Polonia Minor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


 Lesser Poland, often known by its Polish name Małopolska ( la, Polonia Minor), is a
Lesser Poland, often known by its Polish name Małopolska ( la, Polonia Minor), is a
 Lesser Poland lies in the area of the upper confluence of the
Lesser Poland lies in the area of the upper confluence of the  Almost the whole area is located in the Vistula Basin, with the exception of the western and southern parts, belonging to the Odra and Dunaj Basins. The main rivers of the province are the Vistula, upper Warta,
Almost the whole area is located in the Vistula Basin, with the exception of the western and southern parts, belonging to the Odra and Dunaj Basins. The main rivers of the province are the Vistula, upper Warta,  Historically, Lesser Poland was divided into two lands - Kraków Land and Sandomierz Land, both of which emerged after the
Historically, Lesser Poland was divided into two lands - Kraków Land and Sandomierz Land, both of which emerged after the


 Unlike other Polish provinces, especially
Unlike other Polish provinces, especially 
 In the
In the
Borders of the province remained unchanged until 1772. The only exception was large part of contemporary
 In the early 16th century,
In the early 16th century,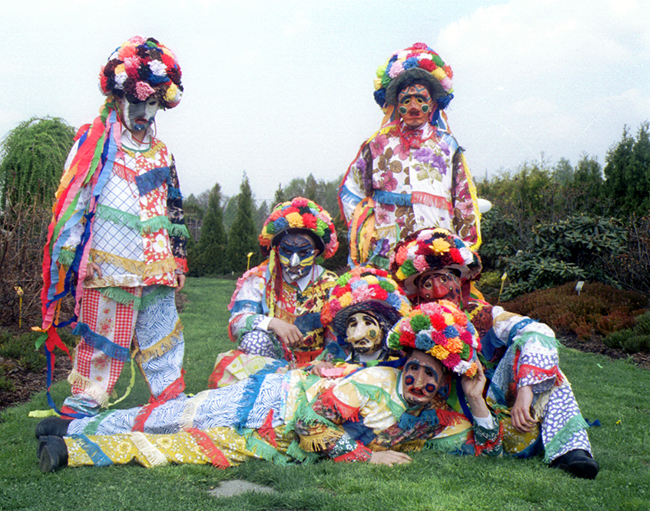  Even though first half of the 17th century was filled with wars, all major conflicts did not reach Lesser Poland, and the province continued to prosper, which was reflected in its castles and palaces, such as the enormous Krzyztopor. Apart from minor wars, such as Zebrzydowski Rebellion, and Kostka-Napierski Uprising, the province remained safe.
Even though first half of the 17th century was filled with wars, all major conflicts did not reach Lesser Poland, and the province continued to prosper, which was reflected in its castles and palaces, such as the enormous Krzyztopor. Apart from minor wars, such as Zebrzydowski Rebellion, and Kostka-Napierski Uprising, the province remained safe.  Swedish invasion of Poland had catastrophic consequences for the hitherto prosperous province. The attackers, supported by their allies from
Swedish invasion of Poland had catastrophic consequences for the hitherto prosperous province. The attackers, supported by their allies from 


 Second Partition of Poland (1793) did not result in significant changes of boundaries in the area, as the Austrian Empire did not participate in it. However, the Prussians moved on, and in 1793 they annexed northwestern corner of the province, together with the city of Częstochowa, and its vicinity, which became part of the newly created province of
Second Partition of Poland (1793) did not result in significant changes of boundaries in the area, as the Austrian Empire did not participate in it. However, the Prussians moved on, and in 1793 they annexed northwestern corner of the province, together with the city of Częstochowa, and its vicinity, which became part of the newly created province of 
 Most of the
Most of the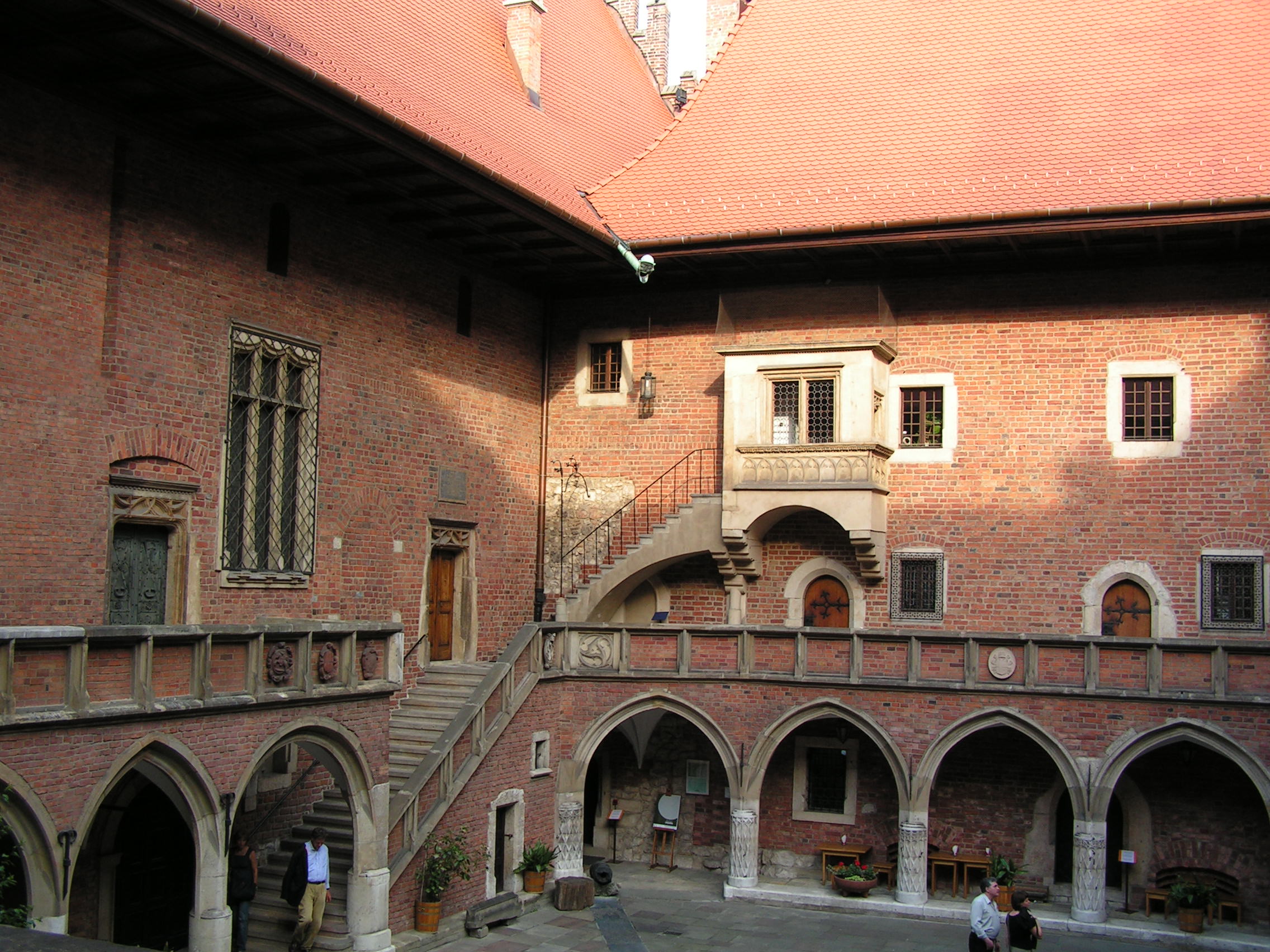  In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Lesser Poland remained one of the centers of Polish culture, especially the city of Kraków, where Jagiellonian University was one of only two Polish-language colleges of that period (the other one was Lviv University, University of Lwów). Another significant center of national culture was the town of
In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Lesser Poland remained one of the centers of Polish culture, especially the city of Kraków, where Jagiellonian University was one of only two Polish-language colleges of that period (the other one was Lviv University, University of Lwów). Another significant center of national culture was the town of  During World War I, Lesser Poland became one of main theaters of the Eastern Front (World War I), Eastern Front. Russian push into the territory of Austria – Hungary resulted in the Battle of Galicia. Among other major battles which took place in Lesser Poland, there are the Battle of the Vistula River, and the Gorlice-Tarnów Offensive. After Russian troops Great Retreat, had retreated east, whole province was under control of the Austrians and the Germans, and northern Lesser Poland was part of the German-sponsored Kingdom of Poland (1916–1918). In later stages of the conflict, the divided province once again became a center of Polish independence movement. An independent Polish government was re-proclaimed in northern Lesser Poland's city of Lublin, on 7 November 1918. Soon afterwards, it formed the basis of the new government of the country. In other parts of the province, other governments were formed – Polish Liquidation Commission in Kraków, also the short-lived Republic of Tarnobrzeg.
The division of Lesser Poland along the Vistula river, which lasted from 1772 until 1918, is visible even today. For more than 100 years, southern Lesser Poland (
During World War I, Lesser Poland became one of main theaters of the Eastern Front (World War I), Eastern Front. Russian push into the territory of Austria – Hungary resulted in the Battle of Galicia. Among other major battles which took place in Lesser Poland, there are the Battle of the Vistula River, and the Gorlice-Tarnów Offensive. After Russian troops Great Retreat, had retreated east, whole province was under control of the Austrians and the Germans, and northern Lesser Poland was part of the German-sponsored Kingdom of Poland (1916–1918). In later stages of the conflict, the divided province once again became a center of Polish independence movement. An independent Polish government was re-proclaimed in northern Lesser Poland's city of Lublin, on 7 November 1918. Soon afterwards, it formed the basis of the new government of the country. In other parts of the province, other governments were formed – Polish Liquidation Commission in Kraków, also the short-lived Republic of Tarnobrzeg.
The division of Lesser Poland along the Vistula river, which lasted from 1772 until 1918, is visible even today. For more than 100 years, southern Lesser Poland (
 At that time Lesser Poland, like other provinces of the country, faced several problems. Even though major post-World War I conflicts (such as Polish–Soviet War) did not take place there, it suffered from unemployment, overpopulation, and poverty, especially in towns and countryside. Furthermore, Polish government had to connect parts of the hitherto divided country. There was no direct rail link between Kraków, and Kielce, Radom, and Lublin, and until 1934, when line from Kraków to Tunel (railroad station), Tunel was opened, all travelers had to go via
At that time Lesser Poland, like other provinces of the country, faced several problems. Even though major post-World War I conflicts (such as Polish–Soviet War) did not take place there, it suffered from unemployment, overpopulation, and poverty, especially in towns and countryside. Furthermore, Polish government had to connect parts of the hitherto divided country. There was no direct rail link between Kraków, and Kielce, Radom, and Lublin, and until 1934, when line from Kraków to Tunel (railroad station), Tunel was opened, all travelers had to go via  Lesser Poland remained a center of Polish culture, with Kraków's
Lesser Poland remained a center of Polish culture, with Kraków's
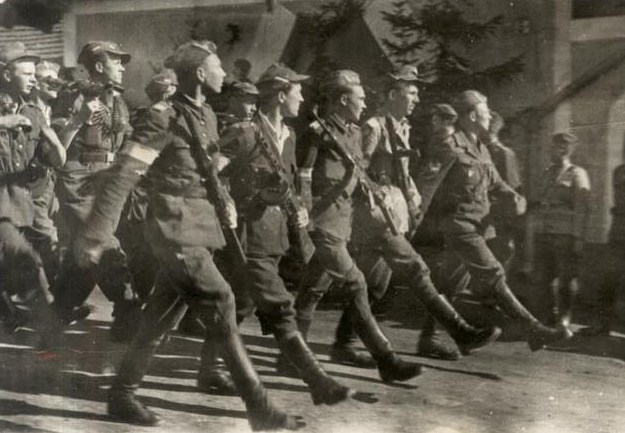 After a few days the Battle of the Border was lost, and forces of German Army Group South advanced deep into Lesser Poland's territory. Polish troops resisted fiercely, and among major battles in initial stages of the war, which took place in Lesser Poland, there are Battle of Mokra, Battle of Jordanów, and Battle of Węgierska Górka. By 6 September, Polish forces were in general retreat and Marshal of Poland Edward Rydz-Śmigły ordered all troops to fall back to the secondary lines of defences at the Vistula and San Rivers. German units entered Częstochowa on 3 September (where on the next day they Częstochowa massacre, murdered hundreds of civilians), Kielce on 5 September, Kraków on 6 September, and Radom on 8 September (see also Battle of Radom). Within a week, almost whole Lesser Poland was under Nazi occupation. Northeastern part of the province, the area of Lublin, was held by the Poles until 17 September, but eventually, and after fierce battles (see Battle of Tomaszów Lubelski), all Lesser Poland was firmly under Nazi control. First draft of Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact stipulated that northeastern Lesser Poland (east of the Vistula river) was to be occupied by the Soviet Union, and forces of the Red Army reached the area of Lublin after 20 September, but withdrew east on 28 September.
On 12 October 1939, upon a decree of Adolf Hitler, General Government, a separate region of the Nazi Germany, Greater German Reich was created, with Hans Frank as its Governor-General. Its capital was established in Kraków, and it covered most of the area of historical Lesser Poland, except for its western counties, which were directly incorporated into Nazi Germany's Upper Silesia Province ( Będzin,
After a few days the Battle of the Border was lost, and forces of German Army Group South advanced deep into Lesser Poland's territory. Polish troops resisted fiercely, and among major battles in initial stages of the war, which took place in Lesser Poland, there are Battle of Mokra, Battle of Jordanów, and Battle of Węgierska Górka. By 6 September, Polish forces were in general retreat and Marshal of Poland Edward Rydz-Śmigły ordered all troops to fall back to the secondary lines of defences at the Vistula and San Rivers. German units entered Częstochowa on 3 September (where on the next day they Częstochowa massacre, murdered hundreds of civilians), Kielce on 5 September, Kraków on 6 September, and Radom on 8 September (see also Battle of Radom). Within a week, almost whole Lesser Poland was under Nazi occupation. Northeastern part of the province, the area of Lublin, was held by the Poles until 17 September, but eventually, and after fierce battles (see Battle of Tomaszów Lubelski), all Lesser Poland was firmly under Nazi control. First draft of Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact stipulated that northeastern Lesser Poland (east of the Vistula river) was to be occupied by the Soviet Union, and forces of the Red Army reached the area of Lublin after 20 September, but withdrew east on 28 September.
On 12 October 1939, upon a decree of Adolf Hitler, General Government, a separate region of the Nazi Germany, Greater German Reich was created, with Hans Frank as its Governor-General. Its capital was established in Kraków, and it covered most of the area of historical Lesser Poland, except for its western counties, which were directly incorporated into Nazi Germany's Upper Silesia Province ( Będzin,
 Other Lesser Poland's major plants were significantly expanded after 1945, including Żywiec Brewery, Okocim Brewery, Fablok, Łucznik Arms Factory, FŁT-Kraśnik, Jaworzno Power Station, Siersza Power Plant, Huta Stalowa Wola, Janina Coal Mine, Sobieski Coal Mine, Grupa Azoty, Zakłady Azotowe Mościce, Tarnów-Mościce. Furthermore, in early 1950s significant sulfur resources were discovered in Tarnobrzeg, as a result of which Siarkopol company was founded, and the city of Tarnobrzeg quickly grew. In 1975, coal was discovered northeast of Lublin, and soon afterwards, Bogdanka Coal Mine and Piaski Coal Mine were opened.
Between 1971 and 1977, Central Rail Line (Poland), Central Trunk Line was opened, which goes along western boundary of the province, and which connects Kraków and Katowice, with Warsaw. In the early 1980s, construction of a highway between Kraków and Katowice began. The 61-kilometer road is now run by Stalexport Autostrada Małopolska, and is part of A4 autostrada (Poland), A4 highway.
Residents of Lesser Poland frequently protested against Communist government. Major centers of anti-Communist resistance were in Kraków, Nowa Huta, Radom, and Lublin. Among major protests that took place in the province were 1968 Polish political crisis (with Kraków as one of major centers of protests), June 1976 protests (in Radom), Lublin 1980 strikes, 31 August 1982 demonstrations in Poland (in several locations), 1988 Polish strikes (with Stalowa Wola as one of major centers). Several anti-Nazi, and anti-Communist leaders hailed from Lesser Poland: Jan Piwnik, Emil August Fieldorf, Leopold Okulicki, Ryszard Siwiec, Stanisław Pyjas, Hieronim Dekutowski, Andrzej Gwiazda, Andrzej Czuma.
A number of key personalities of Communist government were born in Lesser Poland, including Józef Cyrankiewicz, Bolesław Bierut, Edward Gierek, Wojciech Jaruzelski, Czesław Kiszczak, Stanisław Kania, Hilary Minc, Edward Ochab, Michał Rola-Żymierski, Józef Oleksy.
Among prominent personalities of Polish cultural life of the 20th century, who were born in Lesser Poland, there are: Xawery Dunikowski, Witold Gombrowicz, Gustaw Herling-Grudziński, Sławomir Mrożek, Tadeusz Kantor, Jan Kanty Pawluśkiewicz, Marek Kondrat, Maria Pawlikowska-Jasnorzewska, Krzysztof Penderecki, Zbigniew Preisner, Leon Schiller, Jerzy Stuhr, Jan Sztaudynger, Grzegorz Turnau, Jerzy Turowicz.
Other Lesser Poland's major plants were significantly expanded after 1945, including Żywiec Brewery, Okocim Brewery, Fablok, Łucznik Arms Factory, FŁT-Kraśnik, Jaworzno Power Station, Siersza Power Plant, Huta Stalowa Wola, Janina Coal Mine, Sobieski Coal Mine, Grupa Azoty, Zakłady Azotowe Mościce, Tarnów-Mościce. Furthermore, in early 1950s significant sulfur resources were discovered in Tarnobrzeg, as a result of which Siarkopol company was founded, and the city of Tarnobrzeg quickly grew. In 1975, coal was discovered northeast of Lublin, and soon afterwards, Bogdanka Coal Mine and Piaski Coal Mine were opened.
Between 1971 and 1977, Central Rail Line (Poland), Central Trunk Line was opened, which goes along western boundary of the province, and which connects Kraków and Katowice, with Warsaw. In the early 1980s, construction of a highway between Kraków and Katowice began. The 61-kilometer road is now run by Stalexport Autostrada Małopolska, and is part of A4 autostrada (Poland), A4 highway.
Residents of Lesser Poland frequently protested against Communist government. Major centers of anti-Communist resistance were in Kraków, Nowa Huta, Radom, and Lublin. Among major protests that took place in the province were 1968 Polish political crisis (with Kraków as one of major centers of protests), June 1976 protests (in Radom), Lublin 1980 strikes, 31 August 1982 demonstrations in Poland (in several locations), 1988 Polish strikes (with Stalowa Wola as one of major centers). Several anti-Nazi, and anti-Communist leaders hailed from Lesser Poland: Jan Piwnik, Emil August Fieldorf, Leopold Okulicki, Ryszard Siwiec, Stanisław Pyjas, Hieronim Dekutowski, Andrzej Gwiazda, Andrzej Czuma.
A number of key personalities of Communist government were born in Lesser Poland, including Józef Cyrankiewicz, Bolesław Bierut, Edward Gierek, Wojciech Jaruzelski, Czesław Kiszczak, Stanisław Kania, Hilary Minc, Edward Ochab, Michał Rola-Żymierski, Józef Oleksy.
Among prominent personalities of Polish cultural life of the 20th century, who were born in Lesser Poland, there are: Xawery Dunikowski, Witold Gombrowicz, Gustaw Herling-Grudziński, Sławomir Mrożek, Tadeusz Kantor, Jan Kanty Pawluśkiewicz, Marek Kondrat, Maria Pawlikowska-Jasnorzewska, Krzysztof Penderecki, Zbigniew Preisner, Leon Schiller, Jerzy Stuhr, Jan Sztaudynger, Grzegorz Turnau, Jerzy Turowicz.




 In 1998, the government of Poland carried out administrative reform of the country. For the first time in history,
In 1998, the government of Poland carried out administrative reform of the country. For the first time in history,

 Several renowned sportspeople and entertainers come from Lesser Poland. Among them are some of the most famous personalities of contemporary Polish sports – boxer Tomasz Adamek, Formula 1 driver Robert Kubica, swimmer Paweł Korzeniowski, skier Justyna Kowalczyk, tennis player Agnieszka Radwańska, football and volleyball stars Jakub Błaszczykowski, Artur Boruc, and Piotr Gruszka. Among late and retired sports stars who were born in the region, there also are Polish Sportspersonality of the Year, Polish Sportspersonalities of the Year: tennis player and The Championships, Wimbledon, Wimbledon finalist Jadwiga Jędrzejowska, skier Józef Łuszczek, ski jumper Stanisław Marusarz, and driver Sobiesław Zasada.
Kraków's major association football teams – KS Cracovia (football), KS Cracovia, and Wisła Kraków, are multiple champions of the country, also Stal Mielec won Polish championship twice (1973, 1976), and Garbarnia Kraków once (1931). Other popular football teams from Lesser Poland are Zagłębie Sosnowiec (four time Polish Cup winner), Górnik Łęczna, Korona Kielce, Motor Lublin, Radomiak Radom, Raków Częstochowa, Stal Stalowa Wola, and Sandecja Nowy Sącz.
Besides association football, Lesser Poland's teams were multiple national champions in other sports:
* ice-hockey (Podhale Nowy Targ, TH Unia Oświęcim, Cracovia),
* men's and women's volleyball – AZS Częstochowa, Płomień Milowice – Sosnowiec (which in 1978 won the CEV Champions League), Hutnik Kraków, Wisła Kraków, BKS Stal Bielsko-Biała, Muszynianka Muszyna,
* men's and women's Team handball, handball – Hutnik Kraków, Vive Targi Kielce, Cracovia, Montex Lublin,
* men's and women's basketball – Zagłębie Sosnowiec, Cracovia, Wisła Kraków,
* Motorcycle speedway, speedway – Włókniarz Częstochowa, Unia Tarnów (speedway), Unia Tarnów.
Major sports venues of the province are Stadion Miejski in Kraków, Kielce City Stadium, Marshal Józef Piłsudski Stadium in Kraków, Miejski Stadion Sportowy "KSZO" w Ostrowcu Sw., Stadion Ludowy in Sosnowiec, Dębowiec Sports Arena in Bielsko-Biała, ''Hala Legionów'' in Kielce, ''Hala Globus'' in Lublin, ''Arena Częstochowa'', ''Kielce Racetrack'', ''Hala Sportowa MOSiR'' in Radom, Wielka Krokiew in Zakopane.
Among popular rock music bands from Lesser Poland, there are Budka Suflera, Golec uOrkiestra, Maanam, and Zakopower. From Lesser Poland hail composers Jan Kanty Pawluśkiewicz, and Krzysztof Penderecki, as well as singers Basia, Ewa Demarczyk, Justyna Steczkowska, Grzegorz Turnau, Maciej Zembaty. Major music festivals in the province are: ''Coke Live Music Festival'' in Kraków, ''Celtic Music Festival ZAMEK'' in Będzin, ''Film Music Festival'' in Kraków, ''Gaude Mater'' in Częstochowa, ''Boyscout's Festival of School Music'' in Kielce, ''Summer with Chopin'' in Busko-Zdrój, ''Festiwal of Shanties'' in Kraków, and ''Festival of Student Song'' in Kraków.
Several renowned sportspeople and entertainers come from Lesser Poland. Among them are some of the most famous personalities of contemporary Polish sports – boxer Tomasz Adamek, Formula 1 driver Robert Kubica, swimmer Paweł Korzeniowski, skier Justyna Kowalczyk, tennis player Agnieszka Radwańska, football and volleyball stars Jakub Błaszczykowski, Artur Boruc, and Piotr Gruszka. Among late and retired sports stars who were born in the region, there also are Polish Sportspersonality of the Year, Polish Sportspersonalities of the Year: tennis player and The Championships, Wimbledon, Wimbledon finalist Jadwiga Jędrzejowska, skier Józef Łuszczek, ski jumper Stanisław Marusarz, and driver Sobiesław Zasada.
Kraków's major association football teams – KS Cracovia (football), KS Cracovia, and Wisła Kraków, are multiple champions of the country, also Stal Mielec won Polish championship twice (1973, 1976), and Garbarnia Kraków once (1931). Other popular football teams from Lesser Poland are Zagłębie Sosnowiec (four time Polish Cup winner), Górnik Łęczna, Korona Kielce, Motor Lublin, Radomiak Radom, Raków Częstochowa, Stal Stalowa Wola, and Sandecja Nowy Sącz.
Besides association football, Lesser Poland's teams were multiple national champions in other sports:
* ice-hockey (Podhale Nowy Targ, TH Unia Oświęcim, Cracovia),
* men's and women's volleyball – AZS Częstochowa, Płomień Milowice – Sosnowiec (which in 1978 won the CEV Champions League), Hutnik Kraków, Wisła Kraków, BKS Stal Bielsko-Biała, Muszynianka Muszyna,
* men's and women's Team handball, handball – Hutnik Kraków, Vive Targi Kielce, Cracovia, Montex Lublin,
* men's and women's basketball – Zagłębie Sosnowiec, Cracovia, Wisła Kraków,
* Motorcycle speedway, speedway – Włókniarz Częstochowa, Unia Tarnów (speedway), Unia Tarnów.
Major sports venues of the province are Stadion Miejski in Kraków, Kielce City Stadium, Marshal Józef Piłsudski Stadium in Kraków, Miejski Stadion Sportowy "KSZO" w Ostrowcu Sw., Stadion Ludowy in Sosnowiec, Dębowiec Sports Arena in Bielsko-Biała, ''Hala Legionów'' in Kielce, ''Hala Globus'' in Lublin, ''Arena Częstochowa'', ''Kielce Racetrack'', ''Hala Sportowa MOSiR'' in Radom, Wielka Krokiew in Zakopane.
Among popular rock music bands from Lesser Poland, there are Budka Suflera, Golec uOrkiestra, Maanam, and Zakopower. From Lesser Poland hail composers Jan Kanty Pawluśkiewicz, and Krzysztof Penderecki, as well as singers Basia, Ewa Demarczyk, Justyna Steczkowska, Grzegorz Turnau, Maciej Zembaty. Major music festivals in the province are: ''Coke Live Music Festival'' in Kraków, ''Celtic Music Festival ZAMEK'' in Będzin, ''Film Music Festival'' in Kraków, ''Gaude Mater'' in Częstochowa, ''Boyscout's Festival of School Music'' in Kielce, ''Summer with Chopin'' in Busko-Zdrój, ''Festiwal of Shanties'' in Kraków, and ''Festival of Student Song'' in Kraków.
 Lesser Polish dialect is spoken in southeastern corner of Poland, both in lands which belong to historical Lesser Poland, and in areas which are not part of the province (around Sieradz and Łęczyca). On the other hand, as seen on the map, Lesser Polish dialect is not spoken in extreme northeast of Lesser Poland, in
Lesser Polish dialect is spoken in southeastern corner of Poland, both in lands which belong to historical Lesser Poland, and in areas which are not part of the province (around Sieradz and Łęczyca). On the other hand, as seen on the map, Lesser Polish dialect is not spoken in extreme northeast of Lesser Poland, in
Appeal of inhabitants of Western Lesser Poland against calling them Silesians
Castles of Lesser Poland on lonelyplanet
Visit Lesser Poland webpage
Lesser Poland information at University at Buffalo
Portal of citizen journalism for Małopolska region
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20090616065127/http://zachodniamalopolska.republika.pl/ Western Lesser Poland. Webpage of inhabitants of eastern counties of Silesian Voivodeship, who do not wish to be associated with Silesia] {{Authority control Lesser Poland, Historical regions in Poland Historical regions History of Lesser Poland Voivodeship History of Podkarpackie Voivodeship History of Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship History of Masovian Voivodeship History of Lublin Voivodeship History of Silesian Voivodeship


 Lesser Poland, often known by its Polish name Małopolska ( la, Polonia Minor), is a
Lesser Poland, often known by its Polish name Małopolska ( la, Polonia Minor), is a historical region
Historical regions (or historical areas) are geographical regions which at some point in time had a cultural, ethnic, linguistic or political basis, regardless of latterday borders. They are used as delimitations for studying and analysing soc ...
situated in southern and south-eastern Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
. Its capital and largest city is Kraków
Kraków (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula, Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Kraków was the official capital of Poland un ...
. Throughout centuries, Lesser Poland developed a separate culture featuring diverse architecture, folk costumes, dances
Dance is a performing art form consisting of sequences of movement, either improvised or purposefully selected. This movement has aesthetic and often symbolic value. Dance can be categorized and described by its choreography, by its repertoire ...
, cuisine, traditions and a rare Lesser Polish dialect. The region is rich in historical landmarks, monuments, castles, natural scenery and UNESCO World Heritage Sites.
The region should not be confused with the modern Lesser Poland Voivodeship
Lesser Poland Voivodeship or Lesser Poland Province (in pl, województwo małopolskie ), also known as Małopolska, is a voivodeship (province), in southern Poland. It has an area of , and a population of
3,404,863 (2019).
It was created on 1 ...
, which covers only the southwestern part of Lesser Poland. Historical Lesser Poland was much larger than the current voivodeship
A voivodeship is the area administered by a voivode (Governor) in several countries of central and eastern Europe. Voivodeships have existed since medieval times and the area of extent of voivodeship resembles that of a duchy in western medieval ...
that bears its name. It reached from Bielsko-Biała
Bielsko-Biała (; cs, Bílsko-Bělá, german: Bielitz-Biala, szl, Bjylsko-Bjoło) is a city in southern Poland, with a population of approximately 168,319 as of December 2021, making it the 22nd largest city in Poland, and an area of . It is a ...
in the southwest as far as to Siedlce
Siedlce [] ( yi, שעדליץ ) is a city in eastern Poland with 77,354 inhabitants (). Situated in the Masovian Voivodeship (since 1999), previously the city was the capital of a separate Siedlce Voivodeship (1975–1998). The city is situated b ...
in the northeast. It consisted of the three voivodeships of Kraków
Kraków (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula, Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Kraków was the official capital of Poland un ...
, Sandomierz
Sandomierz (pronounced: ; la, Sandomiria) is a historic town in south-eastern Poland with 23,863 inhabitants (as of 2017), situated on the Vistula River in the Sandomierz Basin. It has been part of Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship (Holy Cross Prov ...
and Lublin
Lublin is the ninth-largest city in Poland and the second-largest city of historical Lesser Poland. It is the capital and the center of Lublin Voivodeship with a population of 336,339 (December 2021). Lublin is the largest Polish city east of ...
.
It comprised almost 60,000 km2 in area; today's population in this area is about 9,000,000 inhabitants. Its landscape is mainly hilly, with the Carpathian Mountains
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Urals at and the Scandinavian Mountains at . The range stretche ...
and Tatra Mountain Range in the south; it is located in the basin of the upper Vistula
The Vistula (; pl, Wisła, ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest river in Europe, at in length. The drainage basin, reaching into three other nations, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra in ...
river. It has been noted for its mighty aristocracy
Aristocracy (, ) is a form of government that places strength in the hands of a small, privileged ruling class, the aristocrats. The term derives from the el, αριστοκρατία (), meaning 'rule of the best'.
At the time of the word' ...
(''magnat
The magnate term, from the late Latin ''magnas'', a great man, itself from Latin ''magnus'', "great", means a man from the higher nobility, a man who belongs to the high office-holders, or a man in a high social position, by birth, wealth or ot ...
eria'') and wealthy nobility
Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy. It is normally ranked immediately below royalty. Nobility has often been an estate of the realm with many exclusive functions and characteristics. The character ...
(''szlachta
The ''szlachta'' (Polish: endonym, Lithuanian: šlėkta) were the noble estate of the realm in the Kingdom of Poland, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth who, as a class, had the dominating position in ...
'').
Between the 14th and 18th century, the Lesser Poland Province of the Polish Crown
Lesser Poland Province ( pl, Prowincja małopolska, la, Polonia Minor) was an administrative division of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland from 1569 until 1795 and the biggest province of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. The name of the pro ...
also encompassed the historical region of Red Ruthenia
Red Ruthenia or Red Rus' ( la, Ruthenia Rubra; '; uk, Червона Русь, Chervona Rus'; pl, Ruś Czerwona, Ruś Halicka; russian: Червонная Русь, Chervonnaya Rus'; ro, Rutenia Roșie), is a term used since the Middle Ages fo ...
. In the era of partitions
Partition may refer to:
Computing Hardware
* Disk partitioning, the division of a hard disk drive
* Memory partition, a subdivision of a computer's memory, usually for use by a single job
Software
* Partition (database), the division of ...
, the southern part of Lesser Poland became known as Galicia
Galicia may refer to:
Geographic regions
* Galicia (Spain), a region and autonomous community of northwestern Spain
** Gallaecia, a Roman province
** The post-Roman Kingdom of the Suebi, also called the Kingdom of Gallaecia
** The medieval King ...
, which was under Austrian control until Poland regained its independence in 1918. As a result of this long-lasting division, many inhabitants of the northern part of Lesser Poland (including those in such cities as Lublin
Lublin is the ninth-largest city in Poland and the second-largest city of historical Lesser Poland. It is the capital and the center of Lublin Voivodeship with a population of 336,339 (December 2021). Lublin is the largest Polish city east of ...
, Radom, Kielce
Kielce (, yi, קעלץ, Keltz) is a city in southern Poland, and the capital of the Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship. In 2021, it had 192,468 inhabitants. The city is in the middle of the Świętokrzyskie Mountains (Holy Cross Mountains), on the ban ...
and Częstochowa
Częstochowa ( , ; german: Tschenstochau, Czenstochau; la, Czanstochova) is a city in southern Poland on the Warta River with 214,342 inhabitants, making it the thirteenth-largest city in Poland. It is situated in the Silesian Voivodeship (adm ...
) do not recognize their Lesser Polish identity.
However, while Lublin
Lublin is the ninth-largest city in Poland and the second-largest city of historical Lesser Poland. It is the capital and the center of Lublin Voivodeship with a population of 336,339 (December 2021). Lublin is the largest Polish city east of ...
''(Lubelskie)'' was declared an independent Voivodeship as early as 1474, it still has speakers of the Lesser Polish dialect.
Across history, many ethnic and religious minorities existed in Lesser Poland as they fled persecution from other areas or countries. Poland's once tolerant policy towards these minorities allowed them to flourish and create separate self-governing communities. Some minorities still remain, but are on the verge of extinction, most notably Wymysorys
Wymysorys (, or ), also known as Vilamovian or Wilamowicean, is a West Germanic language spoken by the ethnic Vilamovian minority in the small town of Wilamowice, Poland ( in Wymysorys, ), on the border between Silesia and Lesser Poland, near ...
-speaking Vilamovians, Halcnovians, Gorals
The Gorals ( pl, Górale; Goral dialect: ''Górole''; sk, Gorali; Cieszyn Silesia dialect, Cieszyn Silesian: ''Gorole''), also known as the Highlanders (in Poland as the Polish Highlanders) are an indigenous ethnographic or ethnic group primar ...
, Lemkos
Lemkos ( rue, Лeмкы, translit= Lemkŷ; pl, Łemkowie; uk, Лемки, translit=Lemky) are an ethnic group inhabiting the Lemko Region ( rue, Лемковина, translit=Lemkovyna; uk, Лемківщина, translit=Lemkivshchyna) of Car ...
, and once Polish Jews
The history of the Jews in Poland dates back at least 1,000 years. For centuries, Poland was home to the largest and most significant Ashkenazi Jewish community in the world. Poland was a principal center of Jewish culture, because of the l ...
and Walddeutsche Germans.
Geography and boundaries
 Lesser Poland lies in the area of the upper confluence of the
Lesser Poland lies in the area of the upper confluence of the Vistula
The Vistula (; pl, Wisła, ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest river in Europe, at in length. The drainage basin, reaching into three other nations, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra in ...
river and covers a large upland, including the Świętokrzyskie Mountains with the Kraków-Częstochowa Upland
The Kraków-Częstochowa Upland, also known as the Polish Jurassic Highland or Polish Jura ( pl, Jura Krakowsko-Częstochowska), is part of the Jurassic System of south–central Poland, stretching between the cities of Kraków, Częstochowa an ...
further west, Małopolska Upland Małopolska Upland ( pl, Wyżyna Małopolska, also known as Lesser Poland Upland or Lesser Polish Upland) is an upland located in southern part of Poland, in the historic region of Lesser Poland. It extends from the valley of the upper Vistula, b ...
, Sandomierz Basin, and Lublin Upland
Lublin Upland () is a geographical region in southeastern Poland, located in Lublin Voivodeship, between the rivers Vistula and Bug, around the city of Lublin.
Its area is about 7,200 km² and its highest elevation 314 m above sea level. It ...
. Unlike other historical parts of the country, such as Kujawy, Mazovia
Mazovia or Masovia ( pl, Mazowsze) is a historical region in mid-north-eastern Poland. It spans the North European Plain, roughly between Łódź and Białystok, with Warsaw being the unofficial capital and largest city. Throughout the centurie ...
, Podlachia, Pomerania
Pomerania ( pl, Pomorze; german: Pommern; Kashubian: ''Pòmòrskô''; sv, Pommern) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The western part of Pomerania belongs to ...
, or Greater Poland
Greater Poland, often known by its Polish name Wielkopolska (; german: Großpolen, sv, Storpolen, la, Polonia Maior), is a historical region of west-central Poland. Its chief and largest city is Poznań followed by Kalisz, the oldest cit ...
, Lesser Poland is mainly hilly, with Poland's highest peak, Rysy, located within the borders of the province. Flat are northern and central areas of the province – around Tarnobrzeg, Stalowa Wola, Radom and Siedlce
Siedlce [] ( yi, שעדליץ ) is a city in eastern Poland with 77,354 inhabitants (). Situated in the Masovian Voivodeship (since 1999), previously the city was the capital of a separate Siedlce Voivodeship (1975–1998). The city is situated b ...
, also valleys of the main rivers – the Vistula, the Pilica, and the San. Apart from Rysy, there are several other peaks located in the province – Pilsko
Pilsko is the second highest mountain, , in the Żywiec Beskids ( Oravské Beskydy in Slovakia) mountain range, on the border between Poland and Slovakia. It is a hiking destination in summer and a skiing area in winter. The name Pilsko is freque ...
, Babia Góra, Turbacz
Turbacz is the highest peak of the Gorce Mountains, a mountain range located in southern Lesser Poland. It lies in the middle of the range, and according to most sources, it is 1310 meters high. The peak itself is surrounded by dense pine forest, ...
, as well as Łysica in the Świętokrzyskie Mountains. The southern part of the province is covered by the Carpathian Mountains
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Urals at and the Scandinavian Mountains at . The range stretche ...
, which are made of smaller ranges, such as Pieniny, Tatry, and Beskidy
The Beskids or Beskid Mountains ( pl, Beskidy, cs, Beskydy, sk, Beskydy, rue, Бескиды (''Beskydŷ''), ua, Бескиди (''Beskydy'')) are a series of mountain ranges in the Carpathians, stretching from the Czech Republic in the west ...
.
Soła
The Soła () is a river in southern Poland, a right tributary of the Vistula.
Soła originates in the Western Beskids mountain range near the border with Slovakia. It is made up of the confluence of several small creeks at the village of Rajcza ...
, Skawa
Skawa (german: Schaue) is a river in southern Poland, a right tributary of the Vistula. It originates in the Western Carpathians (Beskids), is long and drains . It passes several towns: Jordanów, Maków Podhalański, Sucha Beskidzka, Wadowice ...
, Raba, Dunajec
The Dunajec (); Goral dialects: ''Dónajec'') is a river running through northeastern Slovakia and southern Poland. It is also regarded as the main river of the Goral Lands. It is a right tributary of the Vistula River. It begins in Nowy Targ at t ...
, Wisłok
Wisłok is a river in south-eastern Poland, a tributary of the San River, with a length of 220 kilometres and a basin area of 3,538 km2 (all in Poland). The root of the name ''Vis-lok'' is Indo-European or pre-Indo-European.
The first meta ...
, Wisłoka, San, Wieprz
The Wieprz (, ; ua, Вепр, Vepr) is a river in central-eastern Poland, a tributary of the Vistula. It is the country's ninth longest river, with a total length of 349 km and a catchment area of 10,497 km2, all within Poland. Its cour ...
, Przemsza
Przemsza (german: Przemsa) is a river in the south of Poland, a tributary of the Vistula. According to one view, it originates at the confluence of the Black ( pl, Czarna) Przemsza and White (''Biała'') Przemsza, between the towns of Mysłowi ...
, Nida, Kamienna, Radomka
The Radomka is a river in central Poland and a left tributary of the Vistula. It has a length of 98 km and a basin area of over 2000 km2 (all in Poland). The river has its source in forests 4 km south from Przysucha, at the height o ...
, and Pilica. The major lakes of the province are Lake Rożnów, Lake Czchów, Lake Dobczyce
Lake Dobczyce ( pl, Jezioro Dobczyckie) is an artificial lake, built in 1985 - 1987. It is located in southern Poland (Lesser Poland Voivodeship), thirty kilometers south of Kraków. The lake, which lies between the Island Beskids, and the Wielicz ...
, Lake Czorsztyn, Lake Czaniec, Lake Międzybrodzie, Lake Klimkówka and Żywiec Lake
Żywiec Lake (Polish: ''Jezioro Żywieckie'') is a reservoir on the Soła river in southern Poland, near the town of Żywiec
Żywiec () (german: Saybusch) is a town in southern Poland with 31,194 inhabitants (2019). Between 1975 and 1998, it wa ...
. Most of them are man-made reservoirs.
Lesser Poland stretches from the Carpathians
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Urals at and the Scandinavian Mountains at . The range stretche ...
in the south to Pilica and Liwiec rivers to the north. It borders Mazovia to the north, Podlaskie to the northeast, Red Ruthenia
Red Ruthenia or Red Rus' ( la, Ruthenia Rubra; '; uk, Червона Русь, Chervona Rus'; pl, Ruś Czerwona, Ruś Halicka; russian: Червонная Русь, Chervonnaya Rus'; ro, Rutenia Roșie), is a term used since the Middle Ages fo ...
to the east, Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the ...
to the south, Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. S ...
to the west, and Greater Poland to the northwest. Currently, the region is divided between Polish voivodeship
A voivodeship is the area administered by a voivode (Governor) in several countries of central and eastern Europe. Voivodeships have existed since medieval times and the area of extent of voivodeship resembles that of a duchy in western medieval ...
s – Lesser Poland Voivodeship
Lesser Poland Voivodeship or Lesser Poland Province (in pl, województwo małopolskie ), also known as Małopolska, is a voivodeship (province), in southern Poland. It has an area of , and a population of
3,404,863 (2019).
It was created on 1 ...
(whole), Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship (whole), Silesian Voivodeship (eastern half), Podkarpackie Voivodeship (western part), Masovian Voivodeship
The Masovian Voivodeship, also known as the Mazovia Province ( pl, województwo mazowieckie ) is a voivodeship (province) in east-central Poland, with its capital located in the city of Warsaw, which also serves as the capital of the country. Th ...
(southern part), Łódź Voivodeship
Łódź Voivodeship (also known as Lodz Province, or by its Polish name ''Województwo łódzkie'' ) is a province- voivodeship in central Poland. It was created on 1 January 1999 out of the former Łódź Voivodeship (1975–1999) and the Sier ...
(southeastern corner), and Lublin Voivodeship
The Lublin Voivodeship, also known as the Lublin Province ( Polish: ''województwo lubelskie'' ), is a voivodeship (province) of Poland, located in southeastern part of the country. It was created on January 1, 1999, out of the former Lublin, C ...
(western part).
In Silesian Voivodeship, the border between Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. S ...
and Lesser Poland is easy to draw, because, with only a few exceptions, it goes along boundaries of local counties
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesChambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
. In the south, it goes along the western boundary of the ancient Duchy of Teschen, with the borderline along the Biała river, with Zwardoń, Milówka and Rajcza
Rajcza is a village in Żywiec County, Silesian Voivodeship, in the historic province of Lesser Poland, close to the border with Slovakia. It is the seat of the gmina (administrative district) called Gmina Rajcza. It lies approximately south of ...
located in Lesser Poland. Bielsko-Biała
Bielsko-Biała (; cs, Bílsko-Bělá, german: Bielitz-Biala, szl, Bjylsko-Bjoło) is a city in southern Poland, with a population of approximately 168,319 as of December 2021, making it the 22nd largest city in Poland, and an area of . It is a ...
is a city made up of two parts – Lesser Poland's Biala (also called ''Biala Krakowska''), makes up the eastern half of the city, and only in 1951 was it merged with Silesian Bielsko. Further north, the border goes along the western boundaries of the cities of Jaworzno, and Sosnowiec
Sosnowiec is an industrial city county in the Dąbrowa Basin of southern Poland, in the Silesian Voivodeship, which is also part of the Silesian Metropolis municipal association.—— Located in the eastern part of the Upper Silesian Indus ...
, along the Przemsza
Przemsza (german: Przemsa) is a river in the south of Poland, a tributary of the Vistula. According to one view, it originates at the confluence of the Black ( pl, Czarna) Przemsza and White (''Biała'') Przemsza, between the towns of Mysłowi ...
and Brynica rivers. Then it goes northwest, leaving Czeladź
Czeladź (; yi, טשעלאַדזש, Chelodz) is a town in Zagłębie Dąbrowskie (part of historic Lesser Poland), in southern Poland, near Katowice and Sosnowiec. Located in the Silesian Highlands, on the Brynica river (tributary of the Vistul ...
, Siewierz
Siewierz is a town in southern Poland, in the Będzin County in the Silesian Voivodeship, seat of Gmina Siewierz.
History
Siewierz was first mentioned in 1125, and was administered by the Castellan of Bytom. In 1177, Casimir II of Poland grant ...
, Koziegłowy, Blachownia
Blachownia is a town in Częstochowa County, Silesian Voivodeship, Poland. It lies about west of the city of Częstochowa. The town belongs to historic Lesser Poland. As of December 2021, it has a population of 9,383.
History
The history of ...
, Kłobuck
Kłobuck (german: Klobutzko) is a town in southern Poland, with 12,934 inhabitants (2019). Located in the Silesian Voivodeship, about 15 km northwest of Częstochowa, it is the capital of Kłobuck County. Historically, Kłobuck belongs to Le ...
and Krzepice
Krzepice (german: Krippitz) is a Polish town near Częstochowa, in Kłobuck County, Silesian Voivodeship, in northwestern corner of Lesser Poland. It is located near the historic border of Lesser Poland and Silesia, which goes along the Liswa ...
within Lesser Poland. From Krzepice, the border goes eastwards, towards Koniecpol
Koniecpol is a town in Częstochowa County, Silesian Voivodeship, Poland, with 5,910 inhabitants (2019). In the times of Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth it was the seat of the Koniecpolski magnate
The magnate term, from the late Latin ''magn ...
, and along the Pilica river, with such towns as Przedborz, Opoczno, Drzewica, Białobrzegi
Białobrzegi is a town in Poland, in Masovian Voivodeship, about south of Warsaw. It is the capital of the Białobrzegi County and Gmina Białobrzegi, Masovian Voivodeship, Gmina Białobrzegi (commune). The town is located on the border of the ...
, and Kozienice
Kozienice (; yi, קאזשניץ ''Kozhnits''; german: Koschnitz) is a town in eastern Poland with 21,500 inhabitants (1995). Located four miles from the Vistula, it is the capital of Kozienice County.
Even though Kozienice is part of Lesser ...
located within Lesser Poland. East of Białobrzegi, the boundary goes mainly along the Radomka
The Radomka is a river in central Poland and a left tributary of the Vistula. It has a length of 98 km and a basin area of over 2000 km2 (all in Poland). The river has its source in forests 4 km south from Przysucha, at the height o ...
river, to the Vistula. East of the Vistula, the boundary goes north of Łaskarzew and Żelechów, and south of Mazovian town of Garwolin, turning northwest. The northernmost point of the province is marked by the Liwiec river, with both Siedlce
Siedlce [] ( yi, שעדליץ ) is a city in eastern Poland with 77,354 inhabitants (). Situated in the Masovian Voivodeship (since 1999), previously the city was the capital of a separate Siedlce Voivodeship (1975–1998). The city is situated b ...
, and Łuków being part of Lesser Poland. The line then goes south, with Miedzyrzec Podlaski being part of the historical Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was Partitions of Poland, partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire, Habsburg Empire of ...
, and Radzyń Podlaski
Radzyń Podlaski is a town in eastern Poland, about 60 km north of Lublin, with 15,808 inhabitants (2017). Situated in the Lublin Voivodeship since 1999, previously it was part of the Biała Podlaska Voivodeship (1975–1998). It is the cap ...
as well as Parczew left in Lesser Poland.
Between the Vistula
The Vistula (; pl, Wisła, ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest river in Europe, at in length. The drainage basin, reaching into three other nations, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra in ...
and the Bug Rivers, the eastern border of Lesser Poland goes west of Leczna, but east of Krasnystaw
Krasnystaw ( uk, Красностав, Krasnostav) is a town in southeastern Poland with 18 630 inhabitants (31 december 2019). Situated in the Lublin Voivodeship (since 1999), previously in Chełm Voivodeship (1975–1998). It is the capital ...
and Szczebrzeszyn
Szczebrzeszyn (; yi, שעברעשין, Shebreshin; uk, Щебрешин, Shchebreshyn) is a city in southeastern Poland in Lublin Voivodeship, in Zamość County, about 20km west of Zamość. From 1975–1999, it was part of the Zamość Voiv ...
, both of which historically belong to Red Ruthenia
Red Ruthenia or Red Rus' ( la, Ruthenia Rubra; '; uk, Червона Русь, Chervona Rus'; pl, Ruś Czerwona, Ruś Halicka; russian: Червонная Русь, Chervonnaya Rus'; ro, Rutenia Roșie), is a term used since the Middle Ages fo ...
. Further south, Lesser Poland includes Frampol, and Biłgoraj, which lie in the southeastern corner on Lesser Poland's historical Lublin Voivodeship, close to the border with Red Ruthenia. The border then goes west of Biłgoraj, turning south, towards Leżajsk (which belongs to Red Ruthenia). The boundary between Lesser Poland and Red Ruthenia was described by Ukrainian historian and geographer Myron Korduba as being along the line Dukla
Dukla is a town and an eponymous municipality in southeastern Poland, in the Subcarpathian Voivodeship. As of December 2021, the town has a population of 2,017. The total area of the commune is . Dukla belongs to Lesser Poland, and until the P ...
– Krosno
Krosno (in full ''The Royal Free City of Krosno'', pl, Królewskie Wolne Miasto Krosno) is a historical town and county in the Subcarpathian Voivodeship, in southeastern Poland. The estimated population of the town is 47,140 inhabitants as of 2 ...
– Domaradz – Czudec
Czudec is a town in Strzyżów County, Subcarpathian Voivodeship, in south-eastern Poland. It is the seat of the gmina (administrative district) called Gmina Czudec. It lies in Lesser Poland, approximately north-east of Strzyżów and south-we ...
– Krzeszów nad Sanem. The border towns of Lesser Poland were: Rudnik, Kolbuszowa, Ropczyce
Ropczyce ( yi, ראָפּשיץ) is a town in the Subcarpathian Voivodeship in south-eastern Poland, situated in the valley of the Wielopolka River (a tributary of the Wisłoka River). The town has a population of 15,098 (). and is the seat of ...
, Sędziszów Małopolski
Sędziszów Małopolski is a town in Ropczyce-Sędziszów County, Subcarpathian Voivodeship, Poland, with a population of 12,226 (1 January 2019). Sędziszów is located in eastern Lesser Poland, near the historic boundary between Lesser Poland a ...
, Strzyżów, Jasło, Gorlice, and Biecz. The southern border of Lesser Poland goes along the Carpathian Mountains
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Urals at and the Scandinavian Mountains at . The range stretche ...
, and, except in a few cases, it has not changed for centuries. The cities of Leżajsk, Rzeszów
Rzeszów ( , ; la, Resovia; yi, ריישא ''Raisha'')) is the largest city in southeastern Poland. It is located on both sides of the Wisłok River in the heartland of the Sandomierz Basin. Rzeszów has been the capital of the Subcarpathian ...
, Sanok
Sanok (in full the Royal Free City of Sanok — pl, Królewskie Wolne Miasto Sanok, rue, Санок, ''Sanok'', ua, Cянік, ''Sianik'', la, Sanocum, yi, סאניק, ''Sonik'') is a town in the Subcarpathian Voivodeship of south-eastern ...
, Brzozów
Brzozów ( uk, Березів, ''Bereziv''; yi, ברעזשוב ''Brezhov''; lat. ''Brozovia'', or ''Prozzow'') is a town in south-eastern Poland, with 7,336 inhabitants as of December 2021. It is situated in Subcarpathian Voivodeship (since 19 ...
, and Krosno
Krosno (in full ''The Royal Free City of Krosno'', pl, Królewskie Wolne Miasto Krosno) is a historical town and county in the Subcarpathian Voivodeship, in southeastern Poland. The estimated population of the town is 47,140 inhabitants as of 2 ...
do not belong to historical Lesser Poland, as they are part of Red Ruthenia (Lwów Voivodeship
Lwów Voivodeship ( pl, Województwo lwowskie) was an administrative unit of interwar Poland (1918–1939). Because of the Nazi-Soviet invasion of Poland in accordance with the secret Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, it became occupied by both the Weh ...
, around today's Lviv
Lviv ( uk, Львів) is the largest city in Western Ukraine, western Ukraine, and the List of cities in Ukraine, seventh-largest in Ukraine, with a population of . It serves as the administrative centre of Lviv Oblast and Lviv Raion, and is o ...
, Ukraine).
 Historically, Lesser Poland was divided into two lands - Kraków Land and Sandomierz Land, both of which emerged after the
Historically, Lesser Poland was divided into two lands - Kraków Land and Sandomierz Land, both of which emerged after the Testament of Bolesław III Krzywousty
A testament is a document that the author has sworn to be true. In law it usually means last will and testament.
Testament or The Testament can also refer to:
Books
* ''Testament'' (comic book), a 2005 comic book
* ''Testament'', a thriller nov ...
. In the 14th century, Sandomierz Voivodeship
Sandomierz Voivodeship ( pl, Województwo Sandomierskie, la, Palatinatus Sandomirensis) was a unit of administration and local government in Poland from the 14th century to the partitions of Poland in 1772–1795. It was part of the Lesser Polan ...
and Kraków Voivodeship were created, and in 1474, Lublin Voivodeship
The Lublin Voivodeship, also known as the Lublin Province ( Polish: ''województwo lubelskie'' ), is a voivodeship (province) of Poland, located in southeastern part of the country. It was created on January 1, 1999, out of the former Lublin, C ...
was carved out of three Sandomierz Voivodeship counties, located on the right bank of the Vistula
The Vistula (; pl, Wisła, ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest river in Europe, at in length. The drainage basin, reaching into three other nations, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra in ...
. Historian Adolf Pawiński, who in the late 19th century was the director of the Polish Central Archives of Historical Records
Central Archives of Historical Records in Warsaw ( pl, Archiwum Główne Akt Dawnych w Warszawie, AGAD) is one of Poland's four national archives. It holds records ranging from 12th century until World War I. The current headquarters is locat ...
, estimated in his book "Polska XVI wieku pod względem geograficzno-statystycznym", that the size of Kraków Voivodeship was 19,028 km2. Sandomierz Voivodeship had an area of 25,762 km2, and Lublin Voivodeship had an area of 11,033 km2. Together with the Duchy of Siewierz (607 km2), and the parts of Spiš
Spiš (Latin: ''Cips/Zepus/Scepus/Scepusia'', german: Zips, hu, Szepesség/Szepes, pl, Spisz) is a region in north-eastern Slovakia, with a very small area in south-eastern Poland (14 villages). Spiš is an informal designation of the territory ...
that belonged to Poland after the Treaty of Lubowla (1211 km2), the total area of Lesser Poland was 57,640 square kilometers. Apart from the three historic lands, Lesser Poland includes other smaller regions, such as Podhale
Podhale (literally "below the mountain pastures") is Poland's southernmost region, sometimes referred to as the "Polish Highlands". The Podhale is located in the foothills of the Tatra range of the Carpathian mountains. It is the most famous ...
, Ponidzie, and Zagłębie Dąbrowskie Zagłębie in Polish means coalfield. It can refer to:
* Górnośląskie Zagłębie Węglowe, a mining region
* Zagłębie Dąbrowskie, a mining region
*Zagłębie Sosnowiec, an association football club
*Zagłębie Lubin
Zagłębie Lubin S.A. ...
.
Etymology
Zygmunt Gloger
Zygmunt Gloger (3 November 1845 in Tybory-Kamianka – 16 August 1910 in Warsaw) was a Polish historian, archaeologist, geographer and ethnographer, bearer of the Wilczekosy coat of arms. Gloger founded the precursor of modern and widely popu ...
in his work ''Historical geography of land of ancient Poland'' (''Geografia historyczna ziem dawnej Polski'') states that according to a Polish custom, whenever a new village was formed next to an older one, the name of the new entity was presented with an adjective ''little'' (or ''lesser''), while the old village was described as ''greater''. The same procedure was used in naming two Polish provincesthe "older" one, the cradle of the Polish state, was called ''Greater Poland'', and its "younger sister", which became part of Poland a few years later, was called ''Lesser Poland''. The name Greater Poland (''Polonia Maior'') was for the first time used in 1242, by princes Boleslaw and Przemysław I, who named themselves ''Duces Majoris Poloniae'' (''Princes of the Older Poland''). Lesser Poland, or ''Polonia Minor'', appeared for the first time in historical documents in 1493, in the Statutes of Piotrków, during the reign of King Jan Olbracht, to distinguish this province from Greater Poland (''Polonia Maior'').
History


Early period and Kingdom of Poland
In the first years of Polish statehood, southern Lesser Poland was inhabited by the West Slavic tribe of Vistulans, with two major centers in Kraków andWiślica
Wiślica is a town in Busko County, Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, in south-central Poland. It is the seat of the gmina (administrative district) called Gmina Wiślica. It lies on the Nida River, approximately south of Busko-Zdrój and so ...
. Their land, which had probably been part of Great Moravia
Great Moravia ( la, Regnum Marahensium; el, Μεγάλη Μοραβία, ''Meghálī Moravía''; cz, Velká Morava ; sk, Veľká Morava ; pl, Wielkie Morawy), or simply Moravia, was the first major state that was predominantly West Slavic to ...
, and Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; cs, Čechy ; ; hsb, Čěska; szl, Czechy) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohem ...
, was annexed by Mieszko I of Poland some time in the late 10th century. Cosmas of Prague in his ''Chronicle of Bohemians'' wrote: "Polish prince Mieszko, a cunning man, seized by ruse the city of Kraków, killing with sword all Czechs he found there". Northern part of Lesser Poland (Lublin and Sandomierz) was probably inhabited by another tribe, the Lendians, and Dr Antoni Podraza, historian of the Jagiellonian University
The Jagiellonian University ( Polish: ''Uniwersytet Jagielloński'', UJ) is a public research university in Kraków, Poland. Founded in 1364 by King Casimir III the Great, it is the oldest university in Poland and the 13th oldest university in ...
claims that ancient division of Lesser Poland into two major parts – Land (Duchy) of Kraków, and Land (Duchy) of Sandomierz, is based on the existence of two Slavic tribes in the area. However, exact location of the Lendians has not been determined to this day. Some historians speculate that they occupied Red Ruthenia, and their center was in Przemyśl
Przemyśl (; yi, פשעמישל, Pshemishl; uk, Перемишль, Peremyshl; german: Premissel) is a city in southeastern Poland with 58,721 inhabitants, as of December 2021. In 1999, it became part of the Subcarpathian Voivodeship; it was p ...
.
Around the year 1000, the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Kraków
The Archdiocese of Kraków ( la, Cracovien(sis), pl, Archidiecezja krakowska) is an archdiocese located in the city of Kraków in Poland. As of 2013 weekly mass attendance was 51.3% of the population (fourth highest in Poland after the diocese ...
was created, and its borders covered whole area of Lesser Poland. During the reign of Casimir I the Restorer, Kraków for the first time became the capital of Poland (around 1040), since Greater Poland and Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. S ...
, with main Polish urban centers, such as Gniezno
Gniezno (; german: Gnesen; la, Gnesna) is a city in central-western Poland, about east of Poznań. Its population in 2021 was 66,769, making it the sixth-largest city in the Greater Poland Voivodeship. One of the Piast dynasty's chief cities, ...
and Poznań
Poznań () is a city on the River Warta in west-central Poland, within the Greater Poland region. The city is an important cultural and business centre, and one of Poland's most populous regions with many regional customs such as Saint Joh ...
were ravaged by Duke Bretislaus I of Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; cs, Čechy ; ; hsb, Čěska; szl, Czechy) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohem ...
. In 1138, following the Testament of Bolesław III Krzywousty
A testament is a document that the author has sworn to be true. In law it usually means last will and testament.
Testament or The Testament can also refer to:
Books
* ''Testament'' (comic book), a 2005 comic book
* ''Testament'', a thriller nov ...
, the country was divided between his sons (see also Fragmentation of Poland). Bolesław III Wrymouth
Bolesław III Wrymouth ( pl, Bolesław III Krzywousty; 20 August 1086 – 28 October 1138), also known as Boleslaus the Wry-mouthed, was the duke of Lesser Poland, Silesia and Sandomierz between 1102 and 1107 and over the whole of Poland between ...
created the Seniorate Province
Seniorate Province, also known as the Senioral Province, , was a district principality in the Duchy of Poland that was formed in 1138, following the fragmentation of the state. Its ruler held the title of the High Duke, ruling all duchies wit ...
, which, among others, consisted of Kraków. At the same time, Lesser Poland was divided into two parts, when its eastern part formed the Duchy of Sandomierz
The Duchy of Sandomierz was a district principality and a fiefdom of the Kingdom of Poland. It was formed in 1138 from the territories of the Kingdom of Poland, following its fragmentation, that was started by the testament of Bolesław III W ...
, carved by the ruler for his son Henry of Sandomierz.
During the fragmentation period, both lands of Lesser Poland were frequently ruled by the same prince. Among them were Bolesław IV the Curly
Bolesław IV the Curly (; 1122 – 5 January 1173), a member of the Piast dynasty, was Duke of Masovia from 1138 and High Duke of Poland from 1146 until his death.
Early life
Bolesław was the third son of Duke Bolesław III Wrymouth of Polan ...
, Mieszko III the Old
Mieszko III the Old (c. 1126/27 – 13 March 1202), of the Piast dynasty, was Duke of Greater Poland from 1138 and High Duke of Poland, with interruptions, from 1173 until his death.
He was the fourth and second surviving son of Duke Bolesła ...
, Casimir II the Just
Casimir II the Just ( pl, Kazimierz II Sprawiedliwy; 28 October 1138 – 5 May 1194) was a Lesser Polish Duke of Wiślica from 1166–1173, and of Sandomierz after 1173. He became ruler over the Polish Seniorate Province at Kraków and thereby Hi ...
, Leszek I the White, Bolesław V the Chaste, Leszek II the Black, Władysław I the Elbow-high Władysław is a Polish given male name, cognate with Vladislav. The feminine form is Władysława, archaic forms are Włodzisław (male) and Włodzisława (female), and Wladislaw is a variation. These names may refer to:
Famous people Mononym
* ...
, and King of Bohemia
The Duchy of Bohemia was established in 870 and raised to the Kingdom of Bohemia in 1198. Several Bohemian monarchs ruled as non-hereditary kings beforehand, first gaining the title in 1085. From 1004 to 1806, Bohemia was part of the Holy Roman ...
, Wenceslaus II of Bohemia
Wenceslaus II Přemyslid ( cs, Václav II.; pl, Wacław II Czeski; 27 SeptemberK. Charvátová, ''Václav II. Král český a polský'', Prague 2007, p. 18. 1271 – 21 June 1305) was King of Bohemia (1278–1305), Duke of Cracow (1291–1 ...
, who united Lesser Poland in 1290/1291. The province was pillaged during the Mongol invasion of Poland, when a combined army of Kraków and Sandomierz was destroyed by Baidar in the Battle of Chmielnik
The Battle of Chmielnik occurred on 18 March 1241 during the Mongol invasion of Poland. It ended in the defeat of the Polish armies of Sandomierz and Kraków provinces. The Mongols were able to move unimpeded, and plunder the abandoned city of K ...
. The loss was so heavy that Norman Davies
Ivor Norman Richard Davies (born 8 June 1939) is a Welsh-Polish historian, known for his publications on the history of Europe, Poland and the United Kingdom. He has a special interest in Central and Eastern Europe and is UNESCO Professor a ...
wrote: "At Chmielnik, the assembled nobility of Małopolska perished to a man." During their 1241, 1259, and 1287
Year 1287 ( MCCLXXXVII) was a common year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar.
Events
By place
Europe
* January 17 – Aragonese forces led by King Alfonso III (the Liberal) conquer ...
invasions, the Mongols burned major cities of Lesser Poland, killing thousands of people. Furthermore, the province, especially its northeastern part, was often raided by the Lithuanians
Lithuanians ( lt, lietuviai) are a Baltic ethnic group. They are native to Lithuania, where they number around 2,378,118 people. Another million or two make up the Lithuanian diaspora, largely found in countries such as the United States, Unite ...
, Rusyns
Rusyns (), also known as Carpatho-Rusyns (), or Rusnaks (), are an East Slavic ethnic group from the Eastern Carpathians in Central Europe. They speak Rusyn, an East Slavic language variety, treated variously as either a distinct lang ...
, Yotvingians, and Old Prussians
Old Prussians, Baltic Prussians or simply Prussians ( Old Prussian: ''prūsai''; german: Pruzzen or ''Prußen''; la, Pruteni; lv, prūši; lt, prūsai; pl, Prusowie; csb, Prësowié) were an indigenous tribe among the Baltic peoples that ...
. The city of Lublin suffered most frequently – among others, it was burnt by the Rusyns in 1244, the Lithuanians 1255, the Prussians in 1266, and the Yotvingians in 1282. Another center of the province, Sandomierz, was destroyed by the Tartars in 1260, and burnt by the Lithuanians in 1349.
 Unlike other Polish provinces, especially
Unlike other Polish provinces, especially Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. S ...
, Lesser Poland did not undergo further fragmentation, and in the early 14th century became the core of the reunited nation (together with Greater Poland). The period of nation's fragmentation came to a symbolic end on 30 January 1320, when Władysław I the Elbow-high Władysław is a Polish given male name, cognate with Vladislav. The feminine form is Władysława, archaic forms are Włodzisław (male) and Włodzisława (female), and Wladislaw is a variation. These names may refer to:
Famous people Mononym
* ...
was crowned as King of Poland
Poland was ruled at various times either by dukes and princes (10th to 14th centuries) or by kings (11th to 18th centuries). During the latter period, a tradition of free election of monarchs made it a uniquely electable position in Europe (16th ...
. The ceremony took place in Kraków's Wawel Cathedral
The Wawel Cathedral ( pl, Katedra Wawelska), formally titled the Royal Archcathedral Basilica of Saints Stanislaus and Wenceslaus, is a Roman Catholic cathedral situated on Wawel Hill in Kraków, Poland. Nearly 1000 years old, it is part of the ...
, and the king of the reunited country decided to choose Kraków as the capital. Through 14th and 15th centuries, Lesser Poland's position as the most important province of the nation was cemented. It became visible during the reign of Casimir III the Great
Casimir III the Great ( pl, Kazimierz III Wielki; 30 April 1310 – 5 November 1370) reigned as the King of Poland from 1333 to 1370. He also later became King of Ruthenia in 1340, and fought to retain the title in the Galicia-Volhynia Wars. He ...
, who favored less known Lesser Poland's noble families, at the expense of Greater Poland's nobility. The reign of Casimir the Great was a period of growing prosperity of Lesser Poland. With high density of population, fertile soils and rich deposits of minerals (especially salt in Bochnia and Wieliczka, as well as lead in Olkusz), the province was the richest part of Poland. After annexation of Red Ruthenia
Red Ruthenia or Red Rus' ( la, Ruthenia Rubra; '; uk, Червона Русь, Chervona Rus'; pl, Ruś Czerwona, Ruś Halicka; russian: Червонная Русь, Chervonnaya Rus'; ro, Rutenia Roșie), is a term used since the Middle Ages fo ...
, Lesser Poland lost its status of the borderland, and both regions created an economic bridge between Poland and the ports of the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
. The king, who drew Jewish settlers from across Europe to his country, built several castles along western border of Lesser Poland, with the most notable ones in Skawina
Skawina is a town in southern Poland with 27,328 inhabitants (2008). Situated in the Lesser Poland Voivodeship (since 1999), previously in Kraków Voivodeship (1975–1998). The town is located on the Skawinka river, in close proximity to the c ...
, Pieskowa Skała, Będzin, Lanckorona
Lanckorona is a village located south-west of Kraków in Lesser Poland. It lies on the Skawinka river, among the hills of the Beskids, above sea level. It is known for the Lanckorona Castle, today in ruins. Lanckorona is also known for the B ...
, Olkusz, Lelów, Bobolice, Krzepice
Krzepice (german: Krippitz) is a Polish town near Częstochowa, in Kłobuck County, Silesian Voivodeship, in northwestern corner of Lesser Poland. It is located near the historic border of Lesser Poland and Silesia, which goes along the Liswa ...
, Ogrodzieniec, Ojców, Olsztyn
Olsztyn ( , ; german: Allenstein ; Old Prussian: ''Alnāsteini''
* Latin: ''Allenstenium'', ''Holstin'') is a city on the Łyna River in northern Poland. It is the capital of the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, and is a city with county rights. ...
, Bobolice, Mirów (see also Eagle Nests Trail). Furthermore, he built or strengthened castles in other parts of the province, such as Szydlow, Chęciny
Chęciny (Yiddish: חענטשין – Khantchin or Chentshin) is a town in Kielce County, Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, southern Poland, with 104,361 inhabitants as of December 2021. It was first mentioned in historical documents from 1275, and ...
, Wiślica
Wiślica is a town in Busko County, Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, in south-central Poland. It is the seat of the gmina (administrative district) called Gmina Wiślica. It lies on the Nida River, approximately south of Busko-Zdrój and so ...
, Radom, Niedzica, Opoczno, Lublin
Lublin is the ninth-largest city in Poland and the second-largest city of historical Lesser Poland. It is the capital and the center of Lublin Voivodeship with a population of 336,339 (December 2021). Lublin is the largest Polish city east of ...
, Sandomierz
Sandomierz (pronounced: ; la, Sandomiria) is a historic town in south-eastern Poland with 23,863 inhabitants (as of 2017), situated on the Vistula River in the Sandomierz Basin. It has been part of Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship (Holy Cross Prov ...
, as well as the Wawel Castle
The Wawel Royal Castle (; ''Zamek Królewski na Wawelu'') and the Wawel Hill on which it sits constitute the most historically and culturally significant site in Poland. A fortified residency on the Vistula River in Kraków, it was established ...
. Also, during his reign (1333–1370), Casimir the Great founded on Magdeburg rights
Magdeburg rights (german: Magdeburger Recht; also called Magdeburg Law) were a set of town privileges first developed by Otto I, Holy Roman Emperor (936–973) and based on the Flemish Law, which regulated the degree of internal autonomy within ...
several cities, urbanizing hitherto rural province. Among major Lesser Poland's cities founded by the King, there are:
:
 In the
In the Kingdom of Poland
The Kingdom of Poland ( pl, Królestwo Polskie; Latin: ''Regnum Poloniae'') was a state in Central Europe. It may refer to:
Historical political entities
* Kingdom of Poland, a kingdom existing from 1025 to 1031
* Kingdom of Poland, a kingdom exi ...
, Lesser Poland was made of three voivodeship
A voivodeship is the area administered by a voivode (Governor) in several countries of central and eastern Europe. Voivodeships have existed since medieval times and the area of extent of voivodeship resembles that of a duchy in western medieval ...
s – Kraków Voivodeship, Sandomierz Voivodeship
Sandomierz Voivodeship ( pl, Województwo Sandomierskie, la, Palatinatus Sandomirensis) was a unit of administration and local government in Poland from the 14th century to the partitions of Poland in 1772–1795. It was part of the Lesser Polan ...
, and Lublin Voivodeship
The Lublin Voivodeship, also known as the Lublin Province ( Polish: ''województwo lubelskie'' ), is a voivodeship (province) of Poland, located in southeastern part of the country. It was created on January 1, 1999, out of the former Lublin, C ...
, created in 1474 out of eastern part of the Sandomierz Voivodeship.Antoni Podraza, Małopolska w przeszłości i dziś. Wspólnota Małopolska, 1 June 1999Borders of the province remained unchanged until 1772. The only exception was large part of contemporary
Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia ( pl, Górny Śląsk; szl, Gůrny Ślůnsk, Gōrny Ślōnsk; cs, Horní Slezsko; german: Oberschlesien; Silesian German: ; la, Silesia Superior) is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia, locate ...
(the area around Bytom
Bytom (Polish pronunciation: ; Silesian: ''Bytōm, Bytōń'', german: Beuthen O.S.) is a city in Upper Silesia, in southern Poland. Located in the Silesian Voivodeship of Poland, the city is 7 km northwest of Katowice, the regional capi ...
, Toszek
Toszek (german: Tost) is a small town in southern Poland. It is situated within Gliwice County in the Silesian Voivodeship (province), and its population was estimated at 3,600 inhabitants in 2019.
History
The beginning of the settlement and fo ...
, Siewierz
Siewierz is a town in southern Poland, in the Będzin County in the Silesian Voivodeship, seat of Gmina Siewierz.
History
Siewierz was first mentioned in 1125, and was administered by the Castellan of Bytom. In 1177, Casimir II of Poland grant ...
, and Oświęcim
Oświęcim (; german: Auschwitz ; yi, אָשפּיצין, Oshpitzin) is a city in the Lesser Poland ( pl, Małopolska) province of southern Poland, situated southeast of Katowice, near the confluence of the Vistula (''Wisła'') and Soła riv ...
), which belonged to Duchy of Kraków until 1179. In that year, prince of Kraków Casimir II the Just
Casimir II the Just ( pl, Kazimierz II Sprawiedliwy; 28 October 1138 – 5 May 1194) was a Lesser Polish Duke of Wiślica from 1166–1173, and of Sandomierz after 1173. He became ruler over the Polish Seniorate Province at Kraków and thereby Hi ...
, handed these lands to Prince of Opole
Opole (; german: Oppeln ; szl, Ôpole) ;
* Silesian:
** Silesian PLS alphabet: ''Ôpole''
** Steuer's Silesian alphabet: ''Uopole''
* Silesian German: ''Uppeln''
* Czech: ''Opolí''
* Latin: ''Oppelia'', ''Oppolia'', ''Opulia'' is a city l ...
Mieszko I Tanglefoot
Mieszko IV Tanglefoot ( pl, Mieszko IV Plątonogi) (c. 1130 – 16 May 1211) was Duke of Kraków and High Duke of Poland from 9 June 1210 until his death one year later. He was also Duke of Silesia from 1163 to 1173 (with his brother as co-ruler) ...
. The Duchy of Siewierz, ruled since 1443 by the Archbishop of Kraków, merged with Lesser Poland in 1790. Other Silesian realms lost in 1179, also returned to Lesser Poland – Duchy of Zator (in 1513), and Duchy of Oświęcim (1564). Both duchies merged into a Silesian County of the Kraków Voivodeship, and shared the fate of Lesser Poland. Apart from Jews, among other ethnic minorities of the province were the Walddeutsche
Walddeutsche (lit. "Forest Germans" or ''Taubdeutsche'' – "Deaf Germans"; pl, Głuchoniemcy – "deaf Germans") was the name for a group of German-speaking people, originally used in the 16th century for two language islands around Łańcut an ...
, who settled the borderland of Lesser Poland and Red Ruthenia (14th through 17th centuries). In the Middle Ages, the Germans inhabited several cities of Lesser Poland, especially Kraków and Sandomierz (see Rebellion of wójt Albert
Mayor Albert's Rebellion ( pl, bunt wójta Alberta) was a 1311–12 rebellion by the burghers of the Polish city of Kraków against Duke Władysław I the Elbow-high. The rebellion was led by Albert, the '' wójt'' ( la, advocatus), who under Mag ...
).
In the late Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, Lesser Poland gradually became the center of Polish statehood, with Kraków being the capital of the country from the mid-11th century until 1596. Its nobility ruled Poland when Queen Jadwiga was too young to control the state, and the Union of Krewo with the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was Partitions of Poland, partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire, Habsburg Empire of ...
was the brainchild of Lesser Poland's szlachta
The ''szlachta'' (Polish: endonym, Lithuanian: šlėkta) were the noble estate of the realm in the Kingdom of Poland, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth who, as a class, had the dominating position in ...
.
In the 15th and 16th centuries, Lesser Poland remained the most important part of the country. After the death of Casimir the Great, Lesser Poland's nobility promoted Louis I of Hungary
Louis I, also Louis the Great ( hu, Nagy Lajos; hr, Ludovik Veliki; sk, Ľudovít Veľký) or Louis the Hungarian ( pl, Ludwik Węgierski; 5 March 132610 September 1382), was King of Hungary and Croatia from 1342 and King of Poland from 1370 ...
as the new king, later supporting his daughter Jadwiga of Poland
Jadwiga (; 1373 or 137417 July 1399), also known as Hedwig ( hu, Hedvig), was the first woman to be crowned as monarch of the Kingdom of Poland. She reigned from 16 October 1384 until her death. She was the youngest daughter of Louis the Grea ...
in exchange for Privilege of Koszyce
The Privilege of Koszyce or Privilege of KassaClifford Rogers (editor): ''The Oxford Encyclopedia of Medieval Warfare and Military Technology'', Oxford University Press, 201/ref> was a set of concessions made by Louis I of Hungary to the Polish ...
. Since Jadwiga, crowned on 16 October 1384, was too young to rule the country, Poland was in fact governed by the Lesser Poland's nobility, who decided to find her a husband, Grand Duke of Lithuania
The monarchy of Lithuania concerned the monarchical head of state of Lithuania, which was established as an absolute and hereditary monarchy. Throughout Lithuania's history there were three ducal dynasties that managed to stay in power— Ho ...
, Jogaila. Consequently, unions of Poland and Lithuania at Krewo and Horodło were the brainchildren of Lesser Poland's nobility, among whom the most influential individuals were Spytek z Melsztyna, and cardinal Zbigniew Olesnicki. Other famous Lesser Poland's families are Lubomirski family
The House of Lubomirski is a Polish princely family. The Lubomirski family's coat of arms is the Drużyna coat of arms, which is similar to the Szreniawa coat of arms but without a cross.
Origin and the coat of arms
The Lubomirski f ...
, Kmita family, Tarnowski family
The House of Tarnowski (plural: Tarnowscy) is the name of a Polish noble and aristocratic family (see: Szlachta). Because Polish adjectives have different forms for the genders, Tarnowska is the form for a female family member.
History
The ...
, Potocki family
The House of Potocki (; plural: Potoccy, male: Potocki, feminine: Potocka) was a prominent Polish noble family in the Kingdom of Poland and magnates of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. The Potocki family is one of the wealthiest and ...
, Sobieski family, Koniecpolski family, Ossolinski family, Poniatowski family.
Since Lesser Poland was the most important province of the country, several important events took place on its territory. In 1364, Casimir the Great called the Congress of Kraków, and in 1401, the Union of Vilnius and Radom
The Pact of Vilnius and Radom ( pl, Unia wileńsko-radomska, lt, Vilniaus-Radomo sutartis) was a set of three acts passed in Vilnius, Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and confirmed by the Crown Council in Radom, Kingdom of Poland in 1401. The union ame ...
was signed. In 1505 in Radom, the Sejm adopted the Nihil novi title, which forbade the King to issue laws without the consent of the nobility. In the same year, also in the same city, Polish law was codified in the Łaski's Statute, and the Crown Tribunal (the highest appeal court in the Crown of the Polish Kingdom) held its sessions in Lublin. In 1525, the Treaty of Kraków was signed, ending the Polish–Teutonic War. Lesser Poland also is home to the oldest Polish university – the Jagiellonian University
The Jagiellonian University ( Polish: ''Uniwersytet Jagielloński'', UJ) is a public research university in Kraków, Poland. Founded in 1364 by King Casimir III the Great, it is the oldest university in Poland and the 13th oldest university in ...
, founded in 1364 by Casimir the Great, and several outstanding figures of early Polish culture were born here, such as Jan Kochanowski
Jan Kochanowski (; 1530 – 22 August 1584) was a Polish Renaissance poet who established poetic patterns that would become integral to the Polish literary language. He is commonly regarded as the greatest Polish poet before Adam Mickiewicz.
...
, Mikołaj Rej, Jan z Lublina
Jan z Lublina, or Joannis de Lublin, was a Polish composer and organist who lived in the first half of the 16th century. Not much is known about his life - he was a member of the Order of Canons Regular of the Lateran, circa 1540 he was possibly t ...
, Mikołaj Gomółka
Mikołaj Gomółka (c. 1535 – after 30 April 1591, most probably 5 March 1609) was a Polish Renaissance composer, and member of the royal court of Sigismund II Augustus, where he was a singer, flutist and trumpeter.
Gomółka was born in S ...
, Maciej Miechowita
Maciej Miechowita (also known as ''Maciej z Miechowa, Maciej of Miechów, Maciej Karpiga, Matthias de Miechow''; 1457 – 8 September 1523) was a Polish renaissance scholar, professor of Jagiellonian University, historian, chronicler, geograp ...
, Marcin Kromer
Marcin Kromer (Latin: ''Martinus Cromerus''; 11 November 1512 – 23 March 1589) was Prince-Bishop of Warmia (Ermland), a Polish cartographer, diplomat and historian in the Kingdom of Poland and later in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. He wa ...
, Łukasz Górnicki, and Mikołaj Radomski
Mikołaj is the Polish cognate of given name Nicholas, used both as a given name and a surname. It may refer to people:
In Polish (or Polish-Lithuanian) nobility:
* Mikołaj Firlej (died 1526), Polish nobleman, Hetman, diplomat, and expert of sou ...
.
Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
In the 16th century, Lesser Poland retained its position as the most important province of the country. As no major conflicts took place on its territory, it was the center of Renaissance in Poland. The province was home to numerous scholars, writers and statesmen, and it was here wherePolish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Crown of the Kingdom of ...
was created in 1569 (see Union of Lublin
The Union of Lublin ( pl, Unia lubelska; lt, Liublino unija) was signed on 1 July 1569 in Lublin, Poland, and created a single state, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, one of the largest countries in Europe at the time. It replaced the per ...
). In the Commonwealth, Lesser Poland proper was the base of the Province of Lesser Poland, which covered southern lands of the vast country. The province was made of Lesser Poland itself, also Red Ruthenia
Red Ruthenia or Red Rus' ( la, Ruthenia Rubra; '; uk, Червона Русь, Chervona Rus'; pl, Ruś Czerwona, Ruś Halicka; russian: Червонная Русь, Chervonnaya Rus'; ro, Rutenia Roșie), is a term used since the Middle Ages fo ...
, Volhynia
Volhynia (also spelled Volynia) ( ; uk, Воли́нь, Volyn' pl, Wołyń, russian: Волы́нь, Volýnʹ, ), is a historic region in Central and Eastern Europe, between south-eastern Poland, south-western Belarus, and western Ukraine. The ...
, Podolia
Podolia or Podilia ( uk, Поділля, Podillia, ; russian: Подолье, Podolye; ro, Podolia; pl, Podole; german: Podolien; be, Падолле, Padollie; lt, Podolė), is a historic region in Eastern Europe, located in the west-centra ...
, and Ukrainian
Ukrainian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Ukraine
* Something relating to Ukrainians, an East Slavic people from Eastern Europe
* Something relating to demographics of Ukraine in terms of demography and population of Ukraine
* So ...
voivodeships – Kijów Voivodeship (Kyiv
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the seventh-most populous city in Europe.
Ky ...
), Czernihów Voivodeship
Czernihów (Chernihiv) Voivodeship ( pl, Województwo czernihowskie, links=no) was a unit of administrative division and local government in the Kingdom of Poland (part of Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth) from 1635 until Khmelnytsky Uprising in ...
(Chernihiv
Chernihiv ( uk, Черні́гів, , russian: Черни́гов, ; pl, Czernihów, ; la, Czernihovia), is a city and municipality in northern Ukraine, which serves as the administrative center of Chernihiv Oblast and Chernihiv Raion within ...
), and Bracław Voivodeship ( Bratslav), which, until 1569, had been part of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was Partitions of Poland, partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire, Habsburg Empire of ...
.
The period in Polish history known as the Polish Golden Age was very fortunate for Lesser Poland. Kings of the Jagiellonian dynasty
The Jagiellonian dynasty (, pl, dynastia jagiellońska), otherwise the Jagiellon dynasty ( pl, dynastia Jagiellonów), the House of Jagiellon ( pl, Dom Jagiellonów), or simply the Jagiellons ( pl, Jagiellonowie), was the name assumed by a cad ...
, especially Sigismund I the Old
Sigismund I the Old ( pl, Zygmunt I Stary, lt, Žygimantas II Senasis; 1 January 1467 – 1 April 1548) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1506 until his death in 1548. Sigismund I was a member of the Jagiellonian dynasty, the ...
(himself born in Lesser Poland's Kozienice
Kozienice (; yi, קאזשניץ ''Kozhnits''; german: Koschnitz) is a town in eastern Poland with 21,500 inhabitants (1995). Located four miles from the Vistula, it is the capital of Kozienice County.
Even though Kozienice is part of Lesser ...
), and his son Sigismund II Augustus
Sigismund II Augustus ( pl, Zygmunt II August, lt, Žygimantas Augustas; 1 August 1520 – 7 July 1572) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania, the son of Sigismund I the Old, whom Sigismund II succeeded in 1548. He was the first ruler ...
(born in Kraków), resided in Kraków, which was the capital of the immense Polish – Lithuanian Commonwealth. Lesser Poland's prosperity was reflected in numerous examples of Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ide ...
architecture complexes, built across the province. In 1499, hitherto Gothic
Gothic or Gothics may refer to:
People and languages
*Goths or Gothic people, the ethnonym of a group of East Germanic tribes
**Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths
**Crimean Gothic, the Gothic language spoken b ...
Wawel Castle
The Wawel Royal Castle (; ''Zamek Królewski na Wawelu'') and the Wawel Hill on which it sits constitute the most historically and culturally significant site in Poland. A fortified residency on the Vistula River in Kraków, it was established ...
was damaged in a fire, and a few years later, Sigismund I, with help of the best native and foreign artists (such as Francesco the Florentine, Bartholomeo Berrecci or Niccolo Castiglione) refurbished the complex into a splendid Renaissance palace. Furthermore, in the early 16th century, several palaces were built in Lesser Poland – in Drzewica, Szydłowiec
Szydłowiec (; Hebrew: שידלוביץ, Yiddish: שידלאָווצע; German: ''Schiedlowietz'') is a town in Szydłowiec County, Mazovian Voivodeship, south-central Poland, with 5,243 inhabitants (December 31, 2005). It is the seat of Gmin ...
, Ogrodzieniec, and Pieskowa Skała. The province became rich mostly due to the grain trade
The grain trade refers to the local and international trade in cereals and other food grains such as wheat, barley, maize, and rice. Grain is an important trade item because it is easily stored and transported with limited spoilage, unlike other ...
, conducted along the Vistula, and among cities which prospered in the 16th century, there are Kraków, Sandomierz, Lublin, Kazimierz Dolny, Pilzno, Tarnów
Tarnów () is a city in southeastern Poland with 105,922 inhabitants and a metropolitan area population of 269,000 inhabitants. The city is situated in the Lesser Poland Voivodeship since 1999. From 1975 to 1998, it was the capital of the Tarn� ...
, Radom, Biecz. In later years of the 16th century, further palaces were built or remodelled in Baranow Sandomierski, and Niepołomice.
 In the early 16th century,
In the early 16th century, Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and i ...
spread across the Commonwealth, and Lesser Poland became one of early centers of the movement, when students from Wittenberg
Wittenberg ( , ; Low Saxon: ''Wittenbarg''; meaning ''White Mountain''; officially Lutherstadt Wittenberg (''Luther City Wittenberg'')), is the fourth largest town in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Wittenberg is situated on the River Elbe, north of ...
brought the news to Cracow. In the first years of the century, professor of Jagiellonian University Jakub of Iłża
Iłża () is a small town in Masovian Voivodeship, Poland. In 2006 Iłża had approximately 5,165 inhabitants. The town belongs to the historical region of Lesser Poland, and from its foundation until 1795, it was part of Lesser Poland’s Sa ...
(Jakub z Ilzy, died 1542) became one of the main promoters of the movement in the region. He actively supported the notions of Martin Luther
Martin Luther (; ; 10 November 1483 – 18 February 1546) was a German priest, theologian, author, hymnwriter, and professor, and Augustinian friar. He is the seminal figure of the Protestant Reformation and the namesake of Lutherani ...
, and in 1528 was called to the Bishop of Kraków's court. Convinced of heresy, he was forced to leave Poland in 1535. Reformation soon became very popular among Lesser Poland's nobility, especially Calvinism
Calvinism (also called the Reformed Tradition, Reformed Protestantism, Reformed Christianity, or simply Reformed) is a major branch of Protestantism that follows the theological tradition and forms of Christian practice set down by John C ...
, and according to one estimate, some 20% of local szlachta
The ''szlachta'' (Polish: endonym, Lithuanian: šlėkta) were the noble estate of the realm in the Kingdom of Poland, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth who, as a class, had the dominating position in ...
converted from Roman Catholicism. They were attracted by Calvinism's democratic character, and Lesser Poland's center of the movement was set in the town of Pińczów, which came to be known as ''Sarmatian Athens''. It was in Pińczów, where a local nobleman converted a Roman Catholic parish into a Protestant one, opened a Calvinist Academy, and published its Antitrinitarian confession in 1560 and in 1561. Several Calvinist synods took place in Lesser Poland – the first one in Słomniki
Słomniki is a town in southern Poland, situated in the Lesser Poland Voivodeship (since 1999), previously in Kraków Voivodeship (1975–1998). Słomniki lies north of Kraków, among the hills of Lesser Poland Upland. On December 31, 2010, its ...
(1554), Pińczów (the first united Synod of Poland and Lithuania – 1556 1561), and Kraków (1562). In 1563, also in Pińczów, the so-called Brest Bible
The Brest Bible ( pl, Biblia Brzeska) was the first complete Protestant Bible translation into Polish, published by Bernard Wojewodka in 1563 in Brest and dedicated to King Sigismund II Augustus.
Polish full original title: ''Biblia święta, ...
was translated into Polish. In 1570, the Sandomierz Agreement was signed by a number of Protestant groups, with the exception of the Polish Brethren
The Polish Brethren (Polish: ''Bracia Polscy'') were members of the Minor Reformed Church of Poland, a Nontrinitarian Protestant church that existed in Poland from 1565 to 1658. By those on the outside, they were called " Arians" or " Socinians" ( ...
, another religious group very influential in Lesser Poland. The Brethren had their center in Lesser Poland's village of Raków, where a main Arian printing press, as well as a college, known as Akademia Rakowska (''Gymnasium Bonarum Artium'') founded in 1602 were located. Among distinguished European scholars associated with the school, there were Johannes Crellius
Johannes Crellius (Polish: ''Jan Crell'', English: John Crell; 26 July 1590 in Hellmitzheim – 11 June 1633 in Raków) was a Polish and German theologian.
Life
Johann Crell's father, Johann Crell Sr., was pastor of the church at Hellmitzheim, ...
, Corderius
Corderius ( Latinized form of the name Mathurin Cordier; c. 1479 – 8 September 1564), was a French-born theologian, teacher, humanist, and pedagogian active in Geneva, Republic of Geneva. He taught at the School of Lausanne (now the University o ...
, and Valentinus Smalcius Valentinus Smalcius (german: Valentin Schmalz or ''Schmaltz''; pl, Walenty Smalc) (Gotha, 1572 – Raków, Kielce county 1622) was a German Socinian theologian. He is known for his German translation of the Racovian Catechism, and Racovian New Test ...
(who translated into German the Racovian Catechism).
In 1572, the Jagiellon dynasty died out, and next year, Henry III of France
Henry III (french: Henri III, né Alexandre Édouard; pl, Henryk Walezy; lt, Henrikas Valua; 19 September 1551 – 2 August 1589) was King of France from 1574 until his assassination in 1589, as well as King of Poland and Grand Duke of Li ...
became first elected king of the country. After his short reign, and War of the Polish Succession (1587–88), which also took place in Lesser Poland, the new ruler was Stephen Báthory of Poland
Stephen or Steven is a common English first name. It is particularly significant to Christians, as it belonged to Saint Stephen ( grc-gre, Στέφανος ), an early disciple and deacon who, according to the Book of Acts, was stoned to death; h ...
, who died in 1586. The ruler from Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the A ...
was followed by Sigismund III Vasa
Sigismund III Vasa ( pl, Zygmunt III Waza, lt, Žygimantas Vaza; 20 June 1566 – 30 April 1632
N.S.) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1587 to 1632 and, as Sigismund, King of Sweden and Grand Duke of Finland from 1592 to ...
of Sweden, whose election marked gradual decline of the province. Sigismund's eyes were set on Sweden, and for many years he concentrated his efforts on a futile attempt to regain his former Swedish throne (see Polish–Swedish union
The Polish–Swedish union was a short-lived personal union between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Kingdom of Sweden between 1592 and 1599. It began when Sigismund III Vasa, elected King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania, was ...
, War against Sigismund). Therefore, Lesser Poland, located in southwestern corner of the Commonwealth, began to lose its importance, which was marked in 1596, when Sigismund moved his permanent residence, court and the crown headquarters to centrally-located Warsaw.
 Even though first half of the 17th century was filled with wars, all major conflicts did not reach Lesser Poland, and the province continued to prosper, which was reflected in its castles and palaces, such as the enormous Krzyztopor. Apart from minor wars, such as Zebrzydowski Rebellion, and Kostka-Napierski Uprising, the province remained safe.
Even though first half of the 17th century was filled with wars, all major conflicts did not reach Lesser Poland, and the province continued to prosper, which was reflected in its castles and palaces, such as the enormous Krzyztopor. Apart from minor wars, such as Zebrzydowski Rebellion, and Kostka-Napierski Uprising, the province remained safe. Cossack
The Cossacks , es, cosaco , et, Kasakad, cazacii , fi, Kasakat, cazacii , french: cosaques , hu, kozákok, cazacii , it, cosacchi , orv, коза́ки, pl, Kozacy , pt, cossacos , ro, cazaci , russian: казаки́ or ...
s of the Khmelnytsky Uprising
The Khmelnytsky Uprising,; in Ukraine known as Khmelʹnychchyna or uk, повстання Богдана Хмельницького; lt, Chmelnickio sukilimas; Belarusian: Паўстанне Багдана Хмяльніцкага; russian: � ...
reached as far west as Zamość and Lwów
Lviv ( uk, Львів) is the largest city in Western Ukraine, western Ukraine, and the List of cities in Ukraine, seventh-largest in Ukraine, with a population of . It serves as the administrative centre of Lviv Oblast and Lviv Raion, and is o ...
, but did not enter Lesser Poland. The province did not witness other wars, such as Polish–Swedish War (1626–29), Polish–Muscovite War (1605–18), Polish–Ottoman War (1620–21), and Smolensk War
The Smolensk War (1632–1634) was a conflict fought between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and Russia.
Hostilities began in October 1632 when Russian forces tried to capture the city of Smolensk. Small military engagements produced mix ...
. Nevertheless, Lesser Poland's nobility took active part in these conflicts – Marina Mniszech
Marina Mniszech, ( pl, Maryna Mniszech; russian: Марина Мнишек, Marina Mnishek, ) also known in Russian lore as Marinka the Witch ( 1588 – 24 December 1614) was a Polish noblewoman who became the Tsaritsa of Russia during the Time ...
, the daughter of Voivode of Sandomierz, Jerzy Mniszech, was wife of False Dmitriy I, as well as False Dmitriy II
False Dmitry II ( rus, Лжедмитрий II, Lzhedmitrii II; died ), historically known as Pseudo-Demetrius II and also called "тушинский вор" ("rebel/criminal of Tushino"), was the second of three pretenders to the Russian throne w ...
. Furthermore, Lesser Poland's lands, especially its northeastern part, became a base for Polish troops, fighting the Cossacks, and King John II Casimir Vasa
John II Casimir ( pl, Jan II Kazimierz Waza; lt, Jonas Kazimieras Vaza; 22 March 1609 – 16 December 1672) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1648 until his abdication in 1668 as well as titular King of Sweden from 1648 ...
often stayed in Lublin with his court, preparing military campaigns in Ukraine. The situation changed with the outbreak of the Russo-Polish War (1654–1667)
The Russo-Polish War of 1654–1667, also called the Thirteen Years' War and the First Northern War, was a major conflict between the Tsardom of Russia and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Between 1655 and 1660, the Swedish invasion was ...
. In October 1655, the Russo-Cossack armies under Ivan Vyhovsky entered eastern Lesser Poland, reaching the Vistula, and pillaging Lublin, Puławy
Puławy (, also written Pulawy) is a city in eastern Poland, in Lesser Poland's Lublin Voivodeship, at the confluence of the Vistula and Kurówka Rivers. Puławy is the capital of Puławy County. The city's 2019 population was estimated at 47,4 ...
, and Kazimierz Dolny. The invaders quickly retreated, but a few months later, Lesser Poland was flooded
A flood is an overflow of water ( or rarely other fluids) that submerges land that is usually dry. In the sense of "flowing water", the word may also be applied to the inflow of the tide. Floods are an area of study of the discipline hydrol ...
by the Swedes
Swedes ( sv, svenskar) are a North Germanic ethnic group native to the Nordic region, primarily their nation state of Sweden, who share a common ancestry, culture, history and language. They mostly inhabit Sweden and the other Nordic countr ...
.
 Swedish invasion of Poland had catastrophic consequences for the hitherto prosperous province. The attackers, supported by their allies from
Swedish invasion of Poland had catastrophic consequences for the hitherto prosperous province. The attackers, supported by their allies from Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the A ...
, seized whole Lesser Poland, reaching as far south as Nowy Targ
Nowy Targ (Officially: ''Royal Free city of Nowy Targ'', Yiddish: ''Naymark'', Goral Dialect: ''Miasto'') is a town in southern Poland, in the Lesser Poland Voivodeship. It is located in the Orava-Nowy Targ Basin at the foot of the Gorce Mounta ...
, Nowy Sącz
Nowy Sącz (; hu, Újszandec; yi, Tzanz, צאַנז; sk, Nový Sonč; german: Neu-Sandez) is a city in the Lesser Poland Voivodeship of southern Poland. It is the district capital of Nowy Sącz County as a separate administrative unit. It has ...
, and Żywiec. All major cities were looted and burned, and some of them, like Radom, did not recover until the 19th century. The Swedes captured and pillaged Sandomierz (where they destroyed the Royal Castle, and after the invasion, the city never recovered), Opoczno, Lublin, Kazimierz Dolny Pilzno, Szydlow, Szydłowiec, Tarnów, Kielce, Kraśnik, and Kraków. The invaders seized the capital of Lesser Poland after a short siege, and their occupation of the province was confirmed after their victories in the Battle of Wojnicz
The Battle of Wojnicz was fought around the medieval town of Wojnicz in Lesser Poland as part of the Second Northern War on October 3, 1655 between forces of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth commanded by Field Crown Hetman Stanisław Lanckoro� ...
, and the Battle of Golab
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force ...
. In those years, one of the most important and symbolic events in the history of the nation took place in Lesser Poland. It was the Siege of Jasna Góra
The siege of Jasna Góra (also known less accurately as the ''Battle of Częstochowa'', pl , Oblężenie Jasnej Góry) took place in the winter of 1655 during the Second Northern War, or 'The Deluge' – as the Swedish invasion of ...
, which, according to some accounts, turned the course of the war. Furthermore, following the Treaty of Radnot, Lesser Poland was invaded in January 1657 by George II Rákóczi, whose troops caused more destruction. Foreign armies were not chased out of Lesser Poland until 1657, Kraków itself was recaptured on 18 August 1657. After these invasions, the province was ruined, with hundreds of villages, towns and cities burned. The population decreased (the urban population by nearly half), the peasantry starved, and like other parts of the Commonwealth, Lesser Poland was devastated. The period of peace lasted for about forty years, when in 1700, another major conflict, the Great Northern War
The Great Northern War (1700–1721) was a conflict in which a coalition led by the Tsardom of Russia successfully contested the supremacy of the Swedish Empire in Northern, Central and Eastern Europe. The initial leaders of the anti-Swe ...
began. Lesser Poland once again became a battleground, with Battle of Kliszów
The Battle of Kliszów (also spelled Klissow or Klezow) took place on July 19, 1702, near Kliszów in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth during the Great Northern War. A numerically superior Polish–Saxon army led by king Augustus II the Str ...
taking place there in 1702, and the Sandomierz Confederation
The Sandomierz Confederation was an anti- Swedish confederation, formed on 20 May 1704 in defense of the King of Poland, August II the Strong. It was formed in reaction to the Warsaw Confederation, and its marshal was Stanisław Ernest Denhoff. ...
formed in 1704.
After the conflict, Lesser Poland began a recovery, which was hampered by several other factors. Province's cities frequently burned (Lublin 1719, Nowy Targ 1784, Nowy Sącz, Dukla 1758, Wieliczka 1718, Miechów 1745, Drzewica), there also were numerous outbreaks of plagues and typhus (in 1707–1708, some 20,000 died in Kraków and its area)
Lesser Poland was one of main centers of the Bar Confederation
The Bar Confederation ( pl, Konfederacja barska; 1768–1772) was an association of Polish nobles ( szlachta) formed at the fortress of Bar in Podolia (now part of Ukraine) in 1768 to defend the internal and external independence of the Polis ...
. On 21 June 1786 in Kraków, local confederation was announced, and on the same day Voievode of Kraków, Michal Czarnocki, urged his citizens to join the movement. Soon afterwards, Kraków was captured by the Russian troops, and the center of Lesser Poland's insurgency moved to the mountainous south – areas around Dukla and Nowy Sącz. During the Confederation, several battles and skirmishes took place there. In 1770, after the Battle of Iwonicz, the Russians ransacked Biecz. The movement ended in 1772, and its decline was connected with the Partitions of Poland
The Partitions of Poland were three partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that took place toward the end of the 18th century and ended the existence of the state, resulting in the elimination of sovereign Poland and Lithuania for 12 ...
. Another local center of the movement was Jasna Góra Monastery
The Jasna Góra Monastery ( pl, Jasna Góra , ''Luminous Mount'', hu, Fényes Hegy, lat, Clarus Mons) in Częstochowa, Poland, is a shrine dedicated to the Virgin Mary and one of the country's places of pilgrimage. The image of the Black Ma ...
in Częstochowa, which was defended by Kazimierz Pulaski
Kazimierz Michał Władysław Wiktor Pułaski of the Ślepowron coat of arms (; ''Casimir Pulaski'' ; March 4 or March 6, 1745 Makarewicz, 1998 October 11, 1779) was a Polish nobleman, soldier, and military commander who has been called, tog ...
for almost two years (1770–1772).

Partitions of Poland (1772–1918)
ThePartitions of Poland
The Partitions of Poland were three partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that took place toward the end of the 18th century and ended the existence of the state, resulting in the elimination of sovereign Poland and Lithuania for 12 ...
began earlier in Lesser Poland than in other provinces of the country. In 1769, Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire (german: link=no, Kaiserthum Oesterreich, modern spelling , ) was a Central- Eastern European multinational great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the realms of the Habsburgs. During its existence, ...
annexed a small territory of Spisz, and next year, the towns of Czorsztyn, Nowy Sącz and Nowy Targ. In 1771, the Russians and the Prussians agreed on the first partition of the country, and in early 1772, Austrian Emperor Maria Theresa
Maria Theresa Walburga Amalia Christina (german: Maria Theresia; 13 May 1717 – 29 November 1780) was ruler of the Habsburg dominions from 1740 until her death in 1780, and the only woman to hold the position '' suo jure'' (in her own right) ...
decided to join the two powers. In the first partition of the Commonwealth, the Austrians seized the territory which would later be called Galicia
Galicia may refer to:
Geographic regions
* Galicia (Spain), a region and autonomous community of northwestern Spain
** Gallaecia, a Roman province
** The post-Roman Kingdom of the Suebi, also called the Kingdom of Gallaecia
** The medieval King ...
, and which included southwestern corner of Lesser Poland (south of the Vistula river), with Żywiec, Tarnów, and Biecz, but without major urban centers of the province, such as Kraków, Sandomierz, Radom, Lublin, Częstochowa, and Kielce.


 Second Partition of Poland (1793) did not result in significant changes of boundaries in the area, as the Austrian Empire did not participate in it. However, the Prussians moved on, and in 1793 they annexed northwestern corner of the province, together with the city of Częstochowa, and its vicinity, which became part of the newly created province of
Second Partition of Poland (1793) did not result in significant changes of boundaries in the area, as the Austrian Empire did not participate in it. However, the Prussians moved on, and in 1793 they annexed northwestern corner of the province, together with the city of Częstochowa, and its vicinity, which became part of the newly created province of South Prussia
South Prussia (german: Südpreußen; pl, Prusy Południowe) was a Provinces of Prussia, province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1793 to 1807.
History
South Prussia was created out of territory annexed in the Second Partition of Poland, Second P ...
. Therefore, in late 1793, Lesser Poland was already divided between three countries – Austrian Empire (south of the Vistula), Kingdom of Prussia (Częstochowa and northwestern corner), and still existing Commonwealth. After the Third Partition (1795), most of Lesser Poland was annexed by Austria, with all major cities. Prussia managed to seize a small, western part of the province, with the towns of Siewierz
Siewierz is a town in southern Poland, in the Będzin County in the Silesian Voivodeship, seat of Gmina Siewierz.
History
Siewierz was first mentioned in 1125, and was administered by the Castellan of Bytom. In 1177, Casimir II of Poland grant ...
, Zawiercie, Będzin, and Myszków
Myszków is a town in Poland, with 31,650 inhabitants (2019). Situated on the Warta river in the Silesian Voivodeship (since 1999), previously in Częstochowa Voivodeship (1975–1998), it is the capital of Myszków County. Myszków historica ...
, calling this land New Silesia, while the Austrians decided to name newly acquired lands of northern Lesser Poland West Galicia
New Galicia or West Galicia ( pl, Nowa Galicja or ''Galicja Zachodnia'', german: Neugalizien or ''Westgalizien'') was an administrative region of the Habsburg monarchy, constituted from the territory annexed in the course of the Third Partition ...
. In 1803, West Galicia was merged with Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria
The Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria,, ; pl, Królestwo Galicji i Lodomerii, ; uk, Королівство Галичини та Володимирії, Korolivstvo Halychyny ta Volodymyrii; la, Rēgnum Galiciae et Lodomeriae also known as ...
, but retained some autonomy. Lesser Poland was one of major centers of Polish resistance against the occupiers. On 24 March 1794 in Kraków, Tadeusz Kościuszko
Andrzej Tadeusz Bonawentura Kościuszko ( be, Andréj Tadévuš Banavientúra Kasciúška, en, Andrew Thaddeus Bonaventure Kosciuszko; 4 or 12 February 174615 October 1817) was a Polish military engineer, statesman, and military leader who ...
announced the general insurrection (see Kościuszko Uprising
The Kościuszko Uprising, also known as the Polish Uprising of 1794 and the Second Polish War, was an uprising against the Russian Empire and the Kingdom of Prussia led by Tadeusz Kościuszko in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and the P ...
), mobilising all able males of Lesser Poland. Two weeks later, Battle of Racławice
The Battle of Racławice was one of the first battles of the Polish-Lithuanian Kościuszko Uprising against Russia. It was fought on 4 April 1794 near the village of Racławice in Lesser Poland.Storozynski, A., 2009, The Peasant Prince, New Y ...
took place, ending with a Polish victory. The uprising was suppressed by combined Prusso – Russian forces, and among battles fought in Lesser Poland, there is Battle of Szczekociny
The Battle of Szczekociny was fought on the 6 June 1794 near the town of Szczekociny, Lesser Poland, between Poland and the combined forces of the Russian Empire and Kingdom of Prussia. Polish forces were led by Tadeusz Kościuszko, and the Rus ...
.
During Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fre ...
, the Duchy of Warsaw
The Duchy of Warsaw ( pl, Księstwo Warszawskie, french: Duché de Varsovie, german: Herzogtum Warschau), also known as the Grand Duchy of Warsaw and Napoleonic Poland, was a French client state established by Napoleon Bonaparte in 1807, during ...
was created by Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
out of Polish lands which had been granted to Prussia in the Partitions. In 1809, after the Polish–Austrian War, and the Treaty of Schönbrunn, the Duchy was expanded, when northern Lesser Poland was added to its territory (with Kielce, Radom, and Lublin). Following the Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon ...
, Duchy of Warsaw was turned into Russian-ruled Congress Poland
Congress Poland, Congress Kingdom of Poland, or Russian Poland, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland, was a polity created in 1815 by the Congress of Vienna as a semi-autonomous Polish state, a successor to Napoleon's Duchy of Warsaw. I ...
, and historical capital of the province, Kraków, was turned into Free City of Kraków, which also included the towns of Trzebinia, Chrzanów, Jaworzno, and Krzeszowice. In Congress Poland, the lands of Lesser Poland were initially divided between four palatinates – Palatinate of Kraków (with capital in Kielce), Palatinate of Sandomierz (with capital in Radom), Palatinate of Lublin, and Palatinate of Podlasie (with capital in Siedlce), (see also Administrative division of Congress Poland
Congress Poland was subdivided several times from its creation in 1815 until its dissolution in 1918. Congress Poland ("Russian Poland") was divided into departments, a relic from the times of the French-dominated Duchy of Warsaw. In 1816 the ...
). Later, the palatinates were turned into governorates. Thus, Russian part of Lesser Poland was divided into Kielce Governorate, Lublin Governorate
Lublin Governorate (russian: Люблинская губерния, pl, Gubernia lubelska) was an administrative unit (governorate) of Congress Poland.
History
The Lublin Governorate was created in 1837 from the Lublin Voivodeship, and had th ...
, Radom Governorate, Siedlce Governorate
Siedlce Governorate (russian: Седлецкая Губерния (pre-1917 orthography: Сѣдлецкая Губернія), pl, Gubernia siedlecka) was an administrative unit (governorate) of Congress Poland.
History
It was created in 1867 f ...
, and Piotrków Governorate
Piotrków Governorate (russian: Петроковская губерния; pl, Gubernia piotrkowska) was one of the administrative divisions ( ; ) in the Kingdom of Poland, established in 1867 by splitting some areas of the Radom and Warsaw Gover ...
(western counties, with Częstochowa and industrial area of Zagłębie Dąbrowskie Zagłębie in Polish means coalfield. It can refer to:
* Górnośląskie Zagłębie Węglowe, a mining region
* Zagłębie Dąbrowskie, a mining region
*Zagłębie Sosnowiec, an association football club
*Zagłębie Lubin
Zagłębie Lubin S.A. ...
). Borders of these administrative units did not reflect historical boundaries of the province.
 Most of the
Most of the November Uprising
The November Uprising (1830–31), also known as the Polish–Russian War 1830–31 or the Cadet Revolution,
was an armed rebellion in the heartland of partitioned Poland against the Russian Empire. The uprising began on 29 November 1830 in W ...
, which began in 1830, missed Lesser Poland, as major battles took place in the area around Warsaw. In early 1831, when Russian forces advanced into Congress Poland, some skirmishes took place in northern counties of the province – at Puławy, Kurow, and Kazimierz Dolny. In early 1846, a group of Polish patriots attempted a failed uprising
Rebellion, uprising, or insurrection is a refusal of obedience or order. It refers to the open resistance against the orders of an established authority.
A rebellion originates from a sentiment of indignation and disapproval of a situation and ...
in the Free City of Kraków. The insurrection was quickly suppressed by the Austrian troops, and as a result, the Free City was annexed by the Austrian Empire. In the same year, Austrian part of Lesser Poland was witness to a massacre of Polish nobility by the peasantry, known as Galician slaughter
The Galician Slaughter, also known as the Galician Rabacja, Peasant Uprising of 1846 or the Szela uprising (german: Galizischer Bauernaufstand; pl, Rzeź galicyjska or ''Rabacja galicyjska''), was a two-month uprising of impoverished Galicia ...
. The peasants, led by Jakub Szela, murdered about 1000 nobles, and destroyed about 500 manors. These events took place in three counties – Sanok
Sanok (in full the Royal Free City of Sanok — pl, Królewskie Wolne Miasto Sanok, rue, Санок, ''Sanok'', ua, Cянік, ''Sianik'', la, Sanocum, yi, סאניק, ''Sonik'') is a town in the Subcarpathian Voivodeship of south-eastern ...
, Jasło and Tarnów
Tarnów () is a city in southeastern Poland with 105,922 inhabitants and a metropolitan area population of 269,000 inhabitants. The city is situated in the Lesser Poland Voivodeship since 1999. From 1975 to 1998, it was the capital of the Tarn� ...
.
Northern and central Lesser Poland (the part of the province which was taken by the Russian Empire) was one of the main centers of the January Uprising
The January Uprising ( pl, powstanie styczniowe; lt, 1863 metų sukilimas; ua, Січневе повстання; russian: Польское восстание; ) was an insurrection principally in Russia's Kingdom of Poland that was aimed at ...
(1863–1864). In the first days of the insurrection, skirmishes with the Russian Army took place in such towns, as Łuków, Kraśnik, Szydłowiec
Szydłowiec (; Hebrew: שידלוביץ, Yiddish: שידלאָווצע; German: ''Schiedlowietz'') is a town in Szydłowiec County, Mazovian Voivodeship, south-central Poland, with 5,243 inhabitants (December 31, 2005). It is the seat of Gmin ...
, Bodzentyn
Bodzentyn is a town in Kielce County, Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, Poland, with 2,168 inhabitants as of December 2021. Bodzentyn belongs to Lesser Poland, and was granted town charter in 1355. The town lies in the Świętokrzyskie Mountains, ...
, and Suchedniów. Since the Poles were poorly armed, the Russians did not have major problems with them, and soon afterwards, the insurrectionists decided to organize military camps. Among biggest camps in Lesser Poland, there were Ojców (3000 soldiers), and Wąchock
Wąchock is a town in Starachowice County, Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, Poland, near Starachowice, within the historical region of Lesser Poland. In 2006, it had 2,777 inhabitants.
History
Wachock received its town charter in 1454, lost it in ...
, where Marian Langiewicz
Marian Langiewicz, full name Marian Antoni Melchior Langiewicz (; 5 August 1827, Krotoszyn – 11 May 1887, Istanbul), was a Polish patriot notable as a military leader of the January Uprising in 1863.
Biography
He was born in the province o ...
gathered up to 1500 people. The uprising died out by early spring of 1864, and among counties where it continued for the longest time, was the extreme northeastern corner of Lesser Poland, around Łuków, where reverend Stanisław Brzóska was active. Since Russian military supremacy was crushing, the Poles were forced to limit their actions to guerrilla warfare. Among the biggest battles which took place in Lesser Poland there are: Battle of Szydłowiec
Szydłowiec (; Hebrew: שידלוביץ, Yiddish: שידלאָווצע; German: ''Schiedlowietz'') is a town in Szydłowiec County, Mazovian Voivodeship, south-central Poland, with 5,243 inhabitants (December 31, 2005). It is the seat of Gmin ...
(23 January 1863); Battle of Miechów
Miechów is a town in Poland, in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, about north of Kraków. It is the capital of Miechów County. Population is 11,852 (2004). Miechów lies on the Miechówka river, along European route E77. The area of the town is ...
(17 February 1863); Battle of Małogoszcz (24 February 1863); Battle of Staszów
Staszów is a town in southeastern Poland, in Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship (historic province of Lesser Poland), about southeast of Kielce, and northeast of Kraków. It is the capital of Staszów County. The population is 15,108 (2010), wh ...
(17 February 1863); Battle of Pieskowa Skała (4 March 1863); two Battles of Opatów
Opatów (; yi, אַפּטאַ, אַפּט) is a town in southeastern Poland, within Opatów County in the Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship (Holy Cross Province). Historically, it was part of a greater region called Lesser Poland. In 2012 the populati ...
(25 November 1863, 21 February 1864).
As a result of their support of the failed insurrection, several Lesser Poland's towns lost their charters and were turned into villages. Among them were Kraśnik, Bodzentyn
Bodzentyn is a town in Kielce County, Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, Poland, with 2,168 inhabitants as of December 2021. Bodzentyn belongs to Lesser Poland, and was granted town charter in 1355. The town lies in the Świętokrzyskie Mountains, ...
, Opatów
Opatów (; yi, אַפּטאַ, אַפּט) is a town in southeastern Poland, within Opatów County in the Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship (Holy Cross Province). Historically, it was part of a greater region called Lesser Poland. In 2012 the populati ...
, Iłża
Iłża () is a small town in Masovian Voivodeship, Poland. In 2006 Iłża had approximately 5,165 inhabitants. The town belongs to the historical region of Lesser Poland, and from its foundation until 1795, it was part of Lesser Poland’s Sa ...
, Małogoszcz, Wąchock
Wąchock is a town in Starachowice County, Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, Poland, near Starachowice, within the historical region of Lesser Poland. In 2006, it had 2,777 inhabitants.
History
Wachock received its town charter in 1454, lost it in ...
, Busko-Zdrój, Jędrzejów, Cmielow, Zwoleń, Drzewica, Wierzbica, Radom County, Wierzbica, Czeladź
Czeladź (; yi, טשעלאַדזש, Chelodz) is a town in Zagłębie Dąbrowskie (part of historic Lesser Poland), in southern Poland, near Katowice and Sosnowiec. Located in the Silesian Highlands, on the Brynica river (tributary of the Vistul ...
, Kazimierz Dolny, Wolborz, Stopnica, Daleszyce, Wiślica
Wiślica is a town in Busko County, Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, in south-central Poland. It is the seat of the gmina (administrative district) called Gmina Wiślica. It lies on the Nida River, approximately south of Busko-Zdrój and so ...
, Pajęczno, Lipsko, Pacanów, Ożarów, Wolbrom, Proszowice, Nowe Miasto Korczyn, Włoszczowa, Przysucha, Opole Lubelskie.
Puławy
Puławy (, also written Pulawy) is a city in eastern Poland, in Lesser Poland's Lublin Voivodeship, at the confluence of the Vistula and Kurówka Rivers. Puławy is the capital of Puławy County. The city's 2019 population was estimated at 47,4 ...
, where in the late 18th century, a local palace owned by Czartoryski family became a museum of Polish national memorabilia and a major cultural and political centre. A number of prominent artists, both representing Romanticism in Poland, Romanticism, and Positivism in Poland, Positivism was born in Lesser Poland, including Wincenty Pol (born in Lublin), Stefan Żeromski (born near Kielce), Aleksander Świętochowski (born near Łuków in extreme northeast corner of Lesser Poland), Walery Przyborowski (born near Kielce), Piotr Michałowski, Helena Modjeska, Henryk Wieniawski (born in Lublin), Leon Wyczółkowski (born near Siedlce), Juliusz Kossak (born in Nowy Wiśnicz), Józef Szujski (born in Tarnów). In the early 20th century, Lesser Poland, especially its part which belonged to Austria-Hungary, was a center of a cultural movement called Young Poland. Many artists associated with the movement were born in Lesser Poland, with the most prominent including Władysław Orkan, Kazimierz Przerwa-Tetmajer, Xawery Dunikowski, Jacek Malczewski, Józef Mehoffer, and Stanisław Wyspiański.
Since Austrian part of Poland enjoyed a wide autonomy, the province of Galicia, whose western part was made of Lesser Poland, became a hotbed of Polish conspirational activities. In anticipation of a future war, Galician Poles, with help of their brethren from other parts of the divided country, created several paramilitary organizations, such as Polish Rifle Squads, and Riflemen's Association. The capital of Lesser Poland, Kraków, was a key center of pro-independence movements, with such individuals, as Józef Piłsudski, being actively involved in those activities. In August 1914, after the outbreak of World War I, Polish Legions in World War I, Pilsudski's Legions crossed the Austrian – Russian border north of Kraków, and entered Congress Poland
Congress Poland, Congress Kingdom of Poland, or Russian Poland, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland, was a polity created in 1815 by the Congress of Vienna as a semi-autonomous Polish state, a successor to Napoleon's Duchy of Warsaw. I ...
. However, the Pilsudski and his soldiers were disappointed to see that the inhabitants of Kielce did not welcome them with joy. The division of Lesser Poland was more visible than ever.
Kraków
Kraków (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula, Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Kraków was the official capital of Poland un ...
, Tarnów
Tarnów () is a city in southeastern Poland with 105,922 inhabitants and a metropolitan area population of 269,000 inhabitants. The city is situated in the Lesser Poland Voivodeship since 1999. From 1975 to 1998, it was the capital of the Tarn� ...
, Bielsko-Biała, Biala Krakowska, and Nowy Sącz
Nowy Sącz (; hu, Újszandec; yi, Tzanz, צאַנז; sk, Nový Sonč; german: Neu-Sandez) is a city in the Lesser Poland Voivodeship of southern Poland. It is the district capital of Nowy Sącz County as a separate administrative unit. It has ...
) was administered by Austria, while northern, larger part of the province (Częstochowa
Częstochowa ( , ; german: Tschenstochau, Czenstochau; la, Czanstochova) is a city in southern Poland on the Warta River with 214,342 inhabitants, making it the thirteenth-largest city in Poland. It is situated in the Silesian Voivodeship (adm ...
, Sosnowiec
Sosnowiec is an industrial city county in the Dąbrowa Basin of southern Poland, in the Silesian Voivodeship, which is also part of the Silesian Metropolis municipal association.—— Located in the eastern part of the Upper Silesian Indus ...
, Kielce, Radom, Lublin, Sandomierz) was forcibly part of the Russian Empire. Inhabitants of Austrian part of Poland enjoyed limited autonomy, with Polish language institutions, such as Jagiellonian University
The Jagiellonian University ( Polish: ''Uniwersytet Jagielloński'', UJ) is a public research university in Kraków, Poland. Founded in 1364 by King Casimir III the Great, it is the oldest university in Poland and the 13th oldest university in ...
. At the same time, Russian-controlled Poland was subject to Russification. As a result of decades of this division, most inhabitants of the areas stolen by Russia are not aware of their Lesser Poland's heritage. Furthermore, current administrative boundaries of the country still reflect the defunct border between the former Russian and Austria–Hungarian Empires.
Interwar Poland (1918–1939)
In 1918, when Second Polish Republic was created, whole historical Lesser Poland became part of restored Second Polish Republic, Poland. The historical area of the province was divided between four voivodeships: Kraków Voivodeship (1919–39), Kraków Voivodeship (whole), Kielce Voivodeship (1919–1939), Kielce Voivodeship (whole),Lwów Voivodeship
Lwów Voivodeship ( pl, Województwo lwowskie) was an administrative unit of interwar Poland (1918–1939). Because of the Nazi-Soviet invasion of Poland in accordance with the secret Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, it became occupied by both the Weh ...
(northwestern corner), and Lublin Voivodeship (1919–1939), Lublin Voivodeship (western part). Furthermore, in the counties of central Lesser Poland, another administrative unit, Sandomierz Voivodeship (1939), Sandomierz Voivodeship was planned, but due to the outbreak of World War II, it was never created. Boundaries between two major Lesser Poland voivodeships – Kraków, and Kielce, were the same as pre-1914 boundaries of Austria-Hungary, and Russia. Nevertheless, in the interbellum period, the notion of Lesser Poland was frequently associated only with former Austrian province of Galicia (Central-Eastern Europe), Galicia. Therefore, Western Galicia to the San river, was called ''Western Lesser Poland'', while Eastern Galicia, east of the San, with the city of Lwów (Lviv
Lviv ( uk, Львів) is the largest city in Western Ukraine, western Ukraine, and the List of cities in Ukraine, seventh-largest in Ukraine, with a population of . It serves as the administrative centre of Lviv Oblast and Lviv Raion, and is o ...
), was called ''Eastern Lesser Poland'' (voivodeships of Tarnopol Voivodeship, Tarnopol, Stanisławów Voivodeship, Stanisławów, and Lwów Voivodeship, Lwów). According to a Polish historian Jan Pisuliński, using the term ''Eastern Lesser Poland'' to denomine Eastern Galicia is incorrect, as it has no historical justification, being only a designation of nationalist and propaganda significance (similarly to analogous term ''Western Ukraine'' used at the same time by the Ukrainian side), which served in the 1920s and 1930s to make a stronger connection of the area between rivers of San and Zbruch with the Polish state and to emphasize the allegedly indigenously Polish nature of that region.
In late 1918, Lesser Poland emerged as one of main centers of fledgling Polish administration and independence movement. According to historian Kazimierz Banburski of Tarnów's District Museum, Tarnów
Tarnów () is a city in southeastern Poland with 105,922 inhabitants and a metropolitan area population of 269,000 inhabitants. The city is situated in the Lesser Poland Voivodeship since 1999. From 1975 to 1998, it was the capital of the Tarn� ...
was the first Polish city which became independent, after 123 years of Partitions of Poland, oppression. On 31 October 1918, at 8 am, Tarnów's inhabitants began disarming demoralized Austrian soldiers, and after three hours, the city was completely in Polish hands. On 28 October 1918, Polish Liquidation Committee was created in Kraków. A few days later, socialist peasants founded the Republic of Tarnobrzeg. In the night of 6/7 November 1918, ''Polish People's Republic'' was proclaimed in Lublin, by Ignacy Daszynski and other activists. In 1919, Polish legislative election, 1919, the legislative election took place in Lesser Poland without major problems.
 At that time Lesser Poland, like other provinces of the country, faced several problems. Even though major post-World War I conflicts (such as Polish–Soviet War) did not take place there, it suffered from unemployment, overpopulation, and poverty, especially in towns and countryside. Furthermore, Polish government had to connect parts of the hitherto divided country. There was no direct rail link between Kraków, and Kielce, Radom, and Lublin, and until 1934, when line from Kraków to Tunel (railroad station), Tunel was opened, all travelers had to go via
At that time Lesser Poland, like other provinces of the country, faced several problems. Even though major post-World War I conflicts (such as Polish–Soviet War) did not take place there, it suffered from unemployment, overpopulation, and poverty, especially in towns and countryside. Furthermore, Polish government had to connect parts of the hitherto divided country. There was no direct rail link between Kraków, and Kielce, Radom, and Lublin, and until 1934, when line from Kraków to Tunel (railroad station), Tunel was opened, all travelers had to go via Sosnowiec
Sosnowiec is an industrial city county in the Dąbrowa Basin of southern Poland, in the Silesian Voivodeship, which is also part of the Silesian Metropolis municipal association.—— Located in the eastern part of the Upper Silesian Indus ...
– Maczki. Lack of rail communication between former Austrian and former Russian parts of Lesser Poland is visible even today. Between Kraków and Dęblin, there are only two rail bridges along the Vistula. Residents of the province tried to improve their conditions using legal means, but when it turned out to be impossible, they took to fighting (1923 Kraków riot, 1937 peasant strike in Poland). As if to exacerbate the desperate situation, Lesser Poland witnessed 1934 flood in Poland, a catastrophic flood in 1934, after which the government decided to construct dams on local rivers.
Even though Lesser Poland's countryside was almost exclusively Polish, its towns and cities were inhabited by numerous History of the Jews in Poland, Jews, whose communities were very vibrant. In Kraków, Jews made 25% of the population, in Lublin – 31%, in Kielce – 30%, and in Radom – 32%. Apart from the Jews, and Gypsies scattered in the south, there were no other significant national minorities in interbellum Lesser Poland.
Since Lesser Poland was safely located in the middle of the country, away from both German and Soviet border, in the mid-1930s Polish government initiated one of the most ambitious project of the Second Polish Republic – Central Industrial Region (Poland), Central Industrial Region, which was located almost exclusively in Lesser Poland. Even though the project was never completed, several plants were constructed, both in Old-Polish Industrial Region, and in other counties of the province. The brand new city of Stalowa Wola was established in dense forests, around a Huta Stalowa Wola, steel mill. In the late 1930s, Lesser Poland was quickly changing, as construction of several factories, and job opportunities caused influx of rural inhabitants to the towns. Such towns, as Dębica, Starachowice, Puławy
Puławy (, also written Pulawy) is a city in eastern Poland, in Lesser Poland's Lublin Voivodeship, at the confluence of the Vistula and Kurówka Rivers. Puławy is the capital of Puławy County. The city's 2019 population was estimated at 47,4 ...
, or Kraśnik, quickly grew, with their population rising. Earlier, in 1927, Lesser Poland's Dęblin became a major center of Polish aviation, when Polish Air Force Academy was opened there, and in Mielec, PZL Mielec was opened, which was the largest aerospace manufacturer in Poland. Central Industrial Region, however, did not affect western counties of Lesser Poland, which had already been urbanized and industrialized (Bielsko-Biała, Biala Krakowska, Żywiec, Kraków
Kraków (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula, Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Kraków was the official capital of Poland un ...
, Jaworzno, Zagłębie Dąbrowskie Zagłębie in Polish means coalfield. It can refer to:
* Górnośląskie Zagłębie Węglowe, a mining region
* Zagłębie Dąbrowskie, a mining region
*Zagłębie Sosnowiec, an association football club
*Zagłębie Lubin
Zagłębie Lubin S.A. ...
, Zawiercie, and Częstochowa
Częstochowa ( , ; german: Tschenstochau, Czenstochau; la, Czanstochova) is a city in southern Poland on the Warta River with 214,342 inhabitants, making it the thirteenth-largest city in Poland. It is situated in the Silesian Voivodeship (adm ...
). The government of Poland planned further investments, such as a major East – West rail line, linking Volhynia
Volhynia (also spelled Volynia) ( ; uk, Воли́нь, Volyn' pl, Wołyń, russian: Волы́нь, Volýnʹ, ), is a historic region in Central and Eastern Europe, between south-eastern Poland, south-western Belarus, and western Ukraine. The ...
, and Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia ( pl, Górny Śląsk; szl, Gůrny Ślůnsk, Gōrny Ślōnsk; cs, Horní Slezsko; german: Oberschlesien; Silesian German: ; la, Silesia Superior) is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia, locate ...
, but they never materialized. Desperate situation and lack of jobs caused thousands of inhabitants of Lesser Poland (especially from its southern part) to leave their land, mostly for the United States of America, but also Brazil, and Canada.
 Lesser Poland remained a center of Polish culture, with Kraków's
Lesser Poland remained a center of Polish culture, with Kraków's Jagiellonian University
The Jagiellonian University ( Polish: ''Uniwersytet Jagielloński'', UJ) is a public research university in Kraków, Poland. Founded in 1364 by King Casimir III the Great, it is the oldest university in Poland and the 13th oldest university in ...
, AGH University of Science and Technology, and John Paul II Catholic University of Lublin, Catholic University of Lublin, which was opened in 1918. Several important figures of interbellum political, military, and cultural life of Poland were born in Lesser Poland. Among them were Wincenty Witos, Władysław Sikorski, Eugeniusz Kwiatkowski, Józef Dowbor-Muśnicki, Józef Haller, Władysław Belina-Prażmowski, Tadeusz Kutrzeba, Feliks Koneczny, Stefan Żeromski, Tadeusz Peiper, Maria Pawlikowska-Jasnorzewska, Witold Gombrowicz, Jan Kiepura, Stefan Jaracz. In 1920, in Lesser Poland's town of Wadowice, Karol Wojtyla, the future Pope John Paul II, was born.
World War II
On 1 September 1939, armed forces of Nazi Germany attacked Poland (see: Invasion of Poland). Lesser Poland, due to its proximity to the then-border with Germany, became a battleground on the first day of the invasion. The Germans attacked the province both in its northwest (area west of Częstochowa), and in the south (Podhale
Podhale (literally "below the mountain pastures") is Poland's southernmost region, sometimes referred to as the "Polish Highlands". The Podhale is located in the foothills of the Tatra range of the Carpathian mountains. It is the most famous ...
), along the border with Slovak Republic (1939–1945), Slovakia, which also Slovak invasion of Poland, participated in the invasion.
Lesser Poland was defended by the following Polish armies:
* Karpaty Army, which covered southern, mountainous border of the province,
* Kraków Army, guarding western part of the province, together with adjacent Polish part of Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia ( pl, Górny Śląsk; szl, Gůrny Ślůnsk, Gōrny Ślōnsk; cs, Horní Slezsko; german: Oberschlesien; Silesian German: ; la, Silesia Superior) is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia, locate ...
. Later in the course of war it joined the Karpaty Army, forming the ''Lesser Poland Army'' (''Armia Małopolska''),
* Łódź Army, which protected extreme northwestern corner of the province, north of Częstochowa,
* Prusy Army, which was main reserve of the Commander in Chief, and was concentrated in central and northern Lesser Poland (between Radom and Kielce),
* Lublin Army, improvised after 4 September, and concentrated in the area of Lublin and Sandomierz in northeastern Lesser Poland.
 After a few days the Battle of the Border was lost, and forces of German Army Group South advanced deep into Lesser Poland's territory. Polish troops resisted fiercely, and among major battles in initial stages of the war, which took place in Lesser Poland, there are Battle of Mokra, Battle of Jordanów, and Battle of Węgierska Górka. By 6 September, Polish forces were in general retreat and Marshal of Poland Edward Rydz-Śmigły ordered all troops to fall back to the secondary lines of defences at the Vistula and San Rivers. German units entered Częstochowa on 3 September (where on the next day they Częstochowa massacre, murdered hundreds of civilians), Kielce on 5 September, Kraków on 6 September, and Radom on 8 September (see also Battle of Radom). Within a week, almost whole Lesser Poland was under Nazi occupation. Northeastern part of the province, the area of Lublin, was held by the Poles until 17 September, but eventually, and after fierce battles (see Battle of Tomaszów Lubelski), all Lesser Poland was firmly under Nazi control. First draft of Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact stipulated that northeastern Lesser Poland (east of the Vistula river) was to be occupied by the Soviet Union, and forces of the Red Army reached the area of Lublin after 20 September, but withdrew east on 28 September.
On 12 October 1939, upon a decree of Adolf Hitler, General Government, a separate region of the Nazi Germany, Greater German Reich was created, with Hans Frank as its Governor-General. Its capital was established in Kraków, and it covered most of the area of historical Lesser Poland, except for its western counties, which were directly incorporated into Nazi Germany's Upper Silesia Province ( Będzin,
After a few days the Battle of the Border was lost, and forces of German Army Group South advanced deep into Lesser Poland's territory. Polish troops resisted fiercely, and among major battles in initial stages of the war, which took place in Lesser Poland, there are Battle of Mokra, Battle of Jordanów, and Battle of Węgierska Górka. By 6 September, Polish forces were in general retreat and Marshal of Poland Edward Rydz-Śmigły ordered all troops to fall back to the secondary lines of defences at the Vistula and San Rivers. German units entered Częstochowa on 3 September (where on the next day they Częstochowa massacre, murdered hundreds of civilians), Kielce on 5 September, Kraków on 6 September, and Radom on 8 September (see also Battle of Radom). Within a week, almost whole Lesser Poland was under Nazi occupation. Northeastern part of the province, the area of Lublin, was held by the Poles until 17 September, but eventually, and after fierce battles (see Battle of Tomaszów Lubelski), all Lesser Poland was firmly under Nazi control. First draft of Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact stipulated that northeastern Lesser Poland (east of the Vistula river) was to be occupied by the Soviet Union, and forces of the Red Army reached the area of Lublin after 20 September, but withdrew east on 28 September.
On 12 October 1939, upon a decree of Adolf Hitler, General Government, a separate region of the Nazi Germany, Greater German Reich was created, with Hans Frank as its Governor-General. Its capital was established in Kraków, and it covered most of the area of historical Lesser Poland, except for its western counties, which were directly incorporated into Nazi Germany's Upper Silesia Province ( Będzin, Sosnowiec
Sosnowiec is an industrial city county in the Dąbrowa Basin of southern Poland, in the Silesian Voivodeship, which is also part of the Silesian Metropolis municipal association.—— Located in the eastern part of the Upper Silesian Indus ...
, Zawiercie, Bielsko-Biała, Biała, Żywiec, Chrzanów, Olkusz).
In Lesser Poland, like in all provinces of the occupied country, the Nazis ruled with savage brutality, killing hundreds of thousands of inhabitants, both Polish and Jewish (see: World War II crimes in Poland, Occupation of Poland (1939–1945), Holocaust in Nazi-occupied Poland, Nazi crimes against ethnic Poles, German AB-Aktion in Poland, Sonderaktion Krakau). The Auschwitz concentration camp, located at the border of Lesser Poland and Upper Silesia, was opened on 14 June 1940, and on 1 October 1941, the Germans opened Majdanek concentration camp on the outskirts of Lublin. The third concentration camp in Lesser Poland was in Kraków-Płaszów concentration camp, Kraków's district of Płaszów. In late 1939 and early 1940, in Lesser Poland's spa of Zakopane, and in Kraków, several Gestapo–NKVD Conferences took place, during which the mutual cooperation between Nazi Germany and Soviet Union was discussed.
Anti-Nazi resistance was particularly strong in Lesser Poland, and it was in the extreme northwestern corner of the province (around Opoczno), that armed struggle against the occupiers began in late 1939 and early 1940 (see Henryk Dobrzański). Structures of the Home Army were well-developed in the region. Lesser Poland's independent areas of the Home Army were located in Kraków, Kielce-Radom, and Lublin. During Operation Tempest in mid-1944, several Lesser Poland's towns were liberated, also Kraków Uprising (1944), uprising in Kraków was prepared, but never realized. Apart from the Home Army, other resistance groups were strong in the province, such as pro-Communist Armia Ludowa, peasant's Bataliony Chłopskie, and right-wing National Armed Forces, with its Holy Cross Mountains Brigade.
In all major Lesser Poland's cities, Jewish ghettos were opened, with the biggest ones in Kraków Ghetto, Kraków, and Lublin Ghetto, Lublin. At first the Nazis were planning to create a so-called "reservation" for European Jews, located around Lesser Poland's town of Nisko (see Nisko Plan), but they changed the plan, and decided to murder all Jews. Condemned to death, Jews in Lesser Poland took to fighting (see Częstochowa Ghetto Uprising), but their efforts failed. As a result of The Holocaust in Poland, once thriving and numerous Jewish population of Lesser Poland was decimated.
In the summer of 1944, after Lvov–Sandomierz Offensive, Red Army pushed the Wehrmacht from eastern Lesser Poland. The city of Lublin was captured by the Soviets on 22 July 1944, Stalowa Wola – on 1 August, and Sandomierz, on the left bank of the Vistula – on 18 August. The front line stabilized along the Vistula for about six months (with some bridgeheads on the western bank on the Vistula – see Battle of Studzianki), and in early 1945, Soviet Vistula–Oder Offensive began, which pushed Germans to the gates of Berlin. The Soviets entered Kielce on 15 January, Częstochowa – on 17 January, and Kraków on 19 January. On 27 January, the Red Army entered Sosnowiec. In took the Soviets much longer to clear the areas in the mountains – they did not enter Żywiec until 5 April 1945.
Post-World War II
Together with the Red Army, NKVD and Soviet authorities followed, whose purpose was to make Poland a Communist country, with a puppet government, formed as Polish Committee of National Liberation. Since 1 August 1944, the provisional government was officially headquartered in Lesser Poland's Lublin. Thousands of people took to the forests, to continue their fight for free Poland (see Anti-communist resistance in Poland (1944–46)). Lesser Poland again was one of the main centers of the resistance. Several skirmishes took place in the province, including Battle of Kuryłówka. The Communists did not hesitate to kill those rebels they captured (Public execution in Dębica (1946)), and by 1947, the resistance movement was crushed. The last Polish Cursed soldiers, cursed soldier, Józef Franczak, was killed in 1963 near Świdnik in northeastern Lesser Poland. Also, all victims of the 1951 Mokotów Prison execution were members of Lesser Poland's branch of Freedom and Independence. Another well-known anti-Communist fighter from Lesser Poland is Józef Kuraś, who was active in the southern region ofPodhale
Podhale (literally "below the mountain pastures") is Poland's southernmost region, sometimes referred to as the "Polish Highlands". The Podhale is located in the foothills of the Tatra range of the Carpathian mountains. It is the most famous ...
.
In early 1945, the lands of Lesser Poland were divided between three voivodeships – those of Kraków, Lublin, and Kielce. Since summer 1945, several counties were transferred to neighboring voivodeships – eastern Lesser Poland (Dębica, Jasło, Mielec) became part of Rzeszów Voivodeship, while western counties of Będzin and Zawiercie were transferred to Katowice Voivodeship. In 1950, the city of Częstochowa became part of Katowice Voivodeship, and next year, the city of Bielsko-Biała
Bielsko-Biała (; cs, Bílsko-Bělá, german: Bielitz-Biala, szl, Bjylsko-Bjoło) is a city in southern Poland, with a population of approximately 168,319 as of December 2021, making it the 22nd largest city in Poland, and an area of . It is a ...
was created out of Lesser Poland's Biala Krakowska, and Upper Silesia's Bielsko. The new city became part of Katowice Voivodeship. Lesser Poland was further divided in 1975, when territorial reform was carried out (see Voivodeships of Poland (1975–1988)). Counties were abolished, and several small voivodeships were created, in such Lesser Poland's towns and cities, as Tarnobrzeg, Tarnów, Nowy Sącz, Bielsko-Biała, Radom, Częstochowa, and Siedlce.
The government of Communist Poland invested in heavy industry, following the pre-1939 idea of Central Industrial Area. In Kraków, a new district of Nowa Huta was constructed in the 1950s. In Częstochowa and Zawiercie, the steelworks were significantly expanded, and in early 1970, the government initiated construction of Katowice Steelworks, which, despite its name, is located in Lesser Poland's Dąbrowa Górnicza. To connect Katowice Steelworks with Soviet plants, in late 1970s Broad Gauge Metallurgy Line was opened, which crossed Lesser Poland from west to east. Among other major factories, opened in Lesser Poland during Communist rule, there are:
* FSC Lublin, opened in 1951,
* FSC Star in Starachowice, opened in 1948, and based on earlier factory,
* PZL-Świdnik, opened in 1951,
* Zaklady Azotowe Puławy
Puławy (, also written Pulawy) is a city in eastern Poland, in Lesser Poland's Lublin Voivodeship, at the confluence of the Vistula and Kurówka Rivers. Puławy is the capital of Puławy County. The city's 2019 population was estimated at 47,4 ...
, opened in 1965,
* Połaniec Power Station, opened in 1979,
* Skawina Power Station, opened in 1957,
* Nowiny Cement Plant, opened in 1960,
* Kozienice Power Station, opened in 1973.
Local Government Reorganization Act (1998)




 In 1998, the government of Poland carried out administrative reform of the country. For the first time in history,
In 1998, the government of Poland carried out administrative reform of the country. For the first time in history, Lesser Poland Voivodeship
Lesser Poland Voivodeship or Lesser Poland Province (in pl, województwo małopolskie ), also known as Małopolska, is a voivodeship (province), in southern Poland. It has an area of , and a population of
3,404,863 (2019).
It was created on 1 ...
was created, with capital in Kraków, and area of 15,108 square kilometers. The new province covers only a small, southwestern part of historical Lesser Poland.
Today, Lesser Poland is divided between several voivodeships: whole Lesser Poland Voivodeship, whole Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, western half of Lublin Voivodeship
The Lublin Voivodeship, also known as the Lublin Province ( Polish: ''województwo lubelskie'' ), is a voivodeship (province) of Poland, located in southeastern part of the country. It was created on January 1, 1999, out of the former Lublin, C ...
, western part of Subcarpathian Voivodeship, eastern half of Silesian Voivodeship, southern part of Mazovian Voivodeship and southeastern corner of Łódź Voivodeship
Łódź Voivodeship (also known as Lodz Province, or by its Polish name ''Województwo łódzkie'' ) is a province- voivodeship in central Poland. It was created on 1 January 1999 out of the former Łódź Voivodeship (1975–1999) and the Sier ...
(around Opoczno).
There were suggestions that Lesser Poland voivodeship should stretch from Bielsko-Biała
Bielsko-Biała (; cs, Bílsko-Bělá, german: Bielitz-Biala, szl, Bjylsko-Bjoło) is a city in southern Poland, with a population of approximately 168,319 as of December 2021, making it the 22nd largest city in Poland, and an area of . It is a ...
, to Ostrowiec Świętokrzyski and Sandomierz. Furthermore, creation of Old Poland Voivodeship was proposed, on the historical lands of northern Lesser Poland. Also, since about half of territory of current Silesian Voivodeship belongs to historical Lesser Poland, there are suggestions to rename it into ''Silesian – Lesser Poland Voivodeship''.
Major cities and towns (by size)
The list is based on the Polish Central Statistical Office list of 100 biggest cities of Poland, as for 30 June 2008. In theKingdom of Poland
The Kingdom of Poland ( pl, Królestwo Polskie; Latin: ''Regnum Poloniae'') was a state in Central Europe. It may refer to:
Historical political entities
* Kingdom of Poland, a kingdom existing from 1025 to 1031
* Kingdom of Poland, a kingdom exi ...
and Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Crown of the Kingdom of ...
, several other locations used to be important urban centers of Lesser Poland, but in the course of the time, their significance declined. The main example is Sandomierz, which for hundreds of years was one of the most important cities of Poland, but now is a town of 25,000. Other examples of historically important places, which are now little towns or villages are:
* Biecz, a town of 5,000, once the seat of a Biecz County, county, incorporated in 1257,
* Chęciny, a village now, once the seat of a Chęciny County, county, with a royal castle,
* Czchów, a town of 2,000, incorporated before 1333, once the seat of a county,
* Goraj, Lublin Voivodeship, Goraj, a village now, which used to be one of urban centers of Lublin Voivodeship,
* Iłża
Iłża () is a small town in Masovian Voivodeship, Poland. In 2006 Iłża had approximately 5,165 inhabitants. The town belongs to the historical region of Lesser Poland, and from its foundation until 1795, it was part of Lesser Poland’s Sa ...
, a town of 5,000, incorporated before 1294, with a royal castle,
* Kazimierz Dolny, which enjoyed its greatest prosperity in the 16th and the first half of the 17th century,
* Koprzywnica, a village now, a town in 1268–1869,
* Książ Wielki, a town in 1385–1875, once the seat of a Książ County, county,
* Lelów, a village now, which used to be the seat of a Lelów County, county. Incorporated in 1314, with a royal castle,
* Nowy Korczyn, Nowe Miasto Korczyn, a town in 1258–1869, with a royal castle, where general sejmiks of Lesser Poland took place,
* Opatów
Opatów (; yi, אַפּטאַ, אַפּט) is a town in southeastern Poland, within Opatów County in the Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship (Holy Cross Province). Historically, it was part of a greater region called Lesser Poland. In 2012 the populati ...
, a town of 7,000, incorporated in 1282, once the seat of sejmiks,
* Parczew, now a town of 10,000, once a major urban center of northeast Lesser Poland,
* Pilzno, now a town of 4,000, once the seat of a Pilzno County, county,
* Sieciechów, Masovian Voivodeship, Sieciechów, a village now, once an important town, incorporated in 1232,
* Stężyca, Lublin Voivodeship, Stężyca, a village now. Once the seat of a Stężyca Land, county, which used to be a town in 1330–1869,
* Szczyrzyc, a village now, which used to be the seat of a Szczyrzyc County, county,
* Szydłowiec
Szydłowiec (; Hebrew: שידלוביץ, Yiddish: שידלאָווצע; German: ''Schiedlowietz'') is a town in Szydłowiec County, Mazovian Voivodeship, south-central Poland, with 5,243 inhabitants (December 31, 2005). It is the seat of Gmin ...
, a town of 12,000, with a royal castle, which in the Renaissance period was an important urban center of northern Lesser Poland,
* Szydłów, a village now, which used to be a major urban center of Sandomierz Voivodeship
Sandomierz Voivodeship ( pl, Województwo Sandomierskie, la, Palatinatus Sandomirensis) was a unit of administration and local government in Poland from the 14th century to the partitions of Poland in 1772–1795. It was part of the Lesser Polan ...
,
* Urzędów, a village now, which in 1405–1869 used to be a town and the seat of a Urzędów County, county,
* Wiślica
Wiślica is a town in Busko County, Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, in south-central Poland. It is the seat of the gmina (administrative district) called Gmina Wiślica. It lies on the Nida River, approximately south of Busko-Zdrój and so ...
, a village now, which was probably the capital of the Vistulans, and the seat of a Wiślica County, county,
* Wojnicz, now a town of 3,500, incorporated in 1278, used to be the seat of a county,
* Zawichost, a town of 2,000, once a royal town with a castle, incorporated before 1255.
Economy and industry
History of industry in Lesser Poland goes back to prehistoric times, when in Świętokrzyskie Mountains, first bloomery, bloomeries were constructed. In the Middle Ages, first plants were opened in that area, and as a result, Old-Polish Industrial Region was created, which was a major industrial region of thePolish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Crown of the Kingdom of ...
. In the 17th century, first Polish blast furnaces were constructed in Samsonów by Italian engineer Hieronim Caccio. Apart from iron products, used for military purposes, Old-Polish Industrial Region also manufactured charcoal and glass. In 1782, in Poland there were 34 bloomeries, out of which 27 were located in Old-Polish Industrial Region. Another major industrial area of Lesser Poland is Zagłębie Dąbrowskie Zagłębie in Polish means coalfield. It can refer to:
* Górnośląskie Zagłębie Węglowe, a mining region
* Zagłębie Dąbrowskie, a mining region
*Zagłębie Sosnowiec, an association football club
*Zagłębie Lubin
Zagłębie Lubin S.A. ...
, where in the 16th century, lead, silver, and zinc were found. As early as in the 15th century, coal was extracted in Trzebinia – Siersza, and in the following centuries, especially in the 19th century, several coal mines and steel mills were opened in Zagłębie and in Zagłębie Krakowskie (first coal mine in Jaworzno was opened in 1792). In nearby Olkusz, the history of zinc mining dates to the 12th century when Casimir II the Just set up a mining settlement. Also, in the towns of Wieliczka and Bochnia, salt mines were established in the 12th and 13th centuries (see Bochnia Salt Mine, Wieliczka Salt Mine).
In the 20th century, natural resources were also discovered in central and eastern counties Lesser Poland.
In 1964, the world's largest open-pit sulfur mine was opened in Machów near Tarnobrzeg. Other sulfur deposits in the area of Tarnobrzeg are Jeziorko, Grzybów-Gacki, and Grębów-Wydza. The mine at Machów is now closed. In the late 1960s, eastern Lesser Poland became one of three coal basins of the country, when Lublin Basin was created. Major coal mine in the area is Bogdanka Coal Mine, KWK Bogdanka near Łęczna, which is the only coal mine in Poland which has continuously generated a profit. Other Polish coal mines located in Lesser Poland are those found in western part of the province, along the boundary with Upper Silesia – Janina Coal Mine, KWK Janina in Jaworzno, Sobieski Coal Mine, KWK Sobieski, and also in Jaworzno. Copper and silver are extracted in Myszków
Myszków is a town in Poland, with 31,650 inhabitants (2019). Situated on the Warta river in the Silesian Voivodeship (since 1999), previously in Częstochowa Voivodeship (1975–1998), it is the capital of Myszków County. Myszków historica ...
(see Myszków mine).
In the late 1930s, the government of the Second Polish Republic created Central Industrial Region (Poland), Central Industrial Region, which was almost exclusively located in Lesser Poland. Currently, within borders of the province, there are following industrial regions:
* ''Bielsko Industrial Region'' (''Bielski Okręg Przemysłowy''), which includes both towns from Lesser Poland, and Upper Silesia (Andrychów, Bielsko-Biała
Bielsko-Biała (; cs, Bílsko-Bělá, german: Bielitz-Biala, szl, Bjylsko-Bjoło) is a city in southern Poland, with a population of approximately 168,319 as of December 2021, making it the 22nd largest city in Poland, and an area of . It is a ...
, Cieszyn, Kęty, Pszczyna, Skoczów, Żywiec),
* ''Częstochowa Industrial Region'' (''Częstochowski Okręg Przemysłowy''), which includes Częstochowa, Myszków
Myszków is a town in Poland, with 31,650 inhabitants (2019). Situated on the Warta river in the Silesian Voivodeship (since 1999), previously in Częstochowa Voivodeship (1975–1998), it is the capital of Myszków County. Myszków historica ...
, and Zawiercie.
* Upper Silesian Industrial Region (''Górnośląski Okręg Przemysłowy''). Despite the name, it also includes cities from Lesser Poland's Zagłębie Dąbrowskie Zagłębie in Polish means coalfield. It can refer to:
* Górnośląskie Zagłębie Węglowe, a mining region
* Zagłębie Dąbrowskie, a mining region
*Zagłębie Sosnowiec, an association football club
*Zagłębie Lubin
Zagłębie Lubin S.A. ...
– Sosnowiec, Będzin, Czeladź
Czeladź (; yi, טשעלאַדזש, Chelodz) is a town in Zagłębie Dąbrowskie (part of historic Lesser Poland), in southern Poland, near Katowice and Sosnowiec. Located in the Silesian Highlands, on the Brynica river (tributary of the Vistul ...
, Dąbrowa Górnicza, Wojkowice,
* ''Jaworzno – Chrzanów Industrial Region'' (''Jaworznicko-Chrzanowski Okręg Przemysłowy''), with the towns of Jaworzno, Chrzanów, Trzebinia, Libiąż, Chełmek, Bukowno, Alwernia, Krzeszowice,
* ''Carpathian Industrial Region'' (''Karpacki Okręg Przemysłowy''), which stretches from Nowy Sącz
Nowy Sącz (; hu, Újszandec; yi, Tzanz, צאַנז; sk, Nový Sonč; german: Neu-Sandez) is a city in the Lesser Poland Voivodeship of southern Poland. It is the district capital of Nowy Sącz County as a separate administrative unit. It has ...
, through Jasło and Gorlice, to Sanok
Sanok (in full the Royal Free City of Sanok — pl, Królewskie Wolne Miasto Sanok, rue, Санок, ''Sanok'', ua, Cянік, ''Sianik'', la, Sanocum, yi, סאניק, ''Sonik'') is a town in the Subcarpathian Voivodeship of south-eastern ...
,
* ''Kraków Industrial Region'' (''Krakowski Okręg Przemysłowy'') – the city of Kraków and the towns of Wieliczka, Skawina
Skawina is a town in southern Poland with 27,328 inhabitants (2008). Situated in the Lesser Poland Voivodeship (since 1999), previously in Kraków Voivodeship (1975–1998). The town is located on the Skawinka river, in close proximity to the c ...
, Myślenice, Bochnia,
* '' Lublin Industrial Region'' (''Lubelski Okręg Przemysłowy'') – the city of Lublin and the towns of Świdnik, Puławy
Puławy (, also written Pulawy) is a city in eastern Poland, in Lesser Poland's Lublin Voivodeship, at the confluence of the Vistula and Kurówka Rivers. Puławy is the capital of Puławy County. The city's 2019 population was estimated at 47,4 ...
, Łęczna,
* ''Tarnobrzeg Industrial Area'' (''Tarnobrzeski Okręg Przemysłowy'') – Stalowa Wola, Tarnobrzeg, Nisko, Staszów
Staszów is a town in southeastern Poland, in Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship (historic province of Lesser Poland), about southeast of Kielce, and northeast of Kraków. It is the capital of Staszów County. The population is 15,108 (2010), wh ...
, Janów Lubelski, Gorzyce, Tarnobrzeg County, Gorzyce, Połaniec, Mielec,
* ''Tarnów – Rzeszów Industrial Region'' (''Tarnowsko-Rzeszowski Okręg Przemysłowy''), which stretches from Tarnów to Rzeszów, with such towns, as Dębica, Niedomice, Sędziszów Małopolski
Sędziszów Małopolski is a town in Ropczyce-Sędziszów County, Subcarpathian Voivodeship, Poland, with a population of 12,226 (1 January 2019). Sędziszów is located in eastern Lesser Poland, near the historic boundary between Lesser Poland a ...
, Ropczyce
Ropczyce ( yi, ראָפּשיץ) is a town in the Subcarpathian Voivodeship in south-eastern Poland, situated in the valley of the Wielopolka River (a tributary of the Wisłoka River). The town has a population of 15,098 (). and is the seat of ...
.
In 2009, Polityka weekly made its own list of 500 biggest Polish companies. According to the list, second biggest company of the country was Polska Grupa Energetyczna, which, as Polityka stated, is headquartered in Lublin. Third biggest company of Poland in 2009 was ''Fiat Auto Poland'' from Bielsko-Biała. Other Lesser Polish companies which ranked high were: ''BP, BP Poland'' from Kraków (ranked 12th), ''Emperia Holding'' from Lublin (ranked 26th), Kolporter Holding from Kielce (ranked 43rd), and Żywiec Brewery (ranked 44th). Other major companies of Lesser Poland are ''Azoty Tarnów'', Bank BPH, Bogdanka Coal Mine, Carlsberg Polska, Comarch, ''Dębica SA'', ''Huta Częstochowa'', ''Huta Katowice'', Fablok, FŁT-Kraśnik, Huta Stalowa Wola, ''Instal-Lublin'', Janina Coal Mine, Jaworzno Power Station, Kozienice Power Station, Łucznik Arms Factory, ''Nowiny Cement Plant'' near Kielce, Połaniec Power Station, PZL Mielec, PZL-Świdnik, Sobieski Coal Mine, Tadeusz Sendzimir Steelworks.
Since the lands of historical Lesser Poland belong now to different voivodeships, unemployment rate differs from one region to another. In January 2010, in Poland the unemployment rate was 12,7%. In Silesian Voivodeship, eastern half of which is Lesser Poland, it was 9,9%, in Lesser Poland Voivodeship – 10,5%, in Subcarpathian Voivodeship – 16,3%, in Holy Cross Voivodeship – 15,5%, in Lublin Voivodeship – 13,6%, and in Mazovian Voivodeship (southern part of which is Lesser Poland) – 9,6%. In Lesser Poland's cities, the best situation was in Kraków (as for November 2009), where 4,1% had no job. In Bielsko-Biała, the rate was 5,7%, in Lublin – 8,8%, in Siedlce – 9,1%, in Tarnów – 9,2%, in Nowy Sącz – 10%, in Kielce and Częstochowa – 10,1%, in Jaworzno – 10,2%, in Dąbrowa Górnicza – 10,3%, in Sosnowiec – 12,2%, and in Tarnobrzeg – 14,3%. The worst situation on the job market (as for November 2009) was in Radom, where unemployment rate was 20,9% (it made Radom second worst city county of the nation, only after Grudziądz).
Transport
Roads
Several European roads (see International E-road network) cross Lesser Poland. The most important one is the European route E40, which goes from west to east, across whole Europe. In Lesser Poland, the E40 goes from Jaworzno, via Kraków and Tarnów, towards eastern border of the country. Another main European road in Lesser Poland is the European route E77, E77, which goes from north to south, via Radom, Kielce and Kraków, to southern border of Poland at Chyżne. Third major European road in Lesser Poland is the European route E30, E30, which crosses the territory of the province in its extreme northeast corner, inSiedlce
Siedlce [] ( yi, שעדליץ ) is a city in eastern Poland with 77,354 inhabitants (). Situated in the Masovian Voivodeship (since 1999), previously the city was the capital of a separate Siedlce Voivodeship (1975–1998). The city is situated b ...
. Apart from these roads, Lesser Poland is crossed by the following European routes:
* European route E371, E371, which begins in Radom, and goes via Ostrowiec Świętokrzyski, Tarnobrzeg, and Rzeszów to the border crossing at Barwinek, Subcarpathian Voivodeship, Barwinek,
* European route E372, E372, which begins in Warsaw, and via northeastern Lesser Poland (Lublin, Świdnik), goes to Ukrainian border at Hrebenne, Tomaszów Lubelski County, Hrebenne,
* European route E462, E462, which goes through southwestern corner of the province, from Czech border and Bielsko-Biała, to John Paul II International Airport Kraków-Balice,
* European route E75, E75, which crosses western counties of Lesser Poland – from Częstochowa, through Dąbrowa Górnicza and Jaworzno, to Bielsko-Biała and Polish – Czech border.
Airports
Within borders of historical Lesser Poland, there are two airports – John Paul II International Airport Kraków – Balice, and Katowice International Airport, which is located in the village of Pyrzowice, on the border between Lesser Poland and Upper Silesia. Pyrzowice is part of Gmina Ożarowice, which afterPartitions of Poland
The Partitions of Poland were three partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that took place toward the end of the 18th century and ended the existence of the state, resulting in the elimination of sovereign Poland and Lithuania for 12 ...
, and Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon ...
belonged to Będzin County of the Russian Empire. In the interbellum, the area of future airport belonged to Lesser Poland's Kielce Voivodeship (1919–1939), Kielce Voivodeship, and in 1945, was transferred to Katowice Voivodeship (initially ''Silesian-Dąbrowa Voivodeship''). In 1998, Ożarowice, together with the airport, was attached to Tarnowskie Góry County, despite the fact that it is not located in Upper Silesia
Further airports in Lesser Poland will be opened in the future – Lublin – Świdnik, Kielce – Obice, and Radom – Sadków. Also, Rzeszów-Jasionka Airport is located on eastern border of the province.
Railroads
Railroad network of Lesser Poland is very unevenly distributed. It is very dense in the west, along the border with Upper Silesia, and sparse in the east, especially along the Vistula, and around Lublin. All major cities of the province are connected with each other, however traveling from Kraków to Lublin is time-consuming, as trains have to take an extended route, via Kielce, Radom, and Dęblin. Also, there is no direct connection between Tarnów and Kielce, as these cities belonged to different countries before 1918. Underdevelopment of the railroads in northern and eastern Lesser Poland is the result of the policy of the Russian Empire. For military reasons, the Russians were not interested in construction of a dense network of lines along the border with Germany and Austria-Hungary, allowing only the construction of narrow-gauge connections. Along the Vistula, between Kraków and Dęblin (the distance of some 320 kilometers), there are only four rail bridges – in Dęblin (rebuilt after the war, in 1947), in Sandomierz (built in 1928), in Tarnobrzeg-Nagnajów (built in 1961, together with a road bridge), and in Zaduszniki, Subcarpathian Voivodeship, Zaduszniki (built in 1979 for the Broad Gauge Metallurgy Line). In Kraków itself, there are three rail bridges over the Vistula. Among rail hubs of Lesser Poland, there are Bielsko-Biała, Chabówka, Częstochowa, Dąbrowa Górnicza, Dębica, Dęblin, Jaworzno-Szczakowa, Kalwaria Zebrzydowska Lanckorona (PKP station), Kalwaria Zebrzydowska Lanckorona, Kielce,Koniecpol
Koniecpol is a town in Częstochowa County, Silesian Voivodeship, Poland, with 5,910 inhabitants (2019). In the times of Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth it was the seat of the Koniecpolski magnate
The magnate term, from the late Latin ''magn ...
, Kozłów, Subcarpathian Voivodeship, Kozłów, Kraków, Lublin, Łuków, Muszyna, Nowy Sącz, Oświęcim, Siedlce, Spytkowice, Wadowice County, Spytkowice, Skarżysko-Kamienna, Stalowa Wola, Stróże, Nowy Sącz County, Stróże, Sucha Beskidzka, Radom, Tarnów, Trzebinia, Tunel (railroad station), Tunel, Zawiercie, and Żywiec.
In the late 1970s, the Communist government built the broad-gauge Broad Gauge Metallurgy Line, which crosses Lesser Poland from west to east along the Vistula.
Tourism and nature
The historical capital of Lesser Poland –Kraków
Kraków (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula, Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Kraków was the official capital of Poland un ...
– is regarded as the cultural capital of Poland, while Zakopane is considered the winter capital of Poland. In 1978, UNESCO placed Kraków's Old Town on the list of World Heritage Sites. From Sandomierz to Kraków goes the re-established Lesser Polish Way, one of the routes of the medieval Way of St. James. Every year, hundreds of thousands of tourists come to Lesser Poland, to see its historic cities – Sandomierz, Kazimierz Dolny, Zakopane, Biecz, Opatów
Opatów (; yi, אַפּטאַ, אַפּט) is a town in southeastern Poland, within Opatów County in the Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship (Holy Cross Province). Historically, it was part of a greater region called Lesser Poland. In 2012 the populati ...
, Szydłów, Lublin, and Kraków. Famous Jasna Góra Monastery
The Jasna Góra Monastery ( pl, Jasna Góra , ''Luminous Mount'', hu, Fényes Hegy, lat, Clarus Mons) in Częstochowa, Poland, is a shrine dedicated to the Virgin Mary and one of the country's places of pilgrimage. The image of the Black Ma ...
in Częstochowa, spiritual capital of the country, attracts hundreds of thousands of pilgrims, as well as Auschwitz concentration camp (also placed on the UNESCO World Heritage Sites List). Lesser Poland has many museums, the city of Kraków itself has about sixty of them. Among the most famous are The Czartoryski Museum, The Galicia Jewish Museum, The National Museum, Kraków, Polish Aviation Museum, Sukiennice Museum, and Wawel Castle
The Wawel Royal Castle (; ''Zamek Królewski na Wawelu'') and the Wawel Hill on which it sits constitute the most historically and culturally significant site in Poland. A fortified residency on the Vistula River in Kraków, it was established ...
. There are museums in other locations of the province, such as Auschwitz-Birkenau State Museum, Bielsko-Biała Museum, Holy Father John Paul II Family Home in Wadowice, ''Jacek Malczewski Museum in Radom'', ''Lublin Museum'', ''Museum of Częstochowa'', ''Museum of Sandomierz Diocese'', ''Museum of Żywiec Brewery'', ''Museum of Zagłębie in Będzin'', Przypkowscy Clock Museum, ''Regional Museum in Wiślica
Wiślica is a town in Busko County, Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, in south-central Poland. It is the seat of the gmina (administrative district) called Gmina Wiślica. It lies on the Nida River, approximately south of Busko-Zdrój and so ...
'', ''Regional Museum in Siedlce'', ''Tytus Chałubiński Tatra Museum in Zakopane''.
Among other major places of interest of the province are: Baranów Sandomierski Castle, Będzin Castle, Chęciny Castle, Czarnolas, Zwoleń County, Czarnolas in Zwoleń, Dunajec river castles, Kalwaria Zebrzydowska park (UNESCO World Heritage Sites List), Krzyżtopór, Lipnica Murowana, Lublin Castle, Łysa Góra, Maczuga Herkulesa, Majdanek concentration camp, Niedzica Castle, Ogrodzieniec, Pieskowa Skała, Temple of the Sibyl, Trail of the Eagles' Nests, Wieliczka Salt Mine (UNESCO World Heritage Sites List), Wooden Churches of Southern Lesser Poland (UNESCO World Heritage Sites List). Furthermore, thousands of tourists come to Radom in northern Lesser Poland, to watch the popular, biannual Radom Air Show. Lesser Poland has a number of open-air museums – ''Góra Birów'' in Kraków-Częstochowa Upland
The Kraków-Częstochowa Upland, also known as the Polish Jurassic Highland or Polish Jura ( pl, Jura Krakowsko-Częstochowska), is part of the Jurassic System of south–central Poland, stretching between the cities of Kraków, Częstochowa an ...
, ''Museum of Kielce Village'' in Kielce, ''Museum of Lublin Village'' in Lublin, ''Museum of Folk Culture'' in Kolbuszowa, ''Museum of Radom Village'' in Radom, ''Vistula River Etnographic Park'' in Babice, Chrzanów County, Babice, ''Nowy Sącz Etnographic Park'' in Nowy Sącz, ''Orawa Etnographic Park'' in Zubrzyca Górna, ''Chabówka Rolling-Stock Heritage Park'' in Chabówka. The Małopolska Institute of Culture, located in Kraków, promotes the activities of regional museums and smaller sites of interest.
Lesser Poland is famous for its underground waters and spas, such as Busko-Zdrój, Solec-Zdrój, Nałęczów, Muszyna, Szczawnica, Piwniczna, Wysowa-Zdrój, Rabka-Zdrój, Rabka, Swoszowice, Kraków, Swoszowice, Żegiestów, Krzeszowice, Wieliczka, and Krynica-Zdrój. Mountains and resorts of the province make it a major center of Polish tourism – Tatra National Park is visited by around 3 million tourists every year.
The following List of national parks of Poland, National Parks are located in Lesser Poland:
Education
Universities
Lesser Poland is home to Poland's oldest university – Kraków'sJagiellonian University
The Jagiellonian University ( Polish: ''Uniwersytet Jagielloński'', UJ) is a public research university in Kraków, Poland. Founded in 1364 by King Casimir III the Great, it is the oldest university in Poland and the 13th oldest university in ...
, which was established in 1364. For centuries, it was the only college of the province, and of the whole country. In December 1918, John Paul II Catholic University of Lublin was opened, becoming second university of Lesser Poland. In 1944, also in Lublin, Maria Curie-Skłodowska University was established.
Technical universities
There are several technical universities in Lesser Poland – Kraków's AGH University of Science and Technology, and Cracow University of Technology, University of Technology, as well as University of Bielsko-Biała, Częstochowa University of Technology, Lublin University of Technology, Kazimierz Pułaski Technical University of Radom, and Kielce University of Technology.Other colleges
Future teachers may study at Pedagogical University of Cracow, or Jan Długosz University in Częstochowa, and future physicians at Jagiellonian University Medical College, and Medical University of Lublin. Other state colleges are Jan Kochanowski University in Kielce, Pontifical University of John Paul II in Kraków, Agricultural University of Cracow, University of Life Sciences in Lublin, and Cracow University of Economics. Unique in the country is the Polish Air Force Academy, located in Dęblin. Among private colleges of Lesser Poland, there is Wyższa Szkoła Biznesu – National-Louis University in Nowy Sącz.Regional identity and culture
Since Lesser Poland ceased to exist as a unified region in the late 18th century, during thePartitions of Poland
The Partitions of Poland were three partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that took place toward the end of the 18th century and ended the existence of the state, resulting in the elimination of sovereign Poland and Lithuania for 12 ...
, most of its inhabitants are not aware of their heritage. Even the residents of Jaworzno, a city which for centuries belonged to Kraków Land and only in 1975 was transferred to Katowice Voivodeship (see Voivodeships of Poland (1975–98)), are not familiar with their Lesser Polish roots. In a poll in April 2011, 57% of Jaworzno's inhabitants stated that their city is historically tied with Lesser Poland, but as many as 36% said their city is tied with Upper Silesia. Polish linguist Jan Miodek emphasizes the fact that linguistically, Będzin is closer to Myślenice than to Tarnowskie Góry, only 20 km away. Miodek wrote that even though Upper Silesia and Lesser Poland's Zagłębie Dąbrowskie are industrially and administratively tied, both regions are culturally and linguistically different from each other. Residents of Zagłębie Dąbrowskie are known for their dislike of Upper Silesians, whom they call ''hanysy'', while the Silesians call them ''gorole''. In recent years, more inhabitants of Zagłębie become aware of their Lesser Poland's heritage, Also, after Partitions of Poland
The Partitions of Poland were three partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that took place toward the end of the 18th century and ended the existence of the state, resulting in the elimination of sovereign Poland and Lithuania for 12 ...
, when Austrian province of Galicia was created, the cities of Rzeszów
Rzeszów ( , ; la, Resovia; yi, ריישא ''Raisha'')) is the largest city in southeastern Poland. It is located on both sides of the Wisłok River in the heartland of the Sandomierz Basin. Rzeszów has been the capital of the Subcarpathian ...
and Przemyśl
Przemyśl (; yi, פשעמישל, Pshemishl; uk, Перемишль, Peremyshl; german: Premissel) is a city in southeastern Poland with 58,721 inhabitants, as of December 2021. In 1999, it became part of the Subcarpathian Voivodeship; it was p ...
, which are part of historical Red Ruthenia
Red Ruthenia or Red Rus' ( la, Ruthenia Rubra; '; uk, Червона Русь, Chervona Rus'; pl, Ruś Czerwona, Ruś Halicka; russian: Червонная Русь, Chervonnaya Rus'; ro, Rutenia Roșie), is a term used since the Middle Ages fo ...
, became associated with Lesser Poland. Therefore, currently the notion of Lesser Poland most commonly applies to the two voivodeships which in the past belonged to Austrian Empire – Lesser Poland Voivodeship, and Subcarpathian Voivodeship
Among several Lesser Poland's regional organizations, one of the most important is ''Stowarzyszenie Gmin i Powiatów Małopolski'' (''The Association of Villages and Counties of Lesser Poland''). It publishes a magazine called ''Wspólnota Małopolska'' (''Lesser Polish Community''), and every year it chooses a ''Lesser Polish Person of the Year'' (among winners are John Paul II, Anna Dymna, and Stanisław Dziwisz). ''The Association of Villages and Counties of Lesser Poland'' has over 120 members from four Polish voivodeships. Among members are cities of Kraków, Częstochowa, Bielsko-Biała, Tarnów, and Przemyśl.
Arguably, the most famous product of Lesser Polish cuisine is the bagel, which was invented in Kraków. Other famous food specialties of the province are oscypek (EU Protected Geographical Status), slivovitz from the village of Łącko, Lesser Poland Voivodeship, Łącko, bublik, papal cream cake from Wadowice, Lisiecka Sausage (EU Protected Geographical Status), and Bryndza Podhalańska. Among other popular products that are made in Lesser Poland, there are beers (Browary Lubelskie, Żywiec Beer, and Carlsberg Polska, Okocim Beer), pastas and snacks from Lublin's Lubella, Kielce Mayonnaise, coffee substitute beverage Inka (drink), INKA from Skawina, chocolates from Kraków's Wawel Factory, juices from Tymbark, vodka Wódka Żołądkowa Gorzka, Żołądkowa Gorzka produced in Lublin, and Chopin (vodka), Chopin produced in Siedlce.
Folk costumes from Lesser Poland are widely known across the country – a dancing couple, dressed in traditional Kraków costume (Krakowiacy), is presented on the logo of renowned Żywiec beer, and Podhale
Podhale (literally "below the mountain pastures") is Poland's southernmost region, sometimes referred to as the "Polish Highlands". The Podhale is located in the foothills of the Tatra range of the Carpathian mountains. It is the most famous ...
is one of few Polish regions, where people regularly wear their traditional costumes. Both Kraków and Podhale folk costumes are among most popular garbs in Poland. Other folk costumes from the region are those of Zagłębie Dąbrowskie, Sandomierz, Rzeszów, Częstochowa, Kielce, Radom (regarded as the most traditional of all Polish costumes), Opoczno, Holy Cross Mountains, Nowy Sącz, and Lublin. There are several folk festivals in Lesser Poland, such as ''On the frontier of Lesser Poland and Mazovia'' (in Opoczno), ''Folk Festival of Józef Myszka'' (in Museum of Radom Village in Iłża), annual ''Days of Lesser Poland's Cultural Heritage'', ''Week of the Beskidy Culture'' (in several locations), Wianki in Kraków, ''Festival of Old Music and Culture'' in Niepołomice, ''Festival of Folk Bands and Folk Singers'' in Kazimierz Dolny, ''International Folklore Meetings of Ignacy Wachowiak'' in Lublin, ''International Festival of Folklore of Mountain Lands'' in Zakopane, Jewish Culture Festival in Kraków. Krakowiak is one of Polish national dances, other popular Lesser Poland's folk dances are ''Zbójnicki'' from Podhale and dances from Lublin. Among Lesser Poland's customs are Lajkonik, and Kraków szopka.

Sports and entertainment
 Several renowned sportspeople and entertainers come from Lesser Poland. Among them are some of the most famous personalities of contemporary Polish sports – boxer Tomasz Adamek, Formula 1 driver Robert Kubica, swimmer Paweł Korzeniowski, skier Justyna Kowalczyk, tennis player Agnieszka Radwańska, football and volleyball stars Jakub Błaszczykowski, Artur Boruc, and Piotr Gruszka. Among late and retired sports stars who were born in the region, there also are Polish Sportspersonality of the Year, Polish Sportspersonalities of the Year: tennis player and The Championships, Wimbledon, Wimbledon finalist Jadwiga Jędrzejowska, skier Józef Łuszczek, ski jumper Stanisław Marusarz, and driver Sobiesław Zasada.
Kraków's major association football teams – KS Cracovia (football), KS Cracovia, and Wisła Kraków, are multiple champions of the country, also Stal Mielec won Polish championship twice (1973, 1976), and Garbarnia Kraków once (1931). Other popular football teams from Lesser Poland are Zagłębie Sosnowiec (four time Polish Cup winner), Górnik Łęczna, Korona Kielce, Motor Lublin, Radomiak Radom, Raków Częstochowa, Stal Stalowa Wola, and Sandecja Nowy Sącz.
Besides association football, Lesser Poland's teams were multiple national champions in other sports:
* ice-hockey (Podhale Nowy Targ, TH Unia Oświęcim, Cracovia),
* men's and women's volleyball – AZS Częstochowa, Płomień Milowice – Sosnowiec (which in 1978 won the CEV Champions League), Hutnik Kraków, Wisła Kraków, BKS Stal Bielsko-Biała, Muszynianka Muszyna,
* men's and women's Team handball, handball – Hutnik Kraków, Vive Targi Kielce, Cracovia, Montex Lublin,
* men's and women's basketball – Zagłębie Sosnowiec, Cracovia, Wisła Kraków,
* Motorcycle speedway, speedway – Włókniarz Częstochowa, Unia Tarnów (speedway), Unia Tarnów.
Major sports venues of the province are Stadion Miejski in Kraków, Kielce City Stadium, Marshal Józef Piłsudski Stadium in Kraków, Miejski Stadion Sportowy "KSZO" w Ostrowcu Sw., Stadion Ludowy in Sosnowiec, Dębowiec Sports Arena in Bielsko-Biała, ''Hala Legionów'' in Kielce, ''Hala Globus'' in Lublin, ''Arena Częstochowa'', ''Kielce Racetrack'', ''Hala Sportowa MOSiR'' in Radom, Wielka Krokiew in Zakopane.
Among popular rock music bands from Lesser Poland, there are Budka Suflera, Golec uOrkiestra, Maanam, and Zakopower. From Lesser Poland hail composers Jan Kanty Pawluśkiewicz, and Krzysztof Penderecki, as well as singers Basia, Ewa Demarczyk, Justyna Steczkowska, Grzegorz Turnau, Maciej Zembaty. Major music festivals in the province are: ''Coke Live Music Festival'' in Kraków, ''Celtic Music Festival ZAMEK'' in Będzin, ''Film Music Festival'' in Kraków, ''Gaude Mater'' in Częstochowa, ''Boyscout's Festival of School Music'' in Kielce, ''Summer with Chopin'' in Busko-Zdrój, ''Festiwal of Shanties'' in Kraków, and ''Festival of Student Song'' in Kraków.
Several renowned sportspeople and entertainers come from Lesser Poland. Among them are some of the most famous personalities of contemporary Polish sports – boxer Tomasz Adamek, Formula 1 driver Robert Kubica, swimmer Paweł Korzeniowski, skier Justyna Kowalczyk, tennis player Agnieszka Radwańska, football and volleyball stars Jakub Błaszczykowski, Artur Boruc, and Piotr Gruszka. Among late and retired sports stars who were born in the region, there also are Polish Sportspersonality of the Year, Polish Sportspersonalities of the Year: tennis player and The Championships, Wimbledon, Wimbledon finalist Jadwiga Jędrzejowska, skier Józef Łuszczek, ski jumper Stanisław Marusarz, and driver Sobiesław Zasada.
Kraków's major association football teams – KS Cracovia (football), KS Cracovia, and Wisła Kraków, are multiple champions of the country, also Stal Mielec won Polish championship twice (1973, 1976), and Garbarnia Kraków once (1931). Other popular football teams from Lesser Poland are Zagłębie Sosnowiec (four time Polish Cup winner), Górnik Łęczna, Korona Kielce, Motor Lublin, Radomiak Radom, Raków Częstochowa, Stal Stalowa Wola, and Sandecja Nowy Sącz.
Besides association football, Lesser Poland's teams were multiple national champions in other sports:
* ice-hockey (Podhale Nowy Targ, TH Unia Oświęcim, Cracovia),
* men's and women's volleyball – AZS Częstochowa, Płomień Milowice – Sosnowiec (which in 1978 won the CEV Champions League), Hutnik Kraków, Wisła Kraków, BKS Stal Bielsko-Biała, Muszynianka Muszyna,
* men's and women's Team handball, handball – Hutnik Kraków, Vive Targi Kielce, Cracovia, Montex Lublin,
* men's and women's basketball – Zagłębie Sosnowiec, Cracovia, Wisła Kraków,
* Motorcycle speedway, speedway – Włókniarz Częstochowa, Unia Tarnów (speedway), Unia Tarnów.
Major sports venues of the province are Stadion Miejski in Kraków, Kielce City Stadium, Marshal Józef Piłsudski Stadium in Kraków, Miejski Stadion Sportowy "KSZO" w Ostrowcu Sw., Stadion Ludowy in Sosnowiec, Dębowiec Sports Arena in Bielsko-Biała, ''Hala Legionów'' in Kielce, ''Hala Globus'' in Lublin, ''Arena Częstochowa'', ''Kielce Racetrack'', ''Hala Sportowa MOSiR'' in Radom, Wielka Krokiew in Zakopane.
Among popular rock music bands from Lesser Poland, there are Budka Suflera, Golec uOrkiestra, Maanam, and Zakopower. From Lesser Poland hail composers Jan Kanty Pawluśkiewicz, and Krzysztof Penderecki, as well as singers Basia, Ewa Demarczyk, Justyna Steczkowska, Grzegorz Turnau, Maciej Zembaty. Major music festivals in the province are: ''Coke Live Music Festival'' in Kraków, ''Celtic Music Festival ZAMEK'' in Będzin, ''Film Music Festival'' in Kraków, ''Gaude Mater'' in Częstochowa, ''Boyscout's Festival of School Music'' in Kielce, ''Summer with Chopin'' in Busko-Zdrój, ''Festiwal of Shanties'' in Kraków, and ''Festival of Student Song'' in Kraków.
Lesser Polish dialect of Polish
Siedlce
Siedlce [] ( yi, שעדליץ ) is a city in eastern Poland with 77,354 inhabitants (). Situated in the Masovian Voivodeship (since 1999), previously the city was the capital of a separate Siedlce Voivodeship (1975–1998). The city is situated b ...
and vicinity, where people rather speak Masovian dialect. Descending from the language of the Vistulans, it is the most numerous dialectal group in modern Poland. According to Wincenty Pol, it is divided into three subdivisions: Sandomierz dialect, Lublin dialect, and Sanok dialect.
In the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
and Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ide ...
, Lesser Polish dialect, together with Greater Polish dialect, contributed to creation of standard Polish, it also greatly influenced Silesian language, Silesian (see Dialects of Polish), as well as dialects of Polish used in southern part of Kresy Wschodnie. Later on, however, its importance diminished and was replaced by Masovian dialect, which became the leading dialect of Polish. After Partitions of Poland
The Partitions of Poland were three partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that took place toward the end of the 18th century and ended the existence of the state, resulting in the elimination of sovereign Poland and Lithuania for 12 ...
, when Lesser Poland was divided between Austria and Russia, northern areas of the province took over many features of the Masovian dialect, while Lesser Polish dialect in Austrian province of Galicia was heavily influenced by German.
According to Multimedia Guide to Polish Dialects, a webpage maintained by University of Warsaw, Lesser Polish dialect is divided into the following subdialects:
* Mazowsze Borderland (Pogranicze Mazowsza – around Radom and Dęblin),
* Łęczyca (around Łódź, Kutno, Tomaszów Mazowiecki – this part of the country is not historical Lesser Poland),
* Kielce (around Kielce),
* Lasowiacy (north of Rzeszów),
* East Kraków,
* West Lublin,
* East Lublin (this area historically belongs to Red Ruthenia
Red Ruthenia or Red Rus' ( la, Ruthenia Rubra; '; uk, Червона Русь, Chervona Rus'; pl, Ruś Czerwona, Ruś Halicka; russian: Червонная Русь, Chervonnaya Rus'; ro, Rutenia Roșie), is a term used since the Middle Ages fo ...
),
* Przemyśl (historical part of Red Ruthenia),
* Biecz,
* Nowy Sącz,
* Podhale,
* Spisz,
* Orawa,
* Żywiec,
* Sieradz,
* Sanok region, or Red-Ruthenian
* Kraków, together with Zagłebie Dąbrowskie.
See also
*Gorals
The Gorals ( pl, Górale; Goral dialect: ''Górole''; sk, Gorali; Cieszyn Silesia dialect, Cieszyn Silesian: ''Gorole''), also known as the Highlanders (in Poland as the Polish Highlanders) are an indigenous ethnographic or ethnic group primar ...
, a group of indigenous people, found in southern Lesser Poland
* Holy Cross Sermons, the oldest existing manuscripts of fine prose in Polish, which come from Lesser Poland
* Lasowiacy, one of subethnic groups, which inhabits eastern Lesser Poland
* Lesser Polish Gorge of the Vistula
* Malopolski – Polish breed of horse, developed in Lesser Poland
* Wymysorys language, Wymysorys, a West Germanic languages, West Germanic micro-language actively spoken in the small town of Wilamowice near Bielsko-Biała, on the border between Silesia and Lesser Poland
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * *External links
Appeal of inhabitants of Western Lesser Poland against calling them Silesians
Castles of Lesser Poland on lonelyplanet
Visit Lesser Poland webpage
Lesser Poland information at University at Buffalo
Portal of citizen journalism for Małopolska region
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20090616065127/http://zachodniamalopolska.republika.pl/ Western Lesser Poland. Webpage of inhabitants of eastern counties of Silesian Voivodeship, who do not wish to be associated with Silesia] {{Authority control Lesser Poland, Historical regions in Poland Historical regions History of Lesser Poland Voivodeship History of Podkarpackie Voivodeship History of Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship History of Masovian Voivodeship History of Lublin Voivodeship History of Silesian Voivodeship