|
4-2-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles, two powered driving wheels on one axle and no trailing wheels. This type of locomotive is often called a Jervis type, the name of the original designer. Overview The wheel arrangement type was common on United States railroads from the 1830s through the 1850s. The first to be built was the ''Experiment'', later named ''Brother Jonathan'', for the Mohawk and Hudson Railroad in 1832. It was built by the West Point Foundry based on a design by John B. Jervis. Having little else to reference, the manufacturers patterned the boiler and valve gear after locomotives built by Robert Stephenson of England. A few examples of Stephenson locomotives were already in operation in America, so engineers did not have to travel too far to get their initial ideas. In England, the was developed around 1840 from the 2-2-2 design of Stephenson's first Long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
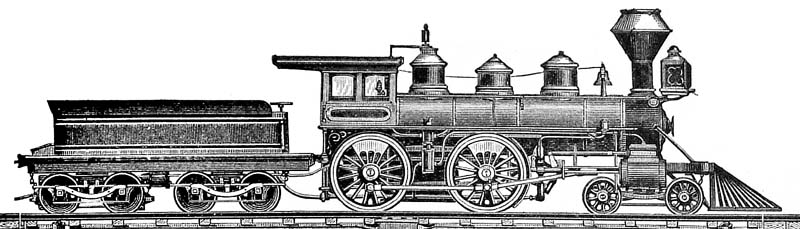
4-4-0
4-4-0 is a locomotive type with a classification that uses the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement and represents the arrangement: four leading wheels on two axles (usually in a leading bogie), four powered and coupled driving wheels on two axles, and a lack of trailing wheels. Due to the large number of the type that were produced and used in the United States, the 4-4-0 is most commonly known as the American type, but the type subsequently also became popular in the United Kingdom, where large numbers were produced.White, John H., Jr. (1968). ''A history of the American locomotive; its development: 1830-1880''. New York: Dover Publications, pp. 46-. Almost every major railroad that operated in North America in the first half of the 19th century owned and operated locomotives of this type. The first use of the name ''American'' to describe locomotives of this wheel arrangement was made by ''Railroad Gazette'' in April 1872. Prior to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Roe Campbell
Henry Roe Campbell (September 9, 1807 – February 6, 1879) was an American surveyor and civil engineer. Campbell contributed to American railroading and bridge-building in the first half of the 19th century. Campbell patented his 4-4-0 design in February 1836, just a few months before the patent law was changed to require that claims include proof of originality or novelty. The 4-4-0 or American type steam locomotive was the most popular wheel arrangement in 19th century American railroads and was widely copied. White noted that the design was successful because it "... met every requirement of early United States railroads". At the end of Campbell's career. a Harper's Magazine article in March 1879 noted that the impact Campbell's design played in railroad development in the United States when it wrote: Not only did the new American Type steam locomotive deliver more horsepower, tractive effort, and reliability it also laid the groundwork for locomotive engineering in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whyte Notation
Whyte notation is a classification method for steam locomotives, and some internal combustion locomotives and electric locomotives, by wheel arrangement. It was devised by Frederick Methvan Whyte, and came into use in the early twentieth century following a December 1900 editorial in ''American Engineer and Railroad Journal''. The notation was adopted and remains in use in North America and the United Kingdom to describe the wheel arrangements of steam locomotives (in the latter case also for diesel and electric locomotives), but for modern locomotives, multiple units and trams it has been supplanted by the UIC system in Europe and by the AAR system (essentially a simplification of the UIC system) in North America. Structure of the system Basic form The notation in its basic form counts the number of leading wheels, then the number of driving wheels, and finally the number of trailing wheels, numbers being separated by dashes. For example, a locomotive with two leadi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long Boiler Locomotive
The Long Boiler locomotive was the object of a patent by Robert Stephenson and the name became synonymous with the pattern. Its defining feature is that the firebox is placed ''behind'' the rearmost driving axle. This gives a long boiler barrel, with long fire-tubes. There is thus a generous heating surface area, giving a boiler that is both powerful and efficient. It is generally perceived that it arose out of attempts to match the power of broad gauge locomotives within the limitations of the standard gauge of Stephenson railways. However, the patent originally arose from a problem which became apparent as trains travelled longer distances, specifically on the North Midland Railway in England around 1841, where fire tubes and smokeboxes were becoming destroyed by the heat. Experiments Experiments at the North Midland's Derby Works showed temperatures as high as , determined by placing a small cup of zinc within the smokebox beneath the chimney. Stephenson extended the boiler, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Norris (locomotive Builder)
William Norris (July 2, 1802 – January 5, 1867) was an American steam locomotive builder. He founded the Norris Locomotive Works and through this company pioneered the use of the 4-2-0 (the ''Norris'' type) locomotive type in America during the 1840s. In 1837, William Norris was elected as a member to the American Philosophical Society The American Philosophical Society (APS), founded in 1743 in Philadelphia, is a scholarly organization that promotes knowledge in the sciences and humanities through research, professional meetings, publications, library resources, and communit .... References * American locomotive engineers'. Retrieved February 9, 2005. 1802 births 1867 deaths Locomotive builders and designers American people in rail transportation American railroad mechanical engineers American railroad pioneers 19th-century American engineers 19th-century American businesspeople {{US-mechanical-engineer-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leading Wheel
The leading wheel or leading axle or pilot wheel of a steam locomotive is an unpowered wheel or axle located in front of the driving wheels. The axle or axles of the leading wheels are normally located on a leading truck. Leading wheels are used to help the locomotive negotiate curves and to support the front portion of the boiler. Overview Importantly, the leading bogie does not have simple rotational motion about a vertical pivot, as might first be thought. It must also be free to slip sideways to a small extent, otherwise the locomotive is unable to follow curves accurately, and some kind of springing mechanism is normally included to control that movement and provide a tendency to return to centre. A sliding bogie of that type was patented by William Adams in 1865. The first use of leading wheels is commonly attributed to John B. Jervis, who employed them in his 1832 design for a locomotive with four leading wheels and two driving wheels (a type that became known as the '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wheel Arrangement
In rail transport, a wheel arrangement or wheel configuration is a system of classifying the way in which wheels are distributed under a locomotive. Several notations exist to describe the wheel assemblies of a locomotive by type, position, and connections, with the adopted notations varying by country. Within a given country, different notations may also be employed for different kinds of locomotives, such as steam, electric, and diesel powered. Especially in steam days, wheel arrangement was an important attribute of a locomotive because there were many different types of layout adopted, each wheel being optimised for a different use (often with only some being actually "driven"). Modern diesel and electric locomotives are much more uniform, usually with all axles driven. Major notation schemes The main notations are the Whyte notation (based on counting the wheels), the AAR wheel arrangement notation (based on counting either the axles or the bogies), and the UIC classificat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lickey Incline
The Lickey Incline, south of Birmingham, is the steepest sustained main-line railway incline in Great Britain. The climb is a gradient of 1 in 37.7 (2.65% or 26.5‰ or 1.52°) for a continuous distance of two miles (3.2 km). Constructed originally for the Birmingham and Gloucester Railway (B&GR) and opened in 1840 it is located on the Cross Country Route between and stations in Worcestershire. In earlier times many trains required the assistance of banking locomotives with associated logistical considerations to ensure that the train reached the top; now only the heaviest of freight trains require such assistance. History and geography A survey by Isambard Kingdom Brunel in 1832 for a line between Birmingham and Gloucester followed a longer route well to the east with a maximum 1 in 300 gradient avoiding population centres, the plan lapsed with the cost being deemed too high. In 1836 William Moorsom was engaged on a ''no success - no fee'' to survey a suitable r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derailment
In rail transport, a derailment occurs when a rail vehicle such as a train comes off its rails. Although many derailments are minor, all result in temporary disruption of the proper operation of the railway system and they are a potentially serious hazard. A derailment of a train can be caused by a collision with another object, an operational error (such as excessive speed through a curve), the mechanical failure of tracks (such as broken rails), or the mechanical failure of the wheels, among other causes. In emergency situations, deliberate derailment with derails or catch points is sometimes used to prevent a more serious accident. History The first recorded train derailment in history is known as the Hightstown Rail Accident in New Jersey that occurred on November 8, 1833. The train was traveling between Hightstown and Spotswood New Jersey and derailed after an axle broke on one of the carriages as a result of a journal box catching fire. The derailment resulted in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistant typically need an additional 11% chromium. Because of its high tensile strength and low cost, steel is used in buildings, infrastructure, tools, ships, trains, cars, machines, electrical appliances, weapons, and rockets. Iron is the base metal of steel. Depending on the temperature, it can take two crystalline forms (allotropic forms): body-centred cubic and face-centred cubic. The interaction of the allotropes of iron with the alloying elements, primarily carbon, gives steel and cast iron their range of unique properties. In pure iron, the crystal structure has relatively little resistance to the iron atoms slipping past one another, and so pure iron is quite ductile, or soft and easily formed. In steel, small amounts of carbon, other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Best Friend Of Charleston
The ''Best Friend of Charleston'' was a steam-powered railroad locomotive widely considered the first locomotive to be built entirely within the United States for revenue service. It produced the first locomotive boiler explosion in the United States. History The locomotive was built for the South Carolina Canal and Rail Road Company by the West Point Foundry of New York in 1830. Disassembled for shipment by boat to Charleston, South Carolina, it arrived in October of that year and was unofficially named ''The Best Friend of Charleston''. After its inaugural run on Christmas Day, it was used in regular passenger service along a demonstration route in Charleston. At the time, it was considered one of the fastest modes of transport, taking its passengers "on the wings of wind at the speed of ." The only faster mode of travel was by an experienced horse and rider. On June 17, 1831, the ''Best Friend'' was the first locomotive in the US to suffer a boiler explosion. The blast i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birmingham And Bristol Railway
The Birmingham and Bristol Railway was a short-lived railway company, formed in 1845 by the merger of the Birmingham and Gloucester Railway and the Bristol and Gloucester Railway. Origin At Gloucester the latter had formed a junction with the broad gauge Cheltenham and Great Western Union Railway running into the town on mixed gauge tracks. In 1843 the C&GWU had been taken over by the Great Western Railway which began putting pressure on the Bristol and Gloucester to join the GWR at Bristol, to subscribe to the proposed South Devon Railway, and to convert to broad gauge track, to the alarm of the Northern "narrow" gauge railways. The "break-of-gauge" at Gloucester was a major problem. It caused pandemonium as whole trainloads of passengers, and their luggage, changed from one to another, together with the transshipment of goods. Formation Parliament had established a commission to examine the problem and there was a consensus that the track should be unified throughout the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |








.jpg)