|
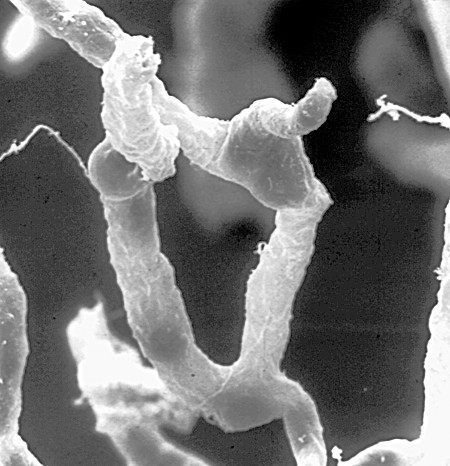
Nanodiamond
Nanodiamonds, or diamond nanoparticles, are diamonds with a size below 100 nanometers. They can be produced by impact events such as an explosion or meteoritic impacts. Because of their inexpensive, large-scale synthesis, potential for surface functionalization, and high biocompatibility, nanodiamonds are widely investigated as a potential material in biological and electronic applications and quantum engineering. History In 1963, Soviet scientists at the All-Union Research Institute of Technical Physics noticed that nanodiamonds were created by nuclear explosions that used carbon-based trigger explosives. Structure and composition There are three main aspects in the structure of diamond nanoparticles to be considered: the overall shape, the core, and the surface. Through multiple diffraction experiments, it has been determined that the overall shape of diamond nanoparticles is either spherical or elliptical. At the core of diamond nanoparticles lies a diamond cage, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
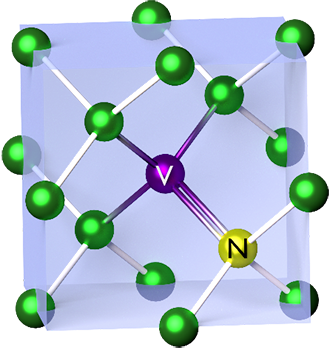
Nitrogen-Vacancy Center
The nitrogen-vacancy center (N-V center or NV center) is one of numerous point defects in diamond. Its most explored and useful property is its photoluminescence, which allows observers to read out its spin-state. The NV center's electron spin, localized at atomic scales, can be manipulated at room temperature by external factors such as magnetic, or electric fields, microwave radiation, or light, resulting in sharp resonances in the intensity of the photoluminescence. These resonances can be explained in terms of electron spin related phenomena such as quantum entanglement, spin–orbit interaction and Rabi oscillations, and analysed using advanced quantum optics theory. An individual NV center can be used as a basic unit for a quantum computer, a qubit, and used for quantum cryptography. Further potential applications in novel fields of electronics and sensing include spintronics, masers, and quantum sensors. If the charge is not specified the term "NV center" refers to the negat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diamond
Diamond is a solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Another solid form of carbon known as graphite is the chemically stable form of carbon at room temperature and pressure, but diamond is metastable and converts to it at a negligible rate under those conditions. Diamond has the highest hardness and thermal conductivity of any natural material, properties that are used in major industrial applications such as cutting and polishing tools. They are also the reason that diamond anvil cells can subject materials to pressures found deep in the Earth. Because the arrangement of atoms in diamond is extremely rigid, few types of impurity can contaminate it (two exceptions are boron and nitrogen). Small numbers of defects or impurities (about one per million of lattice atoms) color diamond blue (boron), yellow (nitrogen), brown (defects), green (radiation exposure), purple, pink, orange, or red. Diamond also has a ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paola Cappellaro
Paola Cappellaro is an Italian-American engineer who is a Professor of Nuclear Science and Engineering at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Her research considers electron-spin resonance, nuclear magnetic resonance and quantum information processing. She leads the MIT Quantum Engineering Group at the Center for Ultracold Atoms. Early life and education Cappellaro was born in Italy. She attended the Polytechnic University of Milan, where she majored in nuclear engineering. She was part of a joint Master's program with the École Centrale Paris, and graduated in 2000. Cappellaro moved to the United States for her graduate studies, where she worked alongside David G. Cory on quantum computation. In 2006, Cappellaro earned her doctorate at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Her doctorate considered quantum state transfer in spin chains, making use of magnetic-based approaches to understand and explore spin transfer dynamics. She completed her postdoctoral trai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteins
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doxorubicin
Doxorubicin, sold under the brand name Adriamycin among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat cancer. This includes breast cancer, bladder cancer, Kaposi's sarcoma, lymphoma, and acute lymphocytic leukemia. It is often used together with other chemotherapy agents. Doxorubicin is given by injection into a vein. Common side effects include hair loss, bone marrow suppression, vomiting, rash, and inflammation of the mouth. Other serious side effects may include allergic reactions such as anaphylaxis, heart damage, tissue damage at the site of injection, radiation recall, and treatment-related leukemia. People often experience red discoloration of the urine for a few days. Doxorubicin is in the anthracycline and antitumor antibiotic family of medications. It works in part by interfering with the function of DNA. Doxorubicin was approved for medical use in the United States in 1974. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Versi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood–brain Barrier
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective semipermeable border of endothelial cells that prevents solutes in the circulating blood from ''non-selectively'' crossing into the extracellular fluid of the central nervous system where neurons reside. The blood–brain barrier is formed by endothelial cells of the capillary wall, astrocyte end-feet ensheathing the capillary, and pericytes embedded in the capillary basement membrane. This system allows the passage of some small molecules by passive diffusion, as well as the selective and active transport of various nutrients, ions, organic anions, and macromolecules such as glucose and amino acids that are crucial to neural function. The blood–brain barrier restricts the passage of pathogens, the diffusion of solutes in the blood, and large or hydrophilic molecules into the cerebrospinal fluid, while allowing the diffusion of hydrophobic molecules (O2, CO2, hormones) and small non-polar molecules. Cells of the barrier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Chemistry
Surface science is the study of physical and chemical phenomena that occur at the interface of two phases, including solid–liquid interfaces, solid– gas interfaces, solid–vacuum interfaces, and liquid– gas interfaces. It includes the fields of '' surface chemistry'' and ''surface physics''. Some related practical applications are classed as surface engineering. The science encompasses concepts such as heterogeneous catalysis, semiconductor device fabrication, fuel cells, self-assembled monolayers, and adhesives. Surface science is closely related to interface and colloid science. Interfacial chemistry and physics are common subjects for both. The methods are different. In addition, interface and colloid science studies macroscopic phenomena that occur in heterogeneous systems due to peculiarities of interfaces. History The field of surface chemistry started with heterogeneous catalysis pioneered by Paul Sabatier on hydrogenation and Fritz Haber on the Haber process. Ir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinetics (chemistry)
Chemical kinetics, also known as reaction kinetics, is the branch of physical chemistry that is concerned with understanding the rates of chemical reactions. It is to be contrasted with chemical thermodynamics, which deals with the direction in which a reaction occurs but in itself tells nothing about its rate. Chemical kinetics includes investigations of how experimental conditions influence the speed of a chemical reaction and yield information about the reaction's mechanism and transition states, as well as the construction of mathematical models that also can describe the characteristics of a chemical reaction. History In 1864, Peter Waage and Cato Guldberg pioneered the development of chemical kinetics by formulating the law of mass action, which states that the speed of a chemical reaction is proportional to the quantity of the reacting substances.C.M. Guldberg and P. Waage,"Studies Concerning Affinity" ''Forhandlinger i Videnskabs-Selskabet i Christiania'' (1864), 35P. W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is a branch of physics that deals with heat, work, and temperature, and their relation to energy, entropy, and the physical properties of matter and radiation. The behavior of these quantities is governed by the four laws of thermodynamics which convey a quantitative description using measurable macroscopic physical quantities, but may be explained in terms of microscopic constituents by statistical mechanics. Thermodynamics applies to a wide variety of topics in science and engineering, especially physical chemistry, biochemistry, chemical engineering and mechanical engineering, but also in other complex fields such as meteorology. Historically, thermodynamics developed out of a desire to increase the efficiency of early steam engines, particularly through the work of French physicist Sadi Carnot (1824) who believed that engine efficiency was the key that could help France win the Napoleonic Wars. Scots-Irish physicist Lord Kelvin was the first to formula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drug Delivery
Drug delivery refers to approaches, formulations, manufacturing techniques, storage systems, and technologies involved in transporting a pharmaceutical compound to its target site to achieve a desired therapeutic effect. Principles related to drug preparation, route of administration, site-specific targeting, metabolism, and toxicity are used to optimize efficacy and safety, and to improve patient convenience and compliance. Drug delivery is aimed at altering a drug's pharmacokinetics and specificity by formulating it with different excipients, drug carriers, and medical devices. There is additional emphasis on increasing the bioavailability and duration of action of a drug to improve therapeutic outcomes. Some research has also been focused on improving safety for the person administering the medication. For example, several types of microneedle patches have been developed for administering vaccines and other medications to reduce the risk of needlestick injury. Drug deli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |