, neighboring_municipalities =
Adliswil,
Dübendorf,
Fällanden,
Kilchberg,
Maur,
Oberengstringen
Oberengstringen is a municipality in the district of Dietikon in the canton of Zürich in Switzerland, located in the Limmat Valley (German: ''Limmattal'').
History
Oberengstringen is first mentioned in 870 as ''Enstelingon''. In 1306 it was ...
,
Opfikon,
Regensdorf
Regensdorf is a municipality in the district of Dielsdorf District of the canton of Zürich, Switzerland. It is the biggest city in the region Furttal (ZH).
Katzensee is a lake that also includes the bath/lido Strandbad Katzensee on the border ...
,
Rümlang,
Schlieren,
Stallikon,
Uitikon,
Urdorf,
Wallisellen,
Zollikon
, twintowns =
Kunming
Kunming (; ), also known as Yunnan-Fu, is the capital and largest city of Yunnan province, China. It is the political, economic, communications and cultural centre of the province as well as the seat of the provincial government. The headquar ...
,
San Francisco

Zürich () is the
largest city in Switzerland and the capital of the
canton of Zürich
The canton of Zürich (german: Kanton Zürich ; rm, Chantun Turitg; french: Canton de Zurich; it, Canton Zurigo) is a Swiss canton in the northeastern part of the country. With a population of (as of ), it is the most populous canton in the ...
. It is located in north-central Switzerland, at the northwestern tip of
Lake Zürich. As of January 2020, the municipality has 434,335 inhabitants, the
urban area 1.315 million (2009),
and the
Zürich metropolitan area 1.83 million (2011).
Zürich is a hub for railways, roads, and air traffic. Both
Zurich Airport and
Zürich's main railway station are the largest and busiest in the country.
Permanently settled for over 2,000 years, Zürich was founded by the
Romans, who called it '. However, early settlements have been found dating back more than 6,400 years (although this only indicates human presence in the area and not the presence of a town that early). During the Middle Ages, Zürich gained the independent and privileged status of
imperial immediacy
Imperial immediacy (german: Reichsfreiheit or ') was a privileged constitutional and political status rooted in German feudal law under which the Imperial estates of the Holy Roman Empire such as Imperial cities, prince-bishoprics and secular prin ...
and, in 1519, became a primary centre of the
Protestant Reformation in Europe under the leadership of
Huldrych Zwingli.
The official language of Zürich is
German, but the main spoken language is
Zürich German, the local variant of the
Alemannic Swiss German
Swiss German (Standard German: , gsw, Schwiizerdütsch, Schwyzerdütsch, Schwiizertüütsch, Schwizertitsch Mundart,Because of the many different dialects, and because there is no defined orthography for any of them, many different spelling ...
dialect.
Many museums and art galleries can be found in the city, including the
Swiss National Museum and
Kunsthaus.
Schauspielhaus Zürich is considered to be one of the most important theatres in the German-speaking world.
Zürich is home to many financial institutions and banking companies.
Name
In
German, the city name is written , and pronounced in
Swiss Standard German
Swiss Standard German (german: Schweizer Standarddeutsch), or Swiss High German (german: Schweizer Hochdeutsch or ''Schweizerhochdeutsch''), referred to by the Swiss as ''Schriftdeutsch'', or ''Hochdeutsch'', is the written form of one of four o ...
or in
German Standard German. In
the local dialect, the name is pronounced without the final consonant, as , although the adjective remains . The city is called in
French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
, in
Italian, and in
Romansh.
The name is traditionally written in English as ''Zurich'', without the
umlaut. It is pronounced or .
The earliest known form of the city's name is , attested on a
tombstone of the late 2nd century AD in the form ("Turicum tax post").The name is interpreted as a derivation from a given name, possibly the
Gaulish personal name
A personal name, or full name, in onomastic terminology also known as prosoponym (from Ancient Greek πρόσωπον / ''prósōpon'' - person, and ὄνομα / ''onoma'' - name), is the set of names by which an individual person is known ...
''Tūros'', for a reconstructed native form of the toponym of . The Latin stress on the long vowel of the Gaulish name, , was lost in German but is preserved in Italian and in Romansh . The first development towards its later
Germanic form is attested as early as the 6th century with the form ''Ziurichi''. From the 9th century onward, the name is established in an
Old High German form (857 ''in villa Zurih'', 924 ''in Zurich curtem'', 1416 ''Zürich Stadt''). In the early modern period, the name became associated with the name of the
Tigurini, and the name rather than the historical is sometimes encountered in
Modern Latin contexts.
History
Early history


Settlements of the
Neolithic and
Bronze Age were found around
Lake Zürich. Traces of pre-Roman Celtic,
La Tène settlements were discovered near the
Lindenhof
The Lindenhof, in the old town of Zürich, Switzerland, is the historical site of the Roman castle, and the later Carolingian Kaiserpfalz. It is situated on Lindenhof hill, on the left side of the Limmat at the Schipfe.
In 1747, a second-century ...
, a
morainic hill dominating the SE - NW waterway constituted by Lake Zurich and the river
Limmat
The Limmat is a river in Switzerland. The river commences at the outfall of Lake Zurich, in the southern part of the city of Zurich. From Zurich it flows in a northwesterly direction, after 35 km reaching the river Aare. The confluenc ...
.
[ In Roman times, during the conquest of the alpine region in 15 BC, the Romans built a '']castellum
A ''castellum'' in Latin is usually:
* a small Roman fortlet or tower,C. Julius Caesar, Gallic War; 2,30 a diminutive of ('military camp'), often used as a watchtower or signal station like on Hadrian's Wall. It should be distinguished from a ...
'' on the Lindenhof.[ Later here was erected '' Turicum'' (a toponym of clear Celtic origin), a tax-collecting point for goods trafficked on the Limmat, which constituted part of the border between Gallia Belgica (from AD 90 ]Germania Superior
Germania Superior ("Upper Germania") was an imperial province of the Roman Empire. It comprised an area of today's western Switzerland, the French Jura and Alsace regions, and southwestern Germany. Important cities were Besançon ('' Vesontio' ...
) and Raetia: this customs point developed later into a '' vicus''.[ After Emperor Constantine's reforms in AD 318, the border between Gaul and Italy (two of the four praetorian prefectures of the Roman Empire) was located east of Turicum, crossing the river Linth between Lake Walen and Lake Zürich, where a castle and garrison looked over Turicum's safety. The earliest written record of the town dates from the 2nd century, with a tombstone referring to it as to the ' ("Zürich post for collecting the 2.5% value tax of the Galliae"), discovered at the ]Lindenhof
The Lindenhof, in the old town of Zürich, Switzerland, is the historical site of the Roman castle, and the later Carolingian Kaiserpfalz. It is situated on Lindenhof hill, on the left side of the Limmat at the Schipfe.
In 1747, a second-century ...
.Alemanni
The Alemanni or Alamanni, were a confederation of Germanic tribes
*
*
*
on the Upper Rhine River. First mentioned by Cassius Dio in the context of the campaign of Caracalla of 213, the Alemanni captured the in 260, and later expanded into pres ...
tribe settled in the Swiss Plateau. The Roman castle remained standing until the 7th century. A Carolingian
The Carolingian dynasty (; known variously as the Carlovingians, Carolingus, Carolings, Karolinger or Karlings) was a Frankish noble family named after Charlemagne, grandson of mayor Charles Martel and a descendant of the Arnulfing and Pippin ...
castle, built on the site of the Roman castle by the grandson of Charlemagne, Louis the German, is mentioned in 835 (''in castro Turicino iuxta fluvium Lindemaci''). Louis also founded the Fraumünster abbey in 853 for his daughter Hildegard. He endowed the Benedictine convent with the lands of Zürich, Uri, and the Albis forest, and granted the convent immunity, placing it under his direct authority. In 1045, King Henry III granted the convent the right to hold markets, collect tolls, and mint coins, and thus effectively made the abbess the ruler of the city.
Zürich gained Imperial immediacy
Imperial immediacy (german: Reichsfreiheit or ') was a privileged constitutional and political status rooted in German feudal law under which the Imperial estates of the Holy Roman Empire such as Imperial cities, prince-bishoprics and secular prin ...
(', becoming an Imperial free city) in 1218 with the extinction of the main line of the Zähringer family and attained a status comparable to statehood. During the 1230s, a city wall was built, enclosing 38 hectares, when the earliest stone houses on the Rennweg were built as well. The Carolingian castle was used as a quarry, as it had started to fall into ruin.
Emperor Frederick II promoted the abbess of the to the rank of a duchess in 1234. The abbess nominated the mayor, and she frequently delegated the minting of coins to citizens of the city. The political power of the convent slowly waned in the 14th century, beginning with the establishment of the ' ( guild laws) in 1336 by Rudolf Brun
Rudolf Brun (1290s – 17 September 1360) was the leader of the Zürich guilds' revolution of 1336, and the city's first independent mayor.
Since 1234, Zürich had been governed by an aristocratic council. One third of the council's members w ...
, who also became the first independent mayor, i.e. not nominated by the abbess.
An important event in the early 14th century was the completion of the Manesse Codex
The Codex Manesse (also Große Heidelberger Liederhandschrift or Pariser Handschrift) is a ''Liederhandschrift'' (manuscript containing songs), the single most comprehensive source of Middle High German ''Minnesang'' poetry, written and illustrat ...
, a key source of medieval German poetry. The famous illuminated manuscript
An illuminated manuscript is a formally prepared document where the text is often supplemented with flourishes such as borders and miniature illustrations. Often used in the Roman Catholic Church for prayers, liturgical services and psalms, the ...
– described as "the most beautifully illumined German manuscript in centuries;" – was commissioned by the Manesse family of Zürich, copied and illustrated in the city at some time between 1304 and 1340. Producing such a work was a highly expensive prestige project, requiring several years work by highly skilled scribes and miniature painters, and it clearly testifies to the increasing wealth and pride of Zürich citizens in this period. The work contains 6 songs by Süsskind von Trimberg, who may have been a Jew, since the work itself contains reflections on medieval Jewish life, though little is known about him.
The first mention of Jews in Zürich was in 1273. Sources show that there was a synagogue in Zürich in the 13th century, implying the existence of a Jewish community. With the rise of the Black Death in 1349, Zürich, like most other Swiss cities, responded by persecuting and burning the local Jews, marking the end of the first Jewish community there. The second Jewish community of Zürich, formed towards the end of the 14th century, was short-lived, and Jews were expulsed and banned from the city from 1423 until the 19th century.
Archaeological findings
A woman who died in about 200 BC was found buried in a carved tree trunk during a construction project at the Kern school complex in March 2017 in Aussersihl. Archaeologists revealed that she was approximately 40 years old when she died and likely carried out little physical labor when she was alive. A sheepskin coat, a belt chain, a fancy wool dress, a scarf and a pendant made of glass and amber beads were also discovered with the woman.
Old Swiss Confederacy
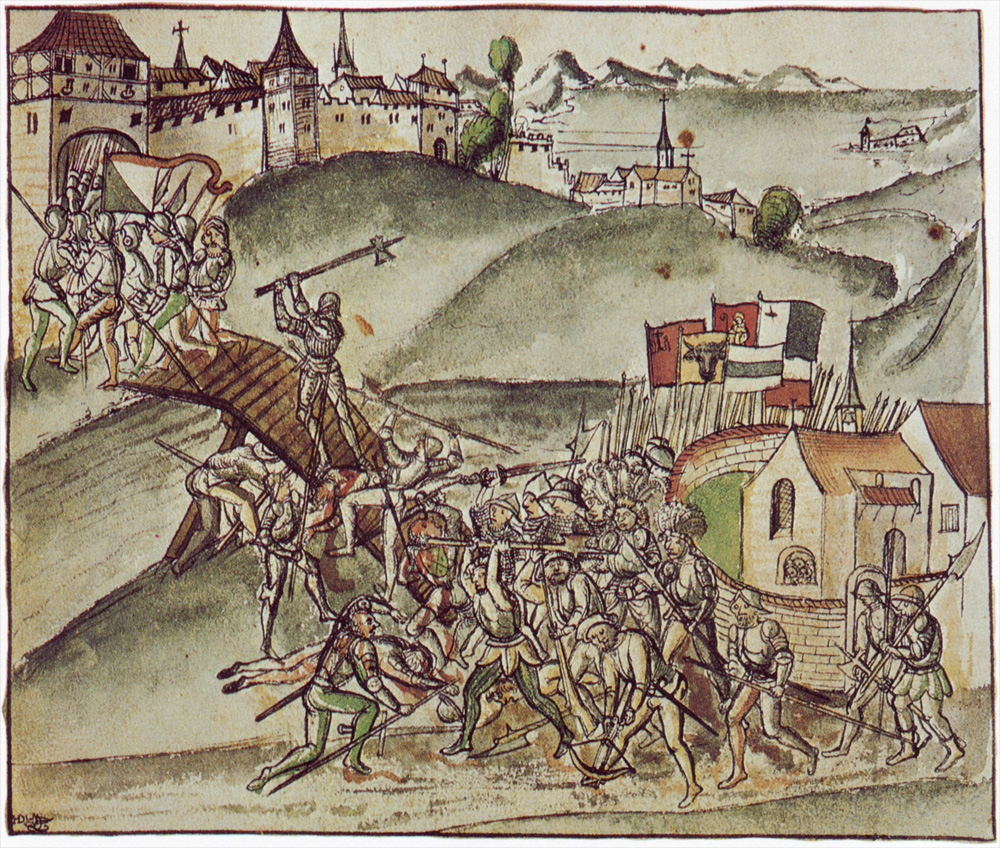 On 1 May 1351, the citizens of Zürich had to swear allegiance before representatives of the cantons of
On 1 May 1351, the citizens of Zürich had to swear allegiance before representatives of the cantons of Lucerne
Lucerne ( , ; High Alemannic German, High Alemannic: ''Lozärn'') or Luzern ()Other languages: gsw, Lozärn, label=Lucerne German; it, Lucerna ; rm, Lucerna . is a city in central Switzerland, in the Languages of Switzerland, German-speaking po ...
, Schwyz, Uri and Unterwalden, the other members of the Swiss Confederacy. Thus, Zürich became the fifth member of the Confederacy, which was at that time a loose confederation of ''de facto'' independent states. Zürich was the presiding canton of the Diet from 1468 to 1519. This authority was the executive council and lawmaking body of the confederacy, from the Middle Ages until the establishment of the Swiss federal state in 1848. Zürich was temporarily expelled from the confederacy in 1440 due to a war with the other member states over the territory of Toggenburg (the Old Zürich War). Neither side had attained significant victory when peace was agreed upon in 1446, and Zürich was readmitted to the confederation in 1450. Zwingli started the
Zwingli started the Swiss Reformation
The Protestant Reformation in Switzerland was promoted initially by Huldrych Zwingli, who gained the support of the magistrate, Mark Reust, and the population of Zürich in the 1520s. It led to significant changes in civil life and state matte ...
at the time when he was the main preacher in the 1520s, at the . He lived there from 1484 until his death in 1531. The Zürich Bible, based on that of Zwingli, was issued in 1531. The Reformation resulted in major changes in state matters and civil life in Zürich, spreading also to a number of other cantons. Several cantons remained Catholic and became the basis of serious conflicts that eventually led to the outbreak of the Wars of Kappel
The wars of Kappel (''Kappelerkriege'') is a collective term for two armed conflicts fought near Kappel am Albis between the Catholic and the Protestant cantons of the Old Swiss Confederacy during the Reformation in Switzerland.
First War
Th ...
.
During the 16th and 17th centuries, the Council of Zürich adopted an isolationist attitude, resulting in a second ring of imposing fortifications built in 1624. The Thirty Years' War which raged across Europe motivated the city to build these walls. The fortifications required a lot of resources, which were taken from subject territories without reaching any agreement. The following revolts were crushed brutally. In 1648, Zürich proclaimed itself a republic, shedding its former status of a free imperial city.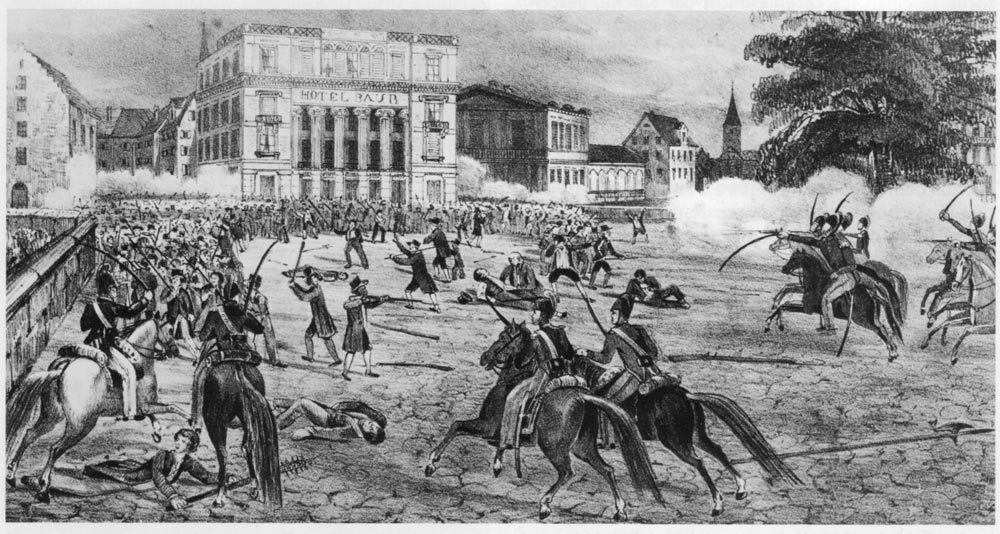 The Helvetic Revolution of 1798 saw the fall of the . Zürich lost control of the land and its economic privileges, and the city and the canton separated their possessions between 1803 and 1805. In 1839, the city had to yield to the demands of its urban subjects, following the of 6 September. Most of the ramparts built in the 17th century were torn down, without ever having been besieged, to allay rural concerns over the city's hegemony. The Treaty of Zürich between Austria, France, and Sardinia was signed in 1859.
The Helvetic Revolution of 1798 saw the fall of the . Zürich lost control of the land and its economic privileges, and the city and the canton separated their possessions between 1803 and 1805. In 1839, the city had to yield to the demands of its urban subjects, following the of 6 September. Most of the ramparts built in the 17th century were torn down, without ever having been besieged, to allay rural concerns over the city's hegemony. The Treaty of Zürich between Austria, France, and Sardinia was signed in 1859.
Modern history
Zürich was the Federal capital for 1839–40, and consequently, the victory of the Conservative party there in 1839 caused a great stir throughout Switzerland. But when in 1845 the Radicals regained power at Zürich, which was again the Federal capital for 1845–46, Zürich took the lead in opposing the Sonderbund cantons. Following the Sonderbund war and the formation of the Swiss Federal State, Zürich voted in favour of the Federal constitutions of 1848 and of 1874. The enormous immigration from the country districts into the town from the 1830s onwards created an industrial class which, though "settled" in the town, did not possess the privileges of burghership, and consequently had no share in the municipal government. First of all in 1860 the town schools, hitherto open to "settlers" only on paying high fees, were made accessible to all, next in 1875 ten years' residence ''ipso facto'' conferred the right of burghership, and in 1893 the eleven outlying districts were incorporated within the town proper.
When Jews also began to settle in Zürich following their equality in 1862, the Israelitische Cultusgemeinde Zürich was founded.Industrialisation
Industrialisation ( alternatively spelled industrialization) is the period of social and economic change that transforms a human group from an agrarian society into an industrial society. This involves an extensive re-organisation of an econo ...
led to migration into the cities and to rapid population growth, particularly in the suburbs of Zürich.
The are an important milestone in the development of the modern city of Zürich, as the construction of the new lake front transformed Zürich from a small medieval town on the rivers Limmat
The Limmat is a river in Switzerland. The river commences at the outfall of Lake Zurich, in the southern part of the city of Zurich. From Zurich it flows in a northwesterly direction, after 35 km reaching the river Aare. The confluenc ...
and Sihl to an attractive modern city on the shore, under the guidance of the city engineer Arnold Bürkli
Arnold Bürkli (February 2, 1833 – May 6, 1894)''Bürkli, Arnold'', Dictionnaire Historique de la Suis. Retrieved 2012-03-02. is principally known as a municipal engineer in Zürich, Zürich, Switzerland.
Life and work
Arnold Bürkli was also ...
.
In 1893, the twelve outlying districts were incorporated into Zürich, including Aussersihl, the workman's quarter on the left bank of the Sihl, and additional land was reclaimed from Lake Zürich.
In 1934, eight additional districts in the north and west of Zürich were incorporated.
Zürich was accidentally bombed during World War II. As persecuted Jews sought refuge in Switzerland, the SIG (Israelite Community of Switzerland) raised financial resources. The central committee for refugee aid, created in 1933, was located in Zürich.
The canton of Zürich did not recognise the Jewish religious communities as legal entities (and therefore as equal to national churches) until 2005.
Coat of arms

 The blue and white coat of arms of Zürich is attested from 1389 and was derived from banners with blue and white stripes in use since 1315. The first certain testimony of banners with the same design is from 1434. The coat of arms is flanked by two lions. The red ' on top of the banner had varying interpretations: For the people of Zürich, it was a mark of honour, granted by Rudolph I. Zürich's neighbours mocked it as a sign of shame, commemorating the loss of the banner at Winterthur in 1292. Today, the Canton of Zürich uses the same coat of arms as the city.
The blue and white coat of arms of Zürich is attested from 1389 and was derived from banners with blue and white stripes in use since 1315. The first certain testimony of banners with the same design is from 1434. The coat of arms is flanked by two lions. The red ' on top of the banner had varying interpretations: For the people of Zürich, it was a mark of honour, granted by Rudolph I. Zürich's neighbours mocked it as a sign of shame, commemorating the loss of the banner at Winterthur in 1292. Today, the Canton of Zürich uses the same coat of arms as the city.
Politics
City districts
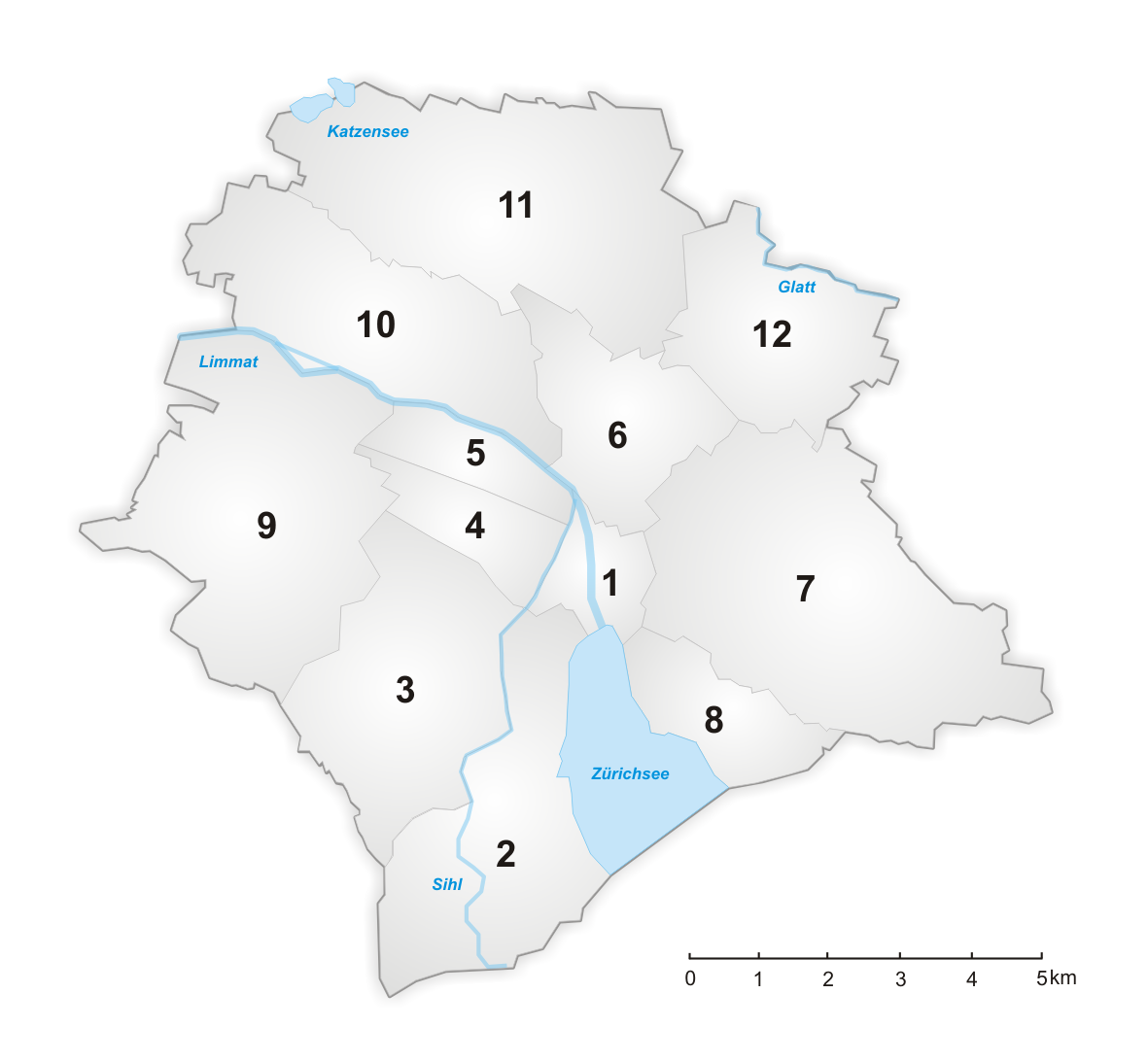 The previous boundaries of the city of Zürich (before 1893) were more or less synonymous with the location of the old town. Two large expansions of the city limits occurred in 1893 and in 1934 when the city of Zürich merged with many surrounding municipalities, that had been growing increasingly together since the 19th century. Today, the city is divided into twelve districts (known as ' in German), numbered 1 to 12, each one of which contains between one and four neighborhoods:
* , known as , contains the old town, both to the east and west of the start of the
The previous boundaries of the city of Zürich (before 1893) were more or less synonymous with the location of the old town. Two large expansions of the city limits occurred in 1893 and in 1934 when the city of Zürich merged with many surrounding municipalities, that had been growing increasingly together since the 19th century. Today, the city is divided into twelve districts (known as ' in German), numbered 1 to 12, each one of which contains between one and four neighborhoods:
* , known as , contains the old town, both to the east and west of the start of the Limmat
The Limmat is a river in Switzerland. The river commences at the outfall of Lake Zurich, in the southern part of the city of Zurich. From Zurich it flows in a northwesterly direction, after 35 km reaching the river Aare. The confluenc ...
. District 1 contains the neighbourhoods of ', ', ', and ''City''.
* lies along the west side of Lake Zürich, and contains the neighbourhoods of ''Enge'', ''Wollishofen'' and ''Leimbach''.
* , known as is between the Sihl and the Uetliberg, and contains the neighbourhoods of ', ' and '.
* , known as lies between the Sihl and the train tracks leaving , and contains the neighbourhoods of ', ', and '.
* , known as , is between the Limmat and the train tracks leaving , it contains the former industrial area of Zürich which has undergone large-scale rezoning to create upscale modern housing, retail, and commercial real estate. It contains the neighborhoods of ' and '.
* is on the edge of the , a hill overlooking the eastern part of the city. District 6 contains the neighbourhoods of ' and '.
* is on the edge of the hill as well as the Zürichberg, on the eastern side of the city. District 7 contains the neighbourhoods of ', ', and '. These neighbourhoods are home to Zürich's wealthiest and more prominent residents. The neighbourhood ' also belongs to district 7.
* , officially called , but colloquially known as Seefeld, lies on the eastern side of Lake Zürich. District 8 consists of the neighbourhoods of ', ', and '.
* is between the Limmat to the north and the to the south. It contains the neighbourhoods ' and '.
* is to the east of the Limmat
The Limmat is a river in Switzerland. The river commences at the outfall of Lake Zurich, in the southern part of the city of Zurich. From Zurich it flows in a northwesterly direction, after 35 km reaching the river Aare. The confluenc ...
and to the south of the and hills. District 10 contains the neighbourhoods of ' and '.
* is in the area north of the and and between the Glatt Valley and the (Cats Lake). It contains the neighbourhoods of ', ' and '.
* , known as , is located in the (Glatt valley) on the northern side of the Zürichberg
The Zürichberg is a wooded hill rising to 679 m (2,228 feet), overlooking Lake Zürich and located immediately to the east of the city of Zürich, Switzerland, between the valleys of the Limmat and the Glatt rivers. Its highest point is about ...
. District 12 contains the neighbourhoods of ', ', and '.
Most of the district boundaries are fairly similar to the original boundaries of the previously existing municipalities before they were incorporated into the city of Zürich.
Government
The City Council () constitutes the executive government of the City of Zürich and operates as a collegiate authority
Collegiate may refer to:
* College
* Webster's Dictionary, a dictionary with editions referred to as a "Collegiate"
* ''Collegiate'' (1926 film), 1926 American silent film directed by Del Andrews
* ''Collegiate'' (1936 film), 1936 American musi ...
. It is composed of nine councilors, each presiding over a department. Departmental tasks, coordination measures and implementation of laws decreed by the Municipal Council are carried out by the City Council. The regular election of the City Council by any inhabitant valid to vote is held every four years. The mayor (german: Stadtpräsident(in)) is elected as such by a public election by a system of Majorz while the heads of the other departments are assigned by the collegiate. Any resident of Zurich allowed to vote can be elected as a member of the City Council. In the mandate period 2018–2022 (''Legislatur'') the City Council is presided by mayor Corine Mauch. The executive body holds its meetings in the City Hall (german: Stadthaus), on the left bank of the Limmat. The building was built in 1883 in Renaissance style.
, the Zürich City Council was made up of three representatives of the SP ( Social Democratic Party, one of whom is the mayor), two members each of the Green Party and the FDP (Free Democratic Party Free Democratic Party is the name of several political parties around the world. It usually designates a party ideologically based on liberalism.
Current parties with that name include:
*Free Democratic Party (Germany), a liberal political party in ...
), and one member each of GLP (Green Liberal Party
The Green Liberal Party of Switzerland (german: Grünliberale Partei der Schweiz, glp; french: Parti vert'libéral, pvl), abbreviated to glp, is a centrist green-liberal political party in Switzerland. Founded in 2007, the party holds sixteen ...
) and AL ( Alternative Left Party), giving the left parties a combined six out of nine seats.
Parliament
The Municipal Council () holds the legislative power. It is made up of 125 members (), with elections held every four years. The Municipal Council decrees regulations and by-laws that are executed by the City Council and the administration. The sessions of the Municipal Council are held in public. Unlike those of the City Council, the members of the Municipal Council are not politicians by profession but are paid a fee based on their attendance. Any resident of Zürich allowed to vote can be elected as a member of the Municipal Council. The legislative body holds its meetings in the town hall
In local government, a city hall, town hall, civic centre (in the UK or Australia), guildhall, or a municipal building (in the Philippines), is the chief administrative building of a city, town, or other municipality. It usually houses ...
(), on the right bank of the Limmat opposite to the City Hall ().
The last election of the Municipal Council was held on 4 March 2018 for the mandate period of 2018–2022.
Elections
National Council
In the 2019 federal election for the Swiss National Council the most popular party was the SPS
SPS may refer to:
Law and government
* Agreement on the Application of Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures of the WTO
* NATO Science for Peace and Security
* Single Payment Scheme, an EU agricultural subsidy
* The Standard Procurement System, fo ...
which received 25.6% (-6) of the vote. The next four most popular parties were the GPS
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a Radionavigation-satellite service, satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of t ...
(20.9%, +9.7), GLP (15.7%, +6.4), SVP (13.7%, -4.3), the FDP (11.8%, -2.2), the AL (4%, new), and the CVP (3.5%, -0.2). In the federal election, a total of 110,760 voters were cast, and the voter turnout was 47.7%.
In the 2015 federal election for the Swiss National Council the most popular party was the SPS
SPS may refer to:
Law and government
* Agreement on the Application of Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures of the WTO
* NATO Science for Peace and Security
* Single Payment Scheme, an EU agricultural subsidy
* The Standard Procurement System, fo ...
which received 31.6% of the vote. The next four most popular parties were the SVP (18%), the FDP (14%), the GPS
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a Radionavigation-satellite service, satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of t ...
(10.7%), the GLP (9.2%). In the federal election, a total of 114,377 voters were cast, and the voter turnout was 46.2%.
International relations
Twin towns and sister cities
Zürich is partnered with two sister cities: Kunming
Kunming (; ), also known as Yunnan-Fu, is the capital and largest city of Yunnan province, China. It is the political, economic, communications and cultural centre of the province as well as the seat of the provincial government. The headquar ...
and San Francisco.
Geography

 Zürich is situated at
Zürich is situated at above sea level
Height above mean sea level is a measure of the vertical distance (height, elevation or altitude) of a location in reference to a historic mean sea level taken as a vertical datum. In geodesy, it is formalized as ''orthometric heights''.
The comb ...
on the lower (northern) end of Lake Zürich (') about north of the Alps, nestling between the wooded hills on the west and east side. The Old Town stretches on both sides of the Limmat
The Limmat is a river in Switzerland. The river commences at the outfall of Lake Zurich, in the southern part of the city of Zurich. From Zurich it flows in a northwesterly direction, after 35 km reaching the river Aare. The confluenc ...
, which flows from the lake, running northwards at first and then gradually turning into a curve to the west. The geographic (and historic) centre of the city is the Lindenhof
The Lindenhof, in the old town of Zürich, Switzerland, is the historical site of the Roman castle, and the later Carolingian Kaiserpfalz. It is situated on Lindenhof hill, on the left side of the Limmat at the Schipfe.
In 1747, a second-century ...
, a small natural hill on the west bank of the Limmat, about north of where the river issues from Lake Zürich. Today the incorporated city stretches somewhat beyond the natural confines of the hills and includes some districts to the northeast in the Glatt Valley (') and to the north in the Limmat Valley ('). The boundaries of the older city are easy to recognize by the Schanzengraben canal. This artificial watercourse has been used for the construction of the third fortress in the 17th and 18th centuries.
Topography
The municipality of Zürich has an area of , of which is made up of Lake Zürich. The area includes a section of the northern Swiss Plateau. The banks of the Limmat constitute the densest part of the city. The river is oriented in the southeast–northwest direction, with the flat valley floor having a width of . The partially channeled and straightened Limmat does not flow in the central part of the valley, but always along its right (northeastern) side. The Sihl meets with the Limmat at the end of Platzspitz, which borders the Swiss National Museum. The Limmat reaches the lowest point of the municipality in Oberengstringen
Oberengstringen is a municipality in the district of Dietikon in the canton of Zürich in Switzerland, located in the Limmat Valley (German: ''Limmattal'').
History
Oberengstringen is first mentioned in 870 as ''Enstelingon''. In 1306 it was ...
at above sea level
Height above mean sea level is a measure of the vertical distance (height, elevation or altitude) of a location in reference to a historic mean sea level taken as a vertical datum. In geodesy, it is formalized as ''orthometric heights''.
The comb ...
.


 On its west side, the Limmat valley is flanked by the wooded heights of the Albis chain, which runs along the western border. The Uetliberg is, with above sea level, the highest elevation of the surrounding area. Its summit can be reached easily by the Uetlibergbahn. From the platform of the observation tower on the summit, an impressive panorama of the city, the lake, and the Alps can be seen.
The northeast side of the Limmat valley includes a range of hills, which marks the watershed between the Limmat and the Glatt. From the northwest to the southeast, the height of the mostly wooded knolls generally increases: the Gubrist (), the Hönggerberg (), the Käferberg (), the
On its west side, the Limmat valley is flanked by the wooded heights of the Albis chain, which runs along the western border. The Uetliberg is, with above sea level, the highest elevation of the surrounding area. Its summit can be reached easily by the Uetlibergbahn. From the platform of the observation tower on the summit, an impressive panorama of the city, the lake, and the Alps can be seen.
The northeast side of the Limmat valley includes a range of hills, which marks the watershed between the Limmat and the Glatt. From the northwest to the southeast, the height of the mostly wooded knolls generally increases: the Gubrist (), the Hönggerberg (), the Käferberg (), the Zürichberg
The Zürichberg is a wooded hill rising to 679 m (2,228 feet), overlooking Lake Zürich and located immediately to the east of the city of Zürich, Switzerland, between the valleys of the Limmat and the Glatt rivers. Its highest point is about ...
(), the Adlisberg () and the Öschbrig (). Between the Käferberg and the Zürichberg is located the saddle of the Milchbuck (about ), an important passage from the Limmat valley to the Glatt valley.
The northernmost part of the municipality extends to the plain of the Glatt valley and to the saddle which makes the connection between the Glattal and Furttal. Also, a part of the Katzensee (nature reserve) and the Büsisee, both of which are drained by the Katzenbach to Glatt, belong to the city.
Climate
Zürich has an oceanic climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the humid temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool summers and mild winters ( ...
( Köppen: ''Cfb''), with warm summers and four distinct seasons. Decisive for the climate of Zürich are both the winds from westerly directions, which often result in precipitation and, on the other hand, the Bise
The Bise (French: ''La Bise'') is a cold, dry wind in Switzerland which blows through the Swiss Plateau from the northeast to the southwest.
Cause and effect
It is caused by canalisation of the air-current along the northern edge of the Alps, du ...
(east or north-east wind), which is usually associated with high-pressure situations, but cooler weather phases with temperatures lower than the average. The Foehn wind, which plays an important role in the northern alpine valleys also has some impact on Zürich.
The annual mean temperature at the measuring station of the Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology in Zürich-Fluntern ( above sea level
Height above mean sea level is a measure of the vertical distance (height, elevation or altitude) of a location in reference to a historic mean sea level taken as a vertical datum. In geodesy, it is formalized as ''orthometric heights''.
The comb ...
on the slope of the Zürichberg, above the level of the city centre) is . The lowest monthly mean of daily minimum temperature are measured in January with and the highest monthly mean of daily maximum temperature are measured in July with . On average there are 74.9 days in which the minimum temperature is below (so-called ''frost days''), and 23.7 days in which the maximum temperature is below (so-called ''ice days''). There are on average 30 so-called ''summer days'' (maximum temperature equal to or above ) throughout the year, while so-called ''heat days'' (with maximum temperature equal to or above ) are 5.8 days.[
]
Climate protection
In November 2008 the people of Zürich voted in a public referendum to write into law the quantifiable and fixed deadline of one tonne of CO2 per person per annum by 2050. This forces any decision of the executive to support this goal, even if the costs are higher in all dimensions. Some examples are the new disinfection section of the public city hospital in Triemli ( Minergie-P quality – passive house), the continued optimisation and creation of public transportation, enlargement of the bicycle-only network, research and projects for renewable energy
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. It includes sources such as sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy ...
and enclosure of speed-ways.
Urban area
The areas surrounding the Limmat are almost completely developed with residential, industrial, and commercial zones. The sunny and desirable residential areas in the hills overlooking Zürich, Waidberg and Zürichberg, and the bottom part of the slope on the western side of the valley on the Uetliberg, are also densely built.
The "green lungs" of the city include the vast forest areas of Adlisberg, Zürichberg, Käferberg, Hönggerberg and Uetliberg. Major parks are also located along the lakeshore (Zürichhorn and Enge), while smaller parks dot the city. Larger contiguous agricultural lands are located near Affoltern and Seebach. Of the total area of the municipality of Zürich (in 1996, without the lake), 45.4% is residential, industrial and commercial, 15.5% is transportation infrastructure, 26.5% is forest, 11%: is agriculture and 1.2% is water.
Transport
Public transport
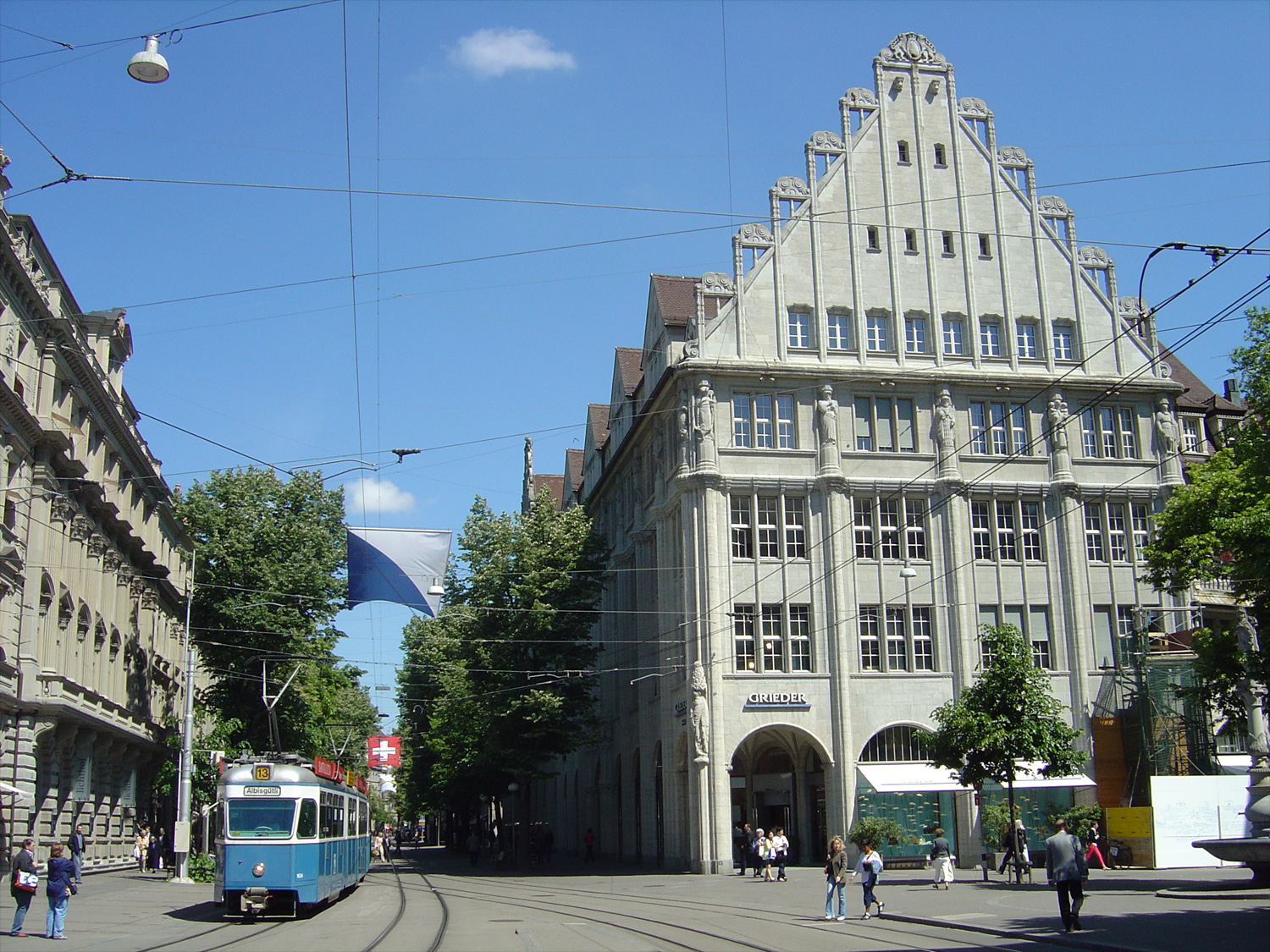
 Public transport is extremely popular in Zürich, and its inhabitants use public transport in large numbers. About 70% of the visitors to the city use the tram or bus, and about half of the journeys within the municipality take place on public transport. The ZVV network of public transport contains at least four means of mass-transit: any train that stops within the network's borders, in particular the S-Bahn (local trains), Zürich trams, and buses (both diesel and electric, also called
Public transport is extremely popular in Zürich, and its inhabitants use public transport in large numbers. About 70% of the visitors to the city use the tram or bus, and about half of the journeys within the municipality take place on public transport. The ZVV network of public transport contains at least four means of mass-transit: any train that stops within the network's borders, in particular the S-Bahn (local trains), Zürich trams, and buses (both diesel and electric, also called trolley buses
A trolleybus (also known as trolley bus, trolley coach, trackless trolley, trackless tramin the 1910s and 1920sJoyce, J.; King, J. S.; and Newman, A. G. (1986). ''British Trolleybus Systems'', pp. 9, 12. London: Ian Allan Publishing. .or troll ...
) and boats on the lake and river. In addition, the public transport network includes funicular railways and even the Luftseilbahn Adliswil-Felsenegg (LAF), a cable car Cable car most commonly refers to the following cable transportation systems:
* Aerial lift, such as aerial tramways and gondola lifts, in which the vehicle is suspended in the air from a cable
** Aerial tramway
** Chairlift
** Gondola lift
*** Bi ...
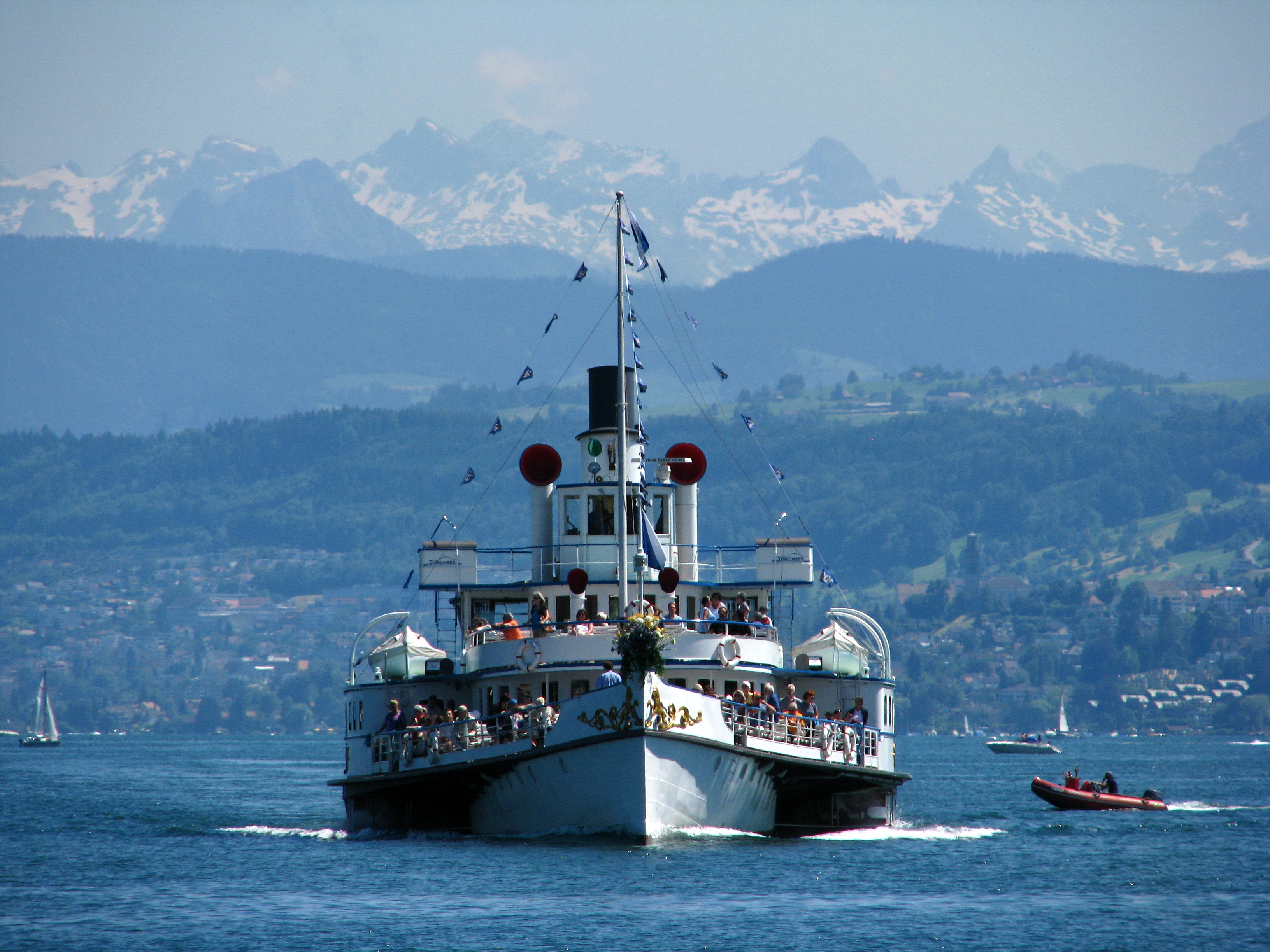
between Adliswil and Felsenegg. Tickets purchased for a trip are valid on all means of public transportation (train, tram, bus, boat). The Zürichsee-Schifffahrtsgesellschaft (commonly abbreviated to ZSG) operates passenger vessels on the Limmat and the Lake Zürich, connecting surrounding towns between Zürich and Rapperswil.
 Zürich is a mixed hub for railways, roads, and air traffic. Zürich Hauptbahnhof (''Zürich HB'') is the largest and busiest station in Switzerland and is an important railway hub in Europe. As of early 2020, Zürich HB served around 470,000 passengers and nearly 3,000 trains every day. Among the 16 railway stations (and 10 additional train stops) within Zürich's city borders, there are five other major passenger railway stations. Three of them belong to the ten most frequented railway stations in Switzerland: Stadelhofen, Oerlikon, Altstetten,
Zürich is a mixed hub for railways, roads, and air traffic. Zürich Hauptbahnhof (''Zürich HB'') is the largest and busiest station in Switzerland and is an important railway hub in Europe. As of early 2020, Zürich HB served around 470,000 passengers and nearly 3,000 trains every day. Among the 16 railway stations (and 10 additional train stops) within Zürich's city borders, there are five other major passenger railway stations. Three of them belong to the ten most frequented railway stations in Switzerland: Stadelhofen, Oerlikon, Altstetten, Hardbrücke
The Hardbrücke (Swiss German: ''Hardbrugg'') is a long road bridge and important north–south connection in the Swiss city of Zürich. As of 2009, 70,000 vehicles use the bridge daily.
From north to south, the bridge crosses ''Wipkingerplatz'' ...
, and Enge. The railway network is mainly operated by the Swiss Federal Railways (SBB CFF FFS), but Zürich is also served by major EuroCity
EuroCity, abbreviated as EC, is a cross-border train category within the European inter-city rail network. In contrast to trains allocated to the lower-level "IC" (InterCity) category, EC trains are international services that meet 20 criteri ...
trains from the neighbouring countries and is a destination for both French/Swiss ( TGV Lyria) and German ( ICE) high-speed trains, as well as by Austrian RailJet.
Zurich Airport
Zurich Airport is located less than northeast of the city in Kloten. Zurich Airport has its own railway station, which is located underground. It is directly connected to Zürich and most of the major Swiss cities. Zurich Airport is served by more than 60 passenger airlines from around the world. It is also served by one cargo airline and is a hub for Swiss International Air Lines. There is also an airfield in Dübendorf.
Road traffic
The A1, A3 and A4 motorways pass close to Zürich. The A1 heads west towards Bern
german: Berner(in)french: Bernois(e) it, bernese
, neighboring_municipalities = Bremgarten bei Bern, Frauenkappelen, Ittigen, Kirchlindach, Köniz, Mühleberg, Muri bei Bern, Neuenegg, Ostermundigen, Wohlen bei Bern, Zollikofen
, website ...
and Geneva and eastwards towards St. Gallen; the A4 leads northwards to Schaffhausen and southwards to Altdorf connecting with the A2 towards Chiasso; and the A3 heads northwest towards Basel and southeast along Lake Zürich and Lake Walen towards Sargans.
Bicycle transport
In 2012, the city council launched a program to improve the city's attractiveness for bicycle traffic. The so-called "Masterplan Velo" is part of the superordinate framework ''Stadtverkehr 2025'' which shapes the future of the different means of transport. Research revealed that infrastructure and the social environment are essential factors in improving a city's appeal to bicycle traffic. Three main goals are specified: First, the modal share of bicycle traffic should be enhanced to twice the value of 2011 by 2015. Second, cyclists' safety should be improved to lower the overall accident risk. Third, cycling should be established as an everyday means of transport with a special focus on children and young people.
In terms of infrastructure, the city aims to build up a network of distinctive bicycle routes in order to achieve these objectives. At a final stage, the network will consist of main routes (''Hauptrouten'') for everyday use and comfort routes (''Komfortrouten''), with the latter focusing on leisure cycling. Additional measures such as special ''Velostationen'' providing bike-related services are expected to help to further improve the quality. One of the key projects of the system is a tunnel beneath the tracks of the main railway station planned to combine a main connection with staffed possibilities where commuters can leave their bikes throughout the day. Apart from infrastructural measures, further approaches are planned in the fields of communication, education and administration.
However, these efforts cause critique, mainly due to postponing. The institution of the bike tunnel at the main railway station, originally planned for 2016, is currently (2016) delayed to at least 2019. Pro Velo, a nationwide interest group, has publicly questioned whether the masterplan already failed. The critique aims at badly governed traffic management at construction sites, missing possibilities to park bikes in the city as well as rather diffident ambitions. In response, the responsible city department points to the big investments made every year and mentions ongoing discussions that would finally lead to even better results.
Demographics
Population
 There are people living in Zürich (as of ), making it Switzerland's largest city. Of registered inhabitants (in 2016), 32% (133,473) do not hold
There are people living in Zürich (as of ), making it Switzerland's largest city. Of registered inhabitants (in 2016), 32% (133,473) do not hold Swiss
Swiss may refer to:
* the adjectival form of Switzerland
* Swiss people
Places
* Swiss, Missouri
* Swiss, North Carolina
*Swiss, West Virginia
* Swiss, Wisconsin
Other uses
*Swiss-system tournament, in various games and sports
*Swiss Internation ...
citizenship.[ Of these, German citizens make up the largest group with 8% (33,548), followed by Italians 3.5% (14,543).][ As of 2011, the population of the city, including suburbs, totaled 1.17 million people.][ The entire metropolitan area (including the cities of Winterthur, Baden, Brugg, Schaffhausen, Frauenfeld, Uster / Wetzikon, Rapperswil-Jona, and Zug) had a population of around 1.82 million people.][
]
Languages
The official formal language used by governmental institutions, print, news, schools and universities, courts, theatres and in any kind of written form is the Swiss variety of Standard German, while the spoken language is Zürich German (''Züritüütsch''), one of the several more or less distinguishable, but mutually intelligible Swiss German
Swiss German (Standard German: , gsw, Schwiizerdütsch, Schwyzerdütsch, Schwiizertüütsch, Schwizertitsch Mundart,Because of the many different dialects, and because there is no defined orthography for any of them, many different spelling ...
dialects of Switzerland with roots in the medieval Alemannic German
Alemannic, or rarely Alemannish (''Alemannisch'', ), is a group of High German dialects. The name derives from the ancient Germanic tribal confederation known as the Alamanni ("all men").
Distribution
Alemannic dialects are spoken by approxim ...
dialect groups. However, because of Zürich's national importance, and therefore its existing high fluctuation, its inhabitants and commuters speak all kinds of Swiss German dialects. As of the December 2010 census, 69.3% of the population speaks diglossic
In linguistics, diglossia () is a situation in which two dialects or languages are used (in fairly strict compartmentalization) by a single language community. In addition to the community's everyday or vernacular language variety (labeled "L ...
Swiss German
Swiss German (Standard German: , gsw, Schwiizerdütsch, Schwyzerdütsch, Schwiizertüütsch, Schwizertitsch Mundart,Because of the many different dialects, and because there is no defined orthography for any of them, many different spelling ...
/Swiss Standard German
Swiss Standard German (german: Schweizer Standarddeutsch), or Swiss High German (german: Schweizer Hochdeutsch or ''Schweizerhochdeutsch''), referred to by the Swiss as ''Schriftdeutsch'', or ''Hochdeutsch'', is the written form of one of four o ...
as their mother-tongue at home. Some 22.7% of inhabitants speak Standard German
Standard High German (SHG), less precisely Standard German or High German (not to be confused with High German dialects, more precisely Upper German dialects) (german: Standardhochdeutsch, , or, in Switzerland, ), is the standardized variety ...
in their family environment ("at home"). Dramatically increasing, according to the last census in 2000, 8.8% now speak English. Italian follows behind at 7.1% of the population, then French at 4.5%. Other languages spoken here include: Bosnian (4.1%), Spanish (3.9%), Portuguese (3.1%), and Albanian (2.3%). (Multiple choices were possible.) Thus, 20% of the population speak two or more languages at home.
Religion
Before the Protestant Reformation reached Zürich, it was ''de jure'' and ''de facto'' Roman Catholic.
The Protestant Reformation, led by Huldrych Zwingli, made Zürich both a theological centre and a stronghold of Protestantism in Switzerland. Another Swiss city with a comparable status was Geneva, the so-called ''Protestant Rome'', where John Calvin
John Calvin (; frm, Jehan Cauvin; french: link=no, Jean Calvin ; 10 July 150927 May 1564) was a French theologian, pastor and reformer in Geneva during the Protestant Reformation. He was a principal figure in the development of the system ...
and his Protestant Reformers
Protestant Reformers were those theologians whose careers, works and actions brought about the Protestant Reformation of the 16th century.
In the context of the Reformation, Martin Luther was the first reformer (sharing his views publicly in 15 ...
operated, as well as Basel. Zürich attracted other influential Protestant Reformers
Protestant Reformers were those theologians whose careers, works and actions brought about the Protestant Reformation of the 16th century.
In the context of the Reformation, Martin Luther was the first reformer (sharing his views publicly in 15 ...
like Heinrich Bullinger. Zwingli translated the Bible ( Zürich Bible) into the local variety of German, and introduced the Reformation by winning support of the magistrates, the princess abbess Katharina von Zimmern, and the largely peasant population of the Canton of Zürich
The canton of Zürich (german: Kanton Zürich ; rm, Chantun Turitg; french: Canton de Zurich; it, Canton Zurigo) is a Swiss canton in the northeastern part of the country. With a population of (as of ), it is the most populous canton in the ...
. The canton unanimously adopted the Reformed tradition, as represented by Zwingli. Religious wars between Catholics and Protestants tormented the Swiss Confederacy. Zwingli died for political and religious reasons by defending the Canton of Zürich in the Battle of Kappel. Bullinger took over his role as the city's spiritual leader.
In 1970, about 53% of the population were Swiss Reformed
The Protestant Church in Switzerland (PCS), (EKS); french: Église évangélique réformée de Suisse (EERS); it, Chiesa evangelica riformata in Svizzera (CERiS); rm, Baselgia evangelica refurmada da la Svizra (BRRS) formerly named Federation o ...
, while almost 40% were Roman Catholic. Since then, both large Swiss churches, the Roman Catholic Church and Swiss Reformed Church, have been constantly losing members, though for the Catholic Church, the decrease started 20 years later, in around 1990. Nevertheless, for the last twenty years, both confessions have been reduced by 10%, to the current figures (census 2010): 30% Roman Catholic, and 26% Swiss Reformed (organized in Evangelical Reformed Church of the Canton of Zürich). In 1970, only 2% of Zürich's inhabitants claimed to be not affiliated with any religious confession. In accordance with the loss by the large Swiss churches, the number of people declaring themselves as non-affiliated rose to 17% in the year 2000. In the last ten years, this figure rose to more than 25%. For the group of people, being between 24 and 44 years old, this is as high as one in every third person.[
The population of Jewish ethnicity and religion has been more or less constant since 1970, at about 1%. The Synagoge Zürich Löwenstrasse is the oldest and largest synagogue of Zürich.]
Social
The level of unemployment in Zürich was 3.2% in July 2012. In 2008, the average monthly income was about CHF 7000 before any deductions for social insurances and taxes. In 2010, there were 12,994 cases (on average per month) of direct or indirect welfare payments from the state.
Quality of living
Zürich often performs very well in international rankings, some of which are mentioned below:
*'' Monocle's'' 2012 "Quality of Life Survey" ranked Zürich first on a list of the top 25 cities in the world "to make a base within". In 2019 Zürich was ranked among the ten most liveable cities in the world by Mercer together with Geneva and Basel.
*In '' fDi Magazine''s "Global Cities of the Future 2021/22" report, Zürich placed 16th in the overall rankings (all categories).
Main sites
 Most of Zürich's sites are located within the area on either side of the Limmat, between the Main railway station and Lake Zürich. The churches and houses of the old town are clustered here, as are the most expensive shops along the famous Bahnhofstrasse. The
Most of Zürich's sites are located within the area on either side of the Limmat, between the Main railway station and Lake Zürich. The churches and houses of the old town are clustered here, as are the most expensive shops along the famous Bahnhofstrasse. The Lindenhof
The Lindenhof, in the old town of Zürich, Switzerland, is the historical site of the Roman castle, and the later Carolingian Kaiserpfalz. It is situated on Lindenhof hill, on the left side of the Limmat at the Schipfe.
In 1747, a second-century ...
in the old town is the historical site of the Roman castle, and the later Carolingian Imperial Palace.
Churches
* Grossmünster (Great Minster) According to legend, Charlemagne discovered the graves of the city's martyrs Felix and Regula and had built the first church as a monastery; start of current building around 1100; in the first half of the 16th century, the Great Minster was the starting point of the Swiss-German Reformation led by Huldrych Zwingli and Heinrich Bullinger; declared by Charlemagne imperial church; romanesque crypt, romanesque capitals in the church and cloister; choir windows by Augusto Giacometti (1932) and Sigmar Polke (2009), bronze doors by Otto Münch (1935 and 1950).
* Fraumünster (Women's Minster) Church of a former abbey for aristocratical women from southern Germany which was founded in 853 by Louis the German for his daughter Hildegard; first church built before 874; the romanesque choir dates from 1250 to 1270; the church enjoyed the patronage of kings and had the right of coinage from Zürich to the 13th century; after the Reformation, church and convent passed into the possession of the city; the most important jewelry – in addition to the largest organ in the canton with its 5,793 pipes and 92 stops – are color windows: the window in the north transept of Augusto Giacometti (1945), the five-part cycle in the choir (1970) and the rosette in the southern transept (1978) are by Marc Chagall
Marc Chagall; russian: link=no, Марк Заха́рович Шага́л ; be, Марк Захаравіч Шагал . (born Moishe Shagal; 28 March 1985) was a Russian-French artist. An early modernism, modernist, he was associated with se ...
; also the church of Zürich's largest choir with 100 and more singers.
*St. Peter
) (Simeon, Simon)
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Bethsaida, Gaulanitis, Syria, Roman Empire
, death_date = Between AD 64–68
, death_place = probably Vatican Hill, Rome, Italia, Roman Empire
, parents = John (or Jonah; Jona)
, occupation ...
romanesque-gothic-baroque church built on remains of former churches from before the 9th century; with the largest church clock face in Europe built 1538; baptismal font of 1598, baroque stucco; individual stalls from the 15th century from city repealed monasteries with rich carvings and armrests; Kanzellettner (increased barrier between the nave and choir with built-pulpit) of 1705 pulpit sounding board about 1790; rich Akanthus embellishment with Bible verse above the pulpit; 1971 new crystal chandelier modeled according 1710 design; organ in 1974 with 53 stops; Bells: five from 1880, the largest, A minor, without clapper weighs about ; fire guard in the tower to the Middle Ages to 1911.
* Predigerkirche is one of the four main churches of the old town, first built in 1231 AD as a Romanesque church of the then Dominican ''Predigerkloster'' nearby the Neumarkt. It was converted in the first half of the 14th century, and the choir rebuilt between 1308 and 1350. Due to its construction and for that time unusual high bell tower, it was regarded as the most high Gothic edifice in Zürich.
Museums
* Zürich Museum of Art – The Museum of Art, also known as ''Kunsthaus Zürich'', is one of the significant art museums of Europe. It holds one of the largest collections in Classic Modern art
Modern art includes artistic work produced during the period extending roughly from the 1860s to the 1970s, and denotes the styles and philosophies of the art produced during that era. The term is usually associated with art in which the tradi ...
in the world (Munch, Picasso, Braque, Giacometti, etc.). The museum also features a large library collection of photographs.
* Swiss National Museum – The National Museum (German: ''Landesmuseum'') displays many objects that illustrate the cultural and historical background of Switzerland. It also contains many ancient artifacts, including stained glass, costumes, painted furniture and weapons. The museum is located in the Platzspitz park opposite to the Hauptbahnhof.
* Centre Le Corbusier – Located on the shore of the Lake Zürich nearby Zürichhorn, the Centre Le Corbusier (also named: ''Heidi Weber Museum''), is an art museum dedicated to the work of the Swiss architect Le Corbusier
Charles-Édouard Jeanneret (6 October 188727 August 1965), known as Le Corbusier ( , , ), was a Swiss-French architect, designer, painter, urban planner, writer, and one of the pioneers of what is now regarded as modern architecture. He was ...
, inside the last house he designed.
* Rietberg Museum – The Rietberg Museum, situated in Gablerstrasse, is one of the great repositories of art and culture in Zürich. The museum also displays exhibits gathered from various corners of the world: bronze artifacts from Tibet, ceramics and jade, Indian sculpture, Chinese grave decorations, masks by African tribes, etc.
* Museum of Design – The Museum of Design is a museum for industrial design, visual communication, architecture and craft. It is part of the Department of Cultural Analysis of the Zürich University of the Arts.
* Haus Konstruktiv – The Haus Konstruktiv is a museum with Swiss-wide and international recognition. The museum is about constructive, concrete and conceptual art and design. It testimonies to Zürich's industrial architecture in the immediate vicinity of the Main Station.
* Uhrenmuseum Beyer – The Uhrenmuseum is located in the heart of the city. Documenting the history of timekeeping and timekeepers, the museum is home to a large collection of mechanical timepieces as well as a collection of primitive time keeping devices such as water clocks, sundials and hourglasses
* No Show Museum – the No Show Museum is the first museum dedicated to nothing and its various manifestations throughout the history of art.
* Guild houses – The Guild houses (German: ''Zunfthaus'') are located along the Limmat (downstream from the Grossmünster): Meisen
is a type of silk fabric traditionally produced in Japan; it is durable, hard-faced, and somewhat stiff, with a slight sheen, and slubbiness is deliberately emphasised. was first produced in the late 19th century, and became widely popular ...
(also a porcelain and faience museum), Rüden, Haue, Saffran, Schneidern, Schmiden, Zimmerleuten, and some more.
* Tram Museum – The Tram Museum is located at Burgwies in Zürich's eastern suburbs, and chronicles the history of Zürich's iconic tram system with exhibits varying in date from 1897 to the present day.
*North America Native Museum
The North American Native Museum, or Nordamerika Native Museum (NONAM), is a museum run by the City of Zurich, Switzerland. The museum specializes in the conservation, documentation, and presentation of ethnographic objects and artwork of Native ...
– The North American Native Museum specializes in the conservation, documentation and presentation of ethnographic objects and art of Native American, First Nation and Inuit cultures.
*FIFA
FIFA (; stands for ''Fédération Internationale de Football Association'' ( French), meaning International Association Football Federation ) is the international governing body of association football, beach football and futsal. It was found ...
Museum - The museum exhibits memorabilities from the world of Association Football (Soccer), founded by the Féderation Internationale de Football Association
Parks and nature
* Zoological Garden – The zoological garden holds about 260 species of animals and houses about 2200 animals. One can come across separate enclosures of snow leopards, India lions, clouded leopards, Amur leopards, otters and pandas in the zoo.
* Botanical Garden – The Botanical Garden houses about 15,000 species of plants and trees and contains as many as three million plants. In the garden, many rare plant species from south western part of Africa, as well as from New Caledonia can be found. The University of Zürich holds the ownership of the Botanical Garden.
*Chinese Garden
The Chinese garden is a landscape garden style which has evolved over three thousand years. It includes both the vast gardens of the Chinese emperors and members of the imperial family, built for pleasure and to impress, and the more intimate ...
– The Chinese Garden is a gift by Zürich's Chinese partner town Kunming
Kunming (; ), also known as Yunnan-Fu, is the capital and largest city of Yunnan province, China. It is the political, economic, communications and cultural centre of the province as well as the seat of the provincial government. The headquar ...
, as remiscence for Zürich's technical and scientific assistance in the development of the Kunming city drinking water supply and drainage. The garden is an expression of one of the main themes of Chinese culture, the « Three Friends of Winter» – three plants that together brave the cold season – pine, bamboo, and plum
A plum is a fruit of some species in ''Prunus'' subg. ''Prunus'.'' Dried plums are called prunes.
History
Plums may have been one of the first fruits domesticated by humans. Three of the most abundantly cultivated species are not found i ...
.
* Uetliberg – Located to the west of the city at an altitude of above sea level
Height above mean sea level is a measure of the vertical distance (height, elevation or altitude) of a location in reference to a historic mean sea level taken as a vertical datum. In geodesy, it is formalized as ''orthometric heights''.
The comb ...
, the Uetliberg is the highest hill and offers views over the city. The summit is easily accessible by train from Zürich main station.
''Kunst und Bau'' (construction permit office)


 In 1922 Augusto Giacometti won the competition to paint the entrance hall of Amtshaus I, which the city promised to brighten up this gloomy room, which was once used as a cellar, and at the same time to alleviate the precarious economic situation of the local artists. Giacometti brought in the painters Jakob Gubler, Giuseppe Scartezzini and Franz Riklin for the execution of this fresco, which encompasses the ceiling and walls, thereby creating a unique color space that appears almost sacred in its luminosity.
In 1922 Augusto Giacometti won the competition to paint the entrance hall of Amtshaus I, which the city promised to brighten up this gloomy room, which was once used as a cellar, and at the same time to alleviate the precarious economic situation of the local artists. Giacometti brought in the painters Jakob Gubler, Giuseppe Scartezzini and Franz Riklin for the execution of this fresco, which encompasses the ceiling and walls, thereby creating a unique color space that appears almost sacred in its luminosity.
Architecture
 Compared to other cities, there are few tall buildings in Zürich. The municipal building regulations (Article 9) limit the construction of high-rise buildings to areas in the west and north of the city. In the industrial district, Altstetten and Oerlikon, buildings up to in height are allowed (high-rise area I). In the adjacent high-rise areas II and III the height is limited to . Around the year 2000, regulations became more flexible and high-rise buildings were again planned and built. The people's initiative " is enough," which would have reduced both the maximum height and the high-rise buildings area, was clearly rejected on 29 November 2009. At this time in Zürich about a dozen high-rise buildings were under construction or in planning, including the Prime Tower as the tallest skyscraper in Switzerland at the time of its construction. There are numerous examples of brutalist buildings throughout the city, including the
Compared to other cities, there are few tall buildings in Zürich. The municipal building regulations (Article 9) limit the construction of high-rise buildings to areas in the west and north of the city. In the industrial district, Altstetten and Oerlikon, buildings up to in height are allowed (high-rise area I). In the adjacent high-rise areas II and III the height is limited to . Around the year 2000, regulations became more flexible and high-rise buildings were again planned and built. The people's initiative " is enough," which would have reduced both the maximum height and the high-rise buildings area, was clearly rejected on 29 November 2009. At this time in Zürich about a dozen high-rise buildings were under construction or in planning, including the Prime Tower as the tallest skyscraper in Switzerland at the time of its construction. There are numerous examples of brutalist buildings throughout the city, including the Swissmill Tower
The Swissmill Tower, also known as Kornhaus, is the tallest operating grain elevator in the world. Standing at , it is the second tallest building in the Swiss city of Zürich.
History and description
The Swissmill Tower is a grain elevator c ...
which, at 118m, is the world's tallest grain silo.
World heritage sites
The prehistoric settlements at Enge Alpenquai and Grosser Hafner and Kleiner Hafner are part of the Prehistoric Pile dwellings around the Alps a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Economy
In a 2009 survey by CityMayors.com, Zürich was ranked 9th among the "World's 10 Most Powerful Cities".[World's 10 Most Powerful Cities](_blank)
prlog.org. Retrieved 10 March 2010 In the 2017 Global Financial Centres Index, Zürich was ranked as having the 11th most competitive financial center in the world, and second most competitive in Europe after London. The Greater Zürich Area
Greater may refer to:
*Greatness, the state of being great
*Greater than, in inequality
* ''Greater'' (film), a 2016 American film
*Greater (flamingo), the oldest flamingo on record
* "Greater" (song), by MercyMe, 2014
*Greater Bank, an Australian ...
is Switzerland's economic centre and home to many international companies. By far the most important sector in the economy of Zürich is the service industry, which employs nearly four-fifths of workers. Other important industries include light industry, machine and textile industries and tourism. Located in Zürich, the Swiss Stock Exchange
SIX Swiss Exchange (formerly SWX Swiss Exchange), based in Zurich, is Switzerland's principal stock exchange (the other being Berne eXchange). SIX Swiss Exchange also trades other securities such as Swiss government bonds and derivatives such as ...
was established in 1877 and is nowadays the fourth most prominent stock exchange in the world. In addition, Zürich is the world's largest gold trading centre.
Ten of the country's 50 largest companies have their head offices in Zürich, among them ABB, UBS
UBS Group AG is a multinational Investment banking, investment bank and financial services company founded and based in Switzerland. Co-headquartered in the cities of Zürich and Basel, it maintains a presence in all major financial centres ...
, Credit Suisse
Credit Suisse Group AG is a global investment bank and financial services firm founded and based in Switzerland. Headquartered in Zürich, it maintains offices in all major financial centers around the world and is one of the nine global " ...
, Swiss Re and Zürich Financial Services. Most Swiss banks have their headquarters in Zürich and there are numerous foreign banks in the Greater Zürich Area. "Gnomes of Zürich
Gnomes of Zürich is a slang term for Swiss bankers.
Swiss bankers are popularly associated with extremely secretive policies, while gnomes in fairy tales live underground, in secret, counting their riches. Zürich is the commercial centre of ...
" is a colloquial term used for Swiss bankers on account of their alleged secrecy and speculative dealing.
Contributory factors to economic strength
The high quality of life has been cited as a reason for economic growth in Zürich. The consulting firm Mercer has for many years ranked Zürich as a city with the highest quality of life in the world.[Zürich: Overview](_blank)
''USA Today''. Retrieved 26 June 2010 Zürich is also ranked the third most expensive city in the world, behind Hong Kong and Tokyo and ahead of Singapore.
The Swiss stock exchange
The Swiss stock exchange is called SIX Swiss Exchange
SIX Swiss Exchange (formerly SWX Swiss Exchange), based in Zurich, is Switzerland's principal stock exchange (the other being Berne eXchange). SIX Swiss Exchange also trades other security (finance), securities such as Swiss government bonds and d ...
, formerly known as SWX. The SIX Swiss Exchange is the head group of several different worldwide operative financial systems: Eurex, Eurex US, EXFEED, STOXX
STOXX Ltd. is a Swiss globally integrated index provider, covering the world markets across all asset classes – developing, maintaining, distributing and marketing a comprehensive global family of strictly rules-based and transparent indices. S ...
, and virt-x. The exchange turnover generated at the SWX was in 2007 of 1,780,499.5 million CHF; the number of transactions arrived in the same period at 35,339,296 and the Swiss Performance Index
The Swiss Performance Index (SPI) is a wide total-return index that tracks equity primarily listed on SIX Swiss Exchange with a free-float of at least 20%, and excluding investment companies. The index covers large, mid and small caps and is w ...
(SPI) arrived at a total market capitalization
Market capitalization, sometimes referred to as market cap, is the total value of a publicly traded company's outstanding common shares owned by stockholders.
Market capitalization is equal to the market price per common share multiplied by t ...
of 1,359,976.2 million CHF.
Education and research
 About 70,000 people study at the 20 universities, colleges and institutions of higher education in Zürich in 2019. Two of Switzerland's most distinguished universities are located in the city: the
About 70,000 people study at the 20 universities, colleges and institutions of higher education in Zürich in 2019. Two of Switzerland's most distinguished universities are located in the city: the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology The Swiss Federal Institutes of Technology are two institutes of higher education in Switzerland (part of the ETH Domain):
* Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Lausanne
Swiss may refer to:
* the adjectival form of Switzerland
*Swiss people ...
(ETH Zurich), which is controlled by the federal government, and the University of Zurich, under direction of the canton of Zürich. Both universities were listed in the top 50 world universities rated in 2007, while the ETH has consistently remained in the top 10 universities worldwide since 2016.
ETH was founded in 1854 by the Swiss Confederation and opened its doors in 1855 as a polytechnic institute. ETH achieved its reputation particularly in the fields of chemistry, mathematics and physics and there are 21 Nobel Laureates who are associated with the institution. ETH is usually ranked the top university in continental Europe. The institution consists of two campuses, the main building in the heart of the city and the new campus on the outskirts of the city.
The University of Zurich was founded in 1833, although its beginnings date back to 1525 when the Swiss reformer Ulrich Zwingli founded a college of theology. Nowadays with its 24,000 students and 1,900 graduations each year, the University of Zürich is the largest in Switzerland and offers the widest range of subjects and courses at any Swiss higher education institution.
The Pedagogical College, the Zurich University of Applied Sciences (ZHAW) and the Zurich University of the Arts (ZHdK) are another three top-class technical colleges which contribute to Zürich's reputation as a knowledge and research pole by providing applied research and development. Zürich is also one of the co-location centres of the Knowledge and Innovation Community (Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation) of the European Institute of Innovation and Technology.
In addition to the university libraries, the city is also served by the Zentralbibliothek Zürich, a research and public library, and the Pestalozzi-Bibliothek Zürich, a public library with 14 locations.
State universities by size in canton of Zürich
Media
Many large Swiss
Swiss may refer to:
* the adjectival form of Switzerland
* Swiss people
Places
* Swiss, Missouri
* Swiss, North Carolina
*Swiss, West Virginia
* Swiss, Wisconsin
Other uses
*Swiss-system tournament, in various games and sports
*Swiss Internation ...
media conglomerates are headquartered in Zürich, such as tamedia, Ringier and the NZZ-Verlag.
Television and radio
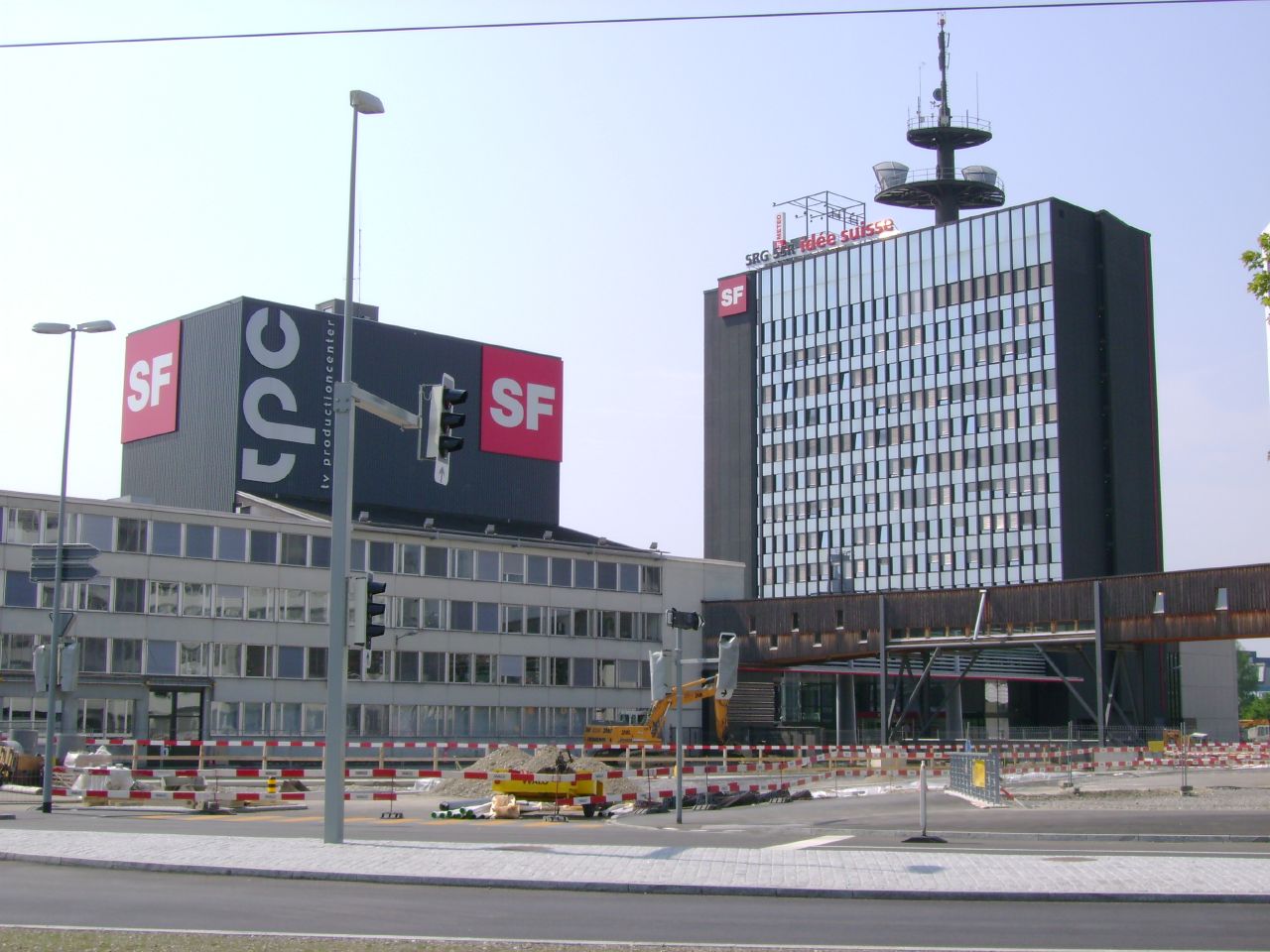 The headquarters of Switzerland's national licence fee-funded German language television network (" SF") are located in the Leutschenbach neighborhood, to the north of the Oerlikon railway station. Regional commercial television station "
The headquarters of Switzerland's national licence fee-funded German language television network (" SF") are located in the Leutschenbach neighborhood, to the north of the Oerlikon railway station. Regional commercial television station "TeleZüri
TeleZüri is a local television channel for the city and agglomeration of Zürich, Switzerland. It was founded by Roger Schawinski, a pioneer of local radio. Today it is owned by the Swiss media company CH Media.
TeleZüri features a daily 45-m ...
" (Zürich Television) has its headquarters near Escher-Wyss Platz. The production facilities for other commercial stations "Star TV", "u1" TV and "3+" are located in Schlieren.
One section of the Swiss German language licence fee-funded public radio
Public broadcasting involves radio, television and other electronic media outlets whose primary mission is public service. Public broadcasters receive funding from diverse sources including license fees, individual contributions, public financing ...
station " Schweizer Radio DRS" is located in Zürich. There are commercial local radio stations broadcasting from Zürich, such as "Radio 24" on the Limmatstrasse, "Energy Zürich" in Seefeld on the Kreuzstrasse, Radio "LoRa" and "Radio 1". There are other radio stations that operate only during certain parts of the year, such as "CSD Radio" (May/June), "Radio Streetparade
The Street Parade is with over 1 Million visitors the most attended technoparade in the world, since the end of Love Parade 2010. It takes place in Zurich, Switzerland and is the largest annual event in Zurich. Officially a demonstration for f ...
" (July/August) and "rundfunk.fm" (August/September).
Print media
There are three large daily newspapers published in Zürich that are known across Switzerland. The ''Neue Zürcher Zeitung
The ''Neue Zürcher Zeitung'' (''NZZ''; "New Journal of Zürich") is a Swiss, German-language daily newspaper, published by NZZ Mediengruppe in Zürich. The paper was founded in 1780. It was described as having a reputation as a high-quality ne ...
'' (''NZZ''), the '' Tages-Anzeiger'' and '' Blick'', the largest Swiss tabloid
Tabloid may refer to:
* Tabloid journalism, a type of journalism
* Tabloid (newspaper format), a newspaper with compact page size
** Chinese tabloid
* Tabloid (paper size), a North American paper size
* Sopwith Tabloid, a biplane aircraft
* ''Ta ...
. All three of those newspapers publish Sunday editions. These are the ''NZZ am Sonntag'', ''SonntagsZeitung'' and ''SonntagsBlick''. Besides the three main daily newspapers, there is a free daily commuter newspaper which is widely distributed: ''20 Minuten
)
, logo = 20Minuten Logo ab mai 2013.jpg
, image =
, caption = 20 Minutes logo (since May 2013)
, alt =
, type = Free daily newspaper
, format = Tab ...
'' (20 minutes), published weekdays in the mornings.
A number of magazines from major publishers are based in Zürich. Some examples are ''Bilanz
''Bilanz'' is a German language biweekly business magazine published in Zurich, Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal instit ...
'', ''Die Weltwoche
''Die Weltwoche'' (German for "The World Week") is a Swiss weekly magazine based in Zürich. Founded in 1933, it has been privately owned by Roger Köppel since 2006.
The magazine's regular columnists include the former president of the Social D ...
'', ''Annabelle'', '' Schweizer Familie'' and '' Schweizer Illustrierte''.
Culture
 In addition to high-quality museums and galleries, Zürich has high-calibre chamber and symphony orchestras and several important theatres.
The Zurich Film Festival is an international film festival, lasting 11 days and featuring popular international productions.
In addition to high-quality museums and galleries, Zürich has high-calibre chamber and symphony orchestras and several important theatres.
The Zurich Film Festival is an international film festival, lasting 11 days and featuring popular international productions.
 One of the largest and most popular annual events in Zürich is the Street Parade, which is also one of the largest techno and dance music festivals in the world. Proceeding along the side of Lake Zürich, it is normally held on the second Saturday in August. The first edition was held in 1992 with about 1,000 participants. By 2001 the event attracted one million participants.
One of the largest and most popular annual events in Zürich is the Street Parade, which is also one of the largest techno and dance music festivals in the world. Proceeding along the side of Lake Zürich, it is normally held on the second Saturday in August. The first edition was held in 1992 with about 1,000 participants. By 2001 the event attracted one million participants.chamber of commerce
A chamber of commerce, or board of trade, is a form of business network. For example, a local organization of businesses whose goal is to further the interests of businesses. Business owners in towns and cities form these local societies to ad ...
) with the cooperation of the city government
Local government is a generic term for the lowest tiers of public administration within a particular sovereign state. This particular usage of the word government refers specifically to a level of administration that is both geographically-l ...
. It consists of decorated sculptures distributed over the city centre, in public places. Past themes have included lions (1986), cows (1998), benches (2003), teddy bears (2005), and huge flower pots (2009). From this originated the concept of the CowParade that has been featured in other major world cities.
Zürich has been the home to several art movements. The Dada movement was founded in 1916 at the Cabaret Voltaire. Artists like Max Bill, Marcel Breuer, Camille Graeser
Camille Graeser (1892–1980) was a Swiss painter and member of the circle of Zurich Concrete artists. He was born in Switzerland but grew up in Stuttgart, Germany where he became a furniture designer. He took part in major exhibitions by the ...
or Richard Paul Lohse had their ateliers in Zürich, which became even more important after the takeover of power by the Nazi regime in Germany and World War II.
The best known traditional holiday in Zürich is the Sechseläuten (''Sächsilüüte''), including a parade of the guilds
A guild ( ) is an association of artisans and merchants who oversee the practice of their craft/trade in a particular area. The earliest types of guild formed as organizations of tradesmen belonging to a professional association. They sometimes ...
and the burning of "winter" in effigy at the Sechseläutenplatz. During this festival the popular march known as the Sechseläutenmarsch is played. It has no known composer but likely originated in Russia. Another is the Knabenschiessen
Knabenschiessen is a traditional target shooting competition in Zürich, held on the second weekend of September each year. The festival, officially held for the first time in 1889, is one of the oldest in Switzerland, dating back to the 17th ce ...
target shooting competition for teenagers (originally boys, open to female participants since 1991).
Opera, ballet, and theaters
 The Zürich Opera House (German: ''Zürcher Opernhaus''), built in 1834, was the first permanent theatre in the heart of Zürich and was at the time, the main seat of
The Zürich Opera House (German: ''Zürcher Opernhaus''), built in 1834, was the first permanent theatre in the heart of Zürich and was at the time, the main seat of Richard Wagner
Wilhelm Richard Wagner ( ; ; 22 May 181313 February 1883) was a German composer, theatre director, polemicist, and conductor who is chiefly known for his operas (or, as some of his mature works were later known, "music dramas"). Unlike most op ...
's activities. Later in 1890, the theatre was re-built as an ornate building with a neo-classical architecture. The portico is made of white and grey stone ornamented with the busts of Wagner, Weber and Mozart. Later, busts of Schiller, Shakespeare and Goethe were also added. The auditorium is designed in the rococo style. Once a year, it hosts the ''Zürcher Opernball'' with the President of the Swiss Confederation and the economic and cultural élite of Switzerland. The Ballet Zürich performs at the opera house. The Zürich Opera Ball, a major social event, is held annually at the Opera House as a fundraiser for the opera and ballet companies.
The Schauspielhaus Zürich is the main theatre complex of the city. It has two dépendances: ''Pfauen'' in the Central City District and ''Schiffbauhalle'', an old industrial hall, in Zürich West. The Schauspielhaus was home to emigrants such as Bertolt Brecht
Eugen Berthold Friedrich Brecht (10 February 1898 – 14 August 1956), known professionally as Bertolt Brecht, was a German theatre practitioner, playwright, and poet. Coming of age during the Weimar Republic, he had his first successes as a pl ...
or Thomas Mann, and saw premieres of works of Max Frisch, Friedrich Dürrenmatt, Botho Strauss or Elfriede Jelinek. The Schauspielhaus is one of the most prominent and important theatres in Switzerland.
The Theater am Neumarkt
The Theater am Neumarkt ( en, Theater at Neumarkt) or by its present official name Theater Neumarkt is a theatre in the German-speaking Switzerland situated at Neumarkt, Zürich. It is part of the building complex '' Bilgeriturm''–Neumarkt and al ...
is one of the oldest theatres of the city. Established by the old guilds in the Old City District, it is located in a baroque palace near Niederdorf Street. It has two stages staging mostly avantgarde works by European directors.
The Zürcher Theater Spektakel is an international theatre festival, featuring contemporary performing arts
The performing arts are arts such as music, dance, and drama which are performed for an audience. They are different from the visual arts, which are the use of paint, canvas or various materials to create physical or static art objects. Perform ...
.
Food
The traditional cuisine of Zürich reflects the centuries of rule by patrician burghers as well as the lasting imprint of Huldrych Zwingli's puritanism. Traditional dishes include '' Zürcher Geschnetzeltes'' and ''Tirggel
''Tirggel'' are traditional Christmas biscuits from Zürich, Switzerland. Made from flour and honey, they are thin, hard, and sweet.
History
''Tirggel'' are first recorded in Zürich as ''Dirgel'' in 1461. They have been manufactured there ever ...
''.
Nightlife and clubbing
 Zürich is host city of the Street Parade, which takes place in August every year (see above).
The most famous districts for Nightlife are the Niederdorf in the old town with bars, restaurants, lounges, hotels, clubs, etc. and a lot of fashion shops for a young and stylish public and the Langstrasse in the districts 4 and 5 of the city. There are authentic amusements: bars, punk clubs, hip hop stages, Caribbean restaurants, arthouse cinemas, Turkish kebabs and Italian espresso-bars, but also sex shops or the famous
Zürich is host city of the Street Parade, which takes place in August every year (see above).
The most famous districts for Nightlife are the Niederdorf in the old town with bars, restaurants, lounges, hotels, clubs, etc. and a lot of fashion shops for a young and stylish public and the Langstrasse in the districts 4 and 5 of the city. There are authentic amusements: bars, punk clubs, hip hop stages, Caribbean restaurants, arthouse cinemas, Turkish kebabs and Italian espresso-bars, but also sex shops or the famous red-light district
A red-light district or pleasure district is a part of an urban area where a concentration of prostitution and sex-oriented businesses, such as sex shops, strip clubs, and adult theaters, are found. In most cases, red-light districts are particu ...
of Zürich.
In the past ten years new parts of the city have risen into the spotlight. Notably, the area known as Zürich West
Zürich West (German: ''Zürich-West'') is an area in the Industriequartier, located in the west of Zürich. It is a former industrial site, stretching between the track leading away from Zürich Hauptbahnhof and the Limmat, and experiencing a gr ...
in district 5, near the Escher-Wyss square and the S-Bahn Station of .
Sports
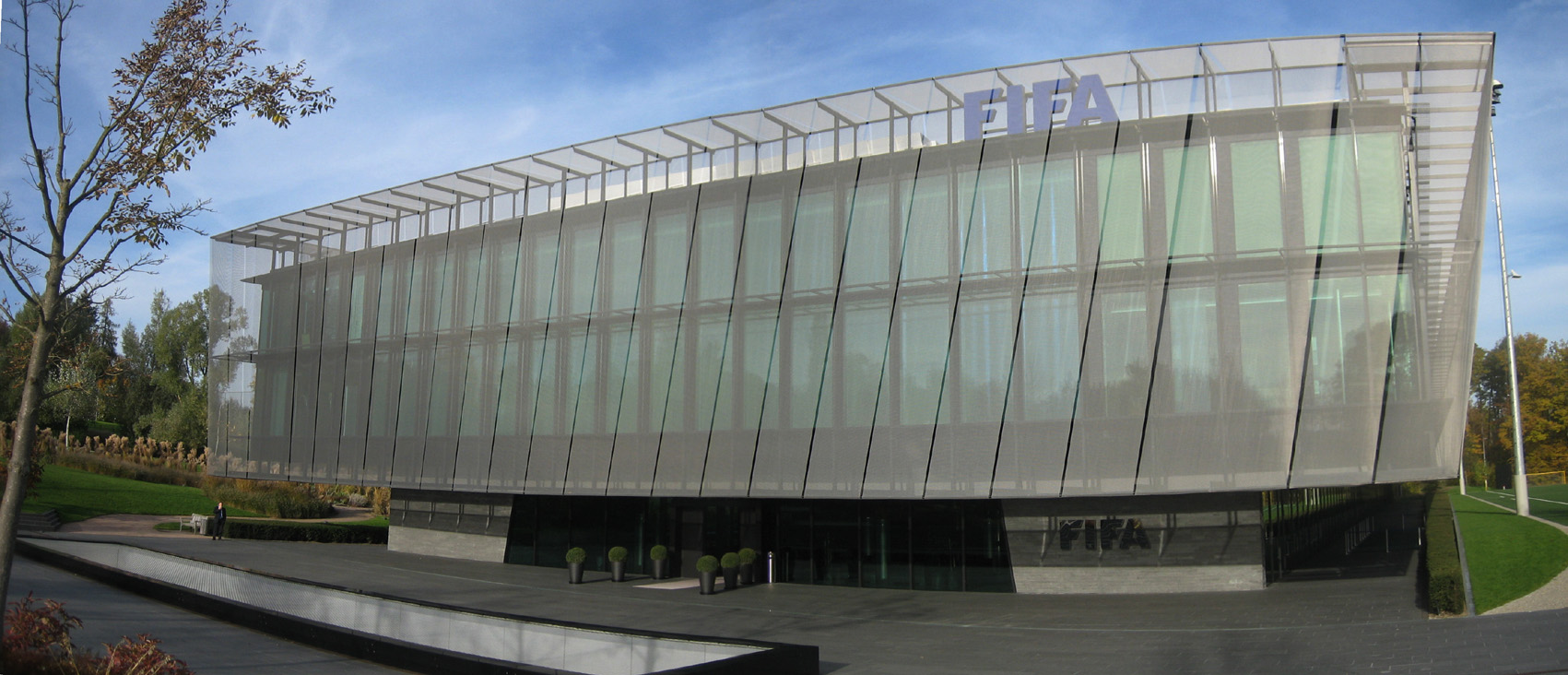 Zürich is home to several international sport federations. The Fédération Internationale de Football Association (FIFA) is headquartered in the city. In 2007 were inaugurated the new FIFA headquarters building, designed by architect Tilla Theus.
Association football is an essential aspect of sports in Zürich. The city is home to two major Swiss football teams;
Zürich is home to several international sport federations. The Fédération Internationale de Football Association (FIFA) is headquartered in the city. In 2007 were inaugurated the new FIFA headquarters building, designed by architect Tilla Theus.
Association football is an essential aspect of sports in Zürich. The city is home to two major Swiss football teams; Grasshopper Club Zürich
Grasshopper Club Zürich, commonly referred to as simply GC, GCZ, or Grasshoppers, is a multisports club based in Zürich, Switzerland. The oldest and best known department of the club is its football team. With 27 titles, Grasshopper holds the ...
founded in 1886 and FC Zürich
Fussballclub Zürich, commonly abbreviated to FC Zürich or simply FCZ, is a Swiss football club based in Zürich. The club was founded in 1896 and has won the Swiss Super League 13 times and the Swiss Cup 10 times. The most recent titles a ...
founded in 1896, both competing in Switzerland's highest league.
Among the most popular sports in Switzerland is ice hockey. In Zürich it is represented by the ZSC Lions. The International Ice Hockey Federation (IIHF) officiating as head organisation for ice hockey leagues worldwide is based in Zürich as well.
Cycling is a popular sport as well as a means of transport in Zürich. Cycling routes are generally marked with red and white signs and the yellow lanes are exclusively meant for cyclists. Also hiking trails are well marked with yellow signs, which give the hiker the probable time it will take them to reach their destination. There are specific maps available for hiking and walking trails throughout Switzerland. Some of the most accessible walks in the Zürich area are the Uetliberg and the Zürichberg. The Offene Rennbahn otherwise known as the Oerlikon Velodrome
Oerlikon Velodrome is an uncovered velodrome in the Oerlikon district of Zürich, Switzerland. It was built in 1912. The track is 333 m in length and is made of concrete. The velodrome holds 3000 spectators. It held the UCI Track Cycling World C ...
deserves a special visit on any Tuesday evening in the summer, for cyclists there are chances to see time trial champions or local Swiss national cyclists challenging other amateurs in a variety of races including Madison or Keirin events.
As many as 30 clubs and seven indoor curling facilities can be found in the greater Zürich area. The curling season starts in early September and continues until the end of April.
Zürich is Switzerland's hub for Lacrosse. The Zürich Lions Lacrosse Academics, who play their home games at the Hochschulsportanlage Fluntern, have been the country's dominant team and a major competitor at international events.
Events
 Weltklasse Zürich, sometimes referred to as the one-day Olympics, is a one-day athletics meet held annually at the
Weltklasse Zürich, sometimes referred to as the one-day Olympics, is a one-day athletics meet held annually at the Letzigrund
is a stadium in Zürich, Switzerland, and the home of the athletics club LC Zürich, and the football clubs FC Zürich and Grasshopper Club Zürich. LC Zürich is a spin-off of FC Zürich whose members constructed the stadium in 1925. Grasshopper ...
Stadium. Since it started on 12 August 1928, the sporting event has witnessed new world records and national records. To date as many as 24 world records were set in Weltklasse.
Zürich Marathon is a popular sport event, inviting numerous athletes from every corner of the globe. Zürich Marathon is a long-distance running event, covering at one stretch. The running course starts in Zürich and passes through Bahnhofstrasse, Bellevueplatz, Mythenquai, Quaibrücke, Talstrasse and Utoquai, and along Lake Zürich to several other places. New Year's Eve run is another important running event. The race is held on 1 January each year and the start takes place at midnight exactly.
Zürich was one of six venues of the 1954 FIFA World Cup
The 1954 FIFA World Cup was the fifth edition of the FIFA World Cup, the quadrennial international football tournament for senior men's national teams of the nations affiliated to FIFA. It was held in Switzerland from 16 June to 4 July. Switzerla ...
and one of eight venues of the UEFA Euro 2008. The Euro 2008 games were held in the Letzigrund Stadium. Work on the new Letzigrund was completed in exceptionally quick time and the stadium opened in August 2007 just one year after the demolition of the old arena.Openair Literatur Festival Zürich {{short description, Aspect of system integration regarding artificial intelligence
The core idea of Artificial Intelligence systems integration is making individual software components, such as speech synthesizers, interoperable with other componen ...
takes place annually in Zurich, presented by Literaturhaus Zürich and Kaufleuten.
Zürich also hosted the 1998 World Ice Hockey Championships. The city previously co-hosted the 1953
Events
January
* January 6 – The Asian Socialist Conference opens in Rangoon, Burma.
* January 12 – Estonian émigrés found a Estonian government-in-exile, government-in-exile in Oslo.
* January 14
** Marshal Josip Broz Tito i ...
and 1939
This year also marks the start of the Second World War, the largest and deadliest conflict in human history.
Events
Below, the events of World War II have the "WWII" prefix.
January
* January 1
** Third Reich
*** Jews are forbidden to ...
editions.
Zürich was also host to the 2012 Men's World Floorball Championships. This was the first time the event had been held in Zürich.
Notable people
Other points of interest
 * The Schwamendingen X: level crossing of tram tracks, necessary because the tunnel uses island platforms for boarding (''between'' trams, whose doors are on the right) while normally (outside the tunnel), passengers board to the outside (''opposite'' the boarding area of oncoming trams). Trams normally travel on the right track, but in the tunnel they travel on the left.
* The Sihlfeld cemetery has a vending machine for funeral cards and other mourning supplies.
* The "Oepfelchammer" tavern in Zürich's Old Town offers an unusual athletic drinking game called : the drinker has to pull themselves up on a ceiling beam, cross over to the next beam, then drink a glass of wine with their head hanging down.
* The Schwamendingen X: level crossing of tram tracks, necessary because the tunnel uses island platforms for boarding (''between'' trams, whose doors are on the right) while normally (outside the tunnel), passengers board to the outside (''opposite'' the boarding area of oncoming trams). Trams normally travel on the right track, but in the tunnel they travel on the left.
* The Sihlfeld cemetery has a vending machine for funeral cards and other mourning supplies.
* The "Oepfelchammer" tavern in Zürich's Old Town offers an unusual athletic drinking game called : the drinker has to pull themselves up on a ceiling beam, cross over to the next beam, then drink a glass of wine with their head hanging down.
Further reading
Architecture
* Hönig, Roderick: ''Zürich wird gebaut. Architekturführer Zürich 1990–2010''. Hochparterre, Zürich 2010, .
* Oechslin, Werner: ''Hochschulstadt Zürich. Bauten der ETH 1855–2005''. GTA, Zürich 2005, .
* Bonte, Alexander, Bürkle, J. Christoph: ''Max Dudler Die neue Dichte – Der neue Stadtteil Europaallee und die Pädagogische Hochschule Zürich'', Jovis, Berlin 2012,
Culture
* Kröger, Ute: ''Zürich, du mein blaues Wunder. Literarische Streifzüge durch eine europäische Kulturstadt''. Limmat, Zürich 2004, .
* Staub, Ueli: ''Jazzstadt Zürich. Von Louis Armstrong bis Zürich Jazz Orchestra''. Neue Zürcher Zeitung, Zürich 2003, .
Others
* Foppa, Daniel: ''Berühmte und vergessene Tote auf Zürichs Friedhöfen''. Limmat
The Limmat is a river in Switzerland. The river commences at the outfall of Lake Zurich, in the southern part of the city of Zurich. From Zurich it flows in a northwesterly direction, after 35 km reaching the river Aare. The confluenc ...
, Zürich 2003, .
* Hegi, Christof u. a.: ''Zürich''. Mairs, Ostfildern 2006, (= ''Marco Polo Reiseführer'').
* Heimgartner, Susanna: ''Zürich komplett''. Regenbogen, Zürich 2005, (= ''Regenbogen Reiseführer'').
* Smith, Duncan J. D.: ''Nur in Zürich – Ein Reiseführer zu einzigartigen Orten, geheimen Plätzen und ungewöhnlichen Sehenswürdigkeiten'' (übersetzt von Walter Goidinger), Brandstätter, Wien 2012, .
See also
*Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
*Bern
german: Berner(in)french: Bernois(e) it, bernese
, neighboring_municipalities = Bremgarten bei Bern, Frauenkappelen, Ittigen, Kirchlindach, Köniz, Mühleberg, Muri bei Bern, Neuenegg, Ostermundigen, Wohlen bei Bern, Zollikofen
, website ...
* List of mayors of Zürich
* PS Stadt Zürich
Notes and references
Notes
References
External links
Stadt Zürich
– official website
City of Zürich
– official website
Zürich Tourism
– official website
Zürich Chamber of Commerce
– official website
Event & Pleasure Calendar
by '' Tages-Anzeiger'' (newspaper)
NYT Travel Guide
by '' The New York Times''
{{DEFAULTSORT:Zurich
Cantonal capitals of Switzerland
Municipalities of the canton of Zürich
Cities in Switzerland
Populated places on Lake Zurich
2nd-century establishments
Populated places established in the 2nd century
1210s establishments in the Holy Roman Empire
1218 establishments in Europe
1350s disestablishments in the Holy Roman Empire
1351 disestablishments in Europe
14th-century establishments in the Old Swiss Confederacy
1350s establishments in the Holy Roman Empire
1351 establishments in Europe
15th-century disestablishments in the Old Swiss Confederacy
1440s disestablishments in the Holy Roman Empire
1440 disestablishments in Europe
15th-century establishments in the Old Swiss Confederacy
1450s establishments in the Holy Roman Empire
1450 establishments in Europe

 Settlements of the Neolithic and Bronze Age were found around Lake Zürich. Traces of pre-Roman Celtic, La Tène settlements were discovered near the
Settlements of the Neolithic and Bronze Age were found around Lake Zürich. Traces of pre-Roman Celtic, La Tène settlements were discovered near the  On 1 May 1351, the citizens of Zürich had to swear allegiance before representatives of the cantons of
On 1 May 1351, the citizens of Zürich had to swear allegiance before representatives of the cantons of  Zwingli started the
Zwingli started the  The Helvetic Revolution of 1798 saw the fall of the . Zürich lost control of the land and its economic privileges, and the city and the canton separated their possessions between 1803 and 1805. In 1839, the city had to yield to the demands of its urban subjects, following the of 6 September. Most of the ramparts built in the 17th century were torn down, without ever having been besieged, to allay rural concerns over the city's hegemony. The Treaty of Zürich between Austria, France, and Sardinia was signed in 1859.
The Helvetic Revolution of 1798 saw the fall of the . Zürich lost control of the land and its economic privileges, and the city and the canton separated their possessions between 1803 and 1805. In 1839, the city had to yield to the demands of its urban subjects, following the of 6 September. Most of the ramparts built in the 17th century were torn down, without ever having been besieged, to allay rural concerns over the city's hegemony. The Treaty of Zürich between Austria, France, and Sardinia was signed in 1859.

 The previous boundaries of the city of Zürich (before 1893) were more or less synonymous with the location of the old town. Two large expansions of the city limits occurred in 1893 and in 1934 when the city of Zürich merged with many surrounding municipalities, that had been growing increasingly together since the 19th century. Today, the city is divided into twelve districts (known as ' in German), numbered 1 to 12, each one of which contains between one and four neighborhoods:
* , known as , contains the old town, both to the east and west of the start of the
The previous boundaries of the city of Zürich (before 1893) were more or less synonymous with the location of the old town. Two large expansions of the city limits occurred in 1893 and in 1934 when the city of Zürich merged with many surrounding municipalities, that had been growing increasingly together since the 19th century. Today, the city is divided into twelve districts (known as ' in German), numbered 1 to 12, each one of which contains between one and four neighborhoods:
* , known as , contains the old town, both to the east and west of the start of the 
 Zürich is a mixed hub for railways, roads, and air traffic. Zürich Hauptbahnhof (''Zürich HB'') is the largest and busiest station in Switzerland and is an important railway hub in Europe. As of early 2020, Zürich HB served around 470,000 passengers and nearly 3,000 trains every day. Among the 16 railway stations (and 10 additional train stops) within Zürich's city borders, there are five other major passenger railway stations. Three of them belong to the ten most frequented railway stations in Switzerland: Stadelhofen, Oerlikon, Altstetten,
Zürich is a mixed hub for railways, roads, and air traffic. Zürich Hauptbahnhof (''Zürich HB'') is the largest and busiest station in Switzerland and is an important railway hub in Europe. As of early 2020, Zürich HB served around 470,000 passengers and nearly 3,000 trains every day. Among the 16 railway stations (and 10 additional train stops) within Zürich's city borders, there are five other major passenger railway stations. Three of them belong to the ten most frequented railway stations in Switzerland: Stadelhofen, Oerlikon, Altstetten,  Most of Zürich's sites are located within the area on either side of the Limmat, between the Main railway station and Lake Zürich. The churches and houses of the old town are clustered here, as are the most expensive shops along the famous Bahnhofstrasse. The
Most of Zürich's sites are located within the area on either side of the Limmat, between the Main railway station and Lake Zürich. The churches and houses of the old town are clustered here, as are the most expensive shops along the famous Bahnhofstrasse. The 

 In 1922 Augusto Giacometti won the competition to paint the entrance hall of Amtshaus I, which the city promised to brighten up this gloomy room, which was once used as a cellar, and at the same time to alleviate the precarious economic situation of the local artists. Giacometti brought in the painters Jakob Gubler, Giuseppe Scartezzini and Franz Riklin for the execution of this fresco, which encompasses the ceiling and walls, thereby creating a unique color space that appears almost sacred in its luminosity.
In 1922 Augusto Giacometti won the competition to paint the entrance hall of Amtshaus I, which the city promised to brighten up this gloomy room, which was once used as a cellar, and at the same time to alleviate the precarious economic situation of the local artists. Giacometti brought in the painters Jakob Gubler, Giuseppe Scartezzini and Franz Riklin for the execution of this fresco, which encompasses the ceiling and walls, thereby creating a unique color space that appears almost sacred in its luminosity.
 Compared to other cities, there are few tall buildings in Zürich. The municipal building regulations (Article 9) limit the construction of high-rise buildings to areas in the west and north of the city. In the industrial district, Altstetten and Oerlikon, buildings up to in height are allowed (high-rise area I). In the adjacent high-rise areas II and III the height is limited to . Around the year 2000, regulations became more flexible and high-rise buildings were again planned and built. The people's initiative " is enough," which would have reduced both the maximum height and the high-rise buildings area, was clearly rejected on 29 November 2009. At this time in Zürich about a dozen high-rise buildings were under construction or in planning, including the Prime Tower as the tallest skyscraper in Switzerland at the time of its construction. There are numerous examples of brutalist buildings throughout the city, including the
Compared to other cities, there are few tall buildings in Zürich. The municipal building regulations (Article 9) limit the construction of high-rise buildings to areas in the west and north of the city. In the industrial district, Altstetten and Oerlikon, buildings up to in height are allowed (high-rise area I). In the adjacent high-rise areas II and III the height is limited to . Around the year 2000, regulations became more flexible and high-rise buildings were again planned and built. The people's initiative " is enough," which would have reduced both the maximum height and the high-rise buildings area, was clearly rejected on 29 November 2009. At this time in Zürich about a dozen high-rise buildings were under construction or in planning, including the Prime Tower as the tallest skyscraper in Switzerland at the time of its construction. There are numerous examples of brutalist buildings throughout the city, including the  The headquarters of Switzerland's national licence fee-funded German language television network (" SF") are located in the Leutschenbach neighborhood, to the north of the Oerlikon railway station. Regional commercial television station "
The headquarters of Switzerland's national licence fee-funded German language television network (" SF") are located in the Leutschenbach neighborhood, to the north of the Oerlikon railway station. Regional commercial television station " In addition to high-quality museums and galleries, Zürich has high-calibre chamber and symphony orchestras and several important theatres.
The Zurich Film Festival is an international film festival, lasting 11 days and featuring popular international productions.
In addition to high-quality museums and galleries, Zürich has high-calibre chamber and symphony orchestras and several important theatres.
The Zurich Film Festival is an international film festival, lasting 11 days and featuring popular international productions.
 One of the largest and most popular annual events in Zürich is the Street Parade, which is also one of the largest techno and dance music festivals in the world. Proceeding along the side of Lake Zürich, it is normally held on the second Saturday in August. The first edition was held in 1992 with about 1,000 participants. By 2001 the event attracted one million participants. The Zürifäscht, on the other hand, is a triennial public festival. It features music, fireworks set to music, and other attractions throughout the old town. It is the largest public festival in Switzerland and attracts up to 2 million visitors.
The Kunst Zürich is an international contemporary art fair with an annual guest city; it combines most recent arts with the works of well-established artists. Another annual public art exhibit is the city campaign, sponsored by the City Vereinigung (the local equivalent of a
One of the largest and most popular annual events in Zürich is the Street Parade, which is also one of the largest techno and dance music festivals in the world. Proceeding along the side of Lake Zürich, it is normally held on the second Saturday in August. The first edition was held in 1992 with about 1,000 participants. By 2001 the event attracted one million participants. The Zürifäscht, on the other hand, is a triennial public festival. It features music, fireworks set to music, and other attractions throughout the old town. It is the largest public festival in Switzerland and attracts up to 2 million visitors.
The Kunst Zürich is an international contemporary art fair with an annual guest city; it combines most recent arts with the works of well-established artists. Another annual public art exhibit is the city campaign, sponsored by the City Vereinigung (the local equivalent of a  The Zürich Opera House (German: ''Zürcher Opernhaus''), built in 1834, was the first permanent theatre in the heart of Zürich and was at the time, the main seat of
The Zürich Opera House (German: ''Zürcher Opernhaus''), built in 1834, was the first permanent theatre in the heart of Zürich and was at the time, the main seat of  Zürich is host city of the Street Parade, which takes place in August every year (see above).
The most famous districts for Nightlife are the Niederdorf in the old town with bars, restaurants, lounges, hotels, clubs, etc. and a lot of fashion shops for a young and stylish public and the Langstrasse in the districts 4 and 5 of the city. There are authentic amusements: bars, punk clubs, hip hop stages, Caribbean restaurants, arthouse cinemas, Turkish kebabs and Italian espresso-bars, but also sex shops or the famous
Zürich is host city of the Street Parade, which takes place in August every year (see above).
The most famous districts for Nightlife are the Niederdorf in the old town with bars, restaurants, lounges, hotels, clubs, etc. and a lot of fashion shops for a young and stylish public and the Langstrasse in the districts 4 and 5 of the city. There are authentic amusements: bars, punk clubs, hip hop stages, Caribbean restaurants, arthouse cinemas, Turkish kebabs and Italian espresso-bars, but also sex shops or the famous  Zürich is home to several international sport federations. The Fédération Internationale de Football Association (FIFA) is headquartered in the city. In 2007 were inaugurated the new FIFA headquarters building, designed by architect Tilla Theus.
Association football is an essential aspect of sports in Zürich. The city is home to two major Swiss football teams;
Zürich is home to several international sport federations. The Fédération Internationale de Football Association (FIFA) is headquartered in the city. In 2007 were inaugurated the new FIFA headquarters building, designed by architect Tilla Theus.
Association football is an essential aspect of sports in Zürich. The city is home to two major Swiss football teams;  Weltklasse Zürich, sometimes referred to as the one-day Olympics, is a one-day athletics meet held annually at the
Weltklasse Zürich, sometimes referred to as the one-day Olympics, is a one-day athletics meet held annually at the  * The Schwamendingen X: level crossing of tram tracks, necessary because the tunnel uses island platforms for boarding (''between'' trams, whose doors are on the right) while normally (outside the tunnel), passengers board to the outside (''opposite'' the boarding area of oncoming trams). Trams normally travel on the right track, but in the tunnel they travel on the left.
* The Sihlfeld cemetery has a vending machine for funeral cards and other mourning supplies.
* The "Oepfelchammer" tavern in Zürich's Old Town offers an unusual athletic drinking game called : the drinker has to pull themselves up on a ceiling beam, cross over to the next beam, then drink a glass of wine with their head hanging down.
* The Schwamendingen X: level crossing of tram tracks, necessary because the tunnel uses island platforms for boarding (''between'' trams, whose doors are on the right) while normally (outside the tunnel), passengers board to the outside (''opposite'' the boarding area of oncoming trams). Trams normally travel on the right track, but in the tunnel they travel on the left.
* The Sihlfeld cemetery has a vending machine for funeral cards and other mourning supplies.
* The "Oepfelchammer" tavern in Zürich's Old Town offers an unusual athletic drinking game called : the drinker has to pull themselves up on a ceiling beam, cross over to the next beam, then drink a glass of wine with their head hanging down.