Gravesend church - geograph.org.uk - 911359.jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Gravesend is a town in northwest Kent, England, situated 21 miles (35 km) east-southeast of
 Recorded as Gravesham in the Domesday Book of 1086 when it belonged to Odo, Earl of Kent and
Recorded as Gravesham in the Domesday Book of 1086 when it belonged to Odo, Earl of Kent and
 Milton Chantry is Gravesend's oldest surviving building and dates from the early 14th century. It was refounded as a chapel in 1320/21 on the original site of a former leper
Milton Chantry is Gravesend's oldest surviving building and dates from the early 14th century. It was refounded as a chapel in 1320/21 on the original site of a former leper  On 21 March 1617, John Rolfe and his Native American wife Rebecca ( Pocahontas), with their two-year-old son, Thomas, boarded a ship in London bound for
On 21 March 1617, John Rolfe and his Native American wife Rebecca ( Pocahontas), with their two-year-old son, Thomas, boarded a ship in London bound for  At Fort Gardens is the ''New Tavern Fort'', built during the 1780s and extensively rebuilt by Major-General Charles Gordon between 1865 and 1879; it is now the Chantry Heritage Centre, under the care of Gravesend Local History Society. The fort is a Scheduled monument.
Journeys by road to Gravesend were historically quite hazardous, since the main London-Dover road crossed
At Fort Gardens is the ''New Tavern Fort'', built during the 1780s and extensively rebuilt by Major-General Charles Gordon between 1865 and 1879; it is now the Chantry Heritage Centre, under the care of Gravesend Local History Society. The fort is a Scheduled monument.
Journeys by road to Gravesend were historically quite hazardous, since the main London-Dover road crossed 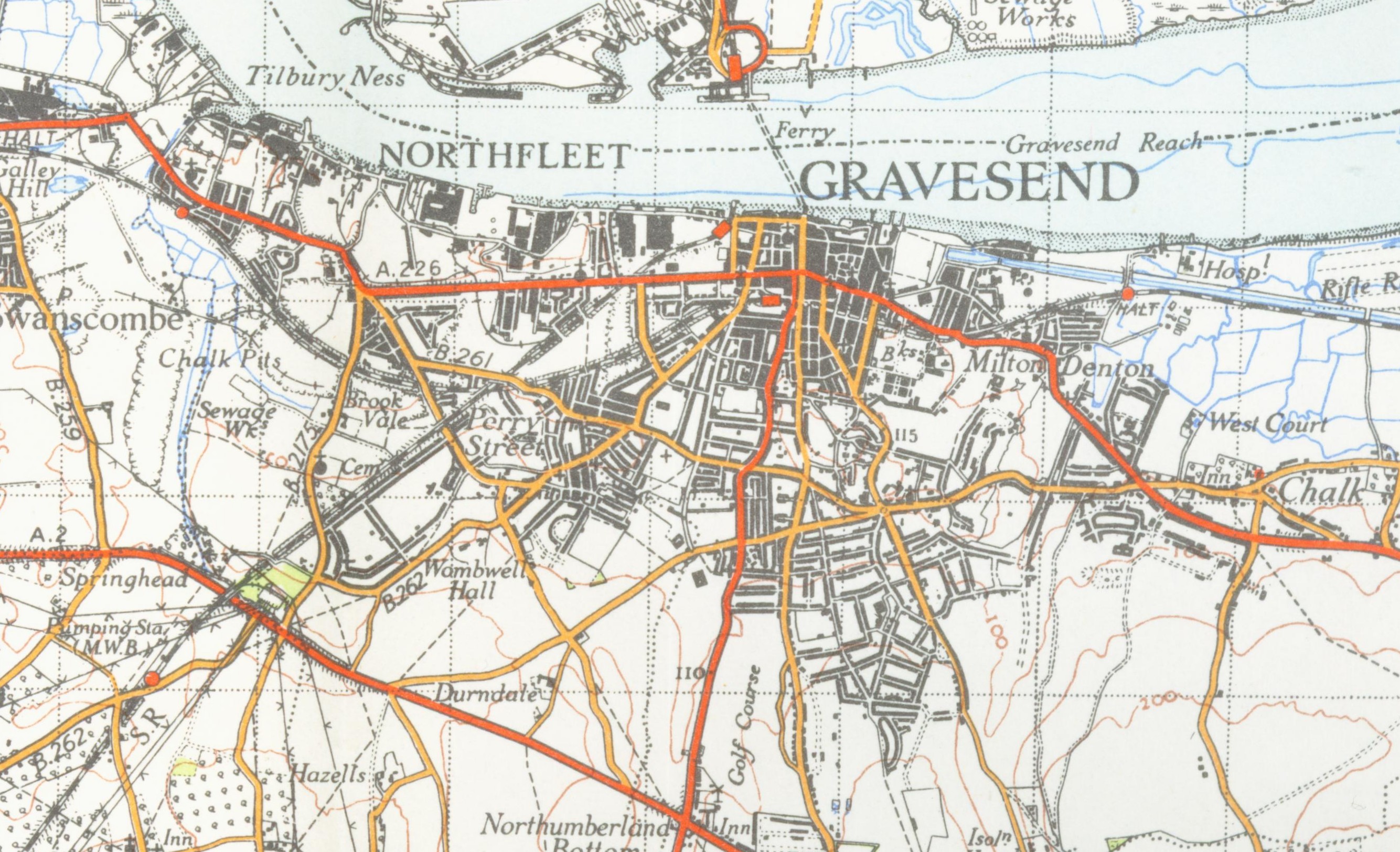 From 1932 to 1956, an airport was located to the east of the town. On Sunday 5 February 1939, Alex Henshaw commenced his record-breaking flight to Cape Town and back from here. He completed the flight in 39 hours 36 minutes over the next four days; his record still stands. Originally a civilian airfield, during World War II it became a fighter station, RAF Gravesend, and so Gravesend was heavily bombed by the Luftwaffe. In 1956 the site was taken over by Gravesend Borough Council; a large housing estate, known as Riverview Park, was built on its site.
From 1932 to 1956, an airport was located to the east of the town. On Sunday 5 February 1939, Alex Henshaw commenced his record-breaking flight to Cape Town and back from here. He completed the flight in 39 hours 36 minutes over the next four days; his record still stands. Originally a civilian airfield, during World War II it became a fighter station, RAF Gravesend, and so Gravesend was heavily bombed by the Luftwaffe. In 1956 the site was taken over by Gravesend Borough Council; a large housing estate, known as Riverview Park, was built on its site.
 Gravesend today is a commercial and commuter town, providing a local shopping district, including the St Georges shopping complex and a regular farmers' market. Gravesend market hall, in the heart of the town, was first chartered in 1268.
Gravesend today is a commercial and commuter town, providing a local shopping district, including the St Georges shopping complex and a regular farmers' market. Gravesend market hall, in the heart of the town, was first chartered in 1268.
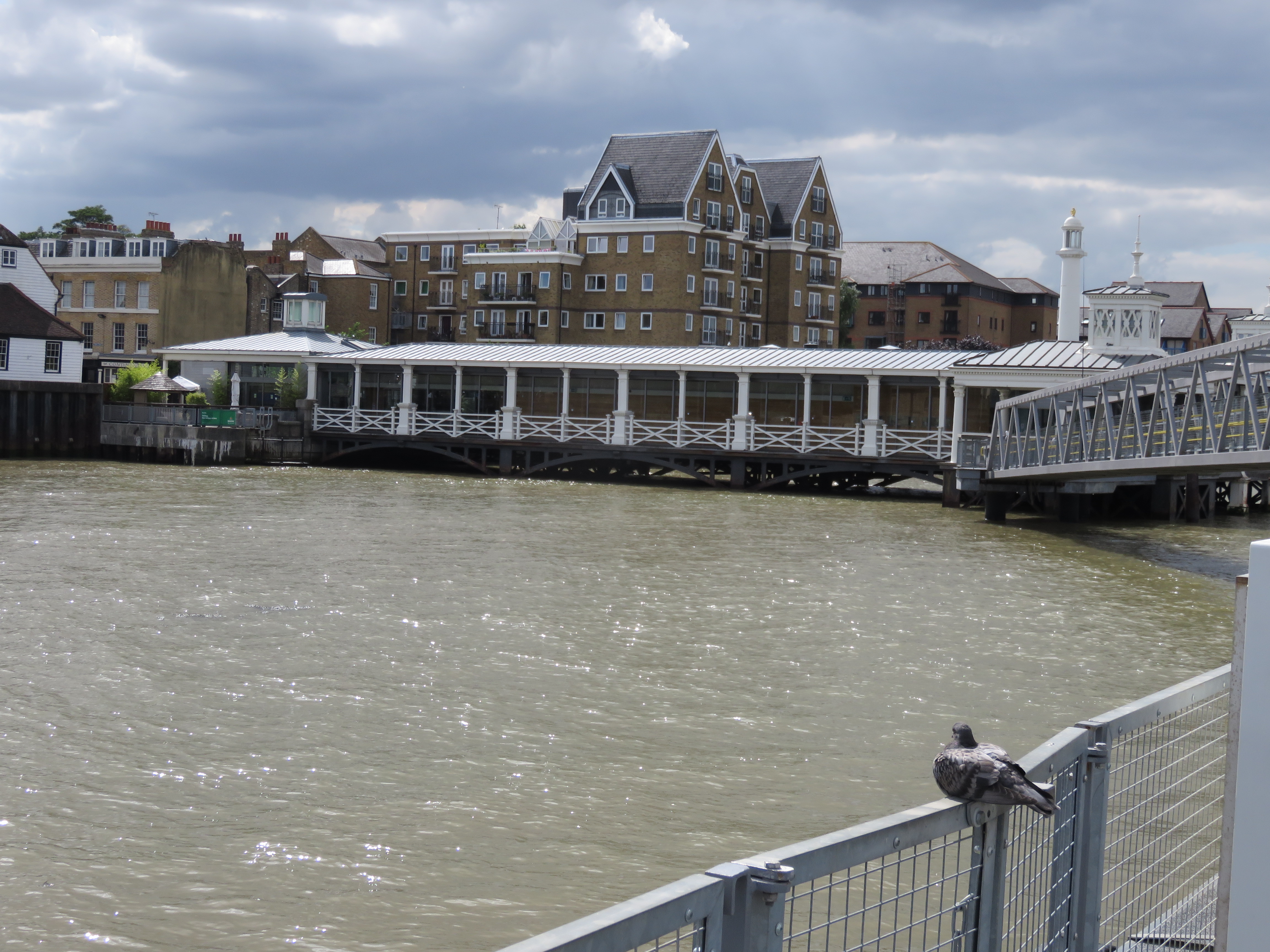 Gravesend has the world's oldest surviving cast iron pier, built in 1834.
It is a unique structure having the first known iron cylinders used in its construction. The pier was completely refurbished in 2004 and now features a bar and restaurant; with public access to the pier head when the premises are open.
A recent £2 million investment in a pontoon is now in place at the pier head onto the Thames, which provides for small and medium-sized craft to land at Gravesend. On 17 September 2012, the
Gravesend has the world's oldest surviving cast iron pier, built in 1834.
It is a unique structure having the first known iron cylinders used in its construction. The pier was completely refurbished in 2004 and now features a bar and restaurant; with public access to the pier head when the premises are open.
A recent £2 million investment in a pontoon is now in place at the pier head onto the Thames, which provides for small and medium-sized craft to land at Gravesend. On 17 September 2012, the
 Built in 1844, the initial construction was funded by the Gravesend Freehold Investment Company, at a cost of £9,200. It was where Princess Alexandra of Denmark arrived on her way to marry Edward, Prince of Wales (later King Edward VII) in March 1865, and
Built in 1844, the initial construction was funded by the Gravesend Freehold Investment Company, at a cost of £9,200. It was where Princess Alexandra of Denmark arrived on her way to marry Edward, Prince of Wales (later King Edward VII) in March 1865, and
 Situated at the junction of Milton Road and Harmer Street, its foundation stone was laid on 6 September 1887. The memorial stone records that the
Situated at the junction of Milton Road and Harmer Street, its foundation stone was laid on 6 September 1887. The memorial stone records that the
 An American sculptor, William Ordway Partridge, created a life-size statue of the 17th-century Native American princess Pocahontas, which was unveiled at
An American sculptor, William Ordway Partridge, created a life-size statue of the 17th-century Native American princess Pocahontas, which was unveiled at
 The Thames has long been an important feature in Gravesend life, and may well have been the deciding factor for the first settlement there. One of the town's first distinctions was in being given the sole right to transport passengers to and from London by water in the late 14th century. The "Tilt Boat" was a familiar sight as it sailed along the Thames, the passengers protected from the weather by a canvas tilt (awning). The first steamboat plied its trade between Gravesend and London in the early 19th century, bringing with it a steadily increasing number of visitors to the Terrace Pier Gardens, Windmill Hill, Springhead Gardens and
The Thames has long been an important feature in Gravesend life, and may well have been the deciding factor for the first settlement there. One of the town's first distinctions was in being given the sole right to transport passengers to and from London by water in the late 14th century. The "Tilt Boat" was a familiar sight as it sailed along the Thames, the passengers protected from the weather by a canvas tilt (awning). The first steamboat plied its trade between Gravesend and London in the early 19th century, bringing with it a steadily increasing number of visitors to the Terrace Pier Gardens, Windmill Hill, Springhead Gardens and  Until the building of
Until the building of
 The
The
 Gravesend railway station lies on the
Gravesend railway station lies on the
Gravesend is also served by Fastrack bus services connecting the town with Bluewater, Darent Valley Hospital and Dartford.
 Passenger ferry services to Tilbury, Essex, operate daily (except Sundays), from
Passenger ferry services to Tilbury, Essex, operate daily (except Sundays), from
 Gravesend has a significant
Gravesend has a significant
 *
*
Charing Cross
Charing Cross ( ) is a junction in Westminster, London, England, where six routes meet. Clockwise from north these are: the east side of Trafalgar Square leading to St Martin's Place and then Charing Cross Road; the Strand leading to the City; ...
(central London) on the south bank
The South Bank is an entertainment and commercial district in central London, next to the River Thames opposite the City of Westminster. It forms a narrow strip of riverside land within the London Borough of Lambeth (where it adjoins Alber ...
of the River Thames and opposite Tilbury in Essex. Located in the diocese of Rochester, it is the administrative centre of the Borough of Gravesham
Gravesham ( ) is a local government district with borough status in north-west Kent, England. Its administrative centre and largest town is Gravesend, which was known as ''Gravesham'' in ancient times.
Gravesham was formed on 1 April 1974 by ...
.
Its geographical situation has given Gravesend strategic importance throughout the maritime and communications history of South East England. A Thames Gateway commuter town, it retains strong links with the River Thames, not least through the Port of London Authority
The Port of London Authority (PLA) is a self-funding public trust established on 31 March 1909 in accordance with the Port of London Act 1908 to govern the Port of London. Its responsibility extends over the Tideway of the River Thames and its ...
Pilot Station and has witnessed rejuvenation since the advent of High Speed 1
High Speed 1 (HS1), legally the Channel Tunnel Rail Link (CTRL), is a high-speed railway linking London with the Channel Tunnel.
It is part of a line carrying international passenger traffic between the United Kingdom and mainland Europe; ...
rail services via Gravesend railway station. The station was recently refurbished and now has a new bridge.
Toponymy
 Recorded as Gravesham in the Domesday Book of 1086 when it belonged to Odo, Earl of Kent and
Recorded as Gravesham in the Domesday Book of 1086 when it belonged to Odo, Earl of Kent and Bishop of Bayeux
The Roman Catholic Diocese of Bayeux and Lisieux (Latin: ''Dioecesis Baiocensis et Lexoviensis''; French: ''Diocèse de Bayeux et Lisieux'') is a diocese of the Catholic Church in France. It is coextensive with the Department of Calvados and is ...
, the half-brother of William the Conqueror, its name probably derives from ''graaf-ham'': the home of the reeve
Reeve may refer to:
Titles
*Reeve (Canada), an elected chief executive of some counties, townships, and equivalents
*Reeve (England), an official elected annually by the serfs to supervise lands for a lord
*High-reeve, a title taken by some Englis ...
or bailiff of the lord of the manor.
Another theory suggests that the name ''Gravesham'' may be a corruption of the words ''grafs-ham'' – a place "at the end of the grove". Frank Carr asserts that the name derives from the Saxon ''Gerevesend'', the end of the authority of the Portreeve (originally ''Portgereve'', chief town administrator).
In the Netherlands, a place called 's-Gravenzande
s-Gravenzande is a town in the province of South Holland, in the Netherlands. It is a part of the municipality of Westland, and lies about southwest of The Hague. Until 2004 it was a separate municipality and covered an area of 20.77 km2 (of ...
is found with its name translating into "Sand (or sandy area) belonging to the Count". The ''s'' is a contraction of the old Dutch genitive article ''des'', and translates into plain English as ''of the''. In Brooklyn, New York, the neighbourhood of Gravesend
Gravesend is a town in northwest Kent, England, situated 21 miles (35 km) east-southeast of Charing Cross (central London) on the Bank (geography), south bank of the River Thames and opposite Tilbury in Essex. Located in the diocese of Ro ...
is said by some to have been named for 's-Gravenzande., though its founding by the English religious dissenter, Lady Deborah Moody, in 1645 strongly indicates that it is named after Gravesend, England. Lady Deborah was originally from London and is credited with being the first woman to found a settlement in the New World.
The Domesday spelling is its earliest known historical record; all other spellings – in the later (c. 1100) Domesday ''Monachorum'' and in ''Textus Roffensis'' the town is ''Gravesend'' and ''Gravesende'', respectively. The variation ''Graveshend'' can be seen in a court record of 1422, where Edmund de Langeford was parson
A parson is an ordained Christian person responsible for a small area, typically a parish. The term was formerly often used for some Anglican clergy and, more rarely, for ordained ministers in some other churches. It is no longer a formal term d ...
, and attributed to where the graves ended after the Black Death
The Black Death (also known as the Pestilence, the Great Mortality or the Plague) was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Western Eurasia and North Africa from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causi ...
. The municipal title Gravesham was formally adopted in 1974 as the name for the new borough.
History
Stone Age
The Stone Age was a broad prehistoric period during which stone was widely used to make tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years, and ended between 4,000 BC and 2,000 BC, with t ...
implements have been found in the locality since the 1900s, as has evidence of an Iron Age settlement at nearby Springhead
Springhead lies at the source of the River Ebbsfleet, just southwest of the Gravesend suburban conurbations. Springhead forms one of the major quarters of the Ebbsfleet Valley development, with housing and the associated facilities now under con ...
. Extensive Roman remains have been found at nearby Vagniacae; and Gravesend lies immediately to the north of the Roman road
Roman roads ( la, viae Romanae ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, and were built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Re ...
connecting London with the Kent coast – now called Watling Street. Domesday Book recorded mills, hythes, and fisheries
Fishery can mean either the enterprise of raising or harvesting fish and other aquatic life; or more commonly, the site where such enterprise takes place ( a.k.a. fishing ground). Commercial fisheries include wild fisheries and fish farms, both ...
here.
 Milton Chantry is Gravesend's oldest surviving building and dates from the early 14th century. It was refounded as a chapel in 1320/21 on the original site of a former leper
Milton Chantry is Gravesend's oldest surviving building and dates from the early 14th century. It was refounded as a chapel in 1320/21 on the original site of a former leper hospital
A hospital is a health care institution providing patient treatment with specialized health science and auxiliary healthcare staff and medical equipment. The best-known type of hospital is the general hospital, which typically has an emerge ...
founded in 1189. It is a Grade II* listed building.
Gravesend has one of the oldest surviving markets in the country. Its earliest charter dates from 1268, with town status being granted to the two parishes of Gravesend
Gravesend is a town in northwest Kent, England, situated 21 miles (35 km) east-southeast of Charing Cross (central London) on the Bank (geography), south bank of the River Thames and opposite Tilbury in Essex. Located in the diocese of Ro ...
and Milton
Milton may refer to:
Names
* Milton (surname), a surname (and list of people with that surname)
** John Milton (1608–1674), English poet
* Milton (given name)
** Milton Friedman (1912–2006), Nobel laureate in Economics, author of '' Free t ...
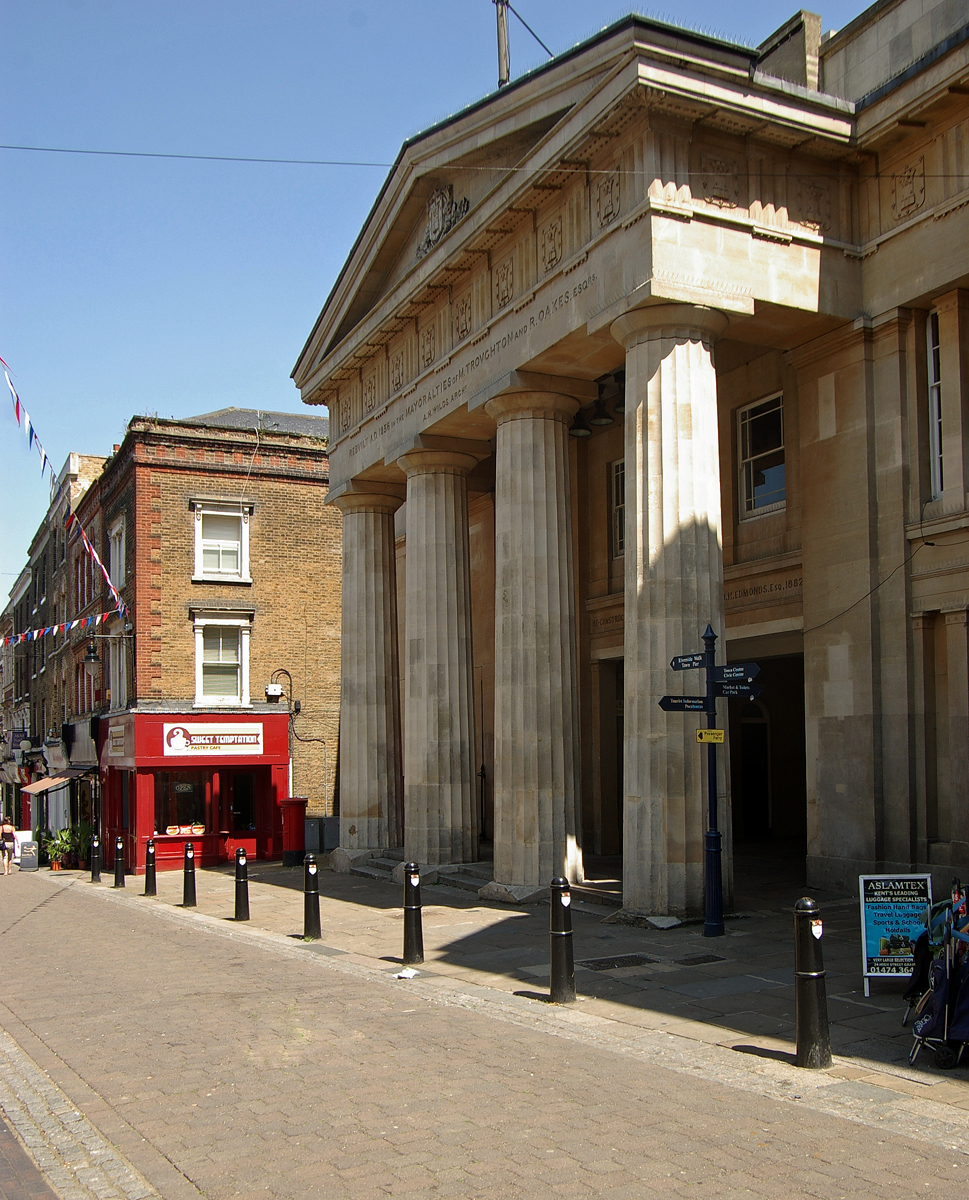
by King Henry III in its Charter of Incorporation of that year. The first Mayor of Gravesend was elected in 1268 but the first town hall was not built until 1573. The current Gravesend Town Hall
Gravesend Town Hall is a municipal building in the High Street in Gravesend, Kent, England. The town hall, which was the headquarters of Gravesend Municipal Borough Council, is a Grade II* listed building.
History
The first town hall in Graves ...
was completed in 1764: although it ceased to operate as a seat of government in 1968 when the new Gravesend Civic Centre was opened, it remained in use as a magistrates' court until 2000. It now operates as a venue for weddings and civil partnership ceremonies.
In 1380, during the Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a series of armed conflicts between the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of France, France during the Late Middle Ages. It originated from disputed claims to the French Crown, ...
, Gravesend suffered being sacked and burned by the Castilian fleet.
In 1401, a further Royal Charter was granted, allowing the men of the town to operate boats between London and the town; these became known as the "Long Ferry". It became the preferred form of passage, because of the perils of road travel (see below).
On Gravesend's river front are the remains of a device fort built by command of King Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is best known for his six marriages, and for his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. His disag ...
in 1543.
 On 21 March 1617, John Rolfe and his Native American wife Rebecca ( Pocahontas), with their two-year-old son, Thomas, boarded a ship in London bound for
On 21 March 1617, John Rolfe and his Native American wife Rebecca ( Pocahontas), with their two-year-old son, Thomas, boarded a ship in London bound for the Commonwealth of Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth are ...
; the ship had only sailed as far as Gravesend before Rebecca fell ill, and she died shortly after she was taken ashore. It is not known what caused her death. Her funeral and interment took place on 21 March 1617 at the parish church of St George, Gravesend. The site of her grave was underneath the church's chancel, though since the previous church was destroyed by fire in 1727 her exact resting place is unknown. Thomas Rolfe survived, but was placed under the supervision of Sir Lewis Stukley at Plymouth
Plymouth () is a port city and unitary authority in South West England. It is located on the south coast of Devon, approximately south-west of Exeter and south-west of London. It is bordered by Cornwall to the west and south-west.
Plymouth ...
, before being sent to his uncle, Henry Rolfe whilst John Rolfe and his late wife's assistant Tomocomo
Uttamatomakkin (known as Tomocomo for short) was a Powhatan holy man who accompanied Pocahontas when she was taken to London in 1616.Dale, Thomas. Letter to Sir Ralph Winwood. 3 June 1616. Repr. in Jamestown Narratives, ed. Edward Wright Haile. Cha ...
reached America under the captaincy of Sir Samuel Argall's ship. Pocahontas (real name: Matoaka) is an important figure in both American and British history and was the inspiration for the popular Disney animated film of the same name.
Blackheath Blackheath may refer to:
Places England
*Blackheath, London, England
** Blackheath railway station
**Hundred of Blackheath, Kent, an ancient hundred in the north west of the county of Kent, England
*Blackheath, Surrey, England
** Hundred of Blackh ...
, notorious for its highwaymen. Stagecoach
A stagecoach is a four-wheeled public transport coach used to carry paying passengers and light packages on journeys long enough to need a change of horses. It is strongly sprung and generally drawn by four horses although some versions are draw ...
es from London to Canterbury, Dover
Dover () is a town and major ferry port in Kent, South East England. It faces France across the Strait of Dover, the narrowest part of the English Channel at from Cap Gris Nez in France. It lies south-east of Canterbury and east of Maidstone ...
and Faversham used Gravesend as one of their "stages" as did those coming north from Tonbridge. In 1840 there were 17 coaches picking up and setting down passengers and changing horses each way per day. There were two coaching inns on what is now Old Road East: ''the Prince of Orange'' and ''the Lord Nelson''. Post coach
A mail coach is a stagecoach that is used to deliver mail. In Great Britain, Ireland, and Australia, they were built to a General Post Office-approved design operated by an independent contractor to carry long-distance mail for the Post Office. M ...
es had been plying the route for at least two centuries: Samuel Pepys
Samuel Pepys (; 23 February 1633 – 26 May 1703) was an English diarist and naval administrator. He served as administrator of the Royal Navy and Member of Parliament and is most famous for the diary he kept for a decade. Pepys had no mariti ...
records having stopped off at Gravesend in 1650 en route to the Royal Dockyards at Chatham.
A permanent military presence was established in the town when Milton Barracks
Milton Barracks was a military installation at Milton Road in Gravesend, Kent.
History
The barracks were built between 1860 and 1862 as temporary accommodation for troops using the Milton Rifle Range which was located just a mile to the east of ...
opened in 1862.
Although much of the town's economy continued to be connected with maritime trade, since the 19th century other major employers have been the cement and paper industries.
 From 1932 to 1956, an airport was located to the east of the town. On Sunday 5 February 1939, Alex Henshaw commenced his record-breaking flight to Cape Town and back from here. He completed the flight in 39 hours 36 minutes over the next four days; his record still stands. Originally a civilian airfield, during World War II it became a fighter station, RAF Gravesend, and so Gravesend was heavily bombed by the Luftwaffe. In 1956 the site was taken over by Gravesend Borough Council; a large housing estate, known as Riverview Park, was built on its site.
From 1932 to 1956, an airport was located to the east of the town. On Sunday 5 February 1939, Alex Henshaw commenced his record-breaking flight to Cape Town and back from here. He completed the flight in 39 hours 36 minutes over the next four days; his record still stands. Originally a civilian airfield, during World War II it became a fighter station, RAF Gravesend, and so Gravesend was heavily bombed by the Luftwaffe. In 1956 the site was taken over by Gravesend Borough Council; a large housing estate, known as Riverview Park, was built on its site.
Governance
Gravesend is part of and is the principal town of the Borough of Gravesham. The borough was formed on 1 April 1974, under theLocal Government Act 1972
The Local Government Act 1972 (c. 70) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that reformed local government in England and Wales on 1 April 1974. It was one of the most significant Acts of Parliament to be passed by the Heath Gov ...
, by the merger of the Municipal Borough of Gravesend
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality'' may also mean the go ...
and Northfleet Urban District along with several parishes from Strood Rural District. Gravesend was incorporated as a Municipal Borough in 1835 under the Municipal Corporations Act 1835
The Municipal Corporations Act 1835 (5 & 6 Will 4 c 76), sometimes known as the Municipal Reform Act, was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that reformed local government in the incorporated boroughs of England and Wales. The legisl ...
and Northfleet was constituted an Urban District in 1894 under the Local Government Act 1894: Gravesend absorbed Milton (1914), Denton, Chalk and part of Northfleet, including Claphall, Singlewell and King's Farm (1935).
Geography
Gravesend is located at a point where the higher land – the lowest point of the dip slope of the North Downs – reaches the Thames. To the east are the low-lying Shorne Marshes; to the west, beyondNorthfleet
Northfleet is a town in the borough of Gravesham in Kent, England. It is located immediately west of Gravesend, and on the border with the Borough of Dartford. Northfleet has its own railway station on the North Kent Line, just east of Ebbsfl ...
and the Swanscombe Marshes. The settlement was thus established as it was a good landing place: it was also sheltered by the prominent height of what is now called Windmill Hill (see Landmarks below); although Windmill Hill still remains a dominant feature, Gravesend's highest point is actually further inland at Marling Cross, adjacent to the A2.
From its origins as a landing place and shipping port, Gravesend gradually extended southwards and eastwards. Better-off people from London visited the town during the summer months; at first by boat, and then by railway. More extensive building began after World War I; this increased after World War II, when many of the housing estates in the locality were built.
Gravesend's built-up areas comprise ''Painters Ash'', adjacent to the A2; ''King's Farm'' (most of King's Farm estate was built in the 1920s); and ''Christianfields''. The latter housing estate has been completely rebuilt over a 6-year project from 2007 to 2013. There is also the aforementioned Riverview Park estate built on the old RAF field in the south-east, in the 1960s, and Singlewell, which is adjacent to the A2 in the South
Part of the southern built-up area of the town was originally two separate rural parishes: ''viz'', Cobham and Northfleet
Northfleet is a town in the borough of Gravesham in Kent, England. It is located immediately west of Gravesend, and on the border with the Borough of Dartford. Northfleet has its own railway station on the North Kent Line, just east of Ebbsfl ...
.
Climate
Gravesend has anoceanic climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the humid temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool summers and mild winters ( ...
similar to much of southern England, being accorded Köppen Climate Classification-subtype of " Cfb" (Marine West Coast Climate).
On 10 August 2003, Gravesend recorded one of the highest temperatures since records began in the United Kingdom, with a reading of , only beaten by Brogdale, near Faversham, to the ESE. Gravesend, which has a Met Office
The Meteorological Office, abbreviated as the Met Office, is the United Kingdom's national weather service. It is an executive agency and trading fund of the Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy and is led by CEO Penelope E ...
site, reports its data each hour.
Being inland and yet relatively close to continental Europe
Continental Europe or mainland Europe is the contiguous continent of Europe, excluding its surrounding islands. It can also be referred to ambiguously as the European continent, – which can conversely mean the whole of Europe – and, by ...
, Gravesend enjoys a somewhat more continental climate than the coastal areas of Kent, Essex and East Anglia and also compared to western parts of Britain. It is therefore less cloudy, drier, and less prone to Atlantic depressions with their associated wind and rain than western parts, as well as being hotter in summer and colder in winter.
Thus Gravesend continues to record higher temperatures in summer
Summer is the hottest of the four temperate seasons, occurring after spring and before autumn. At or centred on the summer solstice, the earliest sunrise and latest sunset occurs, daylight hours are longest and dark hours are shortest, wit ...
, sometimes being the hottest place in the country, ''e.g.'' on the warmest day of 2011, when temperatures reached 33.1 °C. Additionally, the town holds at least two records for the year 2010, of 30.9 °C and 31.7 °C. Another record was set during England's Indian summer of 2011 with 29.9 °C., the highest temperature ever recorded in the UK for October. In 2016 the warmest day of the year occurred very late on 13 September with a very high temperature of 34.4C
Demography
Since 1990 the economy of Gravesham has changed from one based on heavy industry to being service-based. The borough's estimated population in 2012 was 101,700: a 6,000 increase in less than a decade. It has a high population density (almost 10 people per hectare) compared to nationally; it has a relatively young population (40% of the population are below 30); and 60% of the population are of working age. Based upon figures from the 2021 Census, the second largest religious group in the borough areSikhs
Sikhs ( or ; pa, ਸਿੱਖ, ' ) are people who adhere to Sikhism (Sikhi), a monotheistic religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Guru Nanak. The term ...
who at that time made up 8% of the population. However, if the term belief is used, Christians are most numerous at more than (49%), non-religious (32.1%) and third Sikhs
Sikhs ( or ; pa, ਸਿੱਖ, ' ) are people who adhere to Sikhism (Sikhi), a monotheistic religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Guru Nanak. The term ...
(8%).
Shopping
 Gravesend today is a commercial and commuter town, providing a local shopping district, including the St Georges shopping complex and a regular farmers' market. Gravesend market hall, in the heart of the town, was first chartered in 1268.
Gravesend today is a commercial and commuter town, providing a local shopping district, including the St Georges shopping complex and a regular farmers' market. Gravesend market hall, in the heart of the town, was first chartered in 1268.
Landmarks
Gravesend Town Pier
Gravesend–Tilbury Ferry
The Gravesend–Tilbury Ferry is a passenger ferry across the River Thames east of London. It is the last public crossing point before the Thames reaches the sea.
History
''See also notes on Tilbury''
There were many ferries crossing the T ...
, relocated to the Town Pier, from its previous terminal in nearby West Street.
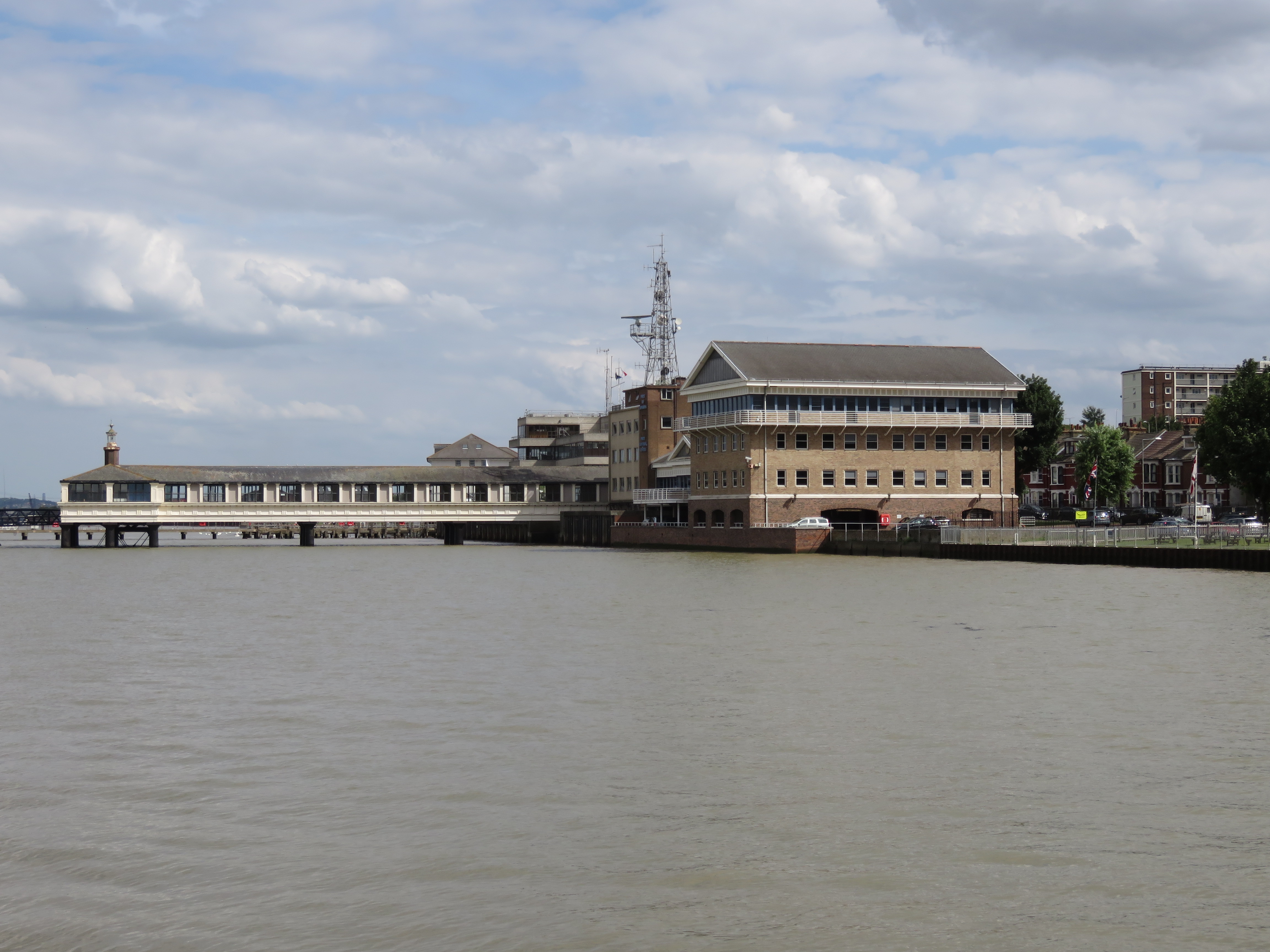
Royal Terrace Pier
River pilot
A maritime pilot, marine pilot, harbor pilot, port pilot, ship pilot, or simply pilot, is a mariner who maneuvers ships through dangerous or congested waters, such as harbors or river mouths. Maritime pilots are regarded as skilled professional ...
s have been based here since the late 19th century.
Today, Royal Terrace Pier is in constant 24-hour use, as part of the Port of London Authority
The Port of London Authority (PLA) is a self-funding public trust established on 31 March 1909 in accordance with the Port of London Act 1908 to govern the Port of London. Its responsibility extends over the Tideway of the River Thames and its ...
main operations centre; thus, its public access is available only occasionally during the year. It is 'T' shaped, with a pontoon at its pier head. Like the Town Pier, Royal Terrace Pier
Royal Terrace Pier is owned and managed by the Port of London Authority (PLA) and is located adjacent to their headquarters at London River House in Gravesend.
History
The Grade II listed pier was built in 1844 by the Gravesend Freehold Inves ...
is also a Grade II
In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern Irel ...
listed structure.
Gravesend Clock Tower, Milton Road
 Situated at the junction of Milton Road and Harmer Street, its foundation stone was laid on 6 September 1887. The memorial stone records that the
Situated at the junction of Milton Road and Harmer Street, its foundation stone was laid on 6 September 1887. The memorial stone records that the clock tower
Clock towers are a specific type of structure which house a turret clock and have one or more clock faces on the upper exterior walls. Many clock towers are freestanding structures but they can also adjoin or be located on top of another buildi ...
was erected by public subscription (£700 was raised toward its construction) and dedicated to Queen Victoria, to commemorate the 50th year of her reign. Built of Portland and Dumfries stone and backed by London stock brick, the design of the structure is based on the design of the Elizabeth Tower in the Palace of Westminster, which houses Big Ben
Big Ben is the nickname for the Great Bell of the Great Clock of Westminster, at the north end of the Palace of Westminster in London, England, and the name is frequently extended to refer also to the clock and the clock tower. The officia ...
. The centre of the clock itself is measured at 50 feet (15 m) above ground and the face measures 5 ft 6 in (1.68 m) in diameter. The tower is Grade II listed.
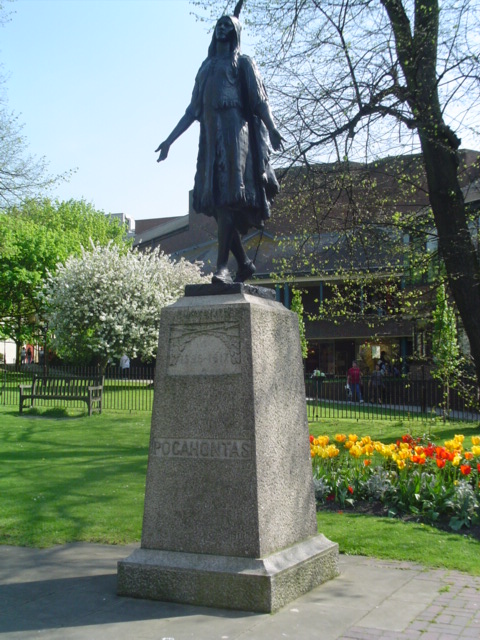
Pocahontas statue
 An American sculptor, William Ordway Partridge, created a life-size statue of the 17th-century Native American princess Pocahontas, which was unveiled at
An American sculptor, William Ordway Partridge, created a life-size statue of the 17th-century Native American princess Pocahontas, which was unveiled at Jamestown, Virginia
The Jamestown settlement in the Colony of Virginia was the first permanent English settlement in the Americas. It was located on the northeast bank of the James (Powhatan) River about southwest of the center of modern Williamsburg. It was ...
in 1922. Queen Elizabeth II
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; 21 April 1926 – 8 September 2022) was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until Death and state funeral of Elizabeth II, her death in 2022. She was queen ...
viewed this statue in 1957 and again on 4 May 2007, while visiting Jamestown on the 400th anniversary of foundation, it being the first successful English colonial settlement in America.
On 5 October 1958, an exact replica of Partridge's statue was dedicated as a memorial to Pocahontas at St George's Parish Church. The Governor of Virginia presented the statue as a gift to the British people in 1958, a gesture prompted by The Queen's visit to the USA
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
in the previous year.
In 2017, US Ambassador Matthew Barzun visited the statue to mark the 400th anniversary of the death and burial of Pocahontas in Gravesend. The Ambassador laid a floral tribute of 21 roses at its base, symbolising each year of Pocahontas' life.
Windmill Hill
Windmill Hill, named after its former windmills, offers extensive views across the Thames and was a popular spot for Victorian visitors to the town because of the camera obscura installed at the ''Old Mill'' and for its tea gardens and other amusements. The hill was the site of a beacon in 1377, which was instituted by King Richard II, and still in use 200 years later at the time of theSpanish Armada
The Spanish Armada (a.k.a. the Enterprise of England, es, Grande y Felicísima Armada, links=no, lit=Great and Most Fortunate Navy) was a Spanish fleet that sailed from Lisbon in late May 1588, commanded by the Duke of Medina Sidonia, an aris ...
, although the hill was then known as "Rouge Hill". A modern beacon was erected and lit in 1988, the 400th anniversary of the Armada.
It was during the reign of Queen Elizabeth I that the first windmill was placed at the highest point in Gravesend, overlooking the high-water mark of the river. One mill burnt down in 1763 but was replaced the following year and that too demolished in 1894. The last surviving windmill is reported as having been destroyed by fire during Mafeking Night celebrations in 1900.
During World War I an Imperial German Navy airship passed over Windmill Hill, dropping bombs on it; today there are three markers indicating where these bombs struck.
Gravesend Power Station
Gravesend power station
Gravesend power station was built by the Gravesend Corporation in 1902–03 to supply the local demand for electricity for lighting. It was built to the west of the municipal gas works, south east of the basin on the Thames and Medway canal. The ...
(TQ 6575 7413) was built by the Gravesend Corporation in 1902–03 to supply local demand for electricity. It was built on the south side of the basin at the west end of the Thames and Medway canal
The Thames and Medway Canal is a disused canal in Kent, south east England, also known as the Gravesend and Rochester Canal. It was originally some long and cut across the neck of the Hoo peninsula, linking the River Thames at Gravesend with th ...
. The buildings were demolished in 1995.
Gravesend and the River Thames
Rosherville Gardens
Rosherville Gardens was a 19th-century pleasure garden in a disused chalk pit in Northfleet, Kent, England. After being laid out in 1837, it stood for seventy years, and was finally closed to the public just before the First World War.
Structu ...
. Gravesend soon became one of the first English resort town
A resort town, often called a resort city or resort destination, is an urban area where tourism or vacationing is the primary component of the local culture and economy. A typical resort town has one or more actual resorts in the surrounding ...
s and thrived from an early tourist trade.
Gravesend "watermen" were often in a family trade; and the town is the headquarters of the Port of London Authority
The Port of London Authority (PLA) is a self-funding public trust established on 31 March 1909 in accordance with the Port of London Act 1908 to govern the Port of London. Its responsibility extends over the Tideway of the River Thames and its ...
Control Centre (formerly known as ''Thames Navigation Service''), has its headquarters
Headquarters (commonly referred to as HQ) denotes the location where most, if not all, of the important functions of an organization are coordinated. In the United States, the corporate headquarters represents the entity at the center or the to ...
at Gravesend, providing maritime pilots who play an important role in navigation on the River Thames.
A dinghy at an unmodernised Gravesend was the backdrop to the 1952 thriller '' The Long Memory'' starring Sir John Mills
Sir John Mills (born Lewis Ernest Watts Mills; 22 February 190823 April 2005) was an English actor who appeared in more than 120 films in a career spanning seven decades. He excelled on camera as an appealing British everyman who often portray ...
. In the film, Mills plays a character living in poverty on a derelict fishing boat stranded in the mud flats.
Gravesend also has one of England's oldest regattas retained from its strong maritime links with the Thames. Although the origins of the regatta are unknown it dates back at least to Tudor times
The Tudor period occurred between 1485 and 1603 in England and Wales and includes the Elizabethan period during the reign of Elizabeth I until 1603. The Tudor period coincides with the dynasty of the House of Tudor in England that began with t ...
. The races are traditionally competed by Gravesend skiffs
A skiff is any of a variety of essentially unrelated styles of small boats. Traditionally, these are coastal craft or river craft used for leisure, as a utility craft, and for fishing, and have a one-person or small crew. Sailing skiffs have devel ...
, oaken round-bottomed, clinker-built boats.
The ''Thames Navigation Service'' was first thought up between 1950 and 1952 by Cdr Peter de Neumann GM RN, while he was captain of HMRC cutter ''Vigilant'' based at Gravesend Reach. It is possible that Vigilant Way in Gravesend is named for her. This idea followed on from considering such incidents as the accidental ramming of HMS ''Truculent'' by the ''Divina'' in 1950, the collision with the ''Nore Forts'' by ''Baalbek'', and the disastrous flooding of Canvey
Canvey Island is a town, civil parish and reclaimed island in the Thames estuary, near Southend-on-Sea, in the Castle Point district, in the county of Essex, England. It has an area of and a population of 38,170.Office for National Statistics. ( ...
, Foulness
Foulness Island () is a closed island on the east coast of Essex in England, which is separated from the mainland by narrow creeks. In the 2001 census, the usually resident population of the civil parish was 212, living in the settlements of C ...
and the East Coast in 1953. In these and other situations, rescue and intelligence gathering were severely hampered by a lack of centralised command and control, and lack of a detailed "picture". De Neumann resigned his command after returning ''Vigilant'' from the Spithead Review and joined the PLA, immediately suggesting, in a report to them submitted in 1953, that a feasibility study of such a system be carried out. He then oversaw its development and ultimate installation at Gravesend.
Tilbury Docks
The Port of Tilbury is a port on the River Thames at Tilbury in Essex, England. It is the principal port for London, as well as being the main United Kingdom port for handling the importation of paper. There are extensive facilities for contai ...
, on the opposite side of the river, between 1882 and 1886, Gravesend was the Thames's first port of entry. Thousands of emigrants, as well as large numbers of troops, embarked from here. Tilbury Docks
The Port of Tilbury is a port on the River Thames at Tilbury in Essex, England. It is the principal port for London, as well as being the main United Kingdom port for handling the importation of paper. There are extensive facilities for contai ...
have expanded considerably since, with the closure of all the London Docks. The entrance to the Docks is somewhat awkward, situated as it is on the sharp bend of the river, and boats often need tugboat assistance, as do the larger ships moored at Tilbury landing stages. There have been many tug companies based at Gravesend: among them the ''Sun Company'', the ''Alexandra Towing Company'' and, today, the ''Smith Howard Towing Company''. East Indiamen traditionally stopped here at a point known as Long Reach to lighten their loads before sailing up the Thames to moorings at Blackwall.
For some years after, war steamer excursions were run on the MV ''Royal Daffodil'' down the Thames from Gravesend to France, but they ceased in 1966. Cruises are now operated by the Lower Thames and Medway Passenger Boat Company
Lower Thames and Medway Passenger Boat Company is a river boat company which provides cruises on the River Thames in Gravesend and London, UK. Bateaux London cruises operate on the Thames under licence from London River Services, part of Tr ...
up the river to Greenwich. The cross-river passenger ferry to Tilbury provides a long-established route to and from Essex. Before the Dartford Crossing came into being, there was a vehicle ferry at Gravesend as well.
There is a RNLI lifeboat station, based at Royal Terrace Pier, which is one of the busiest in the country.
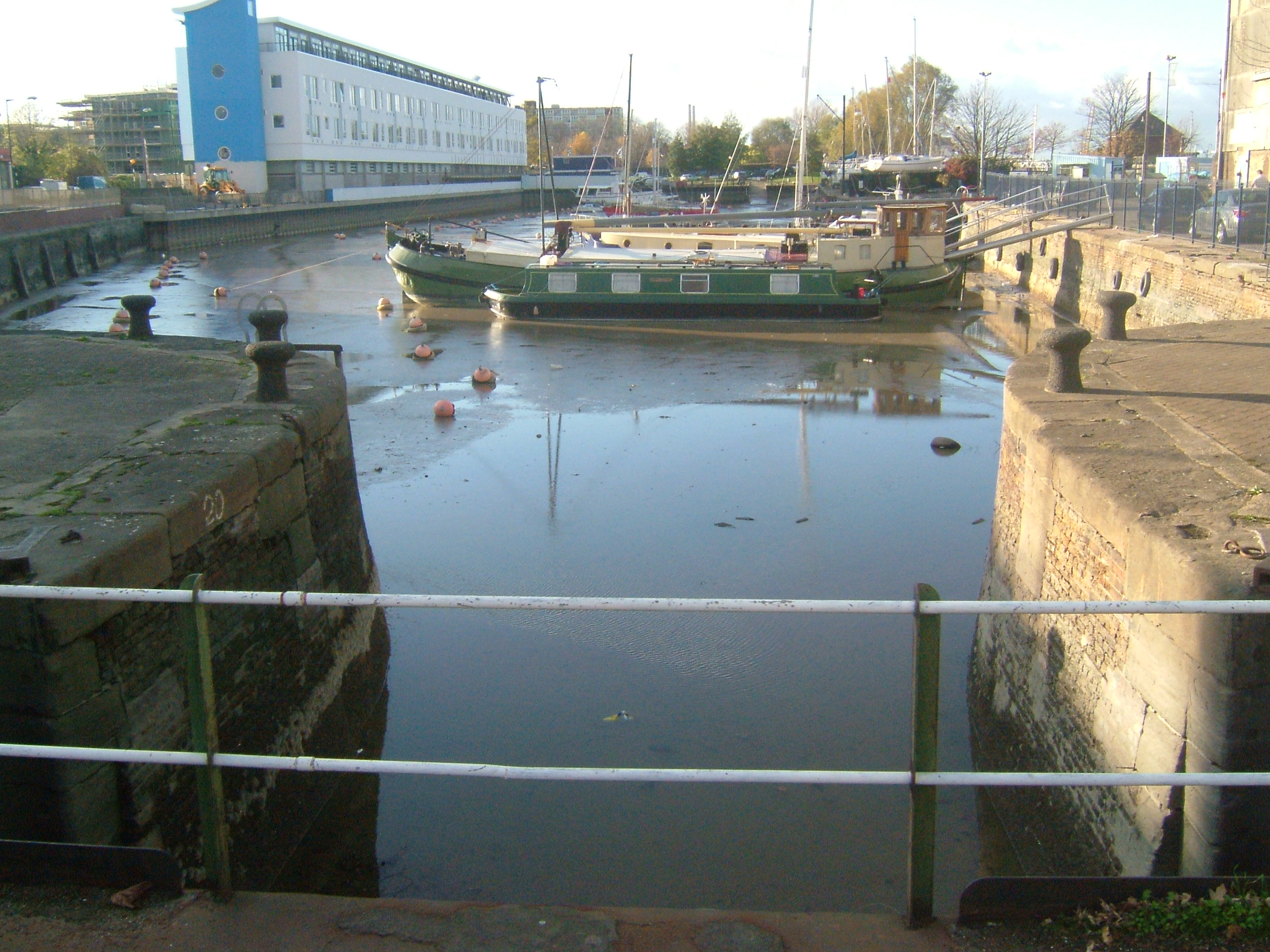
Thames and Medway Canal
Thames and Medway Canal
The Thames and Medway Canal is a disused canal in Kent, south east England, also known as the Gravesend and Rochester Canal. It was originally some long and cut across the neck of the Hoo peninsula, linking the River Thames at Gravesend with th ...
was opened for barge traffic in 1824. It ran from Gravesend on the Thames to Frindsbury
Frindsbury is part of the Medway Towns conurbation in Kent, southern England. It lies on the opposite side of the River Medway to Rochester, Kent, Rochester, and at various times in its history has been considered fully or partially part of the ...
near Strood
Strood is a town in the unitary authority of Medway in Kent, South East England. The town forms a conurbation with neighbouring towns Chatham, Rochester, Gillingham and Rainham. It lies on the northwest bank of the River Medway at its lowes ...
on the Medway
Medway is a unitary authority district and conurbation in Kent, South East England. It had a population of 278,016 in 2019. The unitary authority was formed in 1998 when Rochester-upon-Medway amalgamated with the Borough of Gillingham to for ...
. Although seven miles long, it had only two locks, each by in size, one at each end. Its most notable feature was the tunnel near Strood, which was long, the second longest canal tunnel ever built in the UK. The great cost of the tunnel meant that the canal was not a commercial success.
After only 20 years, most of the canal was closed and the canal's tunnel was converted to railway use. Initially, canal and railway shared the tunnel, with the single track built on timber supports, but by 1847, canal use was abandoned and a double track laid. Today Gravesend Canal Basin is used for the mooring of pleasure craft. Gravesend Sailing Club
Gravesend is a town in northwest Kent, England, situated 21 miles (35 km) east-southeast of Charing Cross (central London) on the south bank of the River Thames and opposite Tilbury in Essex. Located in the diocese of Rochester, it is the ...
, which was founded so that working men could participate in the sport while still having to earn a living is based here. The lock has been dredged, and restoration and strengthening work has been carried out on the basin walls as part of the regeneration of the area.
Transport
Roads
The main roads through the town are the west–eastA226 road
The A226 road travels in a west–east direction in southeast London and north Kent, from Crayford in the London Borough of Bexley, through Dartford, Gravesend to Strood. It is about 15.7 miles in length.
Route
The road begins with an end- ...
from Dartford
Dartford is the principal town in the Borough of Dartford, Kent, England. It is located south-east of Central London and
is situated adjacent to the London Borough of Bexley to its west. To its north, across the Thames estuary, is Thurrock in ...
and beyond to Rochester; and the A227 road to Tonbridge. The A2 road passes two miles (3 km) south of Gravesend town centre; a mile stretch of it was rerouted in the early 2000s to take the traffic away from the south end of the town.
In March 2006 the first of the area's new Fastrack bus services, which use a combination of ordinary roads and dedicated 'bus tracks', opened. The service links to Ebbsfleet International railway station, Greenhithe, Bluewater Shopping Centre
Bluewater Shopping Centre (commonly referred to as Bluewater) is an out-of-town shopping centre in Stone (postally Greenhithe), Kent, England, outside the M25 motorway, east south east of London's centre. Opened on 16 March 1999 in a former chal ...
and Dartford.
Rail
 Gravesend railway station lies on the
Gravesend railway station lies on the North Kent Line
The North Kent Line is a railway line which branches off the South East Main Line at St Johns junction west of Lewisham station in Greater London and runs to Rochester Bridge Junction near Strood, Medway where it links to the Chatham Main Line ...
, and was opened in 1849. The Gravesend West Line
The Gravesend West Line was a short railway line in Kent that branched off the Swanley to Chatham line at Fawkham Junction and continued for a distance of 5 miles (8 km) to Gravesend where the railway company constructed a pier to conne ...
, terminating by the river and for some time operating as a continental ferry connection, closed in 1968.
Gravesend is the primary north Kent
The Flanders Historic District is a historic district that encompasses a small cluster of late-18th to early-19th century residential structures north of the center of Kent, Connecticut, which was the original heart of the community when it was ...
interchange for high speed and metro rail services. In December 2009, the full high-speed timetable between London and Kent came into force and passenger usage from Gravesend has exceeded expectations. High-speed services from London St Pancras and Stratford International
Stratford International is a National Rail station in Stratford and a separate Docklands Light Railway (DLR) station nearby, located in East Village in London. Despite its name, no international services stop at the station; plans for it to ...
, are offered via Gravesend to the Medway
Medway is a unitary authority district and conurbation in Kent, South East England. It had a population of 278,016 in 2019. The unitary authority was formed in 1998 when Rochester-upon-Medway amalgamated with the Borough of Gillingham to for ...
towns, Sittingbourne, Faversham, Margate, Broadstairs
Broadstairs is a coastal town on the Isle of Thanet in the Thanet district of east Kent, England, about east of London. It is part of the civil parish of Broadstairs and St Peter's, which includes St Peter's, and had a population in 2011 of ...
and Ramsgate
Ramsgate is a seaside resort, seaside town in the district of Thanet District, Thanet in east Kent, England. It was one of the great English seaside towns of the 19th century. In 2001 it had a population of about 40,000. In 2011, according to t ...
. Some of these services continue to Ashford International
Ashford International railway station is a National Rail station in Ashford, Kent, England. It connects several railway lines, including High Speed 1 and the South Eastern Main Line. Services are operated by Southeastern and Southern.
The stat ...
via Sandwich and Dover Priory
The Priory of St. Mary the Virgin and St. Martin of the New Work, or Newark, commonly called Dover Priory, was a priory at Dover in southeast England. It was variously independent in rule, then occupied by canons regular of the Augustinian r ...
.
There are also metro services to London Charing Cross
Charing Cross railway station (also known as London Charing Cross) is a central London railway terminus between the Strand and Hungerford Bridge in the City of Westminster. It is the terminus of the South Eastern Main Line to Dover via Ashf ...
, London Waterloo East and London Bridge
Several bridges named London Bridge have spanned the River Thames between the City of London and Southwark, in central London. The current crossing, which opened to traffic in 1973, is a box girder bridge built from concrete and steel. It r ...
via Sidcup, via Woolwich Arsenal and Lewisham and Bexleyheath
Bexleyheath is a town in south-east London, England. It had a population of 31,929 as at 2011.
Bexleyheath is located south-east of Charing Cross, and forms part of the London Borough of Bexley. It is identified in the London Plan as one of ...
, and to Gillingham.
Unusually Gravesend features a Platform 0, one of the few in the country, it is used for terminating services from London Cannon Street
Cannon Street station, also known as London Cannon Street, is a central London railway terminus and connected London Underground station in Travelcard zone 1 located on Cannon Street in the City of London and managed by Network Rail. It is ...
or London Charing Cross via Sidcup.
Buses
Gravesend is served by severalArriva Kent Thameside
Arriva Kent Thameside is a bus operator based in North-West Kent, England. It is a subsidiary of Arriva. The company operates services in Northfleet, Gravesend & Dartford as part of the Arriva Southern Counties division from their Northfleet ...
bus services connecting the town with other areas in Kent including Dartford
Dartford is the principal town in the Borough of Dartford, Kent, England. It is located south-east of Central London and
is situated adjacent to the London Borough of Bexley to its west. To its north, across the Thames estuary, is Thurrock in ...
, Bluewater and Sevenoaks and to the Medway Towns.Gravesend is also served by Fastrack bus services connecting the town with Bluewater, Darent Valley Hospital and Dartford.
Ferry
Gravesend Town Pier
The Gravesend Town Pier is located in Gravesend, Kent, Gravesend, Kent. It was designed by William Tierney Clark and built in 1834 on the site of the earlier Town Quay, Gravesend, Town Quay. Over 3 million passengers were served between 1835 and ...
.
Footpaths
The Saxon Shore Way, along distance footpath
A long-distance trail (or long-distance footpath, track, way, greenway) is a longer recreational trail mainly through rural areas used for hiking, backpacking, cycling, horse riding or cross-country skiing. They exist on all continents exc ...
, starts at Gravesend and traces the coast as in Roman times as far as Hastings, East Sussex
East Sussex is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in South East England on the English Channel coast. It is bordered by Kent to the north and east, West Sussex to the west, and Surrey to the north-west. The largest settlement in East Su ...
; 163 miles (262 km) in total. The Wealdway also starts at the Town Pier, and continues almost due south over the Weald to Eastbourne in East Sussex where it links with South Downs Way, a distance of 80 miles (128 km).
Religious buildings
The town's principal Anglican place of worship is the Church of St George, Gravesend. This Georgian building is a tourist attraction because of its association with Princess Pocahontas, as well as being the parish church. Gravesend has three other Church of England parishes and Roman Catholic, Methodist,United Reformed
The United Reformed Church (URC) is a Protestant Christian church in the United Kingdom. As of 2022 it has approximately 40,000 members in 1,284 congregations with 334 stipendiary ministers.
Origins and history
The United Reformed Church resulte ...
and Baptist churches as well as other smaller chapels.
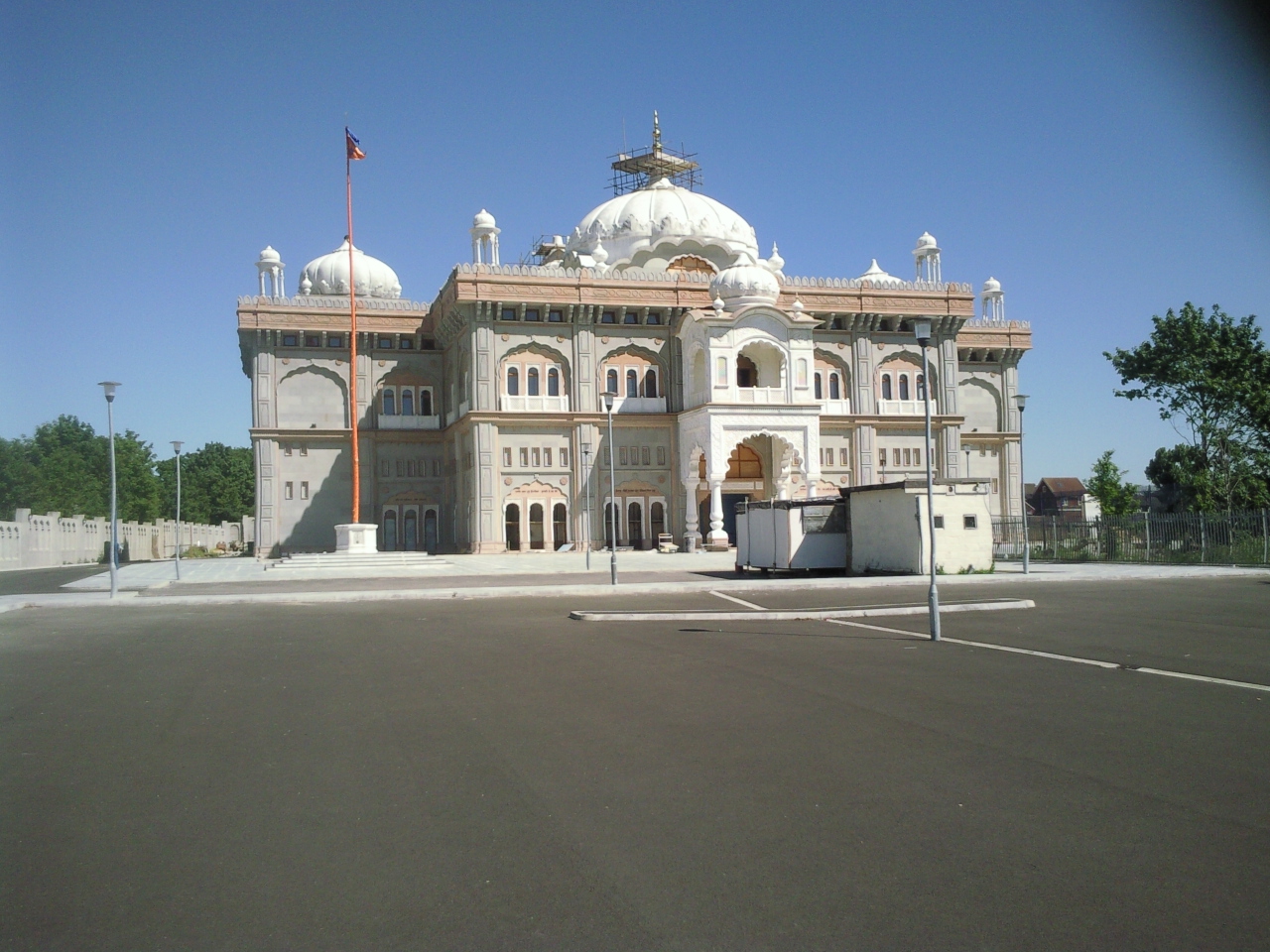
 Gravesend has a significant
Gravesend has a significant Sikh
Sikhs ( or ; pa, ਸਿੱਖ, ' ) are people who adhere to Sikhism, Sikhism (Sikhi), a Monotheism, monotheistic religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Gu ...
population of more than 15,000, representing over 15% of the town's population. Its first gurdwara was founded in 1956 by Bhat Sikh Santokh Singh Takk in Edwin Street with a second one opening, ten years later, in a former Congregationalist church, but this gurdwara closed in 2010. The same year, one of the United Kingdom's largest Sikh temple
A gurdwara (sometimes written as gurudwara) (Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰਦੁਆਰਾ ''guradu'ārā'', meaning "Door to the Guru") is a place of assembly and worship for Sikhs. Sikhs also refer to gurdwaras as ''Gurdwara Sahib''. People from all faiths ...
s was opened at a cost of £12 million.
Education
In secondary education, Gravesend has the following schools:Gravesend Grammar School
Gravesend Grammar School is a selective grammar school with Academy (English school), academy status located in Gravesend, Kent, England. The school accepts boys at age 11 by Eleven-plus exam, examination accepting a cohort of the top 15-20% and ...
; Northfleet School for Girls
Northfleet School for Girls is a high school for girls, located in Northfleet in the English county of Kent.
The school first opened in March 1937 in a new building next to Northfleet School for Boys in Colyer Road. In 1950 The Upper School m ...
; Northfleet Technology College
Northfleet Technology College (formerly Northfleet School for Boys) is located in Northfleet, Kent. It is an all-boys school that offers secondary education for students aged 11+.
As part of the Building Schools for the Future programme, a new ...
(Northfleet School for Boys, on the former sites of Northfleet Secondary School for Boys and Gravesend Technical High School for Boys); Mayfield Grammar School
Mayfield Grammar School (formerly ''Gravesend Grammar School for Girls'') is a grammar school with Academy (English school), academy status, located off Old Road West (B261) in Gravesend, Kent, England. The school accepts girls at age 11 by ele ...
(formerly Gravesend Grammar School for Girls
Mayfield Grammar School (formerly ''Gravesend Grammar School for Girls'') is a grammar school with academy status, located off Old Road West (B261) in Gravesend, Kent, England. The school accepts girls at age 11 by examination and both girls ...
); St John's Catholic Comprehensive School
St John's Catholic Comprehensive School is a Mixed-sex education, coeducational Catholic Church, Roman Catholic secondary school and sixth form, located in Gravesend, Kent, Gravesend in the English county of Kent.
It is a voluntary aided school ...
; Thamesview School
Thamesview School is a coeducational foundation high school and sixth form, located in Gravesend in the English county of Kent.
It is administered by Kent County Council
Kent County Council is a county council that governs most of the co ...
and St George's Church of England School
St George's Church of England School is a mixed all-through school and sixth form located in Gravesend in the English county of Kent.
The school was founded in 1580, and is administered by the Church of England Diocese of Rochester. The sc ...
. There are also primary age schools such as Whitehill Primary School, special schools and several independent schools, such as Bronte School and St Joseph's.
Health
Gravesend Hospital was opened in 1854, following the donation of a site by the 6th Earl of Darnley in 1853; it had its origin on 2 December 1850, as a dispensary on the Milton Road "to assist the really destitute poor of Gravesend and Milton and vicinities ... unable to pay for medical aid". By 1893, 4,699 such people had benefited by its presence. In 2004 the original building, and parts of the newer buildings were demolished to make way for a new community hospital. Gravesend Community Hospital provides a Minor Injury Unit, Dental services, Speech and Language therapy and Physiotherapy. It also has a Stroke Ward and offers inpatient care. The outpatient department provides care for much of the local area and is separate from those offered at Darent Valley Hospital. In addition, Gravesend emergency doctors out of hours service as well as podiatry are offered. In the town centre is a large medical clinic at Swan Yard, next to the Market car park, and several other doctors' surgeries are located in the area.Sport
Football
TheStonebridge Road
Stonebridge Road is a multi-purpose stadium in Northfleet, Gravesend, Kent, England, also known as Kuflink Stadium for sponsorship reasons.
It is primarily used for football matches. Stonebridge Road was constructed in 1905, and was initial ...
football ground at neighbouring Northfleet
Northfleet is a town in the borough of Gravesham in Kent, England. It is located immediately west of Gravesend, and on the border with the Borough of Dartford. Northfleet has its own railway station on the North Kent Line, just east of Ebbsfl ...
is home to Ebbsfleet United F.C.
Ebbsfleet United Football Club is a professional football club based in Northfleet, Kent, England. As of the 2021–22 season, the club competes in the National League South, the sixth tier of English football.
The club was formed in 1946 from ...
, which changed its name from Gravesend and Northfleet F.C. in June 2007. Ebbsfleet currently plays in the National League, and the club won the FA Trophy in May 2008. An agreement was reached for the MyFootballClub
MyFootballClub is an Football in England, English Industrial and Provident Society that sought, starting in August 2007, to recruit at least 50,000 Association football, football enthusiasts from across the world to purchase an English football ...
online community to purchase a 75% stake in the club in November 2007, and its takeover was completed early in 2008.
Cricket
Gravesend Cricket Club
Gravesend Cricket Club is a cricket club which currently plays in Division 1 of the Kent Cricket League. The club was formed in 1881 when the Harkaway and Clarence Cricket Clubs were amalgamated to form the Gravesend Cricket Club. The club conti ...
(founded in 1881 when the Harkaway and Clarence Cricket Clubs amalgamated) is based at the Bat and Ball Ground
The Bat & Ball Ground is a cricket and sports ground in Gravesend in Kent. The ground was used as a first-class cricket venue by Kent County Cricket Club between 1849 and 1971. It remains in use by Gravesend Cricket Club who have used the groun ...
on Wrotham Road, where cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by striki ...
has been played since its foundation at the behest of the 6th Earl of Darnley (grandfather of the celebrated England cricketer, The Hon. Ivo Bligh, later 8th Earl of Darnley) in the mid 19th century.
Rugby Union
Gravesend has two rugby union teams,Gravesend Rugby Football Club
Gravesend is a town in northwest Kent, England, situated 21 miles (35 km) east-southeast of Charing Cross (central London) on the south bank of the River Thames and opposite Tilbury in Essex. Located in the diocese of Rochester, it is the ...
and Old Gravesendians RFC, both situated next to each other opposite the Gravesend Grammar School
Gravesend Grammar School is a selective grammar school with Academy (English school), academy status located in Gravesend, Kent, England. The school accepts boys at age 11 by Eleven-plus exam, examination accepting a cohort of the top 15-20% and ...
.
Old Gravesendians RFC (founded in 1929) consisted traditionally of former Gravesend Grammar School pupils. Prior to the forming of Old Gravesendians RFC, on leaving the Grammar School, former pupils had continued to engage in various sports through the Old Blues Association (founded in 1914). Owing to World War I the Old Blues Association practically went to pieces with only one annual dinner having been held in 1914. After the war a reunion dinner was held in 1920, the second annual dinner, which restarted the Old Blues Association activities. The Old Gravesendians RFC was often referred to as 'Gravesend Old Blues' in match reports.
Old Gravesendians RFC continued to foster rugby in Gravesend during World War II by turning out a side every season. Since 2000 Old Gravesendians (Old G's) have reached six Kent Plate finals, winning two. They achieved promotion to London League rugby in 2009, but were relegated in 2009–10. Old G's put out three sides with the first team playing in Shepherd Neame Kent 1
Kent 1 (known as Shepherd Neame Kent 1 for sponsorship reasons) is an English level 9 Rugby Union League and is made up of teams predominantly from south-east London and Kent. The teams play home and away matches from September through to April ...
during the 2018–19 season. The team colours are light blue and dark blue.
Rowing
Rowing races have been held on the River Thames at Gravesend since at least 1698, with the first organisedRegatta
Boat racing is a sport in which boats, or other types of watercraft, race on water. Boat racing powered by oars is recorded as having occurred in ancient Egypt, and it is likely that people have engaged in races involving boats and other wate ...
recorded in 1715. The first Borough Regatta began in 1882, setting the pattern for an annual event on the River Thames that is carried on to this day. The River Thames in Gravesend is home to the Gravesend Rowing Club (founded in 1878), which the club claims is the oldest existing sporting club in Gravesend, the Regatta Committee's skiff rowers, and Gravesend Sailing Club.
Cycling
To the south of Gravesend on the ancient site of Watling Street on 43ha of land adjacent to the A2,Cyclopark
Cyclopark is a purpose-built facility for cycling and other outdoor activities, located on the south side of Gravesend, north Kent in south-east England, adjacent to the A2 dual carriageway.
History
The site of Cyclopark is on the old re-routed ...
, a venue for cycling events and other activities has been developed. The site which features mountain bike
A mountain bike (MTB) or mountain bicycle is a bicycle designed for off-road cycling. Mountain bikes share some similarities with other bicycles, but incorporate features designed to enhance durability and performance in rough terrain, which ...
trails, a road circuit, a BMX
BMX, an abbreviation for bicycle motocross or bike motocross, is a cycle sport performed on BMX bikes, either in competitive BMX racing or freestyle BMX, or else in general street or off-road recreation.
History
BMX began during the earl ...
racetrack and family cycling paths was formally opened in early 2012.
Culture
The Gravesend Historical Society meets regularly and produces a biannual magazine on its activities. Charles Dickens lived atGad's Hill Place
Gads Hill Place in Higham, Kent, sometimes spelt Gadshill Place and Gad's Hill Place, was the country home of Charles Dickens, the most successful British author of the Victorian era. Today the building is the independent Gad's Hill School.
...
, 2 miles (3.2 km) east of Gravesend and specifically mentions the town and its environs in at least three of his novels. In '' David Copperfield'' Mr. Peggotty, Ham and the Micawbers say their goodbyes and sail away from Gravesend to begin a new life in Australia. In ''Great Expectations
''Great Expectations'' is the thirteenth novel by Charles Dickens and his penultimate completed novel. It depicts the education of an orphan nicknamed Pip (Great Expectations), Pip (the book is a ''bildungsroman''; a coming-of-age story). It ...
'', Pip, with accomplices, rows Magwitch from London downriver in expectation of waylaying a regular steamer (whilst under way in the Lower Hope, off Gravesend) bound for Hamburg. (Gravesend also appears in '' The Pickwick Papers'').
Gravesend is briefly mentioned in the 1818 novel '' Frankenstein'' by Mary Shelley during Victor's travels through the United Kingdom with Clerval; ultimately culminating in Victor's residence in the Orkney Islands
Orkney (; sco, Orkney; on, Orkneyjar; nrn, Orknøjar), also known as the Orkney Islands, is an archipelago in the Northern Isles of Scotland, situated off the north coast of the island of Great Britain. Orkney is 10 miles (16 km) north ...
.
In the 1902 novel ''Heart of Darkness
''Heart of Darkness'' (1899) is a novella by Polish-English novelist Joseph Conrad in which the sailor Charles Marlow tells his listeners the story of his assignment as steamer captain for a Belgian company in the African interior. The novel ...
'' by Joseph Conrad
Joseph Conrad (born Józef Teodor Konrad Korzeniowski, ; 3 December 1857 – 3 August 1924) was a Poles in the United Kingdom#19th century, Polish-British novelist and short story writer. He is regarded as one of the greatest writers in t ...
, Charles Marlow's ship, anchored off Gravesend, is the setting where he tells his tale.
'' The War Game'' was a 1965 BBC television drama-documentary film depicting a nuclear war that was initially banned, and not broadcast until July 1985. The film was shot in Gravesend and in the other Kent towns of Tonbridge, Chatham and Dover, with a cast was almost entirely made up of non-actors.
The 1952 film " The Long Memory" starring John Mills was filmed in and around Gravesend. It features many squalid streets running down towards the river that even then were being progressively cleared for redevelopment. It is also possible to hear in the background steam engines working out of the now closed Gravesend West Line
The Gravesend West Line was a short railway line in Kent that branched off the Swanley to Chatham line at Fawkham Junction and continued for a distance of 5 miles (8 km) to Gravesend where the railway company constructed a pier to conne ...
West Street terminus.
Notable people
 *
* Sir Edwin Arnold
Sir Edwin Arnold KCIE CSI (10 June 183224 March 1904) was an English poet and journalist, who is most known for his work ''The Light of Asia''.Gemma Arterton (born 1986), actress, was born at Northfleet and attended
Gravesend Tourist Information Centre''The History of the Town of Gravesend'' by Robert Peirce Cruden (1843)
{{Authority control Towns in Kent Market towns in Kent Port of London History of Kent Populated places on the River Thames Unparished areas in Kent Gravesham
Gravesend Grammar School for Girls
Mayfield Grammar School (formerly ''Gravesend Grammar School for Girls'') is a grammar school with academy status, located off Old Road West (B261) in Gravesend, Kent, England. The school accepts girls at age 11 by examination and both girls ...
.
* Sir Derek Barton
Sir Derek Harold Richard Barton (8 September 1918 – 16 March 1998) was an English organic chemist and Nobel Prize laureate for 1969.
Education and early life
Barton was born in Gravesend, Kent, to William Thomas and Maude Henrietta Barton ( ...
(1918–1998), English chemist and Nobel Prize winner for "contributions to the development of the concept of conformation and its application in chemistry".
* Admiral Sir Francis Beaufort (1774–1857), creator of the Beaufort Scale, was stationed at Gravesend.
* Sir Peter Blake (born 1932), artist who trained at Gravesend School of Art. ''The Blake Gallery'' has recently been opened at the Woodville Halls in the town.
* George Box
George Edward Pelham Box (18 October 1919 – 28 March 2013) was a British statistician, who worked in the areas of quality control, time-series analysis, design of experiments, and Bayesian inference. He has been called "one of the g ...
(1919–2013), renowned statistician, and a recipient of the FRS.
* Charles Dickens is associated with Gravesend and villages around the borough. Many of the links between him and Gravesham are still in evidence – Gravesend he visited, at Chalk he spent his honeymoon, at Higham he lived and died, and at Cobham he found inspiration for '' The Pickwick Papers''.
* Jessica Dismorr
Jessica Stewart Dismorr (3 March 1885 – 29 August 1939) was an English painter and illustrator. Dismorr participated in almost all of the avant-garde groups active in London between 1912 and 1937 and was one of the few English painters of the ...
(1885-1939), a member of the Vorticism art movement, was born in Gravesend.
* Carl Daniel Ekman
Carl Daniel Ekman (March 17, 1845 – November 3, 1904) was a Swedish chemical engineer who invented the form of the sulfite process of wood pulp manufacturing which was first established on a firm commercial basis, helping to replace rags as the ...
(1845–1904) Swedish chemist and paper-maker who relocated to Gravesend.
* Major-General Charles Gordon (1833–1885), lived in the town from 1865 to 1871. As commander of the Royal Engineers, he supervised the construction of the forts guarding the Thames downstream from Gravesend, at New Tavern Fort in the town, Shornemead Fort
Shornemead Fort is a now-disused artillery fort that was built in the 1860s to guard the entrance to the Thames from seaborne attack. Constructed during a period of tension with France, it stands on the south bank of the river at a point where th ...
on the Thames's south bank, and Coalhouse Fort on the north in Essex. While in Gravesend, Gordon devoted himself to the welfare of the town's "poor boys", establishing a Sunday School
A Sunday school is an educational institution, usually (but not always) Christian in character. Other religions including Buddhism, Islam, and Judaism have also organised Sunday schools in their temples and mosques, particularly in the West.
Su ...
and providing food and clothes for them from his Army wages. His links with Gravesend are commemorated locally on the embankment at the Riverside Leisure Area, which is known as the Gordon Promenade, and at Khartoum Place that lies just to the south.
* Paul Greengrass (born 1955) film director was educated at Gravesend Grammar School for Boys
Gravesend Grammar School is a selective grammar school with academy status located in Gravesend, Kent, England. The school accepts boys at age 11 by examination accepting a cohort of the top 15-20% and boys and girls at 16, based on their GCS ...
.
* Thom Gunn
Thomson William "Thom" Gunn (29 August 1929 – 25 April 2004) was an English poet who was praised for his early verses in England, where he was associated with The Movement, and his later poetry in America, even after moving towards a looser, ...
(1929–2004), Anglo-American poet, was born in Gravesend. His most famous collection, ''The Man With Night Sweats'' (1992), is dominated by AIDS-related elegies. He relocated to San Francisco, California in 1954 to teach writing at Stanford University
Stanford University, officially Leland Stanford Junior University, is a private research university in Stanford, California. The campus occupies , among the largest in the United States, and enrolls over 17,000 students. Stanford is consider ...
and remain close to Mike his partner whom he met whilst at university.
* Katharine Hamnett (born 1947), fashion designer.
* William Hanneford-Smith
William Hanneford-Smith FRSE AMICE ARIBA(Hon) (1878–1954) was a 20th century British engineer and publisher.
Life
He was born in 1878 the son of Francis Smith.
He started working for B. T. Batsford Publishers in London in 1893 aged 15.
He ...
(1878–1954) publisher
* Adam Holloway (born 1965), local Member of Parliament (MP) since 2005, lives on Darnley Road in the town.
* Shadrach Jones
Shadrach Edward Robert Jones ( – 12 July 1895) was a New Zealand doctor, auctioneer, hotel-owner and impresario. He was born in Gravesend, Kent
Kent is a county in South East England and one of the home counties. It borders Greater Lo ...
(c.1822–1895) New Zealand doctor, auctioneer, hotel-owner and impresario; born in Gravesend.
* John MacGregor John MacGregor, John Macgregor or John McGregor may refer to:
Sportsmen
* John McGregor (footballer, born 1851), Scottish international football player
* John McGregor (footballer, born 1900) (1900–1993), English football player
* John McGrego ...
(1825–1892), English writer, who designed the "Rob Roy" canoe.
* Pocahontas (1595–1617), the first female Native American to visit England. She was taken ill on her return voyage to America, and died aged 21 after coming ashore at Gravesend. She was buried under the chancel of St George's parish church.
* Harry Reid (born 1992), actor who appeared in EastEnders
''EastEnders'' is a Television in the United Kingdom, British soap opera created by Julia Smith (producer), Julia Smith and Tony Holland which has been broadcast on BBC One since February 1985. Set in the fictional borough of Walford in the Ea ...
as Ben Mitchell, was born and lives in Gravesend. He attended Northfleet Technology College
Northfleet Technology College (formerly Northfleet School for Boys) is located in Northfleet, Kent. It is an all-boys school that offers secondary education for students aged 11+.
As part of the Building Schools for the Future programme, a new ...
(formerly known as Northfleet School for Boys). Trained in acting, physical theatre and musical theatre at Miskin Theatre in Dartford, Kent.
* The composer Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov
Nikolai Andreyevich Rimsky-Korsakov . At the time, his name was spelled Николай Андреевичъ Римскій-Корсаковъ. la, Nicolaus Andreae filius Rimskij-Korsakov. The composer romanized his name as ''Nicolas Rimsk ...
(1844–1908) was an officer in the Russian Navy and was posted to Gravesend in 1862, where he wrote part of his first symphony, said to be the first such style of composition attempted by a Russian composer.
* David Rutley (born 1961 at Gravesend), first Mormon UK Member of Parliament (MP).
* Chris Simmons
Christopher Matthew Simmons (born 8 January 1975 in Gravesend, Kent) is an English television and stage actor. He is best known for his roles as DC Mickey Webb in ''The Bill'', Mark Garland in '' EastEnders'' and Stuart Summer in ''Hollyoaks''.
...
(born 1975 at Gravesend), television and stage actor best known for his roles as DC Mickey Webb in '' The Bill'', Mark Garland in ''EastEnders
''EastEnders'' is a Television in the United Kingdom, British soap opera created by Julia Smith (producer), Julia Smith and Tony Holland which has been broadcast on BBC One since February 1985. Set in the fictional borough of Walford in the Ea ...
'' and Stuart Summer in '' Hollyoaks''.
* Charles Stewart, 3rd Duke of Richmond
Charles Stewart, 3rd Duke of Richmond, 6th Duke of Lennox KG (7 March 1639December 1672) of Cobham Hall in Kent and of Richmond House in Whitehall, London, 11th Seigneur d'Aubigny in France, was an English nobleman of Franco-Scottish ancestry an ...
, resided at Cobham Hall, 5 miles (8 km) south east of Gravesend, until 1672 (followed by his descendants, the Earls of Darnley
Earl of Darnley is a hereditary title that has been created three times, twice in the Peerage of Scotland and once in the Peerage of Ireland.
The first creation in the Scots Peerage came in 1580 in favour of Esme Stewart, 1st Earl of Lennox ...
).
Twin towns
Gravesend is twinned with: *Cambrai
Cambrai (, ; pcd, Kimbré; nl, Kamerijk), formerly Cambray and historically in English Camerick or Camericke, is a city in the Nord (French department), Nord Departments of France, department and in the Hauts-de-France Regions of France, regio ...
, France
* Chesterfield, Virginia, United States
* Neumünster, Germany
* Brunswick, Victoria
Brunswick is an inner-city suburb in Melbourne, Victoria (Australia), Victoria, Australia, north of Melbourne's Melbourne city centre, Central Business District, located within the City of Merri-bek Local government areas of Victoria, local gov ...
, Australia
See also
* Gravesham (UK Parliament constituency) *Gravesend Grammar School
Gravesend Grammar School is a selective grammar school with Academy (English school), academy status located in Gravesend, Kent, England. The school accepts boys at age 11 by Eleven-plus exam, examination accepting a cohort of the top 15-20% and ...
* List of Battle of Britain airfields
During the Battle of Britain, the defence of the UK's airspace was divided up within RAF Fighter Command into four Groups, each comprising several airfields and squadrons.
The groups involved, 10, 11, 12 and 13, saw very different levels of a ...
* Pocahontas (character)
Pocahontas is the titular character of Walt Disney Pictures' 33rd animated feature film ''Pocahontas'' (1995). The character and the events she goes through are loosely based on the actual historical figure Pocahontas, making her the first Disne ...
References
External links
Gravesend Tourist Information Centre
{{Authority control Towns in Kent Market towns in Kent Port of London History of Kent Populated places on the River Thames Unparished areas in Kent Gravesham