|
Historical Region
Historical regions (or historical areas) are geographical regions which at some point in time had a cultural, ethnic, linguistic or political basis, regardless of latterday borders. They are used as delimitations for studying and analysing social development of period-specific cultures without any reference to contemporary political, economic or social organisations. The fundamental principle underlying this view is that older political and mental structures exist which exercise greater influence on the spatial-social identity of individuals than is understood by the contemporary world, bound to and often blinded by its own worldview - e.g. the focus on the nation-state. Definitions of regions vary,xiii, Tägil and regions can include macroregions such as Europe, territories of traditional states or smaller microregional areas. A geographic proximity is the often required precondition for emergence of a regional identity. In Europe, the regional identities are often deri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographical Region
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and the interaction of humanity and the environment ( environmental geography). Geographic regions and sub-regions are mostly described by their imprecisely defined, and sometimes transitory boundaries, except in human geography, where jurisdiction areas such as national borders are defined in law. Apart from the global continental regions, there are also hydrospheric and atmospheric regions that cover the oceans, and discrete climates above the land and water masses of the planet. The land and water global regions are divided into subregions geographically bounded by large geological features that influence large-scale ecologies, such as plains and features. As a way of describing spatial areas, the concept of regions is important and widely used among the many branche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Regions Of Ancient Armenia
This is a list of regions and or districts of ancient Armenia. A *Aghdznik *Aliovit * Amatunik *Angl * Andzevaciq * Andzith * Aragatzotn * Aranean * Aravelean * Arsharuni *Arsharunik *Armenian Mesopotamia * Artaz * Artokh * Artsakh * Artzruni *Ashotsk *Ayrarat B * Bagrevand * Baluni *Basean *Belahuit * Bznuniq C *Chamchwilde * Shirak * Corduene D *Daranali *Dariunq *Degiq *Dimaksean * Djahan * Djidjrakatsi * Dyarbekir * Dzophq E * Ekeleatzi * Endzaiatsi * Eruandhuni G * Gabelian * Gardman * Garithaianik * Gentuni * Gugark H * Hachdeanq * Hanzith K *Kamsarakan * Karbelian * Karin * Karqayin * Kajberuni * Kenuni * Khorkhoruni *Korduq L * Lesser Armenia M * Malkaz * Manavazian * Mandakuni * Martuni Province * Marzpetuni * Metz_Aghbak * Moxoene N * Norshirakan O * Oghuzstan * Olnut * Orduniq P * Pahlavuni *Parspatunik * Persarmenia Q * Qolian R * Raphsonian * Remposian * Rshtuniq S * Saharuni * Sanasun * Selkuniq * Seruantztian * Sophene * Spanduni * Sper (Armenia) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces Of Sweden
The provinces of Sweden ( sv, Sveriges landskap) are historical, geographical and cultural regions. Sweden has 25 provinces; they have no administrative function (except for in some cases as sport districts), but remain historical legacies and a means of cultural identification as pertains, for example, to dialects and folklore. Several of them were subdivisions of Sweden until 1634, when they were replaced by the counties of Sweden (''län''). Some were conquered later on from Denmark–Norway. Others, like the provinces of Finland, were lost. Lapland is the only province acquired through colonization. In some cases, the administrative counties correspond almost exactly to the provinces, as is Blekinge to Blekinge County and Gotland, which is a province, county and a municipality. While not exactly corresponding with the province, Härjedalen Municipality is beside Gotland the only municipality named after a province. In other cases, the county borders do not correspon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lands Of Sweden
The lands of Sweden ( sv, Sveriges landsdelar) are three traditional and historical regions of the country, each consisting of several provinces. The division into lands goes back to the foundation of modern Sweden, when '' Götaland'', the land of the Geats, merged with ''Svealand'', the land of the Swedes, to form the country, while ''Norrland'' and ''Österland'' (the latter now Finland) were added later. The lands have no administrative function but are still seen by many Swedes as an important part of their identity. Subdivision * Götaland (''Gothenland'' or ''Gothia'', "Land of the Geats") is the southernmost, most densely populated part, consisting of ten provinces. * Svealand (''Swealand'', "Land of the Swedes") is the central, and smallest of the three lands, with six provinces; the administrative centre of Sweden has been situated here at least since the late Middle Ages. * Norrland (literally "Northland") is the northernmost, and largest, of the three lands, covering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Regions Of Serbia
The regions of Serbia include geographical and, to a lesser extent, traditional and historical areas. Geographical regions have no official status, though some of them serve as a basis for the second-level administrative divisions of Serbia, ''okrugs'' (districts of Serbia). Not being administratively defined, the boundaries of the regions are in many cases vague: they may overlap, and various geographers and publications may delineate them differently, not just in the sense of regions' extents, but also in the sense as to whether they form separate geographical entities or subsist as parts of other super-regions, etc. For the most part, regions correspond to the valleys or to the watershed-areas of rivers and were simply named after them (some even a millennium ago), while mountain ridges and peaks often mark boundaries. In some cases, a defined region may refer only to the inhabited parts of the valleys (see župa). Valleys and plains along the largest rivers are special cases. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
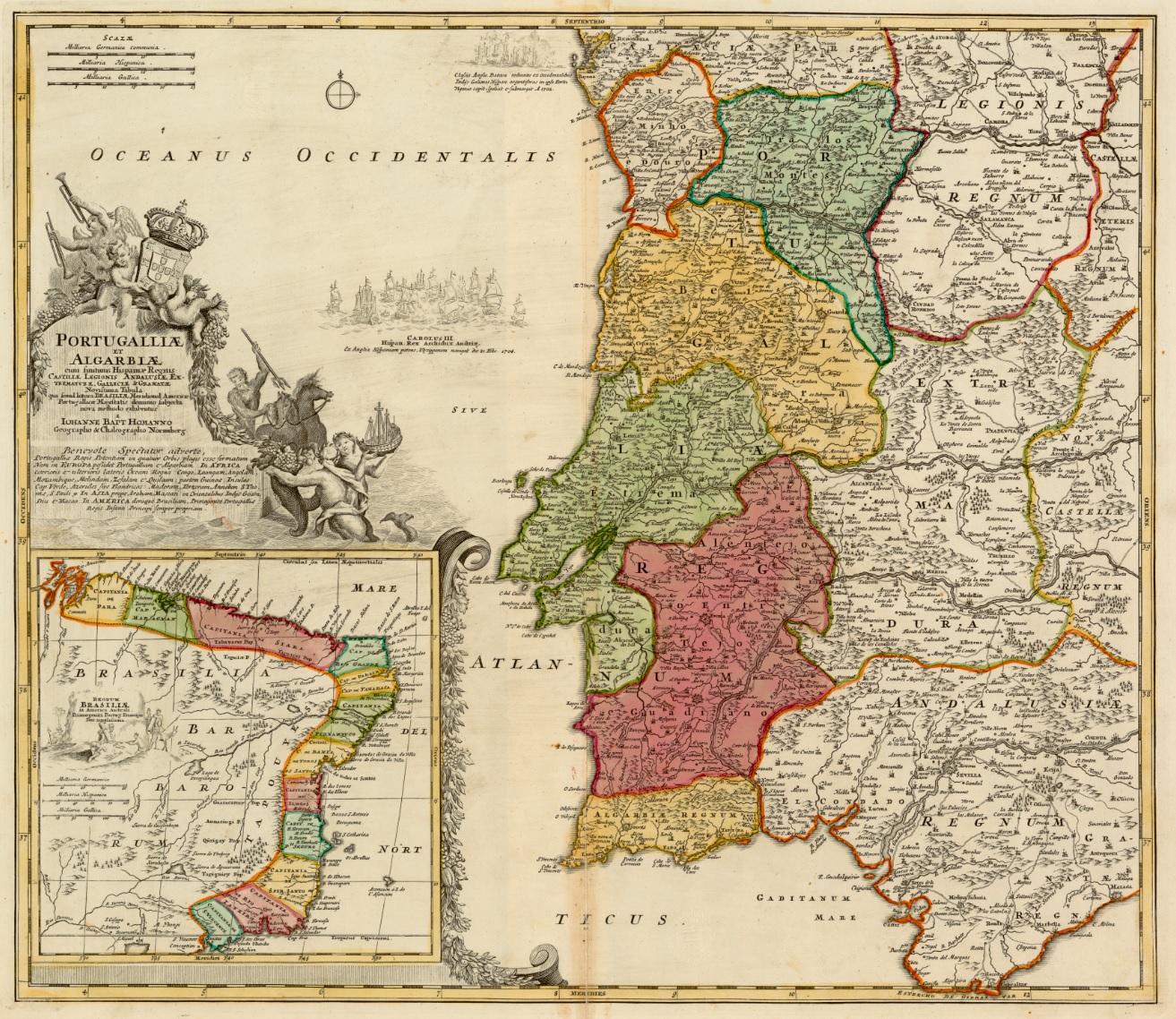
Provinces Of Portugal
The term "provinces" ( pt, províncias) has been used throughout history to identify regions of continental Portugal. Current legal subdivisions of Portugal do not coincide with the provinces, but several provinces, in their 19th- and 20th-century versions, still correspond to culturally relevant, strongly self-identifying categories. They include: *Alentejo *Algarve * Beira * Douro Litoral * Estremadura * Minho *Ribatejo * Trás-os-Montes The islands of Azores and Madeira were never called "provinces". History The first provinces, instituted during the Roman occupation of the Iberian peninsula, divided the peninsula into three areas: Tarraconensis, Lusitania and Baetica, established by Roman Emperor Augustus between 27–13 B.C. Emperor Diocletian reordered these territories in the third century, dividing Tarraconesis into three separate territories: Tarraconensis, Carthaginensis and Gallaecia. At that time Tarraconesis included northern Portugal, Gallaecia and Asturias.Jos� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historical Latvian Lands
Historical Latvian Lands ( lv, Latviešu vēsturiskās zemes) or formerly Cultural regions of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas kultūrvēsturiskie novadi) are several areas within Latvia formally recognised as distinct from the rest of the country. While some of these regions are seen purely as culturally distinct, others have historically been parts of different countries and have been used to divide the country for administrative and other purposes. The Constitution of Latvia recognises four distinct regions: Kurzeme, Zemgale, Latgale and Vidzeme. On 16 June 2021, the Saeima adopted the Historical Latvian Lands Law which aims to create the necessary preconditions for strengthening the common identity of the population and for the preservation and sustainable development of the cultural and historical environment and cultural spaces of the historical Latvian lands. The Law underscores the belonging of each parish and town in Latvia to one of the five historical Latvian lands: Vidzeme, Latga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
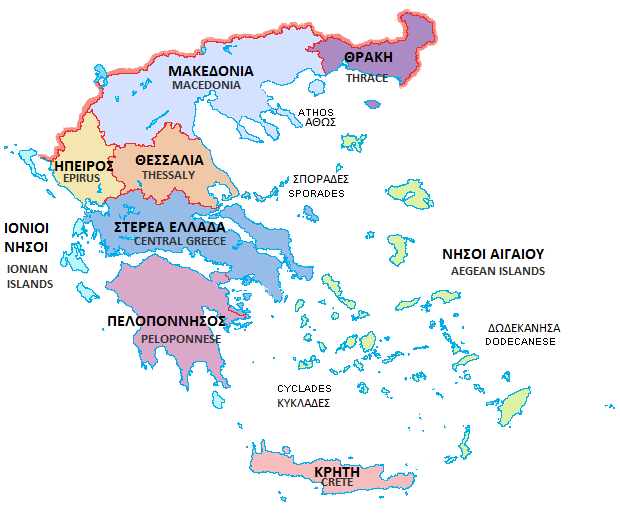
Geographic Regions Of Greece
The traditional geographic regions of Greece ( el, γεωγραφικά διαμερίσματα, , geographic departments) are the country's main historical-geographic regions, and were also official administrative regional subdivisions of Greece until the 1987 administrative reform.Π.Δ. 51/87 "Καθορισμός των Περιφερειών της Χώρας για το σχεδιασμό κ.λ.π. της Περιφερειακής Ανάπτυξης" (''Determination of the Regions of the Country for the planning etc. of regional development, ΦΕΚ A 26/06.03.1987 Despite their replacement as first-level administrative units by only partly identical administrative regions ( el, περιφέρειες), the nine traditional geographic regions—six on the mainland and three island groups—are still widely referred to in unofficial contexts and in daily discourse. , the official administrative divisions of Greece consist of 13 regions ( el, περιφέρειες)—ni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Greek Place Names
This is a list of Greek place names as they exist in the Greek language. *Places involved in the history of Greek culture, including: **Historic Greek regions, including: ***Ancient Greece, including colonies and contacted peoples *** Hellenistic world, including successor states and contacted peoples ***Roman Empire and Byzantine Empire, including successor states ***Ottoman Empire, including successor states ***Septinsular Republic ***Modern Greece and Cyprus, and also what remains of treaty Greek minorities in Turkey **Places that have or had important Greek-speaking or ethnic Greek minorities or exile communities **Places of concern to Greek culture, religion or tradition, including: ***Greek mythology ***Greek Jews, including Romaniotes and exiled Sephardim *** Greco-Buddhism ***Christianity until the Great Schism, and afterwards the Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Rite, etc. ***Greek Muslims, and those outside Greece who are Greek-speaking or ethnic Greek *Places whose of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces Of Finland
Between 1634 and 2009, Finland was administered as several provinces ( fi, Suomen läänit, sv, Finlands län). Finland had always been a unitary state: the provincial authorities were part of the central government's executive branch and apart from Åland, the provinces had little autonomy. There were never any elected provincial parliaments in continental Finland. The system was initially created in 1634. Its makeup was changed drastically on 1 September 1997, when the number of the provinces was reduced from twelve to six. This effectively made them purely administrative units, as linguistic and cultural boundaries no longer followed the borders of the provinces. The provinces were eventually abolished at the end of 2009. Consequently, different ministries may subdivide their areal organization differently. Besides the former provinces, the municipalities of Finland form the fundamental subdivisions of the country. In current use are the regions of Finland, a smaller subdivi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historical Provinces Of Finland
The historical provinces ( fi, historialliset maakunnat, singular ''historiallinen maakunta'', sv, historiska landskap) of Finland are a legacy of the country's joint history with Sweden. The provinces ceased to be administrative entities in 1634 when they were superseded by the counties, a reform which remained in force in Finland until 1997. The provinces remain as a tradition, but have no administrative function today. The spread of Finnish language dialects approximately follows their borders. The first name in the parentheses is the Finnish name and the second is the Swedish one. : Finland Proper (''Varsinais-Suomi, Egentliga Finland'') : Karelia (''Karjala, Karelen'') : Laponia (''Lappi, Lappland'') : Ostrobothnia (''Pohjanmaa, Österbotten'') : Satakunta (''Satakunta, Satakunda'') : Savonia (''Savo, Savolax'') : Tavastia (''Häme, Tavastland'') : Uusimaa (''Uusimaa, Nyland'') : Åland (''Ahvenanmaa, Åland'') Heraldry At the funeral of King Gustav Vasa in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)