Mammals Described In 1799 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a
 Mammal classification has been through several revisions since Carl Linnaeus initially defined the class, and at present, no classification system is universally accepted. McKenna & Bell (1997) and Wilson & Reeder (2005) provide useful recent compendiums. Simpson (1945) provides
Mammal classification has been through several revisions since Carl Linnaeus initially defined the class, and at present, no classification system is universally accepted. McKenna & Bell (1997) and Wilson & Reeder (2005) provide useful recent compendiums. Simpson (1945) provides
 As of the early 21st century, molecular studies based on DNA analysis have suggested new relationships among mammal families. Most of these findings have been independently validated by retrotransposon presence/absence data. Classification systems based on molecular studies reveal three major groups or lineages of placental mammals— Afrotheria, Xenarthra and Boreoeutheria—which diverged in the Cretaceous. The relationships between these three lineages is contentious, and all three possible hypotheses have been proposed with respect to which group is
As of the early 21st century, molecular studies based on DNA analysis have suggested new relationships among mammal families. Most of these findings have been independently validated by retrotransposon presence/absence data. Classification systems based on molecular studies reveal three major groups or lineages of placental mammals— Afrotheria, Xenarthra and Boreoeutheria—which diverged in the Cretaceous. The relationships between these three lineages is contentious, and all three possible hypotheses have been proposed with respect to which group is
 The first fully terrestrial vertebrates were
The first fully terrestrial vertebrates were
 The oldest known fossil among the Eutheria ("true beasts") is the small shrewlike ''
The oldest known fossil among the Eutheria ("true beasts") is the small shrewlike ''
 The earliest clear evidence of hair or fur is in fossils of ''
The earliest clear evidence of hair or fur is in fossils of ''
 On average, male mammals are larger than females, with males being at least 10% larger than females in over 45% of investigated species. Most mammalian orders also exhibit male-biased sexual dimorphism, although some orders do not show any bias or are significantly female-biased ( Lagomorpha). Sexual size dimorphism increases with body size across mammals (
On average, male mammals are larger than females, with males being at least 10% larger than females in over 45% of investigated species. Most mammalian orders also exhibit male-biased sexual dimorphism, although some orders do not show any bias or are significantly female-biased ( Lagomorpha). Sexual size dimorphism increases with body size across mammals (
 The majority of mammals have seven
The majority of mammals have seven 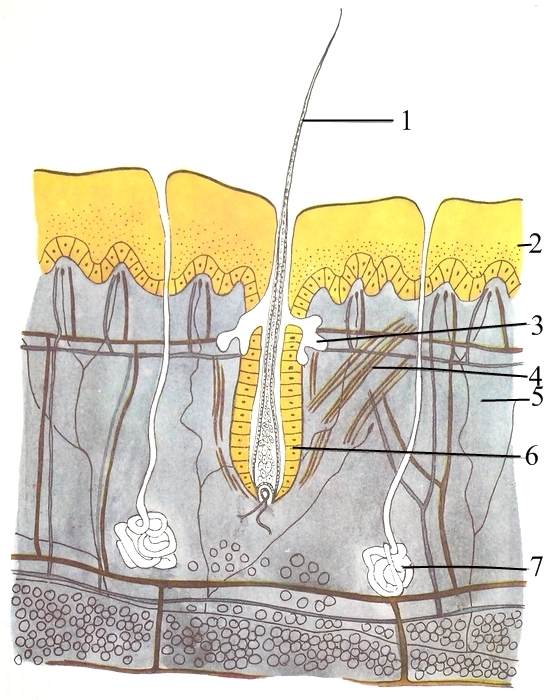 The
The  The mammalian excretory system involves many components. Like most other land animals, mammals are ureotelic, and convert ammonia into urea, which is done by the liver as part of the urea cycle.
The mammalian excretory system involves many components. Like most other land animals, mammals are ureotelic, and convert ammonia into urea, which is done by the liver as part of the urea cycle.
 As in all other tetrapods, mammals have a
As in all other tetrapods, mammals have a
 The primary function of the fur of mammals is thermoregulation. Others include protection, sensory purposes, waterproofing, and camouflage. Different types of fur serve different purposes:
* Definitive – which may be
The primary function of the fur of mammals is thermoregulation. Others include protection, sensory purposes, waterproofing, and camouflage. Different types of fur serve different purposes:
* Definitive – which may be
 Mammals are solely gonochoric (an animal is born with either male or female genitalia, as opposed to
Mammals are solely gonochoric (an animal is born with either male or female genitalia, as opposed to  The ancestral condition for mammal reproduction is the birthing of relatively undeveloped, either through direct vivipary or a short period as soft-shelled eggs. This is likely due to the fact that the torso could not expand due to the presence of epipubic bones. The oldest demonstration of this reproductive style is with '' Kayentatherium'', which produced undeveloped perinates, but at much higher litter sizes than any modern mammal, 38 specimens. Most modern mammals are viviparous, giving birth to live young. However, the five species of monotreme, the platypus and the four species of echidna, lay eggs. The monotremes have a
The ancestral condition for mammal reproduction is the birthing of relatively undeveloped, either through direct vivipary or a short period as soft-shelled eggs. This is likely due to the fact that the torso could not expand due to the presence of epipubic bones. The oldest demonstration of this reproductive style is with '' Kayentatherium'', which produced undeveloped perinates, but at much higher litter sizes than any modern mammal, 38 specimens. Most modern mammals are viviparous, giving birth to live young. However, the five species of monotreme, the platypus and the four species of echidna, lay eggs. The monotremes have a
 Most vertebrates—the amphibians, the reptiles and some mammals such as humans and bears—are
Most vertebrates—the amphibians, the reptiles and some mammals such as humans and bears—are
 Arboreal animals frequently have elongated limbs that help them cross gaps, reach fruit or other resources, test the firmness of support ahead and, in some cases, to brachiate (swing between trees). Many arboreal species, such as tree porcupines, silky anteaters, spider monkeys, and possums, use prehensile tails to grasp branches. In the spider monkey, the tip of the tail has either a bare patch or adhesive pad, which provides increased friction. Claws can be used to interact with rough substrates and reorient the direction of forces the animal applies. This is what allows
Arboreal animals frequently have elongated limbs that help them cross gaps, reach fruit or other resources, test the firmness of support ahead and, in some cases, to brachiate (swing between trees). Many arboreal species, such as tree porcupines, silky anteaters, spider monkeys, and possums, use prehensile tails to grasp branches. In the spider monkey, the tip of the tail has either a bare patch or adhesive pad, which provides increased friction. Claws can be used to interact with rough substrates and reorient the direction of forces the animal applies. This is what allows
 Many mammals communicate by vocalizing. Vocal communication serves many purposes, including in mating rituals, as alarm signal, warning calls, to indicate food sources, and for social purposes. Males often call during mating rituals to ward off other males and to attract females, as in the roar (vocalization), roaring of lions and red deer. The whale song, songs of the humpback whale may be signals to females; they have different dialects in different regions of the ocean. Social vocalizations include the territory (animal), territorial calls of gibbons, and the use of frequency in greater spear-nosed bats to distinguish between groups. The vervet monkey gives a distinct alarm call for each of at least four different predators, and the reactions of other monkeys vary according to the call. For example, if an alarm call signals a python, the monkeys climb into the trees, whereas the eagle alarm causes monkeys to seek a hiding place on the ground. Prairie dogs similarly have complex calls that signal the type, size, and speed of an approaching predator. Elephants communicate socially with a variety of sounds including snorting, screaming, trumpeting, roaring and rumbling. Some of the rumbling calls are infrasound, infrasonic, below the hearing range of humans, and can be heard by other elephants up to away at still times near sunrise and sunset.
file:Killer whale.ogg, left, Orca calling including occasional echolocation clicks
Mammals signal by a variety of means. Many give visual Anti-predator adaptation, anti-predator signals, as when deer and gazelle stotting, stot, honest signal, honestly indicating their fit condition and their ability to escape, or when white-tailed deer and other prey mammals flag with conspicuous tail markings when alarmed, informing the predator that it has been detected. Many mammals make use of scent-marking, sometimes possibly to help defend territory, but probably with a range of functions both within and between species. Microbats and toothed whales including oceanic dolphins vocalize both socially and in echolocation.
Many mammals communicate by vocalizing. Vocal communication serves many purposes, including in mating rituals, as alarm signal, warning calls, to indicate food sources, and for social purposes. Males often call during mating rituals to ward off other males and to attract females, as in the roar (vocalization), roaring of lions and red deer. The whale song, songs of the humpback whale may be signals to females; they have different dialects in different regions of the ocean. Social vocalizations include the territory (animal), territorial calls of gibbons, and the use of frequency in greater spear-nosed bats to distinguish between groups. The vervet monkey gives a distinct alarm call for each of at least four different predators, and the reactions of other monkeys vary according to the call. For example, if an alarm call signals a python, the monkeys climb into the trees, whereas the eagle alarm causes monkeys to seek a hiding place on the ground. Prairie dogs similarly have complex calls that signal the type, size, and speed of an approaching predator. Elephants communicate socially with a variety of sounds including snorting, screaming, trumpeting, roaring and rumbling. Some of the rumbling calls are infrasound, infrasonic, below the hearing range of humans, and can be heard by other elephants up to away at still times near sunrise and sunset.
file:Killer whale.ogg, left, Orca calling including occasional echolocation clicks
Mammals signal by a variety of means. Many give visual Anti-predator adaptation, anti-predator signals, as when deer and gazelle stotting, stot, honest signal, honestly indicating their fit condition and their ability to escape, or when white-tailed deer and other prey mammals flag with conspicuous tail markings when alarmed, informing the predator that it has been detected. Many mammals make use of scent-marking, sometimes possibly to help defend territory, but probably with a range of functions both within and between species. Microbats and toothed whales including oceanic dolphins vocalize both socially and in echolocation.
 Tool use by animals may indicate different levels of learning and Animal cognition, cognition. The Tool use by sea otters, sea otter uses rocks as essential and regular parts of its foraging behaviour (smashing abalone from rocks or breaking open shells), with some populations spending 21% of their time making tools. Other tool use, such as chimpanzees using twigs to "fish" for termites, may be developed by Observational learning, watching others use tools and may even be a true example of animal teaching. Tools may even be used in solving puzzles in which the animal appears to experience a Eureka effect, "Eureka moment". Other mammals that do not use tools, such as dogs, can also experience a Eureka moment.
Brain size was previously considered a major indicator of the intelligence of an animal. Since most of the brain is used for maintaining bodily functions, greater ratios of Brain-to-body mass ratio, brain to body mass may increase the amount of brain mass available for more complex cognitive tasks. Allometric analysis indicates that mammalian brain size scales at approximately the or exponent of the body mass. Comparison of a particular animal's brain size with the expected brain size based on such allometric analysis provides an encephalization quotient, encephalisation quotient that can be used as another indication of animal intelligence. Sperm whales have the largest brain mass of any animal on earth, averaging and in mature males.
Self-awareness appears to be a sign of abstract thinking. Self-awareness, although not well-defined, is believed to be a precursor to more advanced processes such as metacognition, metacognitive reasoning. The traditional method for measuring this is the mirror test, which determines if an animal possesses the ability of self-recognition. Mammals that have passed the mirror test include Asian elephants (some pass, some do not); chimpanzees; bonobos; orangutans; humans, from 18 months (mirror stage); bottlenose dolphins killer whales; and false killer whales.
Tool use by animals may indicate different levels of learning and Animal cognition, cognition. The Tool use by sea otters, sea otter uses rocks as essential and regular parts of its foraging behaviour (smashing abalone from rocks or breaking open shells), with some populations spending 21% of their time making tools. Other tool use, such as chimpanzees using twigs to "fish" for termites, may be developed by Observational learning, watching others use tools and may even be a true example of animal teaching. Tools may even be used in solving puzzles in which the animal appears to experience a Eureka effect, "Eureka moment". Other mammals that do not use tools, such as dogs, can also experience a Eureka moment.
Brain size was previously considered a major indicator of the intelligence of an animal. Since most of the brain is used for maintaining bodily functions, greater ratios of Brain-to-body mass ratio, brain to body mass may increase the amount of brain mass available for more complex cognitive tasks. Allometric analysis indicates that mammalian brain size scales at approximately the or exponent of the body mass. Comparison of a particular animal's brain size with the expected brain size based on such allometric analysis provides an encephalization quotient, encephalisation quotient that can be used as another indication of animal intelligence. Sperm whales have the largest brain mass of any animal on earth, averaging and in mature males.
Self-awareness appears to be a sign of abstract thinking. Self-awareness, although not well-defined, is believed to be a precursor to more advanced processes such as metacognition, metacognitive reasoning. The traditional method for measuring this is the mirror test, which determines if an animal possesses the ability of self-recognition. Mammals that have passed the mirror test include Asian elephants (some pass, some do not); chimpanzees; bonobos; orangutans; humans, from 18 months (mirror stage); bottlenose dolphins killer whales; and false killer whales.
 Eusociality is the highest level of social organization. These societies have an overlap of adult generations, the division of reproductive labor and cooperative caring of young. Usually insects, such as bees, ants and termites, have eusocial behavior, but it is demonstrated in two rodent species: the naked mole-rat and the Damaraland mole-rat.
Presociality is when animals exhibit more than just sexual interactions with members of the same species, but fall short of qualifying as eusocial. That is, presocial animals can display communal living, cooperative care of young, or primitive division of reproductive labor, but they do not display all of the three essential traits of eusocial animals. Humans and some species of Callitrichidae (marmosets and tamarins) are unique among primates in their degree of cooperative care of young. Harry Harlow set up an experiment with rhesus monkeys, presocial primates, in 1958; the results from this study showed that social encounters are necessary in order for the young monkeys to develop both mentally and sexually.
A fission-fusion society is a society that changes frequently in its size and composition, making up a permanent social group called the "parent group". Permanent social networks consist of all individual members of a community and often varies to track changes in their environment. In a fission–fusion society, the main parent group can fracture (fission) into smaller stable subgroups or individuals to adapt to Social environment, environmental or social circumstances. For example, a number of males may break off from the main group in order to hunt or forage for food during the day, but at night they may return to join (fusion) the primary group to share food and partake in other activities. Many mammals exhibit this, such as primates (for example orangutans and spider monkeys), elephants, spotted hyenas, lions, and dolphins.
Solitary animals defend a territory and avoid social interactions with the members of its species, except during breeding season. This is to avoid resource competition, as two individuals of the same species would occupy the same niche, and to prevent depletion of food. A solitary animal, while foraging, can also be less conspicuous to predators or prey.
Eusociality is the highest level of social organization. These societies have an overlap of adult generations, the division of reproductive labor and cooperative caring of young. Usually insects, such as bees, ants and termites, have eusocial behavior, but it is demonstrated in two rodent species: the naked mole-rat and the Damaraland mole-rat.
Presociality is when animals exhibit more than just sexual interactions with members of the same species, but fall short of qualifying as eusocial. That is, presocial animals can display communal living, cooperative care of young, or primitive division of reproductive labor, but they do not display all of the three essential traits of eusocial animals. Humans and some species of Callitrichidae (marmosets and tamarins) are unique among primates in their degree of cooperative care of young. Harry Harlow set up an experiment with rhesus monkeys, presocial primates, in 1958; the results from this study showed that social encounters are necessary in order for the young monkeys to develop both mentally and sexually.
A fission-fusion society is a society that changes frequently in its size and composition, making up a permanent social group called the "parent group". Permanent social networks consist of all individual members of a community and often varies to track changes in their environment. In a fission–fusion society, the main parent group can fracture (fission) into smaller stable subgroups or individuals to adapt to Social environment, environmental or social circumstances. For example, a number of males may break off from the main group in order to hunt or forage for food during the day, but at night they may return to join (fusion) the primary group to share food and partake in other activities. Many mammals exhibit this, such as primates (for example orangutans and spider monkeys), elephants, spotted hyenas, lions, and dolphins.
Solitary animals defend a territory and avoid social interactions with the members of its species, except during breeding season. This is to avoid resource competition, as two individuals of the same species would occupy the same niche, and to prevent depletion of food. A solitary animal, while foraging, can also be less conspicuous to predators or prey.
 In a dominance hierarchy, hierarchy, individuals are either dominant or submissive. A despotic hierarchy is where one individual is dominant while the others are submissive, as in wolves and lemurs, and a pecking order is a linear ranking of individuals where there is a top individual and a bottom individual. Pecking orders may also be ranked by sex, where the lowest individual of a sex has a higher ranking than the top individual of the other sex, as in hyenas. Dominant individuals, or alphas, have a high chance of reproductive success, especially in harems where one or a few males (resident males) have exclusive breeding rights to females in a group. Non-resident males can also be accepted in harems, but some species, such as the common vampire bat (''Desmodus rotundus''), may be more strict.
Some mammals are perfectly Monogamy in animals, monogamous, meaning that they pair bond, mate for life and take no other partners (even after the original mate's death), as with wolves, Eurasian beavers, and otters. There are three types of polygamy: either one or multiple dominant males have breeding rights (polygyny in animals, polygyny), multiple males that females mate with (polyandry), or multiple males have exclusive relations with multiple females (polygynandry). It is much more common for polygynous mating to happen, which, excluding lek mating, leks, are estimated to occur in up to 90% of mammals. Lek mating occurs when males congregate around females and try to attract them with various courtship displays and vocalizations, as in harbor seals.
All higher mammals (excluding monotremes) share two major adaptations for care of the young: live birth and lactation. These imply a group-wide choice of a degree of parental care. They may build nests and dig burrows to raise their young in, or feed and guard them often for a prolonged period of time. Many mammals are K-selected, and invest more time and energy into their young than do r-selected animals. When two animals mate, they both share an interest in the success of the offspring, though often to different extremes. Mammalian females exhibit some degree of maternal aggression, another example of parental care, which may be targeted against other females of the species or the young of other females; however, some mammals may "aunt" the infants of other females, and care for them. Mammalian males may play a role in child rearing, as with tenrecs, however this varies species to species, even within the same genus. For example, the males of the southern pig-tailed macaque (''Macaca nemestrina'') do not participate in child care, whereas the males of the Japanese macaque (''M. fuscata'') do.
In a dominance hierarchy, hierarchy, individuals are either dominant or submissive. A despotic hierarchy is where one individual is dominant while the others are submissive, as in wolves and lemurs, and a pecking order is a linear ranking of individuals where there is a top individual and a bottom individual. Pecking orders may also be ranked by sex, where the lowest individual of a sex has a higher ranking than the top individual of the other sex, as in hyenas. Dominant individuals, or alphas, have a high chance of reproductive success, especially in harems where one or a few males (resident males) have exclusive breeding rights to females in a group. Non-resident males can also be accepted in harems, but some species, such as the common vampire bat (''Desmodus rotundus''), may be more strict.
Some mammals are perfectly Monogamy in animals, monogamous, meaning that they pair bond, mate for life and take no other partners (even after the original mate's death), as with wolves, Eurasian beavers, and otters. There are three types of polygamy: either one or multiple dominant males have breeding rights (polygyny in animals, polygyny), multiple males that females mate with (polyandry), or multiple males have exclusive relations with multiple females (polygynandry). It is much more common for polygynous mating to happen, which, excluding lek mating, leks, are estimated to occur in up to 90% of mammals. Lek mating occurs when males congregate around females and try to attract them with various courtship displays and vocalizations, as in harbor seals.
All higher mammals (excluding monotremes) share two major adaptations for care of the young: live birth and lactation. These imply a group-wide choice of a degree of parental care. They may build nests and dig burrows to raise their young in, or feed and guard them often for a prolonged period of time. Many mammals are K-selected, and invest more time and energy into their young than do r-selected animals. When two animals mate, they both share an interest in the success of the offspring, though often to different extremes. Mammalian females exhibit some degree of maternal aggression, another example of parental care, which may be targeted against other females of the species or the young of other females; however, some mammals may "aunt" the infants of other females, and care for them. Mammalian males may play a role in child rearing, as with tenrecs, however this varies species to species, even within the same genus. For example, the males of the southern pig-tailed macaque (''Macaca nemestrina'') do not participate in child care, whereas the males of the Japanese macaque (''M. fuscata'') do.
 Non-human mammals play a wide variety of roles in human culture. They are the most popular of pets, with tens of millions of dogs, cats and other animals including rabbits and mice kept by families around the world. Mammals such as mammoths, horses and deer are among the earliest subjects of art, being found in Upper Paleolithic cave paintings such as at Lascaux. Major artists such as Albrecht Dürer, George Stubbs and Edwin Landseer are known for their portraits of mammals. Many species of mammals have been hunted for sport and for food; deer and wild boar are especially popular as game (hunting), game animals. Mammals such as horse racing, horses and greyhound racing, dogs are widely raced for sport, often combined with gambling, betting on the outcome. There is a tension between the role of animals as companions to humans, and their existence as individuals with animal rights, rights of their own. Mammals further play a wide variety of roles in literature, film, mythology, and religion.
Non-human mammals play a wide variety of roles in human culture. They are the most popular of pets, with tens of millions of dogs, cats and other animals including rabbits and mice kept by families around the world. Mammals such as mammoths, horses and deer are among the earliest subjects of art, being found in Upper Paleolithic cave paintings such as at Lascaux. Major artists such as Albrecht Dürer, George Stubbs and Edwin Landseer are known for their portraits of mammals. Many species of mammals have been hunted for sport and for food; deer and wild boar are especially popular as game (hunting), game animals. Mammals such as horse racing, horses and greyhound racing, dogs are widely raced for sport, often combined with gambling, betting on the outcome. There is a tension between the role of animals as companions to humans, and their existence as individuals with animal rights, rights of their own. Mammals further play a wide variety of roles in literature, film, mythology, and religion.
 The domestication of mammals was instrumental in the Neolithic Revolution, Neolithic development of agriculture and of civilization, causing farmers to replace hunter-gatherers around the world. This transition from hunting and gathering to pastoralism, herding flocks and agriculture, growing crops was a major step in human history. The new agricultural economies, based on domesticated mammals, caused "radical restructuring of human societies, worldwide alterations in biodiversity, and significant changes in the Earth's landforms and its atmosphere... momentous outcomes".
Domestication, Domestic mammals form a large part of the livestock raised for
The domestication of mammals was instrumental in the Neolithic Revolution, Neolithic development of agriculture and of civilization, causing farmers to replace hunter-gatherers around the world. This transition from hunting and gathering to pastoralism, herding flocks and agriculture, growing crops was a major step in human history. The new agricultural economies, based on domesticated mammals, caused "radical restructuring of human societies, worldwide alterations in biodiversity, and significant changes in the Earth's landforms and its atmosphere... momentous outcomes".
Domestication, Domestic mammals form a large part of the livestock raised for  Mammals serve a major role in science as animal model, experimental animals, both in fundamental biological research, such as in genetics, and in the development of new medicines, which must be tested exhaustively to demonstrate their Pharmacovigilance, safety. Millions of mammals, especially mice and rats, are used in animal testing, experiments each year. A knockout mouse is a genetically modified mouse with an inactivated gene, replaced or disrupted with an artificial piece of DNA. They enable the study of sequencing, sequenced genes whose functions are unknown. A small percentage of the mammals are non-human primates, used in research for their similarity to humans.
Despite the benefits domesticated mammals had for human development, humans have an increasingly detrimental effect on wild mammals across the world. It has been estimated that the mass of all ''wild'' mammals has declined to only 4% of all mammals, with 96% of mammals being humans and their livestock now (see figure). In fact, terrestrial wild mammals make up only 2% of all mammals.
Mammals serve a major role in science as animal model, experimental animals, both in fundamental biological research, such as in genetics, and in the development of new medicines, which must be tested exhaustively to demonstrate their Pharmacovigilance, safety. Millions of mammals, especially mice and rats, are used in animal testing, experiments each year. A knockout mouse is a genetically modified mouse with an inactivated gene, replaced or disrupted with an artificial piece of DNA. They enable the study of sequencing, sequenced genes whose functions are unknown. A small percentage of the mammals are non-human primates, used in research for their similarity to humans.
Despite the benefits domesticated mammals had for human development, humans have an increasingly detrimental effect on wild mammals across the world. It has been estimated that the mass of all ''wild'' mammals has declined to only 4% of all mammals, with 96% of mammals being humans and their livestock now (see figure). In fact, terrestrial wild mammals make up only 2% of all mammals.
 The loss of species from ecological communities, defaunation, is primarily driven by human activity. This has resulted in empty forests, ecological communities depleted of large vertebrates. In the Quaternary extinction event, the mass die-off of megafaunal variety coincided with the appearance of humans, suggesting a human influence. One hypothesis is that humans hunted large mammals, such as the woolly mammoth, into extinction. The 2019 ''Global Assessment Report on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services'' by IPBES states that the total Biomass (ecology), biomass of wild mammals has declined by 82 percent since the beginning of human civilization. Wild animals make up just 4% of mammalian Biomass (ecology), biomass on earth, while humans and their domesticated animals make up 96%.
Various species are predicted to List of critically endangered species, become extinct in the near future, among them the rhinoceros, giraffes, and species of primates and pangolins. According to the WWF's 2020 ''Living Planet Report'', vertebrate wildlife populations have declined by 68% since 1970 as a result of human activities, particularly overconsumption, population growth and intensive farming, which is evidence that humans have triggered a sixth mass extinction event. Hunting alone threatens hundreds of mammalian species around the world. Scientists claim that the growing demand for
The loss of species from ecological communities, defaunation, is primarily driven by human activity. This has resulted in empty forests, ecological communities depleted of large vertebrates. In the Quaternary extinction event, the mass die-off of megafaunal variety coincided with the appearance of humans, suggesting a human influence. One hypothesis is that humans hunted large mammals, such as the woolly mammoth, into extinction. The 2019 ''Global Assessment Report on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services'' by IPBES states that the total Biomass (ecology), biomass of wild mammals has declined by 82 percent since the beginning of human civilization. Wild animals make up just 4% of mammalian Biomass (ecology), biomass on earth, while humans and their domesticated animals make up 96%.
Various species are predicted to List of critically endangered species, become extinct in the near future, among them the rhinoceros, giraffes, and species of primates and pangolins. According to the WWF's 2020 ''Living Planet Report'', vertebrate wildlife populations have declined by 68% since 1970 as a result of human activities, particularly overconsumption, population growth and intensive farming, which is evidence that humans have triggered a sixth mass extinction event. Hunting alone threatens hundreds of mammalian species around the world. Scientists claim that the growing demand for
Biodiversitymapping.org – All mammal orders in the world with distribution maps
Paleocene Mammals
a site covering the rise of the mammals, paleocene-mammals.de
Evolution of Mammals
a brief introduction to early mammals, enchantedlearning.com
European Mammal Atlas EMMA
from Societas Europaea Mammalogica, European-mammals.org
Marine Mammals of the World
– An overview of all marine mammals, including descriptions, both fully aquatic and semi-aquatic, noaa.gov
Mammalogy.org
The American Society of Mammalogists was established in 1919 for the purpose of promoting the study of mammals, and this website includes a mammal image library {{Authority control Mammals, Bathonian first appearances Extant Middle Jurassic first appearances Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus
neocortex
The neocortex, also called the neopallium, isocortex, or the six-layered cortex, is a set of layers of the mammalian cerebral cortex involved in higher-order brain functions such as sensory perception, cognition, generation of motor commands, sp ...
(a region of the brain), fur or hair
Hair is a protein filament that grows from follicles found in the dermis. Hair is one of the defining characteristics of mammals.
The human body, apart from areas of glabrous skin, is covered in follicles which produce thick terminal and f ...
, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptile
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians ( ...
s (including birds) from which they diverged in the Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic that spans 60 million years from the end of the Devonian Period million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Permian Period, million years ago. The name ''Carbonifero ...
, over 300 million years ago. Around 6,400 extant
Extant is the opposite of the word extinct. It may refer to:
* Extant hereditary titles
* Extant literature, surviving literature, such as ''Beowulf'', the oldest extant manuscript written in English
* Extant taxon, a taxon which is not extinct, ...
species of mammals have been described divided into 29 orders
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
* Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of d ...
. The largest orders
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
* Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of d ...
, in terms of number of species, are the rodents
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the order Rodentia (), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are nat ...
, bats, and Eulipotyphla ( hedgehogs, moles, shrews, and others). The next three are the Primates (including humans, apes, monkey
Monkey is a common name that may refer to most mammals of the infraorder Simiiformes, also known as the simians. Traditionally, all animals in the group now known as simians are counted as monkeys except the apes, which constitutes an incomple ...
s, and others), the Artiodactyla (cetacean
Cetacea (; , ) is an infraorder of aquatic mammals that includes whales, dolphins, and porpoises. Key characteristics are their fully aquatic lifestyle, streamlined body shape, often large size and exclusively carnivorous diet. They propel them ...
s and even-toed ungulates), and the Carnivora
Carnivora is a Clade, monophyletic order of Placentalia, placental mammals consisting of the most recent common ancestor of all felidae, cat-like and canidae, dog-like animals, and all descendants of that ancestor. Members of this group are f ...
( cats, dogs, seals
Seals may refer to:
* Pinniped, a diverse group of semi-aquatic marine mammals, many of which are commonly called seals, particularly:
** Earless seal, or "true seal"
** Fur seal
* Seal (emblem), a device to impress an emblem, used as a means of a ...
, and others).
In terms of cladistics, which reflects evolutionary history, mammals are the only living members of the Synapsida (synapsids); this clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, ...
, together with Sauropsida
Sauropsida ("lizard faces") is a clade of amniotes, broadly equivalent to the class Reptilia. Sauropsida is the sister taxon to Synapsida, the other clade of amniotes which includes mammals as its only modern representatives. Although early syna ...
(reptiles and birds), constitutes the larger Amniota clade. The early synapsids were sphenacodonts
Sphenacodontia is a stem-based clade of derived synapsids. It was defined by Amson and Laurin (2011) as "the largest clade that includes ''Haptodus baylei'', ''Haptodus garnettensis'' and ''Sphenacodon ferox'', but not ''Edaphosaurus pogonias'' ...
, a group that included the famous ''Dimetrodon
''Dimetrodon'' ( or ,) meaning "two measures of teeth,” is an extinct genus of non-mammalian synapsid that lived during the Cisuralian (Early Permian), around 295–272 million years ago (Mya). It is a member of the family Sphenacodontid ...
''. The synapsids split into several diverse groups of non-mammalian synapsids — traditionally and incorrectly referred to as mammal-like reptiles or by the term pelycosaurs, and now known as stem mammals or protomammals — before giving rise to therapsids during the beginning of the Middle Permian period. Mammals originated from cynodont
The cynodonts () (clade Cynodontia) are a clade of eutheriodont therapsids that first appeared in the Late Permian (approximately 260 mya), and extensively diversified after the Permian–Triassic extinction event. Cynodonts had a wide variety ...
s, an advanced group of therapsids, during the Late Triassic-Early Jurassic. The modern mammalian orders arose in the Paleogene
The Paleogene ( ; British English, also spelled Palaeogene or Palæogene; informally Lower Tertiary or Early Tertiary) is a geologic period, geologic period and system that spans 43 million years from the end of the Cretaceous Period million yea ...
and Neogene
The Neogene ( ), informally Upper Tertiary or Late Tertiary, is a geologic period and system that spans 20.45 million years from the end of the Paleogene Period million years ago ( Mya) to the beginning of the present Quaternary Period Mya. ...
periods of the Cenozoic
The Cenozoic ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterised by the dominance of mammals, birds and flowering plants, a cooling and drying climate, and the current configura ...
era, after the extinction of non-avian dinosaurs, and have been the dominant terrestrial animal group from 66 million years ago to the present.
The basic body type is quadruped, and most mammals use their four extremities for terrestrial locomotion; but in some, the extremities are adapted for life at sea, in the air, in trees, underground, or on two legs. Mammals range in size from the bumblebee bat to the blue whale—possibly the largest animal to have ever lived. Maximum lifespan varies from two years for the shrew to 211 years for the bowhead whale
The bowhead whale (''Balaena mysticetus'') is a species of baleen whale belonging to the family Balaenidae and the only living representative of the genus ''Balaena''. They are the only baleen whale endemic to the Arctic and subarctic waters, ...
. All modern mammals give birth to live young, except the five species of monotreme
Monotremes () are prototherian mammals of the order Monotremata. They are one of the three groups of living mammals, along with placentals (Eutheria), and marsupials (Metatheria). Monotremes are typified by structural differences in their brain ...
s, which are egg-laying mammals. The most species-rich group of mammals, the cohort called placentals, have a placenta, which enables the feeding of the fetus during gestation
Gestation is the period of development during the carrying of an embryo, and later fetus, inside viviparous animals (the embryo develops within the parent). It is typical for mammals, but also occurs for some non-mammals. Mammals during pregna ...
.
Most mammals are intelligent, with some possessing large brains, self-awareness
In philosophy of self, self-awareness is the experience of one's own personality or individuality. It is not to be confused with consciousness in the sense of qualia. While consciousness is being aware of one's environment and body and lifesty ...
, and tool use. Mammals can communicate and vocalize in several ways, including the production of ultrasound, scent-marking, alarm signals, singing, and echolocation. Mammals can organize themselves into fission-fusion societies, harems, and hierarchies—but can also be solitary and territorial. Most mammals are polygynous
Polygyny (; from Neoclassical Greek πολυγυνία (); ) is the most common and accepted form of polygamy around the world, entailing the marriage of a man with several women.
Incidence
Polygyny is more widespread in Africa than in any ...
, but some can be monogamous
Monogamy ( ) is a form of Dyad (sociology), dyadic Intimate relationship, relationship in which an individual has only one Significant other, partner during their lifetime. Alternately, only one partner at any one time (Monogamy#Serial monogamy, ...
or polyandrous.
Domestication of many types of mammals by humans played a major role in the Neolithic Revolution
The Neolithic Revolution, or the (First) Agricultural Revolution, was the wide-scale transition of many human cultures during the Neolithic period from a lifestyle of hunting and gathering to one of agriculture and settlement, making an incre ...
, and resulted in farming replacing hunting and gathering as the primary source of food for humans. This led to a major restructuring of human societies from nomadic to sedentary, with more co-operation among larger and larger groups, and ultimately the development of the first civilizations. Domesticated mammals provided, and continue to provide, power for transport and agriculture, as well as food (meat
Meat is animal flesh that is eaten as food. Humans have hunted, farmed, and scavenged animals for meat since prehistoric times. The establishment of settlements in the Neolithic Revolution allowed the domestication of animals such as chic ...
and dairy product
Dairy products or milk products, also known as lacticinia, are food products made from (or containing) milk. The most common dairy animals are cow, water buffalo, nanny goat, and ewe. Dairy products include common grocery store food items in th ...
s), fur, and leather. Mammals are also hunted and raced for sport, and are used as model organism
A model organism (often shortened to model) is a non-human species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in the model organism will provide insight into the workin ...
s in science. Mammals have been depicted in art since Paleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic (), also called the Old Stone Age (from Greek: παλαιός ''palaios'', "old" and λίθος ''lithos'', "stone"), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone too ...
times, and appear in literature, film, mythology, and religion. Decline in numbers and extinction of many mammals is primarily driven by human poaching and habitat destruction, primarily deforestation.
Classification
systematics
Biological systematics is the study of the diversification of living forms, both past and present, and the relationships among living things through time. Relationships are visualized as evolutionary trees (synonyms: cladograms, phylogenetic tre ...
of mammal origins and relationships that had been taught universally until the end of the 20th century.
However, since 1945, a large amount of new and more detailed information has gradually been found: The paleontological record has been recalibrated, and the intervening years have seen much debate and progress concerning the theoretical underpinnings of systematization itself, partly through the new concept of cladistics. Though fieldwork and lab work progressively outdated Simpson's classification, it remains the closest thing to an official classification of mammals, despite its known issues.
Most mammals, including the six most species-rich orders
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
* Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of d ...
, belong to the placental group. The three largest orders in numbers of species are Rodentia: mice
A mouse ( : mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus' ...
, rat
Rats are various medium-sized, long-tailed rodents. Species of rats are found throughout the order Rodentia, but stereotypical rats are found in the genus ''Rattus''. Other rat genera include ''Neotoma'' ( pack rats), ''Bandicota'' (bandicoot ...
s, porcupine
Porcupines are large rodents with coats of sharp spines, or quills, that protect them against predation. The term covers two families of animals: the Old World porcupines of family Hystricidae, and the New World porcupines of family, Erethizont ...
s, beaver
Beavers are large, semiaquatic rodents in the genus ''Castor'' native to the temperate Northern Hemisphere. There are two extant species: the North American beaver (''Castor canadensis'') and the Eurasian beaver (''C. fiber''). Beavers ar ...
s, capybara
The capybaraAlso called capivara (in Brazil), capiguara (in Bolivia), chigüire, chigüiro, or fercho (in Colombia and Venezuela), carpincho (in Argentina, Paraguay and Uruguay) and ronsoco (in Peru). or greater capybara (''Hydrochoerus hydro ...
s, and other gnawing mammals; Chiroptera: bats; and Soricomorpha: shrews, moles, and solenodons. The next three biggest orders, depending on the biological classification scheme used, are the Primates: apes, monkey
Monkey is a common name that may refer to most mammals of the infraorder Simiiformes, also known as the simians. Traditionally, all animals in the group now known as simians are counted as monkeys except the apes, which constitutes an incomple ...
s, and lemurs; the Cetartiodactyla: whales and even-toed ungulates; and the Carnivora
Carnivora is a Clade, monophyletic order of Placentalia, placental mammals consisting of the most recent common ancestor of all felidae, cat-like and canidae, dog-like animals, and all descendants of that ancestor. Members of this group are f ...
which includes cats, dogs, weasels, bear
Bears are carnivoran mammals of the family Ursidae. They are classified as caniforms, or doglike carnivorans. Although only eight species of bears are extant, they are widespread, appearing in a wide variety of habitats throughout the Nor ...
s, seals
Seals may refer to:
* Pinniped, a diverse group of semi-aquatic marine mammals, many of which are commonly called seals, particularly:
** Earless seal, or "true seal"
** Fur seal
* Seal (emblem), a device to impress an emblem, used as a means of a ...
, and allies. According to '' Mammal Species of the World'', 5,416 species were identified in 2006. These were grouped into 1,229 genera
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclat ...
, 153 families and 29 orders. In 2008, the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) completed a five-year Global Mammal Assessment for its IUCN Red List, which counted 5,488 species. According to research published in the '' Journal of Mammalogy'' in 2018, the number of recognized mammal species is 6,495, including 96 recently extinct.
Definitions
The word "mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or ...
" is modern, from the scientific name ''Mammalia'' coined by Carl Linnaeus in 1758, derived from the Latin ''mamma
Mama(s) or Mamma or Momma may refer to:
Roles
*Mother, a female parent
*Mama-san, in Japan and East Asia, a woman in a position of authority
*Mamas, a name for female associates of the Hells Angels
Places
*Mama, Russia, an urban-type settlement ...
'' ("teat, pap"). In an influential 1988 paper, Timothy Rowe defined Mammalia phylogenetically
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups o ...
as the crown group
In phylogenetics, the crown group or crown assemblage is a collection of species composed of the living representatives of the collection, the most recent common ancestor of the collection, and all descendants of the most recent common ancestor. ...
of mammals, the clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, ...
consisting of the most recent common ancestor of living monotreme
Monotremes () are prototherian mammals of the order Monotremata. They are one of the three groups of living mammals, along with placentals (Eutheria), and marsupials (Metatheria). Monotremes are typified by structural differences in their brain ...
s ( echidnas and platypuses) and Therian mammals ( marsupials and placentals) and all descendants of that ancestor. Since this ancestor lived in the Jurassic period, Rowe's definition excludes all animals from the earlier Triassic, despite the fact that Triassic fossils in the Haramiyida
Haramiyida ("thief" from Arabic الحرامية (al ḥarāmiyah), "thief, bandit") is a possibly polyphyletic order of mammaliaform cynodonts or mammals of controversial taxonomic affinites. Their teeth, which are by far the most common remains ...
have been referred to the Mammalia since the mid-19th century. If Mammalia is considered as the crown group, its origin can be roughly dated as the first known appearance of animals more closely related to some extant mammals than to others. '' Ambondro'' is more closely related to monotremes than to therian mammals while ''Amphilestes
''Amphilestes'' is a genus of extinct eutriconodont mammal from the Middle Jurassic of the United Kingdom. It was one of the first Mesozoic mammals discovered and described.
Discovery
The first specimen of ''Amphilestes'' was discovered along ...
'' and '' Amphitherium'' are more closely related to the therians; as fossils of all three genera are dated about in the Middle Jurassic
The Middle Jurassic is the second epoch of the Jurassic Period. It lasted from about 174.1 to 163.5 million years ago. Fossils of land-dwelling animals, such as dinosaurs, from the Middle Jurassic are relatively rare, but geological formations co ...
, this is a reasonable estimate for the appearance of the crown group.
T.S. Kemp has provided a more traditional definition: " Synapsids that possess a dentary– squamosal jaw articulation and occlusion between upper and lower molars with a transverse component to the movement" or, equivalently in Kemp's view, the clade originating with the last common ancestor of '' Sinoconodon'' and living mammals. The earliest known synapsid satisfying Kemp's definitions is ''Tikitherium
''Tikitherium'' is an extinct genus of mammaliaforms from the Late Triassic. It is thought to be an insectivore and a close relative to Docodonta. ''Tikitherium'' refers to Tiki, the village located near the Tiki Formation where the specimen wa ...
'', dated , so the appearance of mammals in this broader sense can be given this Late Triassic date.
McKenna/Bell classification
In 1997, the mammals were comprehensively revised byMalcolm C. McKenna
Malcolm Carnegie McKenna (1930–2008) was an American paleontologist and author on the subject.
Paleontologist
McKenna began his paleontology career at the Webb School of California (grades 9-12) in Claremont, California, under noted paleontol ...
and Susan K. Bell, which has resulted in the McKenna/Bell classification. The authors worked together as paleontologists at the American Museum of Natural History
The American Museum of Natural History (abbreviated as AMNH) is a natural history museum on the Upper West Side of Manhattan in New York City. In Theodore Roosevelt Park, across the street from Central Park, the museum complex comprises 26 inter ...
. McKenna inherited the project from Simpson and, with Bell, constructed a completely updated hierarchical system, covering living and extinct taxa, that reflects the historical genealogy of Mammalia. Their 1997 book, ''Classification of Mammals above the Species Level'', is a comprehensive work on the systematics, relationships and occurrences of all mammal taxa, living and extinct, down through the rank of genus, though molecular genetic data challenge several of the groupings.
In the following list, extinct
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and ...
groups are labelled with a dagger (†).
Class Mammalia
* Subclass Prototheria: monotremes: echidnas and the platypus
* Subclass Theriiformes: live-bearing mammals and their prehistoric relatives
** Infraclass † Allotheria: multituberculates
** Infraclass † Eutriconodonta: eutriconodonts
** Infraclass Holotheria: modern live-bearing mammals and their prehistoric relatives
*** Superlegion †Kuehneotheria
Kuehneotheriidae is an extinct family of mammaliaforms traditionally placed within 'Symmetrodonta', though now generally considered more basal than true symmetrodonts. All members of Kuehneotheriidae which have been found so far are represented o ...
*** Supercohort Theria: live-bearing mammals
**** Cohort Marsupialia: marsupials
***** Magnorder Australidelphia
Australidelphia is the superorder that contains roughly three-quarters of all marsupials, including all those native to Australasia and a single species — the monito del monte — from South America. All other American marsupials are members of ...
: Australian marsupials and the monito del monte
***** Magnorder Ameridelphia: New World marsupials. Now considered paraphyletic, with shrew opossums being closer to australidelphians.
**** Cohort Placentalia
Placental mammals (infraclass Placentalia ) are one of the three extant subdivisions of the class Mammalia, the other two being Monotremata and Marsupialia. Placentalia contains the vast majority of extant mammals, which are partly distinguished ...
: placentals
***** Magnorder Xenarthra: xenarthrans
***** Magnorder Epitheria: epitheres
****** Superorder † Leptictida
****** Superorder Preptotheria
******* Grandorder Anagalida: lagomorphs
The lagomorphs are the members of the taxonomic order Lagomorpha, of which there are two living families: the Leporidae ( hares and rabbits) and the Ochotonidae (pikas). The name of the order is derived from the Ancient Greek ''lagos'' (λα� ...
, rodents and elephant shrews
******* Grandorder Ferae: carnivora
Carnivora is a Clade, monophyletic order of Placentalia, placental mammals consisting of the most recent common ancestor of all felidae, cat-like and canidae, dog-like animals, and all descendants of that ancestor. Members of this group are f ...
ns, pangolin
Pangolins, sometimes known as scaly anteaters, are mammals of the order Pholidota (, from Ancient Greek ϕολιδωτός – "clad in scales"). The one extant family, the Manidae, has three genera: '' Manis'', '' Phataginus'', and '' Smut ...
s, † creodonts and relatives
******* Grandorder Lipotyphla: insectivorans
******* Grandorder Archonta: bats, primates, colugos and treeshrews (now considered paraphyletic, with bats being closer to other groups)
******* Grandorder Ungulata
Ungulates ( ) are members of the diverse clade Ungulata which primarily consists of large mammals with hooves. These include odd-toed ungulates such as horses, rhinoceroses, and tapirs; and even-toed ungulates such as cattle, pigs, giraffes, ...
: ungulates
******** Order Tubulidentata '' incertae sedis'': aardvark
******** Mirorder Eparctocyona
Eparctocyona is a clade of placental mammals comprising the artiodactyls (even-toed ungulates), cetacea
Cetacea (; , ) is an infraorder of aquatic mammals that includes whales, dolphins, and porpoises. Key characteristics are their fully aq ...
: † condylarths, whales and artiodactyls (even-toed ungulates)
******** Mirorder † Meridiungulata: South American ungulates
******** Mirorder Altungulata: perissodactyls (odd-toed ungulates), elephants, manatees and hyrax
Hyraxes (), also called dassies, are small, thickset, herbivorous mammals in the order Hyracoidea. Hyraxes are well-furred, rotund animals with short tails. Typically, they measure between long and weigh between . They are superficially simil ...
es
Molecular classification of placentals
basal
Basal or basilar is a term meaning ''base'', ''bottom'', or ''minimum''.
Science
* Basal (anatomy), an anatomical term of location for features associated with the base of an organism or structure
* Basal (medicine), a minimal level that is nec ...
. These hypotheses are Atlantogenata (basal Boreoeutheria), Epitheria (basal Xenarthra) and Exafroplacentalia (basal Afrotheria). Boreoeutheria in turn contains two major lineages— Euarchontoglires and Laurasiatheria.
Estimates for the divergence times between these three placental groups range from 105 to 120 million years ago, depending on the type of DNA used (such as nuclear
Nuclear may refer to:
Physics
Relating to the nucleus of the atom:
*Nuclear engineering
*Nuclear physics
*Nuclear power
*Nuclear reactor
*Nuclear weapon
*Nuclear medicine
*Radiation therapy
*Nuclear warfare
Mathematics
*Nuclear space
* Nuclear ...
or mitochondrial
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is use ...
) and varying interpretations of paleogeographic
Palaeogeography (or paleogeography) is the study of historical geography, generally physical landscapes. Palaeogeography can also include the study of human or cultural environments. When the focus is specifically on landforms, the term paleo ...
data.
The cladogram above is based on Tarver ''et al.''. (2016)
Evolution
Origins
Synapsida, a clade that contains mammals and their extinct relatives, originated during the Pennsylvanian subperiod (~323 million to ~300 million years ago), when they split from the reptile lineage. Crown group mammals evolved from earlier mammaliaforms during the Early Jurassic. The cladogram takes Mammalia to be the crown group.Evolution from older amniotes
 The first fully terrestrial vertebrates were
The first fully terrestrial vertebrates were amniote
Amniotes are a clade of tetrapod vertebrates that comprises sauropsids (including all reptiles and birds, and extinct parareptiles and non-avian dinosaurs) and synapsids (including pelycosaurs and therapsids such as mammals). They are disti ...
s. Like their amphibious early tetrapod predecessors, they had lungs and limbs. Amniotic eggs, however, have internal membranes that allow the developing embryo
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male spe ...
to breathe but keep water in. Hence, amniotes can lay eggs on dry land, while amphibian
Amphibians are tetrapod, four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the Class (biology), class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terres ...
s generally need to lay their eggs in water.
The first amniotes apparently arose in the Pennsylvanian subperiod of the Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic that spans 60 million years from the end of the Devonian Period million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Permian Period, million years ago. The name ''Carbonifero ...
. They descended from earlier reptiliomorph amphibious tetrapods, which lived on land that was already inhabited by insects and other invertebrates as well as ferns, moss
Mosses are small, non-vascular flowerless plants in the taxonomic division Bryophyta (, ) '' sensu stricto''. Bryophyta (''sensu lato'', Schimp. 1879) may also refer to the parent group bryophytes, which comprise liverworts, mosses, and hor ...
es and other plants. Within a few million years, two important amniote lineages became distinct: the synapsids, which would later include the common ancestor of the mammals; and the sauropsid
Sauropsida ("lizard faces") is a clade of amniotes, broadly equivalent to the class Reptilia. Sauropsida is the sister taxon to Synapsida, the other clade of amniotes which includes mammals as its only modern representatives. Although early syna ...
s, which now include turtles, lizard
Lizards are a widespread group of squamate reptiles, with over 7,000 species, ranging across all continents except Antarctica, as well as most oceanic island chains. The group is paraphyletic since it excludes the snakes and Amphisbaenia alt ...
s, snakes, crocodilian
Crocodilia (or Crocodylia, both ) is an order of mostly large, predatory, semiaquatic reptiles, known as crocodilians. They first appeared 95 million years ago in the Late Cretaceous period ( Cenomanian stage) and are the closest living ...
s and dinosaurs (including birds). Synapsids have a single hole ( temporal fenestra) low on each side of the skull. Primitive synapsids included the largest and fiercest animals of the early Permian such as Dimetrodon
''Dimetrodon'' ( or ,) meaning "two measures of teeth,” is an extinct genus of non-mammalian synapsid that lived during the Cisuralian (Early Permian), around 295–272 million years ago (Mya). It is a member of the family Sphenacodontid ...
. Nonmammalian synapsids were traditionally – and incorrectly – called "mammal-like reptiles" or pelycosaurs; we now know they were neither reptiles nor part of reptile lineage.
Therapsids, a group of synapsids, evolved in the Middle Permian, about 265 million years ago, and became the dominant land vertebrates. They differ from basal eupelycosaurs in several features of the skull and jaws, including: larger skulls and incisors which are equal in size in therapsids, but not for eupelycosaurs. The therapsid lineage leading to mammals went through a series of stages, beginning with animals that were very similar to their early synapsid ancestors and ending with probainognathia
Probainognathia is one of the two major subgroups of the clade Eucynodontia, the other being Cynognathia. The earliest forms were carnivorous and insectivorous, though some groups eventually also evolved herbivorous diets. The earliest and most ...
n cynodont
The cynodonts () (clade Cynodontia) are a clade of eutheriodont therapsids that first appeared in the Late Permian (approximately 260 mya), and extensively diversified after the Permian–Triassic extinction event. Cynodonts had a wide variety ...
s, some of which could easily be mistaken for mammals. Those stages were characterized by:
* The gradual development of a bony secondary palate.
* Abrupt acquisition of endothermy among Mammaliamorpha, thus prior to the origin of mammals by 30-50 millions of years '.
* Progression towards an erect limb posture, which would increase the animals' stamina by avoiding Carrier's constraint. But this process was slow and erratic: for example, all herbivorous nonmammaliaform therapsids retained sprawling limbs (some late forms may have had semierect hind limbs); Permian carnivorous therapsids had sprawling forelimbs, and some late Permian ones also had semisprawling hindlimbs. In fact, modern monotremes still have semisprawling limbs.
* The dentary gradually became the main bone of the lower jaw which, by the Triassic, progressed towards the fully mammalian jaw (the lower consisting only of the dentary) and middle ear (which is constructed by the bones that were previously used to construct the jaws of reptiles).
First mammals
The Permian–Triassic extinction event about 252 million years ago, which was a prolonged event due to the accumulation of several extinction pulses, ended the dominance of carnivorous therapsids. In the early Triassic, most medium to large land carnivore niches were taken over byarchosaur
Archosauria () is a clade of diapsids, with birds and crocodilians as the only living representatives. Archosaurs are broadly classified as reptiles, in the cladistic sense of the term which includes birds. Extinct archosaurs include non-avian d ...
s which, over an extended period (35 million years), came to include the crocodylomorphs
Crocodylomorpha is a group of pseudosuchian archosaurs that includes the crocodilians and their extinct relatives. They were the only members of Pseudosuchia to survive the end-Triassic extinction.
During Mesozoic and early Cenozoic times, cr ...
, the pterosaurs and the dinosaurs; however, large cynodonts like '' Trucidocynodon'' and traversodontids
Traversodontidae is an extinct family of herbivorous cynodonts. Traversodonts were primarily Gondwanan, with many species known from Africa and South America. Recently, traversodonts have also been found from Europe and eastern North America. ...
still occupied large sized carnivorous and herbivorous niches respectively. By the Jurassic, the dinosaurs had come to dominate the large terrestrial herbivore niches as well.
The first mammals (in Kemp's sense) appeared in the Late Triassic epoch (about 225 million years ago), 40 million years after the first therapsids. They expanded out of their nocturnal insectivore
A robber fly eating a hoverfly
An insectivore is a carnivorous animal or plant that eats insects. An alternative term is entomophage, which can also refer to the human practice of eating insects.
The first vertebrate insectivores wer ...
niche from the mid-Jurassic onwards; The Jurassic ''Castorocauda
''Castorocauda'' is an extinct, semi-aquatic, superficially otter-like genus of docodont mammaliaforms with one species, ''C. lutrasimilis''. It is part of the Yanliao Biota, found in the Daohugou Beds of Inner Mongolia, China dating to the M ...
'', for example, was a close relative of true mammals that had adaptations for swimming, digging and catching fish. Most, if not all, are thought to have remained nocturnal (the nocturnal bottleneck
The nocturnal bottleneck hypothesis is a hypothesis to explain several mammalian traits. In 1942, Gordon Lynn Walls described this concept which states that placental mammals were mainly or even exclusively nocturnal through most of their evolu ...
), accounting for much of the typical mammalian traits. The majority of the mammal species that existed in the Mesozoic Era
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last Era (geology), era of Earth's Geologic time scale, geological history, lasting from about , comprising ...
were multituberculates, eutriconodonts and spalacotheriid
Spalacotheriidae is a family of extinct mammals belonging to the paraphyletic group ' Symmetrodonta'. They lasted from the Early Cretaceous to the Campanian in North America, Europe, Asia and North Africa.
Spalacotheriids are characterised by ha ...
s. The earliest known metatherian is '' Sinodelphys'', found in 125 million-year-old Early Cretaceous
The Early Cretaceous ( geochronological name) or the Lower Cretaceous (chronostratigraphic name), is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 145 Ma to 100.5 Ma.
Geology
Pro ...
shale
Shale is a fine-grained, clastic sedimentary rock formed from mud that is a mix of flakes of clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4) and tiny fragments (silt-sized particles) of other minerals, especial ...
in China's northeastern Liaoning Province
Liaoning () is a coastal provinces of China, province in Northeast China that is the smallest, southernmost, and most populous province in the region. With its capital at Shenyang, it is located on the northern shore of the Yellow Sea, and i ...
. The fossil is nearly complete and includes tufts of fur and imprints of soft tissues.
 The oldest known fossil among the Eutheria ("true beasts") is the small shrewlike ''
The oldest known fossil among the Eutheria ("true beasts") is the small shrewlike ''Juramaia sinensis
''Juramaia'' is an extinct genus of very basal eutherian mammal known from the Late Jurassic ( Oxfordian stage) deposits of western Liaoning, China. It is a small shrew-like mammal with a body length of approximately 70–100 mm, making it ...
'', or "Jurassic mother from China", dated to 160 million years ago in the late Jurassic. A later eutherian relative, '' Eomaia'', dated to 125 million years ago in the early Cretaceous, possessed some features in common with the marsupials but not with the placentals, evidence that these features were present in the last common ancestor of the two groups but were later lost in the placental lineage. In particular, the epipubic bones extend forwards from the pelvis. These are not found in any modern placental, but they are found in marsupials, monotremes, other nontherian mammals and '' Ukhaatherium'', an early Cretaceous animal in the eutherian order Asioryctitheria. This also applies to the multituberculates. They are apparently an ancestral feature, which subsequently disappeared in the placental lineage. These epipubic bones seem to function by stiffening the muscles during locomotion, reducing the amount of space being presented, which placentals require to contain their fetus during gestation periods. A narrow pelvic outlet indicates that the young were very small at birth and therefore pregnancy was short, as in modern marsupials. This suggests that the placenta was a later development.
One of the earliest known monotremes was '' Teinolophos'', which lived about 120 million years ago in Australia. Monotremes have some features which may be inherited from the original amniotes such as the same orifice to urinate, defecate and reproduce (cloaca
In animal anatomy, a cloaca ( ), plural cloacae ( or ), is the posterior orifice that serves as the only opening for the digestive, reproductive, and urinary tracts (if present) of many vertebrate animals. All amphibians, reptiles and birds, a ...
)—as lizards and birds also do— and they lay eggs which are leathery and uncalcified.
Earliest appearances of features
''Hadrocodium
''Hadrocodium wui'' is an extinct mammaliaform that lived during the Sinemurian stage of the Early Jurassic approximately in the Lufeng Formation of the Lufeng Basin in what is now the Yunnan province in south-western China
(, paleocoordinates ...
'', whose fossils date from approximately 195 million years ago, in the early Jurassic, provides the first clear evidence of a jaw joint formed solely by the squamosal and dentary bones; there is no space in the jaw for the articular, a bone involved in the jaws of all early synapsids.
 The earliest clear evidence of hair or fur is in fossils of ''
The earliest clear evidence of hair or fur is in fossils of ''Castorocauda
''Castorocauda'' is an extinct, semi-aquatic, superficially otter-like genus of docodont mammaliaforms with one species, ''C. lutrasimilis''. It is part of the Yanliao Biota, found in the Daohugou Beds of Inner Mongolia, China dating to the M ...
'' and ''Megaconus
''Megaconus'' is an extinct genus of allotherian mammal from the Middle Jurassic Tiaojishan Formation of Inner Mongolia, China. The type and only species, ''Megaconus mammaliaformis'' was first described in the journal ''Nature'' in 2013. ''Meg ...
'', from 164 million years ago in the mid-Jurassic. In the 1950s, it was suggested that the foramina (passages) in the maxillae and premaxillae (bones in the front of the upper jaw) of cynodonts were channels which supplied blood vessels and nerves to vibrissae ( whiskers) and so were evidence of hair or fur; it was soon pointed out, however, that foramina do not necessarily show that an animal had vibrissae, as the modern lizard '' Tupinambis'' has foramina that are almost identical to those found in the nonmammalian cynodont '' Thrinaxodon''. Popular sources, nevertheless, continue to attribute whiskers to ''Thrinaxodon''. Studies on Permian coprolites suggest that non-mammalian synapsids
Synapsids + (, 'arch') > () "having a fused arch"; synonymous with ''theropsids'' (Greek, "beast-face") are one of the two major groups of animals that evolved from basal amniotes, the other being the Sauropsida, sauropsids, the group that inc ...
of the epoch already had fur, setting the evolution of hairs possibly as far back as dicynodonts.
When endothermy first appeared in the evolution of mammals is uncertain, though it is generally agreed to have first evolved in non-mammalian therapsids. Modern monotremes have lower body temperatures and more variable metabolic rates than marsupials and placentals, but there is evidence that some of their ancestors, perhaps including ancestors of the therians, may have had body temperatures like those of modern therians. Likewise, some modern therians like afrotheres and xenarthrans have secondarily developed lower body temperatures.
The evolution of erect limbs in mammals is incomplete—living and fossil monotremes have sprawling limbs. The parasagittal (nonsprawling) limb posture appeared sometime in the late Jurassic or early Cretaceous; it is found in the eutherian ''Eomaia'' and the metatherian ''Sinodelphys'', both dated to 125 million years ago. Epipubic bones, a feature that strongly influenced the reproduction of most mammal clades, are first found in Tritylodontidae, suggesting that it is a synapomorphy between them and mammaliformes. They are omnipresent in non-placental mammaliformes, though '' Megazostrodon'' and '' Erythrotherium'' appear to have lacked them.
It has been suggested that the original function of lactation ( milk production) was to keep eggs moist. Much of the argument is based on monotremes, the egg-laying mammals. In human females, mammary glands become fully developed during puberty, regardless of pregnancy.
Rise of the mammals
Therian mammals took over the medium- to large-sized ecological niches in theCenozoic
The Cenozoic ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterised by the dominance of mammals, birds and flowering plants, a cooling and drying climate, and the current configura ...
, after the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event approximately 66 million years ago emptied ecological space once filled by non-avian dinosaurs and other groups of reptiles, as well as various other mammal groups, and underwent an exponential increase in body size (megafauna
In terrestrial zoology, the megafauna (from Greek μέγας ''megas'' "large" and New Latin ''fauna'' "animal life") comprises the large or giant animals of an area, habitat, or geological period, extinct and/or extant. The most common threshold ...
). Then mammals diversified very quickly; both birds and mammals show an exponential rise in diversity. For example, the earliest known bat dates from about 50 million years ago, only 16 million years after the extinction of the non-avian dinosaurs.
Molecular phylogenetic studies initially suggested that most placental orders diverged about 100 to 85 million years ago and that modern families appeared in the period from the late Eocene through the Miocene. However, no placental fossils have been found from before the end of the Cretaceous. The earliest undisputed fossils of placentals comes from the early Paleocene, after the extinction of the non-avian dinosaurs. In particular, scientists have identified an early Paleocene animal named ''Protungulatum donnae
''Protungulatum'' ('first ungulate') is a extinct genus of pan-euungulate mammals within extinct family Protungulatidae, and also one of the earliest known placental mammals in the fossil record, that lived in North America from the Late Creta ...
'' as one of the first placental mammals. however it has been reclassified as a non-placental eutherian. Recalibrations of genetic and morphological diversity rates have suggested a Late Cretaceous origin for placentals, and a Paleocene origin for most modern clades.
The earliest known ancestor of primates is '' Archicebus achilles'' from around 55 million years ago. This tiny primate weighed 20–30 grams (0.7–1.1 ounce) and could fit within a human palm.
Anatomy
Distinguishing features
Living mammal species can be identified by the presence ofsweat gland
Sweat glands, also known as sudoriferous or sudoriparous glands, , are small tubular structures of the skin that produce sweat. Sweat glands are a type of exocrine gland, which are glands that produce and secrete substances onto an epithelial sur ...
s, including those that are specialized to produce milk to nourish their young. In classifying fossils, however, other features must be used, since soft tissue glands and many other features are not visible in fossils.
Many traits shared by all living mammals appeared among the earliest members of the group:
* Jaw joint
In anatomy, the temporomandibular joints (TMJ) are the two joints connecting the jawbone to the skull. It is a bilateral synovial articulation between the temporal bone of the skull above and the mandible below; it is from these bones that i ...
– The dentary (the lower jaw bone, which carries the teeth) and the squamosal (a small cranial bone) meet to form the joint. In most gnathostomes, including early therapsids, the joint consists of the articular (a small bone at the back of the lower jaw) and quadrate
Quadrate may refer to:
* Quadrate bone
* Quadrate (heraldry)
* Quadrate lobe of liver
* Quadrate tubercle
The quadrate tubercle is a small tubercle found upon the upper part of the femur. It serves as a point of insertion of the quadratus femori ...
(a small bone at the back of the upper jaw).
* Middle ear – In crown-group mammals, sound is carried from the eardrum
In the anatomy of humans and various other tetrapods, the eardrum, also called the tympanic membrane or myringa, is a thin, cone-shaped membrane that separates the external ear
The outer ear, external ear, or auris externa is the extern ...
by a chain of three bones, the malleus, the incus and the stapes. Ancestrally, the malleus and the incus are derived from the articular and the quadrate bones that constituted the jaw joint of early therapsids.
* Tooth replacement – Teeth can be replaced once ( diphyodonty) or (as in toothed whales and murid rodents) not at all ( monophyodonty). Elephants, manatees, and kangaroos continually grow new teeth throughout their life ( polyphyodonty).
* Prismatic enamel – The enamel coating on the surface of a tooth consists of prisms, solid, rod-like structures extending from the dentin
Dentin () (American English) or dentine ( or ) (British English) ( la, substantia eburnea) is a calcified tissue of the body and, along with enamel, cementum, and pulp, is one of the four major components of teeth. It is usually covered by ena ...
to the tooth's surface.
* Occipital condyles – Two knobs at the base of the skull fit into the topmost neck vertebra
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (singular: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In ...
; most other tetrapods, in contrast, have only one such knob.
For the most part, these characteristics were not present in the Triassic ancestors of the mammals. Nearly all mammaliaforms possess an epipubic bone, the exception being modern placentals.
Sexual dimorphism
 On average, male mammals are larger than females, with males being at least 10% larger than females in over 45% of investigated species. Most mammalian orders also exhibit male-biased sexual dimorphism, although some orders do not show any bias or are significantly female-biased ( Lagomorpha). Sexual size dimorphism increases with body size across mammals (
On average, male mammals are larger than females, with males being at least 10% larger than females in over 45% of investigated species. Most mammalian orders also exhibit male-biased sexual dimorphism, although some orders do not show any bias or are significantly female-biased ( Lagomorpha). Sexual size dimorphism increases with body size across mammals (Rensch's rule
Rensch's rule is a biological rule on allometrics, concerning the relationship between the extent of sexual size dimorphism and which sex is larger. Across species within a lineage, size dimorphism increases with increasing body size when the male ...
), suggesting that there are parallel selection pressures on both male and female size. Male-biased dimorphism relates to sexual selection on males through male–male competition for females, as there is a positive correlation between the degree of sexual selection, as indicated by mating systems, and the degree of male-biased size dimorphism. The degree of sexual selection is also positively correlated with male and female size across mammals. Further, parallel selection pressure on female mass is identified in that age at weaning is significantly higher in more polygynous
Polygyny (; from Neoclassical Greek πολυγυνία (); ) is the most common and accepted form of polygamy around the world, entailing the marriage of a man with several women.
Incidence
Polygyny is more widespread in Africa than in any ...
species, even when correcting for body mass. Also, the reproductive rate is lower for larger females, indicating that fecundity selection selects for smaller females in mammals. Although these patterns hold across mammals as a whole, there is considerable variation across orders.
Biological systems
 The majority of mammals have seven
The majority of mammals have seven cervical vertebrae
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (singular: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In ...
(bones in the neck). The exceptions are the manatee and the two-toed sloth, which have six, and the three-toed sloth which has nine. All mammalian brains possess a neocortex
The neocortex, also called the neopallium, isocortex, or the six-layered cortex, is a set of layers of the mammalian cerebral cortex involved in higher-order brain functions such as sensory perception, cognition, generation of motor commands, sp ...
, a brain region unique to mammals. Placental brains have a corpus callosum, unlike monotremes and marsupials.
The lung
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of t ...
s of mammals are spongy and honeycombed. Breathing is mainly achieved with the diaphragm
Diaphragm may refer to:
Anatomy
* Thoracic diaphragm, a thin sheet of muscle between the thorax and the abdomen
* Pelvic diaphragm or pelvic floor, a pelvic structure
* Urogenital diaphragm or triangular ligament, a pelvic structure
Other
* Diap ...
, which divides the thorax from the abdominal cavity, forming a dome convex to the thorax. Contraction of the diaphragm flattens the dome, increasing the volume of the lung cavity. Air enters through the oral and nasal cavities, and travels through the larynx, trachea and bronchi, and expands the alveoli Alveolus (; pl. alveoli, adj. alveolar) is a general anatomical term for a concave cavity or pit.
Uses in anatomy and zoology
* Pulmonary alveolus, an air sac in the lungs
** Alveolar cell or pneumocyte
** Alveolar duct
** Alveolar macrophage
* ...
. Relaxing the diaphragm has the opposite effect, decreasing the volume of the lung cavity, causing air to be pushed out of the lungs. During exercise, the abdominal wall contracts
A contract is a legally enforceable agreement between two or more parties that creates, defines, and governs mutual rights and obligations between them. A contract typically involves the transfer of goods, services, money, or a promise to tran ...
, increasing pressure on the diaphragm, which forces air out quicker and more forcefully. The rib cage is able to expand and contract the chest cavity through the action of other respiratory muscles. Consequently, air is sucked into or expelled out of the lungs, always moving down its pressure gradient. This type of lung is known as a bellows lung due to its resemblance to blacksmith bellows.
The mammalian heart has four chambers, two upper atria, the receiving chambers, and two lower ventricles, the discharging chambers. The heart has four valves, which separate its chambers and ensures blood flows in the correct direction through the heart (preventing backflow). After gas exchange in the pulmonary capillaries (blood vessels in the lungs), oxygen-rich blood returns to the left atrium via one of the four pulmonary veins. Blood flows nearly continuously back into the atrium, which acts as the receiving chamber, and from here through an opening into the left ventricle. Most blood flows passively into the heart while both the atria and ventricles are relaxed, but toward the end of the ventricular relaxation period, the left atrium will contract, pumping blood into the ventricle. The heart also requires nutrients and oxygen found in blood like other muscles, and is supplied via coronary arteries.
 The
The integumentary system
The integumentary system is the set of organs forming the outermost layer of an animal's body. It comprises the skin and its appendages, which act as a physical barrier between the external environment and the internal environment that it serves ...
(skin) is made up of three layers: the outermost epidermis
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water rele ...
, the dermis
The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. It is divided i ...
and the hypodermis. The epidermis is typically 10 to 30 cells thick; its main function is to provide a waterproof layer. Its outermost cells are constantly lost; its bottommost cells are constantly dividing and pushing upward. The middle layer, the dermis, is 15 to 40 times thicker than the epidermis. The dermis is made up of many components, such as bony structures and blood vessels. The hypodermis is made up of adipose tissue, which stores lipids and provides cushioning and insulation. The thickness of this layer varies widely from species to species; marine mammals require a thick hypodermis (blubber
Blubber is a thick layer of vascularized adipose tissue under the skin of all cetaceans, pinnipeds, penguins, and sirenians.
Description
Lipid-rich, collagen fiber-laced blubber comprises the hypodermis and covers the whole body, except for pa ...
) for insulation, and right whale
Right whales are three species of large baleen whales of the genus ''Eubalaena'': the North Atlantic right whale (''E. glacialis''), the North Pacific right whale (''E. japonica'') and the Southern right whale (''E. australis''). They are clas ...
s have the thickest blubber at . Although other animals have features such as whiskers, feathers, setae, or cilia
The cilium, plural cilia (), is a membrane-bound organelle found on most types of eukaryotic cell, and certain microorganisms known as ciliates. Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea. The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike projecti ...
that superficially resemble it, no animals other than mammals have hair
Hair is a protein filament that grows from follicles found in the dermis. Hair is one of the defining characteristics of mammals.
The human body, apart from areas of glabrous skin, is covered in follicles which produce thick terminal and f ...
. It is a definitive characteristic of the class, though some mammals have very little.
Herbivores have developed a diverse range of physical structures to facilitate the consumption of plant material. To break up intact plant tissues, mammals have developed teeth structures that reflect their feeding preferences. For instance, frugivore
A frugivore is an animal that thrives mostly on raw fruits or succulent fruit-like produce of plants such as roots, shoots, nuts and seeds. Approximately 20% of mammalian herbivores eat fruit. Frugivores are highly dependent on the abundance an ...
s (animals that feed primarily on fruit) and herbivores that feed on soft foliage have low-crowned teeth specialized for grinding foliage and seeds. Grazing animals that tend to eat hard, silica-rich grasses, have high-crowned teeth, which are capable of grinding tough plant tissues and do not wear down as quickly as low-crowned teeth. Most carnivorous mammals have carnassialiforme teeth (of varying length depending on diet), long canines and similar tooth replacement patterns.
The stomach of even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla) is divided into four sections: the rumen, the reticulum, the omasum and the abomasum (only ruminants have a rumen). After the plant material is consumed, it is mixed with saliva in the rumen and reticulum and separates into solid and liquid material. The solids lump together to form a bolus
Bolus may refer to:
Geography
* Bolus, Iran, a village in Ardabil Province, Iran
* Bolus, or Baulus, an Anatolian village on the site of ancient Berissa
Medicine
* Bolus (digestion), a ball-shaped mass moving through the digestive tract
* Bolus ...
(or cud), and is regurgitated. When the bolus enters the mouth, the fluid is squeezed out with the tongue and swallowed again. Ingested food passes to the rumen and reticulum where cellulolytic microbe
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in olde ...
s ( bacteria, protozoa
Protozoa (singular: protozoan or protozoon; alternative plural: protozoans) are a group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic tissues and debris. Histo ...
and fungi) produce cellulase, which is needed to break down the cellulose in plants. Perissodactyls, in contrast to the ruminants, store digested food that has left the stomach in an enlarged cecum, where it is fermented by bacteria. Carnivora have a simple stomach adapted to digest primarily meat, as compared to the elaborate digestive systems of herbivorous animals, which are necessary to break down tough, complex plant fibers. The caecum is either absent or short and simple, and the large intestine is not sacculated or much wider than the small intestine.
 The mammalian excretory system involves many components. Like most other land animals, mammals are ureotelic, and convert ammonia into urea, which is done by the liver as part of the urea cycle.
The mammalian excretory system involves many components. Like most other land animals, mammals are ureotelic, and convert ammonia into urea, which is done by the liver as part of the urea cycle. Bilirubin
Bilirubin (BR) (Latin for "red bile") is a red-orange compound that occurs in the normal catabolic pathway that breaks down heme in vertebrates. This catabolism is a necessary process in the body's clearance of waste products that arise from the ...
, a waste product derived from blood cells, is passed through bile
Bile (from Latin ''bilis''), or gall, is a dark-green-to-yellowish-brown fluid produced by the liver of most vertebrates that aids the digestion of lipids in the small intestine. In humans, bile is produced continuously by the liver (liver bile ...
and urine with the help of enzymes excreted by the liver. The passing of bilirubin via bile through the intestinal tract gives mammalian feces
Feces ( or faeces), known colloquially and in slang as poo and poop, are the solid or semi-solid remains of food that was not digested in the small intestine, and has been broken down by bacteria in the large intestine. Feces contain a relati ...
a distinctive brown coloration. Distinctive features of the mammalian kidney include the presence of the renal pelvis
The renal pelvis or pelvis of the kidney is the funnel-like dilated part of the ureter in the kidney. It is formed by the covnvergence of the major calyces, acting as a funnel for urine flowing from the major calyces to the ureter. It has a mucous ...
and renal pyramids, and of a clearly distinguishable cortex and medulla, which is due to the presence of elongated loops of Henle
In the kidney, the loop of Henle () (or Henle's loop, Henle loop, nephron loop or its Latin counterpart ''ansa nephroni'') is the portion of a nephron that leads from the proximal convoluted tubule to the distal convoluted tubule. Named after its ...
. Only the mammalian kidney has a bean shape, although there are some exceptions, such as the multilobed reniculate kidney The reniculate kidney is a multilobed kidney found in marine and aquatic mammals such as pinnipeds (seals, sea lions and walruses) and cetaceans (dolphins and whales) but absent in terrestrial mammals except bears. Kidneys of this morphology
Morph ...
s of pinnipeds, cetacea
Cetacea (; , ) is an infraorder of aquatic mammals that includes whales, dolphins, and porpoises. Key characteristics are their fully aquatic lifestyle, streamlined body shape, often large size and exclusively carnivorous diet. They propel them ...
ns and bears. Most adult placental mammals have no remaining trace of the cloaca
In animal anatomy, a cloaca ( ), plural cloacae ( or ), is the posterior orifice that serves as the only opening for the digestive, reproductive, and urinary tracts (if present) of many vertebrate animals. All amphibians, reptiles and birds, a ...
. In the embryo, the embryonic cloaca
The cloaca is a structure in the development of the urinary and reproductive organs.
The hind-gut is at first prolonged backward into the body-stalk as the tube of the allantois; but, with the growth and flexure of the tail-end of the embryo, ...
divides into a posterior region that becomes part of the anus, and an anterior region that has different fates depending on the sex of the individual: in females, it develops into the vestibule that receives the urethra and vagina, while in males it forms the entirety of the penile urethra
The spongy urethra (cavernous portion of urethra, penile urethra) is the longest part of the male urethra, and is contained in the corpus spongiosum of the penis.
It is about 15 cm long, and extends from the termination of the membranous po ...
. However, the tenrecs, golden moles, and some shrews retain a cloaca as adults. In marsupials, the genital tract is separate from the anus, but a trace of the original cloaca does remain externally. Monotremes, which translates from Greek into "single hole", have a true cloaca.
Sound production
larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal inlet is about ...
that can quickly open and close to produce sounds, and a supralaryngeal vocal tract which filters this sound. The lungs and surrounding musculature provide the air stream and pressure required to phonate. The larynx controls the pitch and volume of sound, but the strength the lungs exert to exhale
Exhalation (or expiration) is the flow of the breath out of an organism. In animals, it is the movement of air from the lungs out of the airways, to the external environment during breathing.
This happens due to elastic properties of the lungs, ...
also contributes to volume. More primitive mammals, such as the echidna, can only hiss, as sound is achieved solely through exhaling through a partially closed larynx. Other mammals phonate using vocal folds. The movement or tenseness of the vocal folds can result in many sounds such as purring and screaming
A scream is a loud speech production, vocalization in which air is passed through the vocal cords with greater force than is used in regular or close-distance vocalisation. This can be performed by any creature possessing lungs, including human ...
. Mammals can change the position of the larynx, allowing them to breathe through the nose while swallowing through the mouth, and to form both oral and nasal
Nasal is an adjective referring to the nose, part of human or animal anatomy. It may also be shorthand for the following uses in combination:
* With reference to the human nose:
** Nasal administration, a method of pharmaceutical drug delivery
** ...
sounds; nasal sounds, such as a dog whine, are generally soft sounds, and oral sounds, such as a dog bark, are generally loud.
Some mammals have a large larynx and thus a low-pitched voice, namely the hammer-headed bat
The hammer-headed bat ('), also known as hammer-headed fruit bat and big-lipped bat, is a megabat widely distributed in West and Central Africa. It is the only member of the genus ''Hypsignathus'', which is part of the tribe Epomophorini along w ...
(''Hypsignathus monstrosus'') where the larynx can take up the entirety of the thoracic cavity while pushing the lungs, heart, and trachea into the abdomen. Large vocal pads can also lower the pitch, as in the low-pitched roars of big cats. The production of infrasound is possible in some mammals such as the African elephant (''Loxodonta'' spp.) and baleen whale
Baleen whales (systematic name Mysticeti), also known as whalebone whales, are a parvorder of carnivorous marine mammals of the infraorder Cetacea (whales, dolphins and porpoises) which use keratinaceous baleen plates (or "whalebone") in their ...
s. Small mammals with small larynxes have the ability to produce ultrasound, which can be detected by modifications to the middle ear and cochlea. Ultrasound is inaudible to birds and reptiles, which might have been important during the Mesozoic, when birds and reptiles were the dominant predators. This private channel is used by some rodents in, for example, mother-to-pup communication, and by bats when echolocating. Toothed whales also use echolocation, but, as opposed to the vocal membrane that extends upward from the vocal folds, they have a melon to manipulate sounds. Some mammals, namely the primates, have air sacs attached to the larynx, which may function to lower the resonances or increase the volume of sound.
The vocal production system is controlled by the cranial nerve nuclei in the brain, and supplied by the recurrent laryngeal nerve and the superior laryngeal nerve, branches of the vagus nerve. The vocal tract is supplied by the hypoglossal nerve and facial nerves. Electrical stimulation of the periaqueductal gray (PEG) region of the mammalian midbrain elicit vocalizations. The ability to learn new vocalizations is only exemplified in humans, seals, cetaceans, elephants and possibly bats; in humans, this is the result of a direct connection between the motor cortex, which controls movement, and the motor neuron
A motor neuron (or motoneuron or efferent neuron) is a neuron whose cell body is located in the motor cortex, brainstem or the spinal cord, and whose axon (fiber) projects to the spinal cord or outside of the spinal cord to directly or indirectl ...
s in the spinal cord.
Fur
 The primary function of the fur of mammals is thermoregulation. Others include protection, sensory purposes, waterproofing, and camouflage. Different types of fur serve different purposes:
* Definitive – which may be
The primary function of the fur of mammals is thermoregulation. Others include protection, sensory purposes, waterproofing, and camouflage. Different types of fur serve different purposes:
* Definitive – which may be shed
A shed is typically a simple, single-story roofed structure that is used for hobbies, or as a workshop in a back garden or on an allotment. Sheds vary considerably in their size and complexity of construction, from simple open-sided ones de ...
after reaching a certain length
* Vibrissae – sensory hairs, most commonly whiskers
* Pelage – guard hairs, under-fur, and awn hair
Awn hairs are the intermediate hairs in a mammal's coat. They are shorter than the guard hairs and longer than the down hairs. They help with insulation and protect the down hairs underneath. Most of the visible coat is made of this kind of hair.
...
* Spines – stiff guard hair used for defense (such as in porcupine
Porcupines are large rodents with coats of sharp spines, or quills, that protect them against predation. The term covers two families of animals: the Old World porcupines of family Hystricidae, and the New World porcupines of family, Erethizont ...
s)
* Bristles – long hairs usually used in visual signals. (such as a lion's mane)
* Velli – often called "down fur" which insulates newborn mammals
* Wool – long, soft and often curly
Thermoregulation
Hair length is not a factor in thermoregulation: for example, some tropical mammals such as sloths have the same length of fur length as some arctic mammals but with less insulation; and, conversely, other tropical mammals with short hair have the same insulating value as arctic mammals. The denseness of fur can increase an animal's insulation value, and arctic mammals especially have dense fur; for example, the musk ox has guard hairs measuring as well as a dense underfur, which forms an airtight coat, allowing them to survive in temperatures of . Some desert mammals, such as camels, use dense fur to prevent solar heat from reaching their skin, allowing the animal to stay cool; a camel's fur may reach in the summer, but the skin stays at . Aquatic mammals, conversely, trap air in their fur to conserve heat by keeping the skin dry.Coloration
Mammalian coats are colored for a variety of reasons, the major selective pressures including camouflage, sexual selection, communication, and thermoregulation. Coloration in both the hair and skin of mammals is mainly determined by the type and amount of melanin;eumelanin
Melanin (; from el, μέλας, melas, black, dark) is a broad term for a group of natural pigments found in most organisms. Eumelanin is produced through a multistage chemical process known as melanogenesis, where the oxidation of the amin ...
s for brown and black colors and pheomelanin for a range of yellowish to reddish colors, giving mammals an earth tone. Some mammals have more vibrant colors; certain monkeys such mandrill
The mandrill (''Mandrillus sphinx'') is a large Old World monkey native to west central Africa. It is one of the most colorful mammals in the world, with red and blue skin on its face and posterior. The species is sexually dimorphic, as males ...
s and vervet monkeys, and opossums such as the Mexican mouse opossums and Derby's woolly opossums, have blue skin due to light diffraction in collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix found in the body's various connective tissues. As the main component of connective tissue, it is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up from 25% to 35% of the whole ...
fibers. Many sloths appear green because their fur hosts green algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mic ...
; this may be a symbiotic
Symbiosis (from Greek , , "living together", from , , "together", and , bíōsis, "living") is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms, be it mutualistic, commensalistic, or parasit ...
relation that affords camouflage to the sloths.
Camouflage is a powerful influence in a large number of mammals, as it helps to conceal individuals from predators or prey. In arctic and subarctic mammals such as the arctic fox (''Alopex lagopus''), collared lemming (''Dicrostonyx groenlandicus''), stoat (''Mustela erminea''), and snowshoe hare (''Lepus americanus''), seasonal color change between brown in summer and white in winter is driven largely by camouflage. Some arboreal mammals, notably primates and marsupials, have shades of violet, green, or blue skin on parts of their bodies, indicating some distinct advantage in their largely arboreal habitat due to convergent evolution.
Aposematism
Aposematism is the advertising by an animal to potential predators that it is not worth attacking or eating. This unprofitability may consist of any defences which make the prey difficult to kill and eat, such as toxicity, venom, foul taste or ...
, warning off possible predators, is the most likely explanation of the black-and-white pelage of many mammals which are able to defend themselves, such as in the foul-smelling skunk
Skunks are mammals in the family Mephitidae. They are known for their ability to spray a liquid with a strong, unpleasant scent from their anal glands. Different species of skunk vary in appearance from black-and-white to brown, cream or ginge ...
and the powerful and aggressive honey badger. Coat color is sometimes sexually dimorphic, as in many primate species. Differences in female and male coat color may indicate nutrition and hormone levels, important in mate selection. Coat color may influence the ability to retain heat, depending on how much light is reflected. Mammals with a darker colored coat can absorb more heat from solar radiation, and stay warmer, and some smaller mammals, such as voles, have darker fur in the winter. The white, pigmentless fur of arctic mammals, such as the polar bear, may reflect more solar radiation directly onto the skin. The dazzling black-and-white striping of zebras appear to provide some protection from biting flies.
Reproductive system
 Mammals are solely gonochoric (an animal is born with either male or female genitalia, as opposed to
Mammals are solely gonochoric (an animal is born with either male or female genitalia, as opposed to hermaphrodite
In reproductive biology, a hermaphrodite () is an organism that has both kinds of reproductive organs and can produce both gametes associated with male and female sexes.
Many Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic groups of animals (mostly invertebrate ...
s where there is no such schism). In male placentals, the penis is used both for urination and copulation. Depending on the species, an erection
An erection (clinically: penile erection or penile tumescence) is a physiological phenomenon in which the penis becomes firm, engorged, and enlarged. Penile erection is the result of a complex interaction of psychological, neural, vascular, ...
may be fueled by blood flow into vascular, spongy tissue or by muscular action. A penis may be contained in a prepuce
Prepuce , or as an adjective, preputial , refers to two homologous structures of male and female genitals:
*Clitoral hood, skin surrounding and protecting the head of the clitoris
*Foreskin, skin surrounding and protecting the head of the penis in ...
when not erect, and some placentals also have a penis bone (baculum
The baculum (also penis bone, penile bone, or ''os penis'', ''os genitale'' or ''os priapi'') is a bone found in the penis of many placental mammals. It is absent from the human penis, but present in the penises of some primates, such as the ...
). Marsupials typically have forked penises, while the echidna penis generally has four heads with only two functioning. The testes of most mammals descend into the scrotum which is typically posterior to the penis but is often anterior in marsupials. Female mammals generally have a clitoris
The clitoris ( or ) is a female sex organ present in mammals, ostriches and a limited number of other animals. In humans, the visible portion – the glans – is at the front junction of the labia minora (inner lips), above the ope ...
, labia majora and labia minora on the outside, while the internal system contains paired oviducts, 1–2 uteri
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', plural ''uteri'') or womb () is the organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans that accommodates the embryonic and fetal development of one or more embryos until birth. The uteru ...
, 1–2 cervices
The cervix or cervix uteri (Latin, 'neck of the uterus') is the lower part of the uterus (womb) in the human female reproductive system. The cervix is usually 2 to 3 cm long (~1 inch) and roughly cylindrical in shape, which changes during ...
and a vagina. Marsupials have two lateral vaginas and a medial vagina. The "vagina" of monotremes is better understood as a "urogenital sinus". The uterine systems of placental mammals can vary between a duplex, where there are two uteri and cervices which open into the vagina, a bipartite, where two uterine horns have a single cervix that connects to the vagina, a bicornuate
A bicornuate uterus or bicornate uterus (from the Latin ''cornū'', meaning "horn"), is a type of mullerian anomaly in the human uterus, where there is a deep indentation at the fundus (top) of the uterus.
Pathophysiology
A bicornuate uterus ...
, which consists where two uterine horns that are connected distally but separate medially creating a Y-shape, and a simplex, which has a single uterus.
 The ancestral condition for mammal reproduction is the birthing of relatively undeveloped, either through direct vivipary or a short period as soft-shelled eggs. This is likely due to the fact that the torso could not expand due to the presence of epipubic bones. The oldest demonstration of this reproductive style is with '' Kayentatherium'', which produced undeveloped perinates, but at much higher litter sizes than any modern mammal, 38 specimens. Most modern mammals are viviparous, giving birth to live young. However, the five species of monotreme, the platypus and the four species of echidna, lay eggs. The monotremes have a
The ancestral condition for mammal reproduction is the birthing of relatively undeveloped, either through direct vivipary or a short period as soft-shelled eggs. This is likely due to the fact that the torso could not expand due to the presence of epipubic bones. The oldest demonstration of this reproductive style is with '' Kayentatherium'', which produced undeveloped perinates, but at much higher litter sizes than any modern mammal, 38 specimens. Most modern mammals are viviparous, giving birth to live young. However, the five species of monotreme, the platypus and the four species of echidna, lay eggs. The monotremes have a sex determination system
A sex-determination system is a biological system that determines the development of sexual characteristics in an organism. Most organisms that create their offspring using sexual reproduction have two sexes.
In some species there are hermaphr ...
different from that of most other mammals. In particular, the sex chromosomes of a platypus are more like those of a chicken than those of a therian mammal.
Viviparous mammals are in the subclass Theria; those living today are in the marsupial and placental infraclasses. Marsupials have a short gestation
Gestation is the period of development during the carrying of an embryo, and later fetus, inside viviparous animals (the embryo develops within the parent). It is typical for mammals, but also occurs for some non-mammals. Mammals during pregna ...
period, typically shorter than its estrous cycle and generally giving birth to a number of undeveloped newborns that then undergo further development; in many species, this takes place within a pouch-like sac, the marsupium, located in the front of the mother's abdomen. This is the plesiomorphic
In phylogenetics, a plesiomorphy ("near form") and symplesiomorphy are synonyms for an ancestral character shared by all members of a clade, which does not distinguish the clade from other clades.
Plesiomorphy, symplesiomorphy, apomorphy, and ...
condition among viviparous mammals; the presence of epipubic bones in all non-placental mammals prevents the expansion of the torso needed for full pregnancy. Even non-placental eutherians probably reproduced this way. The placentals give birth to relatively complete and developed young, usually after long gestation periods. They get their name from the placenta, which connects the developing fetus to the uterine wall to allow nutrient uptake. In placental mammals, the epipubic is either completely lost or converted into the baculum; allowing the torso to be able to expand and thus birth developed offspring.
The mammary glands of mammals are specialized to produce milk, the primary source of nutrition for newborns. The monotremes branched early from other mammals and do not have the nipples seen in most mammals, but they do have mammary glands. The young lick the milk from a mammary patch on the mother's belly. Compared to placental mammals, the milk of marsupials changes greatly in both production rate and in nutrient composition, due to the underdeveloped young. In addition, the mammary glands have more autonomy allowing them to supply separate milks to young at different development stages. Lactose
Lactose is a disaccharide sugar synthesized by galactose and glucose subunits and has the molecular formula C12H22O11. Lactose makes up around 2–8% of milk (by mass). The name comes from ' (gen. '), the Latin word for milk, plus the suffix '' - ...
is the main sugar in placental mammal milk while monotreme and marsupial milk is dominated by oligosaccharides. Weaning is the process in which a mammal becomes less dependent on their mother's milk and more on solid food.
Endothermy
Nearly all mammals are endothermic ("warm-blooded"). Most mammals also have hair to help keep them warm. Like birds, mammals can forage or hunt in weather and climates too cold for ectothermic ("cold-blooded") reptiles and insects. Endothermy requires plenty of food energy, so mammals eat more food per unit of body weight than most reptiles. Small insectivorous mammals eat prodigious amounts for their size. A rare exception, the naked mole-rat produces little metabolic heat, so it is considered an operational poikilotherm. Birds are also endothermic, so endothermy is not unique to mammals.Species lifespan
Among mammals, species maximum lifespan varies significantly (for example the shrew has a lifespan of two years, whereas the oldestbowhead whale
The bowhead whale (''Balaena mysticetus'') is a species of baleen whale belonging to the family Balaenidae and the only living representative of the genus ''Balaena''. They are the only baleen whale endemic to the Arctic and subarctic waters, ...
is recorded to be 211 years). Although the underlying basis for these lifespan differences is still uncertain, numerous studies indicate that the ability to repair DNA damage is an important determinant of mammalian lifespan. In a 1974 study by Hart and Setlow, it was found that DNA excision repair capability increased systematically with species lifespan among seven mammalian species. Species lifespan was observed to be robustly correlated with the capacity to recognize DNA double-strand breaks as well as the level of the DNA repair protein Ku80. In a study of the cells from sixteen mammalian species, genes employed in DNA repair were found to be up-regulated in the longer-lived species. The cellular level of the DNA repair enzyme poly ADP ribose polymerase was found to correlate with species lifespan in a study of 13 mammalian species. Three additional studies of a variety of mammalian species also reported a correlation between species lifespan and DNA repair capability.
Locomotion
Terrestrial
 Most vertebrates—the amphibians, the reptiles and some mammals such as humans and bears—are
Most vertebrates—the amphibians, the reptiles and some mammals such as humans and bears—are plantigrade
151px, Portion of a human skeleton, showing plantigrade habit
In terrestrial animals, plantigrade locomotion means walking with the toes and metatarsals flat on the ground. It is one of three forms of locomotion adopted by terrestrial mammals. T ...
, walking on the whole of the underside of the foot. Many mammals, such as cats and dogs, are digitigrade
In terrestrial vertebrates, digitigrade () locomotion is walking or running on the toes (from the Latin ''digitus'', 'finger', and ''gradior'', 'walk'). A digitigrade animal is one that stands or walks with its toes (metatarsals) touching the groun ...
, walking on their toes, the greater stride length allowing more speed. Digitigrade mammals are also often adept at quiet movement. Some animals such as horses are unguligrade, walking on the tips of their toes. This even further increases their stride length and thus their speed. A few mammals, namely the great apes, are also known to walk on their knuckles, at least for their front legs. Giant anteaters and platypuses are also knuckle-walkers. Some mammals are bipeds
Bipedalism is a form of terrestrial locomotion where an organism moves by means of its two rear limbs or legs. An animal or machine that usually moves in a bipedal manner is known as a biped , meaning 'two feet' (from Latin ''bis'' 'double' a ...
, using only two limbs for locomotion, which can be seen in, for example, humans and the great apes. Bipedal species have a larger field of vision than quadrupeds, conserve more energy and have the ability to manipulate objects with their hands, which aids in foraging. Instead of walking, some bipeds hop, such as kangaroos and kangaroo rats.
Animals will use different gaits for different speeds, terrain and situations. For example, horses show four natural gaits, the slowest horse gait
Horses can use various gaits (patterns of leg movement) during locomotion across solid ground, either naturally or as a result of specialized training by humans.Ensminger, M. E. ''Horses and Horsemanship'' 6th edition USA: Interstate Publisher ...
is the walk, then there are three faster gaits which, from slowest to fastest, are the trot, the canter and the gallop. Animals may also have unusual gaits that are used occasionally, such as for moving sideways or backwards. For example, the main human gaits are bipedal walking and running, but they employ many other gaits occasionally, including a four-legged crawl in tight spaces. Mammals show a vast range of gait
Gait is the pattern of movement of the limbs of animals, including humans, during locomotion over a solid substrate. Most animals use a variety of gaits, selecting gait based on speed, terrain, the need to maneuver, and energetic efficiency. Di ...
s, the order that they place and lift their appendages in locomotion. Gaits can be grouped into categories according to their patterns of support sequence. For quadrupeds, there are three main categories: walking gaits, running gaits and leaping gaits
Gait is the pattern of movement of the limbs of animals, including humans, during locomotion over a solid substrate. Most animals use a variety of gaits, selecting gait based on speed, terrain, the need to maneuver, and energetic efficiency. Dif ...
. Walking is the most common gait, where some feet are on the ground at any given time, and found in almost all legged animals. Running is considered to occur when at some points in the stride all feet are off the ground in a moment of suspension.
Arboreal
 Arboreal animals frequently have elongated limbs that help them cross gaps, reach fruit or other resources, test the firmness of support ahead and, in some cases, to brachiate (swing between trees). Many arboreal species, such as tree porcupines, silky anteaters, spider monkeys, and possums, use prehensile tails to grasp branches. In the spider monkey, the tip of the tail has either a bare patch or adhesive pad, which provides increased friction. Claws can be used to interact with rough substrates and reorient the direction of forces the animal applies. This is what allows
Arboreal animals frequently have elongated limbs that help them cross gaps, reach fruit or other resources, test the firmness of support ahead and, in some cases, to brachiate (swing between trees). Many arboreal species, such as tree porcupines, silky anteaters, spider monkeys, and possums, use prehensile tails to grasp branches. In the spider monkey, the tip of the tail has either a bare patch or adhesive pad, which provides increased friction. Claws can be used to interact with rough substrates and reorient the direction of forces the animal applies. This is what allows squirrel
Squirrels are members of the family Sciuridae, a family that includes small or medium-size rodents. The squirrel family includes tree squirrels, ground squirrels (including chipmunks and prairie dogs, among others), and flying squirrels. Squ ...
s to climb tree trunks that are so large to be essentially flat from the perspective of such a small animal. However, claws can interfere with an animal's ability to grasp very small branches, as they may wrap too far around and prick the animal's own paw. Frictional gripping is used by primates, relying upon hairless fingertips. Squeezing the branch between the fingertips generates frictional force that holds the animal's hand to the branch. However, this type of grip depends upon the angle of the frictional force, thus upon the diameter of the branch, with larger branches resulting in reduced gripping ability. To control descent, especially down large diameter branches, some arboreal animals such as squirrels have evolved highly mobile ankle joints that permit rotating the foot into a 'reversed' posture. This allows the claws to hook into the rough surface of the bark, opposing the force of gravity. Small size provides many advantages to arboreal species: such as increasing the relative size of branches to the animal, lower center of mass, increased stability, lower mass (allowing movement on smaller branches) and the ability to move through more cluttered habitat. Size relating to weight affects gliding animals such as the sugar glider. Some species of primate, bat and all species of sloth achieve passive stability by hanging beneath the branch. Both pitching and tipping become irrelevant, as the only method of failure would be losing their grip.
Aerial
Bats are the only mammals that can truly fly. They fly through the air at a constant speed by moving their wings up and down (usually with some fore-aft movement as well). Because the animal is in motion, there is some airflow relative to its body which, combined with the velocity of the wings, generates a faster airflow moving over the wing. This generates a lift force vector pointing forwards and upwards, and a drag force vector pointing rearwards and upwards. The upwards components of these counteract gravity, keeping the body in the air, while the forward component provides thrust to counteract both the drag from the wing and from the body as a whole. The wings of bats are much thinner and consist of more bones than those of birds, allowing bats to maneuver more accurately and fly with more lift and less drag. By folding the wings inwards towards their body on the upstroke, they use 35% less energy during flight than birds. The membranes are delicate, ripping easily; however, the tissue of the bat's membrane is able to regrow, such that small tears can heal quickly. The surface of their wings is equipped with touch-sensitive receptors on small bumps called Merkel cells, also found on human fingertips. These sensitive areas are different in bats, as each bump has a tiny hair in the center, making it even more sensitive and allowing the bat to detect and collect information about the air flowing over its wings, and to fly more efficiently by changing the shape of its wings in response.Fossorial and subterranean
A fossorial (from Latin ''fossor'', meaning "digger") is an animal adapted to digging which lives primarily, but not solely, underground. Some examples are badgers, and naked mole-rats. Many rodent species are also considered fossorial because they live in burrows for most but not all of the day. Species that live exclusively underground are subterranean, and those with limited adaptations to a fossorial lifestyle sub-fossorial. Some organisms are fossorial to aid in temperature regulation while others use the underground habitat for protection from predators or forfood storage
Food storage is a way of decreasing the variability of the food supply in the face of natural, inevitable variability. p.507 It allows food to be eaten for some time (typically weeks to months) after harvest rather than solely immediately. I ...
.Damiani, R, 2003, Earliest evidence of cynodont burrowing, The Royal Society Publishing, Volume 270, Issue 1525
Fossorial mammals have a fusiform body, thickest at the shoulders and tapering off at the tail and nose. Unable to see in the dark burrows, most have degenerated eyes, but degeneration varies between species; pocket gophers, for example, are only semi-fossorial and have very small yet functional eyes, in the fully fossorial marsupial mole the eyes are degenerated and useless, talpa moles have vestigial eyes and the cape golden mole has a layer of skin covering the eyes. External ears flaps are also very small or absent. Truly fossorial mammals have short, stout legs as strength is more important than speed to a burrowing mammal, but semi-fossorial mammals have cursorial legs. The front paws are broad and have strong claws to help in loosening dirt while excavating burrows, and the back paws have webbing, as well as claws, which aids in throwing loosened dirt backwards. Most have large incisors to prevent dirt from flying into their mouth.
Many fossorial mammals such as shrews, hedgehogs, and moles were classified under the now obsolete order Insectivora.
Aquatic
Fully aquatic mammals, the cetaceans and sirenians, have lost their legs and have a tail fin to propel themselves through the water. Flipper movement is continuous. Whales swim by moving their tail fin and lower body up and down, propelling themselves through vertical movement, while their flippers are mainly used for steering. Their skeletal anatomy allows them to be fast swimmers. Most species have a dorsal fin to prevent themselves from turning upside-down in the water. The flukes of sirenians are raised up and down in long strokes to move the animal forward, and can be twisted to turn. The forelimbs are paddle-like flippers which aid in turning and slowing.Semi-aquatic
In biology, semiaquatic can refer to various types of animals that spend part of their time in water, or plants that naturally grow partially submerged in water. Examples are given below.
Semiaquatic animals
Semiaquatic animals include:
* Verte ...
mammals, like pinnipeds, have two pairs of flippers on the front and back, the fore-flippers and hind-flippers. The elbows and ankles are enclosed within the body. Pinnipeds have several adaptions for reducing drag
Drag or The Drag may refer to:
Places
* Drag, Norway, a village in Tysfjord municipality, Nordland, Norway
* ''Drág'', the Hungarian name for Dragu Commune in Sălaj County, Romania
* Drag (Austin, Texas), the portion of Guadalupe Street adj ...
. In addition to their streamlined bodies, they have smooth networks of muscle bundles in their skin that may increase laminar flow
In fluid dynamics, laminar flow is characterized by fluid particles following smooth paths in layers, with each layer moving smoothly past the adjacent layers with little or no mixing. At low velocities, the fluid tends to flow without lateral mi ...
and make it easier for them to slip through water. They also lack arrector pili
The arrector pili muscles, also known as hair erector muscles, are small muscles attached to hair follicles in mammals. Contraction of these muscles causes the hairs to stand on end, known colloquially as goose bumps (piloerection).
Structure
E ...
, so their fur can be streamlined as they swim. They rely on their fore-flippers for locomotion in a wing-like manner similar to penguin
Penguins (order (biology), order List of Sphenisciformes by population, Sphenisciformes , family (biology), family Spheniscidae ) are a group of Water bird, aquatic flightless birds. They live almost exclusively in the Southern Hemisphere: on ...
s and sea turtles. Fore-flipper movement is not continuous, and the animal glides between each stroke. Compared to terrestrial carnivorans, the fore-limbs are reduced in length, which gives the locomotor muscles at the shoulder and elbow joints greater mechanical advantage; the hind-flippers serve as stabilizers. Other semi-aquatic mammals include beavers, hippopotamuses, otters and platypuses. Hippos are very large semi-aquatic mammals, and their barrel-shaped bodies have wikt:graviportal, graviportal skeletal structures, adapted to carrying their enormous weight, and their specific gravity allows them to sink and move along the bottom of a river.
Behavior
Communication and vocalization
Feeding
To maintain a high constant body temperature is energy expensive—mammals therefore need a nutritious and plentiful diet. While the earliest mammals were probably predators, different species have since adapted to meet their dietary requirements in a variety of ways. Some eat other animals—this is a carnivore, carnivorous diet (and includes insectivorous diets). Other mammals, called herbivores, eat plants, which contain complex carbohydrates such as cellulose. An herbivorous diet includes subtypes such as granivory (seed eating), folivory (leaf eating), frugivory (fruit eating), nectarivory (nectar eating), gummivory (gum eating) and mycophagy (fungus eating). The digestive tract of an herbivore is host to bacteria that ferment these complex substances, and make them available for digestion, which are either housed in the multichambered stomach or in a large cecum. Some mammals are coprophagous, consumingfeces
Feces ( or faeces), known colloquially and in slang as poo and poop, are the solid or semi-solid remains of food that was not digested in the small intestine, and has been broken down by bacteria in the large intestine. Feces contain a relati ...
to absorb the nutrients not digested when the food was first ingested. An omnivore eats both prey and plants. Carnivorous mammals have a simple digestive system, digestive tract because the proteins, lipids and minerals found in meat require little in the way of specialized digestion. Exceptions to this include baleen whale
Baleen whales (systematic name Mysticeti), also known as whalebone whales, are a parvorder of carnivorous marine mammals of the infraorder Cetacea (whales, dolphins and porpoises) which use keratinaceous baleen plates (or "whalebone") in their ...
s who also house gut flora in a multi-chambered stomach, like terrestrial herbivores.
The size of an animal is also a factor in determining diet type (Allen's rule). Since small mammals have a high ratio of heat-losing surface area to heat-generating volume, they tend to have high energy requirements and a high metabolism, metabolic rate. Mammals that weigh less than about are mostly insectivorous because they cannot tolerate the slow, complex digestive process of an herbivore. Larger animals, on the other hand, generate more heat and less of this heat is lost. They can therefore tolerate either a slower collection process (carnivores that feed on larger vertebrates) or a slower digestive process (herbivores). Furthermore, mammals that weigh more than usually cannot collect enough insects during their waking hours to sustain themselves. The only large insectivorous mammals are those that feed on huge colonies of insects (ants or termites).
Some mammals are omnivores and display varying degrees of carnivory and herbivory, generally leaning in favor of one more than the other. Since plants and meat are digested differently, there is a preference for one over the other, as in bears where some species may be mostly carnivorous and others mostly herbivorous. They are grouped into three categories: mesocarnivore, mesocarnivory (50–70% meat), hypercarnivore, hypercarnivory (70% and greater of meat), and hypocarnivore, hypocarnivory (50% or less of meat). The dentition of hypocarnivores consists of dull, triangular carnassial teeth meant for grinding food. Hypercarnivores, however, have conical teeth and sharp carnassials meant for slashing, and in some cases strong jaws for bone-crushing, as in the case of hyenas, allowing them to consume bones; some extinct groups, notably the Machairodontinae, had saber-shaped maxillary canine, canines.
Some physiological carnivores consume plant matter and some physiological herbivores consume meat. From a behavioral aspect, this would make them omnivores, but from the physiological standpoint, this may be due to zoopharmacognosy. Physiologically, animals must be able to obtain both energy and nutrients from plant and animal materials to be considered omnivorous. Thus, such animals are still able to be classified as carnivores and herbivores when they are just obtaining nutrients from materials originating from sources that do not seemingly complement their classification. For example, it is well documented that some ungulates such as giraffes, camels, and cattle, will gnaw on bones to consume particular minerals and nutrients. Also, cats, which are generally regarded as obligate carnivores, occasionally eat grass to regurgitate indigestible material (such as hairballs), aid with hemoglobin production, and as a laxative.
Many mammals, in the absence of sufficient food requirements in an environment, suppress their metabolism and conserve energy in a process known as hibernation. In the period preceding hibernation, larger mammals, such as bears, become polyphagic to increase fat stores, whereas smaller mammals prefer to collect and stash food. The slowing of the metabolism is accompanied by a decreased heart and respiratory rate, as well as a drop in internal temperatures, which can be around ambient temperature in some cases. For example, the internal temperatures of hibernating arctic ground squirrels can drop to , however the head and neck always stay above . A few mammals in hot environments aestivate in times of drought or extreme heat, for example the fat-tailed dwarf lemur (''Cheirogaleus medius'').
Intelligence
In intelligent mammals, such as primates, the cerebrum is larger relative to the rest of the brain. Intelligence itself is not easy to define, but indications of intelligence include the ability to learn, matched with behavioral flexibility. Rat IQ, Rats, for example, are considered to be highly intelligent, as they can learn and perform new tasks, an ability that may be important when they first colonize a fresh biome, habitat. In some mammals, food gathering appears to be related to intelligence: a deer feeding on plants has a brain smaller than a cat, which must think to outwit its prey. Tool use by animals may indicate different levels of learning and Animal cognition, cognition. The Tool use by sea otters, sea otter uses rocks as essential and regular parts of its foraging behaviour (smashing abalone from rocks or breaking open shells), with some populations spending 21% of their time making tools. Other tool use, such as chimpanzees using twigs to "fish" for termites, may be developed by Observational learning, watching others use tools and may even be a true example of animal teaching. Tools may even be used in solving puzzles in which the animal appears to experience a Eureka effect, "Eureka moment". Other mammals that do not use tools, such as dogs, can also experience a Eureka moment.
Brain size was previously considered a major indicator of the intelligence of an animal. Since most of the brain is used for maintaining bodily functions, greater ratios of Brain-to-body mass ratio, brain to body mass may increase the amount of brain mass available for more complex cognitive tasks. Allometric analysis indicates that mammalian brain size scales at approximately the or exponent of the body mass. Comparison of a particular animal's brain size with the expected brain size based on such allometric analysis provides an encephalization quotient, encephalisation quotient that can be used as another indication of animal intelligence. Sperm whales have the largest brain mass of any animal on earth, averaging and in mature males.
Self-awareness appears to be a sign of abstract thinking. Self-awareness, although not well-defined, is believed to be a precursor to more advanced processes such as metacognition, metacognitive reasoning. The traditional method for measuring this is the mirror test, which determines if an animal possesses the ability of self-recognition. Mammals that have passed the mirror test include Asian elephants (some pass, some do not); chimpanzees; bonobos; orangutans; humans, from 18 months (mirror stage); bottlenose dolphins killer whales; and false killer whales.
Tool use by animals may indicate different levels of learning and Animal cognition, cognition. The Tool use by sea otters, sea otter uses rocks as essential and regular parts of its foraging behaviour (smashing abalone from rocks or breaking open shells), with some populations spending 21% of their time making tools. Other tool use, such as chimpanzees using twigs to "fish" for termites, may be developed by Observational learning, watching others use tools and may even be a true example of animal teaching. Tools may even be used in solving puzzles in which the animal appears to experience a Eureka effect, "Eureka moment". Other mammals that do not use tools, such as dogs, can also experience a Eureka moment.
Brain size was previously considered a major indicator of the intelligence of an animal. Since most of the brain is used for maintaining bodily functions, greater ratios of Brain-to-body mass ratio, brain to body mass may increase the amount of brain mass available for more complex cognitive tasks. Allometric analysis indicates that mammalian brain size scales at approximately the or exponent of the body mass. Comparison of a particular animal's brain size with the expected brain size based on such allometric analysis provides an encephalization quotient, encephalisation quotient that can be used as another indication of animal intelligence. Sperm whales have the largest brain mass of any animal on earth, averaging and in mature males.
Self-awareness appears to be a sign of abstract thinking. Self-awareness, although not well-defined, is believed to be a precursor to more advanced processes such as metacognition, metacognitive reasoning. The traditional method for measuring this is the mirror test, which determines if an animal possesses the ability of self-recognition. Mammals that have passed the mirror test include Asian elephants (some pass, some do not); chimpanzees; bonobos; orangutans; humans, from 18 months (mirror stage); bottlenose dolphins killer whales; and false killer whales.
Social structure
 Eusociality is the highest level of social organization. These societies have an overlap of adult generations, the division of reproductive labor and cooperative caring of young. Usually insects, such as bees, ants and termites, have eusocial behavior, but it is demonstrated in two rodent species: the naked mole-rat and the Damaraland mole-rat.
Presociality is when animals exhibit more than just sexual interactions with members of the same species, but fall short of qualifying as eusocial. That is, presocial animals can display communal living, cooperative care of young, or primitive division of reproductive labor, but they do not display all of the three essential traits of eusocial animals. Humans and some species of Callitrichidae (marmosets and tamarins) are unique among primates in their degree of cooperative care of young. Harry Harlow set up an experiment with rhesus monkeys, presocial primates, in 1958; the results from this study showed that social encounters are necessary in order for the young monkeys to develop both mentally and sexually.
A fission-fusion society is a society that changes frequently in its size and composition, making up a permanent social group called the "parent group". Permanent social networks consist of all individual members of a community and often varies to track changes in their environment. In a fission–fusion society, the main parent group can fracture (fission) into smaller stable subgroups or individuals to adapt to Social environment, environmental or social circumstances. For example, a number of males may break off from the main group in order to hunt or forage for food during the day, but at night they may return to join (fusion) the primary group to share food and partake in other activities. Many mammals exhibit this, such as primates (for example orangutans and spider monkeys), elephants, spotted hyenas, lions, and dolphins.
Solitary animals defend a territory and avoid social interactions with the members of its species, except during breeding season. This is to avoid resource competition, as two individuals of the same species would occupy the same niche, and to prevent depletion of food. A solitary animal, while foraging, can also be less conspicuous to predators or prey.
Eusociality is the highest level of social organization. These societies have an overlap of adult generations, the division of reproductive labor and cooperative caring of young. Usually insects, such as bees, ants and termites, have eusocial behavior, but it is demonstrated in two rodent species: the naked mole-rat and the Damaraland mole-rat.
Presociality is when animals exhibit more than just sexual interactions with members of the same species, but fall short of qualifying as eusocial. That is, presocial animals can display communal living, cooperative care of young, or primitive division of reproductive labor, but they do not display all of the three essential traits of eusocial animals. Humans and some species of Callitrichidae (marmosets and tamarins) are unique among primates in their degree of cooperative care of young. Harry Harlow set up an experiment with rhesus monkeys, presocial primates, in 1958; the results from this study showed that social encounters are necessary in order for the young monkeys to develop both mentally and sexually.
A fission-fusion society is a society that changes frequently in its size and composition, making up a permanent social group called the "parent group". Permanent social networks consist of all individual members of a community and often varies to track changes in their environment. In a fission–fusion society, the main parent group can fracture (fission) into smaller stable subgroups or individuals to adapt to Social environment, environmental or social circumstances. For example, a number of males may break off from the main group in order to hunt or forage for food during the day, but at night they may return to join (fusion) the primary group to share food and partake in other activities. Many mammals exhibit this, such as primates (for example orangutans and spider monkeys), elephants, spotted hyenas, lions, and dolphins.
Solitary animals defend a territory and avoid social interactions with the members of its species, except during breeding season. This is to avoid resource competition, as two individuals of the same species would occupy the same niche, and to prevent depletion of food. A solitary animal, while foraging, can also be less conspicuous to predators or prey.
 In a dominance hierarchy, hierarchy, individuals are either dominant or submissive. A despotic hierarchy is where one individual is dominant while the others are submissive, as in wolves and lemurs, and a pecking order is a linear ranking of individuals where there is a top individual and a bottom individual. Pecking orders may also be ranked by sex, where the lowest individual of a sex has a higher ranking than the top individual of the other sex, as in hyenas. Dominant individuals, or alphas, have a high chance of reproductive success, especially in harems where one or a few males (resident males) have exclusive breeding rights to females in a group. Non-resident males can also be accepted in harems, but some species, such as the common vampire bat (''Desmodus rotundus''), may be more strict.
Some mammals are perfectly Monogamy in animals, monogamous, meaning that they pair bond, mate for life and take no other partners (even after the original mate's death), as with wolves, Eurasian beavers, and otters. There are three types of polygamy: either one or multiple dominant males have breeding rights (polygyny in animals, polygyny), multiple males that females mate with (polyandry), or multiple males have exclusive relations with multiple females (polygynandry). It is much more common for polygynous mating to happen, which, excluding lek mating, leks, are estimated to occur in up to 90% of mammals. Lek mating occurs when males congregate around females and try to attract them with various courtship displays and vocalizations, as in harbor seals.
All higher mammals (excluding monotremes) share two major adaptations for care of the young: live birth and lactation. These imply a group-wide choice of a degree of parental care. They may build nests and dig burrows to raise their young in, or feed and guard them often for a prolonged period of time. Many mammals are K-selected, and invest more time and energy into their young than do r-selected animals. When two animals mate, they both share an interest in the success of the offspring, though often to different extremes. Mammalian females exhibit some degree of maternal aggression, another example of parental care, which may be targeted against other females of the species or the young of other females; however, some mammals may "aunt" the infants of other females, and care for them. Mammalian males may play a role in child rearing, as with tenrecs, however this varies species to species, even within the same genus. For example, the males of the southern pig-tailed macaque (''Macaca nemestrina'') do not participate in child care, whereas the males of the Japanese macaque (''M. fuscata'') do.
In a dominance hierarchy, hierarchy, individuals are either dominant or submissive. A despotic hierarchy is where one individual is dominant while the others are submissive, as in wolves and lemurs, and a pecking order is a linear ranking of individuals where there is a top individual and a bottom individual. Pecking orders may also be ranked by sex, where the lowest individual of a sex has a higher ranking than the top individual of the other sex, as in hyenas. Dominant individuals, or alphas, have a high chance of reproductive success, especially in harems where one or a few males (resident males) have exclusive breeding rights to females in a group. Non-resident males can also be accepted in harems, but some species, such as the common vampire bat (''Desmodus rotundus''), may be more strict.
Some mammals are perfectly Monogamy in animals, monogamous, meaning that they pair bond, mate for life and take no other partners (even after the original mate's death), as with wolves, Eurasian beavers, and otters. There are three types of polygamy: either one or multiple dominant males have breeding rights (polygyny in animals, polygyny), multiple males that females mate with (polyandry), or multiple males have exclusive relations with multiple females (polygynandry). It is much more common for polygynous mating to happen, which, excluding lek mating, leks, are estimated to occur in up to 90% of mammals. Lek mating occurs when males congregate around females and try to attract them with various courtship displays and vocalizations, as in harbor seals.
All higher mammals (excluding monotremes) share two major adaptations for care of the young: live birth and lactation. These imply a group-wide choice of a degree of parental care. They may build nests and dig burrows to raise their young in, or feed and guard them often for a prolonged period of time. Many mammals are K-selected, and invest more time and energy into their young than do r-selected animals. When two animals mate, they both share an interest in the success of the offspring, though often to different extremes. Mammalian females exhibit some degree of maternal aggression, another example of parental care, which may be targeted against other females of the species or the young of other females; however, some mammals may "aunt" the infants of other females, and care for them. Mammalian males may play a role in child rearing, as with tenrecs, however this varies species to species, even within the same genus. For example, the males of the southern pig-tailed macaque (''Macaca nemestrina'') do not participate in child care, whereas the males of the Japanese macaque (''M. fuscata'') do.
Humans and other mammals
In human culture
 Non-human mammals play a wide variety of roles in human culture. They are the most popular of pets, with tens of millions of dogs, cats and other animals including rabbits and mice kept by families around the world. Mammals such as mammoths, horses and deer are among the earliest subjects of art, being found in Upper Paleolithic cave paintings such as at Lascaux. Major artists such as Albrecht Dürer, George Stubbs and Edwin Landseer are known for their portraits of mammals. Many species of mammals have been hunted for sport and for food; deer and wild boar are especially popular as game (hunting), game animals. Mammals such as horse racing, horses and greyhound racing, dogs are widely raced for sport, often combined with gambling, betting on the outcome. There is a tension between the role of animals as companions to humans, and their existence as individuals with animal rights, rights of their own. Mammals further play a wide variety of roles in literature, film, mythology, and religion.
Non-human mammals play a wide variety of roles in human culture. They are the most popular of pets, with tens of millions of dogs, cats and other animals including rabbits and mice kept by families around the world. Mammals such as mammoths, horses and deer are among the earliest subjects of art, being found in Upper Paleolithic cave paintings such as at Lascaux. Major artists such as Albrecht Dürer, George Stubbs and Edwin Landseer are known for their portraits of mammals. Many species of mammals have been hunted for sport and for food; deer and wild boar are especially popular as game (hunting), game animals. Mammals such as horse racing, horses and greyhound racing, dogs are widely raced for sport, often combined with gambling, betting on the outcome. There is a tension between the role of animals as companions to humans, and their existence as individuals with animal rights, rights of their own. Mammals further play a wide variety of roles in literature, film, mythology, and religion.
Uses and importance
 The domestication of mammals was instrumental in the Neolithic Revolution, Neolithic development of agriculture and of civilization, causing farmers to replace hunter-gatherers around the world. This transition from hunting and gathering to pastoralism, herding flocks and agriculture, growing crops was a major step in human history. The new agricultural economies, based on domesticated mammals, caused "radical restructuring of human societies, worldwide alterations in biodiversity, and significant changes in the Earth's landforms and its atmosphere... momentous outcomes".
Domestication, Domestic mammals form a large part of the livestock raised for
The domestication of mammals was instrumental in the Neolithic Revolution, Neolithic development of agriculture and of civilization, causing farmers to replace hunter-gatherers around the world. This transition from hunting and gathering to pastoralism, herding flocks and agriculture, growing crops was a major step in human history. The new agricultural economies, based on domesticated mammals, caused "radical restructuring of human societies, worldwide alterations in biodiversity, and significant changes in the Earth's landforms and its atmosphere... momentous outcomes".
Domestication, Domestic mammals form a large part of the livestock raised for meat
Meat is animal flesh that is eaten as food. Humans have hunted, farmed, and scavenged animals for meat since prehistoric times. The establishment of settlements in the Neolithic Revolution allowed the domestication of animals such as chic ...
across the world. They include (2009) around 1.4 billion cattle, 1 billion sheep, 1 billion domestic pigs, and (1985) over 700 million rabbits. Working animal, Working domestic animals including cattle and horses have been used for work and transport from the origins of agriculture, their numbers declining with the arrival of mechanised transport and agricultural machinery. In 2004 they still provided some 80% of the power for the mainly small farms in the third world, and some 20% of the world's transport, again mainly in rural areas. In mountainous regions unsuitable for wheeled vehicles, pack animals continue to transport goods. Mammal skins provide leather for shoes, clothing and upholstery. Wool from mammals including sheep, goats and alpacas has been used for centuries for clothing.
 Mammals serve a major role in science as animal model, experimental animals, both in fundamental biological research, such as in genetics, and in the development of new medicines, which must be tested exhaustively to demonstrate their Pharmacovigilance, safety. Millions of mammals, especially mice and rats, are used in animal testing, experiments each year. A knockout mouse is a genetically modified mouse with an inactivated gene, replaced or disrupted with an artificial piece of DNA. They enable the study of sequencing, sequenced genes whose functions are unknown. A small percentage of the mammals are non-human primates, used in research for their similarity to humans.
Despite the benefits domesticated mammals had for human development, humans have an increasingly detrimental effect on wild mammals across the world. It has been estimated that the mass of all ''wild'' mammals has declined to only 4% of all mammals, with 96% of mammals being humans and their livestock now (see figure). In fact, terrestrial wild mammals make up only 2% of all mammals.
Mammals serve a major role in science as animal model, experimental animals, both in fundamental biological research, such as in genetics, and in the development of new medicines, which must be tested exhaustively to demonstrate their Pharmacovigilance, safety. Millions of mammals, especially mice and rats, are used in animal testing, experiments each year. A knockout mouse is a genetically modified mouse with an inactivated gene, replaced or disrupted with an artificial piece of DNA. They enable the study of sequencing, sequenced genes whose functions are unknown. A small percentage of the mammals are non-human primates, used in research for their similarity to humans.
Despite the benefits domesticated mammals had for human development, humans have an increasingly detrimental effect on wild mammals across the world. It has been estimated that the mass of all ''wild'' mammals has declined to only 4% of all mammals, with 96% of mammals being humans and their livestock now (see figure). In fact, terrestrial wild mammals make up only 2% of all mammals.
Hybrids
Hybrids are offspring resulting from the breeding of two genetically distinct individuals, which usually will result in a high degree of heterozygosity, though hybrid and heterozygous are not synonymous. The deliberate or accidental hybridizing of two or more species of closely related animals through captive breeding is a human activity which has been in existence for millennia and has grown for economic purposes. Hybrids between different subspecies within a species (such as between the Bengal tiger and Siberian tiger) are known as intra-specific hybrids. Hybrids between different species within the same genus (such as between lions and tigers) are known as interspecific hybrids or crosses. Hybrids between different genera (such as between sheep and goats) are known as intergeneric hybrids. Natural hybrids will occur in hybrid zones, where two populations of species within the same genera or species living in the same or adjacent areas will interbreed with each other. Some hybrids have been recognized as species, such as the red wolf (though this is controversial). Artificial selection, the deliberate selective breeding of domestic animals, is being used to breeding back, breed back Holocene extinction, recently extinct animals in an attempt to achieve an animal breed with a phenotype that resembles that extinct wildtype ancestor. A breeding-back (intraspecific) hybrid may be very similar to the extinct wildtype in appearance, ecological niche and to some extent genetics, but the initial gene pool of that wild type is lost forever with its extinction. As a result, bred-back breeds are at best vague look-alikes of extinct wildtypes, as Heck cattle are of the aurochs. Purebred wild species evolved to a specific ecology can be threatened with extinction through the process of genetic pollution, the uncontrolled hybridization, introgression genetic swamping which leads to homogenization or Fitness (biology), out-competition from the heterosis, heterosic hybrid species. When new populations are imported or selectively bred by people, or when habitat modification brings previously isolated species into contact, extinction in some species, especially rare varieties, is possible. Interbreeding can swamp the rarer gene pool and create hybrids, depleting the purebred gene pool. For example, the endangered wild water buffalo is most threatened with extinction by genetic pollution from the Water buffalo, domestic water buffalo. Such extinctions are not always apparent from a morphology (biology), morphological standpoint. Some degree of gene flow is a normal evolutionary process, nevertheless, hybridization threatens the existence of rare species.Threats
 The loss of species from ecological communities, defaunation, is primarily driven by human activity. This has resulted in empty forests, ecological communities depleted of large vertebrates. In the Quaternary extinction event, the mass die-off of megafaunal variety coincided with the appearance of humans, suggesting a human influence. One hypothesis is that humans hunted large mammals, such as the woolly mammoth, into extinction. The 2019 ''Global Assessment Report on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services'' by IPBES states that the total Biomass (ecology), biomass of wild mammals has declined by 82 percent since the beginning of human civilization. Wild animals make up just 4% of mammalian Biomass (ecology), biomass on earth, while humans and their domesticated animals make up 96%.
Various species are predicted to List of critically endangered species, become extinct in the near future, among them the rhinoceros, giraffes, and species of primates and pangolins. According to the WWF's 2020 ''Living Planet Report'', vertebrate wildlife populations have declined by 68% since 1970 as a result of human activities, particularly overconsumption, population growth and intensive farming, which is evidence that humans have triggered a sixth mass extinction event. Hunting alone threatens hundreds of mammalian species around the world. Scientists claim that the growing demand for
The loss of species from ecological communities, defaunation, is primarily driven by human activity. This has resulted in empty forests, ecological communities depleted of large vertebrates. In the Quaternary extinction event, the mass die-off of megafaunal variety coincided with the appearance of humans, suggesting a human influence. One hypothesis is that humans hunted large mammals, such as the woolly mammoth, into extinction. The 2019 ''Global Assessment Report on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services'' by IPBES states that the total Biomass (ecology), biomass of wild mammals has declined by 82 percent since the beginning of human civilization. Wild animals make up just 4% of mammalian Biomass (ecology), biomass on earth, while humans and their domesticated animals make up 96%.
Various species are predicted to List of critically endangered species, become extinct in the near future, among them the rhinoceros, giraffes, and species of primates and pangolins. According to the WWF's 2020 ''Living Planet Report'', vertebrate wildlife populations have declined by 68% since 1970 as a result of human activities, particularly overconsumption, population growth and intensive farming, which is evidence that humans have triggered a sixth mass extinction event. Hunting alone threatens hundreds of mammalian species around the world. Scientists claim that the growing demand for meat
Meat is animal flesh that is eaten as food. Humans have hunted, farmed, and scavenged animals for meat since prehistoric times. The establishment of settlements in the Neolithic Revolution allowed the domestication of animals such as chic ...
is contributing to biodiversity loss as this is a significant driver of deforestation and habitat destruction; species-rich habitats, such as significant portions of the Amazon rainforest, are being converted to agricultural land for meat production. Another influence is over-hunting and Species affected by poaching, poaching, which can reduce the overall population of game animals, especially those located near villages, as in the case of peccary, peccaries. The effects of poaching can especially be seen in the ivory trade with African elephants. Marine mammals are at risk from entanglement from fishing gear, notably Cetacean bycatch, cetaceans, with discard mortalities ranging from 65,000 to 86,000 individuals annually.
Attention is being given to endangered species globally, notably through the Convention on Biological Diversity, otherwise known as the Rio Accord, which includes 189 signatory countries that are focused on identifying endangered species and habitats. Another notable conservation organization is the IUCN, which has a membership of over 1,200 governmental and Non-governmental organization, non-governmental organizations.
List of recently extinct mammals, Recent extinctions can be directly attributed to human influences. The IUCN characterizes 'recent' extinction as those that have occurred past the cut-off point of 1500, and around 80 mammal species have gone extinct since that time and 2015. Some species, such as the Père David's deer are extinct in the wild, and survive solely in captive populations. Other species, such as the Florida panther, are Ecological extinction, ecologically extinct, surviving in such low numbers that they essentially have no impact on the ecosystem. Other populations are only Local extinction, locally extinct (extirpated), still existing elsewhere, but reduced in distribution, as with the extinction of gray whales in the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic.
Notes
See also
* List of mammal genera – living mammals * List of mammalogists * List of monotremes and marsupials * List of placental mammals * List of prehistoric mammals * List of threatened mammals of the United States * Lists of mammals by population, Lists of mammals by population size * Lists of mammals by region * Mammals described in the 2000s * Mammals in culture * Small mammalReferences
Further reading
* * * * * * * * *External links
Biodiversitymapping.org – All mammal orders in the world with distribution maps
Paleocene Mammals
a site covering the rise of the mammals, paleocene-mammals.de
Evolution of Mammals
a brief introduction to early mammals, enchantedlearning.com
European Mammal Atlas EMMA
from Societas Europaea Mammalogica, European-mammals.org
Marine Mammals of the World
– An overview of all marine mammals, including descriptions, both fully aquatic and semi-aquatic, noaa.gov
Mammalogy.org
The American Society of Mammalogists was established in 1919 for the purpose of promoting the study of mammals, and this website includes a mammal image library {{Authority control Mammals, Bathonian first appearances Extant Middle Jurassic first appearances Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus