|
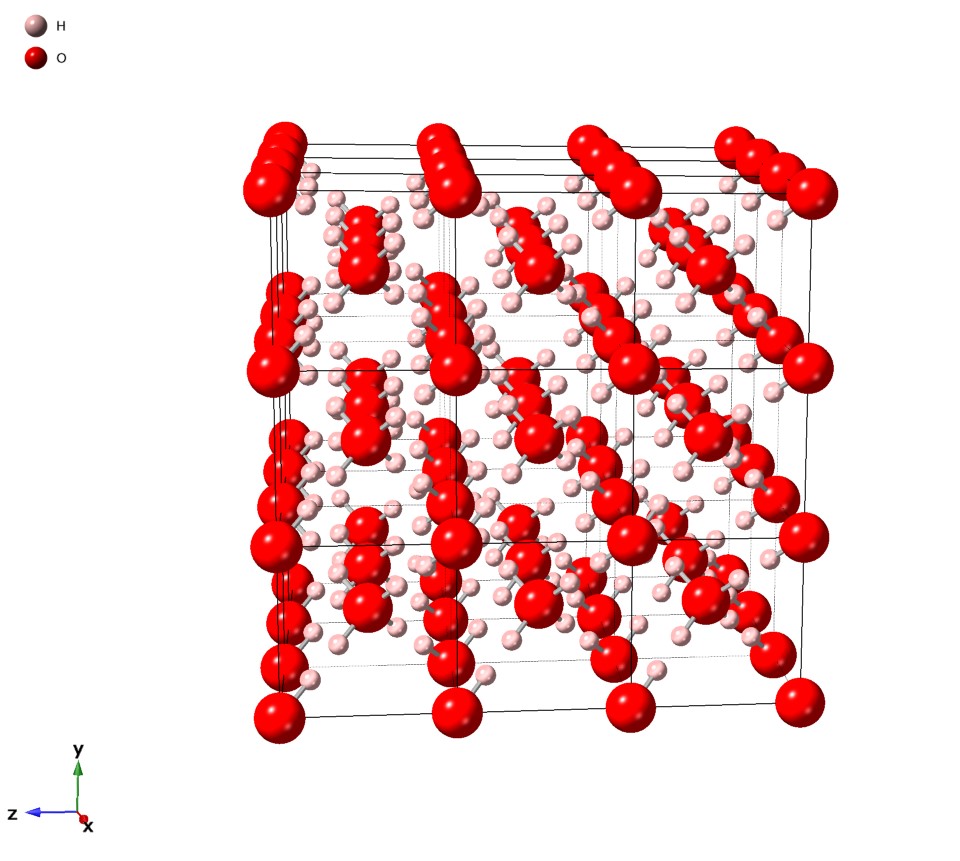
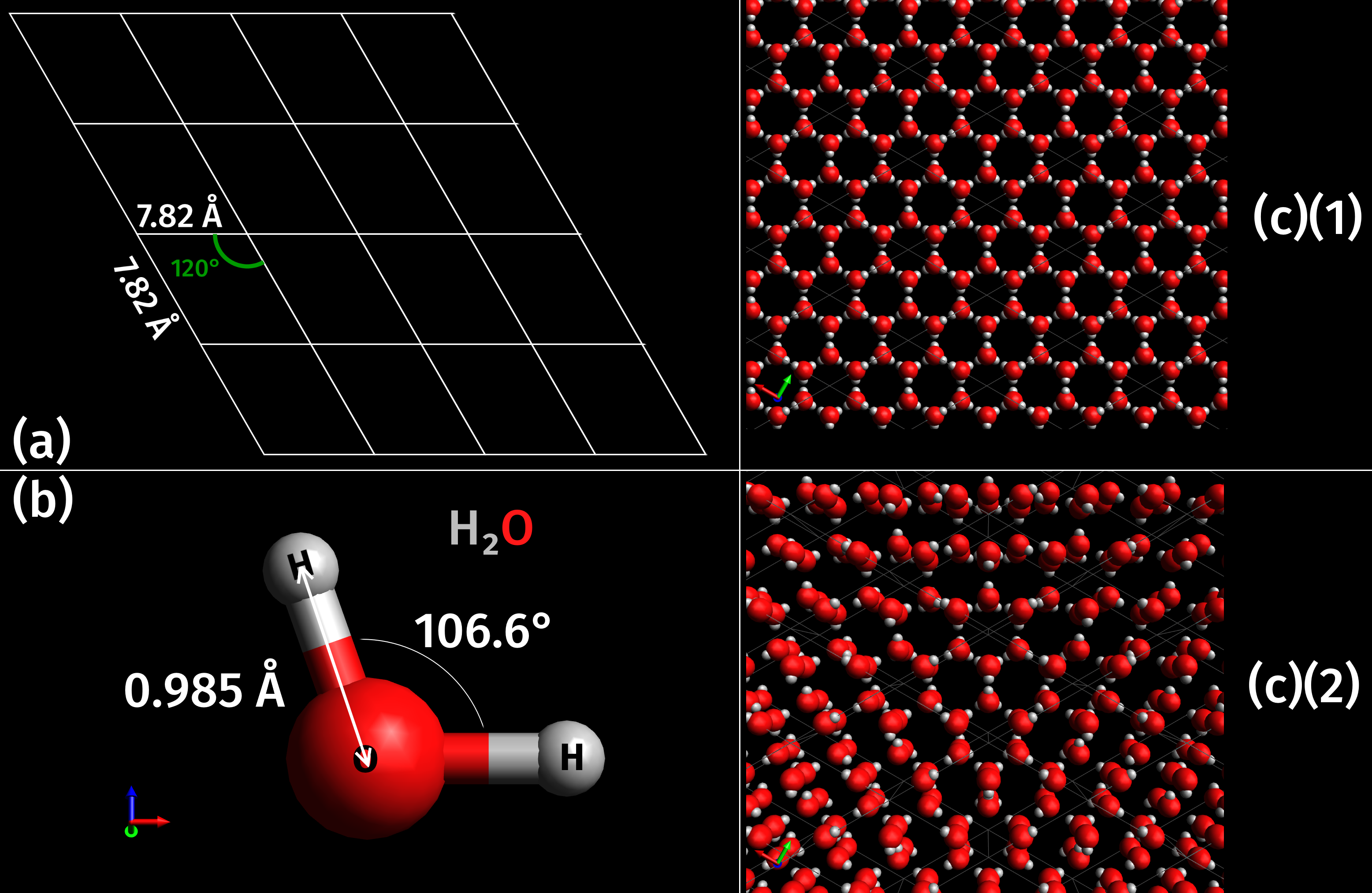
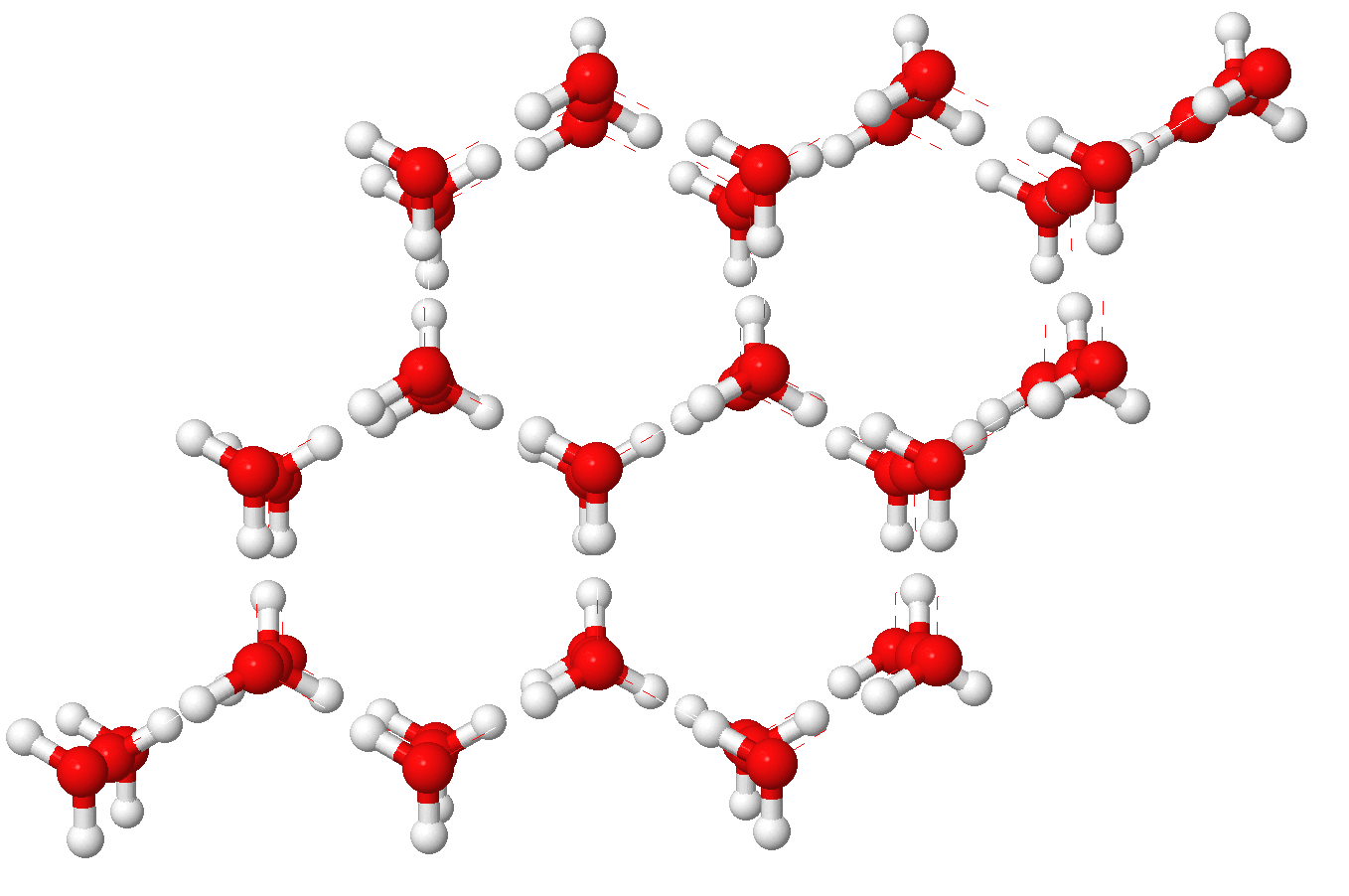
Ice VII
Ice VII is a cubic crystalline form of ice. It can be formed from liquid water above 3 Pascal (unit), GPa (30,000 atmospheres) by lowering its temperature to room temperature, or by decompressing heavy water (D2O) Ice#Phases, ice VI below 95 K. (Different types of ice, from ice II to Superionic water, ice XVIII, have been created in the laboratory at different temperatures and pressures. Ordinary water ice is known as ice Ih, ice Ih in the Percy Williams Bridgman, Bridgman nomenclature.) Ice VII is metastable over a wide range of temperatures and pressures and transforms into low-density amorphous ice (LDA) above . Ice VII has a triple point with liquid water and ice VI at 355 K and 2.216 GPa, with the melt line extending to at least and 10 GPa. Ice VII can be formed within nanoseconds by rapid compression via shock-waves. It can also be created by increasing the pressure on ice VI at ambient temperature. At around 5 GPa, Ice VII becomes the tetragonal Ice VIIt. Like the major ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice VII Crystal Structure
Ice is water frozen into a solid state, typically forming at or below temperatures of 0 degrees Celsius or Depending on the presence of impurities such as particles of soil or bubbles of air, it can appear transparent or a more or less opaque bluish-white color. In the Solar System, ice is abundant and occurs naturally from as close to the Sun as Mercury to as far away as the Oort cloud objects. Beyond the Solar System, it occurs as interstellar ice. It is abundant on Earth's surfaceparticularly in the polar regions and above the snow lineand, as a common form of precipitation and deposition, plays a key role in Earth's water cycle and climate. It falls as snowflakes and hail or occurs as frost, icicles or ice spikes and aggregates from snow as glaciers and ice sheets. Ice exhibits at least eighteen phases ( packing geometries), depending on temperature and pressure. When water is cooled rapidly (quenching), up to three types of amorphous ice can form depending on its hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice XI
Ice XI is the hydrogen-ordered form of Ih, the ordinary form of ice. Different phases of ice, from ice II to ice XVIII, have been created in the laboratory at different temperatures and pressures. The total internal energy of ice XI is about one sixth lower than ice Ih, so in principle it should naturally form when ice Ih is cooled to below 72 K. The low temperature required to achieve this transition is correlated with the relatively low energy difference between the two structures. Water molecules in ice Ih are surrounded by four semi-randomly directed hydrogen bonds. Such arrangements should change to the more ordered arrangement of hydrogen bonds found in ice XI at low temperatures, so long as localized proton hopping is sufficiently enabled; a process that becomes easier with increasing pressure. Correspondingly, ice XI is believed to have a triple point with hexagonal ice and gaseous water at (~72 K, ~0 Pa). Properties Ice XI has an orthorhombic structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
, California. The network was established in 2015 within a former independent division of known as Discovery Digital Networks. Seeker produces online video and editorial content for the digital media landscape, with an emphasis on social platforms and .
History Seeker was relaunched in May 2016 in an effort by[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mantle (geology)
A mantle is a layer inside a planetary body bounded below by a core and above by a crust. Mantles are made of rock or ices, and are generally the largest and most massive layer of the planetary body. Mantles are characteristic of planetary bodies that have undergone differentiation by density. All terrestrial planets (including Earth), a number of asteroids, and some planetary moons have mantles. Earth's mantle The Earth's mantle is a layer of silicate rock between the crust and the outer core. Its mass of 4.01 × 1024 kg is 67% the mass of the Earth. It has a thickness of making up about 84% of Earth's volume. It is predominantly solid, but in geological time it behaves as a viscous fluid. Partial melting of the mantle at mid-ocean ridges produces oceanic crust, and partial melting of the mantle at subduction zones produces continental crust. Other planetary mantles Mercury has a silicate mantle approximately thick, constituting only 28% ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2011): Minerals'; p. 1. In the series ''Geology: Landforms, Minerals, and Rocks''. Rosen Publishing Group. The geological definition of mineral normally excludes compounds that occur only in living organisms. However, some minerals are often biogenic (such as calcite) or are organic compounds in the sense of chemistry (such as mellite). Moreover, living organisms often synthesize inorganic minerals (such as hydroxylapatite) that also occur in rocks. The concept of mineral is distinct from rock, which is any bulk solid geologic material that is relatively homogeneous at a large enough scale. A rock may consist of one type of mineral, or may be an aggregate of two or more different types of minerals, spacially segregated into disti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Mineralogical Association
Founded in 1958, the International Mineralogical Association (IMA) is an international group of 40 national societies. The goal is to promote the science of mineralogy and to standardize the nomenclature of the 5000 plus known mineral species. The IMA is affiliated with the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS). The Association supports the activities of Commissions and Working Groups involved on certain aspects of mineralogical practice and facilitates interactions among mineralogists by sponsoring and organising meetings. In particular, the IMA holds its general meeting every four years. The next meeting is scheduled in 2022 in Lyon, France. Presidents The presidents of the IMA have been: * since 2021: Anhuai Lu ** Peking University *2018–2020: Patrick Cordier (born 1961) ** Université de Lille *2016–2018: Peter C. Burns ** University of Notre Dame *2014–2016: Sergey V. Krivovichev (born 1972) ** Saint Petersburg State University *2012–2014: Walter V. Mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diamonds
Diamond is a solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Another solid form of carbon known as graphite is the chemically stable form of carbon at room temperature and pressure, but diamond is metastable and converts to it at a negligible rate under those conditions. Diamond has the highest hardness and thermal conductivity of any natural material, properties that are used in major industrial applications such as cutting and polishing tools. They are also the reason that diamond anvil cells can subject materials to pressures found deep in the Earth. Because the arrangement of atoms in diamond is extremely rigid, few types of impurity can contaminate it (two exceptions are boron and nitrogen). Small numbers of defects or impurities (about one per million of lattice atoms) color diamond blue (boron), yellow (nitrogen), brown (defects), green (radiation exposure), purple, pink, orange, or red. Diamond also has a v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inclusion (mineral)
In mineralogy, an inclusion is any material that is trapped inside a mineral during its formation. In gemology, an inclusion is a characteristic enclosed within a gemstone, or reaching its surface from the interior. According to Hutton's law of inclusions, fragments included in a host rock are older than the host rock itself. Mineralogy Inclusions are usually other minerals or rocks, but may also be water, gas or petroleum. Liquid or vapor inclusions are known as fluid inclusions. In the case of amber it is possible to find insects and plants as inclusions. The analysis of atmospheric gas bubbles as inclusions in ice cores is an important tool in the study of climate change. A xenolith is a pre-existing rock which has been picked up by a lava flow. Melt inclusions form when bits of melt become trapped inside crystals as they form in the melt. Gemology Inclusions are one of the most important factors when it comes to gem valuation. In many gemstones, such as di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gliese 1214 B
Gliese 1214 b (often shortened to GJ 1214 b) is an exoplanet that orbits the star Gliese 1214, and was discovered in December 2009. Its parent star is 48 light-years from the Sun, in the constellation Ophiuchus. As of 2017, GJ 1214 b is the most likely known candidate for being an ocean planet. For that reason, scientists have nicknamed the planet "the waterworld". It is a super-Earth, meaning it is larger than Earth but is significantly smaller (in mass and radius) than the gas giants of the Solar System. After CoRoT-7b, it was the second super-Earth to have both its mass and radius measured and is the first of a new class of planets with small size and relatively low density. GJ 1214 b is also significant because its parent star is relatively near the Sun and because it transits (crosses in front of) that parent star, which allows the planet's atmosphere to be studied using spectroscopic methods. In December 2013, NASA reported that clouds may have been detected in the atmosp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gliese 436 B
Gliese 436 b (sometimes called GJ 436 b) is a Neptune-sized exoplanet orbiting the red dwarf Gliese 436. It was the first hot Neptune discovered with certainty (in 2007) and was among the smallest-known transiting planets in mass and radius, until the much smaller Kepler exoplanet discoveries began circa 2010. In December 2013, NASA reported that clouds may have been detected in the atmosphere of GJ 436 b. In August 2022, this planet and its host star were included among 20 systems to be named by the third NameExoWorlds project. Discovery Gliese 436 b was discovered in August 2004 by R. Paul Butler and Geoffrey Marcy of the Carnegie Institute of Washington and University of California, Berkeley, respectively, using the radial velocity method. Together with 55 Cancri e, it was the first of a new class of planets with a minimum mass (M sin''i'') different to Neptune. The planet was recorded to transit its star by an automatic process at NMSU on January&nb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exoplanet
An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first possible evidence of an exoplanet was noted in 1917 but was not recognized as such. The first confirmation of detection occurred in 1992. A different planet, initially detected in 1988, was confirmed in 2003. There are many methods of detecting exoplanets. Transit photometry and Doppler spectroscopy have found the most, but these methods suffer from a clear observational bias favoring the detection of planets near the star; thus, 85% of the exoplanets detected are inside the tidal locking zone. In several cases, multiple planets have been observed around a star. About 1 in 5 Sun-like starsFor the purpose of this 1 in 5 statistic, "Sun-like" means G-type star. Data for Sun-like stars was not available so this statistic is an extrapolation from data about K-type stars. have an "Earth-sized"For the purpose of this 1 in 5 statistic, Earth-sized means 1–2 Earth radii. planet in the habitable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europa (moon)
Europa , or Jupiter II, is the smallest of the four Galilean moons orbiting Jupiter, and the sixth-closest to the planet of all the 80 known moons of Jupiter. It is also the sixth-largest moon in the Solar System. Europa was discovered in 1610 by Galileo Galilei and was named after Europa, the Phoenician mother of King Minos of Crete and lover of Zeus (the Greek equivalent of the Roman god Jupiter). Slightly smaller than Earth's Moon, Europa is primarily made of silicate rock and has a water-ice crust and probably an iron–nickel core. It has a very thin atmosphere, composed primarily of oxygen. Its white- beige surface is striated by light tan cracks and streaks, but craters are relatively few. In addition to Earth-bound telescope observations, Europa has been examined by a succession of space-probe flybys, the first occurring in the early 1970s. In September 2022, the ''Juno'' spacecraft flew within about 200 miles of Europa for a more recent close-up view. Europa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |