This is a list of
Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
ese
inventions
An invention is a unique or novel device, method, composition, idea, or process. An invention may be an improvement upon a machine, product, or process for increasing efficiency or lowering cost. It may also be an entirely new concept. If an ...
and
discoveries. The Japanese have made contributions across a number of scientific, technological and art domains. In particular, the country has played a crucial role in the
digital revolution
The Information Age is a History by period, historical period that began in the mid-20th century. It is characterized by a rapid shift from traditional industries, as established during the Industrial Revolution, to an economy centered on info ...
since the 20th century, with many modern revolutionary and widespread technologies in fields such as
electronics
Electronics is a scientific and engineering discipline that studies and applies the principles of physics to design, create, and operate devices that manipulate electrons and other Electric charge, electrically charged particles. It is a subfield ...
and
robotics introduced by Japanese inventors and entrepreneurs.
Arts

*
Kamishibai — Originates from 8th century
Buddhist temple
A Buddhist temple or Buddhist monastery is the place of worship for Buddhism, Buddhists, the followers of Buddhism. They include the structures called vihara, chaitya, stupa, wat, khurul and pagoda in different regions and languages. Temples in B ...
s, where monks used ("picture scrolls"), an early combination of picture and text to convey a story.
**
Costumed superhero —
Ōgon Bat (1930) and
Prince of Gamma (early 1930s) were the earliest costumed
superheroes with
superpowers.
**
Mecha
In science fiction, or mechs are giant robots or machines, typically depicted as piloted, humanoid walking vehicles. The term was first used in Japanese (language), Japanese after shortening the English loanword or , but the meaning in Japan ...
— Dai Ningen Tanku from ''
Ōgon Bat'' (1931) was the first piloted
humanoid giant mecha
robot
A robot is a machine—especially one Computer program, programmable by a computer—capable of carrying out a complex series of actions Automation, automatically. A robot can be guided by an external control device, or the robot control, co ...
.
[ means Giant , is the Japanese title of The Master Mystery(1919), and the Japanese name of the Powered exoskeleton appearing in the film.It was a general Japanese phrase meaning "humanoid tank" too.]
**
Superhero
A superhero or superheroine is a fictional character who typically possesses ''superpowers'' or abilities beyond those of ordinary people, is frequently costumed concealing their identity, and fits the role of the hero, typically using their ...
secret identity
A secret identity is a person's code name, cryptonym, disguise, incognito, Cover (intelligence gathering), cover and/or alter ego which is not known to the general populace, most often used in fiction. Brought into popular culture by the Scarlet Pi ...
—
Prince of Gamma (early 1930s) was the earliest superhero with superpowers and a
secret identity
A secret identity is a person's code name, cryptonym, disguise, incognito, Cover (intelligence gathering), cover and/or alter ego which is not known to the general populace, most often used in fiction. Brought into popular culture by the Scarlet Pi ...
.
*
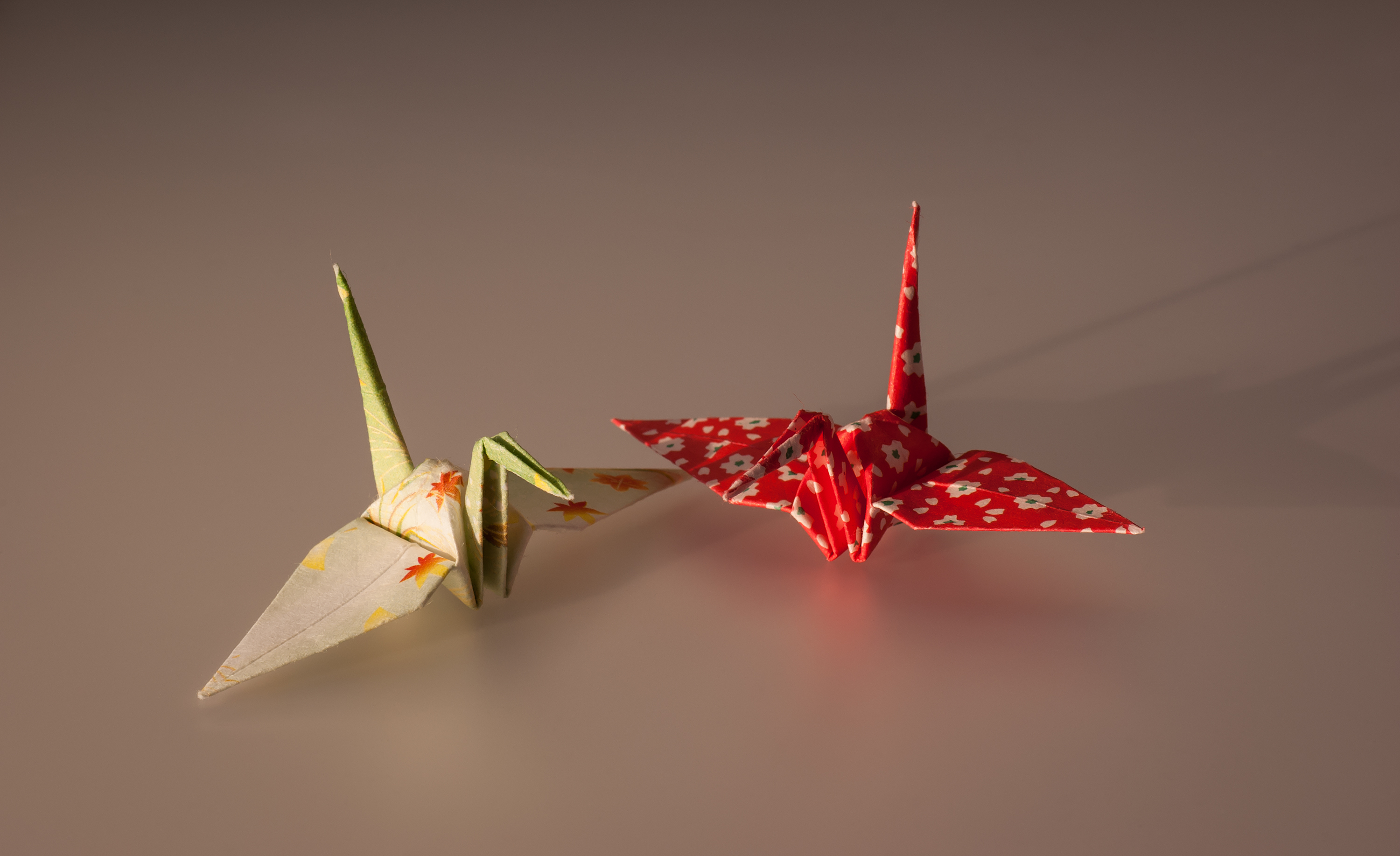
Origami — Folded
paper
Paper is a thin sheet material produced by mechanically or chemically processing cellulose fibres derived from wood, Textile, rags, poaceae, grasses, Feces#Other uses, herbivore dung, or other vegetable sources in water. Once the water is dra ...
began to be used for decorations and tools in
Shinto
, also called Shintoism, is a religion originating in Japan. Classified as an East Asian religions, East Asian religion by Religious studies, scholars of religion, it is often regarded by its practitioners as Japan's indigenous religion and as ...
ceremonies, where paper decorations and wrapped gifts in folded paper became stylized and established as ceremonial origami.
**
Paper crane (orizuru) — The ''
kozuka'' of a
Japanese sword
A is one of several types of traditionally made swords from Japan. Bronze swords were made as early as the Yayoi period (1,000 BC – 300 AD), though most people generally refer to the curved blades made from the Heian period (794–1185) to the ...
made by Gotō Eijō between the 1500s1600s was decorated with a picture of a crane made of origami.
**
Yoshizawa–Randlett system — The Yoshizawa–Randlett system is a diagramming system used for origami models. It was first developed by
Akira Yoshizawa in 1954. It was later improved upon by
Samuel Randlett and
Robert Harbin.
*
Revolving stage — Invented for the Kabuki theatre in Japan in the 18th century, the revolving stage was introduced into Western theater at the
Residenz theatre in Munich in 1896 under the influence of
japonism fever.
Animation
*
Anime
is a Traditional animation, hand-drawn and computer animation, computer-generated animation originating from Japan. Outside Japan and in English, ''anime'' refers specifically to animation produced in Japan. However, , in Japan and in Ja ...
— Japanese animation, or anime, today widely popular both in Japan and abroad, began in the early 20th century.
*
Bishōjo ''—'' Several characters created by
Hayao Miyazaki
is a Japanese animator, filmmaker, and manga artist. He co-founded Studio Ghibli and serves as honorary chairman. Throughout his career, Miyazaki has attained international acclaim as a masterful storyteller and creator of Anime, Japanese ani ...
are considered icons of the boom, the earliest being Lana from the TV series ''
Future Boy Conan'' (1978)
**
Moe — The character of Clarisse from Hayao Miyazaki's ''
The Castle of Cagliostro'' (1979) has been cited as a potential ancestral example.
*
Bullet time — The bullet time
visual effect originated as a
cel animation effect in the anime series ''
Speed Racer'' (1967).
*
CGI in
animated feature film — ''
Golgo 13: The Professional'' (1983) was the first
animated feature film
A feature film or feature-length film (often abbreviated to feature), also called a theatrical film, is a film (Film, motion picture, "movie" or simply “picture”) with a running time long enough to be considered the principal or sole present ...
to incorporate scenes with
CGI animation.
**
Photorealistic CGI animated feature film
A feature film or feature-length film (often abbreviated to feature), also called a theatrical film, is a film (Film, motion picture, "movie" or simply “picture”) with a running time long enough to be considered the principal or sole present ...
— ''
Final Fantasy: The Spirits Within'' (2001) was the first
computer-animated feature film with photorealistic characters.
*
Cyberpunk animation — The earliest animated
cyberpunk
Cyberpunk is a subgenre of science fiction in a dystopian futuristic setting said to focus on a combination of "low-life and high tech". It features futuristic technological and scientific achievements, such as artificial intelligence and cyberwa ...
work was the
original video animation (OVA) ''
Megazone 23'' (1985).
**
Digital rain — Originates from the
cyberpunk anime film ''
Ghost in the Shell'' (1995), a strong influence on ''
The Matrix'' (1999)''.''
[ Joel Silver, interviewed in "Scrolls to Screen: A Brief History of Anime" featurette on '' The Animatrix'' DVD.][Joel Silver, interviewed in "Making ''The Matrix''" featurette on ''The Matrix'' DVD.]
**
Postcyberpunk animation/film — The first postcyberpunk media work in an animated/film format was ''
Ghost in the Shell: Stand Alone Complex'' in 2002. It has been called "the most interesting, sustained postcyberpunk media work in existence".
**
Simulated reality — ''
Megazone 23'' (1985) tackled the concept of a simulated reality more than a decade before live-action films such as ''
Dark City'' (1998), ''The Matrix'' (1999) and ''
Existenz'' (1999).
*
Hadouken — Game designer
Takashi Nishiyama credits an energy attack called Hadouho (lit. the "Wave Motion Gun"), from the 1970s anime ''
Space Battleship Yamato
is a Japanese science fiction anime series written by Yoshinobu Nishizaki, directed by manga artist Leiji Matsumoto, and produced by Academy Productions. The series aired in Yomiuri TV from October 6, 1974 to March 30, 1975, totaling u ...
'', as the origin of Hadouken.
*
Original net animation (ONA) —
Makoto Shinkai was a pioneer of ONA, producing the earliest ONA
short films, including ''Tōi Sekai'' (1997)
and ''Kakomareta Sekai'' (1998).
**
Animated web film — The earliest animated web films were
Makoto Shinkai's ONA short films ''Tōi Sekai'' (1997)
and ''Kakomareta Sekai'' (1998).
**
Anime
is a Traditional animation, hand-drawn and computer animation, computer-generated animation originating from Japan. Outside Japan and in English, ''anime'' refers specifically to animation produced in Japan. However, , in Japan and in Ja ...
web series — The earliest anime web series was the ONA series ''
Infinite Ryvius: Illusion'' (2000).
*
Real robot — ''
Mobile Suit Gundam'' (1979) introduced the real robot concept and, along with ''
The Super Dimension Fortress Macross'' (1982), formed the basis of real robot anime.
[10 commandments of Real robot, Gundam Sentinel introduction, Gundam workshop, Format ACG]
*
Steampunk animation — The earliest example of steampunk
animation
Animation is a filmmaking technique whereby still images are manipulated to create moving images. In traditional animation, images are drawn or painted by hand on transparent celluloid sheets to be photographed and exhibited on film. Animati ...
was
Hayao Miyazaki
is a Japanese animator, filmmaker, and manga artist. He co-founded Studio Ghibli and serves as honorary chairman. Throughout his career, Miyazaki has attained international acclaim as a masterful storyteller and creator of Anime, Japanese ani ...
's anime series ''
Future Boy Conan'' (1978).
*
Superflat — A
postmodern art form, founded by the artist
Takashi Murakami, which is influenced by ''
manga
are comics or graphic novels originating from Japan. Most manga conform to a style developed in Japan in the late 19th century, and the form has a long history in earlier Japanese art. The term is used in Japan to refer to both comics ...
'' and ''
anime
is a Traditional animation, hand-drawn and computer animation, computer-generated animation originating from Japan. Outside Japan and in English, ''anime'' refers specifically to animation produced in Japan. However, , in Japan and in Ja ...
''.
*
Sweat drop — The sweat drop had long been part of
manga iconography
Japanese manga has developed a visual language or iconography for expressing emotion and other internal character states. This drawing style has also migrated into anime, as many manga are adapted into television shows and films and some of th ...
. The first anime to depict a large sweat drop, when a character is in trouble, is believed to be the 1991 anime adaptation of the manga ''
Goldfish Warning!''
*
Time loop animation — The earliest animated work with the time loop concept was
Mamoru Oshii's anime film ''
Urusei Yatsura 2: Beautiful Dreamer'' (1984).
*
Virtual idol — Originates from ''
Macross'' franchise (1982). First virtual idol was
Lynn Minmay from ''Macross''.
*
Virtual influencer — The
Japanese talent agency
Horipro created the first real-life AI virtual influencer,
Kyoko Date, in 1995.
Architecture
*
Capsule hotel — The first capsule hotel in the world opened in 1979 and was the Capsule Inn Osaka, located in the
Umeda district of
Osaka
is a Cities designated by government ordinance of Japan, designated city in the Kansai region of Honshu in Japan. It is the capital of and most populous city in Osaka Prefecture, and the List of cities in Japan, third-most populous city in J ...
, Japan and designed by
Kisho Kurokawa. From there, it spread to other cities within Japan. Since then, the concept has further spread to various other territories, including Belgium, China, Hong Kong, Iceland, India, Indonesia, and Poland.
*
Earthquake-resistant structure —
Shinbashira-based
pagodas and
temples are
earthquake
An earthquakealso called a quake, tremor, or tembloris the shaking of the Earth's surface resulting from a sudden release of energy in the lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those so weak they ...
resistant,
dating back to
Hōryū-ji (7th century).
*
Electronic wallpaper — At the FPD 2008 exhibition, Japanese company Soken demonstrated a wall with
electronic wall-paper.
[Techo]
Soken electronic wall-paper
*
Japanese castle
are fortresses constructed primarily of wood and stone. They evolved from the wooden stockades of earlier centuries and came into their best-known form in the 16th century. Castles in Japan were built to guard important or strategic sites, such a ...
— Fortresses constructed primarily out of stone and wood used for military defence in strategic locations.
*
Japanese pagoda — The Japanese
pagoda originates from the
Chinese pagoda
A pagoda is a tiered tower with multiple eaves common to Thailand, Cambodia, Nepal, India, China, Japan, Korea, Myanmar, Vietnam, and other parts of Asia. Most pagodas were built to have a religious function, most often Buddhism, Buddhist, bu ...
, but was adapted for Japan's environment. Notably, the addition of a
shinbashira pillar to better withstand
earthquakes in Japan
This is a list of earthquakes in Japan with either a magnitude greater than or equal to 7.0 or which caused significant damage or casualties. As indicated below, magnitude is measured on the Richter scale (''ML'') or the moment magnitude scale ('' ...
.
**
Tahōtō — Tahōtō is a form of
Japanese pagoda found primarily at
Esoteric
Western esotericism, also known as the Western mystery tradition, is a wide range of loosely related ideas and movements that developed within Western society. These ideas and currents are united since they are largely distinct both from orthod ...
Shingon
is one of the major schools of Buddhism in Japan and one of the few surviving Vajrayana lineages in East Asian Buddhism. It is a form of Japanese Esoteric Buddhism and is sometimes called "Tōmitsu" (東密 lit. "Esoteric uddhismof Tō- ...
and
Tendai school
Buddhist temples. Unlike most pagodas, it has two stories.
*
Metabolism
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the co ...
— A post-war Japanese architectural movement developed by a wide variety of Japanese architects including
Kiyonori Kikutake
(April 1, 1928 – December 26, 2011) was a prominent Japanese architect known as one of the founders of the Japanese Metabolist group. He was also the tutor and employer of several important Japanese architects, such as Toyo Ito, Shōzō ...
,
Kisho Kurokawa and
Fumihiko Maki, Metabolism aimed to fuse ideas about architectural
megastructures with those of organic biological growth.
[Lin (2010), p. 23]
*
Shinbashira — A central
pillar at the core of a Japanese pagoda or temple. The pillar structure is made out of straight trunks of
Japanese cypress (''hinoki'') trees.
Hōryū-ji (7th century) is an early example.
*
Wooden building
A building or edifice is an enclosed Structure#Load-bearing, structure with a roof, walls and window, windows, usually standing permanently in one place, such as a house or factory. Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, a ...
—
Hōryū-ji, a
Buddhist temple
A Buddhist temple or Buddhist monastery is the place of worship for Buddhism, Buddhists, the followers of Buddhism. They include the structures called vihara, chaitya, stupa, wat, khurul and pagoda in different regions and languages. Temples in B ...
built in the 7th century, is widely recognized as the world's oldest wooden building.
Cinema

*
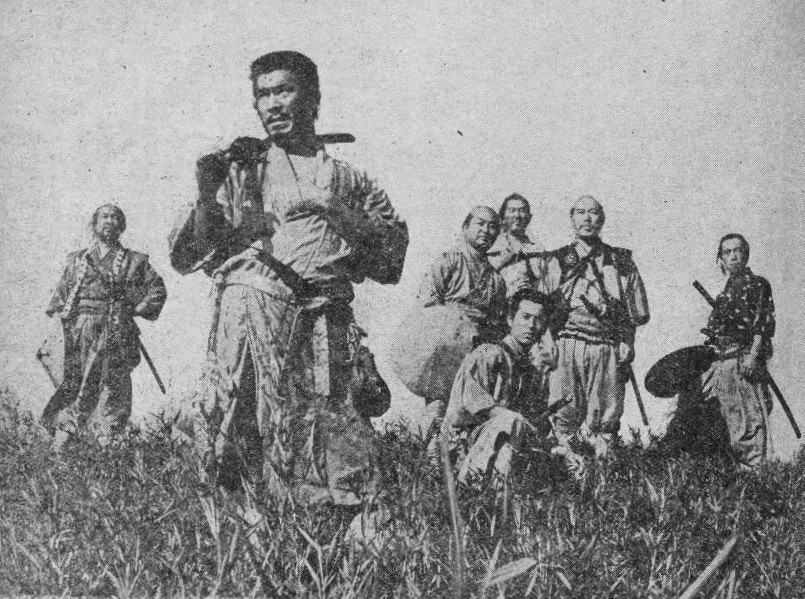
Blockbuster format —
Akira Kurosawa
was a Japanese filmmaker who List of works by Akira Kurosawa, directed 30 feature films in a career spanning six decades. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest and most influential filmmakers in the History of film, history of cinema ...
's ''
Seven Samurai'' (1954) was "the clearest precursor" and "the model for" the
Hollywood blockbuster format in the 1970s.
**
Assembling the team — ''
Seven Samurai'' (1954) originated the "assembling the team" subgenre of
action and
heist films.
**
Modern action film — ''
Seven Samurai'' (1954) is considered to be the first modern action film.
**
Cutting on action —
Akira Kurosawa
was a Japanese filmmaker who List of works by Akira Kurosawa, directed 30 feature films in a career spanning six decades. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest and most influential filmmakers in the History of film, history of cinema ...
's approach to "cutting on motion" has been widely adopted by many
Hollywood blockbuster films.
*
Buddy cop —
Akira Kurosawa
was a Japanese filmmaker who List of works by Akira Kurosawa, directed 30 feature films in a career spanning six decades. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest and most influential filmmakers in the History of film, history of cinema ...
's 1949 Japanese film ''
Stray Dog'', starring
Toshiro Mifune and
Takashi Shimura, is considered a precursor to the buddy cop film genre.
*
Fatality — Fatality finishing moves first appeared in ''
The Street Fighter'' (1974), a Japanese
martial arts film
Martial arts films are a subgenre of action films that feature martial arts combat between characters. These combats are usually the films' primary appeal and entertainment value, and often are a method of storytelling and character expression a ...
.
*
Jidaigeki
is a genre of film, television, and theatre in Japan. Literally meaning "historical drama, period dramas", it refers to stories that take place before the Meiji Restoration of 1868.
''Jidaigeki'' show the lives of the samurai, farmers, crafts ...
— Jidaigeki
silent films date back to the early 20th century.
**
Ninja film — Jidaigeki silent films began depicting
ninjas in the 1910s.
**
Samurai cinema — Jidaigeki silent films began depicting
samurai
The samurai () were members of the warrior class in Japan. They were originally provincial warriors who came from wealthy landowning families who could afford to train their men to be mounted archers. In the 8th century AD, the imperial court d ...
in the 1910s.
*
Kaiju
is a Japanese term that is commonly associated with media involving giant monsters. Its widespread contemporary use is credited to ''tokusatsu'' (special effects) director Eiji Tsuburaya and filmmaker Ishirō Honda, who popularized the ''kaiju'' ...
—
Yoshirō Edamasa's ''
The Great Buddha Arrival'' (1934) is one of the earliest examples of a ''kaiju'' film in
Japanese cinematic history.
**
Giant monster suit —
Eiji Tsuburaya
was a Japanese special effects director, filmmaker, and cinematographer. A co-creator of the ''Godzilla (franchise), Godzilla'' and ''Ultraman'' franchises, he is considered one of the most important and influential figures in the history o ...
, while working on the film ''
Godzilla'' (1954), formulated the technique of using a human actor in a
creature suit to play a
giant monster combined with the use of miniatures and scaled-down city sets.
[''Millennial Monsters: Japanese Toys and the Global Imagination'', pp. 47–48. ]
*
Man with No Name — A
stock character
A stock character, also known as a character archetype, is a type of character in a narrative (e.g. a novel, play, television show, or film) whom audiences recognize across many narratives or as part of a storytelling tradition or convention. Th ...
that originated with
Akira Kurosawa
was a Japanese filmmaker who List of works by Akira Kurosawa, directed 30 feature films in a career spanning six decades. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest and most influential filmmakers in the History of film, history of cinema ...
's ''
Yojimbo'' (1961), where the archetype was first portrayed by
Toshirō Mifune. The archetype was adapted by
Sergio Leone for his
Spaghetti Western
The spaghetti Western is a broad subgenre of Western films produced in Europe. It emerged in the mid-1960s in the wake of Sergio Leone's filmmaking style and international box-office success. The term was used by foreign critics because most o ...
''
Dollars Trilogy
The ''Dollars Trilogy'' (), also known as the ''Man with No Name Trilogy'' (), is an Italian film series consisting of three spaghetti western films directed by Sergio Leone. The films are titled '' A Fistful of Dollars'' (1964), '' For a Few ...
'' (1964–1966), with
Clint Eastwood
Clinton Eastwood Jr. (born May 31, 1930) is an American actor and film director. After achieving success in the Western (genre), Western TV series ''Rawhide (TV series), Rawhide'', Eastwood rose to international fame with his role as the "Ma ...
playing the role of the "Man with No Name" in Japan.
*
Time loop feature film —
''The Girl Who Leapt Through Time'' (1983), based on the
1969 novel of the same name, was the first
feature film
A feature film or feature-length film (often abbreviated to feature), also called a theatrical film, is a film (Film, motion picture, "movie" or simply “picture”) with a running time long enough to be considered the principal or sole present ...
about a
time loop
The time loop or temporal loop is a plot device in fiction whereby Character (arts), characters re-experience a span of time which is repeated, sometimes more than once, with some hope of breaking out of the cycle of repetition. Time loops are co ...
.
*
Tokusatsu
is a Japanese term for live-action films or television programs that make heavy use of practical special effects. Credited to special effects director Eiji Tsuburaya, ''tokusatsu'' mainly refers to science fiction film, science fiction, War fi ...
— ''Tokusatsu''
special effects date back to films by
Shōzō Makino (from 1914 to 1928).
**
Suitmation —
Eiji Tsuburaya
was a Japanese special effects director, filmmaker, and cinematographer. A co-creator of the ''Godzilla (franchise), Godzilla'' and ''Ultraman'' franchises, he is considered one of the most important and influential figures in the history o ...
, while working on the film ''
Godzilla'' (1954), formulated the special effects technique of suitmation, the use of a human actor in a costume to play a giant monster combined with the use of miniatures and scaled-down sets.
**
Suit actor — A notable early example was
Godzilla suit actor
Haruo Nakajima.
