Namco on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
was a Japanese multinational
 Nakamura Seisakusho changed its corporate name to Namco in June 1977. It opened a division in Hong Kong named Namco Enterprises Asia, which maintained video arcades and amusement centers. As Namco's presence in Japan was steadily rising, Nakajima suggested to Nakamura that he open a division in the United States to increase worldwide brand awareness. Nakamura agreed to the proposal, and on September 1, 1978, established Namco America in
Nakamura Seisakusho changed its corporate name to Namco in June 1977. It opened a division in Hong Kong named Namco Enterprises Asia, which maintained video arcades and amusement centers. As Namco's presence in Japan was steadily rising, Nakajima suggested to Nakamura that he open a division in the United States to increase worldwide brand awareness. Nakamura agreed to the proposal, and on September 1, 1978, established Namco America in  The space shooter genre became ubiquitous by the end of the decade, with games such as ''Galaxian'' and ''Space Invaders'' becoming commonplace in Japanese amusement centers. As video games often depicted the killing of enemies and shooting of targets, the industry possessed a predominately male playerbase. Toru Iwatani began work on a
The space shooter genre became ubiquitous by the end of the decade, with games such as ''Galaxian'' and ''Space Invaders'' becoming commonplace in Japanese amusement centers. As video games often depicted the killing of enemies and shooting of targets, the industry possessed a predominately male playerbase. Toru Iwatani began work on a
 In July 1983,
In July 1983,
 In 1989, it was reported that Namco was underway with developing its own video game console to compete against companies such as Nintendo and NEC. ''
In 1989, it was reported that Namco was underway with developing its own video game console to compete against companies such as Nintendo and NEC. '' Manabe resigned as president on May 1, 1992 due to a serious anxiety disorder, and Nakamura once again assumed the role. Manabe instead served as the company's vice chairman until his death in 1994. The company's arcade division, in the meantime, began work on a new 3D arcade board named
Manabe resigned as president on May 1, 1992 due to a serious anxiety disorder, and Nakamura once again assumed the role. Manabe instead served as the company's vice chairman until his death in 1994. The company's arcade division, in the meantime, began work on a new 3D arcade board named
 In early 1994, Sony announced that it was developing its own video game console, the 32-bit
In early 1994, Sony announced that it was developing its own video game console, the 32-bit
 Namco's financial losses worsened in the 2000s. In October 2000, the Japanese newspaper ''
Namco's financial losses worsened in the 2000s. In October 2000, the Japanese newspaper ''
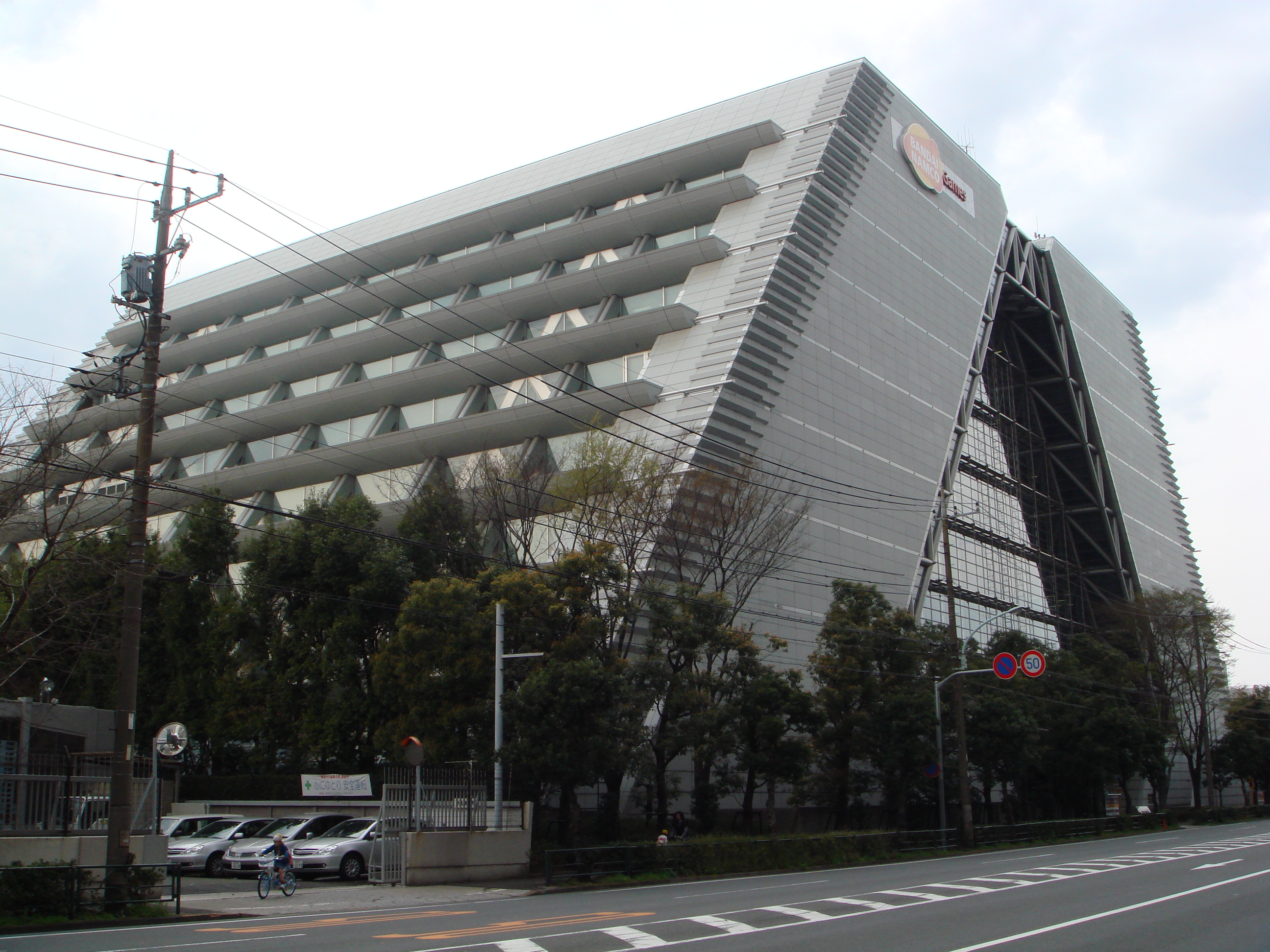 On January 4, 2006, Namco Hometek was merged with Bandai Games—Bandai America's consumer game division—to create Namco Bandai Games America, absorbing Namco America's subsidiaries and completing Namco and Bandai's merge in North America. Namco's console game, business program, mobile phone, and research facility divisions were merged with Bandai's console division to create a new company, Namco Bandai Games, on March 31, as Namco was effectively dissolved.
The Namco name was repurposed for a new Namco Bandai subsidiary the same day, which absorbed its predecessor's amusement facility and theme park operations. Namco's European division was folded into Namco Bandai Networks Europe on January 1, 2007, as it was reorganized into the company's mobile game and website division. Until April 2014, Namco Bandai Games used the Namco logo on its games to represent the brand's legacy.
The Namco Cybertainment division was renamed Namco Entertainment in January 2012, and to Namco USA in 2015. A division of Bandai Namco Holdings USA, Namco USA worked with chains such as
On January 4, 2006, Namco Hometek was merged with Bandai Games—Bandai America's consumer game division—to create Namco Bandai Games America, absorbing Namco America's subsidiaries and completing Namco and Bandai's merge in North America. Namco's console game, business program, mobile phone, and research facility divisions were merged with Bandai's console division to create a new company, Namco Bandai Games, on March 31, as Namco was effectively dissolved.
The Namco name was repurposed for a new Namco Bandai subsidiary the same day, which absorbed its predecessor's amusement facility and theme park operations. Namco's European division was folded into Namco Bandai Networks Europe on January 1, 2007, as it was reorganized into the company's mobile game and website division. Until April 2014, Namco Bandai Games used the Namco logo on its games to represent the brand's legacy.
The Namco Cybertainment division was renamed Namco Entertainment in January 2012, and to Namco USA in 2015. A division of Bandai Namco Holdings USA, Namco USA worked with chains such as
video game
Video games, also known as computer games, are electronic games that involves interaction with a user interface or input device such as a joystick, controller, keyboard, or motion sensing device to generate visual feedback. This fee ...
and entertainment company, headquartered in Ōta, Tokyo
is a Special wards of Tokyo, special ward located in Tokyo, Tokyo Metropolis, Japan. In English, it is often called Ōta City.
, the ward has an estimated population of 716,413, with 379,199 households and a population density of 12,048.65 per ...
. It held several international branches, including Namco America in Santa Clara, California
Santa Clara (; Spanish for " Saint Clare") is a city in Santa Clara County, California. The city's population was 127,647 at the 2020 census, making it the eighth-most populous city in the Bay Area. Located in the southern Bay Area, the cit ...
, Namco Europe in London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
, Namco Taiwan in Kaohsiung
Kaohsiung City (Mandarin Chinese: ; Wade–Giles: ''Kao¹-hsiung²;'' Pinyin: ''Gāoxióng'') is a special municipality located in southern Taiwan. It ranges from the coastal urban center to the rural Yushan Range with an area of . Kaohsi ...
, and Shanghai Namco in mainland China
"Mainland China" is a geopolitical term defined as the territory governed by the People's Republic of China (including islands like Hainan or Chongming), excluding dependent territories of the PRC, and other territories within Greater China. ...
.
Namco was founded by Masaya Nakamura on June 1, 1955, as beginning as an operator of coin-operated amusement rides. After reorganizing to Nakamura Seisakusho Co., Ltd. in 1959, a partnership with Walt Disney Productions
The Walt Disney Company, commonly known as Disney (), is an American multinational mass media and entertainment conglomerate headquartered at the Walt Disney Studios complex in Burbank, California. Disney was originally founded on October ...
provided the company with the resources to expand its operations. In the 1960s, it manufactured electro-mechanical
In engineering, electromechanics combines processes and procedures drawn from electrical engineering and mechanical engineering. Electromechanics focuses on the interaction of electrical and mechanical systems as a whole and how the two systems ...
arcade games
An arcade game or coin-op game is a coin-operated entertainment machine typically installed in public businesses such as restaurants, bars and amusement arcades. Most arcade games are presented as primarily games of skill and include arcade v ...
such as the 1965 hit ''Periscope
A periscope is an instrument for observation over, around or through an object, obstacle or condition that prevents direct line-of-sight observation from an observer's current position.
In its simplest form, it consists of an outer case with ...
''. It entered the video game industry
The video game industry encompasses the development, marketing, and monetization of video games. The industry encompasses dozens of job disciplines and thousands of jobs worldwide.
The video game industry has grown from niches to mainstream. , ...
after acquiring the struggling Japanese division of Atari
Atari () is a brand name that has been owned by several entities since its inception in 1972. It is currently owned by French publisher Atari SA through a subsidiary named Atari Interactive. The original Atari, Inc. (1972–1992), Atari, Inc., ...
in 1974, distributing games such as '' Breakout'' in Japan. The company renamed itself Namco in 1977 and published '' Gee Bee'', its first original video game, a year later. Among Namco's first major hits was the fixed shooter ''Galaxian
is a 1979 fixed shooter arcade video game developed and published by Namco. The player assumes control of the Galaxip starfighter in its mission to protect Earth from waves of aliens. Gameplay involves destroying each formation of aliens, who ...
'' in 1979. It was followed by ''Pac-Man
originally called ''Puck Man'' in Japan, is a 1980 maze action video game developed and released by Namco for arcades. In North America, the game was released by Midway Manufacturing as part of its licensing agreement with Namco America. Th ...
'' in 1980, the best-selling arcade game of all time. Namco prospered during the golden age of arcade video games
The golden age of arcade video games was the period of rapid growth, technological development and cultural influence of arcade video games, from the late 1970s to the early 1980s. The period began with the release of ''Space Invaders'' in 1978, ...
in the early 1980s, releasing popular titles such as ''Galaga
is a 1981 fixed shooter arcade video game developed and published by Namco. In North America, it was released by Midway Manufacturing. It is the sequel to ''Galaxian'' (1979), Namco's first major video game hit in arcades. Controlling a starshi ...
'', ''Xevious
is a vertically scrolling shooter video game developed and published by Namco for arcades in 1982. It was released in Japan and Europe by Namco and in North America by Atari, Inc. Controlling the Solvalou starship, the player attacks Xevious for ...
'', and ''Pole Position
In a motorsports race, the pole position is usually the best and "statistically the most advantageous" starting position on the track. The pole position is usually earned by the driver with the best qualifying times in the trials before the rac ...
''.
Namco entered the home console
A home video game console is a video game console that is designed to be connected to a display device, such as a television, and an external power source as to play video games. Home consoles are generally less powerful and customizable than ...
market in 1984 with conversions of its arcade games for the MSX and the Nintendo
is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational video game company headquartered in Kyoto, Japan. It develops video games and video game consoles.
Nintendo was founded in 1889 as by craftsman Fusajiro Yamauchi and originally produce ...
Family Computer
The Nintendo Entertainment System (NES) is an 8-bit Third generation of video game consoles, third-generation home video game console produced by Nintendo. It was first released in Japan in 1983 as the commonly known as the The NES, a redes ...
. Its American division majority-acquired Atari Games
Atari Games Corporation, known as Midway Games West Inc. after 1999, was an American producer of Arcade game, arcade Video game, games. It was formed in 1985 when the coin-operated Arcade game, arcade game division of Atari, Inc. was transfered ...
in 1985, before selling a portion of it in 1987 following disagreements between the two companies. Arguments over licensing contracts with Nintendo led Namco to produce games for competing platforms, such as the Sega Genesis
The Sega Genesis, known as the outside North America, is a 16-bit Fourth generation of video game consoles, fourth generation home video game console developed and sold by Sega. It was Sega's third console and the successor to the Master Syst ...
, TurboGrafx-16
The TurboGrafx-16, known as the outside North America, is a home video game console designed by Hudson Soft and sold by NEC, NEC Home Electronics. It was the first console marketed in the fourth generation of video game consoles, fourth genera ...
, and PlayStation
is a video gaming brand that consists of five home video game consoles, two handhelds, a media center, and a smartphone, as well as an online service and multiple magazines. The brand is produced by Sony Interactive Entertainment, a divisi ...
.
Namco continued to produce hit games in the 1990s, including ''Ridge Racer
is a racing game, racing video game series developed and published for arcade systems and home game consoles by Bandai Namco Entertainment, formerly Namco. The first game, ''Ridge Racer (1993 video game), Ridge Racer'' (1993), was originally rel ...
'', ''Tekken
is a Japanese Media mix, media franchise centered on a series of fighting game, fighting video and arcade games developed and published by Bandai Namco Entertainment (formerly Namco). The franchise also includes film and print adaptations.
The ...
'', and ''Taiko no Tatsujin
, lead=yes, group=lower-alpha (Japanese: 太鼓の達人, Taiko no Tatsujin, lit. "Master of the drums") is a series of games created by Namco. In the games, players simulate playing a taiko drum in time with music. The series has released games ...
''. Namco endured numerous financial difficulties in the late 1990s and 2000s as a result of the struggling Japanese economy and diminishing arcade market. In 2005, Namco merged with Bandai
is a Japanese multinational toy manufacturer and distributor headquartered in Taitō, Tokyo. Its international branches, Bandai Namco Toys & Collectables America and Bandai UK, are respectively headquartered in Irvine, California and Richmond ...
to form Namco Bandai Holdings
also known as the Bandai Namco Group and generally Bandai Namco, is a Japanese multinational holding company, production enterprise and entertainment conglomerate headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, formed from the merger of Bandai and Namco on ...
, a Japanese entertainment conglomerate. It continued producing games until it was merged into Namco Bandai Games
is a Japanese multinational video game publisher headquartered in Minato-ku, Tokyo. Its international branches, Bandai Namco Entertainment America and Bandai Namco Entertainment Europe, are respectively headquartered in Irvine, California and ...
in 2006.
Namco produced several multi-million-selling game franchises, such as ''Pac-Man
originally called ''Puck Man'' in Japan, is a 1980 maze action video game developed and released by Namco for arcades. In North America, the game was released by Midway Manufacturing as part of its licensing agreement with Namco America. Th ...
'', ''Galaxian
is a 1979 fixed shooter arcade video game developed and published by Namco. The player assumes control of the Galaxip starfighter in its mission to protect Earth from waves of aliens. Gameplay involves destroying each formation of aliens, who ...
'', ''Tekken
is a Japanese Media mix, media franchise centered on a series of fighting game, fighting video and arcade games developed and published by Bandai Namco Entertainment (formerly Namco). The franchise also includes film and print adaptations.
The ...
'', '' Tales'', ''Ridge Racer
is a racing game, racing video game series developed and published for arcade systems and home game consoles by Bandai Namco Entertainment, formerly Namco. The first game, ''Ridge Racer (1993 video game), Ridge Racer'' (1993), was originally rel ...
'', and ''Ace Combat
is an arcade-style combat flight simulation video game franchise published by Bandai Namco Entertainment, formerly Namco. Debuting in 1995 with ''Air Combat'' for the PlayStation, the series includes eight mainline installments, multiple spin- ...
''. It operated video arcades
Video is an electronic medium for the recording, copying, playback, broadcasting, and display of moving visual media. Video was first developed for mechanical television systems, which were quickly replaced by cathode-ray tube (CRT) system ...
and amusement parks globally, and also produced films, toys, and arcade cabinet
An arcade cabinet, also known as an arcade machine or a coin-op cabinet or coin-op machine, is the housing within which an arcade game's electronic hardware resides. Most cabinets designed since the mid-1980s conform to the Japanese Amusement Ma ...
s and operated a chain of restaurants. Namco is remembered in retrospect for its unique corporate model, its importance to the industry, and its advancements in technology. Its successor, Bandai Namco Entertainment
is a Japanese multinational video game video game publisher, publisher headquartered in Minato-ku, Tokyo. Its international branches, Bandai Namco Entertainment America and Bandai Namco Entertainment Europe, are respectively headquartered in ...
, and its subsidiaries continue to use the Namco brand for their video arcades and other entertainment products.
History
Origins and acquisition of Atari Japan (1955–1977)
On June 1, 1955, Japanese businessman Masaya Nakamura founded Nakamura Seisakusho Co., Ltd. in Ikegami, Tokyo. The son of a shotgun repair business owner, Nakamura proved unable to find work in his chosen profession of ship building in the struggling post-World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
economy. Nakamura established his own company after his father's business saw success with producing pop cork guns. Beginning with only ¥300,000 (US$12,000), Nakamura spent the money on two hand-cranked rocking horses that he installed on the roof garden of a Matsuya department store in Yokohama
is the second-largest city in Japan by population and the most populous municipality of Japan. It is the capital city and the most populous city in Kanagawa Prefecture, with a 2020 population of 3.8 million. It lies on Tokyo Bay, south of To ...
.
The horses were loved by children and turned a decent profit for Nakamura, who began expanding his business to cover other smaller locations. A 1959 business reorganization renamed the company Nakamura Seisakusho Company, Ltd. The Mitsukoshi
is an international department store chain with headquarters in Tokyo, Japan. It is a subsidiary of Isetan Mitsukoshi Holdings, which also owns the Isetan department store chain.
History
It was founded in 1673 with the (shop name) , selli ...
department store chain noticed his success in 1963, and approached him with the idea of constructing a rooftop amusement space for its store in Nihonbashi, Tokyo. It consisted of horse rides, a picture viewing machine, and a goldfish scooping
is a traditional Japanese game in which a player scoops goldfish with a paper scooper. It is also called, "Scooping Goldfish", "Dipping for Goldfish", or "Snatching Goldfish". "''Kingyo''" means goldfish and "''sukui''" means scooping. Somet ...
pond, with the centerpiece being a moving train named ''Roadaway Race''. The space was a hit and lead to Mitsukoshi requesting rooftop amusement parks for all of its stores.
Along with Taito
is a Japanese company that specializes in video games, toys, arcade cabinets and game centers, based in Shinjuku, Tokyo. The company was founded by Michael Kogan in 1953 as the importing vodka, vending machines and jukeboxes into Japan. It b ...
, Rosen Enterprises, and Nihon Goraku Bussan, Nakamura Seisakusho became one of Japan's leading amusement companies. As the business grew in size, it used its clout to purchase amusement machines in bulk from other manufacturers at a discount, and then sell them to smaller outlets at full price. While its machines sold well, Nakamura Seisakusho lacked the manufacturing lines and distribution networks of its competitors, which made the production of them longer and more expensive.
The company was unable to place its machines inside stores because other manufacturers already had exclusive rights to these locations. In response, Nakamura Seisakusho opened a production plant in February 1966, moving its corporate office to a four-story building in Ōta, Tokyo
is a Special wards of Tokyo, special ward located in Tokyo, Tokyo Metropolis, Japan. In English, it is often called Ōta City.
, the ward has an estimated population of 716,413, with 379,199 households and a population density of 12,048.65 per ...
. The company secured a deal with Walt Disney Productions
The Walt Disney Company, commonly known as Disney (), is an American multinational mass media and entertainment conglomerate headquartered at the Walt Disney Studios complex in Burbank, California. Disney was originally founded on October ...
to produce children's rides in the likenesses of its characters, in addition to those using popular anime
is Traditional animation, hand-drawn and computer animation, computer-generated animation originating from Japan. Outside of Japan and in English, ''anime'' refers specifically to animation produced in Japan. However, in Japan and in Japane ...
characters like Q-Taro; this move allowed the business to further expand its operations and become a driving force in the Japanese coin-op market.
Though the manufacturing facility was largely reserved for its Disney and anime rides, Nakamura also used it to construct larger, more elaborate electro-mechanical games
Electro-mechanical games (EM games) are types of arcade games that operate on a combination of some electronic circuitry and mechanical actions from the player to move items contained within the game's cabinet. Some of these were early light gun ...
. The first of these was ''Torpedo Launcher'' (1965), a submarine warfare shooting gallery later titled ''Periscope
A periscope is an instrument for observation over, around or through an object, obstacle or condition that prevents direct line-of-sight observation from an observer's current position.
In its simplest form, it consists of an outer case with ...
''. Its other products included ''Ultraman
''Ultraman'', also known as the , is the collective name for all media produced by Tsuburaya Productions featuring Ultraman, his many brethren, and the myriad monsters. Debuting with ''Ultra Q'' and then ''Ultraman'' in 1966, the series is one ...
''-themed gun games and pinball
Pinball games are a family of games in which a ball is propelled into a specially designed table where it bounces off various obstacles, scoring points either en route or when it comes to rest. Historically the board was studded with nails call ...
-like games branded with ''Osomatsu-kun
is a comedy manga series by Fujio Akatsuka which ran in Shogakukan's ''Weekly Shōnen Sunday'' magazine from 1962 to 1969. The series revolves around a group of sextuplet brothers who cause all sorts of mischief. It has been adapted int ...
'' characters.
The name Namco was introduced in 1971 as a brand for several of its machines. The company grew to having ten employees, which included Nakamura himself. It saw continued success with its arcade games, which had become commonplace in bowling alleys and grocery stores. The company also established a robotics division to produce robots for entertainment centers and festivals, such as those that distributed pamphlets, ribbon making machines, and a robot named Putan that solved pre-built mazes.
In August 1973, American game company Atari
Atari () is a brand name that has been owned by several entities since its inception in 1972. It is currently owned by French publisher Atari SA through a subsidiary named Atari Interactive. The original Atari, Inc. (1972–1992), Atari, Inc., ...
began establishing a series of divisions in Asia, one of which was named Atari Japan. Its president, Kenichi Takumi, approached Nakamura in early 1974 to have his business become the distributor of Atari games across Japan. Nakamura, already planning global expansion following his company's success, agreed to the deal. In part due to employee theft, Atari Japan was a financial disaster and nearly collapsed in its first few years of operation.
When Takumi stopped showing up to work, the company was handed to Hideyuki Nakajima, a former employee of the Japan Art Paper Company. Atari co-founder Nolan Bushnell, whose company was already struggling in America, chose to sell the Japanese division. His fixer, Ron Gordon, was given the task of finding the buyer for Atari Japan. After being turned down by Sega and Taito, Gordon's offer was accepted by Nakamura for 296 million ($1.18M), though Nakamura informed Bushnell his company was unable to pay the money by the deadline. With no other takers for Atari Japan, Bushnell ultimately allowed Nakamura to only pay $550,000 and then $250,000 a year for three years. The acquisition allowed Nakamura Seisakusho to distribute Atari games across Japan, and would make it one of the country's largest arcade game companies.
The Atari Japan purchase was not an immediate success, in part due to the medal game
are a type of arcade game commonly found in amusement arcades and casinos, especially in Japan. In order to play a medal game, a customer must first exchange their cash into medals (metal coins, much like an arcade token). The rate of medals v ...
fad of the 1970s. While Nakamura Seisakusho saw some success with imports such as Kee Games
Kee Games was an American arcade game manufacturer that released arcade and video games from 1973 to 1978.
History
Kee was formed by Joe Keenan, a friend and neighbor of Atari co-founder Nolan Bushnell, in September 1973. In reality, Bushnell h ...
's ''Tank
A tank is an armoured fighting vehicle intended as a primary offensive weapon in front-line ground combat. Tank designs are a balance of heavy firepower, strong armour, and good battlefield mobility provided by tracks and a powerful engin ...
'', the Japanese video game industry's decrease in popularity did not make them as profitable as hoped. The market became more viable once restrictions on medal games were imposed by the Japanese government in 1976, as Nakamura Seisakusho began returning higher profits; its import of Atari's '' Breakout'' was so successful that it led to rampant piracy in the industry. By the end of the year, Nakamura Seisakusho was one of Japan's leading video game companies.
Galaxian, Pac-Man, and arcade success (1977–1984)
 Nakamura Seisakusho changed its corporate name to Namco in June 1977. It opened a division in Hong Kong named Namco Enterprises Asia, which maintained video arcades and amusement centers. As Namco's presence in Japan was steadily rising, Nakajima suggested to Nakamura that he open a division in the United States to increase worldwide brand awareness. Nakamura agreed to the proposal, and on September 1, 1978, established Namco America in
Nakamura Seisakusho changed its corporate name to Namco in June 1977. It opened a division in Hong Kong named Namco Enterprises Asia, which maintained video arcades and amusement centers. As Namco's presence in Japan was steadily rising, Nakajima suggested to Nakamura that he open a division in the United States to increase worldwide brand awareness. Nakamura agreed to the proposal, and on September 1, 1978, established Namco America in Sunnyvale, California
Sunnyvale () is a city located in the Santa Clara Valley in northwest Santa Clara County in the U.S. state of California.
Sunnyvale lies along the historic El Camino Real and Highway 101 and is bordered by portions of San Jose to the nort ...
. With Nakajima as its president and Satashi Bhutani as vice president, Namco America's aim was to import games and license them to companies such as Atari and Bally Manufacturing
Bally Manufacturing, later renamed Bally Entertainment, was an American company that began as a pinball and slot machine manufacturer, and later expanded into casinos, video games, health clubs, and theme parks. It was acquired by Hilton Hotel ...
. Namco America would release a few non-video arcade games itself, such as ''Shoot Away
is a 1977 electro-mechanical (EM) light gun shooter arcade game developed and published by Namco. Players use the rifle-shaped light guns to fire at clay pigeons, represented as flying white dots on a projector screen. There are two that must be ...
'' (1977).
As the video game industry prospered in Japan during the 1970s with the release of Taito's ''Space Invaders
is a 1978 shoot 'em up arcade game developed by Tomohiro Nishikado. It was manufactured and sold by Taito in Japan, and licensed to the Midway division of Bally for overseas distribution. ''Space Invaders'' was the first fixed shooter and set ...
'', Namco turned its attention towards making its own video games. While its licensed Atari games were still profitable, sales were decreasing and the quality of the hardware used began deteriorating. Per the recommendation of company engineer Shigekazu Ishimura, the company retrofitted its Ōta manufacturing facility into a small game division and purchased old stock computers from NEC
is a Japanese multinational information technology and electronics corporation, headquartered in Minato, Tokyo. The company was known as the Nippon Electric Company, Limited, before rebranding in 1983 as NEC. It provides IT and network soluti ...
for employees to study.
Namco released '' Gee Bee'', its first original game, in October 1978. Designed by new hire Toru Iwatani
is a Japanese video game designer who spent much of his career working for Namco. He is best known as the creator of the arcade game '' Pac-Man'' (1980).
Early life
Iwatani was born in the Meguro ward of Tokyo, Japan on January 25, 1955. While ...
, it is a video pinball game that incorporates elements from ''Breakout'' and similar "block breaker" clones. Though ''Gee Bee'' fell short of the company's sales expectations and was unable to compete with games such as ''Space Invaders'', it allowed Namco to gain a stronger foothold in the video game market.
In 1979, Namco published its first major hit ''Galaxian
is a 1979 fixed shooter arcade video game developed and published by Namco. The player assumes control of the Galaxip starfighter in its mission to protect Earth from waves of aliens. Gameplay involves destroying each formation of aliens, who ...
'', one of the first video games to incorporate RGB
The RGB color model is an additive color model in which the red, green and blue primary colors of light are added together in various ways to reproduce a broad array of colors. The name of the model comes from the initials of the three addi ...
color graphics, score bonuses, and a tilemap hardware model. ''Galaxian'' is considered historically important for these innovations, and for its mechanics building off those in ''Space Invaders''. It was released in North America by Midway Manufacturing
Midway Games Inc., known previously as Midway Manufacturing and Bally Midway, and commonly known as simply Midway, was an American video game developer and publisher. Midway's franchises included '' Mortal Kombat'', '' Rampage'', ''Spy Hunter'' ...
, the video game division of Bally, where it became one of its best-selling titles and formed a relationship between Midway and Namco.
 The space shooter genre became ubiquitous by the end of the decade, with games such as ''Galaxian'' and ''Space Invaders'' becoming commonplace in Japanese amusement centers. As video games often depicted the killing of enemies and shooting of targets, the industry possessed a predominately male playerbase. Toru Iwatani began work on a
The space shooter genre became ubiquitous by the end of the decade, with games such as ''Galaxian'' and ''Space Invaders'' becoming commonplace in Japanese amusement centers. As video games often depicted the killing of enemies and shooting of targets, the industry possessed a predominately male playerbase. Toru Iwatani began work on a maze video game
Maze game is a video game genre description first used by journalists during the 1980s to describe any game in which the entire playing field is a maze. Quick player action video game, action is required to escape monsters, outrace an opponent, o ...
that was targeted primarily towards women, with simplistic gameplay and recognizable characters. Alongside a small team, he created a game named ''Puck Man'', where players controlled a character that had to eat dots in an enclosed maze while avoiding four ghosts that pursued them.
Iwatani based the gameplay off eating and designed its characters with soft colors and simplistic facial features. ''Puck Man'' was test-marketed in Japan on May 22, 1980 and given a wide-scale in July. It was only a modest success; players were more accustom to the shooting gameplay of ''Galaxian'' as opposed to ''Puck Man''s visually distinctive characters and gameplay style. In North America, it was released as ''Pac-Man
originally called ''Puck Man'' in Japan, is a 1980 maze action video game developed and released by Namco for arcades. In North America, the game was released by Midway Manufacturing as part of its licensing agreement with Namco America. Th ...
'' in November 1980. ''Pac-Man''s simplicity and abstract characters made it a fixture in popular culture, spawning a multi-million-selling media franchise.
Namco regularly released several successful games throughout the early 1980s. It published ''Galaga
is a 1981 fixed shooter arcade video game developed and published by Namco. In North America, it was released by Midway Manufacturing. It is the sequel to ''Galaxian'' (1979), Namco's first major video game hit in arcades. Controlling a starshi ...
'', the follow-up to ''Galaxian'', in 1981 to critical acclaim, usurping its predecessor in popularity with its fast-paced action and power-ups. 1982 saw the release of ''Pole Position
In a motorsports race, the pole position is usually the best and "statistically the most advantageous" starting position on the track. The pole position is usually earned by the driver with the best qualifying times in the trials before the rac ...
'', a racing game that is the first to use a real racetrack (the Fuji Speedway
is a motorsport race track standing in the foothills of Mount Fuji, in Oyama, Suntō District, Shizuoka Prefecture, Japan. It was built in the early 1960s. In the 1980s, Fuji Speedway was used for the FIA World Sportscar Championship and nati ...
) and helped laydown the foundations for the racing genre. It released ''Dig Dug
is a maze game, maze arcade game developed by Namco in 1981 and released in 1982, distributed in North America by Atari, Inc. The player controls Dig Dug to defeat all enemies per stage, by either inflating them to bursting or crushing them unde ...
'' the same year, a maze chaser that allowed players to create their own mazes.
Namco's biggest post-''Pac-Man'' success was the vertical-scrolling shooter ''Xevious
is a vertically scrolling shooter video game developed and published by Namco for arcades in 1982. It was released in Japan and Europe by Namco and in North America by Atari, Inc. Controlling the Solvalou starship, the player attacks Xevious for ...
'' in 1983, designed by new-hire Masanobu Endō
is a game designer, president of Game Studio and Mobile & Game Studio, and the director of Digital Games Research Association Japan. He formerly worked for Namco, where he created arcade games and is best known for ''Xevious'' and ''The Tower of ...
. ''Xevious''s early usage of pre-rendered visuals, boss fights, and a cohesive world made it an astounding success in Japan, recording record-breaking sales figures that hadn't been seen since ''Space Invaders''. The game's success led to merchandise, tournament play, and the first video game soundtrack album. The same year, Namco released ''Mappy
is an arcade game by Namco, introduced in 1983 and distributed in the United States by Bally Midway. A side-scrolling platform game featuring a mouse protagonist and cat antagonists, it runs on Namco Super Pac-Man hardware modified to suppo ...
'', an early side-scrolling platformer, and the ''Pole Position'' sequel '' Pole Position II''.
Endō went on to design ''The Tower of Druaga
is a 1984 Arcade game, arcade action role-playing maze game developed and published in Japan by Namco. Controlling the golden-armored knight Gilgamesh, the player is tasked with scaling 60 floors of the titular tower in an effort to rescue the ...
'' a year later, a maze game that helped establish the concept for the action role-playing game
An action role-playing game (often abbreviated action RPG or ARPG) is a subgenre of video games that combines core elements from both the action game and role-playing genre.
Definition
The games emphasize real-time combat where the player h ...
. ''Druaga''s design influenced games such as Nintendo's ''The Legend of Zelda
''The Legend of Zelda'' is an action-adventure game franchise created by the Japanese game designers Shigeru Miyamoto and Takashi Tezuka. It is primarily developed and published by Nintendo, although some portable installments and re-rele ...
''. 1984 also saw the release of ''Pac-Land
is a 1984 side-scrolling arcade platform game developed and released by Namco. It was distributed in North America by Bally Midway, and in Europe by Atari Games. Controlling Pac-Man (character), Pac-Man, the player must make it to the end of eac ...
'', a ''Pac-Man''-themed platform game that paved the way for similar games such as ''Super Mario Bros.
is a platform game developed and published by Nintendo for the Nintendo Entertainment System (NES). The successor to the 1983 arcade game '' Mario Bros.'' and the first game in the ''Super Mario'' series, it was first released in 1985 for ...
'', and ''Gaplus
is a 1984 fixed shooter arcade game developed and released by Namco. It is the third game in the ''Galaxian'' series, serving as a direct sequel to ''Galaga'' (1981). In North America, a modification kit was later released to change the name to ' ...
'', a moderately successful update to ''Galaga''. The success of Namco's arcade games prompted it to launch its own print publication, '' Namco Community Magazine NG'', to allow its fans to connect with developers.
Success with home consoles (1984–1989)
 In July 1983,
In July 1983, Nintendo
is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational video game company headquartered in Kyoto, Japan. It develops video games and video game consoles.
Nintendo was founded in 1889 as by craftsman Fusajiro Yamauchi and originally produce ...
released the Family Computer
The Nintendo Entertainment System (NES) is an 8-bit Third generation of video game consoles, third-generation home video game console produced by Nintendo. It was first released in Japan in 1983 as the commonly known as the The NES, a redes ...
, a video game console
A video game console is an electronic device that Input/output, outputs a video signal or image to display a video game that can be played with a game controller. These may be home video game console, home consoles, which are generally placed i ...
that utilized interchangeable cartridges to play games. The console's launch came with ports of some of Nintendo's popular arcade games, like ''Donkey Kong
is a video game franchise created by Shigeru Miyamoto and owned by Nintendo. It follows the adventures of a gorilla named Donkey Kong (character), Donkey Kong and his clan of other Ape, apes and monkeys. The franchise primarily consists of plat ...
'', which at the time were considered high quality. Though Namco recognized the system's potential to allow consumers to play accurate versions of its games, the company chose to hold off on the idea after its ports for platforms such as the Sord M5 flopped. Nakamura suggested that his son-in-law, Shigeichi Ishimura, work with a team to reverse-engineer and study the Famicom's hardware in the meantime.
His team created a conversion of ''Galaxian'' with their newfound knowledge of the console's capabilities, which exceeded the quality of previous home releases. The port was presented to Nintendo president Hiroshi Yamauchi
was a Japanese businessman and the third president of Nintendo, joining the company in 1949 until stepping down on 24 May 2002, being subsequently succeeded by Satoru Iwata. During his 53-year tenure, Yamauchi transformed Nintendo from a hanafu ...
alongside notification that Namco intended to release it with or without Nintendo's approval. Namco's demonstration was the impetus for Nintendo's decision to create a licensing program for the console. Namco signed a five-year royalties contract that included several preferential terms, such as the ability to produce its own cartridges.
A subsidiary named was established in 1984 to act as Namco's console game division. It released its first four titles in September: ''Galaxian'', ''Pac-Man'', ''Xevious'', and ''Mappy''. ''Xevious'' sold over 1.5 million copies and became the Famicom's first "killer app
In marketing terminology, a killer application (commonly shortened to killer app) is any computer program or software that is so necessary or desirable that it proves the core value of some larger technology, such as computer hardware, a video game ...
". Namcot also began releasing games for the MSX, a popular Japanese computer. Namco's arcade game ports were considered high-quality and helped increase sales of the console.
Namcot was financially successful and became an important pillar within the company; when Namco moved its headquarters to Ōta, Tokyo in 1985, it used the profits generated from the Famicom conversion of ''Xevious'' to fund its construction (the building was nicknamed "Xevious" as a result). The Talking Aid, a speech impairment device, was part of the company's attempts in venturing into other markets.
By the time the Video game crash of 1983
The video game crash of 1983 (known as the Atari shock in Japan) was a large-scale recession in the video game industry that occurred from 1983 to 1985, primarily in the United States. The crash was attributed to several factors, including ma ...
concluded in 1985 with the release of the Nintendo Entertainment System
The Nintendo Entertainment System (NES) is an 8-bit third-generation home video game console produced by Nintendo. It was first released in Japan in 1983 as the commonly known as the The NES, a redesigned version, was released in America ...
(NES), Atari had effectively collapsed. After enduring numerous financial difficulties and losing its control in the industry, parent Warner Communications
Warner Media, LLC ( traded as WarnerMedia) was an American multinational mass media and entertainment conglomerate. It was headquartered at the 30 Hudson Yards complex in New York City, United States.
It was originally established in 1972 by ...
sold the company's personal computer and home console divisions to Commodore International
Commodore International (other names include Commodore International Limited) was an American home computer and electronics manufacturer founded by Jack Tramiel. Commodore International (CI), along with its subsidiary Commodore Business Mach ...
founder Jack Tramiel
Jack Tramiel ( ; born Idek Trzmiel; December 13, 1928 – April 8, 2012) was an American businessman and Holocaust survivor, best known for founding Commodore International. The Commodore PET, VIC-20 and Commodore 64 are some home compute ...
, who renamed his company Tramel Technology to Atari Corporation
Atari Corporation was an American manufacturer of computers and video game consoles. It was founded by Jack Tramiel on May 17, 1984, as Tramel Technology, Ltd., but then took on the Atari name less than two months later when WarnerMedia, Warn ...
. Warner was left with Atari's arcade game and computer software divisions, which it renamed Atari Games
Atari Games Corporation, known as Midway Games West Inc. after 1999, was an American producer of Arcade game, arcade Video game, games. It was formed in 1985 when the coin-operated Arcade game, arcade game division of Atari, Inc. was transfered ...
. Namco America purchased a 60% stake in Atari Games on February 4, 1985 through its AT Games subsidiary, with Warner holding the remaining 40%. The acquisition gave Namco the exclusive rights to distribute Atari games in Japan.
Nakamura began losing interest and patience in Atari Games not long after the acquisition. As he started viewing Atari as a competitor to Namco, he was hesitant to pour additional funds and resources into the company. Nakamura also disliked having to share ownership with Warner Communications. Nakajima grew frustrated with Nakamura's attempts at marketing Atari video games in Japan, and had constant disagreements with him over which direction to take the company. Viewing the majority-acquisition as a failure, in 1987 Namco America sold 33% of its ownership stake to a group of Atari Games employees led by Nakajima.
This prompted Nakajima to resign from Namco America and become president of Atari Games. He established Tengen, a publisher that challenged Nintendo's licensing restrictions for the NES by selling several unlicensed games, which included ports of Namco arcade games. Though its selloff made Atari Games an independent entity, Namco still held a minority stake in the company and Nakamura retained his position as its board chairman until the middle of 1988.
In Japan, Namco continued to see expeditious growth. It published '' Pro Baseball: Family Stadium'' for the Famicom, which was critically acclaimed and sold over 2.5 million copies. Its sequel, ''Pro Baseball: Family Stadium '87'', sold an additional two million. In 1986, Namco entered the restaurant industry by acquiring the Italian Tomato café chain. It also released ''Sweet Land'', a popular candy-themed prize machine.
One of Namco's biggest hits from the era was the racing game ''Final Lap
is a 1987 racing simulation video game developed and published by Namco. Atari Games published the game in the United States in 1988. It was the first game to run on Namco's then-new System 2 hardware and is a direct successor to Namco's ''Pol ...
'' from 1987. It is credited as the first arcade game to allow multiple machines to be connected—or "linked"—together to allow for additional players. ''Final Lap'' was one of the most-profitable coin-operated games of the era in Japan, remaining towards the top of sales charts for the rest of the decade.
Namco's continued success in arcades provided its arcade division with the revenue and resources needed to fund its research and development (R&D) departments. Among their first creations was the helicopter shooter ''Metal Hawk
is a 1988 multidirectional shooter arcade game developed and published by Namco. Assuming control of the titular attack helicopter, the player is tasked with using a machine gun and air-to-surface missiles to destroy enemies and earn a certain nu ...
'' in 1988, fitted in a motion simulator
A motion simulator or motion platform is a mechanism that creates the feelings of being in a real motion environment. In a simulator, the movement is synchronised with a visual display of the outside world (OTW) scene. Motion platforms can provi ...
arcade cabinet. Its high development costs prevented it from being massed-produced. While most of its efforts were commercially unsuccessful, Namco grew interested in motion-based arcade games and began designing those at a larger scale. In 1988, Namco became involved in film production when it distributed the film '' Mirai Ninja'' in theaters, with a tie-in video game coinciding with its release.
Namco also developed the beat 'em up
The beat 'em up (also known as brawler and, in some markets, beat 'em all) is a video game genre featuring hand-to-hand combat against a large number of opponents. Traditional beat 'em ups take place in scrolling, two-dimensional (2D) levels, ...
''Splatterhouse
is a beat 'em up arcade game developed and published by Namco. It was the first in a series of games released in home console and personal computer formats. This cult classic would later spawn the parody '' Splatterhouse: Wanpaku Graffiti'', the ...
'', which attracted attention for its fixture on gore and dismemberment, and ''Gator Panic
''Gator Panic'' is a redemption arcade game released in 1988 by Namco. The game plays very much like Whac-A-Mole, but features alligators coming out of the cabinet horizontally instead of moles coming out vertically.
Legacy
A digital remake was ...
'', a derivative of ''Whack-a-Mole
Whac-A-Mole is an arcade game, originally known as or in Japan. A typical Whac-A-Mole machine consists of a waist-level cabinet with a play area and display screen, and a large, soft, black mallet. Five holes in the play area top are filled wit ...
'' that became a mainstay in Japanese arcades and entertainment centers. In early 1989, Namco unveiled its System 21 arcade system, one of the earliest arcade boards to utilize true 3D polygonal graphics. Nicknamed "Polygonizer", the company demonstrated its power through the Formula One racer ''Winning Run
is a first-person arcade racing simulation game developed and published by Namco in late December 1988 in Japan, before releasing internationally the following year. The player pilots a Formula One racer, with the objective being to complete eac ...
''.
With an arcade cabinet that shook and swayed the player as they drove, the game was seen as "a breakthrough product in term of programming technique" and garnered significant attention from the press. ''Winning Run'' was commercially successful, convincing Namco to continue researching 3D video game hardware. Video arcades under the Namco banner continued opening up in Japan and overseas, such as the family-friendly Play City Carrot chain.
Expansion into other markets (1989–1994)
Namco saw continued success in the consumer game market as a result of the "Famicom boom" in the late 1980s. By 1989, sales of games for the Famicom and NES accounted for 40% of its annual revenue. During the same time frame, the company's licensing contract with Nintendo expired; when Namco attempted to renew its license, Nintendo chose to revoke many of the preferential terms it originally possessed. Hiroshi Yamauchi insisted that all companies, including Namco, had to follow the same guidelines. The revocation of Namco's terms enraged Nakamura, who announced the company would abandon Nintendo hardware and focus on production of games for competing systems such as thePC Engine
The TurboGrafx-16, known as the outside North America, is a home video game console designed by Hudson Soft and sold by NEC Home Electronics. It was the first console marketed in the fourth generation, commonly known as the 16-bit era, though ...
. Executives resisted the idea, fearing it would severely impact the company financially. Against Nakamura's protest, Namco signed Nintendo's new licensee contract anyway. While it continued to produce games for Nintendo hardware, most of Namco's quality releases came from the PC Engine and Mega Drive
The Sega Genesis, known as the outside North America, is a 16-bit fourth generation home video game console developed and sold by Sega. It was Sega's third console and the successor to the Master System. Sega released it in 1988 in Japan a ...
.
 In 1989, it was reported that Namco was underway with developing its own video game console to compete against companies such as Nintendo and NEC. ''
In 1989, it was reported that Namco was underway with developing its own video game console to compete against companies such as Nintendo and NEC. ''Electronic Gaming Monthly
''Electronic Gaming Monthly'' (often abbreviated to ''EGM'') is a monthly American video game magazine. It offers video game news, coverage of industry events, interviews with gaming figures, editorial content and product reviews.
History
The m ...
'' claimed that the system, which was nearing completion, featured hardware comparable to the then-upcoming Nintendo Super Famicom
The Super Nintendo Entertainment System (SNES), commonly shortened to Super NES or Super Nintendo, is a 16-bit home video game console developed by Nintendo that was released in 1990 in Japan and South Korea, 1991 in North America, 1992 in Euro ...
. According to company engineer Yutaka Isokawa, it was produced to compete against the Mega Drive, a 16-bit console by Namco's arcade rival Sega. With the console industry being crowded by other competing systems, publications were unsure how well it would perform in the market. While the console was never released, it allowed Namco to familiarize itself with designing home video game hardware.
Tadashi Manabe replaced Nakamura as president of Namco on May 2, 1990. Manabe, who had been the company's representative director since 1981, was tasked with strengthening relationships and teamwork ethics of management. Two months later, the company dissolved its remaining connections with Atari Games when Time Warner reacquired Namco America's remaining 40% stake in Atari Games. In return, Namco America was given Atari's video arcade management division, Atari Operations, allowing the company to operate video arcades across the United States. Namco began distributing games in North America directly from its US office, rather than through Atari.
Namco Hometek was established as the home console game division of Namco America; the latter's relations with Atari Games and Tengen made the company ineligible to become a Nintendo third-party licensee, instead relying on publishers such as Bandai
is a Japanese multinational toy manufacturer and distributor headquartered in Taitō, Tokyo. Its international branches, Bandai Namco Toys & Collectables America and Bandai UK, are respectively headquartered in Irvine, California and Richmond ...
to release its games in North America. In Japan, Namco developed two theme park attractions, which were demonstrated at the 1990 International Garden and Greenery Exposition (Expo '90
or The International Garden and Greenery Exposition, organized as a part of the International Expositions Convention, was the first large-scale international gardening exposition in Asia and focused on the theme of the "Harmonious Coexistence of ...
): '' Galaxian3: Project Dragoon'', a 3D rail shooter that supported 28 players, and a dark ride
A dark ride or ghost train is an indoor amusement ride on which passengers aboard guided vehicles travel through specially lit scenes that typically contain Animatronics, animation, sound, music and Special effect#Live special effects, special e ...
based on ''The Tower of Druaga''.
As part of the company's idea of "hyperentertainment" video games, Namco engineers had drafted ideas for a possible theme park based on Namco's experience with designing and operating indoor play areas and entertainment complexes. Both attractions were commercially successful and among the most popular of Expo 90's exhibitions. In arcades, Namco released ''Starblade
is a 1991 3D rail shooter arcade game developed and published by Namco. Controlling the starfighter FX-01 "GeoSword" from a first-person perspective, the player is tasked with eliminating the Unknown Intelligent Mechanized Species (UIMS) before t ...
'', a 3D rail shooter noteworthy for its cinematic presentation. This led to Namco dominating the Japanese dedicated arcade cabinet
An arcade cabinet, also known as an arcade machine or a coin-op cabinet or coin-op machine, is the housing within which an arcade game's electronic hardware resides. Most cabinets designed since the mid-1980s conform to the Japanese Amusement Ma ...
charts by October 1991, holding the top six positions that month with ''Starblade'' at the top.
In February 1992, Namco opened its own theme park, Wonder Eggs, in the Futakotamagawa Time Spark area in Setagaya, Tokyo
is a special ward in Tokyo, Japan. It is also the name of a neighborhood and administrative district within the ward. The ward calls itself Setagaya City in English. Its official bird is the azure-winged magpie, its flower is the fringed orch ...
. Described as an "urban amusement center", Wonder Eggs was the first amusement park operated by a video game company. In addition to ''Galaxian3'' and ''The Tower of Druaga'', the park featured carnival games, carousals, motion simulators, and ''Fighter Camp'', the first flight simulator available to the public. The park saw regularly high attendance numbers; 500,000 visitors attended in its first few months of operation and over one million by the end of the year.
Namco created the park out of its interest in designing a Disneyland-inspired theme park that featured the same kind of stories and characters present in its games. Wonder Eggs contributed to Namco's 34% increase in revenue by December 1992. Namco also designed smaller, indoor theme parks for its larger entertainment complexes across the country, such as Plabo Sennichimae Tenpo in Osaka.
 Manabe resigned as president on May 1, 1992 due to a serious anxiety disorder, and Nakamura once again assumed the role. Manabe instead served as the company's vice chairman until his death in 1994. The company's arcade division, in the meantime, began work on a new 3D arcade board named
Manabe resigned as president on May 1, 1992 due to a serious anxiety disorder, and Nakamura once again assumed the role. Manabe instead served as the company's vice chairman until his death in 1994. The company's arcade division, in the meantime, began work on a new 3D arcade board named System 22
The Namco System 22 is the successor to the Namco System 21 arcade system board. It debuted in 1992 in video gaming, 1992 with ''Ridge Racer (video game)#Development and release, Sim Drive'' Video gaming in Japan, in Japan, followed by a worldwid ...
, capable of displaying polygonal 3D models with fully-textured graphics. Namco enlisted the help of Evans & Sutherland
Evans & Sutherland is a pioneering American computer firm in the computer graphics field. Its current products are used in digital projection environments like planetariums. Its simulation business, which it sold to Rockwell Collins, sold products ...
, a designer of combat flight simulators for The Pentagon
The Pentagon is the headquarters building of the United States Department of Defense. It was constructed on an accelerated schedule during World War II. As a symbol of the U.S. military, the phrase ''The Pentagon'' is often used as a metony ...
, to assist in the board's development.
The System 22 powered ''Ridge Racer
is a racing game, racing video game series developed and published for arcade systems and home game consoles by Bandai Namco Entertainment, formerly Namco. The first game, ''Ridge Racer (1993 video game), Ridge Racer'' (1993), was originally rel ...
'', a racing game, in 1993. ''Ridge Racer''s usage of 3D textured polygons and drifting made it a popular title in arcades and one of Namco's most-successful releases, and is labeled a milestone in 3D computer graphics. The company followed its success with ''Tekken
is a Japanese Media mix, media franchise centered on a series of fighting game, fighting video and arcade games developed and published by Bandai Namco Entertainment (formerly Namco). The franchise also includes film and print adaptations.
The ...
'', a 3D fighting game, a year later. Designed by Seiichi Ishii
Seiichi Ishii (石井 精一 ''Ishii Seiichi'', born 18 August 1967) is a Japanese game designer. He is best known for the development of fighting games.
Ishii was born in Ichinomiya City, Aichi Prefecture, Japan. He was a designer on groundb ...
, the co-creator of Sega's landmark fighting game ''Virtua Fighter
is a series of fighting games created by Sega-AM2 and designer Yu Suzuki. The original ''Virtua Fighter'' was released in October 1993 and has received four main sequels and several spin-offs. The highly influential first ''Virtua Fighter'' game ...
'', ''Tekken''s wide array of playable characters and consistent framerate helped it outperform Sega's game in popularity, and launched a multi-million-selling franchise as a result.
The company continued expanding its operations overseas, such as the acquisition of the Aladdin's Castle chain from Bally Manufacturing. In December, Namco acquired Nikkatsu
is a Japanese entertainment company known for its film and television productions. It is Japan's oldest major movie studio, founded in 1912 during the silent film era. The name ''Nikkatsu'' amalgamates the words Nippon Katsudō Shashin, literally ...
, Japan's oldest-surviving film studio that at the time was undergoing bankruptcy procedures. The purchase allowed Nikkatsu to utilize Namco's computer graphics hardware for its films, while Namco was able to gain a foothold in the Japanese film industry.
Relationship with Sony (1994–1998)
 In early 1994, Sony announced that it was developing its own video game console, the 32-bit
In early 1994, Sony announced that it was developing its own video game console, the 32-bit PlayStation
is a video gaming brand that consists of five home video game consoles, two handhelds, a media center, and a smartphone, as well as an online service and multiple magazines. The brand is produced by Sony Interactive Entertainment, a divisi ...
. The console began as a collaboration between Nintendo and Sony to create a CD-based peripheral for the Super Nintendo Entertainment System
The Super Nintendo Entertainment System (SNES), commonly shortened to Super NES or Super Nintendo, is a 16-bit home video game console developed by Nintendo that was released in 1990 in Japan and South Korea, 1991 in North America, 1992 in Eur ...
in 1988. Fearing that Sony would assume control of the entire project, Nintendo silently scrapped the add-on. Sony chose to refocus its efforts in designing the PlayStation in-house as its own console.
As it lacked the resources to produce its own games, Sony called for the support of third-party companies to develop PlayStation software. Namco, frustrated with Nintendo and Sega's licensing conditions for its consoles, agreed to support the PlayStation and became its first third-party developer. The company began work on a conversion of ''Ridge Racer'', its most-popular arcade game at the time.
The PlayStation was released in Japan on December 3, 1994, with ''Ridge Racer'' as one of its first titles. Sony moved 100,000 units on launch day alone; publications attributed ''Ridge Racer'' to the PlayStation's early success, giving it an edge over its competitor, the Sega Saturn
The is a home video game console developed by Sega and released on November 22, 1994, in Japan, May 11, 1995, in North America, and July 8, 1995, in Europe. Part of the fifth generation of video game consoles, it was the successor to the succ ...
. For a time, it was the best-selling PlayStation game in Japan.
Namcot was consolidated into Namco in 1995; its final game was a PlayStation port of ''Tekken'', published in March in Japan and in November worldwide. ''Tekken'' was designed for Namco's System 11 arcade system board, which was based on raw PlayStation hardware; this allowed the home version to be a near-perfect rendition of its arcade counterpart. ''Tekken'' became the first PlayStation game to sell one million copies and played a vital role in the console's mainstream success.
Sony recognized Namco's commitment to the console, leading to Namco receiving special treatment from Sony and early promotional material adopting the tagline "PlayStation: Powered by Namco". Namco was also given the rights to produce controllers, such as the NeGcon
The , stylized as neGcon, is a motion-based video game controller manufactured in 1995 by Namco for the PlayStation. One of the first third-party peripherals for the system, the controller is connected by a swivel joint, allowing the player to twi ...
, which it designed with the knowledge it gained through developing its cancelled console. Though it had signed contracts to produce games for systems such as the Sega Saturn and 3DO Interactive Multiplayer
The 3DO Interactive Multiplayer, also referred to as simply 3DO, is a home video game console developed by The 3DO Company. Conceived by entrepreneur and Electronic Arts founder Trip Hawkins, the 3DO was not a console manufactured by the company ...
, Namco concentrated its consumer software efforts on PlayStation for the remainder of the decade.
As a means to draw players into its video arcades, Namco's arcade game division began releasing titles that featured unique and novel control styles and gameplay. In 1995, the company released ''Alpine Racer
is a racing sports video game developed and published by Namco for arcades. It had a limited release in December 1994, followed by a wide release in July 1995. It ran on the Namco System 22 arcade hardware.
The player uses a handlebar controll ...
'', an alpine skiing game that was awarded "Best New Equipment" during the year's Amusement and Music Operators Association (AMOA) exposition. ''Time Crisis
''Time Crisis'' is a first-person on-rails light gun shooter series of arcade video games by Namco, introduced in 1995. It is focused on the exploits of a fictional international intelligence agency who assigns its best agents to deal with a m ...
'', a lightgun shooter noteworthy for its pedal ducking mechanic, helped set the standard for the genre as a whole, while ''Prop Cycle
is a 1996 arcade game developed and published by Namco.
Gameplay
''Prop Cycle'' is a 3D flying simulator in which the player uses a human-powered aircraft to pop hot-air balloons in the city of Solitar to prevent the city from floating away ...
'' gained notoriety for its usage of a bicycle controller the player pedaled.
The photo booth
A photo booth is a vending machine or modern kiosk that contains an automated, usually coin-operated, camera and film processor. Today, the vast majority of photo booths are digital.
History
The patent for the first automated photography ma ...
machine ''Star Audition'', which offered players the chance of becoming a star in the show business, became a media sensation in Japan. Namco Operations, which was renamed Namco Cybertainment in 1996, acquired the Edison Brothers Stores
Edison Brothers Stores, Inc., was a retail conglomerate based in St. Louis, Missouri. It operated numerous retail chains mainly located in shopping malls, mostly in the fields of shoes, clothing and entertainment, with Bakers Shoes as its flagship ...
arcade chain in April. Namco also introduced the Postpaid System, a centralized card payment system, as a means to combat the piracy of IC Card
A smart card, chip card, or integrated circuit card (ICC or IC card) is a physical electronic authentication device, used to control access to a resource. It is typically a plastic credit card-sized card with an embedded integrated circuit (IC) c ...
s in Japanese arcades.
In September 1997, Namco announced it would begin development of games for the Nintendo 64
The (N64) is a home video game console developed by Nintendo. The successor to the Super Nintendo Entertainment System, it was released on June 23, 1996, in Japan, on September 29, 1996, in North America, and on March 1, 1997, in Europe and Au ...
, a console struggling to receive support from third-party developers. Namco signed a contract with Nintendo that allowed the company to produce two games for the console: '' Famista 64'', a version of its ''Family Stadium'' series, and an untitled RPG for the 64DD
The is a magnetic floppy disk drive peripheral for the Nintendo 64 game console developed by Nintendo. It was announced in 1995, prior to the Nintendo 64's 1996 launch, and after numerous delays was released in Japan on December 13, 1999. The ...
peripheral. The RPG was never released while the 64DD went on to become a commercial failure
Failure is the state or condition of not meeting a desirable or intended objective, and may be viewed as the opposite of success. The criteria for failure depends on context, and may be relative to a particular observer or belief system. One ...
. In October 1998, which one publication described as being "the most stunning alliance this industry has seen in a long while", Namco announced a partnership deal with long-time rival Sega to bring some of its titles to the newly unveiled Dreamcast
The is a home video game console released by Sega on November 27, 1998, in Japan; September 9, 1999, in North America; and October 14, 1999, in Europe. It was the first sixth-generation video game console, preceding Sony's PlayStation 2, N ...
.
As Namco primarily developed games for Sony hardware, and were among the biggest third-party developers for the PlayStation, the announcement surprised news outlets. For its PlayStation-based System 12 arcade board, Namco released the weapon-based fighting game ''Soulcalibur
is a weapon-based fighting video game franchise by Bandai Namco Entertainment.
There are seven main installments of video games and various media spin-offs, including music albums and a series of manga books. The first game in the series, '' ...
'' in 1998. Its 1999 Dreamcast port, which features multiple graphical enhancements and new gamemodes, is an early instance of a console game being better than its arcade version. ''Soulcalibur'' sold over one million units, won multiple awards, and contributed to the early success of the Dreamcast.
Financial decline and restructuring (1998–2005)
Namco began experiencing decline in its consumer software sales by 1998 as a result of the Japanese recession, which affected the demand for video games as consumers had less time to play them. The company's arcade division had similar struggles, having slumped by 21% at the end of its fiscal year ending March 1998. Namco Cybertainment filed forChapter 11
Chapter 11 of the United States Bankruptcy Code (Title 11 of the United States Code) permits reorganization under the bankruptcy laws of the United States. Such reorganization, known as Chapter 11 bankruptcy, is available to every business, wheth ...
bankruptcy protection in August, being forced to closed several hundreds of its under-performing arcades in North America as its parent underwent reorganization. In its 1998 annual report, Namco reported a 26.3% drop in net sales, which it partly blamed on low consumer spending.
A further 55% drop was reported in November 1999 when its home console game output decreased. As a means to diversify itself from its arcade and consumer game markets, Namco entered the mobile phone game market with the Namco Station, a marketplace for i-Mode
NTT DoCoMo's i-mode is a mobile internet (distinct from wireless internet) service popular in Japan. Unlike Wireless Application Protocols, i-mode encompasses a wider variety of internet standards, including web access, e-mail, and the packet- ...
cellular devices that featured ports of its arcade games like ''Pac-Man'' and ''Galaxian''. The company also majority-acquired Monolith Soft
trading as Monolith Soft, is a Japanese video game development studio originally owned by Namco (later Bandai Namco) until being bought out by Nintendo in 2007. The company was founded in 1999 by Tetsuya Takahashi with the support and coopera ...
, an action role-playing game
An action role-playing game (often abbreviated action RPG or ARPG) is a subgenre of video games that combines core elements from both the action game and role-playing genre.
Definition
The games emphasize real-time combat where the player h ...
developer best known for creating the ''Xenosaga
''Xenosaga'' is a role-playing video game series developed by Monolith Soft and primarily published by Namco. Forming part of the wider '' Xeno'' metaseries, ''Xenosaga'' is set in a science fiction universe and follows a group of characters as th ...
'' series. It continued introducing novel concepts for arcades to help attract players, such as the Cyber Lead II, an arcade cabinet that features PlayStation and Dreamcast VMU memory card slots.
 Namco's financial losses worsened in the 2000s. In October 2000, the Japanese newspaper ''
Namco's financial losses worsened in the 2000s. In October 2000, the Japanese newspaper ''Nihon Keizai Shinbun
''The Nikkei'', also known as , is the flagship publication of Nikkei, Inc. (based in Tokyo) and the world's largest financial newspaper, with a daily circulation exceeding 1.73 million copies. The Nikkei 225, a stock market index for the Tok ...
'' reported that the company projected a loss of 2.1 billion ($19.3M) for the fiscal year ending March 2001. Namco had previously hinted at this during an event with industry analysists, blaming its struggles on the depressed Japanese economy and dwindling arcade game market. The company closed its Wonder Eggs park on December 31, 2000, which by that point saw an attendance number of six million visitors, in addition to shuttering many of its video arcades that returned substandard profits.
In February 2001, Namco updated its projections and reported it now expected a 6.5 billion ($56.3M) net loss and a drop in revenue by 95% for the fiscal year ending March 2001, which severely impacted the company's release schedule and corporate structure. The company's earnings forecasts were lowered to accommodate its losses, its development strategy was reorganized to focus largely on established franchises, and 250 of its employees were laid off in what it described as "early retirement". Namco underwent restructuring to increase its income, which included the shuffling of its management and the announcement of production of games for Nintendo's GameCube
The is a home video game console developed and released by Nintendo in Japan on September 14, 2001, in North America on November 18, 2001, and in PAL territories in 2002. It is the successor to the Nintendo 64 (1996), and predecessor of the Wii ...
and Microsoft's Xbox
Xbox is a video gaming brand created and owned by Microsoft. The brand consists of five video game consoles, as well as applications (games), streaming services, an online service by the name of Xbox network, and the development arm by the na ...
.
Following its financial struggles, Namco's arcade division underwent mass reorganization. This division achieved strong success with ''Taiko no Tatsujin
, lead=yes, group=lower-alpha (Japanese: 太鼓の達人, Taiko no Tatsujin, lit. "Master of the drums") is a series of games created by Namco. In the games, players simulate playing a taiko drum in time with music. The series has released games ...
'', a popular drum-based rhythm game
Rhythm game or rhythm action is a genre of music-themed action video game that challenges a player's sense of rhythm. Games in the genre typically focus on dance or the simulated performance of musical instruments, and require players to pres ...
where players hit a taiko drum
are a broad range of Japanese percussion instruments. In Japanese, the term refers to any kind of drum, but outside Japan, it is used specifically to refer to any of the various Japanese drums called and to the form of ensemble drumming m ...
controller to the beat of a song. ''Taiko no Tatsujin'' became a best-seller and created one of the company's most popular and prolific franchises. Namco's North American divisions, in the meantime, underwent reorganization and restructuring as a result of decreasing profits.
Namco Hometek was stripped of its research and development divisions following Namco's disappointment in the quality of its releases. Its continuing expansion into other non-video game divisions, including rehabilitation
Rehabilitation or Rehab may refer to:
Health
* Rehabilitation (neuropsychology), therapy to regain or improve neurocognitive function that has been lost or diminished
* Rehabilitation (wildlife), treatment of injured wildlife so they can be retur ...
electronics and travel agency websites, prompted the creation of the Namco Incubation Center, which would control these businesses. The Incubation Center also hosted the Namco Digital Hollywood Game Laboratory game school, which designed the sleeper hit
In the entertainment industry, a sleeper hit is a film, television series, music release, video game, or some other entertainment product that was initially unsuccessful on release but became a success later on. A sleeper hit may have little promo ...
''Katamari Damacy
() is a third-person puzzle-action video game developed and published by Namco for the PlayStation 2. It was released in Japan in March 2004 and in North America in September 2004. Designer Keita Takahashi struggled to pitch the game to Namco' ...
'' (2004).
Nakamura resigned as company president later in the year, being replaced with Kyushiro Takagi. Anxious about the company's continuing financial struggles, Nakamura suggested that Namco begin looking into the possibility of merging with another company. Namco first looked to ''Final Fantasy
is a Japanese video game, Japanese science fantasy anthology media franchise created by Hironobu Sakaguchi and developed and owned by Square Enix (formerly Square (video game company), Square). The franchise centers on a series of fantasy and ...
'' developer Square
In Euclidean geometry, a square is a regular quadrilateral, which means that it has four equal sides and four equal angles (90-degree angles, π/2 radian angles, or right angles). It can also be defined as a rectangle with two equal-length adj ...
and ''Dragon Quest
previously published as ''Dragon Warrior'' in North America until 2005, is a franchise of Japanese role-playing video games created by Armor Project (Yuji Horii), Bird Studio (Akira Toriyama) and Sugiyama Kobo (Koichi Sugiyama) to its publi ...
'' publisher Enix
was a Japanese video game publisher that produced video games, anime and manga. Enix is known for publishing the ''Dragon Quest'' series of role-playing video games.
The company was founded by Yasuhiro Fukushima on September 22, 1975, as . Th ...
, offering to combine the three companies into one. Yoichi Wada
is a former president and representative director of the Japanese video game and publishing company Square Enix as well as its subsidiary Taito. He is also the former chairman of the Computer Entertainment Supplier's Association (CESA), the fo ...
, the president of Square, disliked Namco's financial showing and declined the offer. Square instead agreed to a business alliance with Namco. Following this, Namco then approached Sega, a company struggling to stay afloat after the commercial failure of the Dreamcast.
Sega's development teams and extensive catalog of properties caught Namco's interest, and believed a merge could allow the two to increase their competitiveness. Sega was already discussing a merge with pachinko manufacturer Sammy Corporation
is a Japanese developer and retailer of pachinko and pachislot machines, headquartered in Shinagawa, Tokyo. Its South Korean office, Sammy Amusement Service, is headquartered in Seoul, South Korea. Sammy is a subsidiary of the entertainment cong ...
; executives at Sammy were infuriated at Sega's consideration of Namco's offer. A failed attempt to overturn the merge led Namco to withdraw its offer the same day Sega announced it turned down Sammy's. While Namco stated it was willing to negotiate with Sega on a future deal, Sega turned down the idea.
Shigeichi Ishimura, the son in-law of Nakamura, succeeded Takagi as Namco president on April 1, 2005; Nakamura retained his role as the company's executive chairman. This was part of Namco's continuing efforts at reorganizing itself to be in line with changing markets. On July 26, as part of its 50th anniversary event, Namco published ''NamCollection
is a video game compilation released in July 2005 by Namco in Japan only to celebrate the company's 50th anniversary. The compilation includes five PlayStation video games (''Ace Combat 2'', '' Klonoa: Door to Phantomile'', '' Mr. Driller'', ''Rid ...
''—a compilation of several of its PlayStation games—for the PlayStation 2
The PlayStation 2 (PS2) is a home video game console developed and marketed by Sony Computer Entertainment. It was first released in Japan on 4 March 2000, in North America on 26 October 2000, in Europe on 24 November 2000, and in Australia on 3 ...
in Japan.
Namco also opened the Riraku no Mori, a companion to its Namja Town park that held massage parlors for visitors; Namco believed it would help make relaxation a source of entertainment. ''The Idolmaster
is a Japanese media franchise that began in 2005 with a raising simulation and rhythm video game series created by Bandai Namco Entertainment (formerly Namco). The series primarily centers on the career of a producer who works with a group of p ...
'', a rhythm game that incorporated elements of life simulations, was widely successful in Japan and resulted in the creation of a multi-million-grossing franchise.
Bandai takeover and dissolution (2005–2006)
In early 2005, Namco began merger talks with Bandai, a toy and anime company. The two discussed a year prior about a possible business alliance after Namco collaborated with Bandai subsidiaryBanpresto
(formerly Coreland Technology Inc.) was a Japanese video game developer and publisher headquartered in Shinagawa, Tokyo. It had a branch in Hong Kong named Banpresto H.K., which was headquartered in the New Territories. Banpresto was a partly-own ...
to create an arcade game based on ''Mobile Suit Gundam
, also known as ''First Gundam'', ''Gundam 0079'' or simply ''Gundam '79'', is an anime television series, produced and animated by Nippon Sunrise. Created and directed by Yoshiyuki Tomino, it premiered in Japan on Nagoya Broadcasting ...
''. Bandai showed interest in Namco's game development skills and believed combining this with its wide library of profitable characters and franchises, such as ''Sailor Moon
is a Japanese manga series written and illustrated by Naoko Takeuchi. It was originally serialized in Kodansha's ''shōjo'' manga magazine ''Nakayoshi'' from 1991 to 1997; the 52 individual chapters were published in 18 volumes. The seri ...
'' and ''Tamagotchi
The is a handheld digital pet that was created in Japan by Akihiro Yokoi of WiZ and Aki Maita of Bandai. It was released by Bandai on November 23, 1996 in Japan and in the USA on May 1, 1997, quickly becoming one of the biggest toy fads o ...
'', could increase their competitiveness in the industry.
Nakamura and Namco's content development division advisors pushed against the idea, as they felt Bandai's corporate model wouldn't blend well with Namco's more agricultural work environment. Namco's advisors were also critical of Bandai for focusing on promotion and marketing over quality. As Namco's financial state continued to deteriorate, Ishimura pressured Nakamura into supporting the merger. Bandai's offer was accepted on May 2, with both companies stating in a joint statement their financial difficulties were the reason for the merger.
The business takeover
In business, a takeover is the purchase of one company (the ''target'') by another (the ''acquirer'' or ''bidder''). In the UK, the term refers to the acquisition of a public company whose shares are listed on a stock exchange, in contrast to t ...
, where Bandai acquired Namco for 175.3 billion ($1.7B), was finalized on September 29. An entertainment conglomerate named Namco Bandai Holdings
also known as the Bandai Namco Group and generally Bandai Namco, is a Japanese multinational holding company, production enterprise and entertainment conglomerate headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, formed from the merger of Bandai and Namco on ...
was established the same day; while their executive departments merged, Bandai and Namco became independently-operating subsidiaries of the new umbrella holding company. Kyushiro Takagi, Namco's vice chairman, was appointed chairman and director of Namco Bandai Holdings. The combined revenues of the new company were estimated to be 458 billion ($4.34B), making Namco Bandai the third-largest Japanese game company after Nintendo and Sega Sammy Holdings
(also known as the Sega Sammy Group and generally Sega Sammy, stylized as SᴇɢᴀSammy) is a Japanese holding company formed from the merger of Sega and Sammy Corporation in 2004. Both companies are involved in the amusement industry (Sega wi ...
.
As its parent company was preparing for a full business integration, Namco continued its normal operations, such as releasing ''Ridge Racer 6
''Ridge Racer 6'' is a racing game by Namco released in 2005. It was the sixth console game in the ''Ridge Racer'' series but unlike the previous mainline entries, which were released for PlayStation consoles, this entry was released exclusivel ...
'' as a launch title for the newly-unveiled Xbox 360
The Xbox 360 is a home video game console developed by Microsoft. As the successor to the original Xbox, it is the second console in the Xbox series. It competed with Sony's PlayStation 3 and Nintendo's Wii as part of the seventh generation ...
in October and collaborating with Nintendo to produce the arcade game ''Mario Kart Arcade GP
is an arcade sub-series of Nintendo's '' Mario Kart'' series, developed and published by Namco and later Bandai Namco Games under license from Nintendo. In all installments, for an additional fee, a player's data can be saved on a magnetic ca ...
''. The company honored the 25th anniversary of its ''Pac-Man
originally called ''Puck Man'' in Japan, is a 1980 maze action video game developed and released by Namco for arcades. In North America, the game was released by Midway Manufacturing as part of its licensing agreement with Namco America. Th ...
'' series with '' Pac-Pix'', a puzzle game for the Nintendo DS
The is a handheld game console produced by Nintendo, released globally across 2004 and 2005. The DS, an initialism for "Developers' System" or "Dual Screen", introduced distinctive new features to handheld games: two LCD screens working in tan ...
, and entered the massively multiplayer online
A massively multiplayer online game (MMOG or more commonly MMO) is an online video game with a large number of players, often hundreds or thousands, on the same server. MMOs usually feature a huge, persistent open world, although there are ...
game market with '' Tales of Eternia Online'', an action role-playing game based on its '' Tales'' franchise.
AMC Theatres
AMC Entertainment Holdings, Inc. (d/b/a AMC Theatres, originally an abbreviation for American Multi-Cinema; often referred to simply as AMC and known in some countries as AMC Cinemas or AMC Multi-Cinemas) is an American movie theater chain fou ...
to host its video arcades in their respective locations. The second Namco company was renamed Bandai Namco Amusement on April 1, 2018 following a corporate restructuring by its parent. Amusement took over the arcade game development branch of Namco Bandai Games, which renamed itself to Bandai Namco Entertainment in 2015.
Namco USA was absorbed into Bandai Namco Amusement's North American branch in 2021 following its parent company's decision to exit the arcade management industry in the United States. This makes Namco Enterprises Asia and Namco Funscape―Bandai Namco's arcade division in Europe―the last companies to use the original Namco trademark in their names. Bandai Namco Holdings and its subsidiaries continue to use the Namco name for a variety of products, including mobile phone applications, streaming programs, and eSports
Esports, short for electronic sports, is a form of competition using video games. Esports often takes the form of organized, multiplayer video game competitions, particularly between professional players, individually or as teams. Although orga ...
-focused arcade centers in Japan.
Legacy
Namco was one of the world's largest producers of video arcade games, having published over 300 titles since 1978. Many of its games are considered some of the greatest of all time, including ''Pac-Man'', ''Galaga'', ''Xevious'', ''Ridge Racer'', ''Tekken 3
is a fighting game, the third entry in the ''Tekken'' series. It was released to the arcades in 1997, before being ported for the PlayStation in 1998. The arcade version of the game was released in 2005 for the PlayStation 2 as part of ''Tekke ...
'', and ''Katamari Damacy''.
''Pac-Man'' is considered one of the most important video games ever made, having helped encourage originality and creative thinking within the industry. Namco was recognized for the game's worldwide success in 2005 by Guinness World Records
''Guinness World Records'', known from its inception in 1955 until 1999 as ''The Guinness Book of Records'' and in previous United States editions as ''The Guinness Book of World Records'', is a reference book published annually, listing world ...
; by that timeframe, ''Pac-Man'' sold over 300,000 arcade units and grossed over $1 billion in quarters globally. In an obituary
An obituary ( obit for short) is an article about a recently deceased person. Newspapers often publish obituaries as news articles. Although obituaries tend to focus on positive aspects of the subject's life, this is not always the case. Ac ...
for Masaya Nakamura in 2017, ''Nintendo Life
Gamer Network Limited (formerly Eurogamer Network Limited) is a British mass media company based in Brighton. Founded in 1999 by Rupert and Nick Loman, it owns brands—primarily editorial websites—relating to video game journalism and other ...
''s Damien McFerran wrote: "without Namco and ''Pac-Man'', the video game arena would be very different today."
Namco's corporate philosophy and innovation have received recognition from publications. In a 1994 retrospective on the company, a writer for ''Edge
Edge or EDGE may refer to:
Technology Computing
* Edge computing, a network load-balancing system
* Edge device, an entry point to a computer network
* Adobe Edge, a graphical development application
* Microsoft Edge, a web browser developed by ...
'' described Namco as being "among the true pioneers of the coin-op business", a developer with a catalog of well-received and historically significant titles. The writer believed that Namco's success lay in its forward-thinking and firmness on quality, which they argued made it stand out from other developers. A staff member of ''Edge''s sister publication, '' Next Generation'', wrote in 1998: "In a world where today's stars almost always become tomorrow's has-beens, Namco has produced consistently excellent games throughout most of its history." The writer credited the company's connections with its players and its influential releases, namely ''Pac-Man'', ''Xevious'', and ''Winning Run'', as the keys to its success in a rapidly changing industry.
Publications and industry journalists have identified Namco's importance to the industry. Hirokazu Hamamura , former ''Weekly Famitsu'' chief editor, now is president of Enterbrain. He is also the director of Kadokawa Group Holdings, Kadokawa Group Publishing, Kadokawa Games and Walker Books. His pen name
A pen name, also called a ''nom de plume'' or a ...
, chief editor of ''Famitsu
formerly ''Famicom Tsūshin'', is a line of Japanese video game magazines published by Kadokawa Game Linkage (previously known as Gzbrain), a subsidiary of Kadokawa. ''Famitsu'' is published in both weekly and monthly formats as well as in the fo ...
'', credited the company's quality releases to the rise in popularity of video game consoles, and, in turn, the entirety of Japan's video game industry. Writers for ''Ultimate Future Games'' and ''Official UK PlayStation Magazine
An official is someone who holds an office (function or mandate, regardless whether it carries an actual working space with it) in an organization or government and participates in the exercise of authority, (either their own or that of their s ...
'' have credited the company and its games to the early success of the PlayStation, one of the most iconic entertainment brands worldwide. In addition, ''Official UK PlayStation Magazine'' wrote that Namco serves as "the godfather of game developers", and one of the most important video game developers in history.
Staff for ''IGN
''IGN'' (formerly ''Imagine Games Network'') is an American video game and entertainment media website operated by IGN Entertainment Inc., a subsidiary of Ziff Davis, Inc. The company's headquarters is located in San Francisco's SoMa distri ...
'' in 1997 claimed that Namco represents the industry as a whole, with titles like ''Pac-Man'' and ''Galaga'' being associated with and representing video games. They wrote: "Tracing the history of Namco is like tracing the history of the industry itself. From its humble beginnings on the roof of a Yokohama department store, to the impending release of ''Tekken 3'' for the PlayStation, Namco has always stayed ahead of the pack." In 2012, ''IGN'' listed Namco among the greatest video game companies of all time, writing that many of its games—including ''Galaga'', ''Pac-Man'', ''Dig Dug'', and ''Ridge Racer''—were of consistent quality and helped define the industry as a whole.
See also
*List of Namco games
Namco was a video game developer and publisher, originally from Japan.
Bandai Namco Entertainment is the successor to Namco and continues manufacturing and distributing video games worldwide. For Namco games released following the 2006 merger wit ...
Notes
References
External links
* {{Authority control 1955 establishments in Japan Amusement companies of Japan Bandai Namco Holdings Companies disestablished in 2006 Defunct video game companies of Japan Japanese brands Multinational companies headquartered in Japan Software companies based in Tokyo Video game development companies Video game companies established in 1955 Video game companies of Japan Video game publishers