|
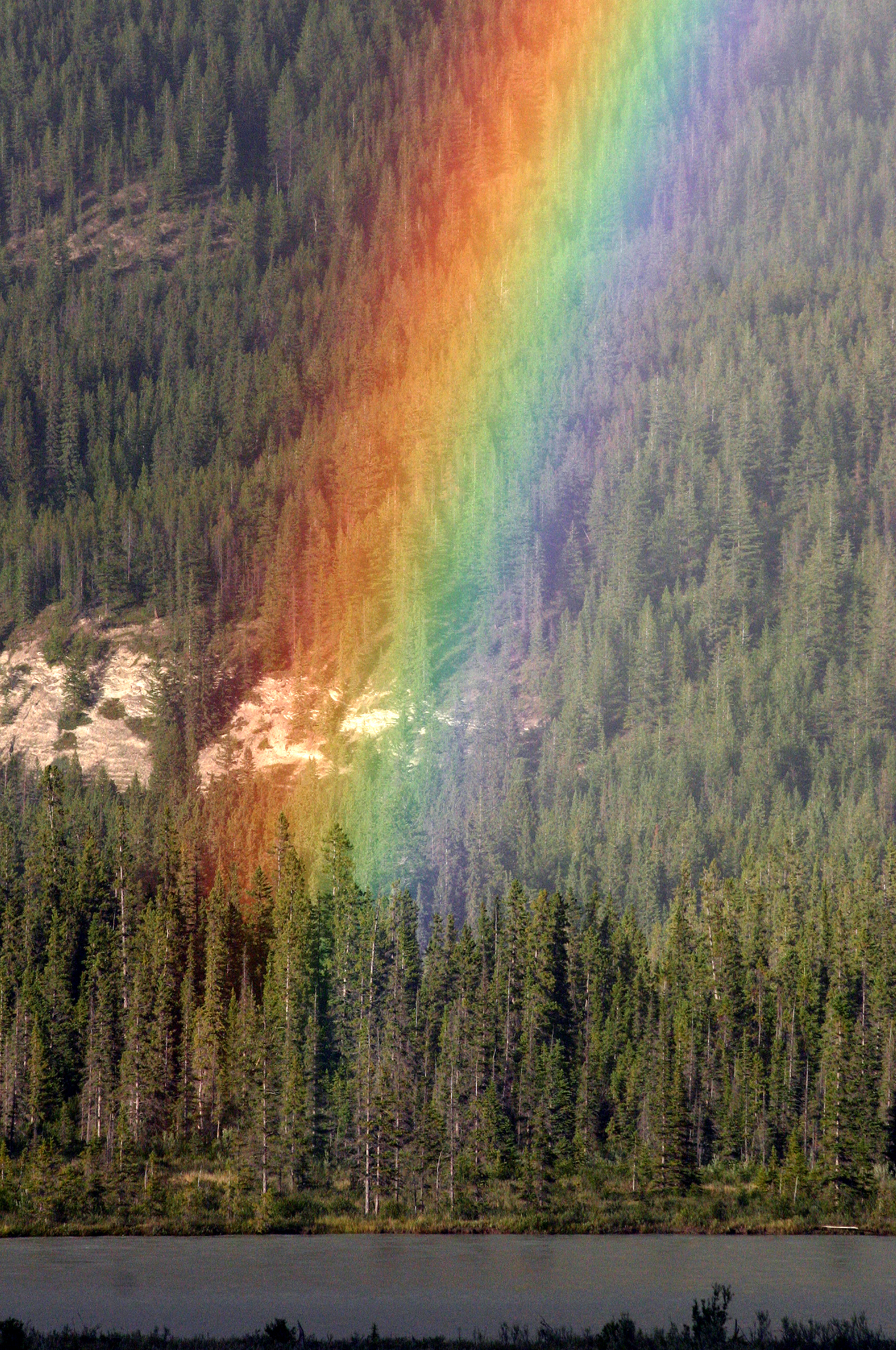
Spectral Color
A spectral color is a color that is evoked by ''monochromatic light'', i.e. either a single wavelength of light in the visible spectrum, or by a relatively narrow band of wavelengths (e.g. lasers). Every wavelength of visible light is perceived as a spectral color; when viewed as a continuous spectrum, these colors are seen as the familiar rainbow. All colors that do not qualify as a spectral color are called ''non-spectral colors'' or ''extra-spectral colors''. Extra-spectral colors cannot be evoked with a single wavelength of light, but rather by a combination of wavelengths. Likewise, light comprising several wavelengths cannot evoke a spectral color. In color spaces In color spaces which include all, or most spectral colors, they form a part of boundary of the set of all real colors. When considering a three-dimensional color space (which including luminance), the spectral colors form a surface. When excluding luminance and considering a two-dimensional color space (c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Color
A set (mathematics), set of primary colors or primary colours (see American and British English spelling differences#-our, -or, spelling differences) consists of colorants or colored lights that can be mixed in varying amounts to produce a gamut of colors. This is the essential method used to create the perception of a broad range of colors in, e.g., electronic displays, color printing, and paintings. Perceptions associated with a given combination of primary colors can be predicted by an appropriate mixing model (e.g., additive mixing, additive, subtractive mixing, subtractive) that reflects the physics of how light interacts with physical media, and ultimately the retina. Primary colors can also be conceptual (not necessarily real), either as additive mathematical elements of a color space or as irreducible phenomenological categories in domains such as psychology and Philosophy of color, philosophy. Color space primaries are precisely defined and empirically rooted in psychop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helmholtz–Kohlrausch Effect
The Helmholtz–Kohlrausch effect (after Hermann von Helmholtz and V. A. Kohlrausch) is a perceptual phenomenon wherein the intense saturation of spectral hue is perceived as part of the color's luminance. This brightness increase by saturation, which grows stronger as saturation increases, might better be called chromatic luminance, since "white" or achromatic luminance is the standard of comparison. It appears in both self-luminous and surface colors, although it is most pronounced in spectral lights. Lightness Even when they have the same luminance, colored lights seem brighter to human observers than white light does. The way humans perceive the brightness of the lights is different for everyone. When the colors are more saturated, our eyes interpret it as the color's luminance and chroma. This makes us believe that the colors are actually brighter. An exception to this is when the human observer is red-green colorblind, they cannot distinguish the differences between the ligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CIELUV
In colorimetry, the CIE 1976 ''L''*, ''u''*, ''v''* color space, commonly known by its abbreviation CIELUV, is a color space adopted by the International Commission on Illumination (CIE) in 1976, as a simple-to-compute transformation of the 1931 CIE XYZ color space, but which attempted perceptual uniformity. It is extensively used for applications such as computer graphics which deal with colored lights. Although additive mixtures of different colored lights will fall on a line in CIELUV's uniform chromaticity diagram (called the ''CIE 1976 UCS''), such additive mixtures will not, contrary to popular belief, fall along a line in the CIELUV color space unless the mixtures are constant in lightness. Historical background CIELUV is an Adams chromatic valence color space and is an update of the CIE 1964 (''U''*, ''V''*, ''W''*) color space (CIEUVW). The differences include a slightly modified lightness scale and a modified uniform chromaticity scale, in which one of the coordinate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamut
In color reproduction, including computer graphics and photography, the gamut, or color gamut , is a certain ''complete subset'' of colors. The most common usage refers to the subset of colors which can be accurately represented in a given circumstance, such as within a given color space or by a certain output device. Another sense, less frequently used but still correct, refers to the complete set of colors found within an image at a given time. In this context, digitizing a photograph, converting a digitized image to a different color space, or outputting it to a given medium using a certain output device generally alters its gamut, in the sense that some of the colors in the original are lost in the process. Introduction The term ''gamut'' was adopted from the field of music, where in middle age Latin "gamut" meant the entire range of musical notes of which musical melodies are composed; Shakespeare's use of the term in ''The Taming of the Shrew'' is sometimes attributed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HSL And HSV
HSL (for hue, saturation, lightness) and HSV (for hue, saturation, value; also known as HSB, for hue, saturation, brightness) are alternative representations of the RGB color model, RGB color model, designed in the 1970s by computer graphics researchers to more closely align with the way human vision perceives color-making attributes. In these models, colors of each ''hue'' are arranged in a radial slice, around a central axis of neutral colors which ranges from black at the bottom to white at the top. The HSL representation models the way different paints mix together to create color in the real world, with the ''lightness'' dimension resembling the varying amounts of black or white paint in the mixture (e.g. to create "light red", a red pigment can be mixed with white paint; this white paint corresponds to a high "lightness" value in the HSL representation). Fully saturated colors are placed around a circle at a lightness value of ½, with a lightness value of 0 or 1 correspon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Model
A color model is an abstract mathematical model describing the way colors can be represented as tuples of numbers, typically as three or four values or color components. When this model is associated with a precise description of how the components are to be interpreted (viewing conditions, etc.), taking account of visual perception, the resulting set of colors is called "color space." This article describes ways in which human color vision can be modeled, and discusses some of the models in common use. Tristimulus color space One can picture this space as a region in three-dimensional Euclidean space if one identifies the ''x'', ''y'', and ''z'' axes with the stimuli for the long-wavelength (''L''), medium-wavelength (''M''), and short-wavelength (''S'') light receptors. The origin, (''S'',''M'',''L'') = (0,0,0), corresponds to black. White has no definite position in this diagram; rather it is defined according to the color temperature or white balance as desired or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ProPhoto RGB Color Space
The ProPhoto RGB color space, also known as ROMM RGB (Reference Output Medium Metric), is an output referred RGB color space developed by Kodak. It offers an especially large gamut designed for use with photographic output in mind. The ProPhoto RGB color space encompasses over 90% of possible surface colors in the CIE L*a*b* color space, and 100% of likely occurring real-world surface colors documented by Michael Pointer in 1980, making ProPhoto even larger than the Wide-gamut RGB color space. The ProPhoto RGB primaries were also chosen in order to minimize hue rotations associated with non-linear tone scale operations. One of the downsides to this color space is that approximately 13% of the representable colors are imaginary colors that do not exist and are not visible colors. When working in color spaces with such a large gamut, it is recommended to work in 16-bit color depth to avoid posterization effects. This will occur more frequently in 8-bit modes as the gradient step ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pantone Matching System
Pantone LLC (stylized as PANTONE) is a limited liability company headquartered in Carlstadt, New Jersey. The company is best known for its Pantone Matching System (PMS), a proprietary color space used in a variety of industries, notably graphic design, fashion design, product design, printing and manufacturing and supporting the management of color from design to production, in physical and digital formats, among coated and uncoated materials, cotton, polyester, nylon and plastics. X-Rite, a supplier of color measurement instruments and software, purchased Pantone for US$180 million in October 2007, and was itself acquired by Danaher Corporation in 2012. Overview Pantone began in New Jersey in the 1950s as the commercial printing company of brothers Mervin and Jesse Levine, M & J Levine Advertising. In 1956, its founders, both advertising executives, hired recent Hofstra University graduate Lawrence Herbert as a part-time employee. Herbert used his chemistry knowledge to systema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Science
Color science is the scientific study of color including lighting and optics; measurement of light and color; the physiology, psychophysics, and modeling of color vision; and color reproduction. History Organizations * International Commission on Illumination (CIE) * Illuminating Engineering Society (IES) * Inter-Society Color Council (ISCC) * Society for Imaging Science and Technology (IS&T) * International Colour Association (AIC) * Optica, formerly the Optical Society of America (OSA) * The Colour Group * Society of Dyers and Colourists (SDC) * American Association of Textile Chemists and Colorists (AATCC) * Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology (ARVO) * ACM SIGGRAPH * Vision Sciences Society (VSS) * Council for Optical Radiation Measurements (CORM) Journals The preeminent scholarly journal publishing research papers in color science is '' Color Research and Application'', started in 1975 by founding editor-in-chief Fred Billmeyer, along with Gunte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around 1 millimeter (300 GHz) to the nominal red edge of the visible spectrum, around 700 nanometers (430 THz). Longer IR wavelengths (30 μm-100 μm) are sometimes included as part of the terahertz radiation range. Almost all black-body radiation from objects near room temperature is at infrared wavelengths. As a form of electromagnetic radiation, IR propagates energy and momentum, exerts radiation pressure, and has properties corresponding to both those of a wave and of a particle, the photon. It was long known that fires emit invisible heat; in 1681 the pioneering experimenter Edme Mariotte showed that glass, though transparent to sunlight, obstructed radiant heat. In 1800 the astronomer Sir William Herschel discovered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bright Green
Varieties of the color green may differ in hue, chroma (also called saturation or intensity) or lightness (or value, tone, or brightness), or in two or three of these qualities. Variations in value are also called tints and shades, a tint being a green or other hue mixed with white, a shade being mixed with black. A large selection of these various colors is shown below. Computer web color greens Green The color defined as ''green'' in the RGB color model is the brightest green that can be reproduced on a computer screen, and is the color named ''green'' in X11. It is one of the three primary colors used in the RGB color space along with red and blue. The three additive primaries in the RGB color system are the three colors of light chosen such as to provide the maximum range of colors that are capable of being represented on a computer or television set. This color is also called ''regular green''. It is at precisely 120 degrees on the HSV color wheel, also known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |