr ...
. It could not be otherwise: the state of boiler technology necessitated the use of low pressure steam acting upon a vacuum in the cylinder; this required a separate
condenser and an
air pump
An air pump is a pump for pushing air. Examples include a bicycle pump, pumps that are used to aerate an aquarium or a pond via an airstone; a gas compressor used to power a pneumatic tool, air horn or pipe organ; a bellows used to encourage ...
. Nevertheless, as the construction of boilers improved, Watt investigated the use of high-pressure steam acting directly upon a piston. This raised the possibility of a smaller engine, that might be used to power a vehicle and he patented a design for a
steam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, oil or, rarely, wood) to heat water in the locomot ...
in 1784. His employee
William Murdoch
William Murdoch (sometimes spelled Murdock) (21 August 1754 – 15 November 1839) was a Scottish engineer and inventor.
Murdoch was employed by the firm of Boulton & Watt and worked for them in Cornwall, as a steam engine erector for ten yea ...
produced a working model of a self-propelled steam carriage in that year.

The first full-scale working railway
steam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, oil or, rarely, wood) to heat water in the locomot ...
was built in the United Kingdom in 1804 by
Richard Trevithick, a British engineer born in
Cornwall
Cornwall (; kw, Kernow ) is a historic county and ceremonial county in South West England. It is recognised as one of the Celtic nations, and is the homeland of the Cornish people. Cornwall is bordered to the north and west by the Atlantic ...
. This used high-pressure steam to drive the engine by one power stroke. The transmission system employed a large
flywheel
A flywheel is a mechanical device which uses the conservation of angular momentum to store rotational energy; a form of kinetic energy proportional to the product of its moment of inertia and the square of its rotational speed. In particular, ass ...
to even out the action of the piston rod. On 21 February 1804, the world's first steam-powered railway journey took place when Trevithick's unnamed steam locomotive hauled a train along the tramway of the
Penydarren ironworks, near
Merthyr Tydfil
Merthyr Tydfil (; cy, Merthyr Tudful ) is the main town in Merthyr Tydfil County Borough, Wales, administered by Merthyr Tydfil County Borough Council. It is about north of Cardiff. Often called just Merthyr, it is said to be named after Tydf ...
in
South Wales
South Wales ( cy, De Cymru) is a loosely defined region of Wales bordered by England to the east and mid Wales to the north. Generally considered to include the historic counties of Glamorgan and Monmouthshire, south Wales extends westwards ...
. Trevithick later demonstrated a locomotive operating upon a piece of circular rail track in
Bloomsbury
Bloomsbury is a district in the West End of London. It is considered a fashionable residential area, and is the location of numerous cultural, intellectual, and educational institutions.
Bloomsbury is home of the British Museum, the largest mus ...
, London, the ''
Catch Me Who Can
''Catch Me Who Can'' was the fourth and last steam railway locomotive created by the inventor and mining engineer Richard Trevithick. It was an evolution of three earlier locomotives which had been built for Coalbrookdale, Penydarren ironwork ...
'', but never got beyond the experimental stage with railway locomotives, not least because his engines were too heavy for the cast-iron plateway track then in use.
The first commercially successful steam locomotive was
Matthew Murray's
rack
Rack or racks may refer to:
Storage and installation
* Amp rack, short for amplifier rack, a piece of furniture in which amplifiers are mounted
* Bicycle rack, a frame for storing bicycles when not in use
* Bustle rack, a type of storage bin ...
locomotive ''
Salamanca'' built for the
Middleton Railway in
Leeds
Leeds () is a city and the administrative centre of the City of Leeds district in West Yorkshire, England. It is built around the River Aire and is in the eastern foothills of the Pennines. It is also the third-largest settlement (by populati ...
in 1812. This twin-cylinder locomotive was not heavy enough to break the
edge-rails track and solved the problem of
adhesion
Adhesion is the tendency of dissimilar particles or surfaces to cling to one another ( cohesion refers to the tendency of similar or identical particles/surfaces to cling to one another).
The forces that cause adhesion and cohesion can be ...
by a
cog-wheel using teeth cast on the side of one of the rails. Thus it was also the first
rack railway
A rack railway (also rack-and-pinion railway, cog railway, or cogwheel railway) is a steep grade railway with a toothed rack rail, usually between the running rails. The trains are fitted with one or more cog wheels or pinions that mesh with ...
.
This was followed in 1813 by the locomotive ''
Puffing Billy'' built by
Christopher Blackett and
William Hedley for the
Wylam Colliery Railway, the first successful locomotive running by
adhesion
Adhesion is the tendency of dissimilar particles or surfaces to cling to one another ( cohesion refers to the tendency of similar or identical particles/surfaces to cling to one another).
The forces that cause adhesion and cohesion can be ...
only. This was accomplished by the distribution of weight between a number of wheels. ''Puffing Billy'' is now on display in the
Science Museum
A science museum is a museum devoted primarily to science. Older science museums tended to concentrate on static displays of objects related to natural history, paleontology, geology, industry and industrial machinery, etc. Modern trends in mu ...
in London, making it the oldest locomotive in existence.

In 1814,
George Stephenson, inspired by the early locomotives of Trevithick, Murray and Hedley, persuaded the manager of the
Killingworth colliery where he worked to allow him to build a
steam-powered machine. Stephenson played a pivotal role in the development and widespread adoption of the steam locomotive. His designs considerably improved on the work of the earlier pioneers. He built the locomotive ''
Blücher'', also a successful
flange
A flange is a protruded ridge, lip or rim (wheel), rim, either external or internal, that serves to increase shear strength, strength (as the flange of an iron beam (structure), beam such as an I-beam or a T-beam); for easy attachment/transfer of ...
d-wheel adhesion locomotive. In 1825, he built the locomotive ''
Locomotion'' for the
Stockton and Darlington Railway
The Stockton and Darlington Railway (S&DR) was a railway company that operated in north-east England from 1825 to 1863. The world's first public railway to use steam locomotives, its first line connected collieries near Shildon with Darl ...
in the north east of England, which became the first public steam railway in the world, although it used both horse power and steam power on different runs. In 1829, he built the locomotive ''
Rocket
A rocket (from it, rocchetto, , bobbin/spool) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using the surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely fr ...
'', which entered in and won the
Rainhill Trials. This success led to Stephenson establishing his company as the pre-eminent builder of steam locomotives for railways in Great Britain and Ireland, the United States, and much of Europe.
The first public railway which used only steam locomotives, all the time, was
Liverpool and Manchester Railway, built in 1830.
Steam power continued to be the dominant power system in railways around the world for more than a century.
Electric power introduced
The first known electric locomotive was built in 1837 by chemist
Robert Davidson of
Aberdeen
Aberdeen (; sco, Aiberdeen ; gd, Obar Dheathain ; la, Aberdonia) is a city in North East Scotland, and is the third most populous city in the country. Aberdeen is one of Scotland's 32 local government council areas (as Aberdeen City), and ...
in Scotland, and it was powered by
galvanic cells (batteries). Thus it was also the earliest battery electric locomotive. Davidson later built a larger locomotive named ''Galvani'', exhibited at the
Royal Scottish Society of Arts Exhibition in 1841. The seven-ton vehicle had two
direct-drive
A direct-drive mechanism is a mechanism design where the force or torque from a prime mover is transmitted directly to the effector device (such as the drive wheels of a vehicle) without involving any intermediate couplings such as a gear train or ...
reluctance motor
A reluctance motor is a type of electric motor that induces non-permanent magnetic poles on the ferromagnetic rotor. The rotor does not have any windings. It generates torque through magnetic reluctance.
Reluctance motor subtypes include synchro ...
s, with fixed electromagnets acting on iron bars attached to a wooden cylinder on each axle, and simple
commutators
In mathematics, the commutator gives an indication of the extent to which a certain binary operation fails to be commutative. There are different definitions used in group theory and ring theory.
Group theory
The commutator of two elements, a ...
. It hauled a load of six tons at four miles per hour (6 kilometers per hour) for a distance of . It was tested on the
Edinburgh and Glasgow Railway
The Edinburgh and Glasgow Railway was authorised by Act of Parliament on 4 July 1838. It was opened to passenger traffic on 21 February 1842, between its Glasgow Queen Street railway station (sometimes referred to at first as Dundas Street) and ...
in September of the following year, but the limited power from batteries prevented its general use. It was destroyed by railway workers, who saw it as a threat to their job security.
[Renzo Pocaterra, ''Treni'', De Agostini, 2003]
Early experimentation with railway electrification was undertaken by the Ukrainian engineer
Fyodor Pirotsky
Fyodor Apollonovich Pirotsky or Fedir Apollonovych Pirotskyy ( ukr, Федір Аполлонович Піроцький; russian: Фёдор Аполлонович Пироцкий; -) was a Ukrainian engineer and inventor of the world's first ra ...
. In 1875, he had electrically-powered railway cars run on
Miller's line, between
Sestroretsk and
Beloostrov. During September 1880, in St. Petersburg, Pirotsky put into operation an electric tram he had converted from a double-decker
horse tramway
A horsecar, horse-drawn tram, horse-drawn streetcar (U.S.), or horse-drawn railway (historical), is an animal-powered (usually horse) tram or streetcar.
Summary
The horse-drawn tram (horsecar) was an early form of public rail transport, wh ...
. Although Pirotsky's own tram project was taken no further, his experiment and work in the field did stimulate interest in electric trams globally.
Carl von Siemens
Carl Heinrich von Siemens (often just Carl von Siemens) (3 March 1829 – 21 March 1906) was a German entrepreneur.
He was born in Menzendorf, Mecklenburg, one of the fourteen children of a tenant farmer of the Siemens family, an old family of G ...
met with Pirotsky and studied exhibits of his work carefully. The Siemens brothers (Carl and Werner) began commercial production of their own design of electric trams soon after, in 1881.

Werner von Siemens
Ernst Werner Siemens (von Siemens from 1888; ; ; 13 December 1816 – 6 December 1892) was a German electrical engineer, inventor and industrialist. Siemens's name has been adopted as the SI unit of electrical conductance, the siemens. He foun ...
demonstrated an electric railway in 1879 in Berlin. One of the world's first electric tram lines,
Gross-Lichterfelde Tramway, opened in
Lichterfelde Lichterfelde may refer to:
* Lichterfelde (Berlin), a locality in the borough of Steglitz-Zehlendorf in Berlin, Germany
* Lichterfelde West, an elegant residential area in Berlin
* Lichterfelde, Saxony-Anhalt, a municipality in the Stendhal Distric ...
near
Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's sixteen constitue ...
, Germany, in 1881. It was built by Siemens. The tram ran on 180 Volt DC, which was supplied by running rails. In 1891 the track was equipped with an
overhead wire
An overhead line or overhead wire is an electrical cable that is used to transmit electrical energy to electric locomotives, trolleybuses or trams. It is known variously as:
* Overhead catenary
* Overhead contact system (OCS)
* Overhead equipmen ...
and the line was extended to
Berlin-Lichterfelde West station
Berlin-Lichterfelde West (in German Bahnhof Berlin-Lichterfelde West) is a railway station in Lichterfelde West, within the district of Lichterfelde (Steglitz-Zehlendorf) in Berlin, Germany. It is served by the Berlin S-Bahn and several local bus l ...
. The
Volk's Electric Railway opened in 1883 in
Brighton
Brighton () is a seaside resort and one of the two main areas of the City of Brighton and Hove in the county of East Sussex, England. It is located south of London.
Archaeological evidence of settlement in the area dates back to the Bronze A ...
, England. The railway is still operational, thus making it the oldest operational electric railway in the world. Also in 1883,
Mödling and Hinterbrühl Tram
Mödling and Hinterbrühl Tram or ''Mödling and Hinterbrühl Local Railway'' (German: ''Lokalbahn Mödling–Hinterbrühl'') was an electric tramway in Austria, running 4.5 km (2.8 mi) from Mödling to Hinterbrühl, in the southwest ...
opened near Vienna in Austria. It was the first tram line in the world in regular service powered from an overhead line. Five years later, in the
US electric
trolleys were pioneered in 1888 on the
Richmond Union Passenger Railway, using equipment designed by
Frank J. Sprague
Frank Julian Sprague (July 25, 1857 in Milford, Connecticut – October 25, 1934) was an American inventor who contributed to the development of the electric motor, electric railways, and electric elevators. His contributions were especially i ...
.

The first use of electrification on a main line was on a four-mile stretch of the
Baltimore Belt Line of the
Baltimore and Ohio Railroad
The Baltimore and Ohio Railroad was the first common carrier railroad and the oldest railroad in the United States, with its first section opening in 1830. Merchants from Baltimore, which had benefited to some extent from the construction of ...
(B&O) in 1895 connecting the main portion of the B&O to the new line to
New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
through a series of tunnels around the edges of Baltimore's downtown.
Electricity quickly became the power supply of choice for subways, abetted by the Sprague's invention of multiple-unit train control in 1897. By the early 1900s, most street railways were electrified.
The first practical
AC electric locomotive was designed by
Charles Brown, then working for
Oerlikon, Zürich. In 1891, Brown had demonstrated long-distance power transmission, using
three-phase AC, between a
hydro-electric plant
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined and ...
at
Lauffen am Neckar
Lauffen am Neckar () or simply Lauffen is a town in the district of Heilbronn, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is on the river Neckar, southwest of Heilbronn. The town is famous as the birthplace of the poet Friedrich Hölderlin and for its qu ...
and
Frankfurt am Main
Frankfurt, officially Frankfurt am Main (; Hessian: , "Frank ford on the Main"), is the most populous city in the German state of Hesse. Its 791,000 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located on its na ...
West, a distance of 280 km. Using experience he had gained while working for
Jean Heilmann on steam-electric locomotive designs, Brown observed that
three-phase motors had a higher power-to-weight ratio than
DC motors and, because of the absence of a
commutator
In mathematics, the commutator gives an indication of the extent to which a certain binary operation fails to be commutative. There are different definitions used in group theory and ring theory.
Group theory
The commutator of two elements, a ...
, were simpler to manufacture and maintain. However, they were much larger than the DC motors of the time and could not be mounted in underfloor
bogie
A bogie ( ) (in some senses called a truck in North American English) is a chassis or framework that carries a wheelset, attached to a vehicle—a modular subassembly of wheels and axles. Bogies take various forms in various modes of transp ...
s: they could only be carried within locomotive bodies.
In 1894, Hungarian engineer
Kálmán Kandó
Kálmán Kandó de Egerfarmos et Sztregova (''egerfarmosi és sztregovai Kandó Kálmán''; 10 July 1869 – 13 January 1931) was a Hungarian engineer, the inventor of phase converter and a pioneer in the development of AC electric railway tract ...
developed a new type 3-phase asynchronous electric drive motors and generators for electric locomotives. Kandó's early 1894 designs were first applied in a short three-phase AC tramway in Evian-les-Bains (France), which was constructed between 1896 and 1898.
In 1896, Oerlikon installed the first commercial example of the system on the
Lugano Tramway. Each 30-tonne locomotive had two motors run by three-phase 750 V 40 Hz fed from double overhead lines. Three-phase motors run at constant speed and provide
regenerative braking, and are well suited to steeply graded routes, and the first main-line three-phase locomotives were supplied by Brown (by then in partnership with
Walter Boveri
Walter Boveri (born 21 February 1865 in Bamberg, Bavaria, died 28 October 1924 in Baden, Switzerland) was a Swiss-German industrialist and co-founder of the global electrical engineering group Brown, Boveri & Cie. (BBC).
Biography
Boveri's ances ...
) in 1899 on the 40 km
Burgdorf–Thun line, Switzerland.

Italian railways were the first in the world to introduce electric traction for the entire length of a main line rather than just a short stretch. The 106 km
Valtellina
Valtellina or the Valtelline (occasionally spelled as two words in English: Val Telline; rm, Vuclina (); lmo, Valtelina or ; german: Veltlin; it, Valtellina) is a valley in the Lombardy region of northern Italy, bordering Switzerland. Toda ...
line was opened on 4 September 1902, designed by Kandó and a team from the Ganz works.
The electrical system was three-phase at 3 kV 15 Hz. In 1918, Kandó invented and developed the
rotary phase converter, enabling electric locomotives to use three-phase motors whilst supplied via a single overhead wire, carrying the simple industrial frequency (50 Hz) single phase AC of the high voltage national networks.
An important contribution to the wider adoption of AC traction came from SNCF of France after World War II. The company conducted trials at 50 Hz, and established it as a standard. Following SNCF's successful trials, 50 Hz (now also called industrial frequency) was adopted as standard for main lines across the world.
Diesel power introduced

Earliest recorded examples of an internal combustion engine for railway use included a prototype designed by
William Dent Priestman, which was examined by
Sir William Thomson
William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin, (26 June 182417 December 1907) was a British mathematician, mathematical physicist and engineer born in Belfast. Professor of Natural Philosophy at the University of Glasgow for 53 years, he did important ...
in 1888 who described it as a "
riestmans' petroleum engine.. mounted upon a truck which is worked on a temporary line of rails to show the adaptation of a petroleum engine for locomotive purposes.". In 1894, a two axle machine built by
Priestman Brothers was used on the
Hull Docks.
In 1906,
Rudolf Diesel,
Adolf Klose
Adolf Klose (21 May 1844 – 2 September 1923) was the chief engineer of the Royal Württemberg State Railways in southern Germany from June 1885 to 1896.
Klose was born in Bernstadt auf dem Eigen, in Saxony. Before his taking up his post in Stu ...
and the steam and diesel engine manufacturer
Gebrüder Sulzer
Sulzer Ltd. is a Swiss industrial engineering and manufacturing firm, founded by Salomon Sulzer-Bernet in 1775 and established as Sulzer Brothers Ltd. (Gebrüder Sulzer) in 1834 in Winterthur, Switzerland. Today it is a publicly traded company w ...
founded Diesel-Sulzer-Klose GmbH to manufacture diesel-powered locomotives. Sulzer had been manufacturing diesel engines since 1898. The Prussian State Railways ordered a diesel locomotive from the company in 1909. The world's first diesel-powered locomotive was operated in the summer of 1912 on the
Winterthur–Romanshorn railway
The Winterthur–Romanshorn railway, also known in German as the ''Thurtallinie'' ("Thur valley line"), is a Swiss railway line and was built as part of the railway between Zürich and Lake Constance (Bodensee). It connects Winterthur with Romansh ...
in Switzerland, but was not a commercial success. The locomotive weight was 95 tonnes and the power was 883 kW with a maximum speed of 100 km/h. Small numbers of prototype diesel locomotives were produced in a number of countries through the mid-1920s.

A significant breakthrough occurred in 1914, when
Hermann Lemp
Hermann Lemp born: Heinrich Joseph Hermann Lemp (August 8, 1862 – March 31, 1954) was a Switzerland, Swiss-United States, American electrical engineer; he is credited as the inventor of the modern system of Diesel-electric transmission, di ...
, a
General Electric
General Electric Company (GE) is an American multinational conglomerate founded in 1892, and incorporated in New York state and headquartered in Boston. The company operated in sectors including healthcare, aviation, power, renewable energ ...
electrical engineer, developed and patented a reliable
direct current
Direct current (DC) is one-directional flow of electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through semiconductors, insulators, or even ...
electrical control system (subsequent improvements were also patented by Lemp). Lemp's design used a single lever to control both engine and generator in a coordinated fashion, and was the
prototype
A prototype is an early sample, model, or release of a product built to test a concept or process. It is a term used in a variety of contexts, including semantics, design, electronics, and Software prototyping, software programming. A prototyp ...
for all
diesel–electric locomotive control systems. In 1914, world's first functional diesel–electric railcars were produced for the ''Königlich-Sächsische Staatseisenbahnen'' (
Royal Saxon State Railways
The Royal Saxon State Railways (german: Königlich Sächsische Staatseisenbahnen) were the state-owned railways operating in the Kingdom of Saxony from 1869 to 1918. From 1918 until their merger into the Deutsche Reichsbahn the title 'Royal' was d ...
) by
Waggonfabrik Rastatt
( en, Rastatt Coach Factory) is a German public-limited company based in Rastatt in the state of Baden-Württemberg in southwestern Germany. Its chief products are tramway vehicles and railway coaches and wagons. The firm was founded in and b ...
with electric equipment from
Brown, Boveri & Cie
Brown, Boveri & Cie. (Brown, Boveri & Company; BBC) was a Swiss group of electrical engineering companies.
It was founded in Zürich, in 1891 by Charles Eugene Lancelot Brown and Walter Boveri who worked at the Maschinenfabrik Oerlikon. In 1 ...
and diesel engines from
Swiss
Swiss may refer to:
* the adjectival form of Switzerland
* Swiss people
Places
* Swiss, Missouri
* Swiss, North Carolina
*Swiss, West Virginia
* Swiss, Wisconsin
Other uses
*Swiss-system tournament, in various games and sports
*Swiss Internation ...
Sulzer AG. They were classified as . The first regular use of diesel–electric locomotives was in
switching (shunter) applications. General Electric produced several small switching locomotives in the 1930s (the famous "
44-tonner
The GE 44-ton switcher is a four-axle diesel-electric locomotive built by General Electric between 1940 and 1956. It was designed for industrial and light switching duties, often replacing steam locomotives that had previously been assigned thes ...
" switcher was introduced in 1940) Westinghouse Electric and Baldwin collaborated to build switching locomotives starting in 1929.
In 1929, the
Canadian National Railways
The Canadian National Railway Company (french: Compagnie des chemins de fer nationaux du Canada) is a Canadian Class I railroad, Class I freight railway headquartered in Montreal, Quebec, which serves Canada and the Midwestern United States, M ...
became the first North American railway to use diesels in mainline service with two units, 9000 and 9001, from Westinghouse.
High-speed rail
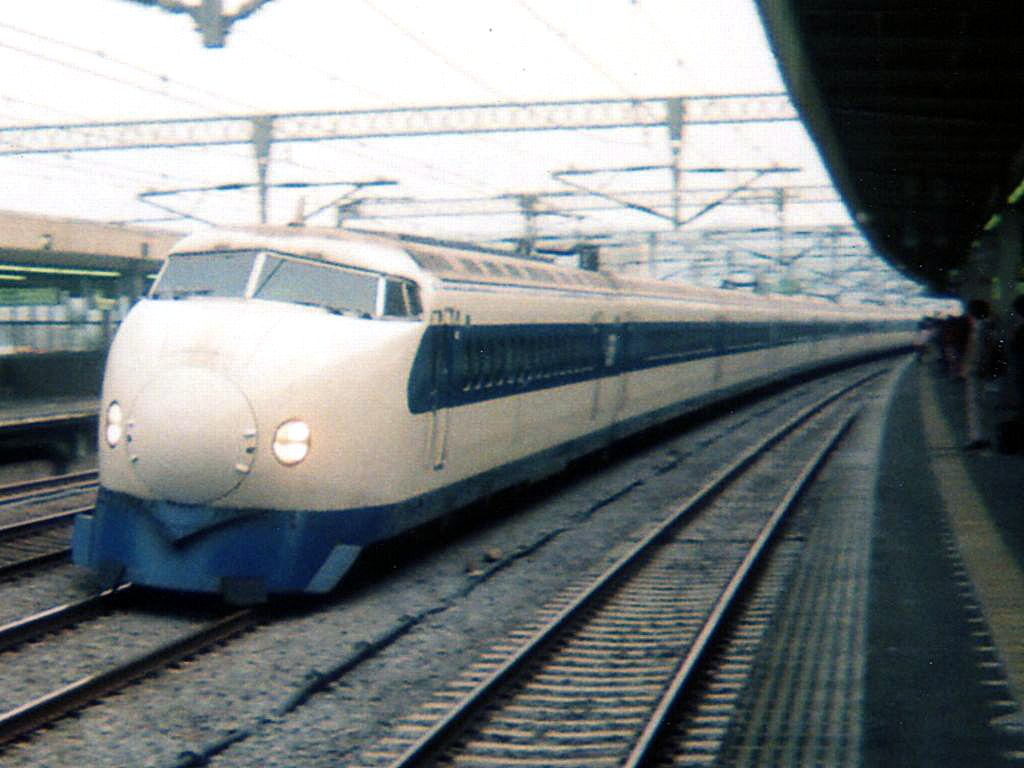

The first electrified
high-speed rail
High-speed rail (HSR) is a type of rail system that runs significantly faster than traditional rail, using an integrated system of specialised rolling stock and dedicated tracks. While there is no single standard that applies worldwide, lines ...
Tōkaidō Shinkansen (series 0) was introduced in 1964 between
Tokyo
Tokyo (; ja, 東京, , ), officially the Tokyo Metropolis ( ja, 東京都, label=none, ), is the capital and largest city of Japan. Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area () is the most populous in the world, with an estimated 37.468 ...
and
Osaka
is a designated city in the Kansai region of Honshu in Japan. It is the capital of and most populous city in Osaka Prefecture, and the third most populous city in Japan, following Special wards of Tokyo and Yokohama. With a population of 2. ...
in Japan. Since then
high-speed rail
High-speed rail (HSR) is a type of rail system that runs significantly faster than traditional rail, using an integrated system of specialised rolling stock and dedicated tracks. While there is no single standard that applies worldwide, lines ...
transport, functioning at speeds up and above 300 km/h(186.4 m/h), has been built in Japan, Spain, France, Germany, Italy,
Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
, the People's Republic of China, the
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
,
South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and sharing a Korean Demilitarized Zone, land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed ...
,
Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion#Europe, subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, ...
,
Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to th ...
and the
Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
. The construction of many of these lines has resulted in the dramatic decline of short haul flights and automotive traffic between connected cities, such as the London–Paris–Brussels corridor, Madrid–Barcelona, Milan–Rome–Naples, as well as many other major lines.
High-speed trains normally operate on
standard gauge
A standard-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge of . The standard gauge is also called Stephenson gauge (after George Stephenson), International gauge, UIC gauge, uniform gauge, normal gauge and European gauge in Europe, and SGR in Ea ...
tracks of
continuously welded rail
A railway track (British English and UIC terminology) or railroad track (American English), also known as permanent way or simply track, is the structure on a railway or railroad consisting of the rails, fasteners, railroad ties (sleepers, ...
on
grade-separated
In civil engineering (more specifically highway engineering), grade separation is a method of aligning a junction of two or more surface transport axes at different heights (grades) so that they will not disrupt the traffic flow on other tran ...
right-of-way
Right of way is the legal right, established by grant from a landowner or long usage (i.e. by prescription), to pass along a specific route through property belonging to another.
A similar ''right of access'' also exists on land held by a gov ...
that incorporates a large
turning radius in its design. While high-speed rail is most often designed for passenger travel, some high-speed systems also offer freight service.
Hydrogen power introduced
Alstom Coradia Lint hydrogen-powered train entered service in
Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony (german: Niedersachsen ; nds, Neddersassen; stq, Läichsaksen) is a German state (') in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ...
,
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
in 2018.
History by country
Europe

In recent years deregulation has been a major topic across Europe.
Belgium
Belgium took the lead in the
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
on the Continent starting in the 1820s. It provided an ideal model for showing the value of the railways for speeding the industrial revolution. After splitting from the
Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
in 1830, the new country decided to stimulate industry. It planned and funded a simple cross-shaped system that connected the major cities, ports and mining areas and linked to neighboring countries. Unusually, the Belgian state became a major contributor to early rail development and championed the creation of a national network with no duplication of lines. Belgium thus became the railway center of the region.
The system was built along British lines, often with British engineers doing the planning. Profits were low but the infrastructure necessary for rapid industrial growth was put in place. The first railway in Belgium, running from northern
Brussels
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Bruss ...
to
Mechelen
Mechelen (; french: Malines ; traditional English name: MechlinMechelen has been known in English as ''Mechlin'', from where the adjective ''Mechlinian'' is derived. This name may still be used, especially in a traditional or historical contex ...
, was completed in May 1835.
Britain

= Early developments
=
The earliest railway in Britain was a
wagonway
Wagonways (also spelt Waggonways), also known as horse-drawn railways and horse-drawn railroad consisted of the horses, equipment and tracks used for hauling wagons, which preceded Steam locomotive, steam-powered rail transport, railways. The t ...
system, a horse drawn wooden rail system, used by German miners at
Caldbeck,
Cumbria
Cumbria ( ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in North West England, bordering Scotland. The county and Cumbria County Council, its local government, came into existence in 1974 after the passage of the Local Government Act 1972. Cumb ...
, England, perhaps from the 1560s.
A wagonway was built at
Prescot, near
Liverpool
Liverpool is a city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. With a population of in 2019, it is the 10th largest English district by population and its metropolitan area is the fifth largest in the United Kingdom, with a popul ...
, sometime around 1600, possibly as early as 1594. Owned by Philip Layton, the line carried coal from a pit near Prescot Hall to a terminus about half a mile away.
On 26 July 1803, Jessop opened the
Surrey Iron Railway, south of London erroneously considered first railway in Britain, also a horse-drawn one. It was not a railway in the modern sense of the word, as it functioned like a
turnpike road
A toll road, also known as a turnpike or tollway, is a public or private road (almost always a controlled-access highway in the present day) for which a fee (or ''toll'') is assessed for passage. It is a form of road pricing typically implemented ...
. There were no official services, as anyone could bring a vehicle on the railway by paying a toll.
The oldest railway in continuous use is the
Tanfield Railway
The Tanfield Railway is a heritage railway in Gateshead and County Durham, England. Running on part of a former horse-drawn colliery wooden waggonway, later rope & horse, lastly rope & loco railway. It operates preserved industrial steam l ...
in County Durham, England. This began life in 1725 as a wooden waggonway worked with horse power and developed by private coal owners and included the construction of the
Causey Arch
The Causey Arch is a bridge near Stanley in County Durham, northern England. It is the oldest surviving single-arch railway bridge in the world, and a key element of the industrial heritage of England. It carried an early wagonway (horse-drawn ...
, the world's oldest purpose built railway bridge. By the mid 19th century it had converted to standard gauge track and steam locomotive power. It continues in operation as a heritage line. The
Middleton Railway in
Leeds
Leeds () is a city and the administrative centre of the City of Leeds district in West Yorkshire, England. It is built around the River Aire and is in the eastern foothills of the Pennines. It is also the third-largest settlement (by populati ...
, opened in 1758, is also still in use as a heritage line and began using steam locomotive power in 1812 before reverting to horsepower and then upgrading to standard gauge. In 1764, the first railway in the Americas was built in
Lewiston, New York.
[
The first passenger ]Horsecar
A horsecar, horse-drawn tram, horse-drawn streetcar (U.S.), or horse-drawn railway (historical), is an animal-powered (usually horse) tram or streetcar.
Summary
The horse-drawn tram (horsecar) was an early form of public rail transport, wh ...
or tram
A tram (called a streetcar or trolley in North America) is a rail vehicle that travels on tramway tracks on public urban streets; some include segments on segregated right-of-way. The tramlines or networks operated as public transport are ...
, Swansea and Mumbles Railway was opened between Swansea
Swansea (; cy, Abertawe ) is a coastal city and the second-largest city of Wales. It forms a principal area, officially known as the City and County of Swansea ( cy, links=no, Dinas a Sir Abertawe).
The city is the twenty-fifth largest in ...
and Mumbles in Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the Wales–England border, east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the ...
in 1807.William James
William James (January 11, 1842 – August 26, 1910) was an American philosopher, historian, and psychologist, and the first educator to offer a psychology course in the United States.
James is considered to be a leading thinker of the lat ...
, a rich and influential surveyor and land agent, was inspired by the development of the steam locomotive to suggest a national network of railways. It seems likelysteam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, oil or, rarely, wood) to heat water in the locomot ...
''Catch me who can
''Catch Me Who Can'' was the fourth and last steam railway locomotive created by the inventor and mining engineer Richard Trevithick. It was an evolution of three earlier locomotives which had been built for Coalbrookdale, Penydarren ironwork ...
'' in London; certainly at this time he began to consider the long-term development of this means of transport. He proposed a number of projects that later came to fruition and is credited with carrying out a survey of the Liverpool and Manchester Railway. Unfortunately he became bankrupt and his schemes were taken over by George Stephenson and others. However, he is credited by many historians with the title of "Father of the Railway".Stockton and Darlington Railway
The Stockton and Darlington Railway (S&DR) was a railway company that operated in north-east England from 1825 to 1863. The world's first public railway to use steam locomotives, its first line connected collieries near Shildon with Darl ...
in County Durham
County Durham ( ), officially simply Durham,UK General Acts 1997 c. 23Lieutenancies Act 1997 Schedule 1(3). From legislation.gov.uk, retrieved 6 April 2022. is a ceremonial county in North East England.North East Assembly �About North East E ...
, England, the world's first public railway to combine locomotive power, malleable iron rails, twin tracks and other innovations such as early signalling, proto-Station buildings and rudimentary timetables in one place It proved to a national and international audience that the railways could be made profitable for passengers and general goods as well as a single commodity such as coal. This railway broke new ground by using rails made of rolled wrought iron
Wrought iron is an iron alloy with a very low carbon content (less than 0.08%) in contrast to that of cast iron (2.1% to 4%). It is a semi-fused mass of iron with fibrous slag Inclusion (mineral), inclusions (up to 2% by weight), which give it a ...
, produced at Bedlington Ironworks in Northumberland
Northumberland () is a county in Northern England, one of two counties in England which border with Scotland. Notable landmarks in the county include Alnwick Castle, Bamburgh Castle, Hadrian's Wall and Hexham Abbey.
It is bordered by land on ...
. Such rails were stronger. This railway linked the coal field of Durham with the towns of Darlington
Darlington is a market town in the Borough of Darlington, County Durham, England. The River Skerne flows through the town; it is a tributary of the River Tees. The Tees itself flows south of the town.
In the 19th century, Darlington underwen ...
and the port of Stockton-on-Tees
Stockton-on-Tees, often simply referred to as Stockton, is a market town in the Borough of Stockton-on-Tees in County Durham, England. It is on the northern banks of the River Tees, part of the Teesside built-up area. The town had an estimated ...
and was intended to enable local collieries (which were connected to the line by short branches) to transport their coal to the docks. As this would constitute the bulk of the traffic, the company took the important step of offering to haul the colliery wagons or chaldrons by locomotive power, something that required a scheduled or timetabled service of trains. However, the line also functioned as a toll railway, on which private horse-drawn wagons could be carried. This hybrid of a system (which also included, at one stage, a horse-drawn passenger traffic when sufficient locomotives weren't available) could not last and within a few years, traffic was restricted to timetabled trains. (However, the tradition of private owned wagons continued on railways in Britain until the 1960s.). The S&DRs chief engineer Timothy Hackworth under the guidance of its principal funder Edward Pease, hosted visiting engineers from the USA, Prussia and France and shared experience and learning on how to build and run a railway so that by 1830 railways were being built in several locations across the UK, USA and Europe. Trained engineers and workers from the S&DR went on to help develop several other lines elsewhere including the Liverpool and Manchester of 1830, the next step forward in railway development.
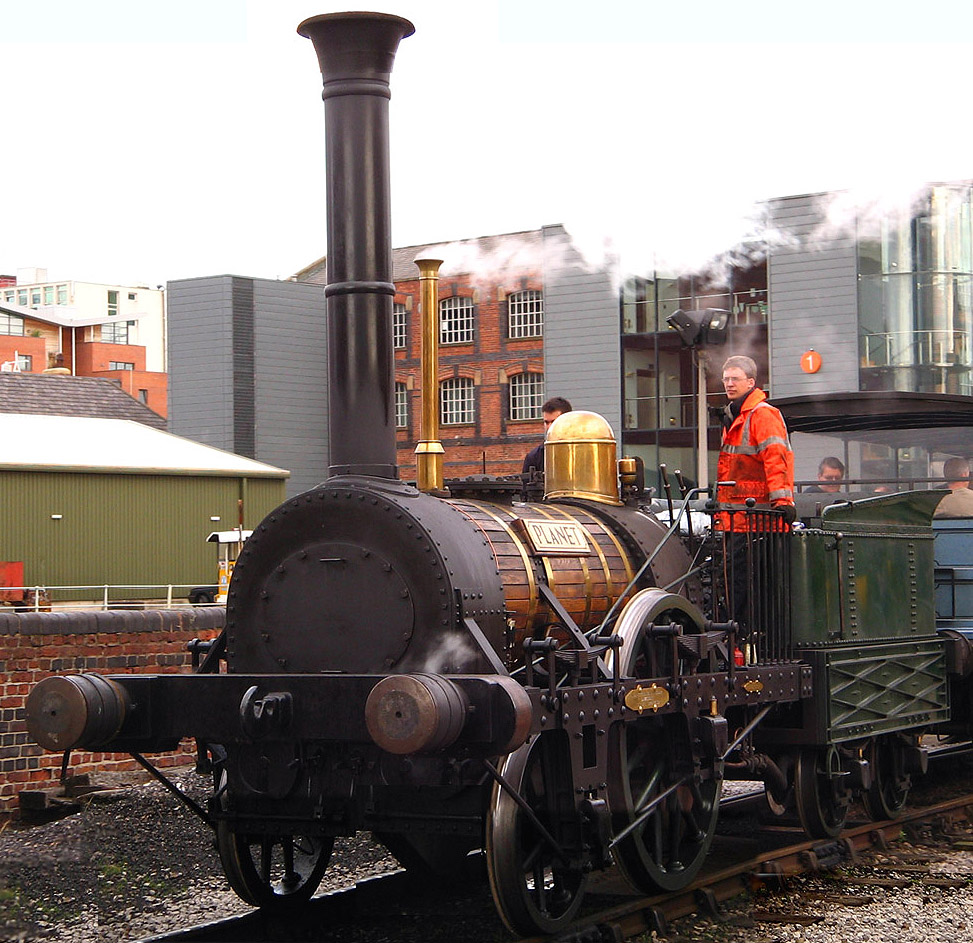 The success of the Stockton and Darlington encouraged the rich investors in the rapidly industrialising North West of England to embark upon a project to link the rich cotton manufacturing town of
The success of the Stockton and Darlington encouraged the rich investors in the rapidly industrialising North West of England to embark upon a project to link the rich cotton manufacturing town of Manchester
Manchester () is a city in Greater Manchester, England. It had a population of 552,000 in 2021. It is bordered by the Cheshire Plain to the south, the Pennines to the north and east, and the neighbouring city of Salford to the west. The t ...
with the thriving port of Liverpool
Liverpool is a city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. With a population of in 2019, it is the 10th largest English district by population and its metropolitan area is the fifth largest in the United Kingdom, with a popul ...
. The Liverpool and Manchester Railway was the first modern railway, in that both the goods and passenger traffic were operated by scheduled or timetabled locomotive hauled trains. When it was built, there was serious doubt that locomotives could maintain a regular service over the distance involved. A widely reported competition was held in 1829 called the Rainhill Trials, to find the most suitable steam engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be trans ...
to haul the trains. A number of locomotives were entered, including '' Novelty'', '' Perseverance'' and '' Sans Pareil''. The winner was Stephenson's Rocket
Stephenson's ''Rocket'' is an early steam locomotive of 0-2-2 wheel arrangement. It was built for and won the Rainhill Trials of the Liverpool and Manchester Railway (L&MR), held in October 1829 to show that improved locomotives would be mo ...
, which steamed better because of its multi-tubular boiler (suggested by Henry Booth
Henry Booth (4 April 1788 – 28 March 1869) was a British corn merchant, businessman and engineer particularly known as one of the key people behind the construction and management of the pioneering Liverpool and Manchester Railway (L&M), the ...
, a director of the railway company).
The promoters were mainly interested in goods traffic, but after the line opened on 15 September 1830, they were surprised to find that passenger traffic was just as remunerative. The success of the Liverpool and Manchester railway added to the influence of the S&DR in the development of railways elsewhere in Britain and abroad. The company hosted many visiting deputations from other railway projects and many railwaymen received their early training and experience upon this line. The Liverpool and Manchester line was, however, only long. The world's first trunk line can be said to be the Grand Junction Railway, opening in 1837 and linking a midpoint on the Liverpool and Manchester Railway with Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands in England. It is the second-largest city in the United Kingdom with a population of 1.145 million in the city proper, 2.92 million in the West ...
, via Crewe
Crewe () is a railway town and civil parish in the unitary authority of Cheshire East in Cheshire, England. The Crewe built-up area had a total population of 75,556 in 2011, which also covers parts of the adjacent civil parishes of Willaston ...
, Stafford
Stafford () is a market town and the county town of Staffordshire, in the West Midlands region of England. It lies about north of Wolverhampton, south of Stoke-on-Trent and northwest of Birmingham. The town had a population of 70,145 in t ...
and Wolverhampton
Wolverhampton () is a city, metropolitan borough and administrative centre in the West Midlands, England. The population size has increased by 5.7%, from around 249,500 in 2011 to 263,700 in 2021. People from the city are called "Wulfrunian ...
.
= Further development
=
The earliest locomotives in revenue service were small four-wheeled ones similar to the Rocket. However, the inclined cylinders caused the engine to rock, so they first became horizontal and then, in his "Planet" design, were mounted inside the frames. While this improved stability, the "crank axles" were extremely prone to breakage. Greater speed was achieved by larger driving wheels at expense of a tendency for wheel slip when starting. Greater tractive effort was obtained by smaller wheels coupled together, but speed was limited by the fragility of the cast iron connecting rods. Hence, from the beginning, there was a distinction between the light fast passenger locomotive and the slower more powerful goods engine. Edward Bury
Edward Bury (22 October 1794 – 25 November 1858) was an English locomotive manufacturer. Born in Salford, Lancashire, he was the son of a timber merchant and was educated at Chester.
Career
By 1823 he was a partner in Gregson and Bury's steam ...
, in particular, refined this design and the so-called "Bury Pattern" was popular for a number of years, particularly on the London and Birmingham.
Meanwhile, by 1840, Stephenson had produced larger, more stable, engines in the form of the 2-2-2
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-2-2 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, two powered driving wheels on one axle, and two trailing wheels on one axle. The wheel arrangement both ...
"Patentee" and six-coupled goods engines. Locomotives were travelling longer distances and being worked more extensively. The North Midland Railway expressed their concern to Robert Stephenson who was, at that time, their general manager, about the effect of heat on their fireboxes. After some experiments, he patented his so-called Long Boiler design. These became a new standard and similar designs were produced by other manufacturers, particularly Sharp Brothers
Sharp, Stewart and Company was a steam locomotive manufacturer, initially located in Manchester, England. The company was formed in 1843 upon the demise of Sharp, Roberts & Co.. It moved to Glasgow, Scotland, in 1888, eventually amalgamating wit ...
whose engines became known affectionately as "Sharpies".
The longer wheelbase for the longer boiler produced problems in cornering. For his six-coupled engines, Stephenson removed the flanges from the centre pair of wheels. For his express engines, he shifted the trailing wheel to the front in the 4-2-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles, two powered driving wheels on one axle and no trailing wheels. This type of locomotive is often called a ...
formation, as in his "Great A". There were other problems: the firebox was restricted in size or had to be mounted behind the wheels; and for improved stability most engineers believed that the centre of gravity should be kept low.
The most extreme outcome of this was the Crampton locomotive
A Crampton locomotive is a type of steam locomotive designed by Thomas Russell Crampton and built by various firms from 1846. The main British builders were Tulk and Ley and Robert Stephenson and Company.
Notable features were a low boiler and l ...
which mounted the driving wheels behind the firebox and could be made very large in diameter. These achieved the hitherto unheard of speed of but were very prone to wheelslip. With their long wheelbase, they were unsuccessful on Britain's winding tracks, but became popular in the US and France, where the popular expression became ''prendre le Crampton''.
John Gray of the London and Brighton Railway
The London and Brighton Railway (L&BR) was a railway company in England which was incorporated in 1837 and survived until 1846. Its railway ran from a junction with the London and Croydon Railway (L&CR) at Norwood – which gives it access fro ...
disbelieved the necessity for a low centre of gravity and produced a series of locomotives that were much admired by David Joy who developed the design at the firm of E. B. Wilson and Company
E. B. Wilson and Company was a locomotive manufacturing company at the Railway Foundry in Hunslet, Leeds, West Yorkshire, England.
Origins
Charles Todd was one of the founders of Todd, Kitson & Laird, but left early in the company's history a ...
to produce the 2-2-2
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-2-2 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, two powered driving wheels on one axle, and two trailing wheels on one axle. The wheel arrangement both ...
Jenny Lind locomotive
Jenny Lind was the first of a class of ten steam locomotives built in 1847 for the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway (LB&SCR) by E. B. Wilson and Company of Leeds, named after Jenny Lind, who was a famous Swedish opera singer of the peri ...
, one of the most successful passenger locomotives of its day. Meanwhile, the Stephenson 0-6-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of no leading wheels, six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles and no trailing wheels. This was the most common wheel arrangemen ...
Long Boiler locomotive with inside cylinders became the archetypal goods engine.
= Expanding network
=
Railways quickly became essential to the swift movement of goods and labour that was needed for industrialization
Industrialisation ( alternatively spelled industrialization) is the period of social and economic change that transforms a human group from an agrarian society into an industrial society. This involves an extensive re-organisation of an econo ...
. In the beginning, canal
Canals or artificial waterways are waterways or engineered channels built for drainage management (e.g. flood control and irrigation) or for conveyancing water transport vehicles (e.g. water taxi). They carry free, calm surface flow un ...
s were in competition with the railways, but the railways quickly gained ground as steam
Steam is a substance containing water in the gas phase, and sometimes also an aerosol of liquid water droplets, or air. This may occur due to evaporation or due to boiling, where heat is applied until water reaches the enthalpy of vaporization ...
and rail technology improved and railways were built in places where canals were not practical.
By the 1850s, many steam-powered railways had reached the fringes of built-up London. But the new companies were not permitted to demolish enough property to penetrate the City or the West End, so passengers had to disembark at Paddington
Paddington is an area within the City of Westminster, in Central London. First a medieval parish then a metropolitan borough, it was integrated with Westminster and Greater London in 1965. Three important landmarks of the district are Paddi ...
, Euston, King's Cross, Fenchurch Street
Fenchurch Street is a street in London linking Aldgate at its eastern end with Lombard Street and Gracechurch Street in the west. It is a well-known thoroughfare in the City of London financial district and is the site of many corporate office ...
, Charing Cross
Charing Cross ( ) is a junction in Westminster, London, England, where six routes meet. Clockwise from north these are: the east side of Trafalgar Square leading to St Martin's Place and then Charing Cross Road; the Strand leading to the City; ...
, Waterloo
Waterloo most commonly refers to:
* Battle of Waterloo, a battle on 18 June 1815 in which Napoleon met his final defeat
* Waterloo, Belgium, where the battle took place.
Waterloo may also refer to:
Other places
Antarctica
*King George Island (S ...
or Victoria and then make their own way by hackney carriage or on foot into the centre, thereby massively increasing congestion in the city. A Metropolitan Railway
The Metropolitan Railway (also known as the Met) was a passenger and goods railway that served London from 1863 to 1933, its main line heading north-west from the capital's financial heart in the City to what were to become the Middlesex su ...
was built underground to connect several of these separate railway terminals and was the world's first "Metro".
= Social and economic consequences
=
The railways changed British society in numerous and complex ways. Although recent attempts to measure the economic significance of the railways have suggested that their overall contribution to the growth of GDP was more modest than an earlier generation of historians sometimes assumed, it is nonetheless clear that the railways had a sizeable impact in many spheres of economic activity. The building of railways and locomotives, for example, called for large quantities of heavy materials and thus provided a significant stimulus or 'backward linkage', to the coal-mining, iron-production, engineering and construction industries.
They also helped to reduce transaction costs, which in turn lowered the costs of goods: the distribution and sale of perishable goods such as meat, milk, fish and vegetables were transformed by the emergence of the railways, giving rise not only to cheaper produce in the shops but also to far greater variety in people's diets.
Finally, by improving personal mobility the railways were a significant force for social change. Rail transport had originally been conceived as a way of moving coal and industrial goods but the railway operators quickly realised the potential market for railway travel, leading to an extremely rapid expansion in passenger services. The number of railway passengers trebled in just eight years between 1842 and 1850: traffic volumes roughly doubled in the 1850s and then doubled again in the 1860s.
As the historian Derek Aldcroft has noted, "in terms of mobility and choice they added a new dimension to everyday life".
Bulgaria
The Ruse
Ruse may refer to:
Places
*Ruse, Bulgaria, a major city of Bulgaria
**Ruse Municipality
** Ruse Province
** 19th MMC – Ruse, a constituency
*Ruše, a town and municipality in north-eastern Slovenia
* Ruše, Žalec, a small settlement in east-ce ...
– Varna
Varna may refer to:
Places Europe
*Varna, Bulgaria, a city in Bulgaria
**Varna Province
**Varna Municipality
** Gulf of Varna
**Lake Varna
**Varna Necropolis
*Vahrn, or Varna, a municipality in Italy
*Varniai, a city in Lithuania
* Varna (Šaba ...
was the first railway line in the modern Bulgarian
Bulgarian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the country of Bulgaria
* Bulgarians, a South Slavic ethnic group
* Bulgarian language, a Slavic language
* Bulgarian alphabet
* A citizen of Bulgaria, see Demographics of Bulgaria
* Bul ...
territory, and also in the former Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
. It was started in 1864 by the Turkish government, by commissioning for it an English company managed by William Gladstone
William Ewart Gladstone ( ; 29 December 1809 – 19 May 1898) was a British statesman and Liberal politician. In a career lasting over 60 years, he served for 12 years as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, spread over four non-conse ...
, a politician, and the Barkley brothers, civil engineers. The line, which was 223 km long, was opened in 1866.
France
 In France, railways were first operated by private coal companies the first legal agreement to build a railway was given in 1823 and the line (from Saint-Étienne to Andrézieux) was operated in 1827. Much of the equipment was imported from Britain but this stimulated machinery makers, which soon created a national heavy industry. Trains became a national medium for the modernization of backward regions and a leading advocate of this approach was the poet-politician Alphonse de Lamartine. One writer hoped that railways might improve the lot of "populations two or three centuries behind their fellows" and eliminate "the savage instincts born of isolation and misery." Consequently, France built a centralized system that radiated from Paris (plus lines that cut east to west in the south). This design was intended to achieve political and cultural goals rather than maximize efficiency.
After some consolidation, six companies controlled monopolies of their regions, subject to close control by the government in terms of fares, finances and even minute technical details. The central government department of Ponts et Chaussées ridges and roadsbrought in British engineers and workers, handled much of the construction work, provided engineering expertise and planning, land acquisition and construction of permanent infrastructure such as the track bed, bridges and tunnels. It also subsidized militarily necessary lines along the German border, which was considered necessary for the national defense. Private operating companies provided management, hired labor, laid the tracks and built and operated stations. They purchased and maintained the rolling stock—6,000 locomotives were in operation in 1880, which averaged 51,600 passengers a year or 21,200 tons of freight.
In France, railways were first operated by private coal companies the first legal agreement to build a railway was given in 1823 and the line (from Saint-Étienne to Andrézieux) was operated in 1827. Much of the equipment was imported from Britain but this stimulated machinery makers, which soon created a national heavy industry. Trains became a national medium for the modernization of backward regions and a leading advocate of this approach was the poet-politician Alphonse de Lamartine. One writer hoped that railways might improve the lot of "populations two or three centuries behind their fellows" and eliminate "the savage instincts born of isolation and misery." Consequently, France built a centralized system that radiated from Paris (plus lines that cut east to west in the south). This design was intended to achieve political and cultural goals rather than maximize efficiency.
After some consolidation, six companies controlled monopolies of their regions, subject to close control by the government in terms of fares, finances and even minute technical details. The central government department of Ponts et Chaussées ridges and roadsbrought in British engineers and workers, handled much of the construction work, provided engineering expertise and planning, land acquisition and construction of permanent infrastructure such as the track bed, bridges and tunnels. It also subsidized militarily necessary lines along the German border, which was considered necessary for the national defense. Private operating companies provided management, hired labor, laid the tracks and built and operated stations. They purchased and maintained the rolling stock—6,000 locomotives were in operation in 1880, which averaged 51,600 passengers a year or 21,200 tons of freight.
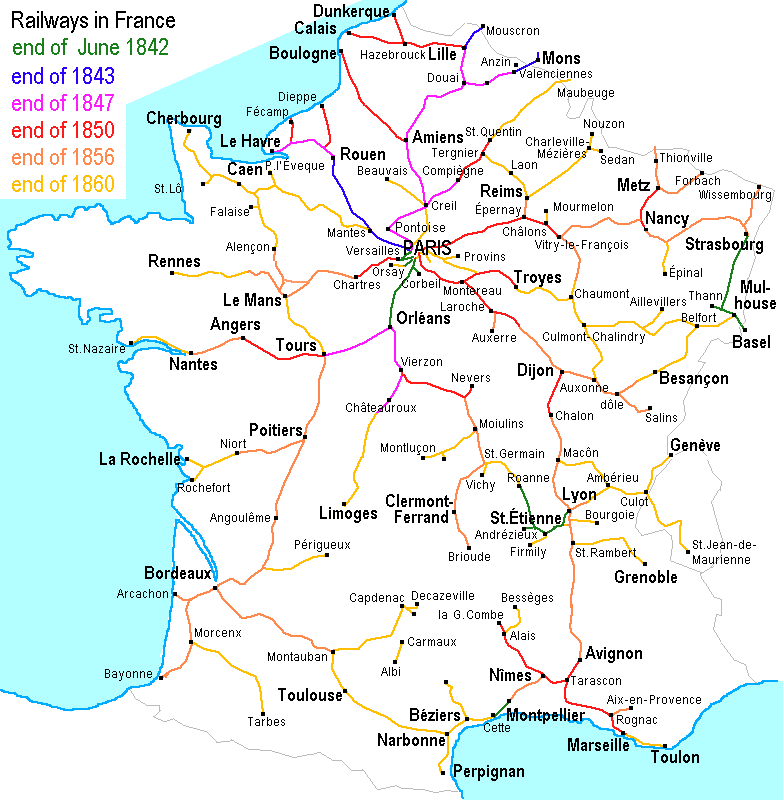 Although starting the whole system at once was politically expedient, it delayed completion and forced even more reliance on temporary experts brought in from Britain. Financing was also a problem. The solution was a narrow base of funding through the Rothschilds and the closed circles of the Bourse in Paris, so France did not develop the same kind of national stock exchange that flourished in London and New York. The system did help modernize the parts of rural France it reached and help to develop many local industrial centers, mostly in the North (coal and iron mines) and in the East (textiles and heavy industry). Critics such as
Although starting the whole system at once was politically expedient, it delayed completion and forced even more reliance on temporary experts brought in from Britain. Financing was also a problem. The solution was a narrow base of funding through the Rothschilds and the closed circles of the Bourse in Paris, so France did not develop the same kind of national stock exchange that flourished in London and New York. The system did help modernize the parts of rural France it reached and help to develop many local industrial centers, mostly in the North (coal and iron mines) and in the East (textiles and heavy industry). Critics such as Émile Zola
Émile Édouard Charles Antoine Zola (, also , ; 2 April 184029 September 1902) was a French novelist, journalist, playwright, the best-known practitioner of the literary school of naturalism, and an important contributor to the development of ...
complained that it never overcame the corruption of the political system, but rather contributed to it.
The railways probably helped the industrial revolution in France by facilitating a national market for raw materials, wines, cheeses and imported and exported manufactured products. In ''The Rise of Rail-Power in War and Conquest, 1833–1914'', published in 1915, Edwin A. Pratt wrote, "the French railways … attained a remarkable degree of success. … It was estimated that the 75,966 men and 4,469 horses transported by rail from Paris to the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the eas ...
or to the frontiers of the Kingdom of Sardinia between 20 and 30 April April uring the 1859 Second Italian War of Independence">Second_Italian_War_of_Independence.html" ;"title="uring the 1859 Second Italian War of Independence">uring the 1859 Second Italian War of Independencewould have taken sixty days to make the journey by road. … This… was about twice as fast as the best achievement recorded up to that time on the German railways. " Yet the goals set by the French for their railway system were moralistic, political and military rather than economic. As a result, the freight trains were shorter and less heavily loaded than those in such rapidly industrializing nations such as Britain, Belgium or Germany. Other infrastructure needs in rural France, such as better roads and canals, were neglected because of the expense of the railways, so it seems likely that there were net negative effects in areas not served by the trains.
Germany
An operation was illustrated in Germany in 1556 by Georgius Agricola in his work '' De re metallica''.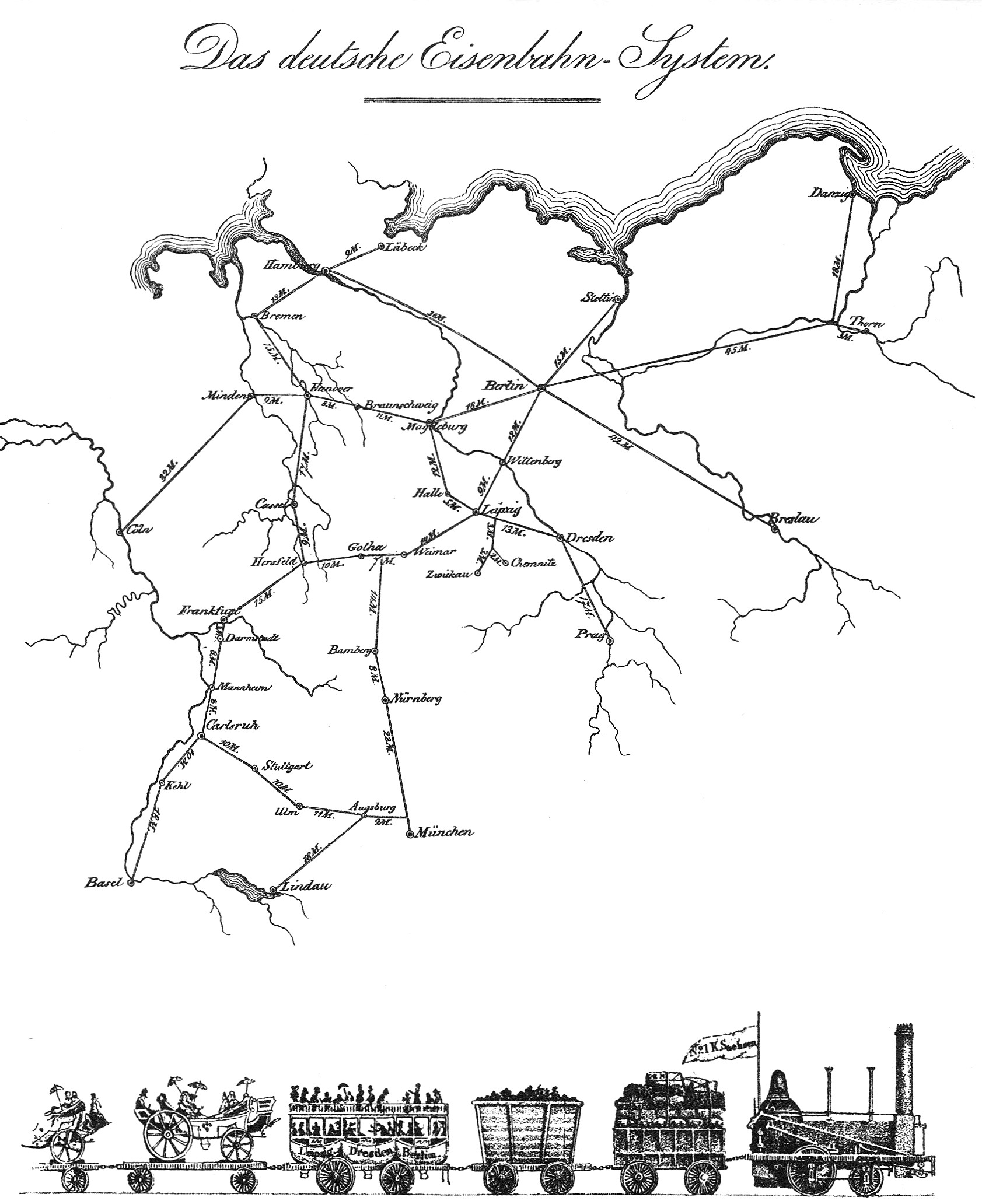 The takeoff stage of economic development came with the railroad revolution in the 1840s, which opened up new markets for local products, created a pool of middle managers, increased the demand for engineers, architects and skilled machinists and stimulated investments in coal and iron. Political disunity of three dozen states and a pervasive conservatism made it difficult to build railways in the 1830s. However, by the 1840s, trunk lines did link the major cities; each German state was responsible for the lines within its own borders. Economist Friedrich List summed up the advantages to be derived from the development of the railway system in 1841:
# As a means of national defence, it facilitates the concentration, distribution and direction of the army.
# It is a means to the improvement of the culture of the nation. It brings talent, knowledge and skill of every kind readily to market.
# It secures the community against dearth and famine and against excessive fluctuation in the prices of the necessaries of life.
# It promotes the spirit of the nation, as it has a tendency to destroy the Philistine spirit arising from isolation and provincial prejudice and vanity. It binds nations by ligaments and promotes an interchange of food and of commodities, thus making it feel to be a unit. The iron rails become a nerve system, which, on the one hand, strengthens public opinion, and, on the other hand, strengthens the power of the state for police and governmental purposes.
Lacking a technological base at first, the Germans imported their engineering and hardware from Britain, but quickly learned the skills needed to operate and expand the railways. In many cities, the new railway shops were the centres of technological awareness and training, so that by 1850, Germany was self-sufficient in meeting the demands of railroad construction and the railways were a major impetus for the growth of the new steel industry. Observers found that even as late as 1890, their engineering was inferior to Britain's. However, German unification in 1870 stimulated consolidation, nationalisation into state-owned companies and further rapid growth. Unlike the situation in France, the goal was support of industrialisation and so heavy lines crisscrossed the Ruhr and other industrial districts and provided good connections to the major ports of Hamburg and Bremen. By 1880, Germany had 9,400 locomotives pulling 43,000 passengers and 30,000 tons of freight a day and forged ahead of France.
The takeoff stage of economic development came with the railroad revolution in the 1840s, which opened up new markets for local products, created a pool of middle managers, increased the demand for engineers, architects and skilled machinists and stimulated investments in coal and iron. Political disunity of three dozen states and a pervasive conservatism made it difficult to build railways in the 1830s. However, by the 1840s, trunk lines did link the major cities; each German state was responsible for the lines within its own borders. Economist Friedrich List summed up the advantages to be derived from the development of the railway system in 1841:
# As a means of national defence, it facilitates the concentration, distribution and direction of the army.
# It is a means to the improvement of the culture of the nation. It brings talent, knowledge and skill of every kind readily to market.
# It secures the community against dearth and famine and against excessive fluctuation in the prices of the necessaries of life.
# It promotes the spirit of the nation, as it has a tendency to destroy the Philistine spirit arising from isolation and provincial prejudice and vanity. It binds nations by ligaments and promotes an interchange of food and of commodities, thus making it feel to be a unit. The iron rails become a nerve system, which, on the one hand, strengthens public opinion, and, on the other hand, strengthens the power of the state for police and governmental purposes.
Lacking a technological base at first, the Germans imported their engineering and hardware from Britain, but quickly learned the skills needed to operate and expand the railways. In many cities, the new railway shops were the centres of technological awareness and training, so that by 1850, Germany was self-sufficient in meeting the demands of railroad construction and the railways were a major impetus for the growth of the new steel industry. Observers found that even as late as 1890, their engineering was inferior to Britain's. However, German unification in 1870 stimulated consolidation, nationalisation into state-owned companies and further rapid growth. Unlike the situation in France, the goal was support of industrialisation and so heavy lines crisscrossed the Ruhr and other industrial districts and provided good connections to the major ports of Hamburg and Bremen. By 1880, Germany had 9,400 locomotives pulling 43,000 passengers and 30,000 tons of freight a day and forged ahead of France.
Italy
The first line to be built on the peninsula was the Naples–Portici line, in the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies
The Kingdom of the Two Sicilies ( it, Regno delle Due Sicilie) was a kingdom in Southern Italy from 1816 to 1860. The kingdom was the largest sovereign state by population and size in Italy before Italian unification, comprising Sicily and a ...
, which was 7.640 km long and was inaugurated on October 3, 1839, nine years after the world's first "modern" inter-city railway, the Liverpool and Manchester Railway. During the first phase of development, it was operated by a locomotive derived by the British ''Planet'', that served the Royal convoy that traveled between the capital city of Naples and the summer residence at Royal Palace of Portici
The Royal Palace of Portici (''Reggia di Portici'' or ''Palazzo Reale di Portici''; nap, Reggia ‘e Puortece) is a former royal palace in Portici, Southeast of Naples along the coast, in the region of Campania, Italy. Today it is the home of t ...
. Soon after, the line lost its exclusive nature and was rapidly expanded toward Salerno
Salerno (, , ; nap, label= Salernitano, Saliernë, ) is an ancient city and ''comune'' in Campania (southwestern Italy) and is the capital of the namesake province, being the second largest city in the region by number of inhabitants, after ...
and Nola
Nola is a town and a municipality in the Metropolitan City of Naples, Campania, southern Italy. It lies on the plain between Mount Vesuvius and the Apennines. It is traditionally credited as the diocese that introduced bells to Christian worship. ...
, serving both public transportation and freight needs.
Netherlands
Rail transport in the Netherlands is generally considered to have begun on 20 September 1839 when the first train, drawn by the locomotive '' De Arend'', successfully made the 16 km trip from Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Amstel'') is the Capital of the Netherlands, capital and Municipalities of the Netherlands, most populous city of the Netherlands, with The Hague being the seat of government. It has a population ...
to Haarlem
Haarlem (; predecessor of ''Harlem'' in English) is a city and municipality in the Netherlands. It is the capital of the province of North Holland. Haarlem is situated at the northern edge of the Randstad, one of the most populated metropoli ...
. However, the first plan for a railroad in the Netherlands was launched only shortly after the first railroad opened in Britain.
The history of rail transport in the Netherlands can be described in six eras:
* the period up to 1839 the first plans were made for a railroad,
* 1840–1860 railroads experienced their early expansion,
* 1860–1890 the government started ordering the construction of new lines,
* 1890–1938 the different railroads were consolidated into two large railroads,
* 1938–1992 Nederlandse Spoorwegen
Nederlandse Spoorwegen (NS; ; en, "Dutch Railways") is the principal passenger railway operator in the Netherlands. It is a Dutch state-owned company founded in 1938. The Dutch rail network is one of the busiest in the European Union, and the ...
was granted a monopoly
A monopoly (from Greek language, Greek el, μόνος, mónos, single, alone, label=none and el, πωλεῖν, pōleîn, to sell, label=none), as described by Irving Fisher, is a market with the "absence of competition", creating a situati ...
on rail transport, and
* 1992 to present the Nederlandse Spoorwegen lost its monopoly.
Poland
Poland restored its own independence as the Second Polish Republic
The Second Polish Republic, at the time officially known as the Republic of Poland, was a country in Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe that existed between 1918 and 1939. The state was established on 6 November 1918, before the end of ...
in 1918 from the German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
, Austro-Hungarian
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
and Russian Empires.
First Polish locomotive Ok22 (100 km/h) started operating in 1923.
Imported electric locomotives English Electric EL.100 (100 km/h) were in use in Warsaw since 1936.
New Polish locomotive Pm36-1 (140 km/h) was shown at the International Exposition of Art and Technology in Modern Life in Paris in 1937.
New Polish electric locomotive EP09
EP09 (also manufactured as Pafawag 104E) is a Polish electric locomotive used by the Polish railways, Polskie Koleje Państwowe (PKP) and produced by Pafawag of Wrocław between 1986 and 1997.
History
Construction
Work on designing new famil ...
(160 km/h) was designed in 1977 and started regular operation linking Warsaw and Kraków in 1987.
On 14 December 2014 PKP Intercity New Pendolino trains by Alstom under the name 'Express Intercity Premium' began operating on the CMK line (224 km line from Kraków and Katowice to Warsaw) with trains reaching 200 km/h (124 mph) as a regularly scheduled operation.
Russia

 In the early 1830s, the Russian father and son inventors the Cherepanovs built the first Russian steam locomotive. The first railway line was built in Russia in 1837 between Saint-Petersburg and Tsarskoye Selo. It was 27 km long and linked the Imperial Palaces at Tsarskoye Selo and Pavlovsk. The track gauge was . Russia was in need of big transportation systems and geographically suited to railroads, with long flat stretches of land and comparatively simple land acquisition. It was hampered, however, by its outmoded political situation and a shortage of capital. Foreign initiative and capital were required. It was the Americans who brought the technology of railway construction to Russia. In 1842, planning began for the building of Russia's first important railway; it linked Moscow and St Petersburg.
In the early 1830s, the Russian father and son inventors the Cherepanovs built the first Russian steam locomotive. The first railway line was built in Russia in 1837 between Saint-Petersburg and Tsarskoye Selo. It was 27 km long and linked the Imperial Palaces at Tsarskoye Selo and Pavlovsk. The track gauge was . Russia was in need of big transportation systems and geographically suited to railroads, with long flat stretches of land and comparatively simple land acquisition. It was hampered, however, by its outmoded political situation and a shortage of capital. Foreign initiative and capital were required. It was the Americans who brought the technology of railway construction to Russia. In 1842, planning began for the building of Russia's first important railway; it linked Moscow and St Petersburg.
Spain
 Cuba, then a Spanish colony, built its first rail line in 1837. The history of rail transport in peninsular Spain begins in 1848 with the construction of a railway line between Barcelona and
Cuba, then a Spanish colony, built its first rail line in 1837. The history of rail transport in peninsular Spain begins in 1848 with the construction of a railway line between Barcelona and Mataró
Mataró () is the capital and largest town of the ''comarca'' of the Maresme, in the province of Barcelona, Catalonia Autonomous Community, Spain. It is located on the Costa del Maresme, to the south of Costa Brava, between Cabrera de Mar and Sa ...
. In 1852, the first narrow gauge line was built. In 1863 a line reached the Portuguese border. By 1864, the Madrid-Irun
Irun ( es, Irún, eu, Irun) is a town of the Bidasoaldea region in the province of Gipuzkoa in the Basque Country (autonomous community), Basque Autonomous Community, Spain.
History
It lies on the foundations of the ancient Oiasso, cited as ...
line had been opened and the French border was reached.
North America
Canada
 The earliest railway in Canada was a wooden railway reportedly used in the construction of the French fortress at
The earliest railway in Canada was a wooden railway reportedly used in the construction of the French fortress at Louisburg, Nova Scotia
Louisbourg is an unincorporated community and former town in Cape Breton Regional Municipality, Nova Scotia.
History
The French military founded the Fortress of Louisbourg in 1713 and its fortified seaport on the southwest part of the harbour, ...
.
The first Canadian railway, the Champlain and St. Lawrence Railroad
The Champlain and St. Lawrence Railroad (C&SL) was a historic railway in Lower Canada, the first Canadian public railway and one of the first railways built in British North America.
Origin
The C&SL was financed by Montreal entrepreneur and br ...
, was opened in 1836 outside of Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-most populous city in Canada and List of towns in Quebec, most populous city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian ...
, a seasonal portage railway to connect river traffic. It was followed by the Albion Railway in Stellarton, Nova Scotia
Stellarton is a town located in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia. It is adjacent and to the south of the larger town of New Glasgow. In pioneer times the area was called Coal Mines Station, and from 1833 until 1889, it was known as Albion Min ...
in 1840, a collier railway connecting coal mines to a seaport. In Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
, the national government strongly supported railway construction for political goals. First it wanted to knit the far-flung provinces together and second, it wanted to maximize trade inside Canada and minimize trade with the United States, to avoid becoming an economic satellite. The Grand Trunk Railway of Canada linked Toronto and Montreal in 1853, then opened a line to Portland, Maine (which was ice-free) and lines to Michigan and Chicago. By 1870 it was the longest railway in the world. The Intercolonial line, finished in 1876, linked the Maritimes to Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ...
and Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Ca ...
, tying them to the new Confederation.
Anglo entrepreneurs in Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-most populous city in Canada and List of towns in Quebec, most populous city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian ...
sought direct lines into the US and shunned connections with the Maritimes, with a goal of competing with American railroad lines heading west to the Pacific. Joseph Howe, Charles Tupper
Sir Charles Tupper, 1st Baronet, (July 2, 1821 – October 30, 1915) was a Canadian Father of Confederation who served as the sixth prime minister of Canada from May 1 to July 8, 1896. As the premier of Nova Scotia from 1864 to 1867, he led N ...
and other Nova Scotia leaders used the rhetoric of a "civilizing mission" centered on their British heritage, because Atlantic-centered railway projects promised to make Halifax the eastern terminus of an intercolonial railway system tied to London. Leonard Tilley
Leonard Percy de Wolfe Tilley (May 21, 1870 – December 26, 1947) was a New Brunswick lawyer, politician and the 21st premier of New Brunswick.
Tilley was born in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada the son of Samuel Leonard Tilley, one of the Fathers o ...
, New Brunswick's most ardent railway promoter, championed the cause of "economic progress," stressing that Atlantic Canadians needed to pursue the most cost-effective transportation connections possible if they wanted to expand their influence beyond local markets. Advocating an intercolonial connection to Canada and a western extension into larger American markets in Maine and beyond, New Brunswick entrepreneurs promoted ties to the United States first, connections with Halifax second and routes into central Canada last. Thus metropolitan rivalries between Montreal, Halifax and Saint John led Canada to build more railway lines per capita than any other industrializing nation, even though it lacked capital resources and had too little freight and passenger traffic to allow the systems to turn a profit.
Den Otter (1997) challenges popular assumptions that Canada built transcontinental railways because it feared the annexationist schemes of aggressive Americans. Instead Canada overbuilt railroads because it hoped to compete with, even overtake Americans in the race for continental riches. It downplayed the more realistic Maritimes-based London-oriented connections and turned to utopian prospects for the farmlands and minerals of the west. The result was closer ties between north and south, symbolized by the Grand Trunk's expansion into the American Midwest. These economic links promoted trade, commerce and the flow of ideas between the two countries, integrating Canada into a North American economy and culture by 1880. About 700,000 Canadians migrated to the US in the late 19th century. The Canadian Pacific, paralleling the American border, opened a vital link to British Canada and stimulated settlement of the Prairies. The CP was affiliated with James J. Hill
James Jerome Hill (September 16, 1838 – May 29, 1916) was a Canadian-American railroad director. He was the chief executive officer of a family of lines headed by the Great Northern Railway, which served a substantial area of the Upper Midwes ...
's American railways and opened even more connections to the South. The connections were two-way, as thousands of American moved to the Prairies after their own frontier had closed.
Two additional transcontinental lines were built to the west coast—three in all—but that was far more than the traffic would bear, making the system simply too expensive. One after another, the federal government was forced to take over the lines and cover their deficits. In 1923, the government merged the Grand Trunk, Grand Trunk Pacific, Canadian Northern and National Transcontinental lines into the new the Canadian National Railways system. Since most of the equipment was imported from Britain or the US and most of the products carried were from farms, mines or forests, there was little stimulation to domestic manufacturing. On the other hand, the railways were essential to the growth of the wheat regions in the Prairies and to the expansion of coal mining, lumbering and paper making. Improvements to the St. Lawrence waterway system continued apace and many short lines were built to river ports.
United States

= Overview
=
Railroads played a large role in the development of the United States from the industrial revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
in the North-east
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each sepa ...
1810–50 to the settlement of the West 1850–1890. The American railroad mania began with the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad
The Baltimore and Ohio Railroad was the first common carrier railroad and the oldest railroad in the United States, with its first section opening in 1830. Merchants from Baltimore, which had benefited to some extent from the construction of ...
in 1828 and flourished until the Panic of 1873 bankrupted many companies and temporarily ended growth.
Although the South started early to build railways, it concentrated on short lines linking cotton regions to oceanic or river ports and the absence of an interconnected network was a major handicap during the Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
. The North and Midwest constructed networks that linked every city by 1860. In the heavily settled Midwestern Corn Belt, over 80 percent of farms were within 10 miles of a railway, facilitating the shipment of grain, hogs and cattle to national and international markets. A large number of short lines were built, but thanks to a fast developing financial system based on Wall Street
Wall Street is an eight-block-long street in the Financial District of Lower Manhattan in New York City. It runs between Broadway in the west to South Street and the East River in the east. The term "Wall Street" has become a metonym for t ...
and oriented to railway bonds, the majority were consolidated into 20 trunk lines by 1890. State and local governments often subsidized lines, but rarely owned them.
The system was largely built by 1910, but then trucks arrived to eat away the freight traffic and automobiles (and later airplanes) to devour the passenger traffic. The use of diesel electric locomotives (after 1940) made for much more efficient operations that needed fewer workers on the road and in repair shops.
= Mileage
=
Route mileage peaked at in 1916 and fell to in 2009.
In 1830, there were about of railroad track, in short lines linked to coal and granite mines.). After this, railroad lines grew rapidly. Ten years later, in 1840, the railways had grown to . By 1860, on the eve of civil war, the length had reached , mostly in the North. The South had much less trackage and it was geared to moving cotton short distances to river or ocean ports. The Southern railroads were destroyed during the war but were soon rebuilt. By 1890, the national system was virtually complete with .
In 1869, the symbolically important transcontinental railroad
A transcontinental railroad or transcontinental railway is contiguous railroad trackage, that crosses a continental land mass and has terminals at different oceans or continental borders. Such networks can be via the tracks of either a single ...
was completed in the United States with the driving of a golden spike (near the city of Ogden).
Latin America

 In Latin America in the late 19th and early 20th centuries railways were critical elements in the early stages of modernization of the
In Latin America in the late 19th and early 20th centuries railways were critical elements in the early stages of modernization of the Latin American economy
Latin America as a region has multiple nation-states, with varying levels of economic complexity. The Latin American economy is an export-based economy consisting of individual countries in the geographical regions of North America, Central Americ ...
, especially in linking agricultural regions to export-oriented seaports. After 1870 Latin American governments encouraged further rail development through generous concessions that included government subsidies for construction. Railway construction is the subject of considerable scholarship, examining the economic, political, and social impacts of railroads. Railways transformed many regions of Latin America beginning in the late nineteenth century. "Increasing exports of primary commodities, rising imports of capital goods, the expansion of activities drawing directly and indirectly on overseas investment, the rising share of manufacturing in output, and a generalized increase in the pace and scope of economic activity were all tied closely to the timing and character of the region's infrastructural development.
Rates of railway line construction were not uniform, but by 1870 railway line construction was underway, with Cuba leading with the largest railway track in service (1,295 km), followed by Chile (797 km), Brazil (744 km), Argentina (732 km), Peru (669 km), and Mexico (417 km). By 1900, Argentina (16,563 km), Brazil (15,316 km) and Mexico (13,615 km) were the leaders in length of track in service, and Peru, which had been an early leader in railway construction, had stagnated (1,790 km). In Mexico, growing nationalistic fervor led the government to bring the bulk of the nation's railroads under national control in 1909, with a new government corporation, Ferrocarriles Nacionales de México
Ferrocarriles Nacionales de México (better known as N de M and especially in its final years as FNM) was Mexico's state owned railroad company from 1938 to 1998, and prior to 1938 (dating from the regime of Porfirio Díaz), a major railroad con ...
(FNM), that exercised control of the main trunk rail lines through a majority of share ownership.
Asia
India
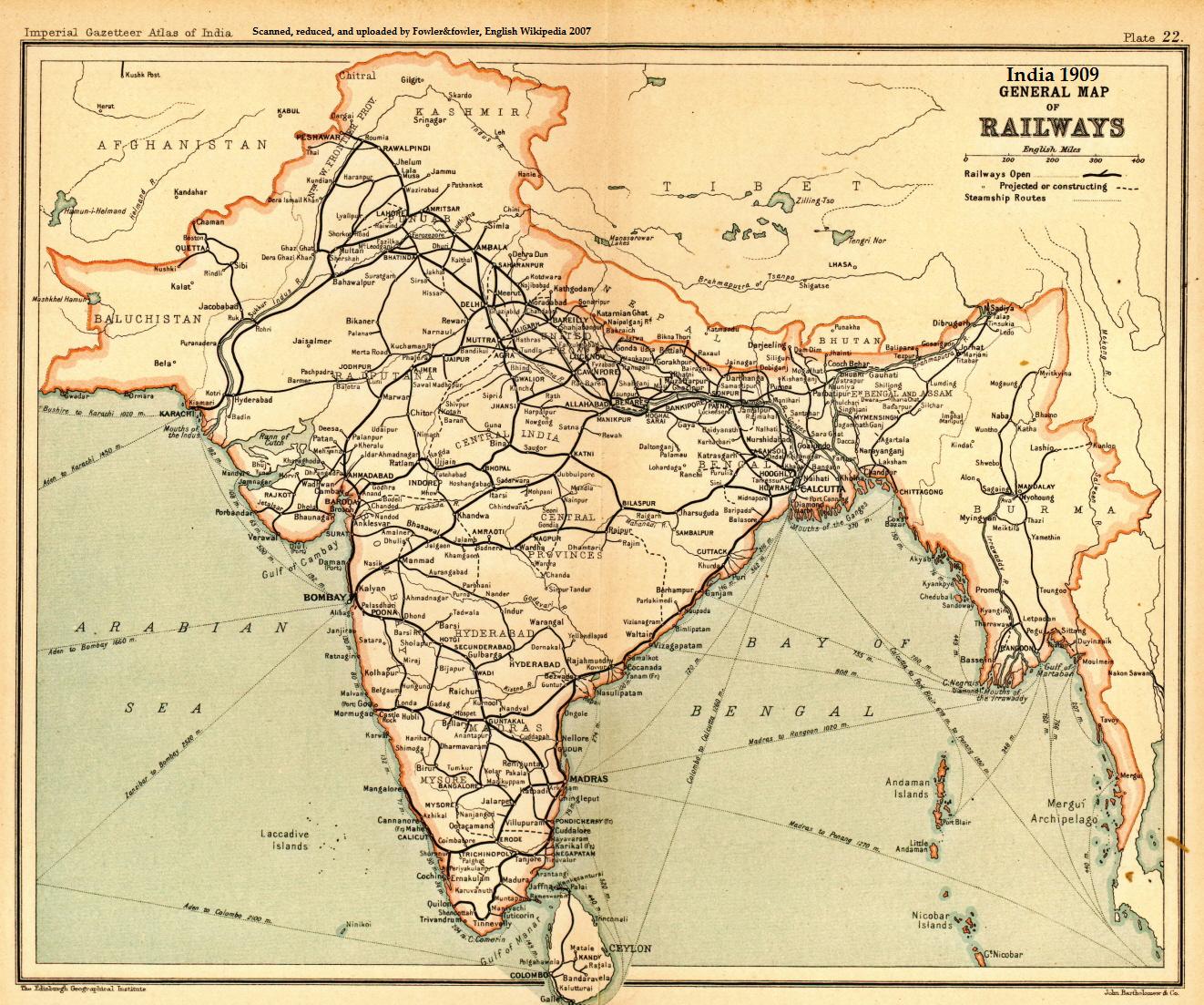 The first proposals for railways in
The first proposals for railways in India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
were made in Madras
Chennai (, ), formerly known as Madras ( the official name until 1996), is the capital city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost Indian state. The largest city of the state in area and population, Chennai is located on the Coromandel Coast of th ...
in 1832.Chintadripet
Chintadripet ('originally Chinna Thari Pettai) is a locality in Chennai, in India. Located on the southern banks of the Cooum River, it is a residential-cum-commercial area surrounded by Chepauk, Island Grounds, Pudupet, Egmore and Anna Salai ...
bridge in Madras
Chennai (, ), formerly known as Madras ( the official name until 1996), is the capital city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost Indian state. The largest city of the state in area and population, Chennai is located on the Coromandel Coast of th ...
in 1837. It was called ''Red Hill Railway''. It was hauled by a rotary steam engine locomotive manufactured by William Avery. It was built by Sir Arthur Cotton
General Sir Arthur Thomas Cotton (15 May 1803 – 24 July 1899) was a British general and irrigation engineer.
Cotton devoted his life to the construction of irrigation and navigation canals throughout British India. He helped many people by b ...
. It was primarily used for transporting granite stones for road building work in Madras.Dowleswaram
Dowleswaram is a part of Greater Rajamahendravaram Municipal Corporation (GRMC). It also forms a part of Godavari Urban Development Authority.
Landmarks
Sir Arthur Cotton built the Dowleswaram Barrage across the Godavari
The Godavari ...
in Rajahmundry
Rajahmundry, officially known as Rajamahendravaram, is a city in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh and District headquarters of East Godavari district. It is the sixth most populated city in the state. During British rule, the District of Rajah ...
. It was called ''Godavari Dam Construction Railway''. It was also built by Arthur Cotton. It was used to supply stones for construction of a dam over Godavari
The Godavari ( IAST: ''Godāvarī'' �od̪aːʋəɾiː is India's second longest river after the Ganga river and drains into the third largest basin in India, covering about 10% of India's total geographical area. Its source is in Trimbakesh ...
.Madras Railway
The Madras Railway (full name Madras Railway Company) played a pioneering role in developing railways in southern India and was merged in 1908 with Southern Mahratta Railway to form Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway.
The Madras Railway was ...
was incorporated. In the same year, the East India Railway
The East Indian Railway Company, operating as the East Indian Railway (reporting mark EIR), introduced railways to East India and North India, while the Companies such as the Great Indian Peninsula Railway, South Indian Railway, Bombay, Barod ...
company was incorporated. On 1 August 1849, Great Indian Peninsular Railway (GIPR) was incorporated. In 1851, a railway was built in Roorkee
Roorkee (Rūṛkī) is a city and a municipal corporation in the Haridwar district of the state of Uttarakhand, India. It is from Haridwar city, the district headquarter. It is spread over a flat terrain under Sivalik Hills of Himalayas. The c ...
. It was called ''Solani Aqueduct Railway''. It was hauled by steam locomotive Thomason, named after a British officer-in-charge. It was used for transporting construction materials for building of aqueduct over Solani river.India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
ran between Bombay
Mumbai (, ; also known as Bombay — the official name until 1995) is the capital city of the Indian state of Maharashtra and the ''de facto'' financial centre of India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Mumbai is the second- ...
( Bori Bunder) and Thane
Thane (; also known as Thana, the official name until 1996) is a metropolitan city in Maharashtra, India. It is situated in the north-eastern portion of the Salsette Island. Thane city is entirely within Thane taluka, one of the seven talukas ...
on 16 April 1853. The 14-carriage train was hauled by three steam locomotives: Sahib, Sindh and Sultan. It ran for about 34 kilometers between these two cities carrying 400 people. The line was built and operated by GIPR. This railway line was built in broad gauge
A broad-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge (the distance between the rails) broader than the used by standard-gauge railways.
Broad gauge of , commonly known as Russian gauge, is the dominant track gauge in former Soviet Union (CIS ...
, which became the standard for the railways in the country. The first passenger railway train in eastern India ran from Howrah
Howrah (, , alternatively spelled as Haora) is a city in the Indian state of West Bengal. Howrah is located on the western bank of the Hooghly River opposite its twin city of Kolkata. Administratively it lies within Howrah district, and is th ...
, near Calcutta
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , List of renamed places in India#West Bengal, the official name until 2001) is the Capital city, capital of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of West Bengal, on the eastern ba ...
to Hoogly, for distance of 24 miles, on 15 August 1854. The line was built and operated by EIR. The first passenger train in South India ran from Royapuram / Veyasarapady (Madras
Chennai (, ), formerly known as Madras ( the official name until 1996), is the capital city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost Indian state. The largest city of the state in area and population, Chennai is located on the Coromandel Coast of th ...
) to Wallajah Road (Arcot
Arcot (natively spelt as Ārkāḍu) is a town and urban area of Ranipet district in the state of Tamil Nadu, India. Located on the southern banks of Palar River, the city straddles a trade route between Chennai and Bangalore or Salem, between t ...
) on 1 July 1856, for a distance of 60 miles. It was built and operated by Madras Railway. On 24 February 1873, the first tram
A tram (called a streetcar or trolley in North America) is a rail vehicle that travels on tramway tracks on public urban streets; some include segments on segregated right-of-way. The tramlines or networks operated as public transport are ...
way (a horse-drawn tramway) opened in Calcutta between Sealdah and Armenian Ghat Street, a distance of 3.8 km.
Iran
Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
ian railway history goes back to 1887 when an approximately 20-km long railway between Tehran
Tehran (; fa, تهران ) is the largest city in Tehran Province and the capital of Iran. With a population of around 9 million in the city and around 16 million in the larger metropolitan area of Greater Tehran, Tehran is the most popul ...
and Ray
Ray may refer to:
Fish
* Ray (fish), any cartilaginous fish of the superorder Batoidea
* Ray (fish fin anatomy), a bony or horny spine on a fin
Science and mathematics
* Ray (geometry), half of a line proceeding from an initial point
* Ray (g ...
was established. After this time many short railways were constructed but the main railway, Trans-Iranian Railway, was started in 1927 and operated in 1938 by connecting the Persian Gulf to the Caspian Sea.
Japan
In 1867, in Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
, Edo period
The or is the period between 1603 and 1867 in the history of Japan, when Japan was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and the country's 300 regional '' daimyo''. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengoku period, the Edo period was characteriz ...
(Tokugawa shogunate
The Tokugawa shogunate (, Japanese 徳川幕府 ''Tokugawa bakufu''), also known as the , was the military government of Japan during the Edo period from 1603 to 1868. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"''Tokugawa-jidai''"in ''Japan Encyclopedia ...
) and its feudal system
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, cultural and political customs that flourished in medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structur ...
was ended, then Meiji period
The is an era of Japanese history that extended from October 23, 1868 to July 30, 1912.
The Meiji era was the first half of the Empire of Japan, when the Japanese people moved from being an isolated feudal society at risk of colonization ...
was entered and the government strived to acquire western culture and technology. In 1872, the first railway in Japan was inaugurated by Japanese Government Railways (JGR), connecting Shimbashi
, sometimes transliterated Shimbashi, is a district of Minato, Tokyo, Japan.
Name
Read literally, the characters in Shinbashi mean "new bridge".
History
The area was the site of a bridge built across the Shiodome River in 1604. The river was l ...
in Tokyo
Tokyo (; ja, 東京, , ), officially the Tokyo Metropolis ( ja, 東京都, label=none, ), is the capital and largest city of Japan. Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area () is the most populous in the world, with an estimated 37.468 ...
and Yokohama
is the second-largest city in Japan by population and the most populous municipality of Japan. It is the capital city and the most populous city in Kanagawa Prefecture, with a 2020 population of 3.8 million. It lies on Tokyo Bay, south of To ...
. The first 10 steam locomotives were ordered to Avonside
Avonside is an eastern suburb in Christchurch, New Zealand. It is one of the oldest suburbs of the city, with only Heathcote being older.
History
The suburb was named after Holy Trinity Avonside, which was built beside the Avon River in 18 ...
, Dübs, Sharp Stewart
Sharp, Stewart and Company was a steam locomotive manufacturer, initially located in Manchester, England. The company was formed in 1843 upon the demise of Sharp, Roberts & Co.. It moved to Glasgow, Scotland, in 1888, eventually amalgamating wit ...
, Vulcan
Vulcan may refer to:
Mythology
* Vulcan (mythology), the god of fire, volcanoes, metalworking, and the forge in Roman mythology
Arts, entertainment and media Film and television
* Vulcan (''Star Trek''), name of a fictional race and their home p ...
and Yorkshire
Yorkshire ( ; abbreviated Yorks), formally known as the County of York, is a Historic counties of England, historic county in northern England and by far the largest in the United Kingdom. Because of its large area in comparison with other Eng ...
companies in United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
. Subsequently, so many locomotives and railroad cars
A railroad car, railcar ( American and Canadian English), railway wagon, railway carriage, railway truck, railwagon, railcarriage or railtruck (British English and UIC), also called a train car, train wagon, train carriage or train truck, is ...
were ordered to United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
, United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
and Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
, before they could be manufactured in Japan. At that time, JGR adopted narrow gauge (1,067 mm) rather than standard gauge
A standard-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge of . The standard gauge is also called Stephenson gauge (after George Stephenson), International gauge, UIC gauge, uniform gauge, normal gauge and European gauge in Europe, and SGR in Ea ...
(1,435 mm), considering its cost of construction, so still now, narrow gauge has been mostly adopted and called "standard gauge in Japan". In 1874, the second railway connected between Osaka
is a designated city in the Kansai region of Honshu in Japan. It is the capital of and most populous city in Osaka Prefecture, and the third most populous city in Japan, following Special wards of Tokyo and Yokohama. With a population of 2. ...
and Kobe
Kobe ( , ; officially , ) is the capital city of Hyōgo Prefecture Japan. With a population around 1.5 million, Kobe is Japan's seventh-largest city and the third-largest port city after Tokyo and Yokohama. It is located in Kansai region, whic ...
by JGR. Following them, railways were spread around Japan, Hokkaido
is Japan's second largest island and comprises the largest and northernmost prefecture, making up its own region. The Tsugaru Strait separates Hokkaidō from Honshu; the two islands are connected by the undersea railway Seikan Tunnel.
The la ...
, Tōhoku, Kantō, Chūbu, Kansai
The or the , lies in the southern-central region of Japan's main island Honshu, Honshū. The region includes the Prefectures of Japan, prefectures of Nara Prefecture, Nara, Wakayama Prefecture, Wakayama, Kyoto Prefecture, Kyoto, Osaka Prefectur ...
, Chūgoku, Shikoku and Kyushu
is the third-largest island of Japan's five main islands and the most southerly of the four largest islands ( i.e. excluding Okinawa). In the past, it has been known as , and . The historical regional name referred to Kyushu and its surroun ...
regions by JGR and many private companies. In 1895, the first electric railway, also the first electric street railway was inaugurated by Kyoto Electric Railway in Kyoto
Kyoto (; Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in Japan. Located in the Kansai region on the island of Honshu, Kyoto forms a part of the Keihanshin metropolitan area along with Osaka and Kobe. , the ci ...
, and the first trams seems to be ordered to J. G. Brill in United States. In 1923, the first diesel locomotive
A diesel locomotive is a type of railway locomotive in which the prime mover is a diesel engine. Several types of diesel locomotives have been developed, differing mainly in the means by which mechanical power is conveyed to the driving whee ...
was ordered to Deutz AG in Germany by Horinouchi Railway Company in Shizuoka prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan located in the Chūbu region of Honshu. Shizuoka Prefecture has a population of 3,637,998 and has a geographic area of . Shizuoka Prefecture borders Kanagawa Prefecture to the east, Yamanashi Prefecture to the northea ...
. In 1927, the first subway
Subway, Subways, The Subway, or The Subways may refer to:
Transportation
* Subway, a term for underground rapid transit rail systems
* Subway (underpass), a type of walkway that passes underneath an obstacle
* Subway (George Bush Interconti ...
was inaugurated by Tokyo Metro, and connected between Ueno
is a district in Tokyo's Taitō Ward, best known as the home of Ueno Park. Ueno is also home to some of Tokyo's finest cultural sites, including the Tokyo National Museum, the National Museum of Western Art, and the National Museum of Na ...
and Asakusa
is a district in Taitō, Tokyo, Japan. It is known as the location of the Sensō-ji, a Buddhist temple dedicated to the bodhisattva Kannon. There are several other temples in Asakusa, as well as various festivals, such as the .
History
The ...
in Tokyo, and the electric railroad cars were ordered to Nippon Sharyo
, formed in 1896, is a major rolling stock manufacturer based in Nagoya, Japan. In 1996, it abbreviated its name to "日本車両" Nippon Sharyō. Its shortest abbreviation is Nissha "日車". It was a listed company on Nikkei 225 until 2 ...
as Class 1000. Then, in 1928, the first diesel railroad car, equipped with diesel engine of MAN AG
MAN Truck & Bus SE (formerly MAN Nutzfahrzeuge AG, ) is a subsidiary of Traton, and one of the leading international providers of commercial vehicles. Headquartered in Munich, Germany, MAN Truck & Bus produces vans in the range from 3.0 to 5.5 t ...
, was ordered and manufactured by Amemiya Manufacturing, for Nagaoka Railway in Niigata prefecture.
Viewing the development of locomotive and railroad car technology in Japan, in 1893, the first steam locomotive was manufactured by Kobe works of JGR as JGR Class 860. Then in 1904, the first electric railroad car seems to be manufactured by Iidabashi
is a district of Chiyoda, Tokyo, Japan. It was in the former ward of Kōjimachi, which existed in Tokyo until 1947.
Etymology
Iidabashi is named after a nearby bridge called Iida Bridge (, ''Iidabashi''), itself named after an Edo-period farm ...
works of Kōbu railway (now Chūō Main Line
The , commonly called the Chūō Line, is one of the major trunk railway lines in Japan. It connects Tokyo and Nagoya, although it is the slowest direct railway connection between the two cities; the coastal Tōkaidō Main Line is slightly faste ...
of JR East
The is a major passenger railway company in Japan and is the largest of the seven Japan Railways Group companies. The company name is officially abbreviated as JR-EAST or JR East in English, and as in Japanese. The company's headquarters are ...
) as Class 950. In 1926, the first electric locomotive
An electric locomotive is a locomotive powered by electricity from overhead lines, a third rail or on-board energy storage such as a battery or a supercapacitor. Locomotives with on-board fuelled prime movers, such as diesel engines or gas ...
was manufactured by Hitachi
() is a Japanese multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate corporation headquartered in Chiyoda, Tokyo, Japan. It is the parent company of the Hitachi Group (''Hitachi Gurūpu'') and had formed part of the Ni ...
as JGR Class ED15. In 1927, the first diesel locomotive, equipped with diesel engine of Niigata Engineering, was manufactured by Amemiya Manufacturing. By World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, Japan also suffered catastrophic damage, however they accomplished reconstruction. In 1964, the first electric high-speed rail
High-speed rail (HSR) is a type of rail system that runs significantly faster than traditional rail, using an integrated system of specialised rolling stock and dedicated tracks. While there is no single standard that applies worldwide, lines ...
in the world, Tōkaidō Shinkansen
The is a Japanese high-speed rail line that is part of the nationwide Shinkansen network. Along with the Sanyo Shinkansen, it forms a continuous high-speed railway through the Taiheiyō Belt, also known as the Tokaido corridor. Opened in 1964, ...
(standard gauge) was inaugurated by Japanese National Railways (JNR), and connected between Tokyo and Osaka. The first high-speed trains were manufactured by Kawasaki Heavy Industries
(or simply Kawasaki) is a Japanese Public company, public multinational corporation manufacturer of motorcycles, engines, Heavy equipment (construction), heavy equipment, aerospace and Military, defense equipment, rolling stock and ships, headq ...
, Nippon Sharyo
, formed in 1896, is a major rolling stock manufacturer based in Nagoya, Japan. In 1996, it abbreviated its name to "日本車両" Nippon Sharyō. Its shortest abbreviation is Nissha "日車". It was a listed company on Nikkei 225 until 2 ...
, Hitachi
() is a Japanese multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate corporation headquartered in Chiyoda, Tokyo, Japan. It is the parent company of the Hitachi Group (''Hitachi Gurūpu'') and had formed part of the Ni ...
, Kinki Sharyo and Tokyu Car Corporation (now J-TREC), as Shinkansen 0 Series. Today, Electric, battery electric, electric hybrid, electric-diesel, diesel locomotives, railroad cars, high-speed trains, and AGTs are manufacrured by Hitachi, Kawasaki, Nippon Sharyo, Kinki Sharyo, J-TREC and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
is a Japanese multinational engineering, electrical equipment and electronics corporation headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. MHI is one of the core companies of the Mitsubishi Group and its automobile division is the predecessor of Mitsubishi Mo ...
, and they are running around the world.
Pakistan
It was in 1847 when the first railway was imagined but it was not until 1861 when it came into existence in the form of the railway built from Karachi
Karachi (; ur, ; ; ) is the most populous city in Pakistan and 12th most populous city in the world, with a population of over 20 million. It is situated at the southern tip of the country along the Arabian Sea coast. It is the former cap ...
to Kotri
Kotri ( sd, ڪوٽڙي, ur, ) is a city and the headquarters of the Kotri Taluka of Jamshoro District of Sindh province in Pakistan. Located on the right bank of the Indus River, it is the 29th largest city in Pakistan by population.
Name
The ...
. Since then rail transport
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a p ...
is a popular mode of non-independent transport in Pakistan.
Africa
Angola
Botswana
Congo
East Africa
The railway was built from the Kenyan port of Mombasa to Kampala, Uganda, and construction was hampered by the presence of man-eating lions.["The maneaters of Tsavo" by Patterson, J. H., Macmillan, 1952]
Egypt
= 1833–1877
=
Robert Stephenson (1803–59) was the engineer of Egypt's first railway
In 1833, Muhammad Ali
Muhammad Ali (; born Cassius Marcellus Clay Jr.; January 17, 1942 – June 3, 2016) was an American professional boxer and activist. Nicknamed "The Greatest", he is regarded as one of the most significant sports figures of the 20th century, a ...
Pasha
Pasha, Pacha or Paşa ( ota, پاشا; tr, paşa; sq, Pashë; ar, باشا), in older works sometimes anglicized as bashaw, was a higher rank in the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman political and military system, typically granted to governors, gener ...
considered building a railway between Suez and Cairo
Cairo ( ; ar, القاهرة, al-Qāhirah, ) is the capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the largest urban agglomeration in Africa, the Arab world and the Middle East: The Greater Cairo metro ...
to improve transit between Europe and India. Muhammad Ali had proceeded to buy the rail when the project was abandoned due to pressure by the French who had an interest in building a canal instead.
Proposed railway from Cairo to the Sea of Suez by C.F. Cheffins, 1840s; state carriage by Wason Manufacturing built for Sa'id Pasha
Mehmed Said Pasha ( ota, محمد سعيد پاشا ; 1838–1914), also known as Küçük Said Pasha ("Said Pasha the Younger") or Şapur Çelebi or in his youth as Mabeyn Başkatibi Said Bey, was an Ottoman monarchist, senator, statesman ...
for state functions, included with 161 less ornate railcars sent by the company in 1860
Muhammad Ali died in 1848, and in 1851 his successor Abbas I contracted Robert Stephenson to build Egypt's first standard gauge
A standard-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge of . The standard gauge is also called Stephenson gauge (after George Stephenson), International gauge, UIC gauge, uniform gauge, normal gauge and European gauge in Europe, and SGR in Ea ...
railway. The first section, between Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandria ...
on the Mediterranean coast and Kafr el-Zayyat on the Rosetta branch of the Nile was opened in 1854. This was the first railway in the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
as well as Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
and the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabian Peninsula, Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Anatolia, Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Pro ...
. In the same year Abbas died and was succeeded by Sa'id Pasha
Mehmed Said Pasha ( ota, محمد سعيد پاشا ; 1838–1914), also known as Küçük Said Pasha ("Said Pasha the Younger") or Şapur Çelebi or in his youth as Mabeyn Başkatibi Said Bey, was an Ottoman monarchist, senator, statesman ...
, in whose reign the section between Kafr el-Zayyat and Cairo
Cairo ( ; ar, القاهرة, al-Qāhirah, ) is the capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the largest urban agglomeration in Africa, the Arab world and the Middle East: The Greater Cairo metro ...
was completed in 1856 followed by an extension from Cairo to Suez in 1858. This completed the first modern transport link between the Mediterranean and the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by th ...
, as Ferdinand de Lesseps did not complete the Suez Canal
The Suez Canal ( arz, قَنَاةُ ٱلسُّوَيْسِ, ') is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia. The long canal is a popular ...
until 1869.
Namibia (South West Africa)
The first railway in the German colony of South West Africa was the -long line running North-East from Walvis Bay to connect with the existing road between Swakopmund and Windhoek
Windhoek (, , ) is the capital and largest city of Namibia. It is located in central Namibia in the Khomas Highland plateau area, at around above sea level, almost exactly at the country's geographical centre. The population of Windhoek in 20 ...
. It was built to gauge and was opened in 1898.
Morocco
The Moroccan rail transport was first developed around 1906 and later during the French and Spanish protectorate. It functioned initially as a means to transport natural resources from in-land mines to the harbors. It was also used to move colonial troops.
Mozambique
South Africa
Sudan
Zambia
Zimbabwe
See also
See also
* :Rail transport timelines
* George Bradshaw
George Bradshaw (29 July 1800 – 6 September 1853) was an English cartographer, printer and publisher. He developed Bradshaw's Guide, a widely sold series of combined railway guides and timetables.
Biography
Bradshaw was born at Windsor Brid ...
, originator of the railway timetable
* Historical sizes of railroads in North America
* John Blenkinsop (1783–1831), inventor
* Matthias W. Baldwin
Matthias William Baldwin (December 10, 1795 – September 7, 1866) was an American inventor and machinery manufacturer, specializing in the production of steam locomotives. Baldwin's small machine shop, established in 1825, grew to become ...
(1795–1866), manufacturer
* Oldest railroads in North America
This is a list of the earliest railroads in North America, including various railroad-like precursors to the general modern form of a company or government agency operating locomotive-drawn trains on metal tracks.
Railroad-like entities (1700s ...
* History of the railway track
* Railway speed record
The world record for a conventional wheeled passenger train is held by France's TGV (''Train à Grande Vitesse''), set in 2007 when it reached on a section of track.
Japan's experimental maglev train L0 Series achieved on a 42.8 km mag ...
* South American Railway Congress
* Thomas Gray (1788–1848), railway advocate, published 1st ed. of ''Observations on a General Iron Railway'', 1820.
* Timeline of railway history
Antiquity
* Verdelis, Nikolaos: "Le diolkos de L'Isthme", ''Bulletin de Correspondance Hellénique'', Vol. 81 (1957), pp. 526-529 (526)Cook, R. M.: "Archaic Greek Trade: Three Conjectures 1. The Diolkos", ''The Journal of Hellenic Studies'', V ...
*History of trams
The history of trams, streetcars, or trolleys began in the early nineteenth century. It can be divided up into several discrete periods defined by the principal means of motive power used.
Horse-drawn
The world's first passenger tram was ...
References
Bibliography
* Cameron, Rondo E. ''France and the Economic Development of Europe, 1800–1914: Conquests of Peace and Seeds of War'' (1961), pp. 304–227 covers France, Spain Russia and others
*
* Coatsworth, John H. "Indispensable Railroads in a Backward Economy: The Case of Mexico," ''Journal of Economic History'' (1979) 39#4 pp. 939–96
in JSTOR
* Duffy, Michael C. ''Electric Railways: 1880-1990'' (2003).
*
* Fremdling, Rainer. "Railroadss and German Economic Growth: A Leading Sector Analysis with a Comparison to the United States and Great Britain," ''Journal of Economic History'' (1977) 37#3 pp. 583–604
in JSTOR
* Hadfield, C. and Skempton, A. W. ''William Jessop, Engineer'' (Newton Abbot 1979)
* Jenks, Leland H.
Leland Hamilton Jenks (April 10, 1892 – February 1, 1976) was an American economic historian, Professor of economics and sociology at Wellesley College, and Professor at Columbia University, where he taught economic history. He is known for his ...
"Railroads as an Economic Force in American Development," ''The Journal of Economic History'', vol. 4, no. 1 (May 1944), 1–20
in JSTOR
* Includes maps of major rail lines on all continents c. 1914
*
* Lewis, M. J. T.
"Railways in the Greek and Roman world"
in Guy, A. / Rees, J. (eds), ''Early Railways. A Selection of Papers from the First International Early Railways Conference'' (2001), pp. 8–19 (10–15)
* Misa, Thomas J. ''A Nation of Steel: The Making of Modern America, 1865–1925'' (1995
*
* Nock, O. S. ed. ''Encyclopedia of Railways'' (London, 1977), worldwide coverage, heavily illustrated
* O’Brien, Patrick. ''Railways and the Economic Development of Western Europe, 1830–1914'' (1983)
* O'Brien, Patrick. ''The New Economic History of the Railways'' (Routledge, 2014)
* Omrani, Bijanbr>Asia Overland: Tales of Travel on the Trans-Siberian and Silk Road
Odyssey Publications, 2010
* Otte, Thomas G. and Keith Neilson, eds. ''Railways and International Politics: Paths of Empire, 1848–1945'' (Routledge, 2012) 11 essays by leading scholars
*
* Riley, C. J. ''The Encyclopedia of Trains & Locomotives'' (2002)
* Savage, Christopher and T. C. Barker. ''Economic History of Transport in Britain'' (Routledge, 2012)
* Schivelbusch, Wolfgang. ''The railway journey: the industrialization of time and space in the nineteenth century'' (Univ of California Press, 2014)
*
* Stover, John. ''American Railways'' (2nd ed 1997)
* Includes numerous c. 1880 diagrams and illustrations
* Jack Simmons and Gordon Biddle (editors). ''The Oxford Companion to British Railway History: From 1603 to the 1990s'' (2nd ed 1999)
* Stover, John. ''The Routledge Historical Atlas of the American Railroads'' (2001)
* Summerhill, William R. "Big Social Savings in a Small Laggard Economy: Railroad-Led Growth in Brazil," ''Journal of Economic History'' (2005) 65#1 pp. 72–10
in JSTOR
* Wolmar, Christian. ''On the wrong line: How ideology and incompetence wrecked Britain's railways'' (Kemsing Publishing, 2005).
* Wolmar, Christian. ''Fire and steam: a new history of the railways in Britain'' (Atlantic Books, 2009).
* Wolmar, Christian. ''Engines of war: how wars were won & lost on the railways'' (PublicAffairs, 2010).
* Wolmar, Christian. ''Blood, iron, and gold: How the railroads transformed the world'' (Public Affairs, 2011).
* Wolmar, Christian. ''The great railroad revolution: The history of trains in America'' (PublicAffairs, 2012).
* Wolmar, Christian. ''The Iron Road: The Illustrated History of Railways'' (Dorling Kindersley, 2014).
* Wolmar, Christian. ''To the Edge of the World: The Story of the Trans-Siberian Express, the World's Greatest Railroad'' (PublicAffairs, 2014).
* Wolmar, Christian. ''Railways and the Raj: How the age of steam transformed India'' (Atlantic Books, 2017).
Historiography
* Hurd II, John and Ian J. Kerr, eds. ''India's railway history: a research handbook'' (Brill, 2012)
* Lee, Robert. "A Fractious Federation: Patterns in Australian Railway Historiography." ''Mobility in History''(2013) 4#1 pp. 149–158
* McDonald, Kate. "Asymmetrical Integration: Lessons from a Railway Empire." ''Technology and Culture'' (2015) 56#1 pp. 115–149
* Pathak, Dev N. "Marian Aguiar, Tracking Modernity: India’s Railway and the Culture of Mobility." ''South Asia: Journal of South Asian Studies'' (2012) 35#4 pp. 900–901
* Salerno, Elena. "The Historiography of Railways in Argentina: Between Foreign Investment, Nationalism and Liberalism." ''Mobility in History'' (2014) 5#1 pp. 105–120
External links
Archives Center, National Museum of American History, Smithsonian Institution.
National Railway Historical Society
''Foreign Railways of the World: Containing in One Volume, the Names of Officers, Length, Capital,...'' (1884)
How the Railroad is Modernising Asia
The Advertiser, Adelaide, S. Australia, 22 March 1913. N.B.: The article is approx. 1,500 words, covering approx. a dozen Asian countries.
{{Authority control
Rail transport
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a p ...
 The history of rail transport began in the BCE times. It can be divided into several discrete periods defined by the principal means of track material and motive power used.
The history of rail transport began in the BCE times. It can be divided into several discrete periods defined by the principal means of track material and motive power used.
 In 1515, Cardinal Matthäus Lang wrote a description of the
In 1515, Cardinal Matthäus Lang wrote a description of the 

 The introduction of steam engines for powering blast air to
The introduction of steam engines for powering blast air to  Cast iron was not a satisfactory material for rails because it was brittle and broke under heavy loads. The wrought iron rail, invented by
Cast iron was not a satisfactory material for rails because it was brittle and broke under heavy loads. The wrought iron rail, invented by  The first full-scale working railway
The first full-scale working railway  In 1814, George Stephenson, inspired by the early locomotives of Trevithick, Murray and Hedley, persuaded the manager of the Killingworth colliery where he worked to allow him to build a steam-powered machine. Stephenson played a pivotal role in the development and widespread adoption of the steam locomotive. His designs considerably improved on the work of the earlier pioneers. He built the locomotive '' Blücher'', also a successful
In 1814, George Stephenson, inspired by the early locomotives of Trevithick, Murray and Hedley, persuaded the manager of the Killingworth colliery where he worked to allow him to build a steam-powered machine. Stephenson played a pivotal role in the development and widespread adoption of the steam locomotive. His designs considerably improved on the work of the earlier pioneers. He built the locomotive '' Blücher'', also a successful 
 The first use of electrification on a main line was on a four-mile stretch of the Baltimore Belt Line of the
The first use of electrification on a main line was on a four-mile stretch of the Baltimore Belt Line of the  Italian railways were the first in the world to introduce electric traction for the entire length of a main line rather than just a short stretch. The 106 km
Italian railways were the first in the world to introduce electric traction for the entire length of a main line rather than just a short stretch. The 106 km  A significant breakthrough occurred in 1914, when
A significant breakthrough occurred in 1914, when  The first electrified
The first electrified  In recent years deregulation has been a major topic across Europe.
In recent years deregulation has been a major topic across Europe.

 The success of the Stockton and Darlington encouraged the rich investors in the rapidly industrialising North West of England to embark upon a project to link the rich cotton manufacturing town of
The success of the Stockton and Darlington encouraged the rich investors in the rapidly industrialising North West of England to embark upon a project to link the rich cotton manufacturing town of  In France, railways were first operated by private coal companies the first legal agreement to build a railway was given in 1823 and the line (from Saint-Étienne to Andrézieux) was operated in 1827. Much of the equipment was imported from Britain but this stimulated machinery makers, which soon created a national heavy industry. Trains became a national medium for the modernization of backward regions and a leading advocate of this approach was the poet-politician Alphonse de Lamartine. One writer hoped that railways might improve the lot of "populations two or three centuries behind their fellows" and eliminate "the savage instincts born of isolation and misery." Consequently, France built a centralized system that radiated from Paris (plus lines that cut east to west in the south). This design was intended to achieve political and cultural goals rather than maximize efficiency.
After some consolidation, six companies controlled monopolies of their regions, subject to close control by the government in terms of fares, finances and even minute technical details. The central government department of Ponts et Chaussées ridges and roadsbrought in British engineers and workers, handled much of the construction work, provided engineering expertise and planning, land acquisition and construction of permanent infrastructure such as the track bed, bridges and tunnels. It also subsidized militarily necessary lines along the German border, which was considered necessary for the national defense. Private operating companies provided management, hired labor, laid the tracks and built and operated stations. They purchased and maintained the rolling stock—6,000 locomotives were in operation in 1880, which averaged 51,600 passengers a year or 21,200 tons of freight.
In France, railways were first operated by private coal companies the first legal agreement to build a railway was given in 1823 and the line (from Saint-Étienne to Andrézieux) was operated in 1827. Much of the equipment was imported from Britain but this stimulated machinery makers, which soon created a national heavy industry. Trains became a national medium for the modernization of backward regions and a leading advocate of this approach was the poet-politician Alphonse de Lamartine. One writer hoped that railways might improve the lot of "populations two or three centuries behind their fellows" and eliminate "the savage instincts born of isolation and misery." Consequently, France built a centralized system that radiated from Paris (plus lines that cut east to west in the south). This design was intended to achieve political and cultural goals rather than maximize efficiency.
After some consolidation, six companies controlled monopolies of their regions, subject to close control by the government in terms of fares, finances and even minute technical details. The central government department of Ponts et Chaussées ridges and roadsbrought in British engineers and workers, handled much of the construction work, provided engineering expertise and planning, land acquisition and construction of permanent infrastructure such as the track bed, bridges and tunnels. It also subsidized militarily necessary lines along the German border, which was considered necessary for the national defense. Private operating companies provided management, hired labor, laid the tracks and built and operated stations. They purchased and maintained the rolling stock—6,000 locomotives were in operation in 1880, which averaged 51,600 passengers a year or 21,200 tons of freight.
 Although starting the whole system at once was politically expedient, it delayed completion and forced even more reliance on temporary experts brought in from Britain. Financing was also a problem. The solution was a narrow base of funding through the Rothschilds and the closed circles of the Bourse in Paris, so France did not develop the same kind of national stock exchange that flourished in London and New York. The system did help modernize the parts of rural France it reached and help to develop many local industrial centers, mostly in the North (coal and iron mines) and in the East (textiles and heavy industry). Critics such as
Although starting the whole system at once was politically expedient, it delayed completion and forced even more reliance on temporary experts brought in from Britain. Financing was also a problem. The solution was a narrow base of funding through the Rothschilds and the closed circles of the Bourse in Paris, so France did not develop the same kind of national stock exchange that flourished in London and New York. The system did help modernize the parts of rural France it reached and help to develop many local industrial centers, mostly in the North (coal and iron mines) and in the East (textiles and heavy industry). Critics such as  The takeoff stage of economic development came with the railroad revolution in the 1840s, which opened up new markets for local products, created a pool of middle managers, increased the demand for engineers, architects and skilled machinists and stimulated investments in coal and iron. Political disunity of three dozen states and a pervasive conservatism made it difficult to build railways in the 1830s. However, by the 1840s, trunk lines did link the major cities; each German state was responsible for the lines within its own borders. Economist Friedrich List summed up the advantages to be derived from the development of the railway system in 1841:
# As a means of national defence, it facilitates the concentration, distribution and direction of the army.
# It is a means to the improvement of the culture of the nation. It brings talent, knowledge and skill of every kind readily to market.
# It secures the community against dearth and famine and against excessive fluctuation in the prices of the necessaries of life.
# It promotes the spirit of the nation, as it has a tendency to destroy the Philistine spirit arising from isolation and provincial prejudice and vanity. It binds nations by ligaments and promotes an interchange of food and of commodities, thus making it feel to be a unit. The iron rails become a nerve system, which, on the one hand, strengthens public opinion, and, on the other hand, strengthens the power of the state for police and governmental purposes.
Lacking a technological base at first, the Germans imported their engineering and hardware from Britain, but quickly learned the skills needed to operate and expand the railways. In many cities, the new railway shops were the centres of technological awareness and training, so that by 1850, Germany was self-sufficient in meeting the demands of railroad construction and the railways were a major impetus for the growth of the new steel industry. Observers found that even as late as 1890, their engineering was inferior to Britain's. However, German unification in 1870 stimulated consolidation, nationalisation into state-owned companies and further rapid growth. Unlike the situation in France, the goal was support of industrialisation and so heavy lines crisscrossed the Ruhr and other industrial districts and provided good connections to the major ports of Hamburg and Bremen. By 1880, Germany had 9,400 locomotives pulling 43,000 passengers and 30,000 tons of freight a day and forged ahead of France.
The takeoff stage of economic development came with the railroad revolution in the 1840s, which opened up new markets for local products, created a pool of middle managers, increased the demand for engineers, architects and skilled machinists and stimulated investments in coal and iron. Political disunity of three dozen states and a pervasive conservatism made it difficult to build railways in the 1830s. However, by the 1840s, trunk lines did link the major cities; each German state was responsible for the lines within its own borders. Economist Friedrich List summed up the advantages to be derived from the development of the railway system in 1841:
# As a means of national defence, it facilitates the concentration, distribution and direction of the army.
# It is a means to the improvement of the culture of the nation. It brings talent, knowledge and skill of every kind readily to market.
# It secures the community against dearth and famine and against excessive fluctuation in the prices of the necessaries of life.
# It promotes the spirit of the nation, as it has a tendency to destroy the Philistine spirit arising from isolation and provincial prejudice and vanity. It binds nations by ligaments and promotes an interchange of food and of commodities, thus making it feel to be a unit. The iron rails become a nerve system, which, on the one hand, strengthens public opinion, and, on the other hand, strengthens the power of the state for police and governmental purposes.
Lacking a technological base at first, the Germans imported their engineering and hardware from Britain, but quickly learned the skills needed to operate and expand the railways. In many cities, the new railway shops were the centres of technological awareness and training, so that by 1850, Germany was self-sufficient in meeting the demands of railroad construction and the railways were a major impetus for the growth of the new steel industry. Observers found that even as late as 1890, their engineering was inferior to Britain's. However, German unification in 1870 stimulated consolidation, nationalisation into state-owned companies and further rapid growth. Unlike the situation in France, the goal was support of industrialisation and so heavy lines crisscrossed the Ruhr and other industrial districts and provided good connections to the major ports of Hamburg and Bremen. By 1880, Germany had 9,400 locomotives pulling 43,000 passengers and 30,000 tons of freight a day and forged ahead of France.

 In the early 1830s, the Russian father and son inventors the Cherepanovs built the first Russian steam locomotive. The first railway line was built in Russia in 1837 between Saint-Petersburg and Tsarskoye Selo. It was 27 km long and linked the Imperial Palaces at Tsarskoye Selo and Pavlovsk. The track gauge was . Russia was in need of big transportation systems and geographically suited to railroads, with long flat stretches of land and comparatively simple land acquisition. It was hampered, however, by its outmoded political situation and a shortage of capital. Foreign initiative and capital were required. It was the Americans who brought the technology of railway construction to Russia. In 1842, planning began for the building of Russia's first important railway; it linked Moscow and St Petersburg.
In the early 1830s, the Russian father and son inventors the Cherepanovs built the first Russian steam locomotive. The first railway line was built in Russia in 1837 between Saint-Petersburg and Tsarskoye Selo. It was 27 km long and linked the Imperial Palaces at Tsarskoye Selo and Pavlovsk. The track gauge was . Russia was in need of big transportation systems and geographically suited to railroads, with long flat stretches of land and comparatively simple land acquisition. It was hampered, however, by its outmoded political situation and a shortage of capital. Foreign initiative and capital were required. It was the Americans who brought the technology of railway construction to Russia. In 1842, planning began for the building of Russia's first important railway; it linked Moscow and St Petersburg.
 Cuba, then a Spanish colony, built its first rail line in 1837. The history of rail transport in peninsular Spain begins in 1848 with the construction of a railway line between Barcelona and
Cuba, then a Spanish colony, built its first rail line in 1837. The history of rail transport in peninsular Spain begins in 1848 with the construction of a railway line between Barcelona and  The earliest railway in Canada was a wooden railway reportedly used in the construction of the French fortress at
The earliest railway in Canada was a wooden railway reportedly used in the construction of the French fortress at 

 In Latin America in the late 19th and early 20th centuries railways were critical elements in the early stages of modernization of the
In Latin America in the late 19th and early 20th centuries railways were critical elements in the early stages of modernization of the  The first proposals for railways in
The first proposals for railways in