|
1995 Enlargement Of The European Union
The 1995 enlargement of the European Union saw Austria, Finland, and Sweden accede to the European Union (EU). This was the EU's fourth enlargement and came into effect on 1 January of that year. All these states were previous members of the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) and had traditionally been less interested in joining the EU than other European countries. Norway had negotiated to join alongside the other three but following the signing of the treaty, membership was turned down by the Norwegian electorate in the 1994 national referendum. Switzerland also applied for membership on 26 May 1992, but withdrew it after a negative referendum result on 6 December 1992 (and that was not changed after a second negative referendum result on 4 March 2001). Closer links The three states, plus Norway and Switzerland (which never joined due to their referendum results) began to look at stronger ties with the EU (which was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacques Delors
Jacques Lucien Jean Delors (born 20 July 1925) is a French politician who served as the 8th President of the European Commission from 1985 to 1995. He served as Minister of Finance of France from 1981 to 1984. He was a Member of the European Parliament from 1979 to 1981. As President, Delors was the most visible and influential leader in European affairs. He implemented the policies that closely linked the member nations together and promoted the need for unity. He created a single market that made the free movement of persons, capital, goods, and services within the European Economic Community (EEC) possible. He also headed the committee that proposed the monetary union to create the Euro, a new single currency to replace individual national currencies. This was achieved by the signing of the Maastricht Treaty in 1992. French politics Born in Paris in a family originating from Corrèze, Delors first held in the 1940s through the 1960s a series of posts in French banking and st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaties Of The European Union
The Treaties of the European Union are a set of international treaties between the European Union (EU) member states which sets out the EU's constitutional basis. They establish the various EU institutions together with their remit, procedures and objectives. The EU can only act within the competences granted to it through these treaties and amendment to the treaties requires the agreement and ratification (according to their national procedures) of every single signatory. Two core functional treaties, the Treaty on European Union (originally signed in Maastricht in 1992, aka The Maastricht Treaty) and the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union (originally signed in Rome in 1957 as the Treaty establishing the European Economic Community, aka The Treaty of Rome), lay out how the EU operates, and there are a number of satellite treaties which are interconnected with them. The treaties have been repeatedly amended by other treaties over the 65 years since they were firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Commissioner
A European Commissioner is a member of the 27-member European Commission. Each member within the Commission holds a specific portfolio. The commission is led by the President of the European Commission. In simple terms they are the equivalent of government ministers. Appointment Commissioners are nominated by member states in consultation with the commission president, who then selects a team of commissioners. This team of nominees are then subject to hearings at the European Parliament, which questions them and then votes on their suitability as a whole. If members of the team are found to be inappropriate, the president must then reshuffle the team or request a new candidate from the member state or risk the whole commission being voted down. As parliament cannot vote against individual commissioners there is usually a compromise whereby the worst candidates are removed but minor objections are put aside, or dealt with by adjusting portfolios, so the commission can take off ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
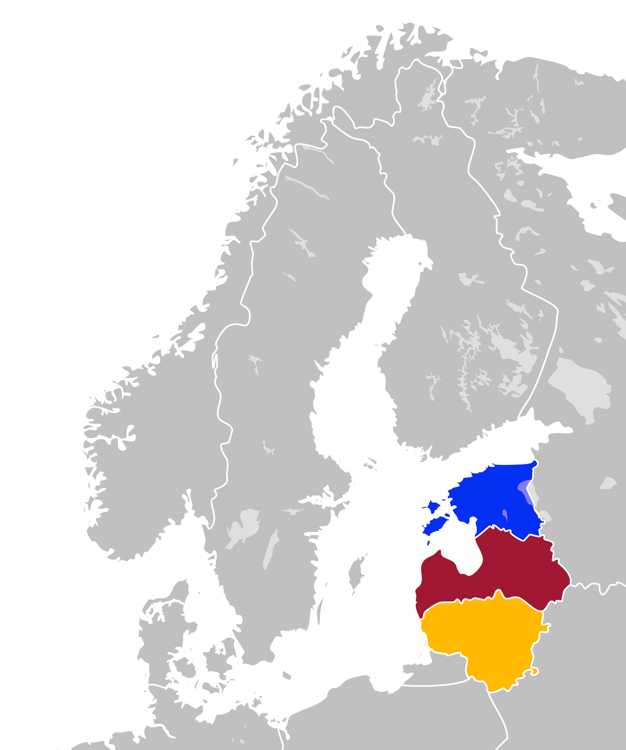
Baltic States
The Baltic states, et, Balti riigid or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term, which currently is used to group three countries: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, and the OECD. The three sovereign states on the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea are sometimes referred to as the "Baltic nations", less often and in historical circumstances also as the "Baltic republics", the "Baltic lands", or simply the Baltics. All three Baltic countries are classified as high-income economies by the World Bank and maintain a very high Human Development Index. The three governments engage in intergovernmental and parliamentary cooperation. There is also frequent cooperation in foreign and security policy, defence, energy, and transportation. The term "Baltic states" ("countries", "nations", or similar) cannot be used unambiguously in the context of cultural areas, national identity, or language. While the majori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enlargement Of The Eurozone
The enlargement of the eurozone is an ongoing process within the European Union (EU). All member states of the European Union, except Denmark which negotiated an opt-out from the provisions, are obliged to adopt the euro as their sole currency once they meet the criteria, which include: complying with the debt and deficit criteria outlined by the Stability and Growth Pact, keeping inflation and long-term governmental interest rates below certain reference values, stabilising their currency's exchange rate versus the euro by participating in the European Exchange Rate Mechanism (ERM II), and ensuring that their national laws comply with the ECB statute, ESCB statute and articles 130+131 of the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union. The obligation for EU member states to adopt the euro was first outlined by article 109.1j of the Maastricht Treaty of 1992, which became binding on all new member states by the terms of their treaties of accession. , there are 19 EU me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurozone
The euro area, commonly called eurozone (EZ), is a currency union of 19 member states of the European Union (EU) that have adopted the euro ( €) as their primary currency and sole legal tender, and have thus fully implemented EMU policies. The 19 eurozone members are Austria, Belgium, Cyprus, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, the Netherlands, Portugal, Slovakia, Slovenia, and Spain. The eight non-eurozone members of the EU are Bulgaria, Czech Republic, Croatia, Denmark, Hungary, Poland, Romania, and Sweden. They continue to use their own national currencies, albeit all but Denmark are obliged to join once they meet the euro convergence criteria. Croatia will become the 20th member on 1 January 2023. Among non-EU member states, Andorra, Monaco, San Marino, and Vatican City have formal agreements with the EU to use the euro as their official currency and issue their own coins. In addition, Kosovo and Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Member Of The European Parliament
A Member of the European Parliament (MEP) is a person who has been elected to serve as a popular representative in the European Parliament. When the European Parliament (then known as the Common Assembly of the European Coal and Steel Community, ECSC) first met in 1952, its members were directly appointed by the governments of member states from among those already sitting in their own national parliaments. Since 1979, however, MEPs have been elected by direct universal suffrage. Earlier European organizations that were a precursor to the European Union did not have MEPs. Each Member state of the European Union, member state establishes its own method for electing MEPs – and in some states this has changed over time – but the system chosen must be a form of proportional representation. Some member states elect their MEPs to represent a single national constituency; other states apportion seats to sub-national regions for election. They are sometimes referred to as delega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Parliament
The European Parliament (EP) is one of the legislative bodies of the European Union and one of its seven institutions. Together with the Council of the European Union (known as the Council and informally as the Council of Ministers), it adopts European legislation, following a proposal by the European Commission. The Parliament is composed of 705 members (MEPs). It represents the second-largest democratic electorate in the world (after the Parliament of India), with an electorate of 375 million eligible voters in 2009. Since 1979, the Parliament has been directly elected every five years by the citizens of the European Union through universal suffrage. Voter turnout in parliamentary elections decreased each time after 1979 until 2019, when voter turnout increased by eight percentage points, and rose above 50% for the first time since 1994. The voting age is 18 in all EU member states except for Malta and Austria, where it is 16, and Greece, where it is 17. Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Åland
Åland ( fi, Ahvenanmaa: ; ; ) is an Federacy, autonomous and Demilitarized zone, demilitarised region of Finland since 1920 by a decision of the League of Nations. It is the smallest region of Finland by area and population, with a size of 1,580 km2, and a population of 30,129, constituting 0.51% of its land area and 0.54% of its population. Its only official language is Swedish language, Swedish and the capital city is Mariehamn. Åland is situated in an archipelago, called the Åland Islands, at the entrance to the Gulf of Bothnia in the Baltic Sea belonging to Finland. It comprises Fasta Åland on which 90% of the population resides and about 6,500 Skerry, skerries and islands to its east. Of Åland's thousands of islands, about 60–80 are inhabited. Fasta Åland is separated from the coast of Roslagen in Sweden by of open water to the west. In the east, the Åland archipelago is Geographic contiguity, contiguous with the Archipelago Sea, Finnish archipelago. Åland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of a new policy or specific law, or the referendum may be only advisory. In some countries, it is synonymous with or commonly known by other names including plebiscite, votation, popular consultation, ballot question, ballot measure, or proposition. Some definitions of 'plebiscite' suggest it is a type of vote to change the constitution or government of a country. The word, 'referendum' is often a catchall, used for both legislative referrals and initiatives. Etymology 'Referendum' is the gerundive form of the Latin verb , literally "to carry back" (from the verb , "to bear, bring, carry" plus the inseparable prefix , here meaning "back"Marchant & Charles, Cassell's Latin Dictionary, 1928, p. 469.). As a gerundive is an adjective,A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2004 Enlargement Of The European Union
The largest expansion of the European Union (EU), in terms of territory, number of states, and population took place on 1 May 2004. The simultaneous accessions concerned the following countries (sometimes referred to as the "A10" countries): Cyprus, the Czech Republic, Estonia, Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Malta, Poland, Slovakia and Slovenia. Seven of these were part of the former Eastern Bloc (of which three were from the former Soviet Union and four were and still are members of the Central European alliance Visegrád Group). Slovenia was a non-aligned country prior to the independence, and it was one of the former republics of Yugoslavia (together sometimes referred to as the "A8" countries), and the remaining two were Mediterranean islands and two Members of Commonwealth of Nations. Part of the same wave of enlargement was the accession of Bulgaria and Romania in 2007, who were unable to join in 2004, but, according to the Commission, constitute part of the fifth enlarg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |