Heinrich Maier, which provided the Allies with plans for V-1,
V-2 rockets, Peenemünde,
Tiger tanks,
Messerschmitt Bf 109
The Messerschmitt Bf 109 is a German World War II fighter aircraft that was, along with the Focke-Wulf Fw 190, the backbone of the Luftwaffe's fighter force. The Bf 109 first saw operational service in 1937 during the Spanish Civil War an ...
,
Messerschmitt Me 163 Komet and other aircraft. The information was important to
Operation Crossbow and
Operation Hydra, both preliminary missions for
Operation Overlord
Operation Overlord was the codename for the Battle of Normandy, the Allies of World War II, Allied operation that launched the successful invasion of German-occupied Western Front (World War II), Western Europe during World War II. The operat ...
. In addition, factory locations for war-essential products were communicated as targets for the Allied Air Force. The group was exposed and most of its members were executed after months of torture by the Gestapo in Vienna. The group around the later executed
Karl Burian Karl may refer to:
People
* Karl (given name), including a list of people and characters with the name
* Karl der Große, commonly known in English as Charlemagne
* Karl Marx, German philosopher and political writer
* Karl of Austria, last Austrian ...
even tried to blow up the Gestapo headquarters in the Hotel Metropole.
On 2 April 1945, the
Soviet Red Army launched the
Vienna Offensive against the Germans holding the city and besieged it. British and American air-raids, as well as artillery duels between the Red Army and the
SS and
Wehrmacht, crippled infrastructure, such as tram services and water- and power-distribution, and destroyed or damaged thousands of public and private buildings. The Red Army was helped by an Austrian resistance group in the German Wehrmacht. The group tried under the code name Radetzky to prevent the destruction and fighting in the city. Vienna fell eleven days later. At the end of the war, Austria again became separated from Germany, and Vienna regained its status as the capital city of the Republic of Austria, but the Soviet hold on the city remained until 1955, when Austria regained full sovereignty.
Four-power Vienna

After the war, Vienna was part of
Soviet-occupied Eastern Austria until September 1945. As in Berlin, Vienna in September 1945 was divided into sectors by the four powers: the US, the UK, France, and the Soviet Union and supervised by an
Allied Commission
Following the termination of hostilities in World War II, the Allies were in control of the defeated Axis countries. Anticipating the defeat of Germany and Japan, they had already set up the European Advisory Commission and a proposed Far Easter ...
. The four-power occupation of Vienna differed in one key respect from that of Berlin: the central area of the city, known as the first district, constituted an ''international zone'' in which the four powers alternated control on a monthly basis. The control was policed by the four powers on a ''de facto'' day-to-day basis, the famous "four soldiers in a jeep" method. The
Berlin Blockade of 1948 raised Western concerns that the Soviets might repeat the blockade in Vienna. The matter was raised in the UK
House of Commons by MP
Anthony Nutting, who asked: "What plans have the Government for dealing with a similar situation in Vienna? Vienna is in exactly a similar position to Berlin."
There was a lack of airfields in the Western sectors, and authorities drafted contingency plans to deal with such a blockade. Plans included the laying down of metal landing mats at Schönbrunn. The Soviets did not blockade the city. The
Potsdam Agreement
The Potsdam Agreement (german: Potsdamer Abkommen) was the agreement between three of the Allies of World War II: the United Kingdom, the United States, and the Soviet Union on 1 August 1945. A product of the Potsdam Conference, it concerned th ...
included written rights of land access to the western sectors, whereas no such written guarantees had covered the western sectors of Berlin. Also, there was no precipitating event to cause a blockade in Vienna. (In Berlin, the Western powers had introduced a new currency in early 1948 to economically freeze out the Soviets.) During the 10 years of the four-power occupation, Vienna became a hotbed for international espionage between the
Western and
Eastern bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc and the Soviet Bloc, was the group of socialist states of Central and Eastern Europe, East Asia, Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America under the influence of the Soviet Union that existed du ...
s. In the wake of the Berlin Blockade, the
Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
in Vienna took on a different dynamic. While accepting that Germany and Berlin would be divided, the Soviets had decided against allowing the same state of affairs to arise in Austria and Vienna. Here, the Soviet forces controlled districts 2, 4, 10, 20, 21, and 22 and all areas incorporated into Vienna in 1938.
Barbed wire fences were installed around the perimeter of
West Berlin in 1953, but not in Vienna. By 1955, the Soviets, by signing the
Austrian State Treaty, agreed to relinquish their occupation zones in Eastern Austria as well as their sector in Vienna. In exchange they required that Austria declare its permanent neutrality after the allied powers had left the country. Thus they ensured that Austria would not be a member of
NATO and that NATO forces would therefore not have direct communications between
Italy and
West Germany.
The atmosphere of four-power Vienna is the background for
Graham Greene's screenplay for the film ''
The Third Man'' (1949). Later he adapted the screenplay as a novel and published it. Occupied Vienna is also depicted in the 1991
Philip Kerr novel, ''
A German Requiem''.
Austrian State Treaty and afterwards

The four-power control of Vienna lasted until the
Austrian State Treaty was signed in May 1955. That year, after years of reconstruction and restoration, the
State Opera and the
Burgtheater
The Burgtheater (literally:"Castle Theater" but alternatively translated as "(Imperial) Court Theater"), originally known as '' K.K. Theater an der Burg'', then until 1918 as the ''K.K. Hofburgtheater'', is the national theater of Austria in Vi ...
, both on the Ringstraße, reopened to the public. The Soviet Union signed the State Treaty only after having been provided with a political guarantee by the federal government to declare Austria's neutrality after the withdrawal of the allied troops. This law of neutrality, passed in late October 1955 (and not the State Treaty itself), ensured that modern Austria would align with neither
NATO nor the
Soviet bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc and the Soviet Bloc, was the group of socialist states of Central and Eastern Europe, East Asia, Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America under the influence of the Soviet Union that existed du ...
, and is considered one of the reasons for Austria's delayed
entry into the European Union in 1995.
In the 1970s,
Austrian Chancellor Bruno Kreisky inaugurated the
Vienna International Center
The Vienna International Centre (VIC) is the campus and building complex hosting the United Nations Office at Vienna (UNOV; in de-AT, Büro der Vereinten Nationen in Wien). It is colloquially also known as UNO City.
Overview
The VIC, designed ...
, a new area of the city created to host international institutions. Vienna has regained much of its former international stature by hosting international organizations, such as the United Nations (
United Nations Industrial Development Organization,
United Nations Office at Vienna and
United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime), the
Preparatory Commission for the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty Organization, the
International Atomic Energy Agency
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) is an intergovernmental organization that seeks to promote the peaceful use of nuclear energy and to inhibit its use for any military purpose, including nuclear weapons. It was established in 1957 ...
, the
Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries, and the
Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe
The Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) is the world's largest regional security-oriented intergovernmental organization with observer status at the United Nations. Its mandate includes issues such as arms control, prom ...
.
Demographics
Because of the industrialization and migration from other parts of the Empire, the population of Vienna increased sharply during its time as the capital of
Austria-Hungary (1867–1918). In 1910, Vienna had more than two million inhabitants, and was the third
largest city in Europe after London and Paris. Around the start of the 20th century, Vienna was the city with the second-largest
Czech population in the world (after
Prague). After World War I, many
Czechs and
Hungarians returned to their ancestral countries, resulting in a decline in the Viennese population. After World War II, the Soviets used force to repatriate key workers of Czech, Slovak and Hungarian origins to return to their ethnic homelands to further the Soviet bloc economy. The population of Vienna generally stagnated or declined through the remainder of the 20th century, not demonstrating significant growth again until the census of 2000. In 2020, Vienna's population remained significantly below its reported peak in 1916.
Under the Nazi regime, 65,000
Jews were deported and murdered in concentration camps by Nazi forces; approximately 130,000 fled.
By 2001, 16% of people living in Austria had nationalities other than Austrian, nearly half of whom were from former
Yugoslavia; the next most numerous nationalities in Vienna were
Turks (39,000; 2.5%),
Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in Ce ...
(13,600; 0.9%) and Germans (12,700; 0.8%).
, an official report from Statistics Austria showed that more than 660,000 (38.8%) of the Viennese population have full or partial migrant background, mostly from Ex-Yugoslavia, Turkey, Germany, Poland, Romania and Hungary.
From 2005 to 2015 the city's population grew by 10.1%. According to
UN-Habitat, Vienna could be the fastest growing city out of 17 European metropolitan areas until 2025 with an increase of 4.65% of its population, compared to 2010.
Religion

According to the 2001 census, 49.2% of Viennese were Catholic, while 25.7% were of no religion, 7.8% were Muslim, 6.0% were members of an Eastern Orthodox Christian denomination, 4.7% were Protestant (mostly Lutheran), 0.5% were Jewish and 6.3% were either of other religions or did not reply.
A 2011 report by the
International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis showed the proportions had changed, with 41.3% Catholic, 31.6% no affiliation, 11.6% Muslim, 8.4% Eastern Orthodox, 4.2% Protestant, and 2.9% other.
Based on information provided to city officials by various religious organizations about their membership, Vienna's Statistical Yearbook 2019 reports in 2018 an estimated 610,269 Roman Catholics, or 32.3% of the population, and 195,000 (10.3%) Muslims, 70,298 (3.7%) Orthodox, 57,502 (3.0%) other Christians, and 9,504 (0.5%) other religions.
A study conducted by the
Vienna Institute of Demography estimated the 2018 proportions to be 34% Catholic, 30% unaffiliated, 15% Muslim, 10% Orthodox, 4% Protestant, and 6% other religions.
Vienna is the seat of the Metropolitan
Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Vienna, in which is also vested the exempt
Ordinariate In the organisation of the Catholic Church and of the Anglican CommunionSee, for example, thAnglican Military Ordinariate in Canada an ordinariate is a pre- or pseudo-diocesan ecclesiastical structure, of geographical or personal nature, headed by a ...
for Byzantine-rite Catholics in Austria; its
Archbishop
In Christian denominations, an archbishop is a bishop of higher rank or office. In most cases, such as the Catholic Church, there are many archbishops who either have jurisdiction over an ecclesiastical province in addition to their own archdi ...
is
Cardinal
Cardinal or The Cardinal may refer to:
Animals
* Cardinal (bird) or Cardinalidae, a family of North and South American birds
**''Cardinalis'', genus of cardinal in the family Cardinalidae
**''Cardinalis cardinalis'', or northern cardinal, the ...
Christoph Schönborn. Many
Catholic churches
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a p ...
in central Vienna feature performances of religious or other music, including masses sung to classical music and organ. Some of Vienna's most significant historical buildings are Catholic churches, including the
St. Stephen's Cathedral (''Stephansdom''),
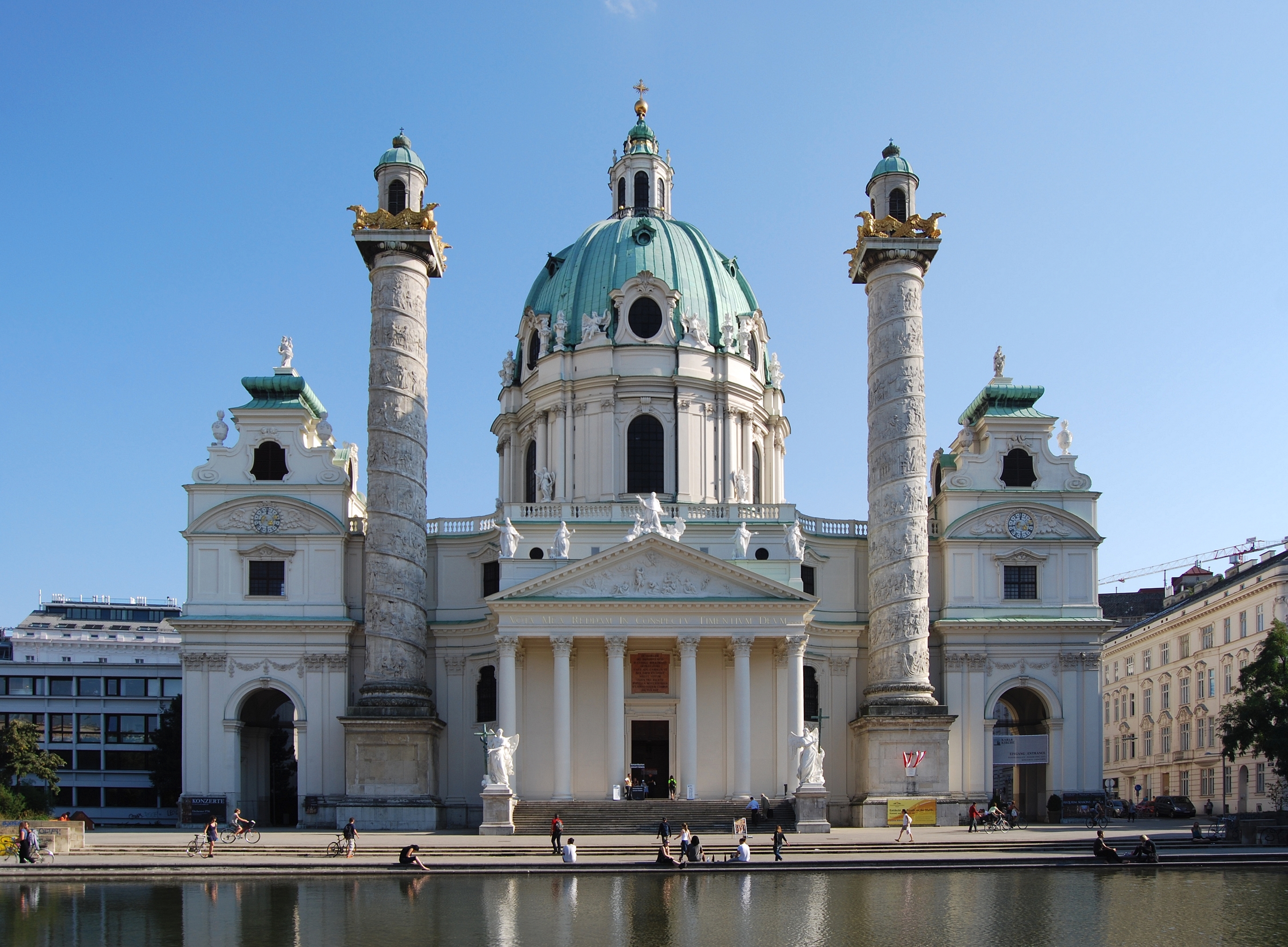
Karlskirche
The ''Rektoratskirche St. Karl Borromäus'', commonly called the ''Karlskirche'' (), is a Baroque church located on the south side of Karlsplatz in Vienna, Austria. Widely considered the most outstanding baroque church in Vienna, as well as one ...
,
Peterskirche
The ''Peterskirche'' ( en, St. Peter's Church) is a Baroque Catholic Church, Roman Catholic parish church in Vienna, Austria. It was transferred in 1970 by the Archbishop of Vienna Franz König, Franz Cardinal König to the priests of the Opus ...
and the
Votivkirche. On the banks of the Danube, there is a Buddhist
Peace Pagoda
A Peace Pagoda is a Buddhist stupa; a monument to inspire peace, designed to provide a focus for people of all races and creeds, and to help unite them in their search for world peace. Most, though not all, peace pagodas built since World War II ...
, built in 1983 by the monks and nuns of
Nipponzan Myohoji.
Geography

Vienna is located in northeastern Austria, at the easternmost extension of the
Alps in the
Vienna Basin. The earliest settlement, at the location of today's
inner city, was south of the meandering Danube while the city now spans both sides of the river. Elevation ranges from . The city has a total area of 414.65 square kilometers (160.1 sq mi), making it the largest city in Austria by area.
Climate
Vienna has an
oceanic climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the humid temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool summers and mild winters ( ...
(
Köppen classification ''Cfb''). The city has warm summers, with periodical precipitations that can reach its yearly peak in July and August (66.6 and 66.5 mm respectively) and average high temperatures from June to September of approximately , with a record maximum exceeding and a record low in September of . Winters are relatively dry and cold with average temperatures at about freezing point. Spring is variable and autumn cool, with possible snowfalls already in November. Precipitation is generally moderate throughout the year, averaging around annually, with considerable local variations, the Vienna Woods region in the west being the wettest part ( annually) and the flat plains in the east being the driest part ( annually). Snow in winter is common, even if not so frequent compared to the Western and Southern regions of Austria.
World heritage in danger
Vienna was moved to the UNESCO world heritage in endangered list in 2017. The main reason was a planned high-rise development.
The city's social democratic party planned construction of a complex in 2019.
The plan includes a -high tower, which was reduced from due to opposition.
UNESCO believed that the project "fails to comply fully with previous committee decisions, notably concerning the height of new constructions, which will impact adversely the outstanding universal value of the site."
UNESCO set the restriction for the height of the construction in the city center to .
The citizens of Vienna also opposed the construction of the complex because they are afraid of losing UNESCO status and also of encouraging future high-rise development.
The city officials replied that they will convince the WHC to maintain UNESCO world heritage status and said that no further high-rise developments are being planned.
UNESCO is concerned about the height of high-rise development in Vienna as it can dramatically influence the visual integrity of the city,
specifically the baroque palaces.
Visual impact studies are being done in the Vienna city center to assess the level of visual disturbance to visitors and how the changes influenced the city's visual integrity.
Districts and enlargement

Vienna is composed of 23 districts (''Bezirke''). Administrative district offices in Vienna (called Magistratische Bezirksämter) serve functions similar to those in the other Austrian states (called Bezirkshauptmannschaften), the officers being subject to the mayor of Vienna; with the notable exception of the police, which is under federal supervision.
District residents in Vienna (Austrians as well as EU citizens with permanent residence here) elect a District Assembly (Bezirksvertretung). City hall has delegated maintenance budgets, e.g., for schools and parks, so that the districts are able to set priorities autonomously. Any decision of a district can be overridden by the city assembly (Gemeinderat) or the responsible city councilor (amtsführender Stadtrat).

The heart and historical city of Vienna, a large part of today's
Innere Stadt
The Innere Stadt (; Central Bavarian: ''Innare Stod'') is the 1st municipal Districts of Vienna, district of Vienna () located in the center of the Austrian capital. The Innere Stadt is the old town of Vienna. Until the city boundaries were expa ...
, was a fortress surrounded by fields in order to defend itself from potential attackers. In 1850, Vienna with the consent of the emperor annexed 34 surrounding villages, called Vorstädte, into the city limits (districts no. 2 to 8, after 1861 with the separation of Margareten from Wieden no. 2 to 9). Consequently, the walls were razed after 1857, making it possible for the city center to expand.
In their place, a broad boulevard called the
Ringstraße was built, along which imposing public and private buildings, monuments, and parks were created by the start of the 20th century. These buildings include the
Rathaus
In local government, a city hall, town hall, civic centre (in the UK or Australia), guildhall, or a municipal building (in the Philippines), is the chief administrative building of a city, town, or other municipality. It usually houses ...
(town hall), the
Burgtheater
The Burgtheater (literally:"Castle Theater" but alternatively translated as "(Imperial) Court Theater"), originally known as '' K.K. Theater an der Burg'', then until 1918 as the ''K.K. Hofburgtheater'', is the national theater of Austria in Vi ...
, the
University, the
Parliament, the twin museums of
natural history and
fine art, and the
Staatsoper. It is also the location of New Wing of the
Hofburg
The Hofburg is the former principal imperial palace of the Habsburg dynasty. Located in the centre of Vienna, it was built in the 13th century and expanded several times afterwards. It also served as the imperial winter residence, as Schönbrunn ...
, the former imperial palace, and the Imperial and Royal War Ministry finished in 1913. The mainly
Gothic Stephansdom is located at the center of the city, on
Stephansplatz. The Imperial-Royal Government set up the Vienna City Renovation Fund (Wiener Stadterneuerungsfonds) and sold many building lots to private investors, thereby partly financing public construction works.

From 1850 to 1890, city limits in the West and the South mainly followed another wall called ''
Linienwall'' at which a
road toll called the ''
Liniengeld'' was charged. Outside this wall from 1873 onwards a
ring road
A ring road (also known as circular road, beltline, beltway, circumferential (high)way, loop, bypass or orbital) is a road or a series of connected roads encircling a town, city, or country. The most common purpose of a ring road is to assist i ...
called
Gürtel was built. In 1890 it was decided to integrate 33 suburbs (called Vororte) beyond that wall into Vienna by 1 January 1892
[Czeike, volume 5, p. 290] and transform them into districts no. 11 to 19 (district no. 10 had been constituted in 1874); hence the Linienwall was torn down beginning in 1894. In 1900, district no. 20, Brigittenau, was created by separating the area from the 2nd district.
From 1850 to 1904, Vienna had expanded only on the right bank of the Danube, following the main branch before the regulation of 1868–1875, i.e., the Old Danube of today. In 1904, the 21st district was created by integrating Floridsdorf, Kagran, Stadlau, Hirschstetten, Aspern and other villages on the left bank of the Danube into Vienna, in 1910 Strebersdorf followed. On 15 October 1938 the Nazis created Great Vienna with 26 districts by merging 97 towns and villages into Vienna, 80 of which were returned to surrounding
Lower Austria in 1954.
Since then Vienna has had 23 districts.
Industries are located mostly in the southern and eastern districts. The
Innere Stadt
The Innere Stadt (; Central Bavarian: ''Innare Stod'') is the 1st municipal Districts of Vienna, district of Vienna () located in the center of the Austrian capital. The Innere Stadt is the old town of Vienna. Until the city boundaries were expa ...
is situated away from the main flow of the
Danube, but is bounded by the ''
Donaukanal'' ("Danube canal"). Vienna's second and twentieth districts are located between the Donaukanal and the
Danube. Across the Danube, where the Vienna International Center is located (districts 21–22), and in the southern areas (district 23) are the newest parts of the city.
Politics
Political history

In the twenty years before the First World War and until 1918, Viennese politics were shaped by the
Christian Social Party. In particular, long-term mayor
Karl Lueger
Karl Lueger (; 24 October 1844 – 10 March 1910) was an Austrian politician, mayor of Vienna, and leader and founder of the Austrian Christian Social Party. He is credited with the transformation of the city of Vienna into a modern city. The pop ...
was able to not apply the general voting rights for men introduced by and for the parliament of imperial Austria, the ''Reichsrat'', in 1907, thereby excluding most of the working class from taking part in decisions. For
Adolf Hitler, who spent some years in Vienna, Lueger was a teacher of how to use
antisemitism
Antisemitism (also spelled anti-semitism or anti-Semitism) is hostility to, prejudice towards, or discrimination against Jews. A person who holds such positions is called an antisemite. Antisemitism is considered to be a form of racism.
Antis ...
in politics.
Vienna is today considered the center of the
Social Democratic Party (SPÖ). During the period of the
First Republic (1918–1934), the Vienna Social Democrats undertook many social reforms. At that time, Vienna's municipal policy was admired by Socialists throughout Europe, who therefore referred to the city as "
Red Vienna" (''Rotes Wien''). In February 1934 troops of the Austrian federal government under
Engelbert Dollfuss, who had closed down the first chamber of the federal parliament, the ''Nationalrat'', in 1933, and paramilitary socialist organizations were engaged in the Austrian Civil War, which led to the ban of the Social Democratic party.
The SPÖ has held the mayor's office and control of the city council/parliament at every free election since 1919. The only break in this SPÖ dominance came between 1934 and 1945, when the Social Democratic Party was illegal, mayors were appointed by the
austro-fascist
The Federal State of Austria ( de-AT, Bundesstaat Österreich; colloquially known as the , "Corporate State") was a continuation of the First Austrian Republic between 1934 and 1938 when it was a one-party state led by the clerical fascist Fa ...
and later by the
Nazi authorities. The mayor of Vienna is
Michael Ludwig
Michael Ludwig (born 3 April 1961) is an Austrian politician of the Social Democratic Party (SPÖ). Since May 2018, he has been Mayor and Governor of Vienna, the capital and largest city of Austria. Since January 2018, he has also served as cha ...
of the SPÖ.
The city has enacted many social democratic policies. The ''
Gemeindebauten'' are social housing assets that are well integrated into the city architecture outside the first or "inner" district. The low rents enable comfortable accommodation and good access to the city amenities. Many of the projects were built after the
Second World War on vacant lots that were destroyed by bombing during the war. The city took particular pride in building them to a high standard.
Government

Since Vienna obtained federal state (''Bundesland'') status of its own by the federal constitution of 1920, the city council also functions as the state parliament (
Landtag), and the mayor (except 1934–1945) also doubles as the ''
Landeshauptmann
Landeshauptmann (if male) or Landeshauptfrau (if female) (, "state captain", plural ''Landeshauptleute'') is the chairman of a state government and the supreme official of an Austrian state and the Italian autonomous provinces of South Tyrol an ...
'' (governor/minister-president) of the state of Vienna. The Rathaus accommodates the offices of the mayor (''
:de:Magistrat der Stadt Wien'') and the state government (''Landesregierung''). The city is administered by a multitude of departments (''Magistratsabteilungen''), politically supervised by ''Amtsführende Stadträte'' (members of the city government/parliament leading offices; according to the Vienna constitution opposition parties have the right to designate members of the city government not leading offices).
Under the city constitution of 1920, municipal and state business must be kept separate. Hence, the city council and state parliament hold separate meetings, with separate presiding officers–the chairman of the city council or the president of the state Landtag–even though the two bodies' memberships are identical. When meeting as a city council, the deputies can only deal with the affairs of the city of Vienna; when meeting as a state parliament, they can only deal with the affairs of the state of Vienna.
In the 1996 City Council election, the SPÖ lost its overall majority in the 100-seat chamber, winning 43 seats and 39.15% of the vote. The SPÖ had held an outright majority at every free municipal election since 1919. In 1996 the
Freedom Party of Austria (FPÖ), which won 29 seats (up from 21 in 1991), beat the ÖVP into third place for the second time running. From 1996 to 2001, the SPÖ governed Vienna in a coalition with the ÖVP. In 2001 the SPÖ regained the overall majority with 52 seats and 46.91% of the vote; in October 2005, this majority was increased further to 55 seats (49.09%). In course of the 2010 city council elections the SPÖ lost their overall majority again and consequently forged a coalition with the
Green Party – the first SPÖ/Green coalition in Austria. This coalition was maintained following the 2015 election. Following the 2020 election, the SPÖ forged a coalition with
NEOS – The New Austria and Liberal Forum.
Economy


Vienna is one of the wealthiest regions in the
European Union: Its
gross regional product of EUR 47,200 per capita constituted 25.7% of Austria's GDP in 2013. It amounts to 159% of the EU average. The city improved its position from 2012 on the ranking of the most economically powerful cities reaching number nine on the listing in 2015.
With a share of 85.5% in gross value added, the service sector is Vienna's most important economic sector. Industry and commerce have a share of 14.5% in gross value added, the
primary sector (agriculture) has a share of 0.07% and therefore plays a minor role in the local added value.
However, the cultivation and production of
wines within the city borders have a high socio-cultural value. The most important business sectors are trade (14.7% of added value in Vienna), scientific and technological services, real estate and housing activities as well as manufacturing of goods. In 2012, Vienna's contribution in Austria's outgoing and incoming
foreign direct investment
A foreign direct investment (FDI) is an investment in the form of a controlling ownership in a business in one country by an entity based in another country. It is thus distinguished from a foreign portfolio investment by a notion of direct co ...
s was of about 60%, which demonstrates Vienna's role as an international hub for domestic and foreign companies.
Since the
fall of the Iron Curtain in 1989, Vienna has expanded its position as gateway to Eastern Europe: 300 international companies have their Eastern European headquarters in Vienna and its environs. Among them are
Hewlett Packard
The Hewlett-Packard Company, commonly shortened to Hewlett-Packard ( ) or HP, was an American multinational information technology company headquartered in Palo Alto, California. HP developed and provided a wide variety of hardware components ...
,
Henkel
AG & Co. KGaA, commonly known as Henkel, is a German multinational chemical and consumer goods company headquartered in Düsseldorf, Germany. It is active in both the consumer and industrial sectors. Founded in 1876, the DAX company is organi ...
,
Baxalta
Baxalta (''Bax'' from the name of its former parent company; ''alta'' a Latin adjective meaning 'high' or 'profound') is a biopharmaceutical company founded on 1 July 2015 after its parent company, Baxter International, spun off biopharmaceutica ...
and
Siemens
Siemens AG ( ) is a German multinational conglomerate corporation and the largest industrial manufacturing company in Europe headquartered in Munich with branch offices abroad.
The principal divisions of the corporation are ''Industry'', '' ...
. Companies in Vienna have extensive contacts and competences in business with Eastern Europe due to the city's historical role as center of the
Habsburg Empire. The number of international businesses in Vienna is still growing: In 2014 159 and in 2015 175 international firms established offices in Vienna.
Altogether, approximately 8,300 new companies have been founded in Vienna every year since 2004. The majority of these companies are operating in fields of industry-oriented services, wholesale trade as well as information and communications technologies and new media. Vienna makes effort to establish itself as a start-up hub. Since 2012, the city hosts the annual Pioneers Festival, the largest start-up event in Central Europe with 2,500 international participants taking place at
Hofburg Palace. Tech Cocktail, an online portal for the start-up scene, has ranked Vienna sixth among the top ten start-up cities worldwide.
Research and development
The city of Vienna attaches major importance to science and research and focuses on creating a positive environment for research and development. In 2014, Vienna has accommodated 1,329 research facilities; 40,400 persons are employed in the R&D sector and 35% of Austria's R&D expenses are invested in the city. With a research quota of 3.4% Vienna exceeds the Austrian average of 2.77% and has already met the EU target of 3.0% by 2020.
A major R&D sector in Vienna are life sciences. The Vienna Life Science Cluster is Austria's major hub for life science research, education and business. Throughout Vienna, five universities and several basic research institutes form the academic core of the hub with more than 12,600 employees and 34,700 students. Here, more than 480 medical device,
biotechnology and
pharmaceutical companies with almost 23,000 employees generate around 12 billion euros in revenue (2017). This corresponds to more than 50% of the revenue generated by life science companies in Austria (22.4 billion euros).
Vienna is home to global players like
Boehringer Ingelheim
C.H. Boehringer Sohn AG & Co. is the parent company of the Boehringer Ingelheim group, which was founded in 1885 by Albert Boehringer in Ingelheim am Rhein, Germany. As of 2018, Boehringer Ingelheim is one of the world's largest pharmaceutical ...
,
Octapharma
Octapharma AG, founded in 1983, is a family-owned pharmaceutical company, and bills itself as "one of the largest human protein manufacturers in the world, developing and producing human proteins from human plasma and human cell lines "
Ther ...
,
Ottobock and
Takeda. However, there is also a growing number of start-up companies in the life sciences and Vienna was ranked first in the 2019 PeoplePerHour Startup Cities Index. Companies such as Apeiron Biologics, Hookipa Pharma, Marinomed, mySugr, Themis Bioscience and Valneva operate a presence in Vienna and regularly hit the headlines internationally. Vienna also houses the headquarters of the
Central European Diabetes Association, a cooperative international medical research association.
To facilitate tapping the economic potential of the multiple facettes of the life sciences at Austria's capital, the Austrian
Federal Ministry for Digital and Economic Affairs and the local government of City of Vienna have joined forces: Since 2002, the LISAvienna platform is available as a central contact point. It provides free business support services at the interface of the Austrian federal promotional bank, Austria Wirtschaftsservice and the Vienna Business Agency and collects data that inform policy making.
The main academic hot spots in Vienna are the Life Science Center Muthgasse with the
University of Natural Resources and Life Sciences (BOKU), the
Austrian Institute of Technology, the
University of Veterinary Medicine, the
AKH Vienna with the
MedUni Vienna and the
Vienna Biocenter
The Vienna BioCenter is a cluster of life science research institutes and biotechnology companies located in the 3rd municipal District of Vienna, Austria. It grew around the Research Institute of Molecular Pathology (IMP), which opened in 19 ...
.
Central European University, a graduate institution expelled from Budapest in the midst of a Hungarian government steps to take control of academic and research organizations, welcomes the first class of students to its new Vienna campus in 2019.
Information technologies
The Viennese sector for information and communication technologies is comparable in size with the sector in
Helsinki,
Milan or
Munich and thus among Europe's largest IT locations. In 2012 8,962 IT businesses with a workforce of 64,223 were located in the Vienna Region. The main products are instruments and appliances for measuring, testing and navigation as well as electronic components. More than ⅔ of the enterprises provide IT services. Among the biggest IT firms in Vienna are
Kapsch,
Beko Engineering & Informatics, air traffic control experts
Frequentis,
Cisco Systems Austria,
Hewlett-Packard
The Hewlett-Packard Company, commonly shortened to Hewlett-Packard ( ) or HP, was an American multinational information technology company headquartered in Palo Alto, California. HP developed and provided a wide variety of hardware components ...
,
Microsoft Austria,
IBM Austria and
Samsung Electronics Austria.
The US technology corporation
Cisco runs its ''Entrepreneurs in Residence'' program for Europe in Vienna in cooperation with th
Vienna Business Agency
The British company
UBM has rated Vienna one of the ''Top 10 Internet Cities'' worldwide, by analyzing criteria like connection speed, WiFi availability, innovation spirit and open government data.
In 2011 74.3% of Viennese households were connected with broadband, 79% were in possession of a computer. According to the broadband strategy of the city, full broadband coverage will be reached by 2020.
Tourism and conferences
There were 17.6 million overnight stays in Vienna in 2019 (+6.8% compared to 2018). The top ten incoming markets in 2019 were
Germany,
Austria, the
United States,
Italy,
United Kingdom,
Spain,
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
,
France,
Russia and
Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
.
In 2019 the International Congress and Convention Association
ICCA ranked Vienna 6th in the world for association meetings. The Union of International Associations
UIA ranked Vienna 5th in the world for 2019 with 306 international meetings, behind Singapore, Brussels, Seoul and Paris. The city's largest conference center, th
Austria Center Vienna (ACV)has a total capacity for around 22,800 people and is situated next to the
United Nations Headquarters in Vienna. Other centers are th
Messe Wien Exhibition & Congress Center(up to 3,000 people) and th
Hofburg Palace(up to 4,900 people).
Rankings
Vienna was ranked top in the ''2019 Quality of Living Ranking'' by the international
Mercer Consulting Group for the tenth consecutive year. In the 2015 liveability report by the
Economist Intelligence Unit as well as in the ''Quality of Life Survey 2015'' of London-based
''Monocle magazine'' Vienna was equally ranked second most livable city worldwide.
The United Nations Human Settlements Programme ''UN-Habitat'' has ranked Vienna the most prosperous city in the world in its flagship report ''State of the World Cities 2012/2013''.
According to the 201
City RepTrackranking by the
Reputation Institute
RepTrak (formerly known as Reputation Institute) is a company that publishes reports on the reputation of corporations and places, based on consumer surveys and media coverage. It is headquartered in Boston, Massachusetts.
History
In 1999, Char ...
, Vienna has the best reputation in comparison with 100 major global cities.
The ''Innovation Cities Global Index 2014'' by the Australian innovation agenc
2thinknowranks Vienna sixth behind
San Francisco-
San Jose,
New York City,
London,
Boston and
Paris. In 2019
PeoplePerHour put Vienna at the top of their Startup Cities Ranking.
US climate strategist
Boyd Cohen placed Vienna first in his first ''global smart cities'' ranking of 2012. In the 2014 ranking, Vienna reached third place among European cities behind
Copenhagen and
Amsterdam.
The ''Mori Memorial Institute for Urban Strategies'' ranked Vienna in the top ten of their
Global Power City Index 2016.
Urban development

Central Railway Station
Vienna's new
Central Railway Station was opened in October 2014. Construction began in June 2007 and was due to last until December 2015. The station is served by 1,100 trains with 145,000 passengers. There is a shopping center with approximately 90 shops and restaurants.
In the vicinity of the station a new district is emerging with office space and 5,000 apartments until 2020.
Aspern
Seestadt Aspern is one of the largest urban expansion projects of Europe. A 5
hectare artificial lake, offices, apartments and a subway station within walking distance are supposed to attract 20,000 new citizens when construction is completed in 2028.
In addition, the highest wooden skyscraper in the world, “HoHo Wien”, will be built within 3 years, starting in 2015.
Smart City
In 2014, the Vienna City Council adopted the Smart City Wien Framework Strategy 2050. It is a long-term umbrella strategy that is supposed to establish a conducive, long-term and structural framework in order to reduce carbon dioxide emissions from 3.1 tonnes per capita to 1 tonne per capita by 2050, have 50% of Vienna's gross energy consumption
originate from renewable sources and to reduce motorized individual traffic from the current 28% to 15% by 2030. A stated goal is that, by 2050, all vehicles within the municipal boundaries will run without conventional propulsion technologies. Additionally, Vienna aims to be one of the five biggest European research and innovation hubs in 2050.
Culture
Music, theater and opera

Famous composers including
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart,
Joseph Haydn
Franz Joseph Haydn ( , ; 31 March 173231 May 1809) was an Austrian composer of the Classical period (music), Classical period. He was instrumental in the development of chamber music such as the string quartet and piano trio. His contributions ...
,
Ludwig van Beethoven,
Ferdinand Ries,
Nina Stollewerk,
Franz Schubert,
Johannes Brahms
Johannes Brahms (; 7 May 1833 – 3 April 1897) was a German composer, pianist, and conductor of the mid- Romantic period. Born in Hamburg into a Lutheran family, he spent much of his professional life in Vienna. He is sometimes grouped wit ...
,
Gustav Mahler
Gustav Mahler (; 7 July 1860 – 18 May 1911) was an Austro-Bohemian Romantic composer, and one of the leading conductors of his generation. As a composer he acted as a bridge between the 19th-century Austro-German tradition and the modernism ...
,
Robert Stolz, and
Arnold Schoenberg
Arnold Schoenberg or Schönberg (, ; ; 13 September 187413 July 1951) was an Austrian-American composer, music theorist, teacher, writer, and painter. He is widely considered one of the most influential composers of the 20th century. He was as ...
have worked in Vienna.
Art and culture had a long tradition in Vienna, including theater, opera, classical music and fine arts. The
Burgtheater
The Burgtheater (literally:"Castle Theater" but alternatively translated as "(Imperial) Court Theater"), originally known as '' K.K. Theater an der Burg'', then until 1918 as the ''K.K. Hofburgtheater'', is the national theater of Austria in Vi ...
is considered one of the best theaters in the German-speaking world alongside its branch, the Akademietheater. The
Volkstheater Wien
The Volkstheater in Vienna (roughly translated as "People's Theatre") was founded in 1889 by request of the citizens of Vienna, amongst them the dramatist Ludwig Anzengruber and the furniture manufacturer Thonet, in order to offer a popular count ...
and the
Theater in der Josefstadt also enjoy good reputations. There is also a multitude of smaller theaters, in many cases devoted to less mainstream forms of the performing arts, such as modern, experimental plays or
cabaret.

Vienna is also home to a number of opera houses, including the
Theater an der Wien, the
Staatsoper and the
Volksoper, the latter being devoted to the typical Viennese
operetta
Operetta is a form of theatre and a genre of light opera. It includes spoken dialogue, songs, and dances. It is lighter than opera in terms of its music, orchestral size, length of the work, and at face value, subject matter. Apart from its s ...
. Classical concerts are performed at venues such as the
Wiener Musikverein, home of the
Vienna Philharmonic Orchestra known across the world for the annual widely broadcast "New Year's Day Concert", as well as the
Wiener Konzerthaus, home of the internationally renowned
Vienna Symphony. Many concert venues offer concerts aimed at tourists, featuring popular highlights of Viennese music, particularly the works of
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart,
Johann Strauss I, and
Johann Strauss II
Johann Baptist Strauss II (25 October 1825 – 3 June 1899), also known as Johann Strauss Jr., the Younger or the Son (german: links=no, Sohn), was an Austrian composer of light music, particularly dance music and operettas. He composed ov ...
.


Up until 2005, the Theater an der Wien hosted premieres of musicals, but since 2006 (a year dedicated to the 250th anniversary of Mozart's birth), has devoted itself to opera again, becoming a stagione opera house offering one new production each month. Since 2012, Theater an der Wien has taken over the Wiener Kammeroper, a historical small theater in the first district of Vienna seating 300 spectators, turning it into its second venue for smaller sized productions and chamber operas created by the young ensemble of Theater an der Wien (JET). Before 2005 the most successful musical was ''
Elisabeth
Elizabeth or Elisabeth may refer to:
People
* Elizabeth (given name), a female given name (including people with that name)
* Elizabeth (biblical figure), mother of John the Baptist
Ships
* HMS ''Elizabeth'', several ships
* ''Elisabeth'' (sc ...
'', which was later translated into several languages and performed all over the world. The
Wiener Taschenoper is dedicated to stage music of the 20th and 21st century. The
Haus der Musik ("house of music") opened in the year 2000.
The
Wienerlied is a unique song genre from Vienna. There are approximately 60,000 – 70,000 Wienerlieder.
In 1981 the popular British new romantic group
Ultravox paid a tribute to Vienna on an album and an artful music video recording called ''Vienna''. The inspiration for this work arose from the cinema production called ''
The Third Man'' with the title
Zither music of
Anton Karas.
The
Vienna's English Theatre
Vienna's English Theatre ''(VET),'' located in Vienna, Austria, is the oldest and most established English-language theatre in continental Europe.
History
It was founded in 1963 by the Austrian director Franz Schafranek and his American wife, ...
(VET) is an English theater in Vienna. It was founded in 1963 and is located in the 8th Vienna's district. It is the oldest English-language theater in continental Europe.
In May 2015, Vienna hosted the
Eurovision Song Contest
The Eurovision Song Contest (), sometimes abbreviated to ESC and often known simply as Eurovision, is an international songwriting competition organised annually by the European Broadcasting Union (EBU), featuring participants representing pr ...
following
Austria's victory in the
2014 contest.
Actors from Vienna
Notable entertainers born in Vienna include
Hedy Lamarr,
Christoph Waltz
Christoph Waltz (; born 4 October 1956) is an Austrian-German actor. Since 2009 he has been primarily active in the United States. His accolades include two Academy Awards, two Golden Globe Awards, two British Academy Film Awards and two Sc ...
,
John Banner,
Christiane Hörbiger
Christiane Hörbiger (13 October 1938 – 30 November 2022) was an Austrian stage, film, and television actress. Her first major film role was Mary Vetsera in '' Kronprinz Rudolfs letzte Liebe'' in 1955. She appeared on the stage of the Burgthe ...
,
Eric Pohlmann,
Boris Kodjoe,
Christine Buchegger
Christine Buchegger (19 November 1942 – 3 March 2014) was an Austrian theater and television actress, born in Vienna, Austria.
Biography
Christine Buchegger was born in Vienna to Maria Buchegger originating from Pettenbach in Upper Austria. ...
,
Mischa Hausserman,
Senta Berger and
Christine Ostermayer
Christine Ostermayer (born 15 December 1936 in Vienna, Austria) is an Austrian actress.
Selected filmography
* Derrick (TV series), Derrick - Season 10, Episode 07: "Lohmanns innerer Frieden" (1983)
External links
*ZBF Agency Munich
Au ...
.
Musicians from Vienna
Notable musicians born in Vienna include
Louie Austen,
Alban Berg
Alban Maria Johannes Berg ( , ; 9 February 1885 – 24 December 1935) was an Austrian composer of the Second Viennese School. His compositional style combined Romantic lyricism with the twelve-tone technique. Although he left a relatively sma ...
,
Falco,
Fritz Kreisler,
Joseph Lanner,
Arnold Schönberg,
Franz Schubert,
Johann Strauss I,
Johann Strauss II
Johann Baptist Strauss II (25 October 1825 – 3 June 1899), also known as Johann Strauss Jr., the Younger or the Son (german: links=no, Sohn), was an Austrian composer of light music, particularly dance music and operettas. He composed ov ...
,
Anton Webern, and
Joe Zawinul
Josef Erich Zawinul ( '; 7 July 1932 – 11 September 2007) was an Austrian jazz and jazz fusion keyboardist and composer. First coming to prominence with saxophonist Cannonball Adderley, Zawinul went on to play with Miles Davis and to bec ...
.

Famous musicians who came here to work from other parts of Austria and Germany were
Kurt Adler,
Johann Joseph Fux,
Joseph Haydn
Franz Joseph Haydn ( , ; 31 March 173231 May 1809) was an Austrian composer of the Classical period (music), Classical period. He was instrumental in the development of chamber music such as the string quartet and piano trio. His contributions ...
,
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart,
Ludwig van Beethoven,
Ferdinand Ries,
Johann Sedlatzek
Johann Jean Sedlatzek (also Johann John Sedlaczek; 6 December 1789 – 11 April 1866) was a Silesian flautist born in Głogówek (Oberglogau),History of Oberglogau in Brief. "http://www.smarzly.de/6.html". Smarzly 2003. Retrieved on 16 September ...
,
Antonio Salieri,
Carl Czerny,
Johann Nepomuk Hummel
Johann Nepomuk Hummel (14 November 177817 October 1837) was an Austrian composer and virtuoso pianist. His music reflects the Transition from Classical to Romantic music, transition from the Classical period (music), Classical to the Romantic ...
,
Franz Liszt
Franz Liszt, in modern usage ''Liszt Ferenc'' . Liszt's Hungarian passport spelled his given name as "Ferencz". An orthographic reform of the Hungarian language in 1922 (which was 36 years after Liszt's death) changed the letter "cz" to simpl ...
,
Franz von Suppé,
Anton Bruckner
Josef Anton Bruckner (; 4 September 182411 October 1896) was an Austrian composer, organist, and music theorist best known for his symphonies, masses, Te Deum and motets. The first are considered emblematic of the final stage of Austro-Germ ...
,
Johannes Brahms
Johannes Brahms (; 7 May 1833 – 3 April 1897) was a German composer, pianist, and conductor of the mid- Romantic period. Born in Hamburg into a Lutheran family, he spent much of his professional life in Vienna. He is sometimes grouped wit ...
,
Gustav Mahler
Gustav Mahler (; 7 July 1860 – 18 May 1911) was an Austro-Bohemian Romantic composer, and one of the leading conductors of his generation. As a composer he acted as a bridge between the 19th-century Austro-German tradition and the modernism ...
and
Rainhard Fendrich.
Notable writers from Vienna
Notable writers from Vienna include
Karl Leopold von Möller,
Carl Julius Haidvogel, and
Stefan Zweig
Stefan Zweig (; ; 28 November 1881 – 22 February 1942) was an Austrian novelist, playwright, journalist, and biographer. At the height of his literary career, in the 1920s and 1930s, he was one of the most widely translated and popular write ...
.
Writers who lived and worked in Vienna include
Franz Kafka,
Arthur Schnitzler,
Elias Canetti,
Ingeborg Bachmann,
Robert Musil
Robert Musil (; 6 November 1880 – 15 April 1942) was an Austrian philosophical writer. His unfinished novel, ''The Man Without Qualities'' (german: link=no, Der Mann ohne Eigenschaften), is generally considered to be one of the most important ...
,
Karl Kraus,
Ernst von Feuchtersleben
Baron Ernst von Feuchtersleben (full name: Ernst Maria Johann Karl ''Freiherr'' von Feuchtersleben; 29 April 18063 September 1849), was an Austrian physician, poet and philosopher. He was a member of the von Feuchtersleben Family
Life
He was born ...
,
Thomas Bernhard and
Elfriede Jelinek.
Notable politicians from Vienna
Notable politicians from Vienna include
Karl Leopold von Möller.
Notable athletes
*
Renato Gligoroski (born 1976), former professional footballer, now coach and engineer
Museums


The
Hofburg
The Hofburg is the former principal imperial palace of the Habsburg dynasty. Located in the centre of Vienna, it was built in the 13th century and expanded several times afterwards. It also served as the imperial winter residence, as Schönbrunn ...
is the location of the
Imperial Treasury
Imperial is that which relates to an empire, emperor, or imperialism.
Imperial or The Imperial may also refer to:
Places
United States
* Imperial, California
* Imperial, Missouri
* Imperial, Nebraska
* Imperial, Pennsylvania
* Imperial, ...
(''Schatzkammer''), holding the imperial jewels of the Habsburg dynasty. The Sisi Museum (a museum devoted to
Empress Elisabeth of Austria) allows visitors to view the imperial apartments as well as the silver cabinet. Directly opposite the Hofburg are the
Kunsthistorisches Museum
The Kunsthistorisches Museum ( "Museum of Art History", often referred to as the "Museum of Fine Arts") is an art museum in Vienna, Austria. Housed in its festive palatial building on the Vienna Ring Road, it is crowned with an octagonal do ...
, which houses many paintings by
, ancient and classical artifacts, and the
Naturhistorisches Museum.

A number of
museums are located in the
Museumsquartier (museum quarter), the former Imperial Stalls which were converted into a museum complex in the 1990s. It houses the Museum of Modern Art, commonly known as the
MUMOK (Ludwig Foundation), the
Leopold Museum (featuring the largest collection of paintings in the world by
Egon Schiele
Egon Leo Adolf Ludwig Schiele (; 12 June 1890 – 31 October 1918) was an Austrian Expressionist painter. His work is noted for its intensity and its raw sexuality, and for the many self-portraits the artist produced, including nude self-portr ...
, as well as works by the
Vienna Secession, Viennese Modernism and Austrian Expressionism), the
AzW (museum of architecture), additional halls with feature exhibitions, and the Tanzquartier. The Liechtenstein Palace contains much of one of the world's
largest private art collections, especially strong in the
Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including t ...
. The
Belvedere, built under
Prince Eugene, has
a gallery
The A Gallery was a contemporary art gallery in Wimbledon, London run by Fraser Kee Scott.
Founding
The A Gallery was founded by Fraser Kee Scott in 1997.Groves, Nancy"The science of art" Newsquest, 13 April 2007. Retrieved 24 December 2008. ...
containing paintings by
Gustav Klimt
Gustav Klimt (July 14, 1862 – February 6, 1918) was an Austrian symbolist painter and one of the most prominent members of the Vienna Secession movement. Klimt is noted for his paintings, murals, sketches, and other objets d'art. Klimt's prim ...
(The Kiss), Egon Schiele, and other painters of the early 20th century, also sculptures by
Franz Xaver Messerschmidt, and changing exhibitions too.
There are a multitude of other museums in Vienna, including the
Albertina, the
Military History Museum, the
Technical Museum
Technical may refer to:
* Technical (vehicle), an improvised fighting vehicle
* Technical analysis, a discipline for forecasting the future direction of prices through the study of past market data
* Technical drawing, showing how something is co ...
, the Burial Museum, the
Museum of Art Fakes
The Museum of Art Fakes (german: Fälschermuseum) is a museum of faked and forged artworks that opened in Vienna, Austria in 2005. This small, privately run museum in the Landstraße district is the only one of its kind in the German-speaking worl ...
, the
KunstHausWien,
Museum of Applied Arts, the
Sigmund Freud Museum, and the
Mozarthaus Vienna. The museums on the history of the city, including the former
Historical Museum of the City of Vienna on
Karlsplatz, the
Hermesvilla, the residences and birthplaces of various composers, the
Museum of the Romans, and the
Vienna Clock Museum, are now gathered together under the group umbrella
Vienna Museum. The
Jewish Museum Vienna, founded 1896, is the oldest of its kind. In addition there are museums dedicated to Vienna's individual districts. They provide a record of individual struggles, achievements and tragedy as the city grew and survived two world wars. For readers seeking family histories these are good sources of information.
Architecture

A variety of architectural styles can be found in Vienna, such as the
Romanesque Ruprechtskirche
St. Rupert's Church (german: Ruprechtskirche) is a Romanesque church in Vienna, Austria. Traditionally considered to be the oldest church in the city, St. Rupert's Church is dedicated to Saint Rupert of Salzburg, patron saint of the salt merchant ...
and the
Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including t ...
Karlskirche
The ''Rektoratskirche St. Karl Borromäus'', commonly called the ''Karlskirche'' (), is a Baroque church located on the south side of Karlsplatz in Vienna, Austria. Widely considered the most outstanding baroque church in Vienna, as well as one ...
. Styles range from
classicist buildings to
modern architecture.
Art Nouveau
Art Nouveau (; ) is an international style of art, architecture, and applied art, especially the decorative arts. The style is known by different names in different languages: in German, in Italian, in Catalan, and also known as the Modern ...
left many architectural traces in Vienna. The
Secession building,
Karlsplatz Stadtbahn Station, and the
Kirche am Steinhof by
Otto Wagner rank among the best known examples of Art Nouveau in the world. Wagner's prominent student
Jože Plečnik from
Slovenia also left important traces in Vienna. His works include the Langer House (1900) and the
Zacherlhaus (1903–1905). Plečnik's 1910–1913 ''Church of the Holy Spirit'' () in Vienna is remarkable for its innovative use of poured-in-place concrete as both structure and exterior surface, and also for its abstracted classical form language. Most radical is the church's crypt, with its slender concrete columns and angular, cubist capitals and bases.
Concurrent to the Art Nouveau movement was the
Wiener Moderne, during which some architects shunned the use of extraneous adornment. A key architect of this period was
Adolf Loos, whose works include the
Looshaus (1909), the Kärntner Bar or American Bar (1908) and the
Steiner House
Steiner House is a building in Vienna, Austria. It is considered one of the major works of architect Adolf Loos.
Background
Loos was still starting his career in 1910 when he designed and constructed the Steiner house in Vienna, Austria. This de ...
(1910).
The
Hundertwasserhaus
The Hundertwasserhaus ("Hundertwasser house") is an apartment house in Vienna, Austria, built after the idea and concept of Austrian artist Friedensreich Hundertwasser.
Outline
This expressionist landmark of Vienna is located in the Landstr ...
by
Friedensreich Hundertwasser, designed to counter the clinical look of modern architecture, is one of Vienna's most popular
tourist attractions. Another example of unique architecture is the
Wotrubakirche by sculptor
Fritz Wotruba. In the 1990s, a number of quarters were adapted and extensive building projects were implemented in the areas around Donaustadt (north of the Danube) and Wienerberg (in southern Vienna).
The 220-meter high
DC Tower 1 located on the Northern bank of the Danube, completed in 2013, is the tallest skyscraper in Vienna. In recent years, Vienna has seen numerous architecture projects completed which combine modern architectural elements with old buildings, such as the remodeling and revitalization of the old
Gasometer
A gas holder or gasholder, also known as a gasometer, is a large container in which natural gas or town gas is stored near atmospheric pressure at ambient temperatures. The volume of the container follows the quantity of stored gas, with pressu ...
in 2001.
Most buildings in Vienna are relatively low; in early 2006 there were around 100 buildings higher than . The number of high-rise buildings is kept low by building legislation aimed at preserving green areas and districts designated as
world cultural heritage. Strong rules apply to the planning, authorization and construction of high-rise buildings. Consequently, much of the inner city is a high-rise free zone.
Ball dances of Vienna
Vienna is the last great capital of the 19th-century
ball
A ball is a round object (usually spherical, but can sometimes be ovoid) with several uses. It is used in ball games, where the play of the game follows the state of the ball as it is hit, kicked or thrown by players. Balls can also be used f ...
. There are over 450 balls per year, some featuring as many as nine live orchestras.
Balls are held in the many palaces in Vienna, with the principal venue being the Hofburg Palace in
Heldenplatz. While the
Opera Ball is the best known internationally of all the Austrian balls,
other balls such as the Kaffeesiederball (Cafe Owners Ball), the Jägerball (Hunter's Ball) and the
Life Ball
The Life Ball in Vienna is the biggest Charitable organization, charity event in Europe supporting people with HIV or AIDS. The event is organized by the nonprofit organization AIDS LIFE, which was founded in 1992 by Gery Keszler and Torgom Petros ...
(AIDS charity event) are almost as well known within Austria and even better appreciated for their cordial atmosphere. Viennese of at least middle class may visit a number of balls in their lifetime.
Dancers and opera singers from the
Vienna State Opera often perform at the openings of the larger balls.
A Vienna ball is an all-night cultural attraction. Major Vienna balls generally begin at 9 pm and last until 5 am, although many guests carry on the celebrations into the next day. Viennese balls are being exported (with support from the City of Vienna) to around 30 cities worldwide such as New York, Barcelona, Hong Kong, Kuala Lumpur, Rome, Prague, Bucharest, Berlin and Moscow.
Language
Vienna is part of the
Austro-Bavarian language area, in particular
Central Bavarian (''Mittelbairisch''). In recent years, linguistics experts have seen a decline in the use of the Viennese variant. Manfred Glauninger, sociolinguist at the Institute for Austrian Dialect and Name Lexica, has observed three issues. First, many parents feel there's a stigma attached to the Viennese dialect so they speak Standard German to their children. Second, many children have recently immigrated to Austria and are learning German as a second language in school. Third, young people are influenced by mass media which is most always delivered in Standard German.
LGBT culture
Vienna is considered the center of
LGBT life in Austria.
The city has an action plan against queerphobic discrimination and, since 1998, has an anti-discriminiation unit within the city's administration. The city has several cafés, bars and clubs frequented by LGBT people. Among the most prominent is
Café Savoy, which is a traditional coffee house built in 1896. In 2015, the city introduced traffic lights with same-sex couples before hosting the
Eurovision Song Contest
The Eurovision Song Contest (), sometimes abbreviated to ESC and often known simply as Eurovision, is an international songwriting competition organised annually by the European Broadcasting Union (EBU), featuring participants representing pr ...
that year, which attracted media attention internationally. Every year in June,
Vienna Pride is organised. In 2019, when the pride parade was also hosting
Europride, it attracted 500.000 visitors.
Education
Vienna is Austria's main center of education and home to many universities, professional colleges and
gymnasiums (high schools).




Universities
*
Academy of Fine Arts Vienna
*
Central European University
*
Diplomatic Academy of Vienna
The Diplomatic Academy of Vienna (DA; German: ''Diplomatische Akademie Wien''), also known as the Vienna School of International Studies, is a postgraduate professional school based in Vienna, Austria, with focused training for students and prof ...
*
Medical University of Vienna
The Medical University of Vienna (German: ''Medizinische Universität Wien'') is a public university located in Vienna, Austria. It is the direct successor to the faculty of medicine at the University of Vienna, founded in 1365 by Rudolf IV, Duk ...
*
PEF Private University of Management Vienna
*
University of Applied Arts Vienna
*
University of Applied Sciences Campus Vienna
*
University of Music and Performing Arts, Vienna
*
University of Veterinary Medicine Vienna
*
University of Vienna
*
Vienna University of Economics and Business
*
University of Natural Resources and Life Sciences, Vienna
*
University of Applied Sciences Technikum Wien
University of Applied Sciences Technikum Vienna (''German:'' Fachhochschule Technikum Wien) was founded in 1994 and became Vienna’s first university of applied sciences in 2000. It is the largest technical university of applied sciences in Aust ...
*
TU Wien
TU Wien (TUW; german: Technische Universität Wien; still known in English as the Vienna University of Technology from 1975–2014) is one of the major universities in Vienna, Austria. The university finds high international and domestic recogn ...
*
Webster University Vienna
*
Sigmund Freud University Vienna
Sigmund Freud University (SFU) is a private and For-profit education, for-profit university accredited by thAustrian Accreditation Councilin August 2005 located in Vienna, Austria. As a university in the field of Human Sciences, SFU specializes i ...
*
International Anti-Corruption Academy (in Laxenburg, south of Vienna)
International schools
*
Danube International School
Danube International School Vienna (DISV) is a private List of international schools, international school in Vienna, Austria. located in the Second District, between the Donaukanal and the Prater.
The school is privately owned and managed, but i ...
*
International University Vienna
*
SAE Vienna
*
Lauder Business School
*
Lycée Français de Vienne
*
Vienna Christian School
The International Christian School of Vienna is an international school
An international school is an institution that promotes education in an international environment or framework. Although there is no uniform definition or criteria, interna ...
*
Vienna International School
*
American International School
*
(Japanese school)
*Amadeus International School
Leisure activities
Parks and gardens
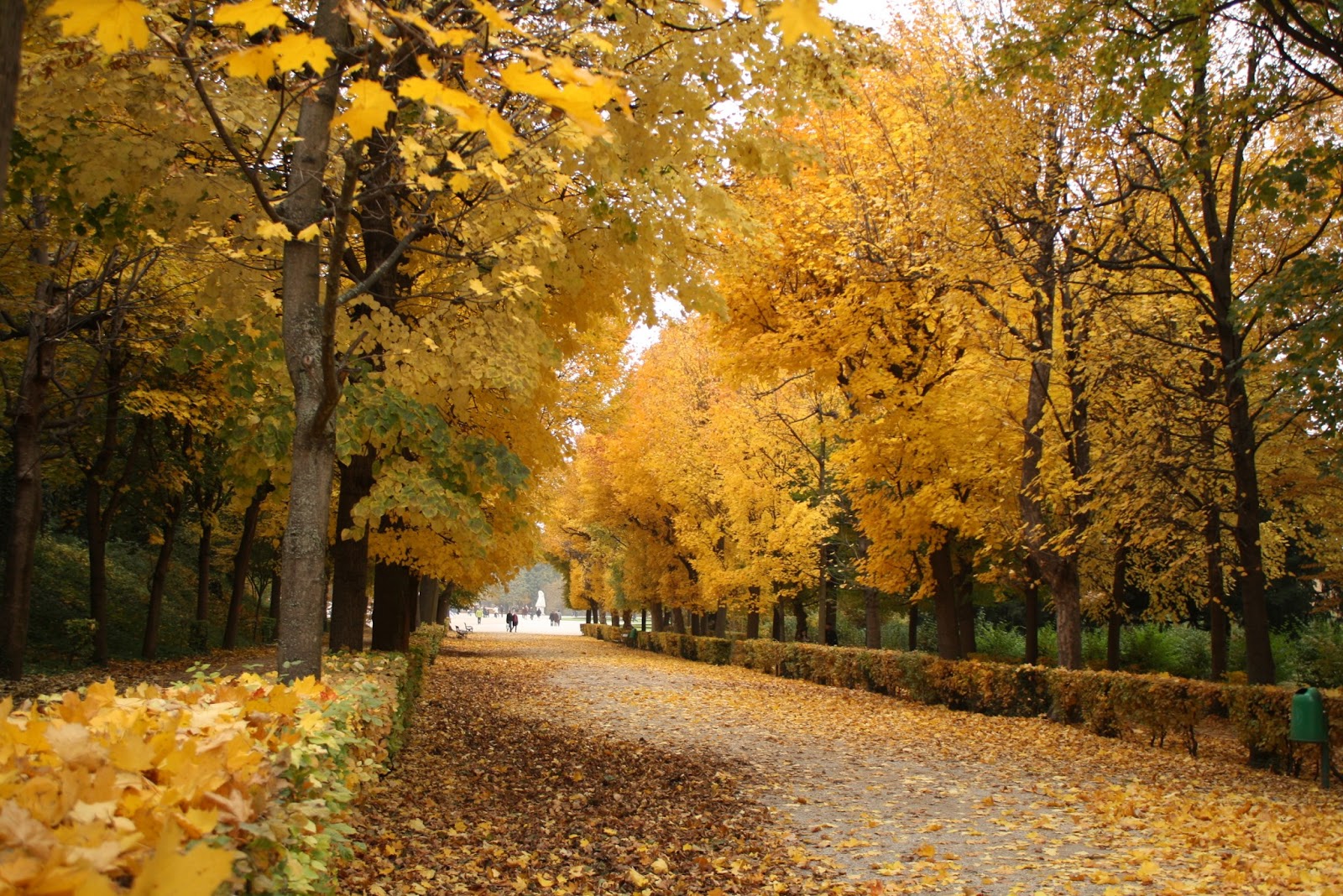

Vienna possesses many parks, including the ''
Stadtpark'', the ''Burggarten'', the ''
Volksgarten'' (part of the ''Hofburg''), the ''Schlosspark'' at Schloss Belvedere (home to the
Vienna Botanic Gardens), the ''Donaupark'', the ''Schönbrunner Schlosspark'', the ''
Prater'', the ''Augarten'', the ''Rathauspark'', the ''
Lainzer Tiergarten'', the ''Dehnepark'', the ''Resselpark'', the ''Votivpark'', the ''Kurpark Oberlaa'', the ''Auer-Welsbach-Park'' and the ''Türkenschanzpark''. Green areas include ''Laaer-Berg'' (including the Bohemian Prater) and the foothills of the ''
Wienerwald'', which reaches into the outer areas of the city. Small parks, known by the Viennese as ''Beserlparks'', are everywhere in the inner city areas.
Many of Vienna's parks include monuments, such as the
Stadtpark with its statue of
Johann Strauss II
Johann Baptist Strauss II (25 October 1825 – 3 June 1899), also known as Johann Strauss Jr., the Younger or the Son (german: links=no, Sohn), was an Austrian composer of light music, particularly dance music and operettas. He composed ov ...
, and the gardens of the
baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including t ...
palace
A palace is a grand residence, especially a royal residence, or the home of a head of state or some other high-ranking dignitary, such as a bishop or archbishop. The word is derived from the Latin name palātium, for Palatine Hill in Rome which ...
, where the
State Treaty
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
was signed. Vienna's principal park is the
Prater which is home to the
Riesenrad
The (; 'Vienna Giant errisWheel'), or simply Riesenrad, is a tall Ferris wheel at the entrance of the Prater amusement park in Leopoldstadt, the 2nd district of Austria's capital Vienna. It is one of Vienna's most popular tourist attractions, an ...
, a
Ferris wheel, and
Kugelmugel, a micronation the shape of a sphere. The imperial
Schönbrunn's grounds contain an 18th-century park which includes
the world's oldest zoo, founded in 1752.
The
Donauinsel, part of Vienna's flood defenses, is a long
artificial island between the Danube and Neue Donau dedicated to leisure activities.
Sport
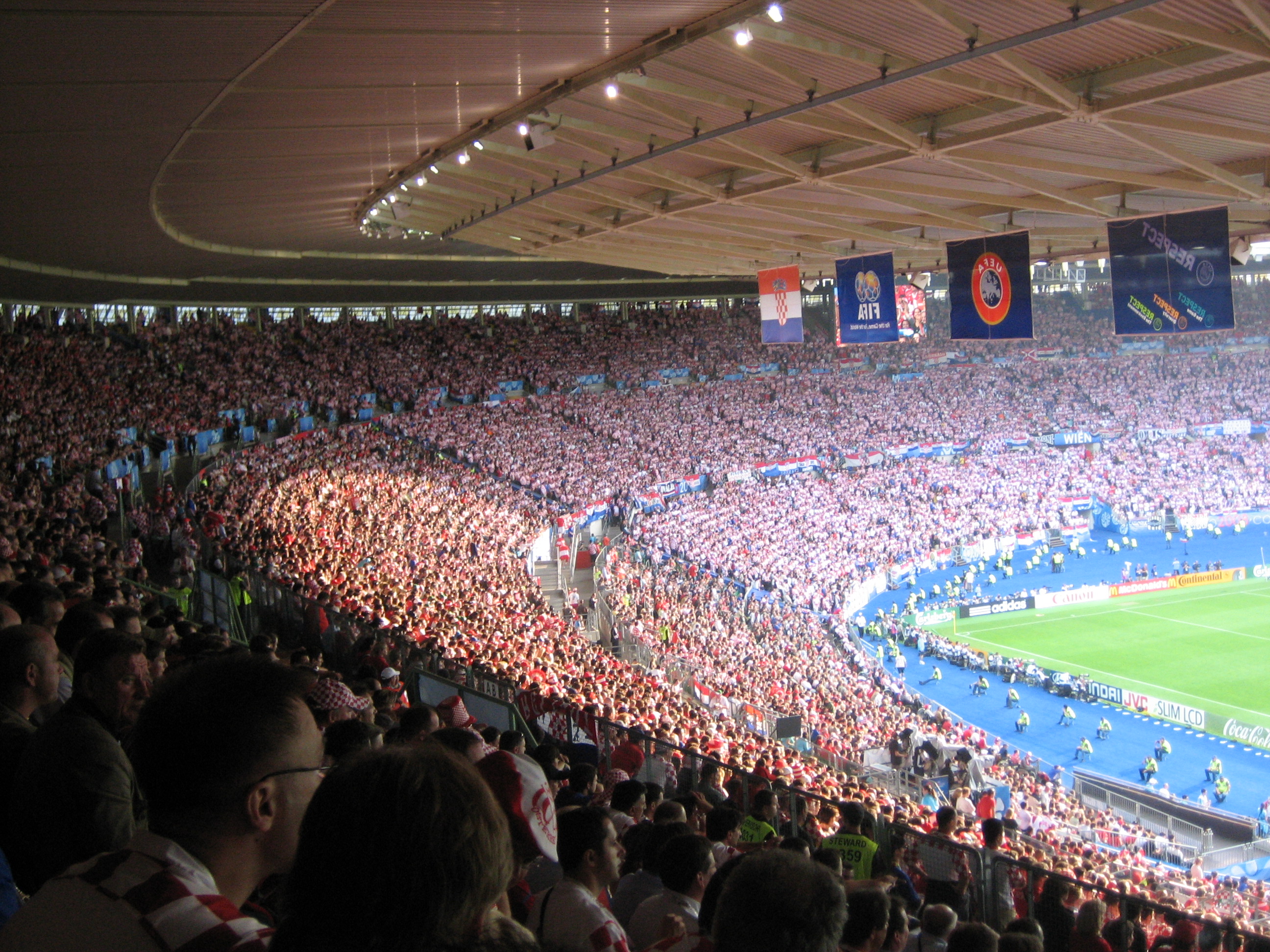

Austria's capital is home to numerous
football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly c ...
teams. The best known are the local football clubs include
FK Austria Wien (21
Austrian Bundesliga
The Austrian Football Bundesliga (german: Österreichische Fußball-Bundesliga, italic=no , "Austrian Football Federal League"), also known as Admiral Bundesliga for sponsorship reasons, is the top level of the Austrian football league system. Th ...
titles and record 27-time cup winners),
SK Rapid Wien (record 32
Austrian Bundesliga
The Austrian Football Bundesliga (german: Österreichische Fußball-Bundesliga, italic=no , "Austrian Football Federal League"), also known as Admiral Bundesliga for sponsorship reasons, is the top level of the Austrian football league system. Th ...
titles), and the oldest team,
First Vienna FC
First Vienna FC is an Austrian association football club based in the Döbling district of Vienna. Established on 22 August 1894, it is the country's oldest team and has played a notable role in the history of the game there. It is familiarly k ...
. Other important
sports clubs include the
Raiffeisen Vikings Vienna
The Vienna Vikings is an American football club based in Vienna, Austria. Founded in 1983, the Vikings are known as one of Europe's most dominant clubs, having won the Eurobowl title five times (2004–2007 and 2013), as well being the runner ...
(
American Football), who won the
Eurobowl title between 2004 and 2007 4 times in a row and had a perfect season in 2013, the
Aon hotVolleys Vienna
aon hotVolleys Vienna is an Austrian volleyball club which is playing their home matches at the Budocenter in Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal co ...
, one of Europe's premier Volleyball organizations, the Vienna Wanderers (baseball) who won the 2012 and 2013 Championship of the Austrian Baseball League, and the
Vienna Capitals (
Ice Hockey). Vienna was also where the European Handball Federation (EHF) was founded. There are also three
rugby clubs;
Vienna Celtic, the oldest rugby club in Austria,
RC Donau
Rugby Union Donau Wien is an Austrian rugby
Rugby may refer to:
Sport
* Rugby football in many forms:
** Rugby league: 13 players per side
*** Masters Rugby League
*** Mod league
*** Rugby league nines
*** Rugby league sevens
*** Touch (sport)
...
, and Stade Viennois
Vienna hosts many different sporting events including the
Vienna City Marathon
The Vienna City Marathon is an annual marathon race over the classic distance of 42.195 km held in Vienna, Austria since 1984.
History
The first edition was held on with a total of 794 competitors. It is Austria's largest road running even ...
, which attracts more than 10,000 participants every year and normally takes place in May. In 2005 the
Ice Hockey World Championships took place in
Austria and the final was played in Vienna. Vienna's
Ernst Happel Stadium was the venue of four
Champions League and European Champion Clubs' Cup finals (1964, 1987, 1990 and 1995) and on 29 June it hosted the final of
Euro 2008 which saw a Spanish 1–0 victory over Germany.
Tennis tournament
Vienna Open also takes place in the city since 1974. The matches are played in the
Wiener Stadthalle.
The Neue Donau, which was formed after the Donauinsel was created, is free of river traffic and a popular destination for leisure and sports activities.
Vienna will host the official 2021
3x3 Basketball World Cup
The FIBA 3x3 World Cup is a 3x3 basketball tournament for national teams organized by the International Basketball Federation (FIBA). The debut of the tournament then named as the FIBA 3x3 World Championship was held in August 2012 in Athens, Gree ...
.
Culinary specialities
Food

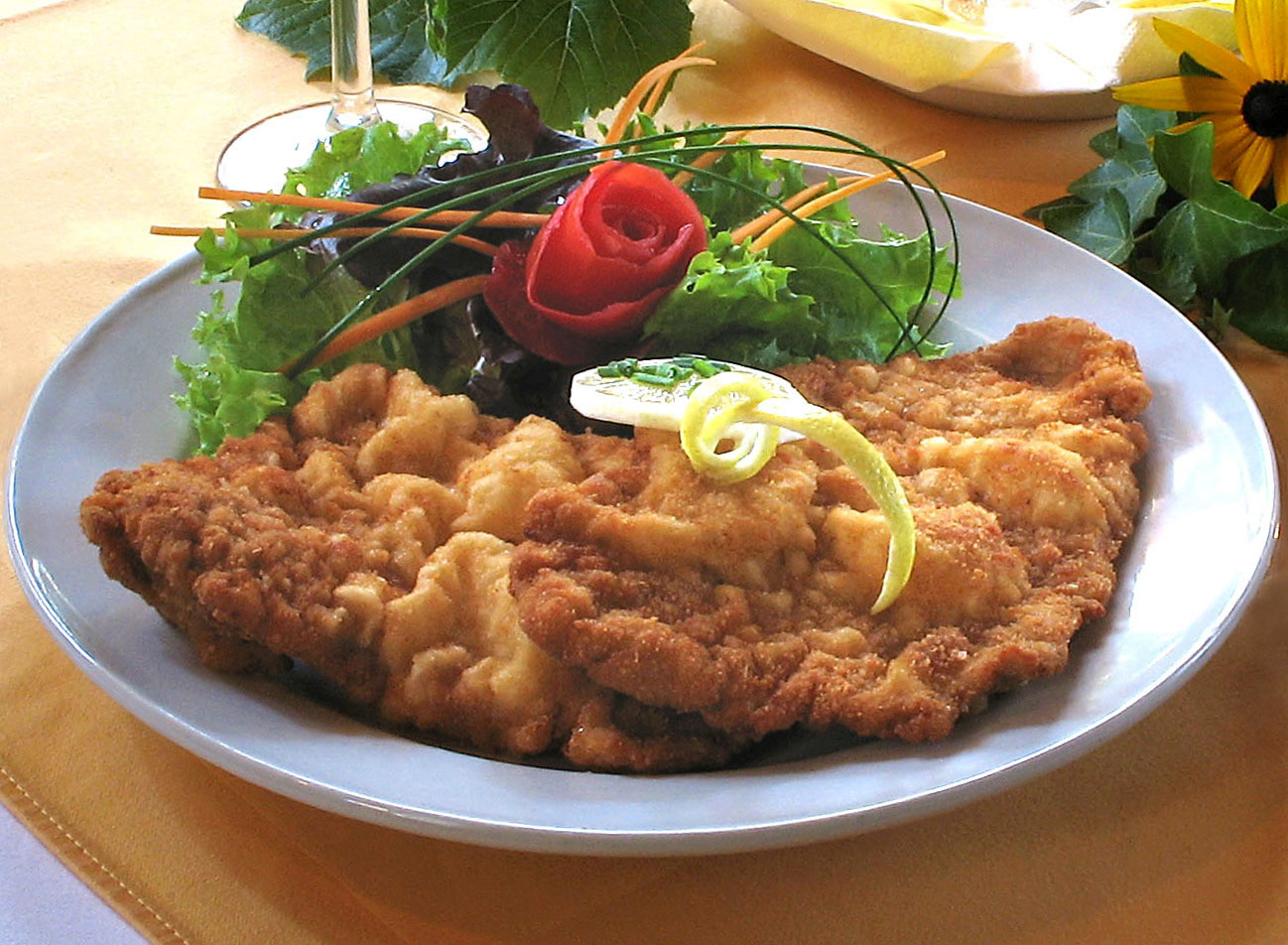
Vienna is well known for ''
Wiener Schnitzel'', a cutlet of
veal
Veal is the meat of calves, in contrast to the beef from older cattle. Veal can be produced from a calf of either sex and any breed, however most veal comes from young male calves of dairy breeds which are not used for breeding. Generally, v ...
''(Kalbsschnitzel)'' or pork ''(Schweinsschnitzel)'' that is pounded flat, coated in flour, egg and breadcrumbs, and fried in
clarified butter. It is available in almost every restaurant that serves
Viennese cuisine and can be eaten hot or cold. It is usually served in many cozy cafeterias in the old town evoking all the history behind the Empire city. The traditional 'Wiener Schnitzel' though is a cutlet of veal. Other examples of Viennese cuisine include ''
Tafelspitz'' (very lean boiled beef), which is traditionally served with ''Geröstete Erdäpfel'' (boiled potatoes mashed with a fork and subsequently fried) and horseradish sauce, ''Apfelkren'' (a mixture of horseradish, cream and apple) and ''Schnittlauchsauce'' (a chives sauce made with mayonnaise and stale bread).

Vienna has a long tradition of producing cakes and desserts. These include ''
Apfelstrudel'' (hot apple strudel), ''
Milchrahmstrudel'' (milk-cream strudel), ''
Palatschinken'' (sweet pancakes), and ''Knödel'' (dumplings) often filled with fruit such as apricots (''
Marillenknödel'').
Sachertorte, a delicately moist chocolate cake with apricot jam created by the
Sacher Hotel
Hotel Sacher is a five-star luxury hotel in Vienna, Austria, facing the Vienna State Opera in the city's central Innere Stadt district. It is famous for the specialty of the house, the Sachertorte, a chocolate cake with apricot filling. There is ...
, is world-famous.
In winter, small street stands sell traditional ''
Maroni'' (hot chestnuts) and potato fritters.
Sausages are popular and available from street vendors (''
Würstelstand'') throughout the day and into the night. The sausage known as ''
Wiener'' (German for Viennese) in the U.S. and in Germany, is called a ''Frankfurter'' in Vienna. Other popular sausages are ''Burenwurst'' (a coarse beef and pork sausage, generally boiled), ''
Käsekrainer'' (spicy pork with small chunks of cheese), and ''
Bratwurst'' (a white pork sausage). Most can be ordered "mit Brot" (with bread) or as a "hot dog" (stuffed inside a long roll). Mustard is the traditional condiment and usually offered in two varieties: "süß" (sweet) or "scharf" (spicy).
Kebab, pizza and noodles are, increasingly, the snack foods most widely available from small stands.
Vienna ranked 10th in vegan friendly European cities in a study by Alternative Traveler.
The ''
Naschmarkt'' is a permanent market for fruit, vegetables, spices, fish, meat, etc., from around the world. The city has many coffee and breakfast stores.
Drinks

Vienna, along with
Paris,
Santiago,
Cape Town,
Prague,
Canberra
Canberra ( )
is the capital city of Australia. Founded following the federation of the colonies of Australia as the seat of government for the new nation, it is Australia's largest inland city and the eighth-largest city overall. The ci ...
,
Bratislava
Bratislava (, also ; ; german: Preßburg/Pressburg ; hu, Pozsony) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Slovakia. Officially, the population of the city is about 475,000; however, it is estimated to be more than 660,000 — approxim ...
and
Warsaw, is one of the few remaining world capital cities with its own vineyards. The wine is served in small Viennese pubs known as
Heuriger, which are especially numerous in the wine growing areas of
Döbling (
Grinzing,
Neustift am Walde,
Nußdorf,
Salmannsdorf
Salmannsdorf (Central Bavarian: ''Salmaunsduaf'') is a part of Döbling, the 19th district of Vienna.
Wien.gv.at webpage (see below: References).
Salmannsdorf was an independent municipality until 1892, when it was incorporated into the Wäh ...
,
Sievering),
Floridsdorf (Stammersdorf, Strebersdorf),
Liesing (
Mauer) and Favoriten (Oberlaa). The wine is often drunk as a Spritzer ("G'spritzter") with sparkling water. The
Grüner Veltliner, a dry white wine, is the most widely cultivated wine in Austria. Another wine very typical for the region is "Gemischter Satz", which is typically a blend of different types of wines harvested from the same vineyard.
Beer is next in importance to wine. Vienna has a single large brewery,
Ottakringer
Ottakringer () is the last large brewery remaining in Vienna, Austria, and is located in Ottakring, the 16th district of Vienna.
History
The Ottakringer brewery was opened in 1837 by the master miller Heinrich Plank under the name of ''Planksch ...
, and more than ten
microbreweries. A "Beisl" is a typical small Austrian pub, of which Vienna has many.
Also, local soft drinks such as
Almdudler are popular around the country as an alternative to alcoholic beverages, placing it on the top spots along American counterparts such as
Coca-Cola in terms of market share. Another popular drink is the so-called "
Spezi", a mix between
Coca-Cola and the original formula of
Orange Fanta or the more locally renowned
Frucade.
Viennese cafés
 Viennese café
Viennese cafés have an extremely long and distinguished history that dates back centuries, and the caffeine addictions of some famous historical patrons of the oldest are something of a local legend. These coffee houses are unique to Vienna and many cities have unsuccessfully sought to copy them. Some people consider cafés as their extended living room where nobody will be bothered if they spend hours reading a newspaper while enjoying their coffee. Traditionally, the coffee comes with a glass of water. Viennese cafés claim to have invented the process of
filtering coffee from booty captured after the second
Turkish siege in 1683. Viennese cafés claim that when the invading Turks left Vienna, they abandoned hundreds of sacks of
coffee beans. The
Polish King
John III Sobieski
John III Sobieski ( pl, Jan III Sobieski; lt, Jonas III Sobieskis; la, Ioannes III Sobiscius; 17 August 1629 – 17 June 1696) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1674 until his death in 1696.
Born into Polish nobility, Sobie ...
, the commander of the anti-Turkish coalition of Poles, Germans, and Austrians, gave
Franz George Kolschitzky (Polish –
Franciszek Jerzy Kulczycki) some of this coffee as a reward for providing information that allowed him to defeat the Turks. Kolschitzky then opened Vienna's first
coffee shop.
Julius Meinl set up a modern roasting plant in the same premises where the coffee sacks were found, in 1891.
Tourist attractions
Major tourist attractions include the imperial palaces of the
Hofburg
The Hofburg is the former principal imperial palace of the Habsburg dynasty. Located in the centre of Vienna, it was built in the 13th century and expanded several times afterwards. It also served as the imperial winter residence, as Schönbrunn ...
and
Schönbrunn (also home to the world's oldest zoo,
Tiergarten Schönbrunn) and the
Riesenrad
The (; 'Vienna Giant errisWheel'), or simply Riesenrad, is a tall Ferris wheel at the entrance of the Prater amusement park in Leopoldstadt, the 2nd district of Austria's capital Vienna. It is one of Vienna's most popular tourist attractions, an ...
in the Prater. Cultural highlights include the
Burgtheater
The Burgtheater (literally:"Castle Theater" but alternatively translated as "(Imperial) Court Theater"), originally known as '' K.K. Theater an der Burg'', then until 1918 as the ''K.K. Hofburgtheater'', is the national theater of Austria in Vi ...
, the
Wiener Staatsoper, the
Lipizzaner horses at the
spanische Hofreitschule, and the
Vienna Boys' Choir, as well as excursions to Vienna's Heurigen district Döbling.
There are also more than 100 art museums, which together attract over eight million visitors per year.
The most popular ones are
Albertina,
Belvedere,
Leopold Museum in the
Museumsquartier,
KunstHausWien,
Bank Austria Kunstforum
This list of museums in Vienna, Austria contains museums which are defined for this context as institutions (including nonprofit organizations, government entities, and private businesses) that collect and care for objects of cultural, artistic, ...
, the twin ''
Kunsthistorisches Museum
The Kunsthistorisches Museum ( "Museum of Art History", often referred to as the "Museum of Fine Arts") is an art museum in Vienna, Austria. Housed in its festive palatial building on the Vienna Ring Road, it is crowned with an octagonal do ...
'' and ''
Naturhistorisches Museum'', and the
Technisches Museum Wien, each of which receives over a quarter of a million visitors per year.
There are many popular sites associated with composers who lived in Vienna including
Beethoven's various residences and grave at
Zentralfriedhof (Central Cemetery) which is the largest cemetery in Vienna and the burial site of many
famous people.
Mozart
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (27 January 17565 December 1791), baptised as Joannes Chrysostomus Wolfgangus Theophilus Mozart, was a prolific and influential composer of the Classical period (music), Classical period. Despite his short life, his ra ...
has a memorial grave at the Habsburg gardens and at
St. Marx cemetery (where his grave was lost). Vienna's many churches also draw large crowds, famous of which are
St. Stephen's Cathedral, the
Deutschordenskirche, the
Jesuitenkirche, the
Karlskirche
The ''Rektoratskirche St. Karl Borromäus'', commonly called the ''Karlskirche'' (), is a Baroque church located on the south side of Karlsplatz in Vienna, Austria. Widely considered the most outstanding baroque church in Vienna, as well as one ...
, the
Peterskirche
The ''Peterskirche'' ( en, St. Peter's Church) is a Baroque Catholic Church, Roman Catholic parish church in Vienna, Austria. It was transferred in 1970 by the Archbishop of Vienna Franz König, Franz Cardinal König to the priests of the Opus ...
,
Maria am Gestade
Maria am Gestade (Mary at the Shore) is a Gothic church in Vienna, Austria. One of the oldest churches in the city—along with St. Peter's Church and St. Rupert's Church—it is one of the few surviving examples of Gothic architecture in Vienna. ...
, the
Minoritenkirche, the
Ruprechtskirche
St. Rupert's Church (german: Ruprechtskirche) is a Romanesque church in Vienna, Austria. Traditionally considered to be the oldest church in the city, St. Rupert's Church is dedicated to Saint Rupert of Salzburg, patron saint of the salt merchant ...
, the
Schottenkirche,
St. Ulrich and the
Votivkirche. In order to get deeper insight in the history of Vienna visitors like to join the popula
Free Walking Tourin Vienna.
Modern attractions include the
Hundertwasserhaus
The Hundertwasserhaus ("Hundertwasser house") is an apartment house in Vienna, Austria, built after the idea and concept of Austrian artist Friedensreich Hundertwasser.
Outline
This expressionist landmark of Vienna is located in the Landstr ...
, the
United Nations headquarters and the view from the
Donauturm.
File:Albertina1.JPG, Albertina
File:Austria Parlament Athena.jpg, Austrian Parliament Building
The Austrian Parliament Building (german: Parlamentsgebäude, colloquially ''das Parlament'') in Vienna is where the two houses of the Austrian Parliament conduct their sessions. The building is located on the ''Ringstraße'' boulevard in the f ...
File:Belveder - widok od frontu - Vienna.jpg, Belvedere Palace
File:Burgtheater Weitwinkel.jpg, Burgtheater
The Burgtheater (literally:"Castle Theater" but alternatively translated as "(Imperial) Court Theater"), originally known as '' K.K. Theater an der Burg'', then until 1918 as the ''K.K. Hofburgtheater'', is the national theater of Austria in Vi ...
File:Graben Vienna June 2006 283.jpg, Graben
In geology, a graben () is a depressed block of the crust of a planet or moon, bordered by parallel normal faults.
Etymology
''Graben'' is a loan word from German, meaning 'ditch' or 'trench'. The word was first used in the geologic contex ...
File:Wien - Hundertwasserhaus (01).JPG, Hundertwasserhaus
The Hundertwasserhaus ("Hundertwasser house") is an apartment house in Vienna, Austria, built after the idea and concept of Austrian artist Friedensreich Hundertwasser.
Outline
This expressionist landmark of Vienna is located in the Landstr ...
File:Karlskirche Wien abends.jpg, Karlskirche
The ''Rektoratskirche St. Karl Borromäus'', commonly called the ''Karlskirche'' (), is a Baroque church located on the south side of Karlsplatz in Vienna, Austria. Widely considered the most outstanding baroque church in Vienna, as well as one ...
at dusk
File:Maria-Theresien-Platz Kunsthistorisches Museum Wien 2010.jpg, Kunsthistorisches Museum
The Kunsthistorisches Museum ( "Museum of Art History", often referred to as the "Museum of Fine Arts") is an art museum in Vienna, Austria. Housed in its festive palatial building on the Vienna Ring Road, it is crowned with an octagonal do ...
File:Wien - Naturhistorisches Museum (1).JPG, Naturhistorisches Museum
File:Wien - Palais Augarten (1).JPG, Palais Augarten
File:Wien Rathaus hochauflösend.jpg, Rathaus
In local government, a city hall, town hall, civic centre (in the UK or Australia), guildhall, or a municipal building (in the Philippines), is the chief administrative building of a city, town, or other municipality. It usually houses ...
File:Kaiserliches Pavillon Schoenbrunn August 2006.jpg, Schönbrunn Zoo
Schönbrunn Zoo (; also simply called Vienna Zoo) is a 17-hectare (42-acre) zoo in the city of Vienna, Austria. Established in 1752, it is the world’s oldest zoo still in operation. It is also a UNESCO World Heritage Site, being a part of the S ...
File:Spanische Hofreitschule3, Vienna.jpg, Spanish Riding School
File:Sttephanplatz, Graben, Vienna, Austria.jpg, Stephansplatz
File:Wien - Stephansdom (1).JPG, St. Stephen's Cathedral
File:Wien - Heldenplatz, Prinz-Eugen-Denkmal (2).JPG, Prince Eugene Monument
File:Kohlmarkt Vienna June 2006 309.jpg, View of Hofburg
The Hofburg is the former principal imperial palace of the Habsburg dynasty. Located in the centre of Vienna, it was built in the 13th century and expanded several times afterwards. It also served as the imperial winter residence, as Schönbrunn ...
File:Secession 2016, Vienna.jpg, Vienna Secession building
File:Wien - Staatsoper (1).JPG, Vienna State Opera
File:20080215-18 Wenen (460).jpg, Wiener Riesenrad
Transportation


Vienna has an extensive transportation network with a unified fare system that integrates municipal, regional and railway systems under the umbrella of the Verkehrsverbund Ost-Region (VOR). Public transport is provided by buses, trams and five underground metro lines (
U-Bahn), most operated by the
Wiener Linien. There are also more than 50
S-train stations within the city limits. Suburban trains are operated by the
ÖBB. The city forms the hub of the Austrian railway system, with services to all parts of the country and abroad. The railway system connects Vienna's main station
Vienna Hauptbahnhof with other European cities, like
Berlin,
Bratislava
Bratislava (, also ; ; german: Preßburg/Pressburg ; hu, Pozsony) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Slovakia. Officially, the population of the city is about 475,000; however, it is estimated to be more than 660,000 — approxim ...
,
Budapest,
Brussels,
Cologne,
Frankfurt,
Hamburg,
Ljubljana,
Munich,
Prague,
Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 ...
,
Wrocław,
Warsaw,
Zagreb and
Zürich.
Vienna has multiple road connections including expressways and motorways.
Vienna is served by
Vienna International Airport, located southeast of the city center next to the town of
Schwechat. The airport handled approximately 31.7 million passengers in 2019. Following lengthy negotiations with surrounding communities, the airport will be expanded to increase its capacity by adding a third runway. The airport is undergoing a major expansion, including a new terminal building that opened in 2012 to prepare for an increase in passengers.
Viennese
International relations
International organizations in Vienna


Vienna is the seat of a number of United Nations offices and various international institutions and companies, including the
International Atomic Energy Agency
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) is an intergovernmental organization that seeks to promote the peaceful use of nuclear energy and to inhibit its use for any military purpose, including nuclear weapons. It was established in 1957 ...
(IAEA), the
United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), the
United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), the
Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC), the
OPEC Fund for International Development (OFID), the
Preparatory Commission for the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty Organization (CTBTO), the
Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE), the
United Nations Office for Outer Space Affairs (UNOOSA) and the
European Union Agency for Fundamental Rights (FRA). Vienna is the world's third "UN city", next to
New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
,
Geneva, and
Nairobi. Additionally, Vienna is the seat of the
United Nations Commission on International Trade Law's secretariat (
UNCITRAL). In conjunction, the
University of Vienna annually hosts the prestigious
Willem C. Vis Moot, an international commercial arbitration competition for students of law from around the world.
Diplomatic meetings have been held in Vienna in the latter half of the 20th century, resulting in documents bearing the name
Vienna Convention or Vienna Document. Among the more important documents negotiated in Vienna are the 1969
Vienna Convention on the Law of Treaties, as well as the 1990
Treaty on Conventional Armed Forces in Europe. Vienna also hosted the negotiations leading to the 2015
Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action
The Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA; fa, برنامه جامع اقدام مشترک , barnāmeye jāme'e eqdāme moshtarak (, ''BARJAM'')), commonly known as the Iran nuclear deal or Iran deal, is an agreement on the Iranian nuclear ...
on Iran's nuclear program as well as the
Vienna peace talks for Syria
The Vienna peace talks for Syria, as of 14 November 2015 known as the talks of the International Syria Support Group (ISSG), are negotiations of foreign powers that began in Vienna, Austria in October 2015 at the level of foreign ministers, to re ...
.
Vienna also headquartered the
International Taekwon-Do Federation (ITF).
Charitable organizations in Vienna
Alongside international and intergovernmental organizations, there are dozens of charitable organizations based in Vienna. One such organization is the network of
SOS Children's Villages, founded by
Hermann Gmeiner in 1949. Today, SOS Children's Villages are active in 132 countries and territories worldwide. Others include
HASCO.
Another popular international event is the annual
Life Ball
The Life Ball in Vienna is the biggest Charitable organization, charity event in Europe supporting people with HIV or AIDS. The event is organized by the nonprofit organization AIDS LIFE, which was founded in 1992 by Gery Keszler and Torgom Petros ...
, which supports people with
HIV or
AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual m ...
. Guests such as
Bill Clinton and
Whoopi Goldberg were recent attendees.
International city cooperations
The general policy of the City of Vienna is not to sign any
twin town
A sister city or a twin town relationship is a form of legal or social agreement between two geographically and politically distinct localities for the purpose of promoting cultural and commercial ties.
While there are early examples of inter ...
agreements with other cities. Instead Vienna has only cooperation agreements in which specific cooperation areas are defined.
*
Belgrade
Belgrade ( , ;, ; Names of European cities in different languages: B, names in other languages) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Serbia, largest city in Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers a ...
, Serbia
*
Bratislava
Bratislava (, also ; ; german: Preßburg/Pressburg ; hu, Pozsony) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Slovakia. Officially, the population of the city is about 475,000; however, it is estimated to be more than 660,000 — approxim ...
, Slovakia
*
Brno
Brno ( , ; german: Brünn ) is a city in the South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. Located at the confluence of the Svitava and Svratka rivers, Brno has about 380,000 inhabitants, making it the second-largest city in the Czech Republic ...
, Czech Republic
*
Budapest, Hungary
*
Hamburg, Germany
*
Kraków, Poland
*
Ljubljana, Slovenia
*
Paris, France
*
Prague, Czech Republic
*
Vancouver, Canada
*
Zagreb, Croatia
*
Zurich, Switzerland
District to district partnerships
In addition, individual Viennese districts have international partnerships all over the world. A detailed list is published on the website of the City of Vienna.
See also
*
Donauinselfest
*
List of honorary citizens of Vienna
*
List of restaurants in Vienna
*
List of Viennese
*
List of World Heritage Sites in Austria
*
List of cities and towns on Danube river
*
OPENCities
*
Outline of Vienna
*
Vienna Biennale
*
Vienna Porcelain Manufactory
*
Viennese German
References
Further reading
*
Pippal, M.: ''A Short History of Art in Vienna'', Munich: C.H. Beck 2000, , provides a concise overview.
*
Dassanowsky, Robert ed.: "World Film Locations: Vienna", London: Intellect/Chicago: U of Chicago Press, 2012, . International films about Vienna or Austria shot on location throughout cinema history.
External links
Official websites
Wien.gv.at– Official site of the municipality, with interactive map.
Wien.info– Official site of the tourism board: events, sightseeing, cultural information, etc.
Geschichtewiki.wien.gv.at
– Vienna History Wiki operated by the city of Vienna
History of Vienna
* ttp://www.battlefieldsww2.com/viennagb.html German flaktowers in Viennabr>History of the Coat of Arms of Vienna and all (former) districts and municipalities
Further information on Vienna
Vienna Information
Sorted by categories. Choose from 5 Languages
Vienna insider travel guideEvents in ViennaEvents and useful information from ViennaWhenWhereWh.at
*English Guide to Events and Contemporary Culture in Vienna
{{Authority control
Vienna
Austrian state capitals
Capitals in Europe
City-states
NUTS 2 statistical regions of the European Union
Populated places established in the 1st millennium BC
Populated places on the Danube
States of Austria
Turkish communities outside Turkey
Wine regions of Austria
World Heritage Sites in Austria
World Heritage Sites in Danger
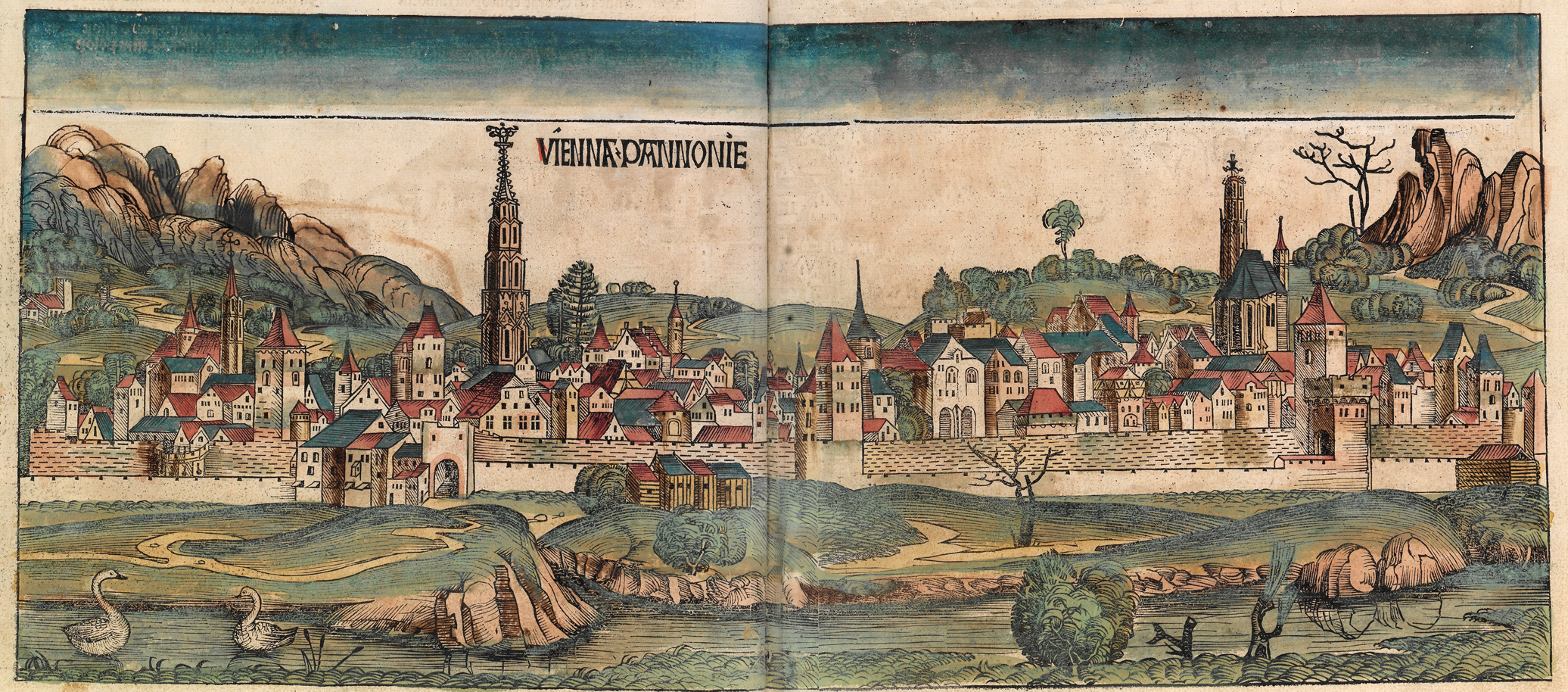

 Evidence has been found of continuous habitation in the Vienna area since 500 BC, when Celts settled the site on the Danube. In 15 BC, the Romans fortified the frontier city they called Vindobona to guard the empire against Germanic tribes to the north.
Close ties with other Celtic peoples continued through the ages. The Irish monk Saint Colman (or Koloman, Irish ''Colmán'', derived from ''colm'' "dove") is buried in Melk Abbey and Saint Fergil ( Virgil the Geometer) served as Bishop of Salzburg for forty years. Irish Benedictines founded twelfth-century monastic settlements; evidence of these ties persists in the form of Vienna's great Schottenstift monastery (Scots Abbey), once home to many Irish monks.
In 976, Leopold I of Babenberg became count of the Eastern March, a district centered on the Danube on the eastern frontier of Bavaria. This initial district grew into the
Evidence has been found of continuous habitation in the Vienna area since 500 BC, when Celts settled the site on the Danube. In 15 BC, the Romans fortified the frontier city they called Vindobona to guard the empire against Germanic tribes to the north.
Close ties with other Celtic peoples continued through the ages. The Irish monk Saint Colman (or Koloman, Irish ''Colmán'', derived from ''colm'' "dove") is buried in Melk Abbey and Saint Fergil ( Virgil the Geometer) served as Bishop of Salzburg for forty years. Irish Benedictines founded twelfth-century monastic settlements; evidence of these ties persists in the form of Vienna's great Schottenstift monastery (Scots Abbey), once home to many Irish monks.
In 976, Leopold I of Babenberg became count of the Eastern March, a district centered on the Danube on the eastern frontier of Bavaria. This initial district grew into the  In 1804, during the Napoleonic Wars, Vienna became the capital of the newly formed Austrian Empire. The city continued to play a major role in European and world politics, including hosting the Congress of Vienna in 1814–15. The city also saw major uprisings against Habsburg rule in
In 1804, during the Napoleonic Wars, Vienna became the capital of the newly formed Austrian Empire. The city continued to play a major role in European and world politics, including hosting the Congress of Vienna in 1814–15. The city also saw major uprisings against Habsburg rule in  During the latter half of the 19th century, Vienna developed what had previously been the
During the latter half of the 19th century, Vienna developed what had previously been the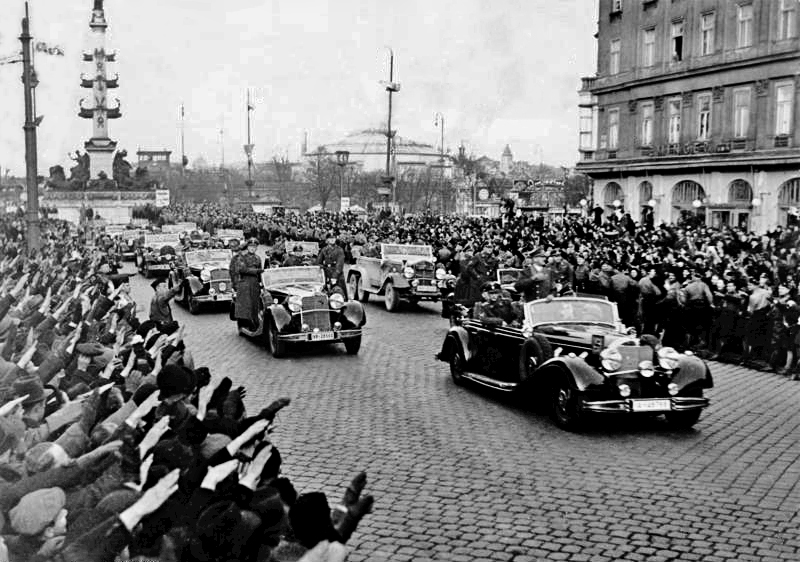  In 1938, after a triumphant entry into Austria, the Austrian-born German Chancellor Adolf Hitler spoke to the
In 1938, after a triumphant entry into Austria, the Austrian-born German Chancellor Adolf Hitler spoke to the  After the war, Vienna was part of Soviet-occupied Eastern Austria until September 1945. As in Berlin, Vienna in September 1945 was divided into sectors by the four powers: the US, the UK, France, and the Soviet Union and supervised by an
After the war, Vienna was part of Soviet-occupied Eastern Austria until September 1945. As in Berlin, Vienna in September 1945 was divided into sectors by the four powers: the US, the UK, France, and the Soviet Union and supervised by an  The four-power control of Vienna lasted until the Austrian State Treaty was signed in May 1955. That year, after years of reconstruction and restoration, the State Opera and the
The four-power control of Vienna lasted until the Austrian State Treaty was signed in May 1955. That year, after years of reconstruction and restoration, the State Opera and the  According to the 2001 census, 49.2% of Viennese were Catholic, while 25.7% were of no religion, 7.8% were Muslim, 6.0% were members of an Eastern Orthodox Christian denomination, 4.7% were Protestant (mostly Lutheran), 0.5% were Jewish and 6.3% were either of other religions or did not reply. A 2011 report by the International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis showed the proportions had changed, with 41.3% Catholic, 31.6% no affiliation, 11.6% Muslim, 8.4% Eastern Orthodox, 4.2% Protestant, and 2.9% other.
Based on information provided to city officials by various religious organizations about their membership, Vienna's Statistical Yearbook 2019 reports in 2018 an estimated 610,269 Roman Catholics, or 32.3% of the population, and 195,000 (10.3%) Muslims, 70,298 (3.7%) Orthodox, 57,502 (3.0%) other Christians, and 9,504 (0.5%) other religions. A study conducted by the Vienna Institute of Demography estimated the 2018 proportions to be 34% Catholic, 30% unaffiliated, 15% Muslim, 10% Orthodox, 4% Protestant, and 6% other religions.
Vienna is the seat of the Metropolitan Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Vienna, in which is also vested the exempt
According to the 2001 census, 49.2% of Viennese were Catholic, while 25.7% were of no religion, 7.8% were Muslim, 6.0% were members of an Eastern Orthodox Christian denomination, 4.7% were Protestant (mostly Lutheran), 0.5% were Jewish and 6.3% were either of other religions or did not reply. A 2011 report by the International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis showed the proportions had changed, with 41.3% Catholic, 31.6% no affiliation, 11.6% Muslim, 8.4% Eastern Orthodox, 4.2% Protestant, and 2.9% other.
Based on information provided to city officials by various religious organizations about their membership, Vienna's Statistical Yearbook 2019 reports in 2018 an estimated 610,269 Roman Catholics, or 32.3% of the population, and 195,000 (10.3%) Muslims, 70,298 (3.7%) Orthodox, 57,502 (3.0%) other Christians, and 9,504 (0.5%) other religions. A study conducted by the Vienna Institute of Demography estimated the 2018 proportions to be 34% Catholic, 30% unaffiliated, 15% Muslim, 10% Orthodox, 4% Protestant, and 6% other religions.
Vienna is the seat of the Metropolitan Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Vienna, in which is also vested the exempt  Vienna is located in northeastern Austria, at the easternmost extension of the Alps in the Vienna Basin. The earliest settlement, at the location of today's inner city, was south of the meandering Danube while the city now spans both sides of the river. Elevation ranges from . The city has a total area of 414.65 square kilometers (160.1 sq mi), making it the largest city in Austria by area.
Vienna is located in northeastern Austria, at the easternmost extension of the Alps in the Vienna Basin. The earliest settlement, at the location of today's inner city, was south of the meandering Danube while the city now spans both sides of the river. Elevation ranges from . The city has a total area of 414.65 square kilometers (160.1 sq mi), making it the largest city in Austria by area.
 The heart and historical city of Vienna, a large part of today's
The heart and historical city of Vienna, a large part of today's  In the twenty years before the First World War and until 1918, Viennese politics were shaped by the Christian Social Party. In particular, long-term mayor
In the twenty years before the First World War and until 1918, Viennese politics were shaped by the Christian Social Party. In particular, long-term mayor 

 Famous composers including Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart,
Famous composers including Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart,  Vienna is also home to a number of opera houses, including the Theater an der Wien, the Staatsoper and the Volksoper, the latter being devoted to the typical Viennese
Vienna is also home to a number of opera houses, including the Theater an der Wien, the Staatsoper and the Volksoper, the latter being devoted to the typical Viennese  Famous musicians who came here to work from other parts of Austria and Germany were Kurt Adler, Johann Joseph Fux,
Famous musicians who came here to work from other parts of Austria and Germany were Kurt Adler, Johann Joseph Fux, 
 The
The  A number of museums are located in the Museumsquartier (museum quarter), the former Imperial Stalls which were converted into a museum complex in the 1990s. It houses the Museum of Modern Art, commonly known as the MUMOK (Ludwig Foundation), the Leopold Museum (featuring the largest collection of paintings in the world by
A number of museums are located in the Museumsquartier (museum quarter), the former Imperial Stalls which were converted into a museum complex in the 1990s. It houses the Museum of Modern Art, commonly known as the MUMOK (Ludwig Foundation), the Leopold Museum (featuring the largest collection of paintings in the world by  A variety of architectural styles can be found in Vienna, such as the Romanesque
A variety of architectural styles can be found in Vienna, such as the Romanesque 

 Austria's capital is home to numerous
Austria's capital is home to numerous  Vienna has a long tradition of producing cakes and desserts. These include '' Apfelstrudel'' (hot apple strudel), '' Milchrahmstrudel'' (milk-cream strudel), '' Palatschinken'' (sweet pancakes), and ''Knödel'' (dumplings) often filled with fruit such as apricots ('' Marillenknödel''). Sachertorte, a delicately moist chocolate cake with apricot jam created by the
Vienna has a long tradition of producing cakes and desserts. These include '' Apfelstrudel'' (hot apple strudel), '' Milchrahmstrudel'' (milk-cream strudel), '' Palatschinken'' (sweet pancakes), and ''Knödel'' (dumplings) often filled with fruit such as apricots ('' Marillenknödel''). Sachertorte, a delicately moist chocolate cake with apricot jam created by the  Vienna, along with Paris, Santiago, Cape Town, Prague,
Vienna, along with Paris, Santiago, Cape Town, Prague,  Viennese cafés have an extremely long and distinguished history that dates back centuries, and the caffeine addictions of some famous historical patrons of the oldest are something of a local legend. These coffee houses are unique to Vienna and many cities have unsuccessfully sought to copy them. Some people consider cafés as their extended living room where nobody will be bothered if they spend hours reading a newspaper while enjoying their coffee. Traditionally, the coffee comes with a glass of water. Viennese cafés claim to have invented the process of filtering coffee from booty captured after the second Turkish siege in 1683. Viennese cafés claim that when the invading Turks left Vienna, they abandoned hundreds of sacks of coffee beans. The Polish King
Viennese cafés have an extremely long and distinguished history that dates back centuries, and the caffeine addictions of some famous historical patrons of the oldest are something of a local legend. These coffee houses are unique to Vienna and many cities have unsuccessfully sought to copy them. Some people consider cafés as their extended living room where nobody will be bothered if they spend hours reading a newspaper while enjoying their coffee. Traditionally, the coffee comes with a glass of water. Viennese cafés claim to have invented the process of filtering coffee from booty captured after the second Turkish siege in 1683. Viennese cafés claim that when the invading Turks left Vienna, they abandoned hundreds of sacks of coffee beans. The Polish King  Vienna has an extensive transportation network with a unified fare system that integrates municipal, regional and railway systems under the umbrella of the Verkehrsverbund Ost-Region (VOR). Public transport is provided by buses, trams and five underground metro lines ( U-Bahn), most operated by the Wiener Linien. There are also more than 50 S-train stations within the city limits. Suburban trains are operated by the ÖBB. The city forms the hub of the Austrian railway system, with services to all parts of the country and abroad. The railway system connects Vienna's main station Vienna Hauptbahnhof with other European cities, like Berlin,
Vienna has an extensive transportation network with a unified fare system that integrates municipal, regional and railway systems under the umbrella of the Verkehrsverbund Ost-Region (VOR). Public transport is provided by buses, trams and five underground metro lines ( U-Bahn), most operated by the Wiener Linien. There are also more than 50 S-train stations within the city limits. Suburban trains are operated by the ÖBB. The city forms the hub of the Austrian railway system, with services to all parts of the country and abroad. The railway system connects Vienna's main station Vienna Hauptbahnhof with other European cities, like Berlin, 
 Vienna is the seat of a number of United Nations offices and various international institutions and companies, including the
Vienna is the seat of a number of United Nations offices and various international institutions and companies, including the