|
Blackett Of Wylam
The Blacketts of Wylam were a branch of the Blackett family of Hoppyland, County Durham, England and were related to the Blackett baronets. John Blackett was High Sheriff of Northumberland in 1692, He married Mary, daughter and heir of Richard Errington. Google Books John Blackett (died 1714) was the son of John (above), grandson of Christopher Blackett of Hoppyland (1612-1675) and the greatnephew of Sir William Blackett. In 1685 he acquired two farms at Wylam, Northumberland, and the Manor estate including the mineral rights, from the exploitation of which the family was to benefit greatly. John was High Sheriff of Northumberland in 1714. His residence was Wylam Hall. He married Elizabeth, daughter of John Bacon. John Blackett (1712-1769), his son, High Sheriff in 1738, sold the families Co Durham properties and established coal mining and Wylam Colliery in the township in the mid 18th century. The waggonway connecting the colliery to the River Tyne at Lemington was built i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackett
Blackett or Blacket is a surname of English derivation. People * Andrea Blackett (born 1976), Barbadian athlete * Basil Phillott Blackett (1882–1935), British civil servant and finance expert * Basil Blackett (1886–1920), British WW1 flying ace *Christopher Blackett, British colliery and newspaper owner and railway innovator * Edmund Blacket (1817–1883), Australian architect *Hill Blackett (1892–1967), American radio advertising pioneer * Blackett baronets **Sir William Blackett, 1st Baronet, of Matfen (1620–1680), businessman and MP **Sir Edward Blackett, 2nd Baronet of Matfen (1649–1718), MP, builder of Newby Hall **Sir Edward Blackett, 3rd Baronet (1683–1756), Royal Navy officer **Sir Edward Blackett, 4th Baronet of Matfen (1719–1804), MP **Sir William Blackett, 1st Baronet, of Newcastle (1657–1705), MP **Sir William Blackett, 2nd Baronet of Newcastle (1690–1728), MP * Calverley-Blackett baronets **Sir Walter Blackett, 2nd Baronet (born Calverley), MP *Jami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Tyne
The River Tyne is a river in North East England. Its length (excluding tributaries) is . It is formed by the North Tyne and the South Tyne, which converge at Warden Rock near Hexham in Northumberland at a place dubbed 'The Meeting of the Waters'. The Tyne Rivers Trust measure the whole Tyne catchment as , containing of waterways. Course North Tyne The North Tyne rises on the Scottish border, north of Kielder Water. It flows through Kielder Forest, and in and out of the border. It then passes through the village of Bellingham before reaching Hexham. South Tyne The South Tyne rises on Alston Moor, Cumbria and flows through the towns of Haltwhistle and Haydon Bridge, in a valley often called the Tyne Gap. Hadrian's Wall lies to the north of the Tyne Gap. Coincidentally, the source of the South Tyne is very close to those of the Tees and the Wear. The South Tyne Valley falls within the North Pennines Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB) – the second largest of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
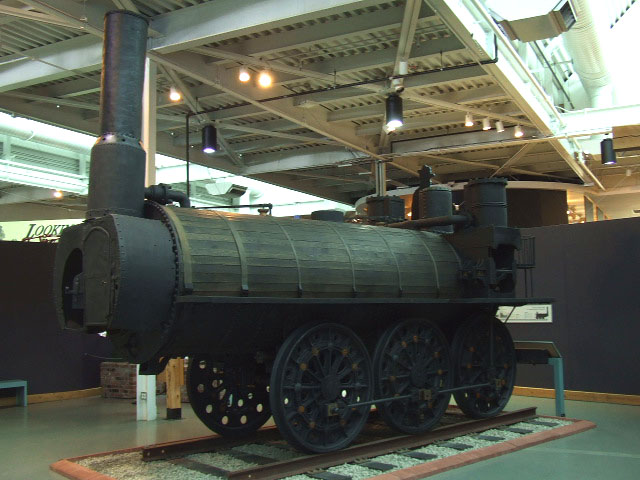
Wylam Dilly
''Wylam Dilly'' is the second oldest surviving rail transport, railway locomotive in the world; it was built circa 1815 by William Hedley and Timothy Hackworth for Christopher Blackett, the owner of Wylam colliery, west of Newcastle upon Tyne. ''Wylam Dilly'' was initially designed for and used on the Wylam Waggonway to transport coal. The four driving wheels are connected by a train of spur wheels driven by a central crankshaft. Because it proved too heavy for the cast iron plateway in its original form, the locomotive was rebuilt with eight wheels in 1815, but returned to its original design in 1830 after the track was relaid with wrought iron Wagonway#Edgeway, edge rails, rails. The locomotive was still at work in 1862 when it was moved to Craghead Colliery. After withdrawal it was presented to the Edinburgh Museum of Science and Art in 1883, now called the National Museum of Scotland, where it is currently on display. The first steam locomotive of its class, ''Puffing Bil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puffing Billy (locomotive)
''Puffing Billy'' is the world's oldest surviving steam locomotive, constructed in 1813–1814 by colliery viewer William Hedley, enginewright Jonathan Forster and blacksmith Timothy Hackworth for Christopher Blackett, the owner of Wylam Colliery near Newcastle upon Tyne, in the United Kingdom. It was employed to haul coal chaldron wagons from the mine at Wylam to the docks at Lemington in Northumberland. History Precursors In 1810 the Durham Coalfield was disrupted by a major strike over the Bond system. During this time Christopher Blackett, owner of the Wylam Colliery, took advantage of the pit's idleness to experiment with the idea of a locomotive-hauled tramway worked purely by adhesion, rather than the Blenkinsop rack system used on the Middleton. These began with a simple hand-cranked wagon, converted from a coal wagon chassis with the addition of a central drive shaft and geared drives to the axles. As this experiment was successful, by 1812 it was followed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
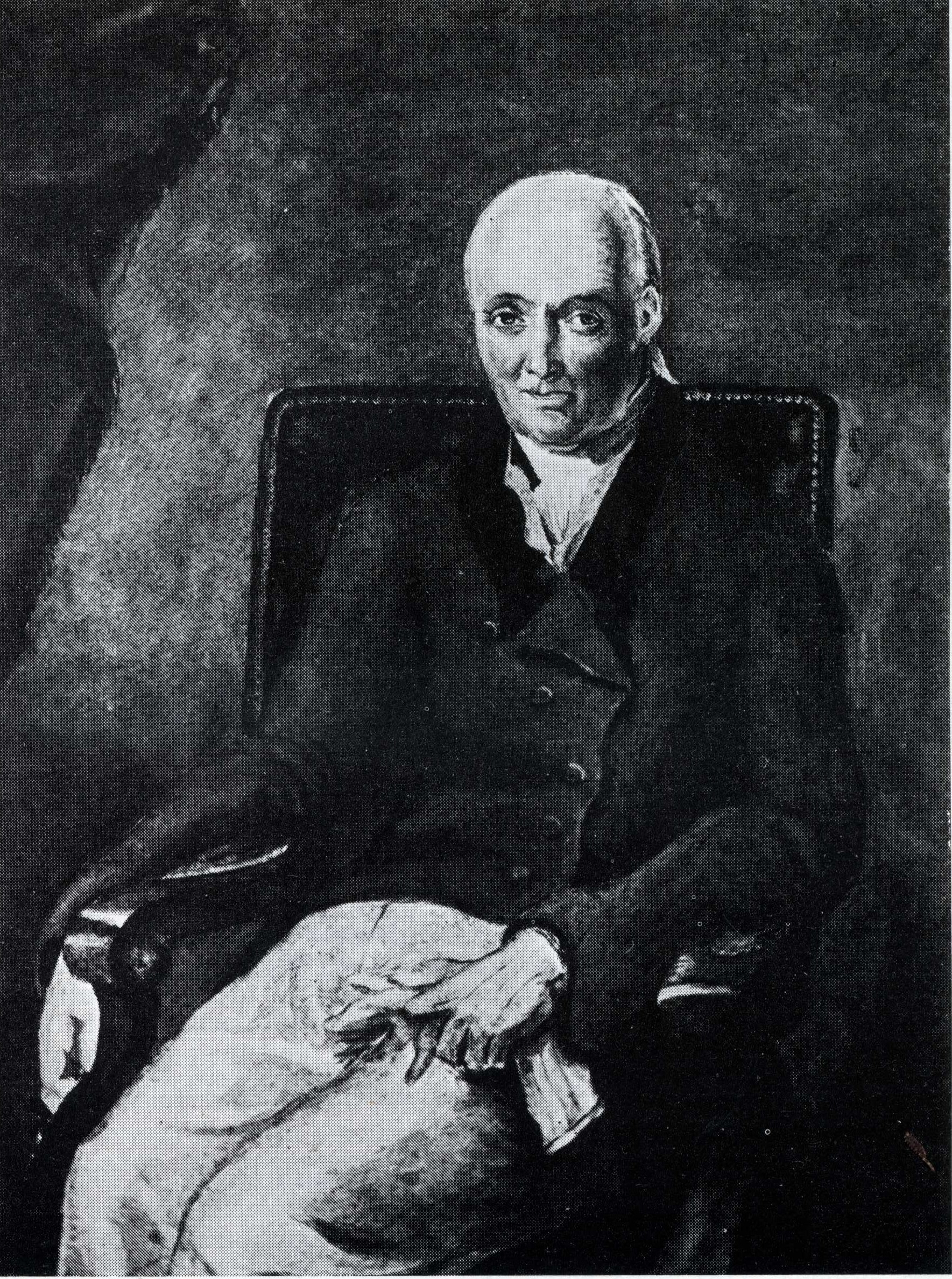
Christopher Blackett
Christopher Blackett (1751 – 25 January 1829) owned the Northumberland colliery at Wylam that built ''Puffing Billy'', the first commercial adhesion steam locomotive. He was also the founding owner of ''The Globe'' newspaper in 1803. Life Blackett was born a Blackett of Wylam and the eldest son by the second marriage of John Blackett, a High Sheriff of Northumberland, whose family descended from Christopher Blackett, an elder brother of Sir William Blackett, and Alice Fenwick, sole heir of her father. In 1659 the coal-rich manor of Wylam passed by inheritance from the Fenwicks to Christopher Blackett (ancestor of article subject) and around 1748 the Wylam waggonway was constructed by John Blackett. This enabled coal to be transported five miles from Wylam colliery to the staithes at Lemington, then on the River Tyne. The Christopher Blackett of this article succeeded to the lordship of the Manor of Wylam and its collieries in 1800. Prior this he had been Postmaster of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timothy Hackworth
Timothy Hackworth (22 December 1786 – 7 July 1850) was an English steam locomotive engineer who lived in Shildon, County Durham, England and was the first locomotive superintendent of the Stockton and Darlington Railway. Youth and early work Timothy Hackworth was born in Wylam in 1786, five years after his fellow railway pioneer George Stephenson had been born in the same village. Hackworth was the eldest son of John Hackworth who occupied the position of foreman blacksmith at Wylam Colliery until his death in 1804; the father had already acquired a considerable reputation as a mechanical worker and boiler maker. At the end of his apprenticeship in 1810 Timothy took over his father's position. Since 1804, the mine owner, Christopher Blackett had been investigating the possibilities of working the mine's short colliery tramroad by steam traction. Blackett set up a four-man working group including himself, William Hedley, the viewer; Timothy Hackworth, the new foreman smith an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Hedley
William Hedley (13 July 1779 – 9 January 1843) was born in Newburn, near Newcastle upon Tyne. He was one of the leading industrial engineers of the early 19th century, and was instrumental in several major innovations in early rail transport, railway development. While working as a 'colliery viewer, viewer' or manager at Wylam Colliery near Newcastle upon Tyne, he built the first practical steam locomotive which relied simply on the Rail adhesion, adhesion of iron wheels on iron rails. Early locomotives Before Hedley's time, such locomotives were far too heavy for the track that was then available. While most lines used cable haulage with stationary engines, various other schemes had been tried. William Chapman at the Butterley Company in 1812, attempted to use a steam engine which hauled itself along a cable, while, at the same company, Brunton had produced the even less successful "mechanical traveller", or Steam Horse locomotive, ''Steam Horse''. However, in 1812, Matthe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Stephenson
George Stephenson (9 June 1781 – 12 August 1848) was a British civil engineer and mechanical engineer. Renowned as the "Father of Railways", Stephenson was considered by the Victorians a great example of diligent application and thirst for improvement. Self-help advocate Samuel Smiles particularly praised his achievements. His chosen rail gauge, sometimes called "Stephenson gauge", was the basis for the standard gauge used by most of the world's railways. Pioneered by Stephenson, rail transport was one of the most important technological inventions of the 19th century and a key component of the Industrial Revolution. Built by George and his son Robert's company Robert Stephenson and Company, the ''Locomotion'' No. 1 was the first steam locomotive to carry passengers on a public rail line, the Stockton and Darlington Railway in 1825. George also built the first public inter-city railway line in the world to use locomotives, the Liverpool and Manchester Railway, which opene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lemington
Lemington is an area and electoral ward of Newcastle upon Tyne in North East England. History Lemington has a strong industrial history. It is famous for its brick glassworks cone, built in 1787. The River Tyne used to pass very close to Lemington, until the Tyne Improvement Commission cut a new, shorter, straighter channel over the Blaydon Haugh, leaving behind the Lemington Gut. Also visible are the ruins of the former Tyne Iron Company Ironworks which were built in 1797 and decommissioned in 1886. Its coke ovens are still evident near Lemington Power Station. The power station was built in 1903 to supply the tram system with electricity. It was largely demolished in 1946. The remains of Lemington Staithes can be seen on the Lemington Gut near the power station. The staithes used to mark the end of the North Wylam to Lemington Point waggonway, which took coal from the local collieries to the staithes for export. On 12 July 1875 Lemington Station opened on the Scotswood, New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waggonway
Wagonways (also spelt Waggonways), also known as horse-drawn railways and horse-drawn railroad consisted of the horses, equipment and tracks used for hauling wagons, which preceded steam-powered railways. The terms plateway, tramway, dramway, were used. The advantage of wagonways was that far bigger loads could be transported with the same power. Ancient systems The earliest evidence is of the 6 to 8.5 km long ''Diolkos'' paved trackway, which transported boats across the Isthmus of Corinth in Greece from around 600 BC. Wheeled vehicles pulled by men and animals ran in grooves in limestone, which provided the track element, preventing the wagons from leaving the intended route. The Diolkos was in use for over 650 years, until at least the 1st century AD. Paved trackways were later built in Roman Egypt. Wooden rails Such an operation was illustrated in Germany in 1556 by Georgius Agricola (image right) in his work De re metallica. This line used "Hund" carts wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Durham
County Durham ( ), officially simply Durham,UK General Acts 1997 c. 23Lieutenancies Act 1997 Schedule 1(3). From legislation.gov.uk, retrieved 6 April 2022. is a ceremonial county in North East England.North East Assembly �About North East England. Retrieved 30 November 2007. The ceremonial county spawned from the historic County Palatine of Durham in 1853. In 1996, the county gained part of the abolished ceremonial county of Cleveland.Lieutenancies Act 1997 . Retrieved 27 October 2014. The county town is the of |
Wylam Colliery
Wylam is a village and civil parish in the county of Northumberland. It is located about west of Newcastle upon Tyne. It is famous for the being the birthplace of George Stephenson, one of the early railway pioneers. George Stephenson's Birthplace, his cottage, can be found on the north bank of the Tyne east of the village centre. It is owned by the National Trust but is not open to the public in 2021 on account of COVID-19. Wylam has further connections with the early railway pioneers. The steam locomotive engineer Timothy Hackworth, who worked with Stephenson, was also born here. William Hedley who was born in the nearby village of Newburn attended the village school. He later went on to design and manufacture Puffing Billy in 1813, two years before George Stephenson produced his first locomotive Blücher. Christopher Blackett as lord of the manor in the first 30 years of the 19th century provided the entrepreneurial drive that encouraged these engineers. History Once a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |