Diamond Back (Frontier City) 1 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Diamond is a solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a
Diamond is a solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a
 The equilibrium pressure and temperature conditions for a transition between graphite and diamond are well established theoretically and experimentally. The equilibrium pressure varies linearly with temperature, between at and at (the diamond/graphite/liquid
The equilibrium pressure and temperature conditions for a transition between graphite and diamond are well established theoretically and experimentally. The equilibrium pressure varies linearly with temperature, between at and at (the diamond/graphite/liquid
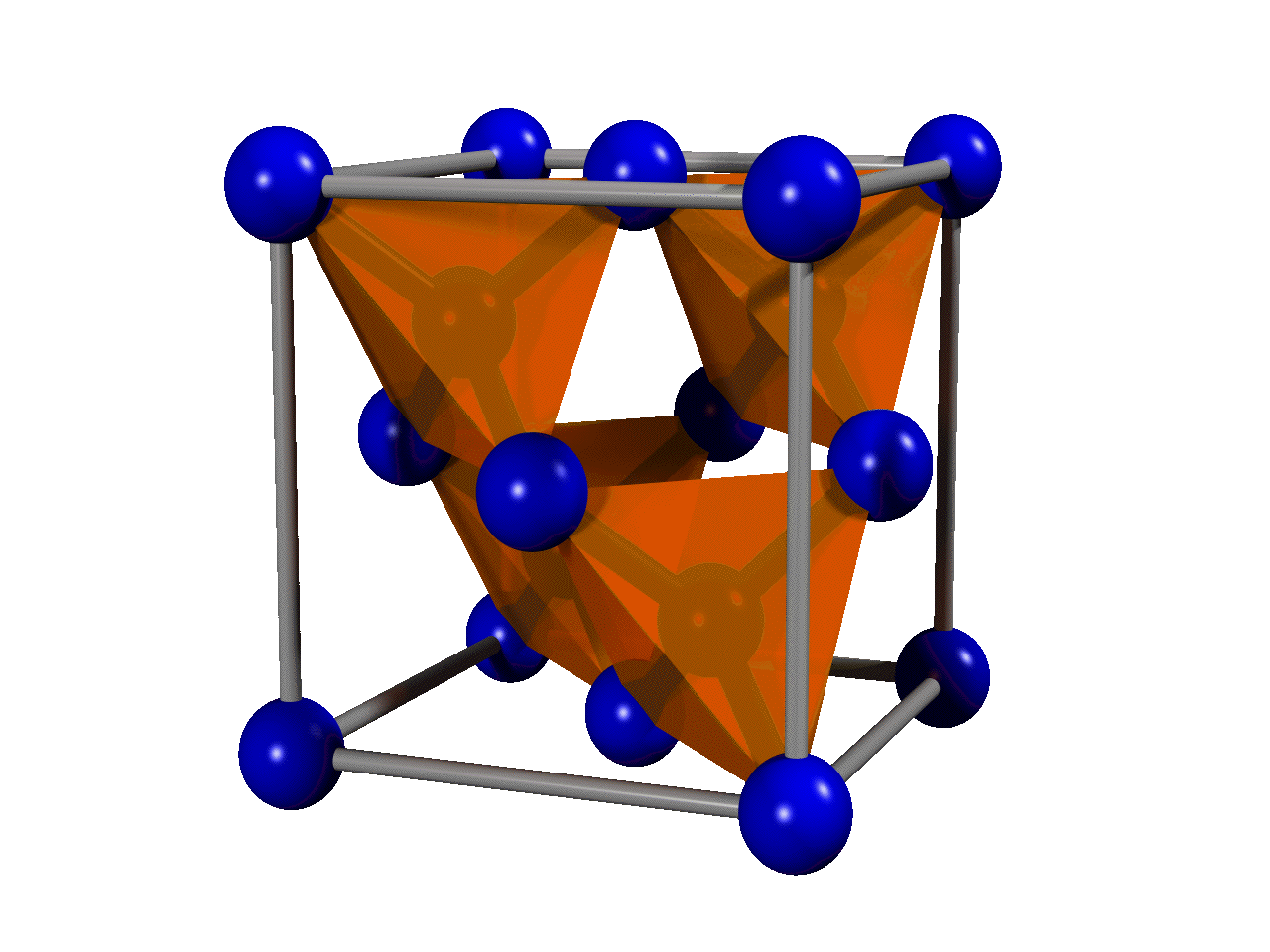 The most common crystal structure of diamond is called
The most common crystal structure of diamond is called
 Diamonds occur most often as
Diamonds occur most often as
 Diamond is the hardest known natural material on both the Vickers scale and the
Diamond is the hardest known natural material on both the Vickers scale and the
 Diamond has a wide
Diamond has a wide
 Between 25% to 35% of natural diamonds exhibit some degree of fluorescence when examined under invisible long-wave Ultraviolet light or higher energy radiation sources such as X-rays and lasers. Incandescent lighting will not cause a diamond to fluoresce. Diamonds can fluoresce in a variety of colours including blue (most common), orange, yellow, white, green and very rarely red and purple. Although the causes are not well understood, variations in the atomic structure, such as the number of nitrogen atoms present are thought to contribute to the phenomenon.
Between 25% to 35% of natural diamonds exhibit some degree of fluorescence when examined under invisible long-wave Ultraviolet light or higher energy radiation sources such as X-rays and lasers. Incandescent lighting will not cause a diamond to fluoresce. Diamonds can fluoresce in a variety of colours including blue (most common), orange, yellow, white, green and very rarely red and purple. Although the causes are not well understood, variations in the atomic structure, such as the number of nitrogen atoms present are thought to contribute to the phenomenon.
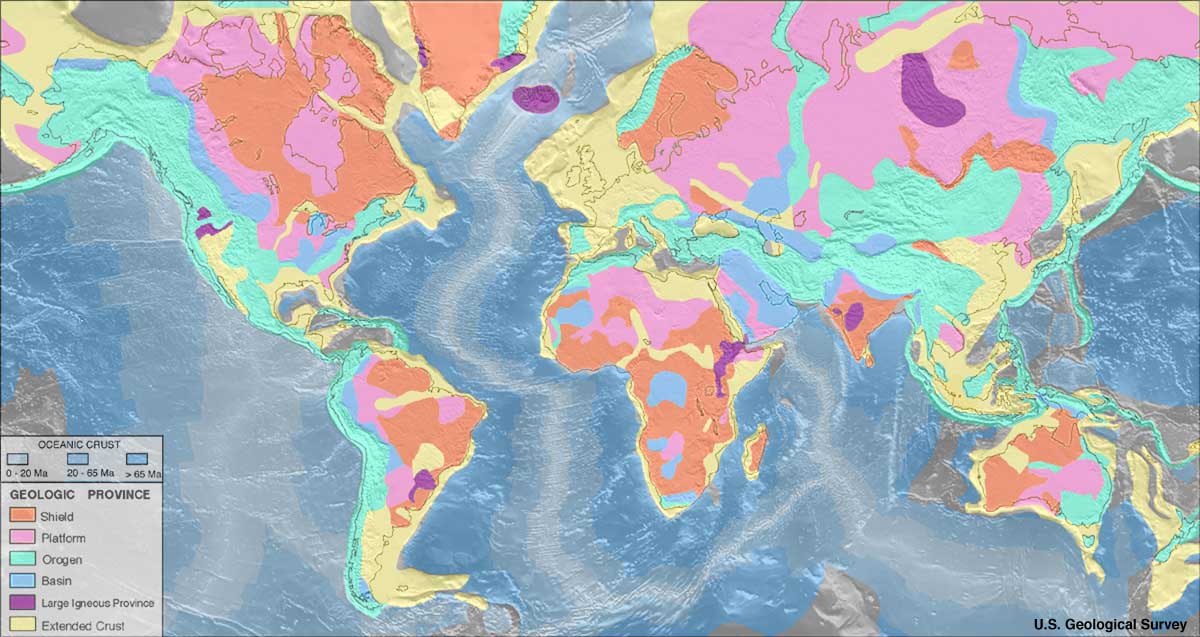 Diamonds are far from evenly distributed over the Earth. A rule of thumb known as Clifford's rule states that they are almost always found in kimberlites on the oldest part of
Diamonds are far from evenly distributed over the Earth. A rule of thumb known as Clifford's rule states that they are almost always found in kimberlites on the oldest part of

 Most gem-quality diamonds come from depths of 150–250 km in the lithosphere. Such depths occur below cratons in ''mantle keels'', the thickest part of the lithosphere. These regions have high enough pressure and temperature to allow diamonds to form and they are not convecting, so diamonds can be stored for billions of years until a kimberlite eruption samples them.
Host rocks in a mantle keel include
Most gem-quality diamonds come from depths of 150–250 km in the lithosphere. Such depths occur below cratons in ''mantle keels'', the thickest part of the lithosphere. These regions have high enough pressure and temperature to allow diamonds to form and they are not convecting, so diamonds can be stored for billions of years until a kimberlite eruption samples them.
Host rocks in a mantle keel include
 Diamonds in the mantle form through a ''
Diamonds in the mantle form through a ''
 Geological evidence supports a model in which kimberlite magma rises at 4–20 meters per second, creating an upward path by hydraulic fracturing of the rock. As the pressure decreases, a vapor phase exsolves from the magma, and this helps to keep the magma fluid. At the surface, the initial eruption explodes out through fissures at high speeds (over ). Then, at lower pressures, the rock is eroded, forming a pipe and producing fragmented rock (
Geological evidence supports a model in which kimberlite magma rises at 4–20 meters per second, creating an upward path by hydraulic fracturing of the rock. As the pressure decreases, a vapor phase exsolves from the magma, and this helps to keep the magma fluid. At the surface, the initial eruption explodes out through fissures at high speeds (over ). Then, at lower pressures, the rock is eroded, forming a pipe and producing fragmented rock (
 In rare cases, diamonds have been found that contain a cavity within which is a second diamond. The first double diamond, the
In rare cases, diamonds have been found that contain a cavity within which is a second diamond. The first double diamond, the
 The most familiar uses of diamonds today are as gemstones used for adornment, and as industrial abrasives for cutting hard materials. The markets for gem-grade and industrial-grade diamonds value diamonds differently.
The most familiar uses of diamonds today are as gemstones used for adornment, and as industrial abrasives for cutting hard materials. The markets for gem-grade and industrial-grade diamonds value diamonds differently.
 Further down the supply chain, members of The
Further down the supply chain, members of The
 Marketing has significantly affected the image of diamond as a valuable commodity.
N. W. Ayer & Son, the advertising firm retained by De Beers in the mid-20th century, succeeded in reviving the American diamond market and the firm created new markets in countries where no diamond tradition had existed before. N. W. Ayer's marketing included product placement, advertising focused on the diamond product itself rather than the De Beers brand, and associations with celebrities and royalty. Without advertising the De Beers brand, De Beers was advertising its competitors' diamond products as well, but this was not a concern as De Beers dominated the diamond market throughout the 20th century. De Beers' market share dipped temporarily to second place in the global market below Alrosa in the aftermath of the global economic crisis of 2008, down to less than 29% in terms of carats mined, rather than sold. The campaign lasted for decades but was effectively discontinued by early 2011. De Beers still advertises diamonds, but the advertising now mostly promotes its own brands, or licensed product lines, rather than completely "generic" diamond products. The campaign was perhaps best captured by the slogan " a diamond is forever". This slogan is now being used by De Beers Diamond Jewelers, a jewelry firm which is a 50/50% joint venture between the De Beers mining company and LVMH, the luxury goods conglomerate.
Brown-colored diamonds constituted a significant part of the diamond production, and were predominantly used for industrial purposes. They were seen as worthless for jewelry (not even being assessed on the
Marketing has significantly affected the image of diamond as a valuable commodity.
N. W. Ayer & Son, the advertising firm retained by De Beers in the mid-20th century, succeeded in reviving the American diamond market and the firm created new markets in countries where no diamond tradition had existed before. N. W. Ayer's marketing included product placement, advertising focused on the diamond product itself rather than the De Beers brand, and associations with celebrities and royalty. Without advertising the De Beers brand, De Beers was advertising its competitors' diamond products as well, but this was not a concern as De Beers dominated the diamond market throughout the 20th century. De Beers' market share dipped temporarily to second place in the global market below Alrosa in the aftermath of the global economic crisis of 2008, down to less than 29% in terms of carats mined, rather than sold. The campaign lasted for decades but was effectively discontinued by early 2011. De Beers still advertises diamonds, but the advertising now mostly promotes its own brands, or licensed product lines, rather than completely "generic" diamond products. The campaign was perhaps best captured by the slogan " a diamond is forever". This slogan is now being used by De Beers Diamond Jewelers, a jewelry firm which is a 50/50% joint venture between the De Beers mining company and LVMH, the luxury goods conglomerate.
Brown-colored diamonds constituted a significant part of the diamond production, and were predominantly used for industrial purposes. They were seen as worthless for jewelry (not even being assessed on the


 Industrial diamonds are valued mostly for their hardness and thermal conductivity, making many of the gemological characteristics of diamonds, such as the 4 Cs, irrelevant for most applications. Eighty percent of mined diamonds (equal to about annually) are unsuitable for use as gemstones and are used industrially. In addition to mined diamonds, synthetic diamonds found industrial applications almost immediately after their invention in the 1950s; in 2014, of synthetic diamonds were produced, 90% of which were produced in China. Approximately 90% of diamond grinding grit is currently of synthetic origin.
The boundary between gem-quality diamonds and industrial diamonds is poorly defined and partly depends on market conditions (for example, if demand for polished diamonds is high, some lower-grade stones will be polished into low-quality or small gemstones rather than being sold for industrial use). Within the category of industrial diamonds, there is a sub-category comprising the lowest-quality, mostly opaque stones, which are known as
Industrial diamonds are valued mostly for their hardness and thermal conductivity, making many of the gemological characteristics of diamonds, such as the 4 Cs, irrelevant for most applications. Eighty percent of mined diamonds (equal to about annually) are unsuitable for use as gemstones and are used industrially. In addition to mined diamonds, synthetic diamonds found industrial applications almost immediately after their invention in the 1950s; in 2014, of synthetic diamonds were produced, 90% of which were produced in China. Approximately 90% of diamond grinding grit is currently of synthetic origin.
The boundary between gem-quality diamonds and industrial diamonds is poorly defined and partly depends on market conditions (for example, if demand for polished diamonds is high, some lower-grade stones will be polished into low-quality or small gemstones rather than being sold for industrial use). Within the category of industrial diamonds, there is a sub-category comprising the lowest-quality, mostly opaque stones, which are known as
 Historically, diamonds were found only in
Historically, diamonds were found only in
File:HPHTdiamonds2.JPG, alt=Six crystals of cubo-octahedral shapes, each about 2 millimeters in diameter. Two are pale blue, one is pale yellow, one is green-blue, one is dark blue and one green-yellow., Synthetic diamonds of various colors grown by the high-pressure high-temperature technique
File:Apollo synthetic diamond.jpg, alt=A round, clear gemstone with many facets, the main face being hexagonal, surrounded by many smaller facets., Colorless gem cut from diamond grown by chemical vapor deposition
 A diamond simulant is a non-diamond material that is used to simulate the appearance of a diamond, and may be referred to as diamante.
A diamond simulant is a non-diamond material that is used to simulate the appearance of a diamond, and may be referred to as diamante.
 Diamond is a solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a
Diamond is a solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure
In crystallography, crystal structure is a description of the ordered arrangement of atoms, ions or molecules in a crystalline material. Ordered structures occur from the intrinsic nature of the constituent particles to form symmetric patterns ...
called diamond cubic
The diamond cubic crystal structure is a repeating pattern of 8 atoms that certain materials may adopt as they solidify. While the first known example was diamond, other elements in group 14 also adopt this structure, including α-tin, the se ...
. Another solid form of carbon known as graphite
Graphite () is a crystalline form of the element carbon. It consists of stacked layers of graphene. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions. Synthetic and natural graphite are consumed on lar ...
is the chemically stable form of carbon at room temperature and pressure, but diamond is metastable
In chemistry and physics, metastability denotes an intermediate energetic state within a dynamical system other than the system's state of least energy.
A ball resting in a hollow on a slope is a simple example of metastability. If the ball i ...
and converts to it at a negligible rate under those conditions. Diamond has the highest hardness
In materials science, hardness (antonym: softness) is a measure of the resistance to localized plastic deformation induced by either mechanical indentation or abrasion. In general, different materials differ in their hardness; for example hard ...
and thermal conductivity
The thermal conductivity of a material is a measure of its ability to conduct heat. It is commonly denoted by k, \lambda, or \kappa.
Heat transfer occurs at a lower rate in materials of low thermal conductivity than in materials of high thermal ...
of any natural material, properties that are used in major industrial applications such as cutting and polishing tools. They are also the reason that diamond anvil cell
A diamond anvil cell (DAC) is a high-pressure device used in geology, engineering, and materials science experiments. It enables the compression of a small (sub-millimeter-sized) piece of material to extreme pressures, typically up to around 1 ...
s can subject materials to pressures found deep in the Earth.
Because the arrangement of atoms in diamond is extremely rigid, few types of impurity can contaminate it (two exceptions are boron and nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
). Small numbers of defects or impurities (about one per million of lattice atoms) color diamond blue (boron), yellow (nitrogen), brown (defects), green (radiation exposure), purple, pink, orange, or red. Diamond also has a very high refractive index
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is a dimensionless number that gives the indication of the light bending ability of that medium.
The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or ...
and a relatively high optical dispersion
In optics, and by analogy other branches of physics dealing with wave propagation, dispersion is the phenomenon in which the phase velocity of a wave depends on its frequency; sometimes the term chromatic dispersion is used for specificity to o ...
.
Most natural diamonds have ages between 1 billion and 3.5 billion years. Most were formed at depths between in the Earth's mantle, although a few have come from as deep as . Under high pressure and temperature, carbon-containing fluids dissolved various minerals and replaced them with diamonds. Much more recently (hundreds to tens of million years ago), they were carried to the surface in volcanic eruption
Several types of volcanic eruptions—during which lava, tephra (ash, lapilli, volcanic bombs and volcanic blocks), and assorted gases are expelled from a volcanic vent or fissure—have been distinguished by volcanologists. These are oft ...
s and deposited in igneous rock
Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ''ignis'' meaning fire), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma o ...
s known as kimberlite
Kimberlite is an igneous rock and a rare variant of peridotite. It is most commonly known to be the main host matrix for diamonds. It is named after the town of Kimberley in South Africa, where the discovery of an diamond called the Star of S ...
s and lamproite
Lamproite is an ultrapotassic mantle-derived volcanic or subvolcanic rock. It has low CaO, Al2O3, Na2O, high K2O/Al2O3, a relatively high MgO content and extreme enrichment in incompatible elements.
Lamproites are geographically widespread ...
s.
Synthetic diamond
Lab-grown diamond (LGD; also called laboratory-grown, laboratory-created, man-made, artisan-created, artificial, synthetic, or cultured diamond) is diamond that is produced in a controlled technological process (in contrast to naturally formed ...
s can be grown from high-purity carbon under high pressures and temperatures or from hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic, and their odors are usually weak or ...
gases by chemical vapor deposition (CVD). Imitation diamonds can also be made out of materials such as cubic zirconia
Cubic zirconia (CZ) is the cubic crystalline form of zirconium dioxide (ZrO2). The synthesized material is hard and usually colorless, but may be made in a variety of different colors. It should not be confused with zircon, which is a zirco ...
and silicon carbide
Silicon carbide (SiC), also known as carborundum (), is a hard chemical compound containing silicon and carbon. A semiconductor, it occurs in nature as the extremely rare mineral moissanite, but has been mass-produced as a powder and crystal s ...
. Natural, synthetic and imitation diamonds are most commonly distinguished using optical techniques or thermal conductivity measurements.
Properties
Diamond is a solid form of pure carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal. Solid carbon comes in different forms known as allotropes depending on the type of chemical bond. The two most common allotropes of pure carbon are diamond andgraphite
Graphite () is a crystalline form of the element carbon. It consists of stacked layers of graphene. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions. Synthetic and natural graphite are consumed on lar ...
. In graphite the bonds are sp2 orbital hybrids and the atoms form in planes, with each bound to three nearest neighbors 120 degrees apart. In diamond they are sp3 and the atoms form tetrahedra with each bound to four nearest neighbors. Tetrahedra are rigid, the bonds are strong, and of all known substances diamond has the greatest number of atoms per unit volume, which is why it is both the hardest and the least compressible
In thermodynamics and fluid mechanics, the compressibility (also known as the coefficient of compressibility or, if the temperature is held constant, the isothermal compressibility) is a measure of the instantaneous relative volume change of a f ...
. It also has a high density, ranging from 3150 to 3530 kilograms per cubic metre (over three times the density of water) in natural diamonds and 3520 kg/m in pure diamond. In graphite, the bonds between nearest neighbors are even stronger, but the bonds between parallel adjacent planes are weak, so the planes easily slip past each other. Thus, graphite is much softer than diamond. However, the stronger bonds make graphite less flammable.
Diamonds have been adopted for many uses because of the material's exceptional physical characteristics. It has the highest thermal conductivity
The thermal conductivity of a material is a measure of its ability to conduct heat. It is commonly denoted by k, \lambda, or \kappa.
Heat transfer occurs at a lower rate in materials of low thermal conductivity than in materials of high thermal ...
and the highest sound velocity. It has low adhesion and friction, and its coefficient of thermal expansion
Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to change its shape, area, volume, and density in response to a change in temperature, usually not including phase transitions.
Temperature is a monotonic function of the average molecular kinetic ...
is extremely low. Its optical transparency extends from the far infrared
Far infrared (FIR) is a region in the infrared spectrum of electromagnetic radiation. Far infrared is often defined as any radiation with a wavelength of 15 micrometers (μm) to 1 mm (corresponding to a range of about 20 THz to ...
to the deep ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation ...
and it has high optical dispersion
In optics, and by analogy other branches of physics dealing with wave propagation, dispersion is the phenomenon in which the phase velocity of a wave depends on its frequency; sometimes the term chromatic dispersion is used for specificity to o ...
. It also has high electrical resistance. It is chemically inert, not reacting with most corrosive substances, and has excellent biological compatibility.
Thermodynamics
 The equilibrium pressure and temperature conditions for a transition between graphite and diamond are well established theoretically and experimentally. The equilibrium pressure varies linearly with temperature, between at and at (the diamond/graphite/liquid
The equilibrium pressure and temperature conditions for a transition between graphite and diamond are well established theoretically and experimentally. The equilibrium pressure varies linearly with temperature, between at and at (the diamond/graphite/liquid triple point
In thermodynamics, the triple point of a substance is the temperature and pressure at which the three phases (gas, liquid, and solid) of that substance coexist in thermodynamic equilibrium.. It is that temperature and pressure at which the sub ...
).
However, the phases have a wide region about this line where they can coexist. At normal temperature and pressure Normal(s) or The Normal(s) may refer to:
Film and television
* Normal (2003 film), ''Normal'' (2003 film), starring Jessica Lange and Tom Wilkinson
* Normal (2007 film), ''Normal'' (2007 film), starring Carrie-Anne Moss, Kevin Zegers, Callum Keit ...
, and , the stable phase of carbon is graphite, but diamond is metastable
In chemistry and physics, metastability denotes an intermediate energetic state within a dynamical system other than the system's state of least energy.
A ball resting in a hollow on a slope is a simple example of metastability. If the ball i ...
and its rate of conversion to graphite is negligible. However, at temperatures above about , diamond rapidly converts to graphite. Rapid conversion of graphite to diamond requires pressures well above the equilibrium line: at , a pressure of is needed.
Above the graphite-diamond-liquid carbon triple point, the melting point of diamond increases slowly with increasing pressure; but at pressures of hundreds of GPa, it decreases. At high pressures, silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic ta ...
and germanium have a BC8 body-centered cubic
In crystallography, the cubic (or isometric) crystal system is a crystal system where the unit cell is in the shape of a cube. This is one of the most common and simplest shapes found in crystals and minerals.
There are three main varieties of ...
crystal structure, and a similar structure is predicted for carbon at high pressures. At , the transition is predicted to occur at .
Research results published in an article in the scientific journal ''Nature Physics
''Nature Physics'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Nature Portfolio. It was first published in October 2005 (volume 1, issue 1). The chief editor is Andrea Taroni, who is a full-time professional editor employed by this ...
'' in 2010 suggest that at ultrahigh pressures and temperatures (about 10 million atmospheres or 1 TPa and 50,000 °C) diamond melts into a metallic fluid. The extreme conditions required for this to occur are present in the ice giant
An ice giant is a giant planet composed mainly of elements heavier than hydrogen and helium, such as oxygen, carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur. There are two ice giants in the Solar System: Uranus and Neptune.
In astrophysics and planetary scienc ...
s Neptune and Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. Its name is a reference to the Greek god of the sky, Uranus ( Caelus), who, according to Greek mythology, was the great-grandfather of Ares (Mars), grandfather of Zeus (Jupiter) and father of ...
. Both planets are made up of approximately 10 percent carbon and could hypothetically contain oceans of liquid carbon. Since large quantities of metallic fluid can affect the magnetic field, this could serve as an explanation as to why the geographic and magnetic poles of the two planets are unaligned.
Crystal structure
 The most common crystal structure of diamond is called
The most common crystal structure of diamond is called diamond cubic
The diamond cubic crystal structure is a repeating pattern of 8 atoms that certain materials may adopt as they solidify. While the first known example was diamond, other elements in group 14 also adopt this structure, including α-tin, the se ...
. It is formed of unit cell
In geometry, biology, mineralogy and solid state physics, a unit cell is a repeating unit formed by the vectors spanning the points of a lattice. Despite its suggestive name, the unit cell (unlike a unit vector, for example) does not necessaril ...
s (see the figure) stacked together. Although there are 18 atoms in the figure, each corner atom is shared by eight unit cells and each atom in the center of a face is shared by two, so there are a total of eight atoms per unit cell. The length of each side of the unit cell is denoted by ''a'' and is 3.567 angstrom
The angstromEntry "angstrom" in the Oxford online dictionary. Retrieved on 2019-03-02 from https://en.oxforddictionaries.com/definition/angstrom.Entry "angstrom" in the Merriam-Webster online dictionary. Retrieved on 2019-03-02 from https://www.m ...
s.
The nearest neighbour distance in the diamond lattice is 1.732''a''/4 where ''a'' is the lattice constant, usually given in Angstrøms as ''a'' = 3.567 Å, which is 0.3567 nm.
A diamond cubic lattice can be thought of as two interpenetrating face-centered cubic
In crystallography, the cubic (or isometric) crystal system is a crystal system where the unit cell is in the shape of a cube. This is one of the most common and simplest shapes found in crystals and minerals.
There are three main varieties of ...
lattices with one displaced by of the diagonal along a cubic cell, or as one lattice with two atoms associated with each lattice point. Viewed from a crystallographic direction, it is formed of layers stacked in a repeating ABCABC ... pattern. Diamonds can also form an ABAB ... structure, which is known as hexagonal diamond or lonsdaleite
Lonsdaleite (named in honour of Kathleen Lonsdale), also called hexagonal diamond in reference to the crystal structure, is an allotrope of carbon with a hexagonal lattice, as opposed to the cubical lattice of conventional diamond. It is found ...
, but this is far less common and is formed under different conditions from cubic carbon.
Crystal habit
 Diamonds occur most often as
Diamonds occur most often as euhedral
Euhedral crystals (also known as idiomorphic or automorphic crystals) are those that are well-formed, with sharp, easily recognised faces. The opposite is anhedral (also known as '' xenomorphic'' or ''allotriomorphic''): a rock with an anhedra ...
or rounded octahedra
In geometry, an octahedron (plural: octahedra, octahedrons) is a polyhedron with eight faces. The term is most commonly used to refer to the regular octahedron, a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet a ...
and twinned octahedra known as ''macle
{{no footnotes, date=April 2009
Macle is a term used in crystallography. It is a crystalline form, twin-crystal or double crystal (such as chiastolite). It is crystallographic twin according to the spinel twin law and is seen in octahedral cryst ...
s''. As diamond's crystal structure has a cubic arrangement of the atoms, they have many facet
Facets () are flat faces on geometric shapes. The organization of naturally occurring facets was key to early developments in crystallography, since they reflect the underlying symmetry of the crystal structure. Gemstones commonly have facets cut ...
s that belong to a cube, octahedron, rhombicosidodecahedron
In geometry, the rhombicosidodecahedron is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids constructed of two or more types of regular polygon faces.
It has 20 regular triangular faces, 30 square faces, 12 regular pen ...
, tetrakis hexahedron, or disdyakis dodecahedron
In geometry, a disdyakis dodecahedron, (also hexoctahedron, hexakis octahedron, octakis cube, octakis hexahedron, kisrhombic dodecahedron), is a Catalan solid with 48 faces and the dual to the Archimedean truncated cuboctahedron. As such it is fa ...
. The crystals can have rounded-off and unexpressive edges and can be elongated. Diamonds (especially those with rounded crystal faces) are commonly found coated in ''nyf'', an opaque gum-like skin.
Some diamonds contain opaque fibers. They are referred to as ''opaque'' if the fibers grow from a clear substrate or ''fibrous'' if they occupy the entire crystal. Their colors range from yellow to green or gray, sometimes with cloud-like white to gray impurities. Their most common shape is cuboidal, but they can also form octahedra, dodecahedra, macles, or combined shapes. The structure is the result of numerous impurities with sizes between 1 and 5 microns. These diamonds probably formed in kimberlite magma and sampled the volatiles.
Diamonds can also form polycrystalline aggregates. There have been attempts to classify them into groups with names such as boart
Bort, boart, or boort is an umbrella term used in the diamond industry to refer to shards of non-gem-grade/quality diamonds. In the manufacturing and heavy industries, "bort" is used to describe dark, imperfectly formed or crystallized diamond ...
, ballas
Ballas or shot bort is a term used in the diamond industry to refer to shards of non-gem-grade and -quality diamonds. It comprises small diamond crystals that are concentrically arranged in rough spherical stones with a fibrous texture. Ballas is ...
, stewartite, and framesite, but there is no widely accepted set of criteria. Carbonado, a type in which the diamond grains were sintered (fused without melting by the application of heat and pressure), is black in color and tougher than single crystal diamond. It has never been observed in a volcanic rock. There are many theories for its origin, including formation in a star, but no consensus.
Mechanical
Hardness
 Diamond is the hardest known natural material on both the Vickers scale and the
Diamond is the hardest known natural material on both the Vickers scale and the Mohs scale
The Mohs scale of mineral hardness () is a qualitative ordinal scale, from 1 to 10, characterizing scratch resistance of various minerals through the ability of harder material to scratch softer material.
The scale was introduced in 1812 by th ...
. Diamond's great hardness relative to other materials has been known since antiquity, and is the source of its name. This does not mean that it is infinitely hard, indestructible, or unscratchable. Indeed, diamonds can be scratched by other diamonds and worn down over time even by softer materials, such as vinyl phonograph records.
Diamond hardness depends on its purity, crystalline perfection, and orientation: hardness is higher for flawless, pure crystals oriented to the <111> direction (along the longest diagonal of the cubic diamond lattice). Therefore, whereas it might be possible to scratch some diamonds with other materials, such as boron nitride
Boron nitride is a thermally and chemically resistant refractory compound of boron and nitrogen with the chemical formula BN. It exists in various crystalline forms that are isoelectronic to a similarly structured carbon lattice. The hexagonal ...
, the hardest diamonds can only be scratched by other diamonds and nanocrystalline diamond aggregates.
The hardness of diamond contributes to its suitability as a gemstone. Because it can only be scratched by other diamonds, it maintains its polish extremely well. Unlike many other gems, it is well-suited to daily wear because of its resistance to scratching—perhaps contributing to its popularity as the preferred gem in engagement or wedding ring
A wedding ring or wedding band is a finger ring that indicates that its wearer is married. It is usually forged from metal, traditionally gold or another precious metal. Rings were used in ancient Rome during marriage, though the modern prac ...
s, which are often worn every day.
The hardest natural diamonds mostly originate from the Copeton and Bingara
Bingara (Aboriginal for 'creek') is a small town on the Gwydir River in Murchison County in the New England region of New South Wales, Australia. Bingara is currently the administrative centre for the Gwydir Shire that was created in 2003. The ...
fields located in the New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the Can ...
area in New South Wales
)
, nickname =
, image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, es ...
, Australia. These diamonds are generally small, perfect to semiperfect octahedra, and are used to polish other diamonds. Their hardness is associated with the crystal growth
A crystal is a solid material whose constituent atoms, molecules, or ions are arranged in an orderly repeating pattern extending in all three spatial dimensions. Crystal growth is a major stage of a crystallization process, and consists of the ...
form, which is single-stage crystal growth. Most other diamonds show more evidence of multiple growth stages, which produce inclusions, flaws, and defect planes in the crystal lattice, all of which affect their hardness. It is possible to treat regular diamonds under a combination of high pressure and high temperature to produce diamonds that are harder than the diamonds used in hardness gauges.
Diamonds cut glass, but this does not positively identify a diamond because other materials, such as quartz, also lie above glass on the Mohs scale
The Mohs scale of mineral hardness () is a qualitative ordinal scale, from 1 to 10, characterizing scratch resistance of various minerals through the ability of harder material to scratch softer material.
The scale was introduced in 1812 by th ...
and can also cut it. Diamonds can scratch other diamonds, but this can result in damage to one or both stones. Hardness tests are infrequently used in practical gemology because of their potentially destructive nature. The extreme hardness and high value of diamond means that gems are typically polished slowly, using painstaking traditional techniques and greater attention to detail than is the case with most other gemstones; these tend to result in extremely flat, highly polished facets with exceptionally sharp facet edges. Diamonds also possess an extremely high refractive index and fairly high dispersion. Taken together, these factors affect the overall appearance of a polished diamond and most diamantaire
A diamantaire (''French origin'') is a gem-quality diamond manufacturer or producer, master diamond cutter, and graduate gemologist specializing in diamonds.
Such individuals demonstrate considerable expertise in different types of gemstones, pa ...
s still rely upon skilled use of a loupe
A loupe ( ) is a simple, small magnification device used to see small details more closely. They generally have higher magnification than a magnifying glass, and are designed to be held or worn close to the eye. A loupe does not have an attached h ...
(magnifying glass) to identify diamonds "by eye".
Toughness
Somewhat related to hardness is another mechanical property ''toughness'', which is a material's ability to resist breakage from forceful impact. Thetoughness
In materials science and metallurgy, toughness is the ability of a material to absorb energy and plastically deform without fracturing.MPa
MPA or mPa may refer to:
Academia
Academic degrees
* Master of Performing Arts
* Master of Professional Accountancy
* Master of Public Administration
* Master of Public Affairs
Schools
* Mesa Preparatory Academy
* Morgan Park Academy
* Mou ...
·m1/2. This value is good compared to other ceramic materials, but poor compared to most engineering materials such as engineering alloys, which typically exhibit toughnesses over 100MPa·m1/2. As with any material, the macroscopic geometry of a diamond contributes to its resistance to breakage. Diamond has a cleavage plane
Cleavage, in mineralogy and materials science, is the tendency of crystalline materials to split along definite crystallographic structural planes. These planes of relative weakness are a result of the regular locations of atoms and ions in th ...
and is therefore more fragile in some orientations than others. Diamond cutters use this attribute to cleave some stones, prior to faceting. "Impact toughness" is one of the main indexes to measure the quality of synthetic industrial diamonds.
Yield strength
Diamond has compressive yield strength of 130–140GPa. This exceptionally high value, along with the hardness and transparency of diamond, are the reasons thatdiamond anvil
A diamond anvil cell (DAC) is a high-pressure device used in geology, engineering, and materials science experiments. It enables the compression of a small (sub-millimeter-sized) piece of material to extreme pressures, typically up to around 10 ...
cells are the main tool for high pressure experiments. These anvils have reached pressures of . Much higher pressures may be possible with nanocrystalline
A nanocrystalline (NC) material is a polycrystalline material with a crystallite size of only a few nanometers. These materials fill the gap between amorphous materials without any long range order and conventional coarse-grained materials. De ...
diamonds.
Elasticity and tensile strength
Usually, attempting to deform bulk diamond crystal by tension or bending results in brittle fracture. However, when single crystalline diamond is in the form of micro/nanoscale wires or needles (~100–300nanometers in diameter, micrometers long), they can be elastically stretched by as much as 9-10 percent tensile strain without failure, with a maximum local tensile stress of , very close to the theoretical limit for this material.Electrical conductivity
Other specialized applications also exist or are being developed, including use assemiconductor
A semiconductor is a material which has an electrical conductivity value falling between that of a conductor, such as copper, and an insulator, such as glass. Its resistivity falls as its temperature rises; metals behave in the opposite way. ...
s: some blue diamond
Blue diamond is a type of diamond which exhibits all of the same inherent properties of the mineral except with the additional element of blue color in the stone. They are colored blue by trace amounts of boron that contaminate the crystalline l ...
s are natural semiconductors, in contrast to most diamonds, which are excellent electrical insulators. The conductivity and blue color originate from boron impurity. Boron substitutes for carbon atoms in the diamond lattice, donating a hole into the valence band
In solid-state physics, the valence band and conduction band are the bands closest to the Fermi level, and thus determine the electrical conductivity of the solid. In nonmetals, the valence band is the highest range of electron energies in w ...
.
Substantial conductivity is commonly observed in nominally undoped diamond grown by chemical vapor deposition. This conductivity is associated with hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
-related species adsorbed at the surface, and it can be removed by annealing or other surface treatments.
Thin needles of diamond can be made to vary their electronic band gap
In solid-state physics, a band gap, also called an energy gap, is an energy range in a solid where no electronic states can exist. In graphs of the electronic band structure of solids, the band gap generally refers to the energy difference ( ...
from the normal 5.6 eV to near zero by selective mechanical deformation.
High-purity diamond wafers 5 cm in diameter exhibit perfect resistance in one direction and perfect conductance in the other, creating the possibility of using them for quantum data storage. The material contains only 3 parts per million of nitrogen. The diamond was grown on a stepped substrate, which eliminated cracking.
Surface property
Diamonds are naturallylipophilic
Lipophilicity (from Greek λίπος "fat" and φίλος "friendly"), refers to the ability of a chemical compound to dissolve in fats, oils, lipids, and non-polar solvents such as hexane or toluene. Such non-polar solvents are themselves lipo ...
and hydrophobic
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the physical property of a molecule that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water (known as a hydrophobe). In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water.
Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, t ...
, which means the diamonds' surface cannot be wet by water, but can be easily wet and stuck by oil. This property can be utilized to extract diamonds using oil when making synthetic diamonds. However, when diamond surfaces are chemically modified with certain ions, they are expected to become so hydrophilic
A hydrophile is a molecule or other molecular entity that is attracted to water molecules and tends to be dissolved by water.Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon'' Oxford: Clarendon Press.
In contrast, hydrophobes are ...
that they can stabilize multiple layers of water ice Water ice could refer to:
* Ice formed by water (as opposed to other substances)
*The alternate term for various similar frozen fruit-flavoured desserts:
** Italian ice primarily in Philadelphia and the Delaware Valley
**Sorbet
Sorbet (), also ...
at human body temperature
Normal human body-temperature (normothermia, euthermia) is the typical temperature range found in humans. The normal human body temperature range is typically stated as .
Human body temperature varies. It depends on sex, age, time of day, exert ...
.
The surface of diamonds is partially oxidized. The oxidized surface can be reduced by heat treatment under hydrogen flow. That is to say, this heat treatment partially removes oxygen-containing functional groups. But diamonds (sp3C) are unstable against high temperature (above about ) under atmospheric pressure. The structure gradually changes into sp2C above this temperature. Thus, diamonds should be reduced under this temperature.
Chemical stability
At room temperature, diamonds do not react with any chemical reagents including strong acids and bases. In an atmosphere of pure oxygen, diamond has anignition point
The fire point of a fuel is the lowest temperature at which the vapour of that fuel will continue to burn for at least five seconds after ignition by an open flame of standard dimension. At the flash point, a lower temperature, a substance will ...
that ranges from to ; smaller crystals tend to burn more easily. It increases in temperature from red to white heat and burns with a pale blue flame, and continues to burn after the source of heat is removed. By contrast, in air the combustion will cease as soon as the heat is removed because the oxygen is diluted with nitrogen. A clear, flawless, transparent diamond is completely converted to carbon dioxide; any impurities will be left as ash. Heat generated from cutting a diamond will not ignite the diamond, and neither will a cigarette lighter, but house fires and blow torches are hot enough. Jewelers must be careful when molding the metal in a diamond ring.
Diamond powder of an appropriate grain size (around 50microns) burns with a shower of sparks after ignition from a flame. Consequently, pyrotechnic composition
A pyrotechnic composition is a substance or mixture of substances designed to produce an effect by heat, light, sound, gas/smoke or a combination of these, as a result of non-detonative self-sustaining exothermic chemical reactions. Pyrotechnic s ...
s based on synthetic diamond
Lab-grown diamond (LGD; also called laboratory-grown, laboratory-created, man-made, artisan-created, artificial, synthetic, or cultured diamond) is diamond that is produced in a controlled technological process (in contrast to naturally formed ...
powder can be prepared. The resulting sparks are of the usual red-orange color, comparable to charcoal, but show a very linear trajectory which is explained by their high density. Diamond also reacts with fluorine gas above about .
Color
band gap
In solid-state physics, a band gap, also called an energy gap, is an energy range in a solid where no electronic states can exist. In graphs of the electronic band structure of solids, the band gap generally refers to the energy difference ( ...
of corresponding to the deep ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation ...
wavelength of 225nanometers. This means that pure diamond should transmit visible light and appear as a clear colorless crystal. Colors in diamond originate from lattice defects and impurities. The diamond crystal lattice is exceptionally strong, and only atoms of nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
, boron, and hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
can be introduced into diamond during the growth at significant concentrations (up to atomic percents). Transition metals nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow ...
and cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element with the symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. The free element, p ...
, which are commonly used for growth of synthetic diamond by high-pressure high-temperature techniques, have been detected in diamond as individual atoms; the maximum concentration is 0.01% for nickel and even less for cobalt. Virtually any element can be introduced to diamond by ion implantation.
Nitrogen is by far the most common impurity found in gem diamonds and is responsible for the yellow and brown color in diamonds. Boron is responsible for the blue color. Color in diamond has two additional sources: irradiation (usually by alpha particles), that causes the color in green diamonds, and plastic deformation
In engineering, deformation refers to the change in size or shape of an object. ''Displacements'' are the ''absolute'' change in position of a point on the object. Deflection is the relative change in external displacements on an object. Strain ...
of the diamond crystal lattice. Plastic deformation is the cause of color in some brown and perhaps pink and red diamonds. In order of increasing rarity, yellow diamond is followed by brown, colorless, then by blue, green, black, pink, orange, purple, and red. "Black", or carbonado
Carbonado, commonly known as black diamond, is one of the toughest forms of natural diamond. It is an impure, high-density, micro-porous form of polycrystalline diamond consisting of diamond, graphite, and amorphous carbon, with minor crysta ...
, diamonds are not truly black, but rather contain numerous dark inclusions that give the gems their dark appearance. Colored diamonds contain impurities or structural defects that cause the coloration, while pure or nearly pure diamonds are transparent and colorless. Most diamond impurities replace a carbon atom in the crystal lattice, known as a carbon flaw. The most common impurity, nitrogen, causes a slight to intense yellow coloration depending upon the type and concentration of nitrogen present. The Gemological Institute of America
The Gemological Institute of America (GIA) is a nonprofit institute based in Carlsbad, California. It is dedicated to research and education in the field of gemology and the jewelry arts. Founded in 1931, GIA's mission is to protect buyers and se ...
(GIA) classifies low saturation yellow and brown diamonds as diamonds in the ''normal color range'', and applies a grading scale from "D" (colorless) to "Z" (light yellow). Yellow diamonds of high color saturation or a different color, such as pink or blue, are called ''fancy colored'' diamonds and fall under a different grading scale.
In 2008, the Wittelsbach Diamond
The Wittelsbach-Graff Diamond is a deep-blue diamond with internally flawless clarity, originating in the Kollur Mine, India. Laurence Graff purchased the Wittelsbach Diamond in 2008 for £16.4 million. In 2010, Graff revealed he had h ...
, a blue diamond
Blue diamond is a type of diamond which exhibits all of the same inherent properties of the mineral except with the additional element of blue color in the stone. They are colored blue by trace amounts of boron that contaminate the crystalline l ...
once belonging to the King of Spain, fetched over US$24 million at a Christie's auction. In May 2009, a blue diamond
Blue diamond is a type of diamond which exhibits all of the same inherent properties of the mineral except with the additional element of blue color in the stone. They are colored blue by trace amounts of boron that contaminate the crystalline l ...
fetched the highest price per carat ever paid for a diamond when it was sold at auction for 10.5 million Swiss francs (6.97 million euros, or US$9.5 million at the time). That record was, however, beaten the same year: a vivid pink diamond was sold for $10.8 million in Hong Kong on December 1, 2009.
Clarity
Clarity is one of the 4C's (color, clarity, cut and carat weight) that helps in identifying the quality of diamonds. TheGemological Institute of America
The Gemological Institute of America (GIA) is a nonprofit institute based in Carlsbad, California. It is dedicated to research and education in the field of gemology and the jewelry arts. Founded in 1931, GIA's mission is to protect buyers and se ...
(GIA) developed 11 clarity scales to decide the quality of a diamond for its sale value. The GIA clarity scale spans from Flawless (FL) to included (I) having internally flawless (IF), very, very slightly included (VVS), very slightly included (VS) and slightly included (SI) in between. Impurities in natural diamonds are due to the presence of natural minerals and oxides. The clarity scale grades the diamond based on the color, size, location of impurity and quantity of clarity visible under 10x magnification. Inclusions in diamond can be extracted by optical methods. The process is to take pre-enhancement images, identifying the inclusion removal part and finally removing the diamond facets and noises.
Fluorescence
 Between 25% to 35% of natural diamonds exhibit some degree of fluorescence when examined under invisible long-wave Ultraviolet light or higher energy radiation sources such as X-rays and lasers. Incandescent lighting will not cause a diamond to fluoresce. Diamonds can fluoresce in a variety of colours including blue (most common), orange, yellow, white, green and very rarely red and purple. Although the causes are not well understood, variations in the atomic structure, such as the number of nitrogen atoms present are thought to contribute to the phenomenon.
Between 25% to 35% of natural diamonds exhibit some degree of fluorescence when examined under invisible long-wave Ultraviolet light or higher energy radiation sources such as X-rays and lasers. Incandescent lighting will not cause a diamond to fluoresce. Diamonds can fluoresce in a variety of colours including blue (most common), orange, yellow, white, green and very rarely red and purple. Although the causes are not well understood, variations in the atomic structure, such as the number of nitrogen atoms present are thought to contribute to the phenomenon.
Thermal Conductivity
Diamonds can be identified by their high thermal conductivity (900–). Their highrefractive index
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is a dimensionless number that gives the indication of the light bending ability of that medium.
The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or ...
is also indicative, but other materials have similar refractivity.
Geology
Diamonds are extremely rare, with concentrations of at most parts per billion in source rock. Before the 20th century, most diamonds were found inalluvial deposit
Alluvium (from Latin ''alluvius'', from ''alluere'' 'to wash against') is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. Alluv ...
s. Loose diamonds are also found along existing and ancient shore
A shore or a shoreline is the fringe of land at the edge of a large body of water, such as an ocean, sea, or lake. In physical oceanography, a shore is the wider fringe that is geologically modified by the action of the body of water past a ...
lines, where they tend to accumulate because of their size and density. Rarely, they have been found in glacial till
image:Geschiebemergel.JPG, Closeup of glacial till. Note that the larger grains (pebbles and gravel) in the till are completely surrounded by the matrix of finer material (silt and sand), and this characteristic, known as ''matrix support'', is d ...
(notably in Wisconsin
Wisconsin () is a state in the upper Midwestern United States. Wisconsin is the 25th-largest state by total area and the 20th-most populous. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake M ...
and Indiana
Indiana () is a U.S. state in the Midwestern United States. It is the 38th-largest by area and the 17th-most populous of the 50 States. Its capital and largest city is Indianapolis. Indiana was admitted to the United States as the 19th s ...
), but these deposits are not of commercial quality. These types of deposit were derived from localized igneous intrusions through weathering
Weathering is the deterioration of rocks, soils and minerals as well as wood and artificial materials through contact with water, atmospheric gases, and biological organisms. Weathering occurs ''in situ'' (on site, with little or no movement) ...
and transport
Transport (in British English), or transportation (in American English), is the intentional movement of humans, animals, and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land ( rail and road), water, cable, pipelin ...
by wind
Wind is the natural movement of air or other gases relative to a planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few ho ...
or water
Water (chemical formula ) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living ...
.
Most diamonds come from the Earth's mantle
Earth's mantle is a layer of silicate rock between the crust and the outer core. It has a mass of 4.01 × 1024 kg and thus makes up 67% of the mass of Earth. It has a thickness of making up about 84% of Earth's volume. It is predominantly so ...
, and most of this section discusses those diamonds. However, there are other sources. Some blocks of the crust, or terrane
In geology, a terrane (; in full, a tectonostratigraphic terrane) is a crust (geology), crust fragment formed on a tectonic plate (or broken off from it) and Accretion (geology), accreted or "Suture (geology), sutured" to crust lying on another pla ...
s, have been buried deep enough as the crust thickened so they experienced ultra-high-pressure metamorphism Ultra-high-pressure metamorphism refers to metamorphic processes at pressures high enough to stabilize coesite, the high-pressure polymorph of SiO2. It is important because the processes that form and exhume ultra-high-pressure (UHP) metamorphic r ...
. These have evenly distributed ''microdiamonds'' that show no sign of transport by magma. In addition, when meteorites strike the ground, the shock wave can produce high enough temperatures and pressures for ''microdiamonds'' and '' nanodiamonds'' to form. Impact-type microdiamonds can be used as an indicator of ancient impact craters. Popigai impact structure
The Popigai impact structure is the eroded remnant of an impact crater in northern Siberia, Russia. It is tied with the Manicouagan structure as the fourth largest verified impact structure on Earth. A large bolide impact created the diameter ...
in Russia may have the world's largest diamond deposit, estimated at trillions of carats, and formed by an asteroid impact.
A common misconception is that diamonds form from highly compressed coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal is formed when ...
. Coal is formed from buried prehistoric plants, and most diamonds that have been dated are far older than the first land plants
The Embryophyta (), or land plants, are the most familiar group of green plants that comprise vegetation on Earth. Embryophytes () have a common ancestor with green algae, having emerged within the Phragmoplastophyta clade of green algae as sist ...
. It is possible that diamonds can form from coal in subduction zones, but diamonds formed in this way are rare, and the carbon source is more likely carbonate
A carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid (H2CO3), characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, a polyatomic ion with the formula . The word ''carbonate'' may also refer to a carbonate ester, an organic compound containing the carbonate ...
rocks and organic carbon in sediments, rather than coal.
Surface distribution
 Diamonds are far from evenly distributed over the Earth. A rule of thumb known as Clifford's rule states that they are almost always found in kimberlites on the oldest part of
Diamonds are far from evenly distributed over the Earth. A rule of thumb known as Clifford's rule states that they are almost always found in kimberlites on the oldest part of craton
A craton (, , or ; from grc-gre, κράτος "strength") is an old and stable part of the continental lithosphere, which consists of Earth's two topmost layers, the crust and the uppermost mantle. Having often survived cycles of merging an ...
s, the stable cores of continents with typical ages of 2.5billion years or more. However, there are exceptions. The Argyle diamond mine
The Argyle Diamond Mine was a diamond mine located in the East Kimberley region in the remote north of Western Australia. Argyle was at times the largest diamond producer in the world by volume (14 million carats in 2018), although the propor ...
in Australia, the largest producer of diamonds by weight in the world, is located in a ''mobile belt'', also known as an ''orogenic belt
An orogenic belt, or orogen, is a zone of Earth's crust affected by orogeny. An orogenic belt develops when a continental plate crumples and is uplifted to form one or more mountain ranges; this involves a series of geological processes collec ...
'', a weaker zone surrounding the central craton that has undergone compressional tectonics. Instead of kimberlite
Kimberlite is an igneous rock and a rare variant of peridotite. It is most commonly known to be the main host matrix for diamonds. It is named after the town of Kimberley in South Africa, where the discovery of an diamond called the Star of S ...
, the host rock is lamproite
Lamproite is an ultrapotassic mantle-derived volcanic or subvolcanic rock. It has low CaO, Al2O3, Na2O, high K2O/Al2O3, a relatively high MgO content and extreme enrichment in incompatible elements.
Lamproites are geographically widespread ...
. Lamproites with diamonds that are not economically viable are also found in the United States, India, and Australia. In addition, diamonds in the Wawa belt of the Superior province
The Superior Craton is a stable fault block, crustal block covering Quebec, Ontario, and southeast Manitoba in Canada, and northern Minnesota in the United States. It is the biggest craton among those formed during the Archean period. A craton is ...
in Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
and microdiamonds in the island arc of Japan are found in a type of rock called lamprophyre
Lamprophyres () are uncommon, small-volume ultrapotassic igneous rocks primarily occurring as dikes, lopoliths, laccoliths, stocks, and small intrusions. They are alkaline silica- undersaturated mafic or ultramafic rocks with high magnesium ...
.
Kimberlite
Kimberlite is an igneous rock and a rare variant of peridotite. It is most commonly known to be the main host matrix for diamonds. It is named after the town of Kimberley in South Africa, where the discovery of an diamond called the Star of S ...
s can be found in narrow (1 to 4 meters) dikes and sills, and in pipes with diameters that range from about 75 m to 1.5 km. Fresh rock is dark bluish green to greenish gray, but after exposure rapidly turns brown and crumbles. It is hybrid rock with a chaotic mixture of small minerals and rock fragments (clasts
Clastic rocks are composed of fragments, or clasts, of pre-existing minerals and rock. A clast is a fragment of geological detritus,Essentials of Geology, 3rd Ed, Stephen Marshak, p. G-3 chunks, and smaller grains of rock broken off other rocks ...
) up to the size of watermelons. They are a mixture of xenocryst
A xenolith ("foreign rock") is a rock fragment ( country rock) that becomes enveloped in a larger rock during the latter's development and solidification. In geology, the term ''xenolith'' is almost exclusively used to describe inclusions in ign ...
s and xenolith
A xenolith ("foreign rock") is a rock fragment ( country rock) that becomes enveloped in a larger rock during the latter's development and solidification. In geology, the term ''xenolith'' is almost exclusively used to describe inclusions in ig ...
s (minerals and rocks carried up from the lower crust and mantle), pieces of surface rock, altered minerals such as serpentine, and new minerals that crystallized during the eruption. The texture varies with depth. The composition forms a continuum with carbonatite
Carbonatite () is a type of intrusive or extrusive igneous rock defined by mineralogic composition consisting of greater than 50% carbonate minerals. Carbonatites may be confused with marble and may require geochemical verification.
Carbonati ...
s, but the latter have too much oxygen for carbon to exist in a pure form. Instead, it is locked up in the mineral calcite ().
All three of the diamond-bearing rocks (kimberlite, lamproite and lamprophyre) lack certain minerals (melilite
Melilite refers to a mineral of the melilite group. Minerals of the group are solid solutions of several endmembers, the most important of which are gehlenite and åkermanite. A generalized formula for common melilite is ( Ca, Na)2( Al, Mg, ...
and kalsilite
Kalsilite ( K Al Si O4) is a vitreous white to grey feldspathoidal mineral that is found in some potassium-rich lavas, such as from Chamengo Crater in Uganda. It has a relative hardness
In materials science, hardness (antonym: softness) is a ...
) that are incompatible with diamond formation. In kimberlite, olivine
The mineral olivine () is a magnesium iron silicate with the chemical formula . It is a type of nesosilicate or orthosilicate. The primary component of the Earth's upper mantle, it is a common mineral in Earth's subsurface, but weathers quickl ...
is large and conspicuous, while lamproite has Ti-phlogopite
Phlogopite is a yellow, greenish, or reddish-brown member of the mica family of phyllosilicates. It is also known as magnesium mica.
Phlogopite is the magnesium endmember of the biotite solid solution series, with the chemical formula KMg3AlSi3O ...
and lamprophyre has biotite and amphibole. They are all derived from magma types that erupt rapidly from small amounts of melt, are rich in volatiles
Volatiles are the group of chemical elements and chemical compounds that can be readily vaporized. In contrast with volatiles, elements and compounds that are not readily vaporized are known as refractory substances.
On planet Earth, the term ...
and magnesium oxide
Magnesium oxide ( Mg O), or magnesia, is a white hygroscopic solid mineral that occurs naturally as periclase and is a source of magnesium (see also oxide). It has an empirical formula of MgO and consists of a lattice of Mg2+ ions and O2− ions ...
, and are less oxidizing
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a d ...
than more common mantle melts such as basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90 ...
. These characteristics allow the melts to carry diamonds to the surface before they dissolve.
Exploration
Kimberlite
Kimberlite is an igneous rock and a rare variant of peridotite. It is most commonly known to be the main host matrix for diamonds. It is named after the town of Kimberley in South Africa, where the discovery of an diamond called the Star of S ...
pipes can be difficult to find. They weather quickly (within a few years after exposure) and tend to have lower topographic relief than surrounding rock. If they are visible in outcrops, the diamonds are never visible because they are so rare. In any case, kimberlites are often covered with vegetation, sediments, soils, or lakes. In modern searches, geophysical methods such as aeromagnetic survey
An aeromagnetic survey is a common type of geophysical survey carried out using a magnetometer aboard or towed behind an aircraft. The principle is similar to a magnetic survey carried out with a hand-held magnetometer, but allows much larger ar ...
s, electrical resistivity
Electrical resistivity (also called specific electrical resistance or volume resistivity) is a fundamental property of a material that measures how strongly it resists electric current. A low resistivity indicates a material that readily allows ...
, and gravimetry
Gravimetry is the measurement of the strength of a gravitational field. Gravimetry may be used when either the magnitude of a gravitational field or the properties of matter responsible for its creation are of interest.
Units of measurement
G ...
, help identify promising regions to explore. This is aided by isotopic dating and modeling of the geological history. Then surveyors must go to the area and collect samples, looking for kimberlite fragments or ''indicator minerals''. The latter have compositions that reflect the conditions where diamonds form, such as extreme melt depletion or high pressures in eclogite
Eclogite () is a metamorphic rock containing garnet (almandine- pyrope) hosted in a matrix of sodium-rich pyroxene (omphacite). Accessory minerals include kyanite, rutile, quartz, lawsonite, coesite, amphibole, phengite, paragonite, ...
s. However, indicator minerals can be misleading; a better approach is geothermobarometry
Geothermobarometry is the science of measuring the previous pressure and temperature history of a metamorphic or intrusive igneous rocks. Geothermobarometry is a combination of ''geobarometry'', where a pressure of mineral formation is resolved, an ...
, where the compositions of minerals are analyzed as if they were in equilibrium with mantle minerals.
Finding kimberlites requires persistence, and only a small fraction contain diamonds that are commercially viable. The only major discoveries since about 1980 have been in Canada. Since existing mines have lifetimes of as little as 25 years, there could be a shortage of new diamonds in the future.
Ages
Diamonds are dated by analyzing inclusions using the decay of radioactive isotopes. Depending on the elemental abundances, one can look at the decay of rubidium to strontium, samarium to neodymium, uranium to lead, argon-40 to argon-39, or rhenium to osmium. Those found in kimberlites have ages ranging from , and there can be multiple ages in the same kimberlite, indicating multiple episodes of diamond formation. The kimberlites themselves are much younger. Most of them have ages between tens of millions and 300 million years old, although there are some older exceptions (Argyle, Premier and Wawa). Thus, the kimberlites formed independently of the diamonds and served only to transport them to the surface. Kimberlites are also much younger than the cratons they have erupted through. The reason for the lack of older kimberlites is unknown, but it suggests there was some change in mantle chemistry or tectonics. No kimberlite has erupted in human history.Origin in mantle

 Most gem-quality diamonds come from depths of 150–250 km in the lithosphere. Such depths occur below cratons in ''mantle keels'', the thickest part of the lithosphere. These regions have high enough pressure and temperature to allow diamonds to form and they are not convecting, so diamonds can be stored for billions of years until a kimberlite eruption samples them.
Host rocks in a mantle keel include
Most gem-quality diamonds come from depths of 150–250 km in the lithosphere. Such depths occur below cratons in ''mantle keels'', the thickest part of the lithosphere. These regions have high enough pressure and temperature to allow diamonds to form and they are not convecting, so diamonds can be stored for billions of years until a kimberlite eruption samples them.
Host rocks in a mantle keel include harzburgite
Harzburgite, an ultramafic, igneous rock, is a variety of peridotite consisting mostly of the two minerals olivine and low-calcium (Ca) pyroxene ( enstatite); it is named for occurrences in the Harz Mountains of Germany. It commonly contains ...
and lherzolite
Lherzolite is a type of ultramafic igneous rock. It is a coarse-grained rock consisting of 40 to 90% olivine along with significant orthopyroxene and lesser amounts of calcic chromium-rich clinopyroxene. Minor minerals include chromium and alu ...
, two type of peridotite. The most dominant rock type in the upper mantle
The upper mantle of Earth is a very thick layer of rock inside the planet, which begins just beneath the crust (at about under the oceans and about under the continents) and ends at the top of the lower mantle at . Temperatures range from appr ...
, peridotite is an igneous rock
Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ''ignis'' meaning fire), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma o ...
consisting mostly of the minerals olivine
The mineral olivine () is a magnesium iron silicate with the chemical formula . It is a type of nesosilicate or orthosilicate. The primary component of the Earth's upper mantle, it is a common mineral in Earth's subsurface, but weathers quickl ...
and pyroxene; it is low in silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is ...
and high in magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ta ...
. However, diamonds in peridotite rarely survive the trip to the surface. Another common source that does keep diamonds intact is eclogite
Eclogite () is a metamorphic rock containing garnet (almandine- pyrope) hosted in a matrix of sodium-rich pyroxene (omphacite). Accessory minerals include kyanite, rutile, quartz, lawsonite, coesite, amphibole, phengite, paragonite, ...
, a metamorphic
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock (protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, causi ...
rock that typically forms from basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90 ...
as an oceanic plate plunges into the mantle at a subduction zone.
A smaller fraction of diamonds (about 150 have been studied) come from depths of 330–660 km, a region that includes the transition zone. They formed in eclogite but are distinguished from diamonds of shallower origin by inclusions of majorite
Majorite is a type of garnet mineral found in the mantle of the Earth. Its chemical formula is Mg3(MgSi)(SiO4)3. It is distinguished from other garnets in having Si in octahedral as well as tetrahedral coordination. Majorite was first described ...
(a form of garnet
Garnets () are a group of silicate minerals that have been used since the Bronze Age as gemstones and abrasives.
All species of garnets possess similar physical properties and crystal forms, but differ in chemical composition. The different s ...
with excess silicon). A similar proportion of diamonds comes from the lower mantle at depths between 660 and 800 km.
Diamond is thermodynamically stable at high pressures and temperatures, with the phase transition from graphite
Graphite () is a crystalline form of the element carbon. It consists of stacked layers of graphene. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions. Synthetic and natural graphite are consumed on lar ...
occurring at greater temperatures as the pressure increases. Thus, underneath continents it becomes stable at temperatures of 950degrees Celsius and pressures of 4.5 gigapascals, corresponding to depths of 150kilometers or greater. In subduction zones, which are colder, it becomes stable at temperatures of 800 °C and pressures of 3.5gigapascals. At depths greater than 240 km, iron-nickel metal phases are present and carbon is likely to be either dissolved in them or in the form of carbide
In chemistry, a carbide usually describes a compound composed of carbon and a metal. In metallurgy, carbiding or carburizing is the process for producing carbide coatings on a metal piece.
Interstitial / Metallic carbides
The carbides of th ...
s. Thus, the deeper origin of some diamonds may reflect unusual growth environments.
In 2018 the first known natural samples of a phase of ice called Ice VII
Ice VII is a cubic crystalline form of ice. It can be formed from liquid water above 3 GPa (30,000 atmospheres) by lowering its temperature to room temperature, or by decompressing heavy water (D2O) ice VI below 95 K. (Different types of ice, fr ...
were found as inclusions in diamond samples. The inclusions formed at depths between 400 and 800 km, straddling the upper and lower mantle, and provide evidence for water-rich fluid at these depths.
Carbon sources
The mantle has roughly one billiongigatonnes
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the short ton (United States c ...
of carbon (for comparison, the atmosphere-ocean system has about 44,000 gigatonnes). Carbon has two stable isotopes, 12C and 13C, in a ratio of approximately 99:1 by mass. This ratio has a wide range in meteorites, which implies that it also varied a lot in the early Earth. It can also be altered by surface processes like photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored i ...
. The fraction is generally compared to a standard sample using a ratio δ13C expressed in parts per thousand. Common rocks from the mantle such as basalts, carbonatites, and kimberlites have ratios between −8 and −2. On the surface, organic sediments have an average of −25 while carbonates have an average of 0.
Populations of diamonds from different sources have distributions of δ13C that vary markedly. Peridotitic diamonds are mostly within the typical mantle range; eclogitic diamonds have values from −40 to +3, although the peak of the distribution is in the mantle range. This variability implies that they are not formed from carbon that is ''primordial'' (having resided in the mantle since the Earth formed). Instead, they are the result of tectonic processes, although (given the ages of diamonds) not necessarily the same tectonic processes that act in the present.
Formation and growth
 Diamonds in the mantle form through a ''
Diamonds in the mantle form through a ''metasomatic
Metasomatism (from the Greek μετά ''metá'' "change" and σῶμα ''sôma'' "body") is the chemical alteration of a rock by hydrothermal and other fluids. It is the replacement of one rock by another of different mineralogical and chemical com ...
'' process where a C-O-H-N-S fluid or melt dissolves minerals in a rock and replaces them with new minerals. (The vague term C-O-H-N-S is commonly used because the exact composition is not known.) Diamonds form from this fluid either by reduction of oxidized carbon (e.g., CO2 or CO3) or oxidation of a reduced phase such as methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane on Ea ...
.
Using probes such as polarized light, photoluminescence, and cathodoluminescence
Cathodoluminescence is an optical and electromagnetic phenomenon in which electrons impacting on a luminescent material such as a phosphor, cause the emission of photons which may have wavelengths in the visible spectrum. A familiar example is ...
, a series of growth zones can be identified in diamonds. The characteristic pattern in diamonds from the lithosphere involves a nearly concentric series of zones with very thin oscillations in luminescence and alternating episodes where the carbon is resorbed by the fluid and then grown again. Diamonds from below the lithosphere have a more irregular, almost polycrystalline texture, reflecting the higher temperatures and pressures as well as the transport of the diamonds by convection.
Transport to the surface
 Geological evidence supports a model in which kimberlite magma rises at 4–20 meters per second, creating an upward path by hydraulic fracturing of the rock. As the pressure decreases, a vapor phase exsolves from the magma, and this helps to keep the magma fluid. At the surface, the initial eruption explodes out through fissures at high speeds (over ). Then, at lower pressures, the rock is eroded, forming a pipe and producing fragmented rock (
Geological evidence supports a model in which kimberlite magma rises at 4–20 meters per second, creating an upward path by hydraulic fracturing of the rock. As the pressure decreases, a vapor phase exsolves from the magma, and this helps to keep the magma fluid. At the surface, the initial eruption explodes out through fissures at high speeds (over ). Then, at lower pressures, the rock is eroded, forming a pipe and producing fragmented rock (breccia
Breccia () is a rock composed of large angular broken fragments of minerals or rocks cemented together by a fine-grained matrix.
The word has its origins in the Italian language, in which it means "rubble". A breccia may have a variety of ...
). As the eruption wanes, there is pyroclastic phase and then metamorphism and hydration produces serpentinite
Serpentinite is a rock composed predominantly of one or more serpentine group minerals, the name originating from the similarity of the texture of the rock to that of the skin of a snake. Serpentinite has been called ''serpentine'' or ''se ...
s.
Double diamonds
 In rare cases, diamonds have been found that contain a cavity within which is a second diamond. The first double diamond, the
In rare cases, diamonds have been found that contain a cavity within which is a second diamond. The first double diamond, the Matryoshka
Matryoshka dolls ( ; rus, матрёшка, p=mɐˈtrʲɵʂkə, a=Ru-матрёшка.ogg), also known as stacking dolls, nesting dolls, Russian tea dolls, or Russian dolls, are a set of wooden dolls of decreasing size placed one inside ano ...
, was found by Alrosa in Yakutia
Sakha, officially the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia),, is the largest republic of Russia, located in the Russian Far East, along the Arctic Ocean, with a population of roughly 1 million. Sakha comprises half of the area of its governing Far E ...
, Russia, in 2019. Another one was found in the Ellendale Diamond Field
The Ellendale Diamond Field is a cluster of lamproite intrusions located 125 km ESE of Derby within the WNW trending Lennard Shelf to the south of the Kimberley Block in the West Kimberley, West Kimberly region of Australia. The Ellendale diam ...
in Western Australia
Western Australia (commonly abbreviated as WA) is a state of Australia occupying the western percent of the land area of Australia excluding external territories. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to th ...
in 2021.
In space
Although diamonds onEarth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
are rare, they are very common in space. In meteorites, about three percent of the carbon is in the form of nanodiamond
Nanodiamonds, or diamond nanoparticles, are diamonds with a size below 100 nanometers. They can be produced by impact events such as an explosion or meteoritic impacts. Because of their inexpensive, large-scale synthesis, potential for surfa ...
s, having diameters of a few nanometers. Sufficiently small diamonds can form in the cold of space because their lower surface energy makes them more stable than graphite. The isotopic signatures of some nanodiamonds indicate they were formed outside the Solar System in stars.
High pressure experiments predict that large quantities of diamonds condense from methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane on Ea ...
into a "diamond rain" on the ice giant planets Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. Its name is a reference to the Greek god of the sky, Uranus ( Caelus), who, according to Greek mythology, was the great-grandfather of Ares (Mars), grandfather of Zeus (Jupiter) and father of ...
and Neptune. Some extrasolar planets may be almost entirely composed of diamond.
Diamonds may exist in carbon-rich stars, particularly white dwarf
A white dwarf is a stellar core remnant composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. A white dwarf is very dense: its mass is comparable to the Sun's, while its volume is comparable to the Earth's. A white dwarf's faint luminosity comes ...
s. One theory for the origin of carbonado
Carbonado, commonly known as black diamond, is one of the toughest forms of natural diamond. It is an impure, high-density, micro-porous form of polycrystalline diamond consisting of diamond, graphite, and amorphous carbon, with minor crysta ...
, the toughest form of diamond, is that it originated in a white dwarf or supernova. Diamonds formed in stars may have been the first minerals.
Industry
 The most familiar uses of diamonds today are as gemstones used for adornment, and as industrial abrasives for cutting hard materials. The markets for gem-grade and industrial-grade diamonds value diamonds differently.
The most familiar uses of diamonds today are as gemstones used for adornment, and as industrial abrasives for cutting hard materials. The markets for gem-grade and industrial-grade diamonds value diamonds differently.
Gem-grade diamonds
Thedispersion
Dispersion may refer to:
Economics and finance
* Dispersion (finance), a measure for the statistical distribution of portfolio returns
* Price dispersion, a variation in prices across sellers of the same item
*Wage dispersion, the amount of variat ...
of white light into spectral colors is the primary gemological characteristic of gem diamonds. In the 20th century, experts in gemology developed methods of grading diamonds and other gemstones based on the characteristics most important to their value as a gem. Four characteristics, known informally as the ''four Cs'', are now commonly used as the basic descriptors of diamonds: these are its mass in '' carats'' (a carat being equal to 0.2grams), ''cut
Cut may refer to:
Common uses
* The act of cutting, the separation of an object into two through acutely-directed force
** A type of wound
** Cut (archaeology), a hole dug in the past
** Cut (clothing), the style or shape of a garment
** Cut (ea ...
'' (quality of the cut is graded according to proportions, symmetry and polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, w ...
), ''color
Color (American English) or colour (British English) is the visual perceptual property deriving from the spectrum of light interacting with the photoreceptor cells of the eyes. Color categories and physical specifications of color are assoc ...
'' (how close to white or colorless; for fancy diamonds how intense is its hue), and ''clarity
Clarity may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities
* Clarity, a magic spell in the online game ''EverQuest''
* Clarity, a fictional drug from the film '' Minority Report''
Music Albums
* ''Clarity'' (Jimmy Eat World album)
...
'' (how free is it from inclusions). A large, flawless diamond is known as a paragon
Paragon may refer to:
Places
*Paragon, Indiana, a town in the United States
* Paragon, Nebraska, former community in the United States
*The Paragon, Bath, a Georgian street in the Walcot area of Bath
* The Paragon, Blackheath, London, built by Mi ...
.
A large trade in gem-grade diamonds exists. Although most gem-grade diamonds are sold newly polished, there is a well-established market for resale of polished diamonds (e.g. pawnbroking, auctions, second-hand jewelry stores, diamantaires, bourses, etc.). One hallmark of the trade in gem-quality diamonds is its remarkable concentration: wholesale trade and diamond cutting is limited to just a few locations; in 2003, 92% of the world's diamonds were cut and polished in Surat, India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
. Other important centers of diamond cutting and trading are the Antwerp diamond district
Antwerp's diamond district, also known as the Diamond Quarter (''Diamantkwartier''), and dubbed the Square Mile, is an area within the city of Antwerp, Belgium. It consists of several square blocks covering an area of about one square mile. While a ...
in Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to th ...
, where the International Gemological Institute
International Gemological Institute (IGI) is a diamond, colored stone and jewelry certification organization. IGI is headquartered in Antwerp and has offices in New York City, Hong Kong, Mumbai, Bangkok, Tokyo, Dubai, Tel Aviv, Toronto, Los Ang ...
is based, London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
, the Diamond District in New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the Un ...
, the Diamond Exchange District
The Diamond Exchange District (Hebrew: מִתְחַם הַבּוּרְסָה, ''Mitham HaBursa'', lit. "The Exchange District") is a diamond district and commercial area in the Tel Aviv District city of Ramat Gan, Israel. the district is the hub ...
in Tel Aviv
Tel Aviv-Yafo ( he, תֵּל־אָבִיב-יָפוֹ, translit=Tēl-ʾĀvīv-Yāfō ; ar, تَلّ أَبِيب – يَافَا, translit=Tall ʾAbīb-Yāfā, links=no), often referred to as just Tel Aviv, is the most populous city in the ...
and Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Amstel'') is the capital and most populous city of the Netherlands, with The Hague being the seat of government. It has a population of 907,976 within the city proper, 1,558,755 in the urban ar ...
. One contributory factor is the geological nature of diamond deposits: several large primary kimberlite-pipe mines each account for significant portions of market share (such as the Jwaneng mine in Botswana, which is a single large-pit mine that can produce between of diamonds per year). Secondary alluvial diamond deposits, on the other hand, tend to be fragmented amongst many different operators because they can be dispersed over many hundreds of square kilometers (e.g., alluvial deposits in Brazil).
The production and distribution of diamonds is largely consolidated in the hands of a few key players, and concentrated in traditional diamond trading centers, the most important being Antwerp, where 80% of all rough diamond
A rough diamond is a diamond that has not been cut or processed. They come in a variety of naturally occurring shapes, including octahedral (eight-sided bipyramid), cubic, and triangular (most commonly macles).
A raw diamond or rough diamond ...
s, 50% of all cut diamonds and more than 50% of all rough, cut and industrial diamonds combined are handled. This makes Antwerp a de facto "world diamond capital". The city of Antwerp also hosts the Antwerpsche Diamantkring, created in 1929 to become the first and biggest diamond bourse dedicated to rough diamonds. Another important diamond center is New York City, where almost 80% of the world's diamonds are sold, including auction sales.
The De Beers company, as the world's largest diamond mining company, holds a dominant position in the industry, and has done so since soon after its founding in 1888 by the British businessman Cecil Rhodes. De Beers is currently the world's largest operator of diamond production facilities (mines) and distribution channels
Distribution (or place) is one of the four elements of the marketing mix. Distribution is the process of making a product or service available for the consumer or business user who needs it. This can be done directly by the producer or service p ...
for gem-quality diamonds. The Diamond Trading Company (DTC) is a subsidiary of De Beers and markets rough diamonds from De Beers-operated mines. De Beers and its subsidiaries own mines that produce some 40% of annual world diamond production. For most of the 20th century over 80% of the world's rough diamonds passed through De Beers, but by 2001–2009 the figure had decreased to around 45%, and by 2013 the company's market share had further decreased to around 38% in value terms and even less by volume. De Beers sold off the vast majority of its diamond stockpile in the late 1990s – early 2000s and the remainder largely represents working stock (diamonds that are being sorted before sale). This was well documented in the press but remains little known to the general public.
As a part of reducing its influence, De Beers withdrew from purchasing diamonds on the open market in 1999 and ceased, at the end of 2008, purchasing Russian diamonds mined by the largest Russian diamond company Alrosa. As of January 2011, De Beers states that it only sells diamonds from the following four countries: Botswana, Namibia, South Africa and Canada. Alrosa had to suspend their sales in October 2008 due to the global energy crisis, but the company reported that it had resumed selling rough diamonds on the open market by October 2009. Apart from Alrosa, other important diamond mining companies include BHP
BHP Group Limited (formerly known as BHP Billiton) is an Australian multinational mining, metals, natural gas petroleum public company that is headquartered in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia.
The Broken Hill Proprietary Company was founded ...
, which is the world's largest mining company; Rio Tinto Rio Tinto, meaning "red river", may refer to:
Businesses
* Rio Tinto (corporation), an Anglo-Australian multinational mining and resources corporation
** Rio Tinto Alcan, based in Canada
** Rio Tinto Borax in America
*** Rio Tinto Borax Mine, ...
, the owner of the Argyle (100%), Diavik (60%), and Murowa (78%) diamond mines; and Petra Diamonds
Petra Diamonds Ltd is a diamond mining group headquartered in Jersey. Petra own one of the world's most productive mines historically, the Premier Mine, Cullinan Diamond Mine is famed for having produced the Cullinan Diamond, world's largest roug ...
, the owner of several major diamond mines in Africa.
 Further down the supply chain, members of The
Further down the supply chain, members of The World Federation of Diamond Bourses
The World Federation of Diamond Bourses, founded in 1947, was created to provide bourses trading in rough and polished diamonds and precious stones with a common set of trading practices. It is composed of 30 member diamond bourses. Their headqu ...
(WFDB) act as a medium for wholesale diamond exchange, trading both polished and rough diamonds. The WFDB consists of independent diamond bourses in major cutting centers such as Tel Aviv, Antwerp, Johannesburg and other cities across the US, Europe and Asia. In 2000, the WFDB and The International Diamond Manufacturers Association established the World Diamond Council The World Diamond Council is an organization representing the entire diamond value chain including representatives from diamond mining, manufacturing, trading and retail. The council was established in July 2000. The purpose was to create a system ...
to prevent the trading of diamonds used to fund war and inhumane acts. WFDB's additional activities include sponsoring the World Diamond Congress The World Diamond Congress is a bi-annual industry event organized by World Federation of Diamond Bourses and the International Diamond Manufacturers Association. The first World Diamond Congress was held in Antwerpen, Belgium in 1947. It was held ...
every two years, as well as the establishment of the ''International Diamond Council The World Diamond Council is an organization representing the entire diamond value chain including representatives from diamond mining, manufacturing, trading and retail. The council was established in July 2000. The purpose was to create a system t ...
'' (IDC) to oversee diamond grading.
Once purchased by Sightholders (which is a trademark term referring to the companies that have a three-year supply contract with DTC), diamonds are cut and polished in preparation for sale as gemstones ('industrial' stones are regarded as a by-product of the gemstone market; they are used for abrasives). The cutting and polishing of rough diamonds is a specialized skill that is concentrated in a limited number of locations worldwide. Traditional diamond cutting centers are Antwerp, Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Amstel'') is the capital and most populous city of the Netherlands, with The Hague being the seat of government. It has a population of 907,976 within the city proper, 1,558,755 in the urban ar ...
, Johannesburg, New York City, and Tel Aviv. Recently, diamond cutting centers have been established in China, India, Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is b ...
, Namibia and Botswana. Cutting centers with lower cost of labor, notably Surat in Gujarat, India
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth ...
, handle a larger number of smaller carat diamonds, while smaller quantities of larger or more valuable diamonds are more likely to be handled in Europe or North America. The recent expansion of this industry in India, employing low cost labor, has allowed smaller diamonds to be prepared as gems in greater quantities than was previously economically feasible.
Diamonds prepared as gemstones are sold on diamond exchanges called '' bourses''. There are 28 registered diamond bourses in the world. Bourses are the final tightly controlled step in the diamond supply chain; wholesalers and even retailers are able to buy relatively small lots of diamonds at the bourses, after which they are prepared for final sale to the consumer. Diamonds can be sold already set in jewelry, or sold unset ("loose"). According to the Rio Tinto, in 2002 the diamonds produced and released to the market were valued at US$9 billion as rough diamonds, US$14 billion after being cut and polished, US$28 billion in wholesale diamond jewelry, and US$57 billion in retail sales.
Cutting
Mined rough diamonds are converted into gems through a multi-step process called "cutting". Diamonds are extremely hard, but also brittle and can be split up by a single blow. Therefore, diamond cutting is traditionally considered as a delicate procedure requiring skills, scientific knowledge, tools and experience. Its final goal is to produce a faceted jewel where the specific angles between the facets would optimize the diamond luster, that is dispersion of white light, whereas the number and area of facets would determine the weight of the final product. The weight reduction upon cutting is significant and can be of the order of 50%. Several possible shapes are considered, but the final decision is often determined not only by scientific, but also practical considerations. For example, the diamond might be intended for display or for wear, in a ring or a necklace, singled or surrounded by other gems of certain color and shape. Some of them may be considered as classical, such asround
Round or rounds may refer to:
Mathematics and science
* The contour of a closed curve or surface with no sharp corners, such as an ellipse, circle, rounded rectangle, cant, or sphere
* Rounding, the shortening of a number to reduce the number ...
, pear
Pears are fruits produced and consumed around the world, growing on a tree and harvested in the Northern Hemisphere in late summer into October. The pear tree and shrub are a species of genus ''Pyrus'' , in the family Rosaceae, bearing the po ...
, marquise, oval
An oval () is a closed curve in a plane which resembles the outline of an egg. The term is not very specific, but in some areas (projective geometry, technical drawing, etc.) it is given a more precise definition, which may include either one ...
, hearts and arrows
Hearts and Arrows (H&A) diamonds are precision-cut variations of the traditional 57 faceted round brilliant cut. They are cut to "ideal" proportions with good optical symmetry, polish and a specific faceting pattern. When all these factors are p ...
diamonds, etc. Some of them are special, produced by certain companies, for example, Phoenix
Phoenix most often refers to:
* Phoenix (mythology), a legendary bird from ancient Greek folklore
* Phoenix, Arizona, a city in the United States
Phoenix may also refer to:
Mythology
Greek mythological figures
* Phoenix (son of Amyntor), a ...
, Cushion
A cushion is a soft bag of some ornamental material, usually stuffed with wool, hair, feathers, polyester staple fiber, non-woven material, cotton, or even paper torn into fragments. It may be used for sitting or kneeling upon, or to soften th ...
, Sole Mio
SOL3 MIO (stylised as SOLΞ MIO) is a New Zealand musical trio consisting of Moses Mackay, Pene Pati and Amitai Pati. Of Samoan descent and classically trained, Moses is a baritone, and the Pati brothers are operatic tenors.
Albums and tour ...
diamonds, etc.
The most time-consuming part of the cutting is the preliminary analysis of the rough stone. It needs to address a large number of issues, bears much responsibility, and therefore can last years in case of unique diamonds. The following issues are considered:
* The hardness of diamond and its ability to cleave strongly depend on the crystal orientation. Therefore, the crystallographic structure of the diamond to be cut is analyzed using X-ray diffraction to choose the optimal cutting directions.
* Most diamonds contain visible non-diamond inclusions and crystal flaws. The cutter has to decide which flaws are to be removed by the cutting and which could be kept.
* The diamond can be split by a single, well calculated blow of a hammer to a pointed tool, which is quick, but risky. Alternatively, it can be cut with a diamond saw
A diamond blade is a saw blade which has diamonds fixed on its edge for cutting hard or abrasive materials. There are many types of diamond blade, and they have many uses, including cutting stone, concrete, asphalt, bricks, coal balls, glass, a ...
, which is a more reliable but tedious procedure.
After initial cutting, the diamond is shaped in numerous stages of polishing. Unlike cutting, which is a responsible but quick operation, polishing removes material by gradual erosion and is extremely time-consuming. The associated technique is well developed; it is considered as a routine and can be performed by technicians. After polishing, the diamond is reexamined for possible flaws, either remaining or induced by the process. Those flaws are concealed through various diamond enhancement
Diamond enhancements are specific treatments, performed on natural diamonds (usually those already cut and polished into gems), which are designed to improve the visual gemological characteristics of the diamond in one or more ways. These include ...
techniques, such as repolishing, crack filling, or clever arrangement of the stone in the jewelry. Remaining non-diamond inclusions are removed through laser drilling and filling of the voids produced.
Marketing
 Marketing has significantly affected the image of diamond as a valuable commodity.
N. W. Ayer & Son, the advertising firm retained by De Beers in the mid-20th century, succeeded in reviving the American diamond market and the firm created new markets in countries where no diamond tradition had existed before. N. W. Ayer's marketing included product placement, advertising focused on the diamond product itself rather than the De Beers brand, and associations with celebrities and royalty. Without advertising the De Beers brand, De Beers was advertising its competitors' diamond products as well, but this was not a concern as De Beers dominated the diamond market throughout the 20th century. De Beers' market share dipped temporarily to second place in the global market below Alrosa in the aftermath of the global economic crisis of 2008, down to less than 29% in terms of carats mined, rather than sold. The campaign lasted for decades but was effectively discontinued by early 2011. De Beers still advertises diamonds, but the advertising now mostly promotes its own brands, or licensed product lines, rather than completely "generic" diamond products. The campaign was perhaps best captured by the slogan " a diamond is forever". This slogan is now being used by De Beers Diamond Jewelers, a jewelry firm which is a 50/50% joint venture between the De Beers mining company and LVMH, the luxury goods conglomerate.
Brown-colored diamonds constituted a significant part of the diamond production, and were predominantly used for industrial purposes. They were seen as worthless for jewelry (not even being assessed on the
Marketing has significantly affected the image of diamond as a valuable commodity.
N. W. Ayer & Son, the advertising firm retained by De Beers in the mid-20th century, succeeded in reviving the American diamond market and the firm created new markets in countries where no diamond tradition had existed before. N. W. Ayer's marketing included product placement, advertising focused on the diamond product itself rather than the De Beers brand, and associations with celebrities and royalty. Without advertising the De Beers brand, De Beers was advertising its competitors' diamond products as well, but this was not a concern as De Beers dominated the diamond market throughout the 20th century. De Beers' market share dipped temporarily to second place in the global market below Alrosa in the aftermath of the global economic crisis of 2008, down to less than 29% in terms of carats mined, rather than sold. The campaign lasted for decades but was effectively discontinued by early 2011. De Beers still advertises diamonds, but the advertising now mostly promotes its own brands, or licensed product lines, rather than completely "generic" diamond products. The campaign was perhaps best captured by the slogan " a diamond is forever". This slogan is now being used by De Beers Diamond Jewelers, a jewelry firm which is a 50/50% joint venture between the De Beers mining company and LVMH, the luxury goods conglomerate.
Brown-colored diamonds constituted a significant part of the diamond production, and were predominantly used for industrial purposes. They were seen as worthless for jewelry (not even being assessed on the diamond color
A chemically pure and structurally perfect diamond is perfectly transparent with no hue, or ''color''. However, in reality almost no gem-sized natural diamonds are absolutely perfect. The color of a diamond may be affected by chemical impurities ...
scale). After the development of Argyle diamond mine in Australia in 1986, and marketing, brown diamonds have become acceptable gems. The change was mostly due to the numbers: the Argyle mine, with its of diamonds per year, makes about one-third of global production of natural diamonds; 80% of Argyle diamonds are brown.
Industrial-grade diamonds


 Industrial diamonds are valued mostly for their hardness and thermal conductivity, making many of the gemological characteristics of diamonds, such as the 4 Cs, irrelevant for most applications. Eighty percent of mined diamonds (equal to about annually) are unsuitable for use as gemstones and are used industrially. In addition to mined diamonds, synthetic diamonds found industrial applications almost immediately after their invention in the 1950s; in 2014, of synthetic diamonds were produced, 90% of which were produced in China. Approximately 90% of diamond grinding grit is currently of synthetic origin.
The boundary between gem-quality diamonds and industrial diamonds is poorly defined and partly depends on market conditions (for example, if demand for polished diamonds is high, some lower-grade stones will be polished into low-quality or small gemstones rather than being sold for industrial use). Within the category of industrial diamonds, there is a sub-category comprising the lowest-quality, mostly opaque stones, which are known as
Industrial diamonds are valued mostly for their hardness and thermal conductivity, making many of the gemological characteristics of diamonds, such as the 4 Cs, irrelevant for most applications. Eighty percent of mined diamonds (equal to about annually) are unsuitable for use as gemstones and are used industrially. In addition to mined diamonds, synthetic diamonds found industrial applications almost immediately after their invention in the 1950s; in 2014, of synthetic diamonds were produced, 90% of which were produced in China. Approximately 90% of diamond grinding grit is currently of synthetic origin.
The boundary between gem-quality diamonds and industrial diamonds is poorly defined and partly depends on market conditions (for example, if demand for polished diamonds is high, some lower-grade stones will be polished into low-quality or small gemstones rather than being sold for industrial use). Within the category of industrial diamonds, there is a sub-category comprising the lowest-quality, mostly opaque stones, which are known as bort
Bort, boart, or boort is an umbrella term used in the diamond industry to refer to shards of non-gem-grade/quality diamonds. In the manufacturing and heavy industries, "bort" is used to describe dark, imperfectly formed or crystallized diamonds ...
.
Industrial use of diamonds has historically been associated with their hardness, which makes diamond the ideal material for cutting and grinding tools. As the hardest known naturally occurring material, diamond can be used to polish, cut, or wear away any material, including other diamonds. Common industrial applications of this property include diamond-tipped drill bit
Drill bits are cutting tools used in a drill to remove material to create holes, almost always of circular cross-section. Drill bits come in many sizes and shapes and can create different kinds of holes in many different materials. In order ...
s and saws, and the use of diamond powder as an abrasive
An abrasive is a material, often a mineral, that is used to shape or finish a workpiece through rubbing which leads to part of the workpiece being worn away by friction. While finishing a material often means polishing it to gain a smooth, reflec ...
. Less expensive industrial-grade diamonds (bort) with more flaws and poorer color than gems, are used for such purposes. Diamond is not suitable for machining ferrous
In chemistry, the adjective Ferrous indicates a compound that contains iron(II), meaning iron in its +2 oxidation state, possibly as the divalent cation Fe2+. It is opposed to " ferric" or iron(III), meaning iron in its +3 oxidation state, suc ...
alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which at least one is a metal. Unlike chemical compounds with metallic bases, an alloy will retain all the properties of a metal in the resulting material, such as electrical conductivity, ductilit ...
s at high speeds, as carbon is soluble in iron at the high temperatures created by high-speed machining, leading to greatly increased wear on diamond tools compared to alternatives.
Specialized applications include use in laboratories as containment for high-pressure experiments (see diamond anvil cell
A diamond anvil cell (DAC) is a high-pressure device used in geology, engineering, and materials science experiments. It enables the compression of a small (sub-millimeter-sized) piece of material to extreme pressures, typically up to around 1 ...
), high-performance bearings, and limited use in specialized window
A window is an opening in a wall, door, roof, or vehicle that allows the exchange of light and may also allow the passage of sound and sometimes air. Modern windows are usually glazed or covered in some other transparent or translucent mat ...
s. With the continuing advances being made in the production of synthetic diamonds, future applications are becoming feasible. The high thermal conductivity
The thermal conductivity of a material is a measure of its ability to conduct heat. It is commonly denoted by k, \lambda, or \kappa.
Heat transfer occurs at a lower rate in materials of low thermal conductivity than in materials of high thermal ...
of diamond makes it suitable as a heat sink
A heat sink (also commonly spelled heatsink) is a passive heat exchanger that transfers the heat generated by an electronic or a mechanical device to a fluid medium, often air or a liquid coolant, where it is dissipated away from the device, th ...
for integrated circuits in electronics
The field of electronics is a branch of physics and electrical engineering that deals with the emission, behaviour and effects of electrons using electronic devices. Electronics uses active devices to control electron flow by amplification ...
.
Mining
Approximately of diamonds are mined annually, with a total value of nearly US$9 billion, and about are synthesized annually. Roughly 49% of diamonds originate from Central andSouthern Africa
Southern Africa is the southernmost subregion of the African continent, south of the Congo and Tanzania. The physical location is the large part of Africa to the south of the extensive Congo River basin. Southern Africa is home to a number o ...
, although significant sources of the mineral have been discovered in Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
, India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
, Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
, and Australia. They are mined from kimberlite and lamproite volcanic pipes, which can bring diamond crystals, originating from deep within the Earth where high pressures and temperatures enable them to form, to the surface. The mining and distribution of natural diamonds are subjects of frequent controversy such as concerns over the sale of '' blood diamonds'' or ''conflict diamonds'' by African paramilitary groups.
The diamond supply chain is controlled by a limited number of powerful businesses, and is also highly concentrated in a small number of locations around the world.
Only a very small fraction of the diamond ore consists of actual diamonds. The ore is crushed, during which care is required not to destroy larger diamonds, and then sorted by density. Today, diamonds are located in the diamond-rich density fraction with the help of X-ray fluorescence
X-ray fluorescence (XRF) is the emission of characteristic "secondary" (or fluorescent) X-rays from a material that has been excited by being bombarded with high-energy X-rays or gamma rays. The phenomenon is widely used for elemental analysis ...
, after which the final sorting steps are done by hand. Before the use of X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
s became commonplace, the separation was done with grease belts; diamonds have a stronger tendency to stick to grease than the other minerals in the ore.
alluvial deposit
Alluvium (from Latin ''alluvius'', from ''alluere'' 'to wash against') is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. Alluv ...
s in Guntur and Krishna district of the Krishna River delta in Southern India
South India, also known as Dakshina Bharata or Peninsular India, consists of the peninsular southern part of India. It encompasses the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Telangana, as well as the union territ ...
. India led the world in diamond production from the time of their discovery in approximately the 9th century BC to the mid-18th century AD, but the commercial potential of these sources had been exhausted by the late 18th century and at that time India was eclipsed by Brazil where the first non-Indian diamonds were found in 1725. Currently, one of the most prominent Indian mines is located at Panna.
Diamond extraction from primary deposits (kimberlites and lamproites) started in the 1870s after the discovery of the Diamond Fields
Kimberley is the capital and largest city of the Northern Cape province of South Africa. It is located approximately 110 km east of the confluence of the Vaal and Orange Rivers. The city has considerable historical significance due to its ...
in South Africa.
Production has increased over time and now an accumulated total of have been mined since that date. Twenty percent of that amount has been mined in the last five years, and during the last 10 years, nine new mines have started production; four more are waiting to be opened soon. Most of these mines are located in Canada, Zimbabwe, Angola, and one in Russia.
In the U.S., diamonds have been found in Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the South Central United States. It is bordered by Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, and Texas and Oklahoma to the west. Its name is from the O ...
, Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the wes ...
, New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Tiguex
, OfficialLang = None
, Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ke ...
, Wyoming, and Montana
Montana () is a state in the Mountain West division of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota and South Dakota to the east, Wyoming to the south, and the Canadian provinces of Alberta, British Columb ...
. In 2004, the discovery of a microscopic diamond in the U.S. led to the January 2008 bulk-sampling of kimberlite pipe
Volcanic pipes or volcanic conduits are subterranean geology, geological structures formed by the violent, supersonic eruption of deep-origin volcanoes. They are considered to be a type of ''diatreme''. Volcanic pipes are composed of a deep, narro ...
s in a remote part of Montana. The Crater of Diamonds State Park
Crater of Diamonds State Park is a Arkansas state park in Pike County, Arkansas, in the United States. The park features a 37.5-acre (15.2 ha) plowed field, the world's only diamond-bearing site accessible to the public. Diamonds have continuou ...
in Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the South Central United States. It is bordered by Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, and Texas and Oklahoma to the west. Its name is from the O ...
is open to the public, and is the only mine in the world where members of the public can dig for diamonds.
Today, most commercially viable diamond deposits are in Russia (mostly in Sakha Republic, for example Mir pipe and Udachnaya pipe
The Udachnaya pipe (russian: тру́бка Уда́чная, literally ''lucky pipe'') is a diamond deposit in the Daldyn- Alakit kimberlite field in Sakha Republic, Russia. It is an open-pit mine, and is located just outside the Arctic ...
), Botswana
Botswana (, ), officially the Republic of Botswana ( tn, Lefatshe la Botswana, label= Setswana, ), is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. Botswana is topographically flat, with approximately 70 percent of its territory being the Kalaha ...
, Australia ( Northern and Western Australia
Western Australia (commonly abbreviated as WA) is a state of Australia occupying the western percent of the land area of Australia excluding external territories. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to th ...
) and the Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (french: République démocratique du Congo (RDC), colloquially "La RDC" ), informally Congo-Kinshasa, DR Congo, the DRC, the DROC, or the Congo, and formerly and also colloquially Zaire, is a country in ...
.
In 2005, Russia produced almost one-fifth of the global diamond output, according to the British Geological Survey. Australia boasts the richest diamantiferous pipe, with production from the Argyle diamond mine reaching peak levels of 42metric tons per year in the 1990s.
There are also commercial deposits being actively mined in the Northwest Territories of Canada and Brazil.
Diamond prospectors continue to search the globe for diamond-bearing kimberlite and lamproite pipes.
Political issues
] In some of the more politically unstable central African and west African countries, revolutionary groups have taken control of List of diamond mines, diamond mines, using proceeds from diamond sales to finance their operations. Diamonds sold through this process are known as ''conflict diamonds'' or ''blood diamonds''. In response to public concerns that their diamond purchases were contributing to war andhuman rights abuses
Human rights are moral principles or normsJames Nickel, with assistance from Thomas Pogge, M.B.E. Smith, and Leif Wenar, 13 December 2013, Stanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyHuman Rights Retrieved 14 August 2014 for certain standards of hu ...
in central and western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
Africa, the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
, the diamond industry and diamond-trading nations introduced the Kimberley Process in 2002. The Kimberley Process aims to ensure that conflict diamonds do not become intermixed with the diamonds not controlled by such rebel groups. This is done by requiring diamond-producing countries to provide proof that the money they make from selling the diamonds is not used to fund criminal or revolutionary activities. Although the Kimberley Process has been moderately successful in limiting the number of conflict diamonds entering the market, some still find their way in. According to the International Diamond Manufacturers Association, conflict diamonds constitute 2–3% of all diamonds traded. Two major flaws still hinder the effectiveness of the Kimberley Process: (1) the relative ease of smuggling diamonds across African borders, and (2) the violent nature of diamond mining in nations that are not in a technical state of war and whose diamonds are therefore considered "clean".
The Canadian Government has set up a body known as the Canadian Diamond Code of Conduct to help authenticate Canadian diamonds. This is a stringent tracking system of diamonds and helps protect the "conflict free" label of Canadian diamonds.
Mineral resource exploitation in general causes irreversible environmental damage, which must be weighed against the socio-economic benefits to a country.
Synthetics, simulants, and enhancements
Synthetics
Synthetic diamonds are diamonds manufactured in a laboratory, as opposed to diamonds mined from the Earth. The gemological and industrial uses of diamond have created a large demand for rough stones. This demand has been satisfied in large part by synthetic diamonds, which have been manufactured by various processes for more than half a century. However, in recent years it has become possible to produce gem-quality synthetic diamonds of significant size. It is possible to make colorless synthetic gemstones that, on a molecular level, are identical to natural stones and so visually similar that only a gemologist with special equipment can tell the difference. The majority of commercially available synthetic diamonds are yellow and are produced by so-called ''high-pressure high-temperature'' (HPHT
Lab-grown diamond (LGD; also called laboratory-grown, laboratory-created, man-made, artisan-created, artificial, synthetic, or cultured diamond) is diamond that is produced in a controlled technological process (in contrast to naturally formed ...
) processes. The yellow color is caused by nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
impurities. Other colors may also be reproduced such as blue, green or pink, which are a result of the addition of boron or from irradiation
Irradiation is the process by which an object is exposed to radiation. The exposure can originate from various sources, including natural sources. Most frequently the term refers to ionizing radiation, and to a level of radiation that will serve ...
after synthesis.
Another popular method of growing synthetic diamond is chemical vapor deposition (CVD). The growth occurs under low pressure (below atmospheric pressure). It involves feeding a mixture of gases (typically to hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
) into a chamber and splitting them into chemically active radicals in a plasma ignited by microwaves
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths ranging from about one meter to one millimeter corresponding to frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz respectively. Different sources define different frequency rang ...
, hot filament
The hot-filament ionization gauge, sometimes called a hot-filament gauge or hot-cathode gauge, is the most widely used low-pressure (vacuum) measuring device for the region from 10−3 to 10−10 Torr. It is a triode, with the filament being the ...
, arc discharge
An electric arc, or arc discharge, is an electrical breakdown of a gas that produces a prolonged electrical discharge. The current through a normally nonconductive medium such as air produces a plasma; the plasma may produce visible light. An ...
, welding torch
Principle of burn cutting
Oxy-fuel welding (commonly called oxyacetylene welding, oxy welding, or gas welding in the United States) and oxy-fuel cutting are processes that use fuel gases (or liquid fuels such as gasoline or petrol, diesel, ...
, or laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The fi ...
. This method is mostly used for coatings, but can also produce single crystals several millimeters in size (see picture).
As of 2010, nearly all 5,000 million carats (1,000tonnes) of synthetic diamonds produced per year are for industrial use. Around 50% of the 133 million carats of natural diamonds mined per year end up in industrial use. Mining companies' expenses average 40 to 60 US dollars per carat for natural colorless diamonds, while synthetic manufacturers' expenses average for synthetic, gem-quality colorless diamonds. However, a purchaser is more likely to encounter a synthetic when looking for a fancy-colored diamond because nearly all synthetic diamonds are fancy-colored, while only 0.01% of natural diamonds are.
Simulants
Cubic zirconia
Cubic zirconia (CZ) is the cubic crystalline form of zirconium dioxide (ZrO2). The synthesized material is hard and usually colorless, but may be made in a variety of different colors. It should not be confused with zircon, which is a zirco ...
is the most common. The gemstone moissanite
Moissanite () is naturally occurring silicon carbide and its various crystalline polymorphs. It has the chemical formula SiC and is a rare mineral, discovered by the French chemist Henri Moissan in 1893. Silicon carbide is useful for commercial ...
(silicon carbide) can be treated as a diamond simulant, though more costly to produce than cubic zirconia. Both are produced synthetically.
Enhancements
Diamond enhancements are specific treatments performed on natural or synthetic diamonds (usually those already cut and polished into a gem), which are designed to better the gemological characteristics of the stone in one or more ways. These include laser drilling to remove inclusions, application of sealants to fill cracks, treatments to improve a white diamond's color grade, and treatments to give fancy color to a white diamond. Coatings are increasingly used to give a diamond simulant such as cubic zirconia a more "diamond-like" appearance. One such substance is diamond-like carbon—an amorphous carbonaceous material that has some physical properties similar to those of the diamond. Advertising suggests that such a coating would transfer some of these diamond-like properties to the coated stone, hence enhancing the diamond simulant. Techniques such as Raman spectroscopy should easily identify such a treatment.Identification
Early diamond identification tests included a scratch test relying on the superior hardness of diamond. This test is destructive, as a diamond can scratch another diamond, and is rarely used nowadays. Instead, diamond identification relies on its superior thermal conductivity. Electronic thermal probes are widely used in the gemological centers to separate diamonds from their imitations. These probes consist of a pair of battery-poweredthermistor
A thermistor is a type of resistor whose resistance is strongly dependent on temperature, more so than in standard resistors. The word thermistor is a portmanteau of ''thermal'' and ''resistor''.
Thermistors are divided based on their conduction ...
s mounted in a fine copper tip. One thermistor functions as a heating device while the other measures the temperature of the copper tip: if the stone being tested is a diamond, it will conduct the tip's thermal energy rapidly enough to produce a measurable temperature drop. This test takes about two to three seconds.
Whereas the thermal probe can separate diamonds from most of their simulants, distinguishing between various types of diamond, for example synthetic or natural, irradiated or non-irradiated, etc., requires more advanced, optical techniques. Those techniques are also used for some diamonds simulants, such as silicon carbide, which pass the thermal conductivity test. Optical techniques can distinguish between natural diamonds and synthetic diamonds. They can also identify the vast majority of treated natural diamonds. "Perfect" crystals (at the atomic lattice level) have never been found, so both natural and synthetic diamonds always possess characteristic imperfections, arising from the circumstances of their crystal growth, that allow them to be distinguished from each other.
Laboratories use techniques such as spectroscopy, microscopy, and luminescence under shortwave ultraviolet light to determine a diamond's origin. They also use specially made instruments to aid them in the identification process. Two screening instruments are the ''DiamondSure'' and the ''DiamondView'', both produced by the DTC and marketed by the GIA.
Several methods for identifying synthetic diamonds can be performed, depending on the method of production and the color of the diamond. CVD diamonds can usually be identified by an orange fluorescence. D-J colored diamonds can be screened through the Swiss Gemmological Institute's Diamond Spotter. Stones in the D-Z color range can be examined through the DiamondSure UV/visible spectrometer, a tool developed by De Beers. Similarly, natural diamonds usually have minor imperfections and flaws, such as inclusions of foreign material, that are not seen in synthetic diamonds.
Screening devices based on diamond type detection can be used to make a distinction between diamonds that are certainly natural and diamonds that are potentially synthetic. Those potentially synthetic diamonds require more investigation in a specialized lab. Examples of commercial screening devices are D-Screen (WTOCD / HRD Antwerp), Alpha Diamond Analyzer (Bruker / HRD Antwerp), and D-Secure (DRC Techno).
Etymology, earliest use and composition discovery
The name ''diamond'' is derived from grc, ἀδάμας (''adámas''), 'proper, unalterable, unbreakable, untamed', from ἀ- (''a-''), 'not' + grc, δαμάω (''damáō''), 'to overpower, tame'. Diamonds are thought to have been first recognized and mined inIndia
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
, where significant alluvial deposit
Alluvium (from Latin ''alluvius'', from ''alluere'' 'to wash against') is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. Alluv ...
s of the stone could be found many centuries ago along the rivers Penner, Krishna
Krishna (; sa, कृष्ण ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme god in his own right. He is the god of protection, compassion, tenderness, and love; and is one ...
, and Godavari
The Godavari (IAST: ''Godāvarī'' �od̪aːʋəɾiː is India's second longest river after the Ganga river and drains into the third largest basin in India, covering about 10% of India's total geographical area. Its source is in Trimbakeshwa ...
. Diamonds have been known in India for at least 3,000years but most likely 6,000years.
Diamonds have been treasured as gemstones since their use as religious icons
An icon () is a religious work of art, most commonly a painting, in the cultures of the Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox, and Catholic churches. They are not simply artworks; "an icon is a sacred image used in religious devotion". The most c ...
in ancient India
According to consensus in modern genetics, anatomically modern humans first arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa between 73,000 and 55,000 years ago. Quote: "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by m ...
. Their usage in engraving tools also dates to early human history
Human history, also called world history, is the narrative of humanity's past. It is understood and studied through anthropology, archaeology, genetics, and linguistics. Since the invention of writing, human history has been studied throug ...
. The popularity of diamonds has risen since the 19th century because of increased supply, improved cutting and polishing techniques, growth in the world economy, and innovative and successful advertising campaigns.
In 1772, the French scientist Antoine Lavoisier
Antoine-Laurent de Lavoisier ( , ; ; 26 August 17438 May 1794),
CNRS (
Properties of diamond: Ioffe database
* (2007) Gemological Institute of America (GIA) * Tyson, Peter (November 2000)
Retrieved March 10, 2005.
Have You Ever Tried to Sell a Diamond?
{{Authority control Abrasives Articles containing video clips Crystals Cubic minerals Economic geology Group IV semiconductors Impact event minerals Industrial minerals Luminescent minerals Minerals in space group 227 Native element minerals Transparent materials
CNRS (
oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as ...
, and showed that the only product of the combustion was carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is trans ...
, proving that diamond is composed of carbon. Later in 1797, the English chemist Smithson Tennant
Smithson Tennant FRS (30 November 1761 – 22 February 1815) was an English chemist. He is best known for his discovery of the elements iridium and osmium, which he found in the residues from the solution of platinum ores in 1803. He also con ...
repeated and expanded that experiment. By demonstrating that burning diamond and graphite releases the same amount of gas, he established the chemical equivalence of these substances.
See also
* Deep carbon cycle *Diamondoid In chemistry, diamondoids are variants of the carbon cage molecule known as adamantane (C10H16), the smallest unit cage structure of the diamond crystal lattice. Diamondoids also known as nanodiamonds or condensed adamantanes may include one or more ...
* List of diamonds
Diamonds become famous typically for some combination of their size, color and quality. Diamonds occur naturally in many different colors, so the largest diamond of a particular color may not be large in absolute terms, but it may still be consid ...
** List of largest rough diamonds
This is a partial list of the largest non-synthetic diamonds with a rough stone (uncut) weight of over 200 carats (40 grams). The list is not intended to be complete – e.g., the Cullinan (formerly Premier) mine alone has produced 135 diamond ...
* List of minerals
This is a list of minerals for which there are articles on Wikipedia.
Minerals are distinguished by various chemical and physical properties. Differences in chemical composition and crystal structure distinguish the various ''species''. Within a m ...
* Superhard material
A superhard material is a material with a hardness value exceeding 40 gigapascals (GPa) when measured by the Vickers hardness test. They are virtually incompressible solids with high electron density and high bond covalency. As a result of their ...
References
Books
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Properties of diamond: Ioffe database
* (2007) Gemological Institute of America (GIA) * Tyson, Peter (November 2000)
Retrieved March 10, 2005.
Have You Ever Tried to Sell a Diamond?
{{Authority control Abrasives Articles containing video clips Crystals Cubic minerals Economic geology Group IV semiconductors Impact event minerals Industrial minerals Luminescent minerals Minerals in space group 227 Native element minerals Transparent materials