[Kawakita, Kōichi (February 20, 1999). ''Nihon tokusatsu eiga zukan : tōhōhen Best54''. Tōkyō: Seibidō Shuppan. .]
*
Yakuza film —
Mark Schilling named
Akira Kurosawa
was a Japanese filmmaker who List of works by Akira Kurosawa, directed 30 feature films in a career spanning six decades. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest and most influential filmmakers in the History of film, history of cinema ...
's ''
Drunken Angel'' from 1948 as the first to depict post-war
yakuza.
Comics

*
Comic book
A comic book, comic-magazine, or simply comic is a publication that consists of comics art in the form of sequential juxtaposed panel (comics), panels that represent individual scenes. Panels are often accompanied by descriptive prose and wri ...
— Adam L. Kern has suggested that ''
kibyoshi'', picture books from the late 18th century, may have been the world's first comic books. These graphical narratives share with modern
manga
are comics or graphic novels originating from Japan. Most manga conform to a style developed in Japan in the late 19th century, and the form has a long history in earlier Japanese art. The term is used in Japan to refer to both comics ...
humorous, satirical, and romantic themes.
Some works were mass-produced as serials using
woodblock printing.
*
Manga
are comics or graphic novels originating from Japan. Most manga conform to a style developed in Japan in the late 19th century, and the form has a long history in earlier Japanese art. The term is used in Japan to refer to both comics ...
— The
history of manga
Manga, in the sense of narrative multi-panel cartoons made in Japan, originated from Western style cartoons featured in late 19th-century Japanese publications. The form of manga as speech-balloon-based comics more specifically originated from ...
has origins in scrolls dating back to the 12th century, and it is believed they represent the basis for the right-to-left reading style. During the
Edo period
The , also known as the , is the period between 1600 or 1603 and 1868 in the history of Japan, when the country was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and some 300 regional ''daimyo'', or feudal lords. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengok ...
(1603–1867), ''Toba Ehon'' embedded the concept of manga.
The word itself first came into common usage in 1798,
[ ]
with the publication of works such as
Santō Kyōden's picturebook ''Shiji no yukikai'' (1798), and in the early 19th century with such works as Aikawa Minwa's ''Manga hyakujo'' (1814) and the ''
Hokusai Manga'' books (1814–1834).
**
Binge-viewing — ''
Shōnen Jump Shōnen Jump or Shonen Jump may refer to:
*''Weekly Shōnen Jump'', a Japanese manga anthology magazine published by Shueisha since 1968
*Jump (magazine line), ''Jump'' (magazine line)
**''Shōnen Jump+'', a digital magazine and mobile application s ...
'' (founded 1968) developed a formula of compiling chapters into standalone
tankōbon
A is a standard publishing format for books in Japan, alongside other formats such as ''shinsho'' (17x11 cm paperback books) and ''bunkobon''. Used as a loanword in English, the term specifically refers to a printed collection of a manga that w ...
volumes that could be "binged" all at once.
**
Cyberpunk manga — Began with
Katsuhiro Otomo's
manga
are comics or graphic novels originating from Japan. Most manga conform to a style developed in Japan in the late 19th century, and the form has a long history in earlier Japanese art. The term is used in Japan to refer to both comics ...
series ''
Akira'' (1982)''.''
**
Lone Wolf and Cub — A genre spawned by ''
Lone Wolf and Cub'' (1970).
Earliest example of genre is
Osamu Tezuka
Osamu Tezuka (, born , ''Tezuka Osamu'', – 9 February 1989) was a Japanese manga artist, cartoonist and animator. Considered to be among the greatest and most influential cartoonists of all time, his prolific output, pioneering techniques an ...
's ''
Dororo'' (1967).
**
Magical girl
is a Genre#Subgenre, subgenre of primarily Japanese fantasy media (including anime, manga, light novels, and live-action media) centered on young girls who possess magical abilities, which they typically use through an ideal alter ego into wh ...
— ''
Princess Knight'' (1953) was a prototype for the genre.
*
Mobile comic — Following the launch of
NTT's
i-mode (1999), Japanese mobile phone began offering downloadable mobile manga comics.
*
Steampunk comic —
Steampunk
Steampunk is a subgenre of science fiction that incorporates retrofuturistic technology and Applied arts, aesthetics inspired by, but not limited to, 19th-century Industrial Revolution, industrial steam engine, steam-powered machinery. Steampun ...
manga appeared in the 1940s, starting with
Osamu Tezuka
Osamu Tezuka (, born , ''Tezuka Osamu'', – 9 February 1989) was a Japanese manga artist, cartoonist and animator. Considered to be among the greatest and most influential cartoonists of all time, his prolific output, pioneering techniques an ...
's ''
Lost World
The lost world is a subgenre of the fantasy or science fiction genres that involves the discovery of an unknown Earth civilization. It began as a subgenre of the late- Victorian adventure romance and remains popular into the 21st century.
The ...
'' (1948).
*
Super robot — Introduced by
Go Nagai's manga series ''
Mazinger Z'' (1972).
Digital graphics

*
3D computer graphics software — Earliest was ''3D Art Graphics'', a set of
3D computer graphics
3D computer graphics, sometimes called Computer-generated imagery, CGI, 3D-CGI or three-dimensional Computer-generated imagery, computer graphics, are graphics that use a three-dimensional representation of geometric data (often Cartesian coor ...
effects written by Kazumasa Mitazawa and released for the
Apple II
Apple II ("apple Roman numerals, two", stylized as Apple ][) is a series of microcomputers manufactured by Apple Computer, Inc. from 1977 to 1993. The Apple II (original), original Apple II model, which gave the series its name, was designed ...
in 1978.
* Cel shading — First appeared in Riverhillsoft's
video game
A video game or computer game is an electronic game that involves interaction with a user interface or input device (such as a joystick, game controller, controller, computer keyboard, keyboard, or motion sensing device) to generate visual fe ...
''Doctor Hauzer'' (1994).
* Digital Visual Interface (DVI) — Developed in 1999 by the Digital Display Working Group (DDWG), which included Japanese companies
Fujitsu and
NEC.
*
Emoji
An emoji ( ; plural emoji or emojis; , ) is a pictogram, logogram, ideogram, or smiley embedded in text and used in electronic messages and web pages. The primary function of modern emoji is to fill in emotional cues otherwise missing from type ...
— The first emoji was created in 1998 or 1999 in Japan by
Shigetaka Kurita.
**
Face with Tears of Joy emoji —
NTT DoCoMo's emoji set in 1999 included the "Face with Tears of Joy" emoji.
*
Graphics processing unit
A graphics processing unit (GPU) is a specialized electronic circuit designed for digital image processing and to accelerate computer graphics, being present either as a discrete video card or embedded on motherboards, mobile phones, personal ...
(GPU) —
Fujitsu MB14241 was the first GPU, used to accelerate
framebuffer graphics for ''
Gun Fight'' (1975) and ''
Space Invaders
is a 1978 shoot 'em up video game developed and published by Taito for Arcade video game, arcades. It was released in Japan in April 1978, with the game being released by Midway Manufacturing overseas. ''Space Invaders'' was the first fixed s ...
'' (1978).
**
16-bit
16-bit microcomputers are microcomputers that use 16-bit microprocessors.
A 16-bit register can store 216 different values. The range of integer values that can be stored in 16 bits depends on the integer representation used. With the two ...
GPU — The
NEC μPD7220 (1981) was the first specialized 16-bit GPU on a single
largescale integration (LSI) chip.
**
32-bit
In computer architecture, 32-bit computing refers to computer systems with a processor, memory, and other major system components that operate on data in a maximum of 32- bit units. Compared to smaller bit widths, 32-bit computers can perform la ...
GPU —
Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
developed the first 32-bit GPU for the
Sega X Board (1987)
arcade system.
**
3D GPU — From 1985 to 1988,
Namco developed the first GPU dedicated to
3D polygon graphics, for the arcade
Namco System 21.
**
Floating-point
In computing, floating-point arithmetic (FP) is arithmetic on subsets of real numbers formed by a ''significand'' (a Sign (mathematics), signed sequence of a fixed number of digits in some Radix, base) multiplied by an integer power of that ba ...
GPU — The
Namco System 21 (1988) had the earliest GPU capable of
floating-point arithmetic
In computing, floating-point arithmetic (FP) is arithmetic on subsets of real numbers formed by a ''significand'' (a Sign (mathematics), signed sequence of a fixed number of digits in some Radix, base) multiplied by an integer power of that ba ...
.
**
64-bit GPU — Sega and Fujitsu developed the first 64-bit GPU for the
Sega Model 1 (1992) arcade system.
**
T&L GPU — In 1995,
Fujitsu developed the first integrated 3D GPU with hardware T&L.
[
* ]
*
High color — The
Sega Super Scaler (1985)
arcade system board
An arcade video game is an arcade game that takes player input from its controls, processes it through electrical or computerized components, and displays output to an electronic monitor or similar display. All arcade video games are coin-opera ...
introduced a
16-bit color palette.
**
24-bit color — The
Namco System 2 (1987) arcade board introduced a 24-bit color palette.
*
High resolution (hi-res) — The
NEC μPD7220 (1981) GPU introduced hi-res graphics above
480p display resolution
The display resolution or display modes of a digital television, computer monitor, or other display device is the number of distinct pixels in each dimension that can be displayed. It can be an ambiguous term especially as the displayed resoluti ...
.
**
High-definition graphics (HD) — The
NEC μPD7220 (1981) was capable of
HD resolutions including
720p
720p (720 lines progressive) is a progressive HD signal format with 720 horizontal lines/1280 columns and an aspect ratio (AR) of 16:9, normally known as widescreen HD (1.78:1). All major HD broadcasting standards (such as SMPTE 292M) includ ...
and
1080i
In high-definition television (HDTV) and video display technology, 1080i is a video display format with 1080 lines of vertical resolution and Interlaced video, interlaced scanning method. This format was once a standard in HDTV. It was particular ...
.
**
Super VGA (SVGA) — In 1988,
NEC Home Electronics created the
Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA) to develop the SVGA
computer display standard
Computer display standards are a combination of aspect ratio, display size, display resolution, color depth, and refresh rate. They are associated with specific expansion cards, video connectors, and monitors.
History
Various computer dis ...
. The development of SVGA was led by
NEC.
**
Ultra-high-definition (UHD) —
Hitachi
() is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate founded in 1910 and headquartered in Chiyoda, Tokyo. The company is active in various industries, including digital systems, power and renewable ener ...
's
ARTC HD63484 (1984) GPU was capable of displaying UHD resolutions up to
4K when in
monochrome
A monochrome or monochromatic image, object or palette is composed of one color (or values of one color). Images using only shades of grey are called grayscale (typically digital) or black-and-white (typically analog). In physics, mon ...
mode. The resolution was targeted at the
bit-mapped desktop publishing
Desktop publishing (DTP) is the creation of documents using dedicated software on a personal ("desktop") computer. It was first used almost exclusively for print publications, but now it also assists in the creation of various forms of online co ...
market.
*
Isometric graphics — Introduced by
Data East
, also abbreviated as DECO, was a Japanese video game, pinball and electronic engineering company. The company was in operation from 1976 to 2003, and released 150 video game titles. At one time, the company had annual sales of 20 billion yen in ...
's
arcade video game ''
Treasure Island'', debuted in September 1981.
**
Isometric scrolling — Introduced by
Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
's arcade game ''
Zaxxon'',
which debuted in December 1981.
*
Scrolling — Introduced by
Tomohiro Nishikado's
arcade racing game ''
Speed Race'' (1974).
**
Vertical scrolling — Introduced by Tomohiro Nishikado's ''
Speed Race'' (1974).
**
Side-scrolling — Dates back to
Taito
is a Japanese company that specializes in video games, Toy, toys, arcade cabinets, and game centers, based in Shinjuku, Tokyo. The company was founded by Michael Kogan in 1953 as the importing vodka, Vending machine, vending machines, and Juk ...
's arcade racing game ''Dead Heat'' (1975).
**
Multi-directional scrolling — Introduced by
Tomohiro Nishikado's arcade
shooter game ''Interceptor'' (1975).
**
Forward scrolling — Introduced by
Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
's arcade
driving game ''
Road Race'' (1976).
**
Parallax scrolling —
Alpha Denshi's ''
Jump Bug'' (1981) introduced a limited form of parallax scrolling.
's ''
Moon Patrol'' (1982) introduced full parallax scrolling, with three background layers scrolling at different speeds.
*
JPEG
JPEG ( , short for Joint Photographic Experts Group and sometimes retroactively referred to as JPEG 1) is a commonly used method of lossy compression for digital images, particularly for those images produced by digital photography. The degr ...
arithmetic coding
Arithmetic coding (AC) is a form of entropy encoding used in lossless data compression. Normally, a String (computer science), string of characters is represented using a fixed number of bits per character, as in the American Standard Code for In ...
— Patents providing the basis for JPEG's arithmetic coding algorithm include two
Mitsubishi Electric patents by Toshihiro Kimura, Shigenori Kino, Fumitaka Ono and Masayuki Yoshida in 1989 and 1990.
*
Multisync monitor — The first was the
NEC Multisync, released in 1985 for use with
personal computers
A personal computer, commonly referred to as PC or computer, is a computer designed for individual use. It is typically used for tasks such as Word processor, word processing, web browser, internet browsing, email, multimedia playback, and PC ...
. It supported a wide range of sync frequencies.
*
PC TV set — In 1982, the
Sharp X1 was the first PC with a
TV tuner, functioning as both a
computer
A computer is a machine that can be Computer programming, programmed to automatically Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (''computation''). Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic set ...
and
television
Television (TV) is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. Additionally, the term can refer to a physical television set rather than the medium of transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertising, ...
.
The
RGB display monitor could superimpose a computer screen over a TV screen, allowing both on the same display.
*
Tile-based graphics — The tile-map model was introduced by
Namco's arcade game ''
Galaxian
is a 1979 fixed shooter video game developed and published by Namco for arcades. The player assumes control of the Galaxip starfighter in its mission to protect Earth from waves of aliens. Gameplay involves destroying each formation of alien ...
'' (
1979
Events
January
* January 1
** United Nations Secretary-General Kurt Waldheim heralds the start of the ''International Year of the Child''. Many musicians donate to the ''Music for UNICEF Concert'' fund, among them ABBA, who write the song ...
), which ran on the
Namco Galaxian arcade system board
An arcade video game is an arcade game that takes player input from its controls, processes it through electrical or computerized components, and displays output to an electronic monitor or similar display. All arcade video games are coin-opera ...
.
**
Hardware scrolling — The
Namco Galaxian arcade system board introduced with ''
Galaxian
is a 1979 fixed shooter video game developed and published by Namco for arcades. The player assumes control of the Galaxip starfighter in its mission to protect Earth from waves of aliens. Gameplay involves destroying each formation of alien ...
'' (1979) pioneered a hardware
sprite system that animates pre-loaded sprites over a
scrolling background, the basis for later
2D game systems.
*
Ray-tracing hardware — In 1982, the first
interactive ray tracer was
Osaka University's
LINKS-1 Computer Graphics System, a
massively parallel computer processing system used to render
3D graphics
3D computer graphics, sometimes called CGI, 3D-CGI or three-dimensional computer graphics, are graphics that use a three-dimensional representation of geometric data (often Cartesian) that is stored in the computer for the purposes of perfor ...
with high-speed
ray tracing.
*
Render farm — The
LINKS-1 Computer Graphics System (1982) was a massively parallel processing system with up to 256
computer nodes, used to render 3D graphics with high-speed ray tracing.
Literature

*
Isekai
is a sub-genre of fiction. It includes novels, light novels, films, manga, webtoons, anime, and video games that revolve around a person or people who are transported to and have to survive in another world such as a fantasy world, virtual wor ...
— The concept has origins in the story of fisherman
Urashima Tarō (8th century), who saves a turtle and is brought to a wondrous undersea kingdom.
*
Novel
A novel is an extended work of narrative fiction usually written in prose and published as a book. The word derives from the for 'new', 'news', or 'short story (of something new)', itself from the , a singular noun use of the neuter plural of ...
— (10th century) has been called the "world's first full-length novel". ''
The Tale of Genji'' (11th century) is often cited as "the first novel".
**
Historical novel
Historical fiction is a literary genre in which a fictional plot takes place in the setting of particular real historical events. Although the term is commonly used as a synonym for historical fiction literature, it can also be applied to oth ...
— ''
The Tale of Genji'' (11th century) is considered to be the first historical novel.
**
I-novel — The first I-novels are believed to be
Tōson Shimazaki's ''
The Broken Commandment'' (1906) and
Katai Tayama's ''
Futon'' (1907).
**
Light novel
A is a type of Genre fiction, popular literature novel from Japan usually classified as young adult fiction, generally targeting Adolescence, teens to Young adult, twenties or older. The definition is very vague, and wide-ranging.
The abbr ...
— Origins trace back to the serialization of ''
Record of Lodoss War'' (1986–1989) in the magazine ''
Comptiq''. Keita Kamikita is usually credited with coining the term "light novel" in 1990.
**
Cell phone novel — The first
cell phone
A mobile phone or cell phone is a portable telephone that allows users to make and receive calls over a radio frequency link while moving within a designated telephone service area, unlike fixed-location phones ( landline phones). This radio ...
novel was ''
Deep Love'' (2002)''.''
*
Science fiction
Science fiction (often shortened to sci-fi or abbreviated SF) is a genre of speculative fiction that deals with imaginative and futuristic concepts. These concepts may include information technology and robotics, biological manipulations, space ...
—
Urashima Tarō story from ''
Nihongi'' (720) involves
time travel.
''
The Tale of the Bamboo Cutter'' (10th century) is considered science fiction.
[ (]cf.
The abbreviation cf. (short for either Latin or , both meaning 'compare') is generally used in writing to refer the reader to other material to make a comparison with the topic being discussed. However some sources offer differing or even contr ...
)
**
Flying saucer — The 10th-century Japanese narrative ''
The Tale of the Bamboo Cutter'' has a manuscript illustration depicting a round flying machine similar to a flying saucer.
**
Time travel — The tale of
Urashima Tarō from the ''
Manyoshu'' (8th century), tells of a young fisherman who visits an undersea palace. After three days, he returns home to his village and finds himself 300 years in the future.
**
Time loop
The time loop or temporal loop is a plot device in fiction whereby Character (arts), characters re-experience a span of time which is repeated, sometimes more than once, with some hope of breaking out of the cycle of repetition. Time loops are co ...
— The earliest novel about a time loop was
Yasutaka Tsutsui's ''
The Girl Who Leapt Through Time'' (1965).
*
Superhero
A superhero or superheroine is a fictional character who typically possesses ''superpowers'' or abilities beyond those of ordinary people, is frequently costumed concealing their identity, and fits the role of the hero, typically using their ...
—
Sarutobi Sasuke was a superhero
ninja from 1910s
children's novels.
By 1914, he had superpowers.
*
Unreliable narrator
In literature, film, and other such arts, an unreliable narrator is a narrator who cannot be trusted, one whose credibility is compromised. They can be found in a wide range from children to mature characters. While unreliable narrators are al ...
— Dates back to
Ryūnosuke Akutagawa's novel ''
In a Grove'' (1922) and
Akira Kurosawa
was a Japanese filmmaker who List of works by Akira Kurosawa, directed 30 feature films in a career spanning six decades. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest and most influential filmmakers in the History of film, history of cinema ...
's film adaptation ''
Rashomon'' (1950).
Combat
Airsoft

*
Airsoft
Airsoft, also known as survival game () in Japan where it was popular, is a team sport, team-based shooting sport, shooting game in which participants eliminate opposing players out of play by shooting them with airsoft pellets, spherical plast ...
— Airsoft originated in Japan, then spread to Hong Kong and China in the late 1970s.
*
Airsoft gun
Airsoft guns are air guns used in airsoft sports. They are a special type of low-power smoothbore guns designed to shoot Airsoft pellets, plastic pellets often colloquially (but incorrectly) referred to as "BB (ammunition), BBs", which are typ ...
— The inventor of the first airsoft gun is Tanio Kobayashi.
Martial arts
*
Aikido
Aikido ( , , , ) is a gendai budō, modern Japanese martial art which is split into many different styles including Iwama Ryu, Iwama Shin Shin Aiki Shuren Kai, Shodokan Aikido, Yoshinkan, Renshinkai, Aikikai, and Ki Aikido. Aikido is now practic ...
— Aikido was created and developed by
Morihei Ueshiba in first half of the 20th century.
*
Bushido
is a Samurai moral code concerning samurai attitudes, behavior and lifestyle. Its origins date back to the Kamakura period, but it was formalized in the Edo period (1603–1868). There are multiple types of bushido which evolved significantl ...
*
Judo
is an unarmed gendai budō, modern Japanese martial art, combat sport, Olympic sport (since 1964), and the most prominent form of jacket wrestling competed internationally.『日本大百科全書』電子版【柔道】(CD-ROM version of Encyc ...
— It was created as a physical, mental and moral
pedagogy
Pedagogy (), most commonly understood as the approach to teaching, is the theory and practice of learning, and how this process influences, and is influenced by, the social, political, and psychological development of learners. Pedagogy, taken ...
in Japan, in 1882, by
Kanō Jigorō
was a Japanese judoka, educator, politician, and the founder of judo. Judo was one of the first Japanese martial arts to gain widespread international recognition, and the first to become an official Olympic Games, Olympic sport. Pedagogical ...
.
*
Jujutsu
Jujutsu ( , or ), also known as jiu-jitsu and ju-jitsu (both ), is a Japanese martial art and a system of close combat that can be used in a defensive or offensive manner to kill or subdue one or more weaponless or armed and armored opponent ...
— Jujutsu, the "way of yielding", is a collective name for Japanese martial art styles including unarmed and armed techniques. Jujutsu evolved among the samurai of feudal Japan as a method for defeating an armed and armored opponent without weapons. Due to the ineffectiveness of striking against an armored opponent, the most efficient methods for neutralizing an enemy took the form of pins, joint locks, and throws. These techniques were developed around the principle of using an attacker's energy against him, rather than directly opposing it.
*
Karate
(; ; Okinawan language, Okinawan pronunciation: ), also , is a martial arts, martial art developed in the Ryukyu Kingdom. It developed from the Okinawan martial arts, indigenous Ryukyuan martial arts (called , "hand"; ''tī'' in Okinawan) un ...
— It began as a common fighting system known as "''
ti''" (or "''te''") among the
pechin class of the
Ryukyuans
The are a Japonic-speaking East Asian ethnic group indigenous to the Ryukyu Islands, which stretch from the island of Kyushu to the island of Taiwan. With Japan, most Ryukyuans live in the Okinawa Prefecture or Kagoshima Prefecture. They sp ...
. There were few formal styles of ''ti'', but rather many practitioners with their own methods. One surviving example is the
Motobu-ryū
is a karate school founded in 1922 by Motobu Chōki from Okinawa. Its official name is ''Nihon Denryū Heihō Motobu Kenpō'' ("Japan Traditional Fighting Tactics Motobu Kenpō"), or Motobu Kenpō for short. Motobu-ryū has the characteristics ...
school passed down from the Motobu family by Seikichi Uehara. Early styles of karate are often generalized as
Shuri-te
Okinawan martial arts refers to the martial arts, such as karate, tegumi and Okinawan kobudō, kobudō, which originated among the indigenous people of Okinawa Island. Due to its location (between "Mainland Japan" and Taiwan), Okinawa was influenc ...
,
Naha-te, and
Tomari-te, named after the three cities from which they emerged.
*
Kendo
*
Mixed martial arts
Mixed martial arts (MMA) is a full-contact fighting combat sport, sport based on strike (attack), striking and grappling; incorporating techniques from various combat sports from around the world.
In the early 20th century, various inter-s ...
(MMA) — Mixed bouts date back to 1890s Japan. Other examples included
Kimura vs. Gracie (1951) and
Ali vs. Inoki (1976). Modern MMA arose from
shootfighting contests like
Shooto (1985) to
Pancrase
is a Japanese mixed martial arts (MMA) promoter (entertainment), promotion company based in Tokyo. It was founded in 1993 by professional wrestlers Masakatsu Funaki and Minoru Suzuki.
The name was based on pankration, a fighting sport in the An ...
(1993).
*
Ninjutsu
, and are terms for the techniques and skills used by spies and scouts in pre-modern Japan known as ninja. Some of these techniques are recorded in ninja scrolls, some which have been published and translated. The study of these scrolls have c ...
— Developed by groups of people mainly from the
Iga Province
was a Provinces of Japan, province of Japan located in what is today part of western Mie Prefecture.Louis-Frédéric, Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "Iga" in . Its abbreviated name was . Iga is classified as one of the provinces of the T� ...
and
Kōka, Shiga of
Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
. Throughout history, many different schools (''
ryū'') have taught their unique versions of ''ninjutsu''. An example of these is the
Togakure-ryū. This ''ryū'' was developed after a defeated samurai warrior called Daisuke Togakure escaped to the region of Iga. Later he came in contact with the warrior-monk Kain Doshi who taught him a new way of viewing life and the means of survival (''ninjutsu'').
*
Okinawan martial arts — In the 14th century, when the three kingdoms on Okinawa (
Chūzan,
Hokuzan, and
Nanzan) entered into a
tributary relationship with the
Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty, officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming was the last imperial dynasty of ...
of
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
, Chinese Imperial
envoys and other Chinese arrived, some of whom taught Chinese
Chuan Fa (
Kempo) to the Okinawans. The Okinawans combined Chinese Chuan Fa with the existing martial art of Te to form , sometimes called .
[msisshinryu.com , Okinawan Masters](_blank)
/ref> By the 18th century, different types of Te had developed in three different villages – Naha, Shuri, and Tomari. The styles were named Naha-te, Shuri-te, and Tomari-te, respectively. Practitioners from these three villages went on to develop modern karate.[msisshinryu.com , History of Karate](_blank)
/ref>
* Puroresu
** Strong style
Strong may refer to:
Education
* The Strong, an educational institution in Rochester, New York, United States
* Strong Hall (Lawrence, Kansas), an administrative hall of the University of Kansas
* Strong School, New Haven, Connecticut, United Sta ...
* Soccer kick — High-profile early users of soccer kicks as a finishing move include Katsuyori Shibata and Antonio Inoki. In a 1977 puroresu match, Inoki used soccer kicks to legitimately knock out Great Antonio.
* Shoot wrestling
Shoot wrestling is a Japanese hybrid grappling style and combat sport. Shoot wrestling incorporates techniques from various wrestling, submission grappling, kickboxing and karate styles. It was particularly inspired and influenced by catch ...
— Originates from 1970s Japanese '' puroresu''.Caesar Takeshi
(born August 17, 1955), better known by his ring name , is a Japanese actor, retired kickboxer and the founder of shoot boxing.http://news.livedoor.com/article/detail/2649221/
Career
Murata started competing in kickboxing at age of 16, bei ...
.
** Shootfighting
* Sumo
is a form of competitive full-contact wrestling where a ''rikishi'' (wrestler) attempts to force his opponent out of a circular ring (''dohyō'') or into touching the ground with any body part other than the soles of his feet (usually by th ...
— According to the ''Nihon shoki'', published in 720, the origin of sumo is the contest of strength between Nomi no Sukune and Taima no Kehaya in 26 B.C. ''Haniwa
The are terracotta clay figures that were made for ritual use and buried with the dead as funerary objects during the Kofun period (3rd to 6th centuries AD) of the history of Japan. ''Haniwa'' were created according to the ''wazumi'' technique ...
'' of sumo wrestlers are made in the Kofun period (300–538). The imperial family often watches sumo as a form of entertainment in the Heian period (794–1192). It has evolved over the centuries with professional sumo wrestlers appearing in the Edo period (1603–1868). The word ''sumo'' is written with the Chinese characters or Kanji of "mutual bruising".
Military
 * Air raid — Early in
* Air raid — Early in World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
(1914), the Imperial Japanese Navy
The Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN; Kyūjitai: Shinjitai: ' 'Navy of the Greater Japanese Empire', or ''Nippon Kaigun'', 'Japanese Navy') was the navy of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945, Potsdam Declaration, when it was dissolved followin ...
ship conducted the world's first carrier-launched air raid.
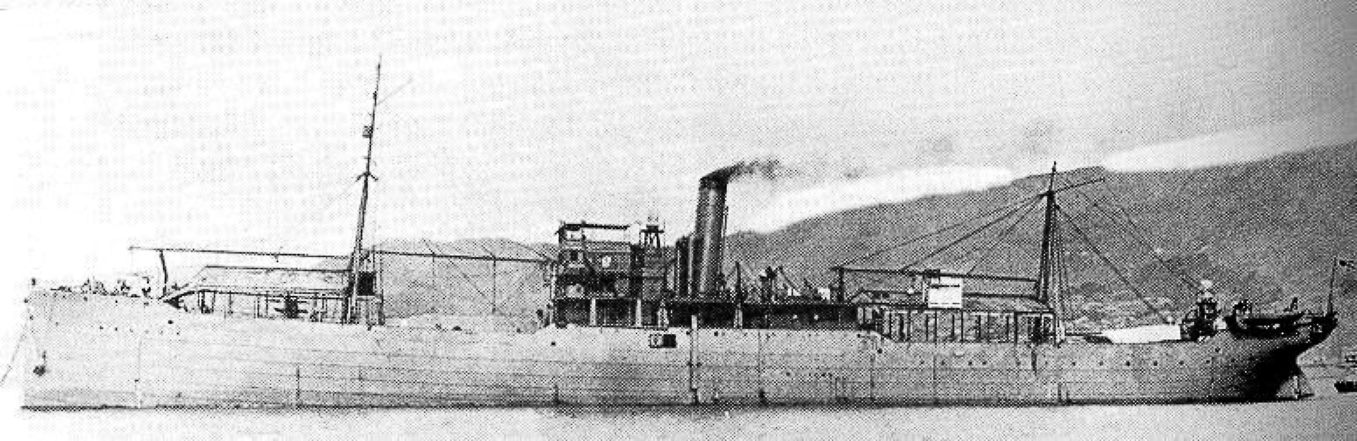
* Amphibious assault ship
An amphibious assault ship is a type of warship employed to land and support ground forces on enemy territory during an armed conflict. The design evolved from aircraft carriers converted for use as helicopter carriers (which, as a result, ar ...
— Imperial Japanese Army '' Akitsu maru'' is regarded as the first of the kind.
* Dock landing ship — Imperial Japanese Army '' Shinshu maru'' is regarded as the first of the kind.
* Fire balloon — A fire balloon, or balloon bomb, was an experimental weapon launched by Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
from 1944 to 1945, during World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
. *
* Katana
A is a Japanese sword characterized by a curved, single-edged blade with a circular or squared guard and long grip to accommodate two hands. Developed later than the ''tachi'', it was used by samurai in feudal Japan and worn with the edge fa ...
— The katana were traditional Japanese sword
A is one of several types of traditionally made swords from Japan. Bronze swords were made as early as the Yayoi period (1,000 BC – 300 AD), though most people generally refer to the curved blades made from the Heian period (794–1185) to the ...
s used by samurai warriors of ancient and feudal Japan. The swords originated in the Muromachi period (1392–1573) as a result of changing battle conditions requiring faster response times. The katana facilitated this by being worn with the blade facing up, which allowed the samurai to draw their blade and slash at their enemy in a single motion. Previously, the curved sword of the samurai was worn with the blade facing down. The ability to draw and cut in one motion also became increasingly useful in the daily life of the samurai.
Culture
* Folding hand fan — In ancient Japan, the first hand fans were oval and rigid fans, influenced greatly by Chinese fans. The earliest visual depiction of fans in Japan dates back to the 6th century AD, with burial tomb paintings showed drawings of fans. The folding fan was invented in Japan, with dates ranging from the 6th to 9th centuries and later exported to East Asia, Southeast Asia, and the West. Such a flourishing trade involving Japanese hand fans existed in the Ming dynasty times, when folding fans almost absolutely displaced the old rigid type in China.
* Kawaii — Roots date back to ''The Pillow Book
is a book of observations and musings recorded by Sei Shōnagon during her time as court lady to Fujiwara no Teishi, Empress Consort Teishi during the 990s and early 1000s in Heian-period Japan. The book was completed in the year 1002.
The wor ...
'' (1002) and Edo period
The , also known as the , is the period between 1600 or 1603 and 1868 in the history of Japan, when the country was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and some 300 regional ''daimyo'', or feudal lords. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengok ...
fashion such as netsuke.[''TheAge.Com:'' "Japan smitten by love of cute" http://www.theage.com.au/news/people/cool-or-infantile/2006/06/18/1150569208424.html ]
* Netsuke — A miniature sculpture, originating in 17th-century Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
. Initially a simply carved button fastener on the cords of an box, later developed into ornately sculpted objects of craftsmanship.[Yuji Yamashita (2014), ''Meiji no saimitsu kogei''. pp. 86-87. Heibonsha ]
* Purikura — Conceived in 1994 by Sasaki Miho for Atlus.Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
introduced ''Print Club'', the first purikura.
Finance
 * Candlestick chart — Candlestick charts have been developed in the 18th century by Munehisa Homma, a Japanese rice trader of financial instruments. They were introduced to the Western world by Steve Nison in his book, Japanese Candlestick Charting Techniques.
*
* Candlestick chart — Candlestick charts have been developed in the 18th century by Munehisa Homma, a Japanese rice trader of financial instruments. They were introduced to the Western world by Steve Nison in his book, Japanese Candlestick Charting Techniques.
* Futures contract
In finance, a futures contract (sometimes called futures) is a standardized legal contract to buy or sell something at a predetermined price for delivery at a specified time in the future, between parties not yet known to each other. The item tr ...
— The first futures exchange market was the Dōjima Rice Exchange in Japan in the 1730s.
* Mobile payment — Mobile payments began adoption in Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
during the early 2000s.
** Mobile wallet — In 2004, NTT DoCoMo and Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
introduced the first mobile wallets, for 3G mobile phones in Japan.
* Smart card
A smart card (SC), chip card, or integrated circuit card (ICC or IC card), is a card used to control access to a resource. It is typically a plastic credit card-sized card with an Embedded system, embedded integrated circuit (IC) chip. Many smart ...
— Kunitaka Arimura of the Arimura Technology Institute in Japan independently developed the idea of incorporating an integrated circuit
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
onto a plastic card
Plastic cards usually serve as identity documents, thus providing authentication. In combination with other assets that complement the data stored on the card, like Personal identification number, PIN numbers, they also serve authorization purpose ...
, and filed a smart card patent in March 1970.
Food and drink
 * Canned coffee — Canned coffee was invented in 1965 by Miura Yoshitake, a coffee shop owner in Hamada, Shimane Prefecture, Japan.
* Cooking comic —
* Canned coffee — Canned coffee was invented in 1965 by Miura Yoshitake, a coffee shop owner in Hamada, Shimane Prefecture, Japan.
* Cooking comic — Manga
are comics or graphic novels originating from Japan. Most manga conform to a style developed in Japan in the late 19th century, and the form has a long history in earlier Japanese art. The term is used in Japan to refer to both comics ...
has long contained references to food and cooking. Genre emerged in 1970, with ''Totsugeki Ramen'', ''Cake Cake Cake'' and ''Kitchen Kenpo''.
* Fake food — Simulated food was invented after Japan's surrender ending World War II in 1945. Westerners traveling to Japan had trouble reading Japanese menus and in response, Japanese artisans
An artisan (from , ) is a skilled worker, skilled craft worker who makes or creates material objects partly or entirely by handicraft, hand. These objects may be wikt:functional, functional or strictly beauty, decorative, for example furnit ...
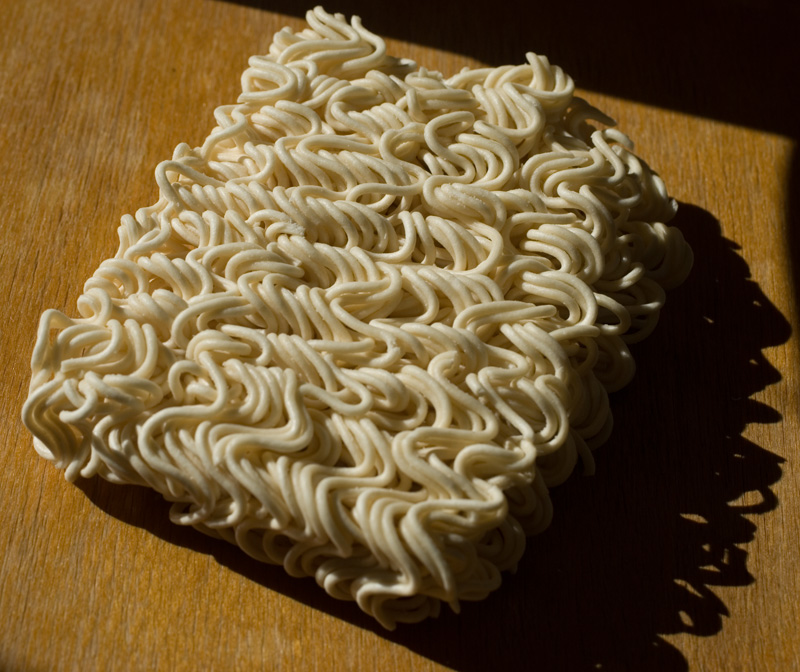
and candlemakers created wax food so foreigners could easily order something that looked appetizing.Instant noodle
Instant noodles, or instant ramen, is a type of food consisting of noodles sold in a precooked and dried block with flavoring powder and/or seasoning oil. The dried noodle block was originally created by Deep frying, flash-frying cooked noodles, ...
— Invented by Momofuku Ando, a Taiwanese-Japanese inventor, in 1958.
* Monosodium glutamate — Invented and patent
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an sufficiency of disclosure, enabling discl ...
ed by Kikunae Ikeda.
* Umami — Umami as a separate taste
The gustatory system or sense of taste is the sensory system that is partially responsible for the perception of taste. Taste is the perception stimulated when a substance in the mouth biochemistry, reacts chemically with taste receptor cells l ...
was first identified in 1908 by Kikunae Ikeda of the Tokyo Imperial University while researching the strong flavor in seaweed broth.[ (partial translation of )]
* Fortune cookie — Although popular in Western Chinese restaurants, fortune cookies did not originate in China and are in fact rare there. They most likely originated from cookies made by Japanese immigrants to the United States in the late 19th or early 20th century. The Japanese version had a fortune, but not lucky numbers, and was commonly eaten with tea.
Philosophy
* Kokugaku
* Lean manufacturing — A generic process management philosophy derived mostly from the Toyota Production System
The Toyota Production System (TPS) is an integrated socio-technical system, developed by Toyota, that comprises its management philosophy and practices. The TPS is a management system that organizes manufacturing and logistics for the automobile ...
(TPS) (hence the term Toyotism is also prevalent) and identified as "Lean" only in the 1990s.Hideo Kojima
is a Japanese video game designer. Regarded as one of the pioneering auteurs of video games, he developed a strong passion for film and literature during his childhood and adolescence, which in turn has had a significant influence on his game ...
's '' Metal Gear Solid 2: Sons of Liberty'' (2001) is cited as an early work that anticipated contemporary post-truth politics.Akira Kurosawa
was a Japanese filmmaker who List of works by Akira Kurosawa, directed 30 feature films in a career spanning six decades. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest and most influential filmmakers in the History of film, history of cinema ...
's film '' Rashomon'' (1950).
* Uncanny valley — Masahiro Mori first introduced the concept in his 1970 essay .
Games
 * Pachinko — Pachinko machines were first built during the 1920s as a children's toy called the .
* Pachinko — Pachinko machines were first built during the 1920s as a children's toy called the .
Board games
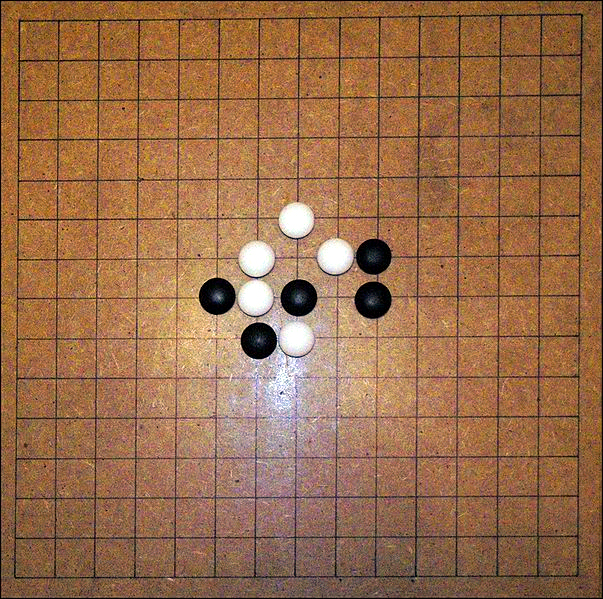 * Go (modern rules) — Though the game originated in China, free opening of the game as it is played globally began in the 16th century Japan.
*
* Go (modern rules) — Though the game originated in China, free opening of the game as it is played globally began in the 16th century Japan.
* Gomoku
''Gomoku'', also called ''five in a row'', is an Abstract strategy game, abstract strategy board game. It is traditionally played with Go (game), Go pieces (black and white stones) on a 15×15 Go board while in the past a 19×19 board was standa ...
— Historical records indicate the origins of gomoku can be traced back to the mid-1700s during the Edo period
The , also known as the , is the period between 1600 or 1603 and 1868 in the history of Japan, when the country was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and some 300 regional ''daimyo'', or feudal lords. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengok ...
. By the late Edo period, around 1850, books had been published on gomoku.
* Renju — A professional variant of gomoku
''Gomoku'', also called ''five in a row'', is an Abstract strategy game, abstract strategy board game. It is traditionally played with Go (game), Go pieces (black and white stones) on a 15×15 Go board while in the past a 19×19 board was standa ...
. It was named renju by journalist Ruikou Kuroiwa in 1899.[連珠…その起源](_blank)
/ref>
Electro-mechanical
* Audio-visual novelty game — EM genre originating from Japan,Periscope
A periscope is an instrument for observation over, around or through an object, obstacle or condition that prevents direct line-of-sight observation from an observer's current position.
In its simplest form, it consists of an outer case with ...
'' (1965).Periscope
A periscope is an instrument for observation over, around or through an object, obstacle or condition that prevents direct line-of-sight observation from an observer's current position.
In its simplest form, it consists of an outer case with ...
'' (1965) by Namco and Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
introduced electronic sound.Periscope
A periscope is an instrument for observation over, around or through an object, obstacle or condition that prevents direct line-of-sight observation from an observer's current position.
In its simplest form, it consists of an outer case with ...
'' (1965) introduced special effects.Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
's EM arcade games.Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
's ''MotoPolo'' (1968) introduced an 8-track player unit that plays sounds from endless tape cartridge through a speaker.[
* ]Tape loop
In music, tape loops are loops of magnetic tape used to create repetitive, rhythmic musical patterns or dense layers of sound when played on a tape recorder. Originating in the 1940s with the work of Pierre Schaeffer, they were used among ...
— Sega introduced tape music loops to arcades with EM games such as ''Sand Buggy'' (1972).
* Bonus points — The concept dates back to Sega's electro-mechanical arcade light gun shooter ''Duck Hunt'' (1968). The game awarded the player a higher score for a head shot, earning 15 points, whereas a standard body shot earned 10 points.racing game
Racing games are a video game genre in which the player participates in a motor racing, racing competition. They may be based on anything from real-world racing leagues to fantastical settings. They are distributed along a spectrum between more re ...
conventions by making vehicle collisions the objective of the gameplay.Periscope
A periscope is an instrument for observation over, around or through an object, obstacle or condition that prevents direct line-of-sight observation from an observer's current position.
In its simplest form, it consists of an outer case with ...
'' (1965) by Namco and Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
was both a single-player game and a three-player co-op game.Periscope
A periscope is an instrument for observation over, around or through an object, obstacle or condition that prevents direct line-of-sight observation from an observer's current position.
In its simplest form, it consists of an outer case with ...
'' (1965) was both a single-player game and a three-player game.Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
's ''Duck Hunt'' (1968) was the first shooter game to project first-person graphics on a screen.Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
's ''Duck Hunt'' (1968). The game awarded the player a higher score for a head shot, earning 15 points, whereas a standard body shot earned 10 points.First-person shooter
A first-person shooter (FPS) is a video game genre, video game centered on gun fighting and other weapon-based combat seen from a First person (video games), first-person perspective, with the player experiencing the action directly through t ...
(FPS) — Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
's ''Jet Rocket'' (1970) was the earliest FPS, with free-roaming first-person movement.microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor (computing), processor for which the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit (IC), or a small number of ICs. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, a ...
technology.racing game
Racing games are a video game genre in which the player participates in a motor racing, racing competition. They may be based on anything from real-world racing leagues to fantastical settings. They are distributed along a spectrum between more re ...
— Kasco's arcade racer ''Indy 500'' (1968) introduced pseudo-3D graphics projected using mirrors to give a first-person perspective on a screen.Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
's ''Jet Rocket'' (1970), a first-person combat flight simulator, was the first flight simulator game.Nintendo
is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational video game company headquartered in Kyoto. It develops, publishes, and releases both video games and video game consoles.
The history of Nintendo began when craftsman Fusajiro Yamauchi ...
's EM arcade game '' Wild Gunman'' (1974), published by Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
in North America, was the first FMV game.narrator
Narration is the use of a written or spoken commentary to convey a story to an audience. Narration is conveyed by a narrator: a specific person, or unspecified literary voice, developed by the creator of the story to deliver information to the ...
giving gameplay instructions.Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
.
* Handheld electronic game — Waco's ''Electronic Tic-Tac-Toe'' (1972) s commonly cited as the first commercial handheld electronic game.shooter video games
Shooter video games, or shooters, are a subgenre of action video games where the focus is on the defeat of the character's enemies using ranged weapons given to the player. Usually these weapons are firearms or some other long-range weapons, an ...
.
* Holography
Holography is a technique that allows a wavefront to be recorded and later reconstructed. It is best known as a method of generating three-dimensional images, and has a wide range of other uses, including data storage, microscopy, and interfe ...
— In 1975, Taito
is a Japanese company that specializes in video games, Toy, toys, arcade cabinets, and game centers, based in Shinjuku, Tokyo. The company was founded by Michael Kogan in 1953 as the importing vodka, Vending machine, vending machines, and Juk ...
announced the first holographic arcade gun game at the 1975 AMOA show. The same year, Kasco released ''Gun Smoke'', an arcade gun game using rotating cylindrical hologram technology.Nintendo
is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational video game company headquartered in Kyoto. It develops, publishes, and releases both video games and video game consoles.
The history of Nintendo began when craftsman Fusajiro Yamauchi ...
's electro-mechanical arcade game '' Wild Gunman'' (1974) featured the earliest quick time events (QTE).
* Rhythm game — In the early 1970s, Kasco created a rhythm-based EM arcade game, designed by Kenzou Furukawa, whose idea was "a game where you'd lift girls skirts in time to some rhythm" inspired by the 1969 ''Oh! Mouretsu'' commercials.
* Submarine simulator — ''Periscope
A periscope is an instrument for observation over, around or through an object, obstacle or condition that prevents direct line-of-sight observation from an observer's current position.
In its simplest form, it consists of an outer case with ...
'' (1965), by Namco and Sega, used lights and plastic waves to simulate sinking ships from a submarine.
* Whac-A-Mole — Invented in 1975 by Kazuo Yamada of TOGO
Togo, officially the Togolese Republic, is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Ghana to Ghana–Togo border, the west, Benin to Benin–Togo border, the east and Burkina Faso to Burkina Faso–Togo border, the north. It is one of the le ...
, based on the designer's 1974 pencil sketches.
Game consoles
 * 8-bit handheld console —
* 8-bit handheld console — Nintendo
is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational video game company headquartered in Kyoto. It develops, publishes, and releases both video games and video game consoles.
The history of Nintendo began when craftsman Fusajiro Yamauchi ...
's Game Boy (1989) was the first handheld game console
A handheld game console, or simply handheld console, is a small, portable self-contained video game console with a built-in screen, game controls and speakers. Handheld game consoles are smaller than home video game consoles and contain the con ...
with an 8-bit CPU.
** 16-bit
16-bit microcomputers are microcomputers that use 16-bit microprocessors.
A 16-bit register can store 216 different values. The range of integer values that can be stored in 16 bits depends on the integer representation used. With the two ...
handheld console — Neo Geo Pocket Color (1998) was the first handheld console with a 16-bit CPU.
** 24-bit game console — SNK's Neo Geo (1990) was the first video game console
A video game console is an electronic device that Input/output, outputs a video signal or image to display a video game that can typically be played with a game controller. These may be home video game console, home consoles, which are generally ...
with a 24-bit graphics processor.
** 32-bit console — Fujitsu's FM Towns Marty
The FM Towns Marty is a home video game console released in 1993 by Fujitsu, exclusively for the Japanese market. It uses the AMD 386SX, a CPU that is internally 32-bit but with a 16-bit data bus. The console comes with a built-in CD-ROM dri ...
(1993) was the console with a 32-bit
In computer architecture, 32-bit computing refers to computer systems with a processor, memory, and other major system components that operate on data in a maximum of 32- bit units. Compared to smaller bit widths, 32-bit computers can perform la ...
central processing unit
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor, or just processor, is the primary Processor (computing), processor in a given computer. Its electronic circuitry executes Instruction (computing), instructions ...
(CPU).[''Die, 16-bit, Die!''](_blank)
at IGN
''IGN'' is an American video gaming and entertainment media website operated by IGN Entertainment Inc., a subsidiary of Ziff Davis, Inc. The company's headquarters is located in San Francisco's SoMa district and is headed by its former e ...
** 64-bit game console — Nintendo 64 (1996) was the first console with 64-bit CPU.Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
's Dreamcast (1998) was the first console with a 128-bit
General home computing and gaming utility emerged at 8-bit word sizes, as 28=256 Word (computer architecture), words, a natural unit of data, became possible. Early 8-bit CPUs (such as the Zilog Z80 and MOS Technology 6502, used in the 1977 Co ...
graphics floating-point unit
A floating-point unit (FPU), numeric processing unit (NPU), colloquially math coprocessor, is a part of a computer system specially designed to carry out operations on floating-point numbers. Typical operations are addition, subtraction, multip ...
(FPU).Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
's PlayStation 3
The PlayStation 3 (PS3) is a home video game console developed and marketed by Sony Computer Entertainment (SCE). It is the successor to the PlayStation 2, and both are part of the PlayStation brand of consoles. The PS3 was first released on ...
(2006) was the first console with a 256-bit GPU.Bandai
is a Japanese multinational corporation, multinational toy manufacturer and distributor headquartered in Taitō, Taitō, Tokyo. Its international branches, Bandai Namco Toys & Collectables America and Bandai UK, are respectively headquartered ...
's ''Terror House'' (1982) produced an early 3D-like effect. Tomy
(trade name, trading as Takara Tomy in Asia and Tomy elsewhere) is a Japanese toy company. It was established in 1924 by Eiichirō Tomiyama as , became known for creating popular toys like the B-29 friction toy and luck-based game Pop-up Pi ...
's Tomytronic 3D (1983) featured an early stereoscopic 3D display.video game
A video game or computer game is an electronic game that involves interaction with a user interface or input device (such as a joystick, game controller, controller, computer keyboard, keyboard, or motion sensing device) to generate visual fe ...
— In 1982, the Bandai LCD Solarpower was the first solarpowered video game device.Sega Saturn
The is a home video game console developed by Sega and released on November 22, 1994, in Japan, May 11, 1995, in North America, and July 8, 1995, in Europe. Part of the fifth generation of video game consoles, it is the successor to the succes ...
(1994) was the first console with a 3D geometry processor.
** Game console with T&L GPU — The Nintendo 64 (1996) was the first console with a graphics processing unit
A graphics processing unit (GPU) is a specialized electronic circuit designed for digital image processing and to accelerate computer graphics, being present either as a discrete video card or embedded on motherboards, mobile phones, personal ...
(GPU) capable of transform, clipping, and lighting (T&L).
** Game console with FPU and Z-buffer — The Nintendo 64 (1996) was the first console with a floating-point unit
A floating-point unit (FPU), numeric processing unit (NPU), colloquially math coprocessor, is a part of a computer system specially designed to carry out operations on floating-point numbers. Typical operations are addition, subtraction, multip ...
(FPU) and Zbuffering hardware.
* Console with optical disk drive — The CD-ROM² add-on for NEC's PC Engine, released in November 1988, was the first game console to use CD-ROM
A CD-ROM (, compact disc read-only memory) is a type of read-only memory consisting of a pre-pressed optical compact disc that contains computer data storage, data computers can read, but not write or erase. Some CDs, called enhanced CDs, hold b ...
as storage media.
* Dual-port VRAM — First console to use dual-port VRAM was the Sega Mega Drive, released in 1988.
** Synchronous Graphics RAM (SGRAM) — The earliest commercial use of SGRAM was the NEC μPD481850 memory chip in the Sony PlayStation, included in models from December 1995 onwards.Three-dimensional integrated circuit
A three-dimensional integrated circuit (3D IC) is a MOSFET, MOS (metal-oxide semiconductor) integrated circuit (IC) manufactured by stacking as many as 16 or more ICs and interconnecting them vertically using, for instance, through-silicon vias (TS ...
(3D IC) — The earliest commercial use of a 3D IC was Toshiba's eDRAM memory chip in the PlayStation Portable (2004).Nintendo
is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational video game company headquartered in Kyoto. It develops, publishes, and releases both video games and video game consoles.
The history of Nintendo began when craftsman Fusajiro Yamauchi ...
's Game & Watch series.Nintendo
is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational video game company headquartered in Kyoto. It develops, publishes, and releases both video games and video game consoles.
The history of Nintendo began when craftsman Fusajiro Yamauchi ...
— Gunpei Yokoi was the creator of the Game Boy and Virtual Boy and worked on Famicom (NES), the ''Metroid'' series, Game Boy Pocket and did extensive work on the system we know today as the Nintendo Entertainment System (called the Famicom in Japan).
** Sprite (computer graphics), Multi-color hardware sprite — The Famicom (1983) was the first console featuring a graphics chip (by Ricoh) with hardware support for multi-colored sprites.Nintendo
is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational video game company headquartered in Kyoto. It develops, publishes, and releases both video games and video game consoles.
The history of Nintendo began when craftsman Fusajiro Yamauchi ...
launched the Family Computer Network System for the Famicom in Japan. Online games developed for the system include a graphical, competitive online multiplayer version of Go (game), Go.Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
were planning to release a Game Gear successor with a touchscreen interface. However, touchscreen technology was expensive, so they instead released the Sega Nomad in 1995.Taito
is a Japanese company that specializes in video games, Toy, toys, arcade cabinets, and game centers, based in Shinjuku, Tokyo. The company was founded by Michael Kogan in 1953 as the importing vodka, Vending machine, vending machines, and Juk ...
's arcade video game '' Speed Race'' (1974).
** Scrolling Tile-based video game, tiled background — The Famicom (1983) was the first console featuring a graphics chip with hardware support for scrolling tiled backgrounds.
Game controllers
 * Analog stick, Analog thumbstick — Introduced by Dempa's XE-1 AP controller (1989) for the Sega Mega Drive console and Japanese computers.
* Analog stick, Analog thumbstick — Introduced by Dempa's XE-1 AP controller (1989) for the Sega Mega Drive console and Japanese computers. * D-pad — In 1982,
* D-pad — In 1982, Nintendo
is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational video game company headquartered in Kyoto. It develops, publishes, and releases both video games and video game consoles.
The history of Nintendo began when craftsman Fusajiro Yamauchi ...
's Gunpei Yokoi elaborated on the idea of a circular pad, shrinking it and altering the points into the familiar modern "cross" design for control of on-screen characters in their ''Donkey Kong (arcade game), Donkey Kong'' handheld game. It came to be known as the "D-pad".Bandai
is a Japanese multinational corporation, multinational toy manufacturer and distributor headquartered in Taitō, Taitō, Tokyo. Its international branches, Bandai Namco Toys & Collectables America and Bandai UK, are respectively headquartered ...
's Power Pad, released for the Nintendo Entertainment System in 1987.
* D-pad, Directional buttons — Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
's arcade electro-mechanical game ''Electro-mechanical game, Missile'' (1969) had two D-pad, directional buttons are used to move a motorized tank.Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
's EM game Electro-mechanical game, ''Missile'' (969 ) had Dual analog control, dual-control scheme, with two directional buttons moving a tank and a joystick used to shoot and steer the missile.Taito
is a Japanese company that specializes in video games, Toy, toys, arcade cabinets, and game centers, based in Shinjuku, Tokyo. The company was founded by Michael Kogan in 1953 as the importing vodka, Vending machine, vending machines, and Juk ...
's ''Western Gun'' (1975), which used one joystick for movement and a second for firing.[Stephen Totilo]
In Search Of The First Video Game Gun
Kotaku
** Dual analog control — Sony's Dual Analog Controller, Dual Analog and DualShock controllers in 1997 were the first to feature two analog sticks.
* Force feedback — Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
's arcade motorbike game ''Man T.T.'' (1976), also known as ''Fonz'', was the first game using haptic technology for vibrating collisions.
* Gamepad — Nintendo
is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational video game company headquartered in Kyoto. It develops, publishes, and releases both video games and video game consoles.
The history of Nintendo began when craftsman Fusajiro Yamauchi ...
developed the standard gamepad design, with a D-pad, for the ''Donkey Kong (1981 video game), Donkey Kong'' Game & Watch handheld (1982) and the NES controller (1983).Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
's EM arcade game ''MotoPolo'', released in early 1968, introduced joystick controllers, used to move miniature motorbikes in any direction on the table.Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
's ''Missile'' (1969), which used a joystick to shoot and steer the missile.Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
's ''Space Harrier'' (1985) introduced an Analog stick, analog flight stick for movement. It could register movement in any direction as well as measure the degree of push.
** Joystick, Rotary joystick — Joystickknob hybrid, where the joystick can be moved in various directions and/or rotated like a knob, like for 8direction movement and 360-degree aiming.Nintendo
is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational video game company headquartered in Kyoto. It develops, publishes, and releases both video games and video game consoles.
The history of Nintendo began when craftsman Fusajiro Yamauchi ...
introduced a light gun toy to the home market with the :ja:光線銃シリーズ, Kōsenjū SP (Beam Gun) in 1970. The gun was developed by Nintendo's Gunpei Yokoi with Sharp Corporation, Sharp's Masayuki Uemura.Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
's arcade game ''Heavyweight Champ'' (1985) featured the first motion-based controllers.
** Wii Remote, Motion-sensing controller — Invented by Nintendo
is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational video game company headquartered in Kyoto. It develops, publishes, and releases both video games and video game consoles.
The history of Nintendo began when craftsman Fusajiro Yamauchi ...
for the Wii, the Wii Remote is the first Game controller, controller with Motion detection, motion-sensing capability. It was a candidate for Time (magazine), ''Time'''s Best Invention of 2006.
* Motion simulator — The first hydraulic motion simulator arcade cabinets were developed by Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
for the arcade games ''Space Tactics'' (1981), ''Hang-On'' (1985) and ''Space Harrier'' (1985).Periscope
A periscope is an instrument for observation over, around or through an object, obstacle or condition that prevents direct line-of-sight observation from an observer's current position.
In its simplest form, it consists of an outer case with ...
'' (1965), an EM arcade game by NamcoSega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
,Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
's ''Light gun shooter#History, Sea Devil'' (1972) and Taito
is a Japanese company that specializes in video games, Toy, toys, arcade cabinets, and game centers, based in Shinjuku, Tokyo. The company was founded by Michael Kogan in 1953 as the importing vodka, Vending machine, vending machines, and Juk ...
's ''Light gun shooter#History, Attack'' (1976).
* Racing wheel with accelerator pedal — Kasco's EM game ''Indy 500'' (1968) featured a steering wheel along with an accelerator pedal.
** Handheld game, Handheld racing wheel — Tomy
(trade name, trading as Takara Tomy in Asia and Tomy elsewhere) is a Japanese toy company. It was established in 1924 by Eiichirō Tomiyama as , became known for creating popular toys like the B-29 friction toy and luck-based game Pop-up Pi ...
's Demon Driver (1978) and Turnin’ Turbo Dashboard (1983) were the first handheld games with racing wheels.Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
's arcade List of association football video games, football/soccer game ''List of Sega arcade video games, World Cup'', released in March 1978.
Sports
* Air hockey — Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
's Electro-mechanical game, electro-mechanical (EM) arcade game ''MotoPolo'' (1968) anticipated air hockey gameplay.Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
's ''MotoPolo'' (1968) was the first electronic sports game featuring motorbikes.Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
's All Japan TV Game Championships, a nationwide tournament in Japan.video game
A video game or computer game is an electronic game that involves interaction with a user interface or input device (such as a joystick, game controller, controller, computer keyboard, keyboard, or motion sensing device) to generate visual fe ...
— Taito
is a Japanese company that specializes in video games, Toy, toys, arcade cabinets, and game centers, based in Shinjuku, Tokyo. The company was founded by Michael Kogan in 1953 as the importing vodka, Vending machine, vending machines, and Juk ...
's arcade title ''Alpine Ski'' (1981) was the first skiing video game.
** Olympic video game — Konami's arcade title Track & Field (video game), ''Track & Field'' (1983) was the first officially licensed video game based on the Olympic Games.
** List of rugby union video games, Rugby video game — Data East
, also abbreviated as DECO, was a Japanese video game, pinball and electronic engineering company. The company was in operation from 1976 to 2003, and released 150 video game titles. At one time, the company had annual sales of 20 billion yen in ...
's ''Scrum Try'' (1984) for arcade DECO Cassette System was the first Rugby union, rugby video game.Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
's arcade game ''Heavyweight Champ'' (1976) was the first combat sports video game.
Video games
 *
* 16-bit
16-bit microcomputers are microcomputers that use 16-bit microprocessors.
A 16-bit register can store 216 different values. The range of integer values that can be stored in 16 bits depends on the integer representation used. With the two ...
video game
A video game or computer game is an electronic game that involves interaction with a user interface or input device (such as a joystick, game controller, controller, computer keyboard, keyboard, or motion sensing device) to generate visual fe ...
— Universal Entertainment, Universal's arcade video game ''Get A Way'' (1978) was the first game with a 16-bit
16-bit microcomputers are microcomputers that use 16-bit microprocessors.
A 16-bit register can store 216 different values. The range of integer values that can be stored in 16 bits depends on the integer representation used. With the two ...
CPU.32-bit
In computer architecture, 32-bit computing refers to computer systems with a processor, memory, and other major system components that operate on data in a maximum of 32- bit units. Compared to smaller bit widths, 32-bit computers can perform la ...
video game
A video game or computer game is an electronic game that involves interaction with a user interface or input device (such as a joystick, game controller, controller, computer keyboard, keyboard, or motion sensing device) to generate visual fe ...
— The Sega X Board arcade system, which debuted with ''After Burner'' (1987), featured the first 32-bit graphics processing unit
A graphics processing unit (GPU) is a specialized electronic circuit designed for digital image processing and to accelerate computer graphics, being present either as a discrete video card or embedded on motherboards, mobile phones, personal ...
(GPU).video game
A video game or computer game is an electronic game that involves interaction with a user interface or input device (such as a joystick, game controller, controller, computer keyboard, keyboard, or motion sensing device) to generate visual fe ...
— The Sega Model 1 arcade system, which debuted with ''Virtua Racing'' (1992), featured the first 64-bit GPU.128-bit
General home computing and gaming utility emerged at 8-bit word sizes, as 28=256 Word (computer architecture), words, a natural unit of data, became possible. Early 8-bit CPUs (such as the Zilog Z80 and MOS Technology 6502, used in the 1977 Co ...
arcade system — The Sega NAOMI, launched in 1998, was the first arcade system with a 128-bit floating-point, 128-bit floating-point unit
A floating-point unit (FPU), numeric processing unit (NPU), colloquially math coprocessor, is a part of a computer system specially designed to carry out operations on floating-point numbers. Typical operations are addition, subtraction, multip ...
(FPU).Taito
is a Japanese company that specializes in video games, Toy, toys, arcade cabinets, and game centers, based in Shinjuku, Tokyo. The company was founded by Michael Kogan in 1953 as the importing vodka, Vending machine, vending machines, and Juk ...
's arcade title ''Super Speed Race'' (1977) was the first video game with multi-color sprites.
** Digitized image, Digitized sprite — Magical Company's 2D arcade fighting game ''Last Apostle Puppet Show'' (1988) was the first game to feature Digitized image, digitized Sprite (computer graphics), sprites.racing game
Racing games are a video game genre in which the player participates in a motor racing, racing competition. They may be based on anything from real-world racing leagues to fantastical settings. They are distributed along a spectrum between more re ...
''Plazma Line'' (1984) was the first home computer game with realtime 3D polygon graphics.Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
's ''SubRoc-3D'' (1982) was the first 3D stereoscopic game.[''Electronic Gaming Monthly'', issue 93 (April 1997), page 22]
* Multiplayer video game, 6-player video game — Dates back to Taito
is a Japanese company that specializes in video games, Toy, toys, arcade cabinets, and game centers, based in Shinjuku, Tokyo. The company was founded by Michael Kogan in 1953 as the importing vodka, Vending machine, vending machines, and Juk ...
's arcade racing game ''Dead Heat'' (1975).[Sam Derboo (2 June 2013)]
Dark Age of JRPGs (7): Panorama Toh ぱのらま島 – PC-88 (1983)
Hardcore Gaming 101 and ''Bokosuka Wars'' in 1983.[Gems In The Rough: Yesterday's Concepts Mined For Today](_blank)
Gamasutra
** Role-playing video game, 3D role-playing game (RPG) — Arsys Software's ''Wibarm'' (1986) and ''Star Cruiser (1988 video game), Star Cruiser'' (1988) were the first role-playing video games to used 3D polygon graphics.
** Experience point, Activity-based progression — Nihon Falcom's ''Xanadu: Dragon Slayer II'' (1985) was the earliest role-playing video game where individual stats increase based on activity levels.
** Alignment (role-playing games), Morality meter — ''Xanadu (video game), Xanadu'' (1985) had a Karma meter, which affects the temple's reaction.
Translation
[ (Reprinted from ''Retro Gamer'', Issue 67, 2009)]
** Soulslike — A subgenre of action role-playing and action-adventure games that originate from FromSoftware's ''Demon's Souls'' in 2009.
* Adult video game — The first erotic video game was Hudson Soft's '':ja:野球拳 (ハドソンのゲーム), Yakyūken'' (1981) for the Sharp MZ-80K computer.arcade system board
An arcade video game is an arcade game that takes player input from its controls, processes it through electrical or computerized components, and displays output to an electronic monitor or similar display. All arcade video games are coin-opera ...
that supported interchangeable games.[ Translation available a]
''Shmuplations''
* Beat 'em up — In 1984, Hong Kong action cinema, Hong Kong cinema-inspired ''Kung-Fu Master (video game), Kung-Fu Master'' laid the foundations for scrolling beat 'em ups with its simple gameplay and multiple enemies.[Spencer, Spanner]
The Tao of Beat-'em-ups
''Eurogamer'', February 6, 2008, Accessed March 18, 2009[Kunkel, Bill; Worley, Joyce; Katz, Arnie, "The Furious Fists of Sega!", ''Computer Gaming World'', October 1988, pp. 48–49] ''Renegade (video game), Nekketsu Kōha Kunio-kun'', released in 1986 in Japan, deviated from the martial arts themes of earlier games and introduced street brawling to the genre. ''Renegade (video game), Renegade'' (released the same year) added an underworld revenge plot that proved more popular with gamers than the principled combat sport of other games.[Spencer, Spanner]
The Tao of Beat-'em-ups (part 2)
''EuroGamer'', February 12, 2008, Accessed March 18, 2009 ''Renegade'' set the standard for future beat 'em up games as it introduced the ability to move both horizontally and vertically.
** Belt scrolling— Introduced by ''Nekketsu Kōha Kunio-kun'' (1986).Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
's ''Samurai,'' released March 1980, had the player samurai
The samurai () were members of the warrior class in Japan. They were originally provincial warriors who came from wealthy landowning families who could afford to train their men to be mounted archers. In the 8th century AD, the imperial court d ...
fight a number of swordsmen before confronting a more powerful boss samurai.Data East
, also abbreviated as DECO, was a Japanese video game, pinball and electronic engineering company. The company was in operation from 1976 to 2003, and released 150 video game titles. At one time, the company had annual sales of 20 billion yen in ...
's arcade DECO Cassette System game ''Flash Boy'' (1981), a scrolling action game, had the earliest combo mechanic. When the player punches an enemy and it explodes, debris can destroy other enemies.
** Combo (video games), Combo system — The first fighting game with a combo system was Culture Brain's ''Shanghai Kid'' (1985), with "rush" attacks similar to custom combos in ''Street Fighter Alpha 2'' (1996).
** Super combo — Introduced by SNK's Art of Fighting (video game), ''Art of Fighting'' (1992).
Translation
)[ (Reprinted at )]Taito
is a Japanese company that specializes in video games, Toy, toys, arcade cabinets, and game centers, based in Shinjuku, Tokyo. The company was founded by Michael Kogan in 1953 as the importing vodka, Vending machine, vending machines, and Juk ...
's '' Gun Fight'' (1975),Taito
is a Japanese company that specializes in video games, Toy, toys, arcade cabinets, and game centers, based in Shinjuku, Tokyo. The company was founded by Michael Kogan in 1953 as the importing vodka, Vending machine, vending machines, and Juk ...
's ''Space Invaders Part II'' (1979) introduced cutscenes as brief comical intermissions between levels.[Space Invaders Deluxe](_blank)
klov.com. Accessed on line March 28, 2011.
** Cutscene, Narrative cutscene — Dates back to Nintendo
is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational video game company headquartered in Kyoto. It develops, publishes, and releases both video games and video game consoles.
The history of Nintendo began when craftsman Fusajiro Yamauchi ...
's ''Sheriff (video game), Sheriff'' (1979).
* Damsel in distress — Dates back to Nintendo's ''Sheriff (video game), Sheriff'' (1979).
* Destructible environment — Destructible objects introduced by Taito Corporation, Taito's '' Gun Fight'' (1975).Space Invaders
is a 1978 shoot 'em up video game developed and published by Taito for Arcade video game, arcades. It was released in Japan in April 1978, with the game being released by Midway Manufacturing overseas. ''Space Invaders'' was the first fixed s ...
'' (1978).
* Drifting (motorsport), Drifting mechanic — Introduced by Sega's ''Out Run'' (1986). The mechanic incorporates Artificial intelligence in video games, AI assistance and details such as, if the car's tires grip the road surface too closely, the car's handling becomes too twitchy.Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
's black and white boxing game ''Heavyweight Champ'' was released in 1976 as the first video game
A video game or computer game is an electronic game that involves interaction with a user interface or input device (such as a joystick, game controller, controller, computer keyboard, keyboard, or motion sensing device) to generate visual fe ...
to feature fist fighting. However, Data East
, also abbreviated as DECO, was a Japanese video game, pinball and electronic engineering company. The company was in operation from 1976 to 2003, and released 150 video game titles. At one time, the company had annual sales of 20 billion yen in ...
's ''Karate Champ'' from 1984 is credited with establishing and popularizing the one-on-one fighting game genre, and went on to influence Konami's ''Yie Ar Kung-Fu'' from 1985.Taito
is a Japanese company that specializes in video games, Toy, toys, arcade cabinets, and game centers, based in Shinjuku, Tokyo. The company was founded by Michael Kogan in 1953 as the importing vodka, Vending machine, vending machines, and Juk ...
's arcade video game ''Interceptor'' (1975), designed by Tomohiro Nishikado, was a crude early First-person shooter, first-person combat flight simulator video game.Taito
is a Japanese company that specializes in video games, Toy, toys, arcade cabinets, and game centers, based in Shinjuku, Tokyo. The company was founded by Michael Kogan in 1953 as the importing vodka, Vending machine, vending machines, and Juk ...
's arcade video game ''Interceptor'' (1975), designed by Tomohiro Nishikado, is considered an early first-person shooter (FPS).
** 3D computer graphics, 3D first-person shooter (3D FPS) — Earliest FPS to use 3D polygons was ASCII Corporation, ASCII's ''Amnork'' (1986) for the FM-7, FM77 AV computer.
** Strafing (video games), Strafing — ''Star Cruiser (1988 video game), Star Cruiser'' (1988) was an early first-person shooter with strafing controls, considered ahead of its time.Taito
is a Japanese company that specializes in video games, Toy, toys, arcade cabinets, and game centers, based in Shinjuku, Tokyo. The company was founded by Michael Kogan in 1953 as the importing vodka, Vending machine, vending machines, and Juk ...
's Gun Buster (arcade game), ''Gun Buster'' (1992) was an early arcade first-person shooter with strafing controls, considered revolutionary for its time.anime
is a Traditional animation, hand-drawn and computer animation, computer-generated animation originating from Japan. Outside Japan and in English, ''anime'' refers specifically to animation produced in Japan. However, , in Japan and in Ja ...
scenes from an Electronic Video Recording (EVR) video tape on a CRT display.
** FMV cutscene — Data East
, also abbreviated as DECO, was a Japanese video game, pinball and electronic engineering company. The company was in operation from 1976 to 2003, and released 150 video game titles. At one time, the company had annual sales of 20 billion yen in ...
's laserdisc video game ''Bega's Battle'' (1983) introduced animated FMV cutscenes with voice acting to develop a story between the game's Shooter game, shooting stages.[''Electronic Gaming Monthly'', Ziff Davis (40): 78,80. November 1992. ISSN 1058-918X] with a limited release in 1992,Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
's action game ''Samurai'' (1980), the player samurai
The samurai () were members of the warrior class in Japan. They were originally provincial warriors who came from wealthy landowning families who could afford to train their men to be mounted archers. In the 8th century AD, the imperial court d ...
swordsman must fight a number of other swordsmen.Taito
is a Japanese company that specializes in video games, Toy, toys, arcade cabinets, and game centers, based in Shinjuku, Tokyo. The company was founded by Michael Kogan in 1953 as the importing vodka, Vending machine, vending machines, and Juk ...
's arcade game ''The Legend of Kage'' (1985).Data East
, also abbreviated as DECO, was a Japanese video game, pinball and electronic engineering company. The company was in operation from 1976 to 2003, and released 150 video game titles. At one time, the company had annual sales of 20 billion yen in ...
's ''Flash Boy'' (1981) for the DECO Cassette System introduced an energy bar.
** Health regeneration, Health meter regeneration — In ''Punch-Out!! (arcade game), Punch-Out'' (developed 1983), a stamina meter replenishes when the player strikes the opponent.[(]cf.
The abbreviation cf. (short for either Latin or , both meaning 'compare') is generally used in writing to refer the reader to other material to make a comparison with the topic being discussed. However some sources offer differing or even contr ...
)
* High score — Defined by Taito
is a Japanese company that specializes in video games, Toy, toys, arcade cabinets, and game centers, based in Shinjuku, Tokyo. The company was founded by Michael Kogan in 1953 as the importing vodka, Vending machine, vending machines, and Juk ...
's ''Space Invaders
is a 1978 shoot 'em up video game developed and published by Taito for Arcade video game, arcades. It was released in Japan in April 1978, with the game being released by Midway Manufacturing overseas. ''Space Invaders'' was the first fixed s ...
'' (1978), with high scores determined by playing to stay alive for as long as possible, as scores keep rising.video game
A video game or computer game is an electronic game that involves interaction with a user interface or input device (such as a joystick, game controller, controller, computer keyboard, keyboard, or motion sensing device) to generate visual fe ...
— Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
released the first holographic video games for arcades, ''Time Traveler (video game), Time Traveler'' (1991) and ''Holosseum'' (1992).Space Invaders
is a 1978 shoot 'em up video game developed and published by Taito for Arcade video game, arcades. It was released in Japan in April 1978, with the game being released by Midway Manufacturing overseas. ''Space Invaders'' was the first fixed s ...
'' (1978) was a precursor to horror games, as it involved a survival scenario which created a sense of panic in players upon release.Taito
is a Japanese company that specializes in video games, Toy, toys, arcade cabinets, and game centers, based in Shinjuku, Tokyo. The company was founded by Michael Kogan in 1953 as the importing vodka, Vending machine, vending machines, and Juk ...
contractor) for the PET 2001 and published by ASCII Corporation, ASCII for the PC-6001 in 1981.video game
A video game or computer game is an electronic game that involves interaction with a user interface or input device (such as a joystick, game controller, controller, computer keyboard, keyboard, or motion sensing device) to generate visual fe ...
— The first video game to use optical disc technology was Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
's arcade game ''Astron Belt'', which debuted in 1982.CD-ROM
A CD-ROM (, compact disc read-only memory) is a type of read-only memory consisting of a pre-pressed optical compact disc that contains computer data storage, data computers can read, but not write or erase. Some CDs, called enhanced CDs, hold b ...
video game
A video game or computer game is an electronic game that involves interaction with a user interface or input device (such as a joystick, game controller, controller, computer keyboard, keyboard, or motion sensing device) to generate visual fe ...
— The first CD games were ''Fighting Street'' and '':ja:No・Ri・Ko, No-Ri-Ko'', released for the PC Engine CD-ROM² in 1988.CD-ROM
A CD-ROM (, compact disc read-only memory) is a type of read-only memory consisting of a pre-pressed optical compact disc that contains computer data storage, data computers can read, but not write or erase. Some CDs, called enhanced CDs, hold b ...
role-playing video game, RPG — ''Tengai Makyō: Ziria'' (''Far East of Eden: Ziria'') for the PC Engine CD-ROM² was the first role-playing video game, RPG released on CD-ROM. After a mockup demo was shown in 1987,Space Invaders
is a 1978 shoot 'em up video game developed and published by Taito for Arcade video game, arcades. It was released in Japan in April 1978, with the game being released by Midway Manufacturing overseas. ''Space Invaders'' was the first fixed s ...
'' (1978) introduced the "concept of going Level (video games), round after round."Taito
is a Japanese company that specializes in video games, Toy, toys, arcade cabinets, and game centers, based in Shinjuku, Tokyo. The company was founded by Michael Kogan in 1953 as the importing vodka, Vending machine, vending machines, and Juk ...
's classic arcade video game ''Space Invaders
is a 1978 shoot 'em up video game developed and published by Taito for Arcade video game, arcades. It was released in Japan in April 1978, with the game being released by Midway Manufacturing overseas. ''Space Invaders'' was the first fixed s ...
'' (1978) is credited with introducing multiple lives to video games.
* Maze chase game, Maze chase — ''Heiankyo Alien'' (1979) was an early List of maze chase games, maze chase game predating Namco's ''Pac-Man'' (1980), which established the maze chase genre and spawning many imitations.Taito
is a Japanese company that specializes in video games, Toy, toys, arcade cabinets, and game centers, based in Shinjuku, Tokyo. The company was founded by Michael Kogan in 1953 as the importing vodka, Vending machine, vending machines, and Juk ...
's ''Western Gun'' (1975) laid the foundations for the multi-directional shooter genre.
* Ninja video games, Ninja video game — Emerged in the early 1980s,Nintendo
is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational video game company headquartered in Kyoto. It develops, publishes, and releases both video games and video game consoles.
The history of Nintendo began when craftsman Fusajiro Yamauchi ...
, released in July 1981, was the first game that allowed players to jump over obstacles and across gaps, making it the first true platformer.
** Metroidvania — Spawned by ''Metroid'' and ''Castlevania'', with template based on ''Metroid (video game), Metroid'' (1986), ''Castlevania II: Simon's Quest, Castlevania II'' (1987), ''Super Metroid'' (1994) and ''Castlevania: Symphony of the Night'' (1997).Taito
is a Japanese company that specializes in video games, Toy, toys, arcade cabinets, and game centers, based in Shinjuku, Tokyo. The company was founded by Michael Kogan in 1953 as the importing vodka, Vending machine, vending machines, and Juk ...
released ''Jungle Hunt, Jungle King'', which featured scrolling jump and run sequences that had players hopping over obstacles. Namco took the scrolling platformer a step further with the 1984 release ''Pac-Land''. ''Pac-Land'' came after the genre had a few years to develop, and was an evolution of earlier platform games, aspiring to be more than a simple game of hurdle jumping, like some of its predecessors. It closely resembled later scrolling platformers like ''Wonder Boy'' and ''Super Mario Bros.'' and was probably a direct influence on them. It also had multi-layered parallax scrolling.
Translation
video game
A video game or computer game is an electronic game that involves interaction with a user interface or input device (such as a joystick, game controller, controller, computer keyboard, keyboard, or motion sensing device) to generate visual fe ...
— Hideo Kojima
is a Japanese video game designer. Regarded as one of the pioneering auteurs of video games, he developed a strong passion for film and literature during his childhood and adolescence, which in turn has had a significant influence on his game ...
's '' Metal Gear Solid 2: Sons of Liberty'' (2001) is considered the first postmodern video game.
* Power-up — ''Pac-Man'' from 1980 is credited as the first video game to feature a power-up mechanic, * 2.5D, Pseudo-3D sprite scaling — Introduced by Tomohiro Nishikado's arcade shooter ''Interceptor'' (1975).
* 2.5D, Pseudo-3D sprite scaling — Introduced by Tomohiro Nishikado's arcade shooter ''Interceptor'' (1975).Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
's arcade game '' Road Race'' (1976).
** 2.5D, Pseudo-3D Third-person (video games), third-person perspective — Introduced by Sega's '' Road Race'' (1976).[Dru Hill: The Chronicle of Druaga](_blank)
, 1UP.com, 1UP ''Gain Ground'' and ''Herzog (video game), Herzog'' (1988). ''Herzog Zwei'' (1989) is considered the first true RTS.[''GameAxis Unwired'']
p. 52
December 2008, SPH Magazines, ISSN 0219-872X[Greg Lockley (3 June 2014)]
MOBA: The story so far
, MCV (magazine), MCV or early example of, the MOBA genre.[Andrew Groen (7 March 2012)]
Ask GR Anything: What's a MOBA?
, GamesRadar
* Rhythm video game — ''Dance Aerobics'' was released in 1987, and allowed players to create music by stepping on Nintendo's Power Pad peripheral. It has been called the first rhythm-action game in retrospect,[Block, Gerry]
NES Power Pad Rocking Rhythm-Action Play
, ''IGN'', July 7, 2008, Accessed April 10, 2009 although the 1996 title ''PaRappa the Rapper'' has also been deemed the first rhythm game, whose basic template forms the core of subsequent games in the genre. In 1997, Konami's ''Beatmania'' sparked an emergent market for rhythm games in Japan. The company's music division, Bemani, released a number of music games over the next several years.
* Saved game, Save data — The first game to save the player's high score was Taito
is a Japanese company that specializes in video games, Toy, toys, arcade cabinets, and game centers, based in Shinjuku, Tokyo. The company was founded by Michael Kogan in 1953 as the importing vodka, Vending machine, vending machines, and Juk ...
's ''Space Invaders
is a 1978 shoot 'em up video game developed and published by Taito for Arcade video game, arcades. It was released in Japan in April 1978, with the game being released by Midway Manufacturing overseas. ''Space Invaders'' was the first fixed s ...
'' (1978).Taito
is a Japanese company that specializes in video games, Toy, toys, arcade cabinets, and game centers, based in Shinjuku, Tokyo. The company was founded by Michael Kogan in 1953 as the importing vodka, Vending machine, vending machines, and Juk ...
's '':ja:未来神話ジャーヴァス, Mirai Shinwa Jarvas'' (1986) introduced the concept of saved games stored in battery-backed random-access memory on the game cartridge.
** Ferroelectric RAM, FRAM Saved game, save — Ferroelectric RAM (FRAM) was commercialized in the mid-1990s. Its first high-profile commercial use was by game company Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
, who used FRAM chips to store saved games in ''Sonic the Hedgehog 3'' (1994) game cartridges.
* Shoot 'em up — ''Space Invaders
is a 1978 shoot 'em up video game developed and published by Taito for Arcade video game, arcades. It was released in Japan in April 1978, with the game being released by Midway Manufacturing overseas. ''Space Invaders'' was the first fixed s ...
'' is frequently cited as the "first" or "original" in the genre.[Game Genres: Shmups](_blank)
Jim Whitehead, January 29, 2007. Retrieved June 17, 2008. [Buchanan, Levi]
, ''IGN'', March 31, 2003, Accessed June 14, 2008 ''Space Invaders'' pitted the player against multiple enemies descending from the top of the screen at a constantly increasing speed.Galaxian
is a 1979 fixed shooter video game developed and published by Namco for arcades. The player assumes control of the Galaxip starfighter in its mission to protect Earth from waves of aliens. Gameplay involves destroying each formation of alien ...
'' took the genre further with more complex enemy patterns and richer graphics.[Ashcraft, p. 77] The ''Touhou Project'' series is one of the most popular bullet hell franchises.
* Speech synthesis — In 1980, the first known video game to feature speech synthesis was released: Sunsoft's shoot 'em up game ''Stratovox''.Hideo Kojima
is a Japanese video game designer. Regarded as one of the pioneering auteurs of video games, he developed a strong passion for film and literature during his childhood and adolescence, which in turn has had a significant influence on his game ...
's ''Metal Gear'' (1987), the first in the Metal Gear (series), ''Metal Gear'' series. It was followed by ''Metal Gear 2: Solid Snake'' (1990) which significantly expanded the genre, and then ''Metal Gear Solid (1998 video game), Metal Gear Solid'' (1998).
** Stealth game, 3D stealth game — A gameplay demo of ''Metal Gear Solid (1998 video game), Metal Gear Solid'' was first revealed to the public at the 1996 Tokyo Game Show and was later shown at E3 1997 as a short video.Space Invaders
is a 1978 shoot 'em up video game developed and published by Taito for Arcade video game, arcades. It was released in Japan in April 1978, with the game being released by Midway Manufacturing overseas. ''Space Invaders'' was the first fixed s ...
'' (1978), ''Pac-Man'' (1980) and survival horror.[Kurt Kalata]
SOS / Septentrion (プテントリオン) - Super NES (1993)
, Hardcore Gaming 101
* Texture mapping — Namco's ''SimDrive'' (''SimRoad'') for the Namco System 22,[Kurt Kalata]
Konami Run 'n Guns
Hardcore Gaming 101 ''List of Sega arcade games, Last Survivor'' (1989) added freeroaming and Deathmatch (video games), deathmatch.
** Third-person shooter, 3D third-person shooter (3D TPS) — Namco's ''Cyber Sled'' (1993) was the earliest TPS with 3D polygon graphics.
** Over-the-shoulder shot, Over-the-shoulder (OTS) — ''Resident Evil 4'' (2005) redefined the third-person shooter genreSpace Invaders
is a 1978 shoot 'em up video game developed and published by Taito for Arcade video game, arcades. It was released in Japan in April 1978, with the game being released by Midway Manufacturing overseas. ''Space Invaders'' was the first fixed s ...
'' (1978).
Sciences
Atmospheric science
 * Downburst — Downbursts, strong ground-level wind systems that emanate from a point above and blow radially, were discovered by Ted Fujita.
* Downburst — Downbursts, strong ground-level wind systems that emanate from a point above and blow radially, were discovered by Ted Fujita.[Tornado Damage Scales: Fujita Scale and Enhanced Fujita Scale](_blank)
/ref>
* Fujiwhara effect — The Fujiwhara effect is an atmospheric phenomenon where two nearby cyclone, cyclonic vortex, vortices orbit each other and close the distance between the circulations of their corresponding low-pressure areas. The effect was first described by Sakuhei Fujiwhara in 1921.
* Jet stream — Jet streams were first discovered by Japanese meteorologist Wasaburo Oishi by tracking ceiling balloons. However, Oishi's work largely went unnoticed outside Japan because it was published in Esperanto.
* Microburst — The microburst was first discovered and identified as a small scale downburst affecting an area 4 km (2.5 mi) in diameter or less by Ted Fujita in 1974. Microbursts are recognized as capable of generating wind speeds higher than 270 km/h (170 mph). In addition, Fujita also discovered macrobursts and classified them as downbursts larger than 4 km (2.5 mi).
Chemistry and biomedical
* Agar — Agar was discovered in Japan around 1658 by Mino Tarōzaemon.
* Aspergillus oryzae#Genome, Aspergillus oryzae — The genome for ''Aspergillus oryzae'' was sequenced and released by a consortium of Japanese biotechnology companies, in late 2005.
* CRISPR — Yoshizumi Ishino discovered CRISPR in 1987. * Digital microscope — Japanese company Hirox created the first ever digital microscope. A variation of a traditional microscope using optics and a digital camera to output an image to a monitor.
* Ephedrine, Ephedrine synthesis — Ephedrine in its natural form, known as Ephedra (plant), ''má huáng'' (麻黄) in traditional Chinese medicine, had been documented in China since the Han dynasty.
* Digital microscope — Japanese company Hirox created the first ever digital microscope. A variation of a traditional microscope using optics and a digital camera to output an image to a monitor.
* Ephedrine, Ephedrine synthesis — Ephedrine in its natural form, known as Ephedra (plant), ''má huáng'' (麻黄) in traditional Chinese medicine, had been documented in China since the Han dynasty. * Methamphetamine — Methamphetamine was first synthesized from ephedrine in Japan in 1894 by chemist Nagayoshi Nagai. In 1919, methamphetamine hydrochloride was synthesized by pharmacologist Akira Ogata.
* Methamphetamine — Methamphetamine was first synthesized from ephedrine in Japan in 1894 by chemist Nagayoshi Nagai. In 1919, methamphetamine hydrochloride was synthesized by pharmacologist Akira Ogata.["Discovery and applications of photocatalysis — Creating a comfortable future by making use of light energy"](_blank)
''Japan Nanonet Bulletin'' Issue 44, 12 May 2005.
* Pulse oximetry — Pulse oximetry was developed in 1972, by Takuo Aoyagi and Michio Kishi, bioengineers, at Nihon Kohden using the ratio of red to infrared light absorption of pulsating components at the measuring site. Susumu Nakajima, a surgeon, and his associates first tested the device in patients, reporting it in 1975.[Takemi Program in International Health
Dr. Taro Takem]
* Statin — The statin class of drugs was first discovered by Akira Endo (biochemist), Akira Endo, a Japanese biochemist working for the pharmaceutical company Daiichi Sankyo, Sankyo. Mevastatin was the first discovered member of the statin class.[Pulvers, Roger,]
Jokichi Takamine: a man with fire in his belly whatever the odds
, ''Japan Times'', June 28, 2009, p. 8.
* Thiamine, Thiamine (Vitamin B1) — Thiamine was the first of the water-soluble vitamins to be described,[Mahan LK, Escott-Stump S, editors. ''Krause's food, nutrition, & diet therapy''. 10th ed. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Company; 2000] leading to the discovery of more such trace compounds essential for survival and to the notion of vitamin. It was not until 1884 that Kanehiro Takaki (1849–1920) attributed beriberi to insufficient nitrogen intake (protein deficiency). In 1910, Japanese scientist Umetaro Suzuki succeeded in extracting a water-soluble complex of micronutrients from rice bran and named it aberic acid. He published this discovery in a Japanese scientific journal. The Polish biochemist Kazimierz Funk later proposed the complex be named "Vitamine" (a portmanteau of "vital amine") in 1912.
* Urushiol — Urushiol, a mixture of alkyl catechols, was discovered by Rikou Majima. Majima also discovered that Urushiol was an allergen which gave members of the genus ''Toxicodendron'', such as Toxicodendron radicans, poison ivy and Toxicodendron diversilobum, poison oak, their skin-irritating properties.
Mathematics
 * Bernoulli number — Studied by Seki Kōwa and published after his death, in 1712. Jacob Bernoulli independently developed the concept in the same period, though his work was published a year later.
* Bernoulli number — Studied by Seki Kōwa and published after his death, in 1712. Jacob Bernoulli independently developed the concept in the same period, though his work was published a year later.[Helaine Selin, Selin, Helaine. (1997), ''An Introduction to the History of Mathematics''. Saunders College Publishing. p. 891, ][Poole, David. (2005), ''Linear algebra: a modern introductio''. p. 279, .][Styan, George P. H.; Trenkler, Götz. (2007)]
. Journal of Applied Mathematics and Decision Sciences
2007, Hindawi Publishing Corporation, pp. 2
* Calculus — Seki Kōwa (1642–1708) founded ''Enri'', a mathematical system with the same purpose as calculus.
** Itô calculus — Developed by Kiyosi Itô throughout the 20th century, Itô calculus extends calculus to stochastic processes such as Brownian motion (Wiener process). Its basic concept is the Itô integral, and among the most important results is a change of variable formula known as Itô's lemma. Itô calculus is widely applied in various fields, but is perhaps best known for its use in mathematical finance.
* Determinant — In Japan, determinants were introduced to study Elimination theory, elimination of variables in systems of higher-order algebraic equations. They used it to give shorthand representation for the resultant. The determinant as an independent function was first studied by Seki Kōwa in 1683.[Howard Eves: "''An Introduction to the History of Mathematics''", page 405, Saunders College Publishing, 1990. ()]
* Elimination theory — In 1683 (''Kai-Fukudai-no-Hō''), Seki Kōwa came up with elimination theory, based on resultant.[Johnson, Roger A., ''Advanced Euclidean Geometry'', Dover Publ., 2007 (orig. 1929), p. 193] This result comes from a sangaku tablet dated 1800.Edo period
The , also known as the , is the period between 1600 or 1603 and 1868 in the history of Japan, when the country was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and some 300 regional ''daimyo'', or feudal lords. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengok ...
(1603–1867) by members of all social classes. The Dutch Japanologist Isaac Titsingh introduced ''sangaku'' to the West when he returned to Europe in the late 1790s.
* Soddy's hexlet — Irisawa Shintarō Hiroatsu analyzed Soddy's hexlet in a Sangaku in 1822 and was the first person to do so.
* Takagi existence theorem — Takagi existence theorem was developed by Teiji Takagi in isolation during World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
. He presented it at the International Congress of Mathematicians in 1920.
* Two-element Boolean algebra, Two-valued Boolean algebra — Discovered independently by NEC engineer Akira Nakashima. From 1934 to 1936, his switching circuit theory showed that two-valued Boolean algebra can describe the operation of switching circuits.[History of Research on Switching Theory in Japan](_blank)
''IEEJ Transactions on Fundamentals and Materials'', Vol. 124 (2004) No. 8, pp. 720–726, Institute of Electrical Engineers of Japan[Switching Theory/Relay Circuit Network Theory/Theory of Logical Mathematics](_blank)
IPSJ Computer Museum, Information Processing Society of Japan[Radomir S. Stanković (University of Niš), Jaakko T. Astola (Tampere University of Technology), Mark G. Karpovsky (Boston University)]
Some Historical Remarks on Switching Theory
2007, DOI 10.1.1.66.1248
Physics
 * Blue laser — In 1992, Japanese inventor Shuji Nakamura invented the first efficient blue LED.
* Blue laser — In 1992, Japanese inventor Shuji Nakamura invented the first efficient blue LED.[NobelPrize.org Press Release (7 October 2014): The Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences has decided to award the Nobel Prize in Physics for 2014 to Isamu Akasaki (Meijo University, Nagoya, Japan and Nagoya University, Japan), Hiroshi Amano (Nagoya University, Japan) and Shuji Nakamura (University of California, Santa Barbara, CA, USA) "for the invention of efficient blue light-emitting diodes which has enabled bright and energy-saving white light sources" ](_blank)
/ref>
* Cabibbo–Kobayashi–Maskawa matrix — Building off the work of Nicola Cabibbo, Makoto Kobayashi (physicist), Makoto Kobayashi and Toshihide Maskawa introduced the Cabibbo–Kobayashi–Maskawa matrix which introduced for three generations of quarks. In 2008, Kobayashi and Maskawa shared one half of the Nobel Prize in Physics "for the discovery of the origin of the broken symmetry which predicts the existence of at least three families of quarks in nature".
* High definition video, High definition List of cameras on the International Space Station, space camera — NHK and Sony developed the first high definition video camcorder used on a spacecraft, the Space Shuttle Discovery in 1998.[
][
]
* Planetarium projector with Ray tracing (graphics), 3D ray tracing — LINKS-1 Computer Graphics System was used to create the first 3D planetarium video made with ray-traced 3D computer graphics
3D computer graphics, sometimes called Computer-generated imagery, CGI, 3D-CGI or three-dimensional Computer-generated imagery, computer graphics, are graphics that use a three-dimensional representation of geometric data (often Cartesian coor ...
. It was presented with Fujitsu at a 1985 Tsukuba event.
Semiconductors
 * Avalanche photodiode — Invented by Jun-ichi Nishizawa in 1952.
* Avalanche photodiode — Invented by Jun-ichi Nishizawa in 1952.[Jun-ichi Nishizawa: Engineer, Sophia University Special Professor](_blank)
(interview), ''Japan Quality Review'', 2011
* Blue LED — In 1992 Japanese inventor Shuji Nakamura invented the first efficient Blue laser, blue LED.integrated circuit
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
— Shunpei Yamazaki invented an integrated circuit
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
made entirely from glass and with an 8-bit central processing unit
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor, or just processor, is the primary Processor (computing), processor in a given computer. Its electronic circuitry executes Instruction (computing), instructions ...
.[The Third Industrial Revolution Occurred in Sendai](_blank)
Soh-VEHE International Patent Office, Japan Patent Attorneys Association
* LED, Green LED — Developed by Junichi Nishizawa in 1971.Three-dimensional integrated circuit
A three-dimensional integrated circuit (3D IC) is a MOSFET, MOS (metal-oxide semiconductor) integrated circuit (IC) manufactured by stacking as many as 16 or more ICs and interconnecting them vertically using, for instance, through-silicon vias (TS ...
(3D IC) — In 1969, a 3D MOS integrated circuit, MOS IC (3D IC) memory chip was proposed by NEC.Hitachi
() is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate founded in 1910 and headquartered in Chiyoda, Tokyo. The company is active in various industries, including digital systems, power and renewable ener ...
(1983) and Fujitsu (1984).Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
.[ In the first public report of the discovery (presentation at the 12th annual meeting of the Physical Society of Japan in October 1957), Takashi Suzuki, who was a student at Tokyo University of Science and doing his internship at Tokyo Tsushin Kogyo under Esaki's supervision, was a co-author. Suzuki, along with Yuriko Kurose, first observed the negative differential resistance when they were testing heavily doped P-N junctions.]
* OLED, White OLED — Pioneered by J. Kido's team at Yamagata University in 1995. It led to the commercialization of OLED display, OLED displays and Solid-state lighting, lighting.
Transistors
 * Field-effect transistor (FET) — The first type of FET to be successfully built was the JFET.
* Field-effect transistor (FET) — The first type of FET to be successfully built was the JFET.[Junction Field-Effect Devices](_blank)
''Semiconductor Devices for Power Conditioning'', 1982
** Static induction transistor (SIT) — Invented by Jun-ichi Nishizawa and Y. Watanabe in 1950.
** CMOS, C²MOS — Toshiba developed C²MOS (Clocked CMOS), a circuit technology with lower power consumption and faster operating speed than ordinary CMOS, in 1969.Hitachi
() is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate founded in 1910 and headquartered in Chiyoda, Tokyo. The company is active in various industries, including digital systems, power and renewable ener ...
team introduced the twin-well Hi-CMOS process with the HM6147 memory chip.patent
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an sufficiency of disclosure, enabling discl ...
S47-21739, filed in 1968.
** Latch-up, Non-latch-up IGBT — Akio Nakagawa's Toshiba team invented the device design concept of non-latch-up IGBTs in 1984.patent
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an sufficiency of disclosure, enabling discl ...
describing the XMOS transistor.Hitachi
() is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate founded in 1910 and headquartered in Chiyoda, Tokyo. The company is active in various industries, including digital systems, power and renewable ener ...
team in 1989.Hitachi
() is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate founded in 1910 and headquartered in Chiyoda, Tokyo. The company is active in various industries, including digital systems, power and renewable ener ...
introduced a vertical power MOSFET. Jun-ichi Nishizawa invented a power MOSFET in 1974. JVC, Pioneer Corporation, Pioneer, Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
and Toshiba began manufacturing power MOSFETs in 1974.Hitachi
() is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate founded in 1910 and headquartered in Chiyoda, Tokyo. The company is active in various industries, including digital systems, power and renewable ener ...
introduced the LDMOS transistor. They were the only LDMOS manufacturer between 1977 and 1983, mainly for audio power amplifiers and PA systems.Hitachi
() is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate founded in 1910 and headquartered in Chiyoda, Tokyo. The company is active in various industries, including digital systems, power and renewable ener ...
in 1969.
Technology
 * Advanced boiling water reactor (ABWR) — Developed by Toshiba,
* Advanced boiling water reactor (ABWR) — Developed by Toshiba, Hitachi
() is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate founded in 1910 and headquartered in Chiyoda, Tokyo. The company is active in various industries, including digital systems, power and renewable ener ...
and GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy, GE. In 1996, the first ABWR entered commercial operation in Japan. for the URL of the English Wikipedia mobile main page
* QR code — The QR code, a type of matrix barcode, was invented by Denso#Denso Wave, Denso Wave in 1994.
for the URL of the English Wikipedia mobile main page
* QR code — The QR code, a type of matrix barcode, was invented by Denso#Denso Wave, Denso Wave in 1994.paper
Paper is a thin sheet material produced by mechanically or chemically processing cellulose fibres derived from wood, Textile, rags, poaceae, grasses, Feces#Other uses, herbivore dung, or other vegetable sources in water. Once the water is dra ...
had been introduced to Japan from Korea. The washi papermaking technique was developed in Japan during the Heian period around 805 to 809.
Audio
 *3.5 mm headphone jack — Introduced with the
*3.5 mm headphone jack — Introduced with the Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
EFM-117J transistor radio in 1964.
*Record player, Automatic dual-side record player — In 1981, Sharp Corporation, Sharp released the first record player that automatically switches sides of a vinyl record.Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
, used for the Super Nintendo, Philips CD-i, Sony PlayStation, and Apple Inc., Apple Macintosh Quadra.
* Compact Disc Digital Audio (CD-DA) — Developed by Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
and Philips in 1980. Its 16-bit audio bit depth and 44.1 sample rate was proposed by Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
, based on their earlier PCM adaptor technology.Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
released the world's first CD Player, called the Sony CDP-101, CDP-101, in 1982, using a slide-out tray design for the Compact Disc.
** Portable CD player — Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
's Discman, released in 1984, was the first portable CD player.
* Digital audio Digital recording, tape recorder — Heitaro Nakajima, head of NHK's Technical Research Laboratories, in 1967 had commenced work on the digitization of sound and within two years had developed the first digital audio tape recorder.Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
's PCM adaptor, PCM-1, introduced in 1976, was the first commercial product allowing digital audio recording and playback, using Betamax cassette tapes as a storage medium.Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
's TA-1120 (1965) was the first silicon transistor Stereophonic sound, stereo integrated amplifier. Compared to vacuum tube amplifiers at the time, the TA-1120 offered higher output with lower distortion.Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
, in 1971.
* Microprocessor music sequencer — In 1977, the Roland MC-8 Microcomposer was an early stand-alone, microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor (computing), processor for which the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit (IC), or a small number of ICs. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, a ...
based, digital CV/gate sequencer.[Patent S27-001322](_blank)
(Japanese) A patent was issued in 1952.Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
's PCM adaptor, PCM-1, a pulse-code modulation (PCM) processor chip introduced in 1976.
Batteries
 * Lithium-ion battery — Akira Yoshino invented the modern li-ion battery in 1985. In 1991,
* Lithium-ion battery — Akira Yoshino invented the modern li-ion battery in 1985. In 1991, Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
and Asahi Kasei released the first commercial lithium-ion battery using Yoshino's design.
* Dry cell — The world's first dry-battery was invented in Japan during the Meiji Era. The inventor was Sakizou Yai. The company Yai founded no longer exists
Calculators
 * Calculator, All-electric compact calculator — In 1957, Casio's Model 14-A was the first all-electric compact calculator, based on relay technology.
** Transistor, All-transistor desktop calculator — In 1964, Sharp Corporation's CS-10A was the first Transistor diode model, all-transistor-diode electronic desktop calculator.
* Calculator, All-electric compact calculator — In 1957, Casio's Model 14-A was the first all-electric compact calculator, based on relay technology.
** Transistor, All-transistor desktop calculator — In 1964, Sharp Corporation's CS-10A was the first Transistor diode model, all-transistor-diode electronic desktop calculator.integrated circuit
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
(IC) chips.microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor (computing), processor for which the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit (IC), or a small number of ICs. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, a ...
, the Intel 4004. It was the first commercial product to use a microprocessor.
* Pocket calculator — The first portable calculators appeared in Japan in 1970, and were soon marketed around the world. These included the Sanyo ICC-0081 "Mini Calculator", the Canon (company), Canon Pocketronic, and the Sharp Corporation, Sharp QT-8B "micro Compet". Sharp put in great efforts in size and power reduction and introduced in January 1971 the Sharp EL-8, also marketed as the Facit 1111, which was close to being a pocket calculator. It weighed about one pound, had a vacuum fluorescent display, and rechargeable NiCad batteries. The first truly pocket-sized electronic calculator was the Busicom LE-120A "HANDY", which was marketed early in 1971.
** LED calculator — Busicom's LE-120A (Handy-LE) and LE-120S (Handy), released in 1971, were the first calculators to use LED displays.Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
. It is derived from the History of Science and Technology in China, ancient Chinese suanpan, imported to Japan in the 14th century.
Cameras
 * Active-pixel sensor (APS) — The first MOSFET, MOS APS image sensor was invented by Olympus Corporation, Olympus in Japan during the mid-1980s.
* Active-pixel sensor (APS) — The first MOSFET, MOS APS image sensor was invented by Olympus Corporation, Olympus in Japan during the mid-1980s.Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
released the first stacked CMOS sensor, the Exmor RS.
** Intelligent vision sensor — In 2020, Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
has launched the first intelligent vision sensors with AI edge computing capabilies.
* Camcorder — In 1983, Sony released the first camcorder, the Betacam system, for professional use.[David Buckingham, Rebekah Willett, Maria Pini (2011)]
''Home Truths? Video Production and Domestic Life'', page 9
, University of Michigan Press Sony released the first consumer camcorder in 1983, the Betamovie BMC-100P.Nintendo
is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational video game company headquartered in Kyoto. It develops, publishes, and releases both video games and video game consoles.
The history of Nintendo began when craftsman Fusajiro Yamauchi ...
's Game Boy Camera, released as an accessory for the Game Boy handheld game console
A handheld game console, or simply handheld console, is a small, portable self-contained video game console with a built-in screen, game controls and speakers. Handheld game consoles are smaller than home video game consoles and contain the con ...
in February 1998.
** MPEG-4 video camera — In 1999, Sharp Corporation's Internet Viewcam was the first video camera to support MPEG-4 Part 2, MPEG-4 video files.[Nikon SLR-type digital cameras](_blank)
Pierre Jarleton
** Full-frame DSLR — The first full-frame DSLR cameras were developed in Japan from around 2000 to 2002: the Pentax MZ-D, MZ-D by Pentax, the Contax N Digital, N Digital by Contax,[''British Journal of Photography'']
Issues 7410-7422
2003, page 2 and the Canon EOS-1Ds, EOS-1Ds by Canon Inc.
* DV (video format), DV format — Introduced in 1995, the format was developed by Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
and several other Japanese video camera manufacturers.
Chindōgu
Chindōgu is the Japanese art of inventing ingenious everyday gadgets that, on the face of it, seem like an ideal solution to a particular problem. However, Chindōgu has a distinctive feature: anyone actually attempting to use one of these inventions would find that it causes so many new problems, or such significant social embarrassment, that effectively it has no utility whatsoever. Thus, Chindōgu are sometimes described as "unuseless" – that is, they cannot be regarded as 'useless' in an absolute sense, since they do actually solve a problem; however, in practical terms, they cannot positively be called "useful". The term "Chindōgu" was coined by Kenji Kawakami.
Computing
 * E-reader with electronic paper — The Sony Librie, released in 2004 and the precursor to the Sony Reader, was the first ereader to use electronic paper.
* Fifth generation computer — Ministry of International Trade and Industry, MITI's Fifth Generation Computer Systems (FGCS) project launched in 1982 researched massively parallel processing, logic programming, artificial intelligence, AI, natural language processing and interactive processing.
* E-reader with electronic paper — The Sony Librie, released in 2004 and the precursor to the Sony Reader, was the first ereader to use electronic paper.
* Fifth generation computer — Ministry of International Trade and Industry, MITI's Fifth Generation Computer Systems (FGCS) project launched in 1982 researched massively parallel processing, logic programming, artificial intelligence, AI, natural language processing and interactive processing.microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor (computing), processor for which the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit (IC), or a small number of ICs. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, a ...
s.[Epson HX-20](_blank)
Old Computers[【Shinshu Seiki / Suwa Seikosha】 HC-20](_blank)
Information Processing Society of Japan In North America, Epson introduced it as the Epson HX-20 in 1981, at the COMDEX computer show in Las Vegas, where it drew significant attention for its portability.[Michael R. Peres]
''The Focal Encyclopedia of Photography'', page 306
Taylor & Francis It was the first notebook-sized handheld computer,[Japanese PCs (1984)](_blank)
(13:13), ''Computer Chronicles''
* Microcomputer — The Sord Computer Corporation, Sord SMP80/08, developed from 1972 to early 1973, was one of the first microcomputers, using the Intel 8008 microprocessor. In early 1974, the Sord SMP80/x was the first microcomputer to use the Intel 8080 microprocessor.16-bit
16-bit microcomputers are microcomputers that use 16-bit microprocessors.
A 16-bit register can store 216 different values. The range of integer values that can be stored in 16 bits depends on the integer representation used. With the two ...
microcomputer — In March 1977, the Panafacom Lkit-16 was released. It was an early 16-bit microcomputer, based on the 16-bit Panafacom MN1610 (1975) microprocessor.
** Home computer with floppy disk drive — In 1977, Sord Computer Corporation, Sord's M200 Smart Home Computer was an early integrated home desktop computer with a Zilog Z80 CPU, keyboard, CRT display, floppy disk drive and MF-DOS operating system.microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor (computing), processor for which the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit (IC), or a small number of ICs. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, a ...
central processing unit
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor, or just processor, is the primary Processor (computing), processor in a given computer. Its electronic circuitry executes Instruction (computing), instructions ...
(CPU) was conceived in a 1968 meeting in Japan between Sharp Corporation, Sharp engineer Tadashi Sasaki (engineer), Tadashi Sasaki and a software engineering researcher from Nara Women's University, Nara Women's College. Sasaki discussed the microprocessor concept with Busicom and Intel in 1968.[Federico Faggin]
The Making of the First Microprocessor
''IEEE Solid-State Circuits Magazine'', Winter 2009, IEEE Xplore in 1968 as Masatoshi Shima's three-chip CPU design,[Masatoshi Shima](_blank)
IEEE
** NMOS logic, NMOS microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor (computing), processor for which the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit (IC), or a small number of ICs. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, a ...
— NEC's μCOM-4 (1973) was the earliest NMOS microprocessor, Semiconductor device fabrication, fabricated by the NEC Large-scale integration, LSI team consisting of five researchers led by Sohichi Suzuki.microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor (computing), processor for which the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit (IC), or a small number of ICs. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, a ...
— The Toshiba TLCS-12 (1973) was the first 12-bit microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor (computing), processor for which the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit (IC), or a small number of ICs. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, a ...
.16-bit
16-bit microcomputers are microcomputers that use 16-bit microprocessors.
A 16-bit register can store 216 different values. The range of integer values that can be stored in 16 bits depends on the integer representation used. With the two ...
microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor (computing), processor for which the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit (IC), or a small number of ICs. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, a ...
— The first single-chip 16-bit microprocessor was the Panafacom MN1610 (1975).Hitachi
() is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate founded in 1910 and headquartered in Chiyoda, Tokyo. The company is active in various industries, including digital systems, power and renewable ener ...
for their SuperH (SH) series of central processing unit
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor, or just processor, is the primary Processor (computing), processor in a given computer. Its electronic circuitry executes Instruction (computing), instructions ...
(CPU) microprocessors, introduced in 1992.integrated circuit
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
chip made entirely from glass and with an 8-bit central processing unit
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor, or just processor, is the primary Processor (computing), processor in a given computer. Its electronic circuitry executes Instruction (computing), instructions ...
.central processing unit
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor, or just processor, is the primary Processor (computing), processor in a given computer. Its electronic circuitry executes Instruction (computing), instructions ...
(CPU) chip made entirely from plastic.[Martin Fransman (1993)]
''The Market and Beyond: Cooperation and Competition in Information Technology'', page 19
Cambridge University Press and was completed in 1956, created by the Electrotechnical Laboratory.[Early Computers](_blank)
Information Processing Society of Japan It was the first stored-program transistor computer.[Early Computers: Brief History](_blank)
Information Processing Society of Japan
* Switching circuit theory — From 1934 to 1936, NEC engineer Akira Nakashima introduced switching circuit theory in a series of papers showing that Two-element Boolean algebra, two-valued Boolean algebra can describe the operation of switching circuits.[ (3+207+1 pages]
10:00 min
/ref>
* Text-to-speech (TTS) — Noriko Umeda ''et al.'' developed the first general English text-to-speech system in 1968, at the Electrotechnical Laboratory in Japan.
* Universal Serial Bus (USB) — The USB standard was co-developed by NEC in 1996.
Domestic appliances
 * Bladeless fan — The first bladeless fan was patented by Toshiba in 1981.
* Bread machine — The bread machine was developed and released in
* Bladeless fan — The first bladeless fan was patented by Toshiba in 1981.
* Bread machine — The bread machine was developed and released in Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
in 1986 by the Matsushita Electric Industrial Company.
* Rice cooker, Electric rice cooker — Invented by designers at the Toshiba Corporation in the late 1940s.
* RFIQin — An automatic cooking device, invented by Mamoru Imura and patent
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an sufficiency of disclosure, enabling discl ...
ed in 2007.
Memory and storage
 * 3.5 inch floppy disk — Pioneered by
* 3.5 inch floppy disk — Pioneered by Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
in 1981.
* Compact Disc (CD) — The compact disc was jointly developed by Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
(Toshitada Doi) and Philips (Joop Sinjou). Sony first publicly demonstrated an optical digital audio disc in September 1976. In September 1978, they demonstrated an optical digital audio disc with a 150 minute playing time, and with specifications of 44,056 Hz sampling rate, 16-bit linear resolution, Cross-interleaved Reed-Solomon coding, cross-interleaved error correction code, that were similar to those of the Compact Disc they introduced in 1982.CD-ROM
A CD-ROM (, compact disc read-only memory) is a type of read-only memory consisting of a pre-pressed optical compact disc that contains computer data storage, data computers can read, but not write or erase. Some CDs, called enhanced CDs, hold b ...
— Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
and Philips created the technical standard that defines the format of a CD-ROM in 1983.Sega
is a Japanese video game company and subsidiary of Sega Sammy Holdings headquartered in Tokyo. It produces several List of best-selling video game franchises, multi-million-selling game franchises for arcade game, arcades and video game cons ...
and Yamaha Corporation, Yamaha for the Dreamcast (1998) and other Sega systems.Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
, Toshiba and Panasonic) and one Dutch company (Philips).
** DVD recordable (DVD-R) — The DVD-R format was developed by Pioneer Corporation, Pioneer in 1997.Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
started two projects applying the new diodes: Ultra Density Optical, UDO (Ultra Density Optical) and DVR Blue (together with Pioneer Corporation, Pioneer), a format of rewritable discs which would eventually become the Blu-ray Disc. The Blu-ray Disc Association was founded by nine companies: five from Japan, two from South Korea, one Netherlands, and one France. The format was launched in 2006.
* Dynamic random-access memory (DRAM) — In 1965, Toshiba introduced bipolar dynamic RAM (DRAM) for electronic calculator Toscal BC-1411.Hitachi
() is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate founded in 1910 and headquartered in Chiyoda, Tokyo. The company is active in various industries, including digital systems, power and renewable ener ...
HM5283206, an Mebibyte, 8Mbit SGRAM chip that debuted in November 1994.Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
introduced the MiniDisc. Recordable MiniDiscs used HAMR, but the discs were read Optical, optically via the Kerr effect.Hitachi
() is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate founded in 1910 and headquartered in Chiyoda, Tokyo. The company is active in various industries, including digital systems, power and renewable ener ...
introduced a video disc system in which chrominance, luminance and sound information are encoded Holographic data storage, holographically. It had a capacity of 54,000 frames.Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
introduced a laserdisc format designed to store digital data, with a capacity of 3.28 Gigabyte, GB.
* Memory card — In 1985, the earliest memory card formats were the Bee Card (game cartridge), Bee Card and Astron SoftCard for the MSX,Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
introduced the MiniDisc (MD), a music recording and playback format intended to replace Compact cassette, audio cassettes.[''Lasers & Optronics'', Volume 6](_blank)
page 77 Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
, and Kokusai Denshin Denwa.
* Quad-level cell (QLC) — NEC demonstrated QLC in 1996, with flash memory storing 2 bits per cell. In 1997, NEC demonstrated DRAM with QLC cells.[IEEE Magnetics Society Oral History: Shun-Ichi Iwasaki, 29 March 2022](_blank)
/ref>
** Giant magnetoresistance, GMR Disk read-and-write head, head — In 1997, Toshiba released the first practical hard disk drive (HDD) equipped with a giant magnetoresistance (GMR) disk read-and-write head.
Music instruments
 *Analog modeling synthesizer — The Roland D-50 from 1987 was the first virtual analog synthesizer.
** Linear arithmetic synthesis (LA synthesis) — Invented by Roland Corporation, Roland for the Roland D-50, D-50 synthesizer (1987).
** Supersaw — A waveform created by Roland Corporation, Roland for its Roland JP-8000, JP-8000 (1996) analog modeling synthesizer.
* Bass synthesizer–Music sequencer, sequencer — The first was Firstman SQ-01,
*Analog modeling synthesizer — The Roland D-50 from 1987 was the first virtual analog synthesizer.
** Linear arithmetic synthesis (LA synthesis) — Invented by Roland Corporation, Roland for the Roland D-50, D-50 synthesizer (1987).
** Supersaw — A waveform created by Roland Corporation, Roland for its Roland JP-8000, JP-8000 (1996) analog modeling synthesizer.
* Bass synthesizer–Music sequencer, sequencer — The first was Firstman SQ-01,[ ("''Keyboard Report, Oct. '81''", according to the )] released in 1980 by Japanese company Hillwood/Firstman.[Mark Jenkins (2009)]
''Analog Synthesizers'', pages 107-108
CRC Press[A TALE OF TWO STRING SYNTHS](_blank)
''Sound on Sound'', July 2002
** Acid house, Acid bass — Acid house music was characterized by the distinctive squelching Bassline, basslines of the Roland TB-303 bass synthesizer-sequencer.Osaka
is a Cities designated by government ordinance of Japan, designated city in the Kansai region of Honshu in Japan. It is the capital of and most populous city in Osaka Prefecture, and the List of cities in Japan, third-most populous city in J ...
.[Brian Coleman]
The Technics 1200 — Hammer Of The Gods
Medium (website), Medium In 1969, Matsushita released it as the Technics (brand), SP-10, the first in their influential Technics (brand), Technics series of turntables.[Trevor Pinch, Karin Bijsterveld]
''The Oxford Handbook of Sound Studies'', page 515
Oxford University Press The Technics SL-1100, released in 1971, was adopted by early Hip hop music, hip hop DJs for turntablism,microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor (computing), processor for which the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit (IC), or a small number of ICs. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, a ...
based programmable rhythm machine.[''Keyboard (magazine), Contemporary Keyboard'']
Volume 7, Issues 1–6
1981: "''The Roland TR-808 will undoubtedly become the standard for rhythm machines of the future because it does what no rhythm machine of the past has ever done. Not only does the TR-808 allow programming of individual rhythm patterns, it can also program the entire percussion track of a song from beginning to end, complete with breaks, rolls, literally anything you can think of.''" Created by Ikutaro Kakehashi, the 808 has been fundamental to hip hop music and electronic dance music since the 1980s,['':nl:Rockin'f, Rockin'f'', March 1982]
pages 140–141
/ref>
* Phaser (effect), Phaser effects pedal — In 1968, Shin-ei's Uni-Vibe effects pedal, designed by audio engineer Fumio Mieda, incorporated phase shift and Chorus effect, chorus effects, soon becoming favorite effects of guitarists such as Jimi Hendrix and Robin Trower.
* Physical modelling synthesis — The first commercially available physical modelling synthesizer was Yamaha Corporation, Yamaha's VL-1 in 1994.
* Polyphony and monophony in instruments, Polyphonic string synthesizer — Roland Corporation released early polyphonic string synthesizers, RS-101 in 1975 and Roland RS-202, RS-202 in 1976.
Nanotechnology
*Carbon nanofiber (CNF) — Discovered by Morinobu Endo in the early 1970s.
Printing
* 3D printing — In 1981, Hideo Kodama of Nagoya Municipal Industrial Research Institute invented two additive methods for fabricating three-dimensional plastic models with photo-hardening thermosetting polymer, thermoset polymer, where the UV exposure area is controlled by a mask pattern or a scanning fiber transmitter.
* Desktop printer, Desktop laser printer — Japanese company Canon Inc., Canon developed in 1979 the Canon LBP-10, a low-cost desktop laser printer. Canon then began work on a much-improved print engine, the Canon CX, resulting in the LBP-CX printer.
Robotics
 * Android (robot), Android — Waseda University initiated the WABOT project in 1967, and in 1972 completed the WABOT-1, the world's first full-scale humanoid intelligent robot. Its limb control system allowed it to walk with the lower limbs, and to grip and transport objects with hands, using tactile sensors. Its vision system allowed it to measure distances and directions to objects using external receptors, artificial eyes and ears. And its conversation system allowed it to communicate with a person in Japanese, with an artificial mouth. This made it the first Android (robot), android.
* Actroid — DER 01 was developed by a Japanese research group, The Intelligent Robotics Lab, directed by Hiroshi Ishiguro at Osaka University, and Kokoro Co., Ltd. The Actroid is a humanoid robot with strong visual human-likeness developed by Osaka University and manufactured by Kokoro Company Ltd. (the animatronics division of Sanrio). It was first unveiled at the 2003 International Robot Exposition in Tokyo,
* Android (robot), Android — Waseda University initiated the WABOT project in 1967, and in 1972 completed the WABOT-1, the world's first full-scale humanoid intelligent robot. Its limb control system allowed it to walk with the lower limbs, and to grip and transport objects with hands, using tactile sensors. Its vision system allowed it to measure distances and directions to objects using external receptors, artificial eyes and ears. And its conversation system allowed it to communicate with a person in Japanese, with an artificial mouth. This made it the first Android (robot), android.
* Actroid — DER 01 was developed by a Japanese research group, The Intelligent Robotics Lab, directed by Hiroshi Ishiguro at Osaka University, and Kokoro Co., Ltd. The Actroid is a humanoid robot with strong visual human-likeness developed by Osaka University and manufactured by Kokoro Company Ltd. (the animatronics division of Sanrio). It was first unveiled at the 2003 International Robot Exposition in Tokyo, Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
. The Actroid woman is a pioneer example of a real machine similar to imagined machines called by the science fiction terms ''android'' or ''gynoid'', so far used only for List of fictional robots and androids, fictional robots. It can mimic such lifelike functions as blinking, speaking, and breathing. The "Repliee" models are interactive robots with the ability to recognise and process speech and respond in kind.
* Kuratas, Giant boarding robot — Kuratas, revealed in 2012, was described as the first giant Boarding (transport), boarding robot
A robot is a machine—especially one Computer program, programmable by a computer—capable of carrying out a complex series of actions Automation, automatically. A robot can be guided by an external control device, or the robot control, co ...
, modelled after the mechs from mecha anime and manga.
* Micro robot — NEC's ARMS-D, introduced in 1981, was the first industrial robot with micrometre level precision, enabled by NEC 8085 microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor (computing), processor for which the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit (IC), or a small number of ICs. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, a ...
technology.Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
ese mechanized puppets or automata, originally made from the 17th century to the 19th century. The word ''karakuri'' means "mechanisms" or "trick". The dolls' gestures provided a form of entertainment. Three main types of karakuri exist. were used in theatre. were small and used in homes. were used in religious festivals, where the puppets were used to perform reenactments of traditional mythology, myths and legends.
* Hybrid Assistive Limb, Robotic exoskeleton for motion support (medicine) — The first HAL prototype was proposed by Yoshiyuki Sankai, a professor at Tsukuba University. Fascinated with robots since he was in the third grade, Sankai had striven to make a robotic suit in order "to support humans". In 1989, after receiving his Ph.D. in robotics, he began the development of HAL. Sankai spent three years, from 1990 to 1993, mapping out the neurons that govern leg movement. It took him and his team an additional four years to make a prototype of the hardware.
* QRIO, Running humanoid robot — Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
's QRIO (2003) was the first humanoid robot capable of running.
* Toy robot arm — Tomy
(trade name, trading as Takara Tomy in Asia and Tomy elsewhere) is a Japanese toy company. It was established in 1924 by Eiichirō Tomiyama as , became known for creating popular toys like the B-29 friction toy and luck-based game Pop-up Pi ...
's Armatron, introduced in 1982, was the first toy robot arm, moved by dual analog control joysticks. It had a significant influence on the development of modern robotics and artificial intelligence.
* Wind-up toy robot
A robot is a machine—especially one Computer program, programmable by a computer—capable of carrying out a complex series of actions Automation, automatically. A robot can be guided by an external control device, or the robot control, co ...
— Lilliput, a Japanese robot introduced in 1932, was the first wind-up toy robot.
Television and displays
 * Active shutter 3D system — Matsushita Electric developed a 3D television that employed active-shutter Stereoscopy, stereoscopic technology in the late 1970s, unveiled in 1981, while adapting the technology for the first stereoscopic video game, ''SubRoc-3D'' (1982).
* Active shutter 3D system — Matsushita Electric developed a 3D television that employed active-shutter Stereoscopy, stereoscopic technology in the late 1970s, unveiled in 1981, while adapting the technology for the first stereoscopic video game, ''SubRoc-3D'' (1982).Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
's Masaru Ibuka predicted that transistors would lead to more portable TV set, TV sets. The first fully transistorized, portable Solid-state electronics, solid-state TV set was the Sony TV8-301, developed in 1959 and released in 1960.
** Automatic fine tuning (AFT) — In 1969, Toshiba released the first color TV with AFT integrated circuit
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
technology.integrated circuit
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
(IC) chip. In 1971, they released the first color TV with mostly IC chips.display resolution
The display resolution or display modes of a digital television, computer monitor, or other display device is the number of distinct pixels in each dimension that can be displayed. It can be an ambiguous term especially as the displayed resoluti ...
to 100 lines.Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
with their Trinitron television
Television (TV) is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. Additionally, the term can refer to a physical television set rather than the medium of transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertising, ...
in 1968.
** High-definition television, High definition Cathode-ray tube, CRT (HD CRT) — In 1990, the first CRT with HD resolution, the Sony KW-3600HD, was released to the market.
** Surface-conduction electron-emitter display (SED) — Canon Inc., Canon began SED research in 1986.Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
and NEC released TV sets with digital capabilities. These early digital TV sets converted analog TV signals into digital video signals.
** Digital TV, DTV broadcast — Proposed in 1986 by Nippon Telegraph and Telephone, NTT and Ministry of Posts and Telecommunications (Japan), MPT, as part of the Integrated Network System (INS).television
Television (TV) is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. Additionally, the term can refer to a physical television set rather than the medium of transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertising, ...
that was small enough to fit in a large pocket, the Panasonic IC TV MODEL TR-001. It featured a 1.5-inch display, along with a 1.5-inch speaker.
* High-definition television (HDTV) — NHK began researching HDTV in 1964 Tokyo Olympics, 1964.display resolution
The display resolution or display modes of a digital television, computer monitor, or other display device is the number of distinct pixels in each dimension that can be displayed. It can be an ambiguous term especially as the displayed resoluti ...
.Hitachi
() is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate founded in 1910 and headquartered in Chiyoda, Tokyo. The company is active in various industries, including digital systems, power and renewable ener ...
, Panasonic, Maxell, Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
and Toshiba.Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
at the Expo '85 held in May 1985 at Tsukuba, Ibaraki.television
Television (TV) is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. Additionally, the term can refer to a physical television set rather than the medium of transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertising, ...
s were invented as handheld televisions in Japan. In 1980, Hattori Seiko's R&D group began development on color LCD pocket televisions.[''Spin (magazine), Spin'']
Jul 1985, page 55
/ref> In 1982, Seiko Epson released the first LCD television, the Epson TV Watch, a wristwatch equipped with an Active-matrix liquid crystal display, active-matrix LCD television.[''Popular Science'']
May 1984, page 150
/ref>
** LCD projector, Color LCD projector — The 3LCD, Epson VPJ-700, released in January 1989, was the first compact color LCD projector.
* LED-backlit LCD — The world's first LED-backlit LCD television was Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
's Qualia (Sony), Qualia 005, released in 2004.
** QLED, Quantum dot LED (QLED) — The first manufacturer shipping QLED TVs was Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
in 2013 as ''Triluminos'', Sony's trademark for the technology.
 * OLED display — Manufacturing of OLED displays began in 1997 by Pioneer Corporation, followed by TDK in 2001.
** OLED TV — In 2007, the Sony XEL-1 was the world's first OLED TV.
* OLED display — Manufacturing of OLED displays began in 1997 by Pioneer Corporation, followed by TDK in 2001.
** OLED TV — In 2007, the Sony XEL-1 was the world's first OLED TV.[Sony XEL-1:The world's first OLED TV](_blank)
, OLED-Info.com (2008-11-17).
** OLED head-mounted display (HMD) — Sony's HMZ-T1 (2011) was the first 3D HMD equipped with a HD OLED display.
* On-screen display (OSD) — In 1972, Sharp Corporation introduced the first television set to display a television channel number on the corner of the screen.
Textiles
* Power loom, Automatic power loom with non-stop shuttle-change motion — Sakichi Toyoda invented numerous weaving devices. His most famous invention was the automatic power loom in which he implemented the principle of ''Jidoka'' (autonomation or autonomous automation). It was the 1924 Toyoda Automatic Loom, Type G, a completely automatic high-speed loom featuring the ability to change shuttles without stopping and dozens of other innovations. At the time it was the world's most advanced loom, delivering a dramatic improvement in quality and a twenty-fold increase in productivity.This loom automatically stopped when it detected a problem such as thread breakage.
Timekeeping
 * Myriad year clock — The Myriad year clock (万年自鳴鐘 Mannen Jimeishou, lit. Ten-Thousand Year Self-ringing Bell), was a universal clock designed by the Japanese inventor Hisashige Tanaka in 1851. It belongs to the category of Japanese clocks called Wadokei.
* Quartz clock, Quartz Watch, wristwatch — The world's first quartz Watch, wristwatch was revealed in 1967: the prototype of the Astron (wristwatch), Astron revealed by Seiko in Japan, where it was in development since 1958. It was eventually released to the public in 1969.
* Myriad year clock — The Myriad year clock (万年自鳴鐘 Mannen Jimeishou, lit. Ten-Thousand Year Self-ringing Bell), was a universal clock designed by the Japanese inventor Hisashige Tanaka in 1851. It belongs to the category of Japanese clocks called Wadokei.
* Quartz clock, Quartz Watch, wristwatch — The world's first quartz Watch, wristwatch was revealed in 1967: the prototype of the Astron (wristwatch), Astron revealed by Seiko in Japan, where it was in development since 1958. It was eventually released to the public in 1969.
Video

 * Digital video disc — In 1972, :ja:TOSBAC, TOSBAC was using digital Videodisc, video disks to display color digital images. In 1995, DVD co-developed in 1995 by
* Digital video disc — In 1972, :ja:TOSBAC, TOSBAC was using digital Videodisc, video disks to display color digital images. In 1995, DVD co-developed in 1995 by Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
Toshiba and Panasonic.
** DVD player — The first DVD player was released by Toshiba in November 1996.
** Video CD — The Video CD standard was created in 1993 by JVC, Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
, Panasonic, Matsushita and Philips.
* Helical scan — Norikazu Sawazaki invented a helical scan video tape recorder (VTR) in 1953. In 1959, Toshiba released the first commercial helical scan VTR.
** Transistor video tape recorder (VTR) — Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
's SV-201 (1961) was the first transistor-based VTR.
** Videocassette recorder (VCR) — The first machines (the VP-1100 videocassette player and the VO-1700 videocassette recorder) to use the first videocassette format, U-matic, were introduced by Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
in 1971.
** Betamax — Betamax was an analog videocassette magnetic tape marketed to consumers released by Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
on May 10, 1975.Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
and Toshiba in 1991.
* H.261 — The majority of patents for H.261 (1988) were from Japanese companies, including Hitachi
() is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate founded in 1910 and headquartered in Chiyoda, Tokyo. The company is active in various industries, including digital systems, power and renewable ener ...
, Nippon Telegraph and Telephone, NTT, Toshiba, KDDI, Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
, Sharp Corporation, Sharp, OKI (conglomerate company), Oki and Panasonic, Matsushita.Hitachi
() is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate founded in 1910 and headquartered in Chiyoda, Tokyo. The company is active in various industries, including digital systems, power and renewable ener ...
, Mitsubishi Electric, Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
, JVC Kenwood, Toshiba, Fujitsu, Sharp Corporation, and Nippon Telegraph and Telephone.Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
, Mitsubishi, Panasonic, JVC Kenwood, Toshiba, Hitachi
() is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate founded in 1910 and headquartered in Chiyoda, Tokyo. The company is active in various industries, including digital systems, power and renewable ener ...
, Fujitsu, Canon Inc., Canon, KDDI, Nippon Telegraph and Telephone, NTT, Sanyo Electric, Sanyo and Sharp Corporation, Sharp.Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
and introduced under the ''Mavipak'' name in 1981 for their prototype Mavica.
Writing
 * Correction tape — Correction tape was invented in 1989 by the Japanese product manufacturer Seed. It is an alternative to correction fluid.
* Gel pen — The gel pen was invented in 1984 by the Sakura Color Products Corporation of Osaka.
* Japanese typewriter — The first typewriter to be based on the Japanese writing system was invented by Kyota Sugimoto in 1929.
* Japanese writing Graphics tablet, touch tablet — In 1971,
* Correction tape — Correction tape was invented in 1989 by the Japanese product manufacturer Seed. It is an alternative to correction fluid.
* Gel pen — The gel pen was invented in 1984 by the Sakura Color Products Corporation of Osaka.
* Japanese typewriter — The first typewriter to be based on the Japanese writing system was invented by Kyota Sugimoto in 1929.
* Japanese writing Graphics tablet, touch tablet — In 1971, Hitachi
() is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate founded in 1910 and headquartered in Chiyoda, Tokyo. The company is active in various industries, including digital systems, power and renewable ener ...
's Hidekazu Terai and Kazuo Nakata invented a touch tablet with Japanese writing character recognition for computer use.
* Mail sorter with optical character recognition (OCR) — Developed by Toshiba between 1966 and 1967.[Nanette Gottlieb]
''Word-Processing Technology in Japan: Kanji and the Keyboard''
Routledge In 1979, Sharp Corporation, Sharp's Shoin WD3000 had touch tablet input with a Stylus (computing), touch pen.
Telecommunication
 * Caller ID — In May 1976, Kazuo Hashimoto first built a prototype of a caller ID display device that could receive caller ID information. His work on caller ID devices and early prototypes was received in the Smithsonian Institution and National Museum of American History in 2000.
* Videophone, Digital videophone — The first practical videophone for home use was Mitsubishi Electric, Mitsubishi's Luma 1000 in 1986. It could send digital images over a phone line. By 1988,
* Caller ID — In May 1976, Kazuo Hashimoto first built a prototype of a caller ID display device that could receive caller ID information. His work on caller ID devices and early prototypes was received in the Smithsonian Institution and National Museum of American History in 2000.
* Videophone, Digital videophone — The first practical videophone for home use was Mitsubishi Electric, Mitsubishi's Luma 1000 in 1986. It could send digital images over a phone line. By 1988, Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
and Nippon Telegraph and Telephone, NTT had developed their own similar digital videophone for home use.
* Fiber-optic communication — Proposed by Jun-ichi Nishizawa in 1963.
Mobile phones
* Mobile phone, Commercial mobile phone — The first commercial mobile phone was the Panasonic TZ801, released in 1979. It used Nippon Telegraph and Telephone, NTT's 1G mobile network and was initially only available in Tokyo.cell phone
A mobile phone or cell phone is a portable telephone that allows users to make and receive calls over a radio frequency link while moving within a designated telephone service area, unlike fixed-location phones ( landline phones). This radio ...
capability. Kyocera VP-210 was the first commercial camera phone.
** List of 3D-enabled mobile phones, Steroscopic 3D mobile phone — In the early 2000s, Sharp Corporation, Sharp released parallax barrier flat-panels.Hitachi
() is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate founded in 1910 and headquartered in Chiyoda, Tokyo. The company is active in various industries, including digital systems, power and renewable ener ...
released the first autostereoscopic 3D phone under KDDI, the Hitachi Wooo Ketai H001.
* Foldable smartphone — The earliest commercial foldable smartphone was Kyocera's Kyocera Echo, Echo (2011).
* Front-facing camera, Front-facing camera phone — The first front-facing camera phone was the Kyocera Visual Phone VP-210, released in May 1999.[Kyocera visual phone VP-210, Japan, 1999](_blank)
Science & Society Picture Library, retrieved August 9, 2013.
*Picture messaging (MMS) — Picture messaging was invented in Japan. The J-SH04, released by Sharp Corporation and J-Phone in 2000, could instantly transmit pictures via cell phone telecommunication.
*Ringtone — In September 1996, KDDI, IDO sold Digital Minimo D319 by Denso. It was the first mobile phone where a user could input an original melody, rather than having to use preloaded melodies. These phones proved to be popular in Japan.
** Polyphonic ringtone — Polyphonic ringtone technology dates back to 1999, when the Yamaha Corporation, Yamaha MA-1 sound chip was introduced, including four 2-op FM synthesis channels.
*Smartphone — NTT's i-mode (1999) was a mobile internet platform giving phones access to various web services, such as online shopping, mobile payments, near-field communication, NFC (mobile wallets), 1seg mobile TV, ringtones, Mobile game, games and Mobile comic, comics.
Wireless
 * Meteor burst communications — The first observation of interaction between meteors and radio propagation was reported by Hantaro Nagaoka in 1929.
* Near-field communication (NFC) — In March 2002,
* Meteor burst communications — The first observation of interaction between meteors and radio propagation was reported by Hantaro Nagaoka in 1929.
* Near-field communication (NFC) — In March 2002, Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
and Philips established a technology specification for NFC and created a technical outline.Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
, with the collaboration of Hidetsugu Yagi, also of Tohoku Imperial University. Yagi published the first English-language reference on the antenna in a 1928 survey article on short wave research in Japan and it came to be associated with his name. However, Yagi always acknowledged Uda's principal contribution to the design, and the proper name for the antenna is, as above, the Yagi-Uda antenna (or array).
Transportation
 *Shinkansen, Bullet train — The world's first high volume capable (initially 12 car maximum) "High-speed rail, high-speed train" was Japan's Tōkaidō Shinkansen, which officially opened in October 1964, with construction commencing in April 1959.
*Shinkansen, Bullet train — The world's first high volume capable (initially 12 car maximum) "High-speed rail, high-speed train" was Japan's Tōkaidō Shinkansen, which officially opened in October 1964, with construction commencing in April 1959.[Shinkansen Chronology](_blank)
, byun byun Shinkansen. The 0 Series Shinkansen, built by Kawasaki Heavy Industries, achieved maximum passenger service speeds of 210 km/h (130 mph) on the Tokyo–Nagoya–Kyoto–Osaka
is a Cities designated by government ordinance of Japan, designated city in the Kansai region of Honshu in Japan. It is the capital of and most populous city in Osaka Prefecture, and the List of cities in Japan, third-most populous city in J ...
route, with earlier test runs hitting top speeds in 1963 at 256 km/h.
Automobiles
* 4 wheel steering, 4-wheel steering (4WS) — Mazda were pioneers in applying four-wheel steering to automobiles, showing it on their 1984 Mazda MX-02 concept car, where the rear wheels counter-steered at low speeds.[The Nissan Altra EV - Nissan Launching Electrick Minivan](_blank)
/ref>
**Plug-in electric vehicle (PEV) — The first Battery electric vehicle, all-electric PEV was the Mitsubishi i-MiEV, launched in June 2009.["Geneva 2010: Mitsubishi ASX (Outlander Sport) Debuts in Geneva"](_blank)
autoguide.com
* Common rail Diesel engine, diesel truck — In 1995, the first mass production vehicle with common rail was the Hino Ranger#3rd Generation .281989-2002.29, Hino Ranger truck, using the ECD-U2 common rail system developed by Denso.
* Diesel engine, Diesel boxer engine — In 2008, the List of Subaru engines#Subaru EE engine (diesel), Subaru EE engine became the world's first passenger car diesel boxer engine. This engine is a turbocharged Boxer four engine, boxer-four with common rail fuel injection.[Voelcker, John]
"Decades Of Promises: 'Dude, Where's My Hydrogen Fuel-Cell Car?'"
Yahoo.com, March 31, 2015 The Mirai has a range of 312 miles (502 km) and takes about five minutes to refuel. The initial sale price was roughly 7 million yen ($69,000).
* Hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) — The first commercial hybrid vehicle was the Toyota Prius launched in 1997.["Minicars: Cheap and Cheerful"](_blank)
, Peter Nunn, Japan Automobile Manufacturers Association, JAMA, January–February 2005[, ALTs in Sendai]
** Automatic transmission Kei car, mini car — Honda N360, Honda N360 AT (1968).[Steam: Its Generation and Uses. Babcock & Wilcox.]
* Self-driving car — The first self-driving car that did not rely upon rails or wires under the road is designed by the Tsukuba Mechanical Engineering Laboratory in 1977. The car was equipped with two cameras that used analog computer technology for signal processing.
** Automatic parking — Toyota's Intelligent Parking Assist System (IPAS) is the first production automatic parking system developed in 1999, initially for the Hybrid vehicle, hybrid Prius models and Lexus models. It assists drivers in parking a Automobile, vehicle.
* Semi-monocoque car — The Honda NSX (1990) was the first production car to feature an aluminium alloy, all-aluminium Semimonocoque, semi-monocoque.
Automotive electronics
 *Adaptive cruise control (ACC) — In 1992, Mitsubishi Motors was the first to offer a lidar-based distance detection system on the Japanese market Mitsubishi Debonair#Third generation, Debonair.
*Adaptive cruise control (ACC) — In 1992, Mitsubishi Motors was the first to offer a lidar-based distance detection system on the Japanese market Mitsubishi Debonair#Third generation, Debonair.integrated circuit
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
s and microcontrollers for controlling engines. In 1971, the Toyota Crown introduced Electronic control unit, electronically controlled anti-skid brakes.microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor (computing), processor for which the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit (IC), or a small number of ICs. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, a ...
was a 12-bit central processing unit
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor, or just processor, is the primary Processor (computing), processor in a given computer. Its electronic circuitry executes Instruction (computing), instructions ...
manufactured by Toshiba, the Toshiba TLCS-12, TLCS-12, which began development in 1971 and was completed in 1973. The system began production in 1974, and went into mass production in 1975.microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor (computing), processor for which the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit (IC), or a small number of ICs. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, a ...
-controlled ECU for diesel engines.[
]
** Continuously variable transmission, Toroidal continuously variable transmission (toroidal CVT) – Introduced in 1999 with Toyota's Extroid CVT for the Nissan Cedric, Nissan Cedric (Y34) and Nissan Gloria.
*Electronic stability control (ESC) – In 1983, a four-wheel electronic "Anti-lock braking system, Anti-Skid Control" system was introduced on the Toyota Crown. Toyota introduced their first traction control system (TCS) in 1987 and Vehicle Stability Control (VCS) in 1995.
Motorcycles
 *Air bag vest — Honda introduced the first motorcycle airbag system in 2005.
*Motorcycle frame, Double cradle frame — The Honda CB750, released in 1969, was the first mass-production motorcycle with a double cradle motorcycle frame.
*Air bag vest — Honda introduced the first motorcycle airbag system in 2005.
*Motorcycle frame, Double cradle frame — The Honda CB750, released in 1969, was the first mass-production motorcycle with a double cradle motorcycle frame.
Navigation
 * Automotive navigation system — In 1973, Ministry of International Trade and Industry, MITI and Fuji Heavy Industries, Fuji sponsored CATC (Comprehensive Automobile Traffic Control).
* Automotive navigation system — In 1973, Ministry of International Trade and Industry, MITI and Fuji Heavy Industries, Fuji sponsored CATC (Comprehensive Automobile Traffic Control).[''Cartographies of Travel and Navigation'', James R. Akerman]
p.279
/ref> In 1980, the Toyota Crown had Electronic Auto Compass.32-bit
In computer architecture, 32-bit computing refers to computer systems with a processor, memory, and other major system components that operate on data in a maximum of 32- bit units. Compared to smaller bit widths, 32-bit computers can perform la ...
CPU and Nissan image processor. Its map view became the standard for satnav devices.[R Sakaguchi, S Takasu, T Akiyama. (2000). "Study concerning the colors of tactile blocks for the visually handicapped – Visibility for the visually handicapped and scenic congruence for those with ordinary sight and vision.". SEPT.] The paving was first introduced in a street in Okayama, Okayama city, Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
, in 1967. Its use gradually spread in Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
and then around the world.
* Wireless navigation system — In 1961, Hidetsugu Yagi designed the first wireless navigation system for military use.
See also
*History of science and technology in Japan
*History of typography in East Asia
*List of automotive superlatives
*List of Chinese inventions
*List of Chinese discoveries
*List of Korean inventions and discoveries
*List of Taiwanese inventions and discoveries
*Science and technology in Japan
*Ten Japanese Great Inventors
References
Bibliography
*
*
*
*
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:Japanese Inventions
Japan history-related lists, Inventions
Japanese inventions,
Lists of inventions or discoveries

 * Kamishibai — Originates from 8th century
* Kamishibai — Originates from 8th century  * Blockbuster format —
* Blockbuster format —  *
*  *
*  *
*  * Air raid — Early in
* Air raid — Early in  *
*  * Canned coffee — Canned coffee was invented in 1965 by Miura Yoshitake, a coffee shop owner in Hamada, Shimane Prefecture, Japan.
* Cooking comic —
* Canned coffee — Canned coffee was invented in 1965 by Miura Yoshitake, a coffee shop owner in Hamada, Shimane Prefecture, Japan.
* Cooking comic —  * Go (modern rules) — Though the game originated in China, free opening of the game as it is played globally began in the 16th century Japan.
*
* Go (modern rules) — Though the game originated in China, free opening of the game as it is played globally began in the 16th century Japan.
*  * 8-bit handheld console —
* 8-bit handheld console —  * Analog stick, Analog thumbstick — Introduced by Dempa's XE-1 AP controller (1989) for the Sega Mega Drive console and Japanese computers.
** Nintendo 64 controller, Digital-analog thumbstick — Introduced with the Nintendo 64 controller, debuted in 1995 and released in 1996. Its thumbstick was a digital-analog hybrid.
* Analog stick, Analog thumbstick — Introduced by Dempa's XE-1 AP controller (1989) for the Sega Mega Drive console and Japanese computers.
** Nintendo 64 controller, Digital-analog thumbstick — Introduced with the Nintendo 64 controller, debuted in 1995 and released in 1996. Its thumbstick was a digital-analog hybrid.
 * D-pad — In 1982,
* D-pad — In 1982,  *
*  * Downburst — Downbursts, strong ground-level wind systems that emanate from a point above and blow radially, were discovered by Ted Fujita.
* Fujita scale — The first scale designed to measure tornado intensity, the Fujita scale, was first introduced by Ted Fujita (in collaboration with Allen Pearson) in 1971. The scale was widely adopted throughout the world until the development of the Enhanced Fujita scale.Tornado Damage Scales: Fujita Scale and Enhanced Fujita Scale
* Downburst — Downbursts, strong ground-level wind systems that emanate from a point above and blow radially, were discovered by Ted Fujita.
* Fujita scale — The first scale designed to measure tornado intensity, the Fujita scale, was first introduced by Ted Fujita (in collaboration with Allen Pearson) in 1971. The scale was widely adopted throughout the world until the development of the Enhanced Fujita scale.Tornado Damage Scales: Fujita Scale and Enhanced Fujita Scale * Digital microscope — Japanese company Hirox created the first ever digital microscope. A variation of a traditional microscope using optics and a digital camera to output an image to a monitor.
* Ephedrine, Ephedrine synthesis — Ephedrine in its natural form, known as Ephedra (plant), ''má huáng'' (麻黄) in traditional Chinese medicine, had been documented in China since the Han dynasty. However, it was not until 1885 that the chemical synthesis of ephedrine was first accomplished by Japanese organic chemist Nagai Nagayoshi.
* Epinephrine, Epinephrine (Adrenaline) — Japanese chemist Takamine Jōkichi, Jōkichi Takamine and his assistant Keizo Uenaka first discovered epinephrine in 1900. In 1901 Takamine successfully isolated and purified the hormone from the adrenal glands of sheep and oxen.
* Esophagogastroduodenoscopy, Esophagogastroduodenoscope — Mutsuo Sugiura was a Japanese engineer famous for being the first to develop a Gastro-camera (a present-day Esophagogastroduodenoscope). His story was illustrated in the NHK TV documentary feature, "Project X: Challengers: The Development of a Gastro-camera Wholly Made in Japan". Sugiura graduated from Tokyo Polytechnic University in 1938 and then joined Olympus Corporation. While working at this company, he first developed an esophagogastroduodenoscope in 1950.
* Frontier molecular orbital theory — Kenichi Fukui developed and published a paper on Frontier molecular orbital theory in 1952.
* General anesthesia — Hanaoka Seishū was the first surgeon in the world who used the general anaesthesia in surgery, in 1804, and who dared to operate on cancers of the breast and oropharynx, to remove necrotic bone, and to perform amputations of the extremities in Japan.
* High resolution ultrasound machine — Developed by Toshiba between 1971 and 1975.
* Immunoglobulin E, Immunoglobulin E (IgE) — Immunoglobulin E is a type of antibody only found in mammals. IgE was simultaneously discovered in 1966-7 by two independent groups: Kimishige Ishizaka's team at the Children's Asthma Research Institute and Hospital in Denver, Colorado, and by Gunnar Johansson (biochemist), Gunnar Johansson and Hans Bennich in Uppsala, Sweden. Their joint paper was published in April 1969.
* Induced pluripotent stem cell — The induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSCs) is a kind of pluripotent stem cell which can be created using a mature cell. iPSCs technology was developed by Shinya Yamanaka and his lab workers in 2006.
* Digital microscope — Japanese company Hirox created the first ever digital microscope. A variation of a traditional microscope using optics and a digital camera to output an image to a monitor.
* Ephedrine, Ephedrine synthesis — Ephedrine in its natural form, known as Ephedra (plant), ''má huáng'' (麻黄) in traditional Chinese medicine, had been documented in China since the Han dynasty. However, it was not until 1885 that the chemical synthesis of ephedrine was first accomplished by Japanese organic chemist Nagai Nagayoshi.
* Epinephrine, Epinephrine (Adrenaline) — Japanese chemist Takamine Jōkichi, Jōkichi Takamine and his assistant Keizo Uenaka first discovered epinephrine in 1900. In 1901 Takamine successfully isolated and purified the hormone from the adrenal glands of sheep and oxen.
* Esophagogastroduodenoscopy, Esophagogastroduodenoscope — Mutsuo Sugiura was a Japanese engineer famous for being the first to develop a Gastro-camera (a present-day Esophagogastroduodenoscope). His story was illustrated in the NHK TV documentary feature, "Project X: Challengers: The Development of a Gastro-camera Wholly Made in Japan". Sugiura graduated from Tokyo Polytechnic University in 1938 and then joined Olympus Corporation. While working at this company, he first developed an esophagogastroduodenoscope in 1950.
* Frontier molecular orbital theory — Kenichi Fukui developed and published a paper on Frontier molecular orbital theory in 1952.
* General anesthesia — Hanaoka Seishū was the first surgeon in the world who used the general anaesthesia in surgery, in 1804, and who dared to operate on cancers of the breast and oropharynx, to remove necrotic bone, and to perform amputations of the extremities in Japan.
* High resolution ultrasound machine — Developed by Toshiba between 1971 and 1975.
* Immunoglobulin E, Immunoglobulin E (IgE) — Immunoglobulin E is a type of antibody only found in mammals. IgE was simultaneously discovered in 1966-7 by two independent groups: Kimishige Ishizaka's team at the Children's Asthma Research Institute and Hospital in Denver, Colorado, and by Gunnar Johansson (biochemist), Gunnar Johansson and Hans Bennich in Uppsala, Sweden. Their joint paper was published in April 1969.
* Induced pluripotent stem cell — The induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSCs) is a kind of pluripotent stem cell which can be created using a mature cell. iPSCs technology was developed by Shinya Yamanaka and his lab workers in 2006.
 * Bernoulli number — Studied by Seki Kōwa and published after his death, in 1712. Jacob Bernoulli independently developed the concept in the same period, though his work was published a year later.Helaine Selin, Selin, Helaine. (1997), ''An Introduction to the History of Mathematics''. Saunders College Publishing. p. 891, Poole, David. (2005), ''Linear algebra: a modern introductio''. p. 279, .Styan, George P. H.; Trenkler, Götz. (2007)
* Bernoulli number — Studied by Seki Kōwa and published after his death, in 1712. Jacob Bernoulli independently developed the concept in the same period, though his work was published a year later.Helaine Selin, Selin, Helaine. (1997), ''An Introduction to the History of Mathematics''. Saunders College Publishing. p. 891, Poole, David. (2005), ''Linear algebra: a modern introductio''. p. 279, .Styan, George P. H.; Trenkler, Götz. (2007) * Blue laser — In 1992, Japanese inventor Shuji Nakamura invented the first efficient blue LED. He won a 2014 Nobel Prize in Physics, Nobel Prize with Isamu Akasaki and Hiroshi Amano.NobelPrize.org Press Release (7 October 2014): The Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences has decided to award the Nobel Prize in Physics for 2014 to Isamu Akasaki (Meijo University, Nagoya, Japan and Nagoya University, Japan), Hiroshi Amano (Nagoya University, Japan) and Shuji Nakamura (University of California, Santa Barbara, CA, USA) "for the invention of efficient blue light-emitting diodes which has enabled bright and energy-saving white light sources"
* Blue laser — In 1992, Japanese inventor Shuji Nakamura invented the first efficient blue LED. He won a 2014 Nobel Prize in Physics, Nobel Prize with Isamu Akasaki and Hiroshi Amano.NobelPrize.org Press Release (7 October 2014): The Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences has decided to award the Nobel Prize in Physics for 2014 to Isamu Akasaki (Meijo University, Nagoya, Japan and Nagoya University, Japan), Hiroshi Amano (Nagoya University, Japan) and Shuji Nakamura (University of California, Santa Barbara, CA, USA) "for the invention of efficient blue light-emitting diodes which has enabled bright and energy-saving white light sources"  * Avalanche photodiode — Invented by Jun-ichi Nishizawa in 1952.Jun-ichi Nishizawa: Engineer, Sophia University Special Professor
* Avalanche photodiode — Invented by Jun-ichi Nishizawa in 1952.Jun-ichi Nishizawa: Engineer, Sophia University Special Professor * Advanced boiling water reactor (ABWR) — Developed by Toshiba,
* Advanced boiling water reactor (ABWR) — Developed by Toshiba,  *3.5 mm headphone jack — Introduced with the
*3.5 mm headphone jack — Introduced with the  * Lithium-ion battery — Akira Yoshino invented the modern li-ion battery in 1985. In 1991,
* Lithium-ion battery — Akira Yoshino invented the modern li-ion battery in 1985. In 1991,  * Calculator, All-electric compact calculator — In 1957, Casio's Model 14-A was the first all-electric compact calculator, based on relay technology.
** Transistor, All-transistor desktop calculator — In 1964, Sharp Corporation's CS-10A was the first Transistor diode model, all-transistor-diode electronic desktop calculator.
* Integrated circuit calculator — Between 1964 and 1966, Sharp Corporation developed the CS-31A, the first electronic calculator incorporating
* Calculator, All-electric compact calculator — In 1957, Casio's Model 14-A was the first all-electric compact calculator, based on relay technology.
** Transistor, All-transistor desktop calculator — In 1964, Sharp Corporation's CS-10A was the first Transistor diode model, all-transistor-diode electronic desktop calculator.
* Integrated circuit calculator — Between 1964 and 1966, Sharp Corporation developed the CS-31A, the first electronic calculator incorporating  * E-reader with electronic paper — The Sony Librie, released in 2004 and the precursor to the Sony Reader, was the first ereader to use electronic paper.
* Fifth generation computer — Ministry of International Trade and Industry, MITI's Fifth Generation Computer Systems (FGCS) project launched in 1982 researched massively parallel processing, logic programming, artificial intelligence, AI, natural language processing and interactive processing.
** Artificial intelligence, AI home computer — The earliest home computer specialized for AI natural language processing was the Sega AI Computer, released in 1986. Its AI technology was based on Prolog, like the fifth generation project.
** Massively parallel — FGCS initiative was launched in 1982 to develop computers based on massively parallel computing. Supercomputing in Japan, LINKS-1 (1982) was a massively parallel computer with 514
* E-reader with electronic paper — The Sony Librie, released in 2004 and the precursor to the Sony Reader, was the first ereader to use electronic paper.
* Fifth generation computer — Ministry of International Trade and Industry, MITI's Fifth Generation Computer Systems (FGCS) project launched in 1982 researched massively parallel processing, logic programming, artificial intelligence, AI, natural language processing and interactive processing.
** Artificial intelligence, AI home computer — The earliest home computer specialized for AI natural language processing was the Sega AI Computer, released in 1986. Its AI technology was based on Prolog, like the fifth generation project.
** Massively parallel — FGCS initiative was launched in 1982 to develop computers based on massively parallel computing. Supercomputing in Japan, LINKS-1 (1982) was a massively parallel computer with 514  * Bladeless fan — The first bladeless fan was patented by Toshiba in 1981.
* Bread machine — The bread machine was developed and released in
* Bladeless fan — The first bladeless fan was patented by Toshiba in 1981.
* Bread machine — The bread machine was developed and released in  * 3.5 inch floppy disk — Pioneered by
* 3.5 inch floppy disk — Pioneered by  *Analog modeling synthesizer — The Roland D-50 from 1987 was the first virtual analog synthesizer.
** Linear arithmetic synthesis (LA synthesis) — Invented by Roland Corporation, Roland for the Roland D-50, D-50 synthesizer (1987).
** Supersaw — A waveform created by Roland Corporation, Roland for its Roland JP-8000, JP-8000 (1996) analog modeling synthesizer.
* Bass synthesizer–Music sequencer, sequencer — The first was Firstman SQ-01, ("''Keyboard Report, Oct. '81''", according to the ) released in 1980 by Japanese company Hillwood/Firstman.Mark Jenkins (2009)
*Analog modeling synthesizer — The Roland D-50 from 1987 was the first virtual analog synthesizer.
** Linear arithmetic synthesis (LA synthesis) — Invented by Roland Corporation, Roland for the Roland D-50, D-50 synthesizer (1987).
** Supersaw — A waveform created by Roland Corporation, Roland for its Roland JP-8000, JP-8000 (1996) analog modeling synthesizer.
* Bass synthesizer–Music sequencer, sequencer — The first was Firstman SQ-01, ("''Keyboard Report, Oct. '81''", according to the ) released in 1980 by Japanese company Hillwood/Firstman.Mark Jenkins (2009) * Android (robot), Android — Waseda University initiated the WABOT project in 1967, and in 1972 completed the WABOT-1, the world's first full-scale humanoid intelligent robot. Its limb control system allowed it to walk with the lower limbs, and to grip and transport objects with hands, using tactile sensors. Its vision system allowed it to measure distances and directions to objects using external receptors, artificial eyes and ears. And its conversation system allowed it to communicate with a person in Japanese, with an artificial mouth. This made it the first Android (robot), android.
* Actroid — DER 01 was developed by a Japanese research group, The Intelligent Robotics Lab, directed by Hiroshi Ishiguro at Osaka University, and Kokoro Co., Ltd. The Actroid is a humanoid robot with strong visual human-likeness developed by Osaka University and manufactured by Kokoro Company Ltd. (the animatronics division of Sanrio). It was first unveiled at the 2003 International Robot Exposition in Tokyo,
* Android (robot), Android — Waseda University initiated the WABOT project in 1967, and in 1972 completed the WABOT-1, the world's first full-scale humanoid intelligent robot. Its limb control system allowed it to walk with the lower limbs, and to grip and transport objects with hands, using tactile sensors. Its vision system allowed it to measure distances and directions to objects using external receptors, artificial eyes and ears. And its conversation system allowed it to communicate with a person in Japanese, with an artificial mouth. This made it the first Android (robot), android.
* Actroid — DER 01 was developed by a Japanese research group, The Intelligent Robotics Lab, directed by Hiroshi Ishiguro at Osaka University, and Kokoro Co., Ltd. The Actroid is a humanoid robot with strong visual human-likeness developed by Osaka University and manufactured by Kokoro Company Ltd. (the animatronics division of Sanrio). It was first unveiled at the 2003 International Robot Exposition in Tokyo,  * Active shutter 3D system — Matsushita Electric developed a 3D television that employed active-shutter Stereoscopy, stereoscopic technology in the late 1970s, unveiled in 1981, while adapting the technology for the first stereoscopic video game, ''SubRoc-3D'' (1982).
** 3D HDTV — In the 1998 Nagano Olympics, some sporting events were filmed in 3D high definition.
** Autostereoscopy — A prototype single-viewer display, the Floating Image System, was presented by Sega AM3 in 1997. In the early 2000s, Sharp Corporation, Sharp released electronic parallax barrier flat-panels, selling laptops with the first 3D LCD screens.
* Kenjiro Takayanagi, All-electronic television (TV) — In 1926, Kenjiro Takayanagi invented the world's first all-electronic television, preceding Philo T. Farnsworth by several months. By 1927, Takayanagi improved the resolution to 100 lines, which was not surpassed until 1931. By 1928, he was the first to transmit human faces in halftones. His work had an influence on the later work of Vladimir K. Zworykin.
** Transistor TV — In 1952,
* Active shutter 3D system — Matsushita Electric developed a 3D television that employed active-shutter Stereoscopy, stereoscopic technology in the late 1970s, unveiled in 1981, while adapting the technology for the first stereoscopic video game, ''SubRoc-3D'' (1982).
** 3D HDTV — In the 1998 Nagano Olympics, some sporting events were filmed in 3D high definition.
** Autostereoscopy — A prototype single-viewer display, the Floating Image System, was presented by Sega AM3 in 1997. In the early 2000s, Sharp Corporation, Sharp released electronic parallax barrier flat-panels, selling laptops with the first 3D LCD screens.
* Kenjiro Takayanagi, All-electronic television (TV) — In 1926, Kenjiro Takayanagi invented the world's first all-electronic television, preceding Philo T. Farnsworth by several months. By 1927, Takayanagi improved the resolution to 100 lines, which was not surpassed until 1931. By 1928, he was the first to transmit human faces in halftones. His work had an influence on the later work of Vladimir K. Zworykin.
** Transistor TV — In 1952,  * OLED display — Manufacturing of OLED displays began in 1997 by Pioneer Corporation, followed by TDK in 2001.
** OLED TV — In 2007, the Sony XEL-1 was the world's first OLED TV.Sony XEL-1:The world's first OLED TV
* OLED display — Manufacturing of OLED displays began in 1997 by Pioneer Corporation, followed by TDK in 2001.
** OLED TV — In 2007, the Sony XEL-1 was the world's first OLED TV.Sony XEL-1:The world's first OLED TV * Myriad year clock — The Myriad year clock (万年自鳴鐘 Mannen Jimeishou, lit. Ten-Thousand Year Self-ringing Bell), was a universal clock designed by the Japanese inventor Hisashige Tanaka in 1851. It belongs to the category of Japanese clocks called Wadokei.
* Quartz clock, Quartz Watch, wristwatch — The world's first quartz Watch, wristwatch was revealed in 1967: the prototype of the Astron (wristwatch), Astron revealed by Seiko in Japan, where it was in development since 1958. It was eventually released to the public in 1969.
** Automatic quartz — The first watch to combine self-winding with a crystal oscillator for timekeeping was unveiled by Seiko in 1986.
* Spring Drive — A watch movement which was first conceived by Yoshikazu Akahane working for Seiko in 1977 and was patented in 1982. It features a true continuously sweeping second hand, rather than the traditional beats per time unit, as seen with traditional mechanical and most quartz watches.
* Smartwatch — In the 1980s, Seiko began to develop computers in the form of watches, starting with the Data 2000 watch, released in 1984. It was followed by Seiko Epson's RC-1000 Wrist Terminal (1984), able to interface with a computer.
* Television watch — The world's first television watch, the TV-Watch, was developed by Seiko in 1982.
* Myriad year clock — The Myriad year clock (万年自鳴鐘 Mannen Jimeishou, lit. Ten-Thousand Year Self-ringing Bell), was a universal clock designed by the Japanese inventor Hisashige Tanaka in 1851. It belongs to the category of Japanese clocks called Wadokei.
* Quartz clock, Quartz Watch, wristwatch — The world's first quartz Watch, wristwatch was revealed in 1967: the prototype of the Astron (wristwatch), Astron revealed by Seiko in Japan, where it was in development since 1958. It was eventually released to the public in 1969.
** Automatic quartz — The first watch to combine self-winding with a crystal oscillator for timekeeping was unveiled by Seiko in 1986.
* Spring Drive — A watch movement which was first conceived by Yoshikazu Akahane working for Seiko in 1977 and was patented in 1982. It features a true continuously sweeping second hand, rather than the traditional beats per time unit, as seen with traditional mechanical and most quartz watches.
* Smartwatch — In the 1980s, Seiko began to develop computers in the form of watches, starting with the Data 2000 watch, released in 1984. It was followed by Seiko Epson's RC-1000 Wrist Terminal (1984), able to interface with a computer.
* Television watch — The world's first television watch, the TV-Watch, was developed by Seiko in 1982.

 * Digital video disc — In 1972, :ja:TOSBAC, TOSBAC was using digital Videodisc, video disks to display color digital images. In 1995, DVD co-developed in 1995 by
* Digital video disc — In 1972, :ja:TOSBAC, TOSBAC was using digital Videodisc, video disks to display color digital images. In 1995, DVD co-developed in 1995 by  * Correction tape — Correction tape was invented in 1989 by the Japanese product manufacturer Seed. It is an alternative to correction fluid.
* Gel pen — The gel pen was invented in 1984 by the Sakura Color Products Corporation of Osaka.
* Japanese typewriter — The first typewriter to be based on the Japanese writing system was invented by Kyota Sugimoto in 1929.
* Japanese writing Graphics tablet, touch tablet — In 1971,
* Correction tape — Correction tape was invented in 1989 by the Japanese product manufacturer Seed. It is an alternative to correction fluid.
* Gel pen — The gel pen was invented in 1984 by the Sakura Color Products Corporation of Osaka.
* Japanese typewriter — The first typewriter to be based on the Japanese writing system was invented by Kyota Sugimoto in 1929.
* Japanese writing Graphics tablet, touch tablet — In 1971,  * Caller ID — In May 1976, Kazuo Hashimoto first built a prototype of a caller ID display device that could receive caller ID information. His work on caller ID devices and early prototypes was received in the Smithsonian Institution and National Museum of American History in 2000.
* Videophone, Digital videophone — The first practical videophone for home use was Mitsubishi Electric, Mitsubishi's Luma 1000 in 1986. It could send digital images over a phone line. By 1988,
* Caller ID — In May 1976, Kazuo Hashimoto first built a prototype of a caller ID display device that could receive caller ID information. His work on caller ID devices and early prototypes was received in the Smithsonian Institution and National Museum of American History in 2000.
* Videophone, Digital videophone — The first practical videophone for home use was Mitsubishi Electric, Mitsubishi's Luma 1000 in 1986. It could send digital images over a phone line. By 1988,  *Shinkansen, Bullet train — The world's first high volume capable (initially 12 car maximum) "High-speed rail, high-speed train" was Japan's Tōkaidō Shinkansen, which officially opened in October 1964, with construction commencing in April 1959.Shinkansen Chronology
*Shinkansen, Bullet train — The world's first high volume capable (initially 12 car maximum) "High-speed rail, high-speed train" was Japan's Tōkaidō Shinkansen, which officially opened in October 1964, with construction commencing in April 1959.Shinkansen Chronology *Adaptive cruise control (ACC) — In 1992, Mitsubishi Motors was the first to offer a lidar-based distance detection system on the Japanese market Mitsubishi Debonair#Third generation, Debonair.
** Lidar, Laser ACC — In 1995, Mitsubishi Diamante introduced laser "Preview Distance Control". This system controlled speed through throttle control and downshifting.
** Camera Adaptive cruise control, ACC — In 1999, Subaru introduced world's first camera-based ACC on the Subaru Legacy Lancaster.
* Advanced driver-assistance system (ADAS) — ADAS were first being used in the 1970s with the adoption of the anti-lock braking system (ABS). Electronic ABS was introduced in 1971 by Toyota and Nissan.
** Active night vision, Active automotive night vision — In 2002, Toyota's Night View was the first worldwide series production active automotive night vision system, introduced on the Toyota Landcruiser Cygnus or Lexus LX, Lexus LX470.
** Automotive head-up display (auto-HUD) — In 1988, Nissan was the first manufacturer to offer a HUD with the 1988 Nissan Silvia S13.
** Electrochromic rear-view mirror — Invented by Nissan engineers Harutoshi Miyagi, Masazumi Ishikawa and Yasuyuki Murofushi between 1985 and 1986.
** Lane departure warning system (LDWS) — In 2001, Nissan, Nissan Motors began offering a lane-keeping support system on the Nissan Cima#Fourth generation (F50; 2001), Cima 450XV Limited (F500).
** Parking sensor — Toyota introduced ultrasonic Back Sonar on the 1982 Toyota Corona, offering it until 1988.
** Voice command — In 1982, the Nissan Silvia (S110), Nissan Silvia S110 introduced speech recognition, voice recognition for operating the power windows.
** Voice warning system — In 1980, the Toyota Mark II was the first car with a voice warning system.
** Windshield wiper sensor — In 1983, the Nissan Cedric, Nissan Cedric Y30 and Nissan Gloria, Gloria Y30 introduced the world's first windshield wipers that adjust to changes in rain and snow levels.
* Automotive microcomputer — The earliest microcomputer designed for an automobile was developed by Toshiba for Ford's Electronic Engine Control (EEC) in the early 1970s.
** Automotive engine microcomputer — Toshiba developed a close relationship with Ford for the supply of rectifier diodes for automobile AC alternators. In March 1971, Ford unexpectedly sent a set bulky specifications asking Toshiba to join a project to make an Electronic Engine Control in response to US Clean Air Act (sometimes known as the Muskie Act). The system began production in 1974.
** Fiber-optic communication — Introduced in 1982 with the Toyota Century. It was the first application of fiber-optic communication in an automobile, with optical fibers used to transmit fast signals between microcomputer components.
** Carputer — By 1987, Toyota's Electro Multi Vision for the Toyota Crown was an integrated car computer system with a wide range of features. Clarion (company), Clarion is credited with introducing the first carputer in December 1998.
* Car audio features
** Vehicle audio, Component car stereo — In 1975, Pioneer Corporation released the first component car stereo.
** Remote control, Audio control on steering wheel — In 1984, the Nissan 300ZX introduced car radio controls on the steering wheel.
** CD player — In 1984, Pioneer introduced the CDX-1, the first car CD player.
** MP3 player — In 2001, the Mazda Protegé, Mazda Protegé MP3 was the first vehicle to play MP3 files from the CD player.
** 5.1 surround sound — In 2003, Honda's Acura TL was the first car with 5.1 surround sound.
** Active noise cancellation (ANC) — In 2004, Honda's Acura RL was the first car with active noise cancellation.
* Collision avoidance system (CAS) — In 2000, Toyota's laser adaptive cruise control (ACC) system added brake control, which applies brakes. In February 2003, Toyota launched the Pre-Collision System (PCS) with radar technology in the Toyota Harrier, Harrier.
** Driver monitoring system (DMS) — It was first introduced by Toyota in 2006 for its Lexus models. It was first offered in Japan on the Lexus GS (S190)#GWS191 .282007.29, GS 450h. The system's functions co-operate with the pre-collision system (PCS).
** Eye tracking, Driver eyelid Driver monitoring system, monitoring system — Introduced in 2008 on the Toyota Crown's Driver Monitoring System.
* Electro Multi Vision — Toyota's Electro Multi Vision system was an integrated computer system introduced for the Toyota Soarer in 1985 and then further developed for the Toyota Crown in 1987. Electro Multi Vision introduced new features including:
** Cathode-ray tube, CRT Electronic instrument cluster, digital display panel (1985)
** High resolution user interface with on-board diagnostics (1985)
** Television receiver (1985)
** Video tape recorder (1985)
** CD-ROM drive (1987)
** Hands free car phone (1987)
** Touchscreen interface (1987)
* Electronically adjustable damper, Electronically adjustable suspension dampers — In 1981, the Nissan Skyline (R30), Nissan Skyline Turbo GT-ES introduced the first Active suspension, electronically adjustable suspension shock absorbers.
** Electronically controlled suspension (ECS) — In 1983, the Toyota Soarer introduced the Toyota Electronic Modulated Suspension (TEMS), the first Electronic control unit, electronically controlled car suspension, using a shock absorber control actuator.
** Semi-active suspension (SAS) — The first production car was the Toyota Soarer with the semi-active Toyota Electronic Modulated Suspension, TEMS, from 1983. In 1985, Nissan introduced ultrasound "Super Sonic Suspension" optionally on the Nissan Cedric#Y30, Cedric, Gloria and Nissan Laurel#C32, Laurel.
** Active suspension, Active air suspension — Introduced in 1984 with the Mitsubishi Galant's CECS (Chassis Electronic Control Systems).
** Electronic Air Suspension, Electronically controlled air suspension (ECAS) — In 1986, the Toyota Soarer had the first electronically controlled full air suspension (spring constant, variable attenuation force) installed.
** Active suspension, Fully active suspension without anti-roll bars: Introduced in 1989 on the Toyota Celica, with the Toyota Active Control Suspension.
* Electronic control unit (ECU) — In the early 1970s, the Electronics industry in Japan, Japanese electronics industry began producing
*Adaptive cruise control (ACC) — In 1992, Mitsubishi Motors was the first to offer a lidar-based distance detection system on the Japanese market Mitsubishi Debonair#Third generation, Debonair.
** Lidar, Laser ACC — In 1995, Mitsubishi Diamante introduced laser "Preview Distance Control". This system controlled speed through throttle control and downshifting.
** Camera Adaptive cruise control, ACC — In 1999, Subaru introduced world's first camera-based ACC on the Subaru Legacy Lancaster.
* Advanced driver-assistance system (ADAS) — ADAS were first being used in the 1970s with the adoption of the anti-lock braking system (ABS). Electronic ABS was introduced in 1971 by Toyota and Nissan.
** Active night vision, Active automotive night vision — In 2002, Toyota's Night View was the first worldwide series production active automotive night vision system, introduced on the Toyota Landcruiser Cygnus or Lexus LX, Lexus LX470.
** Automotive head-up display (auto-HUD) — In 1988, Nissan was the first manufacturer to offer a HUD with the 1988 Nissan Silvia S13.
** Electrochromic rear-view mirror — Invented by Nissan engineers Harutoshi Miyagi, Masazumi Ishikawa and Yasuyuki Murofushi between 1985 and 1986.
** Lane departure warning system (LDWS) — In 2001, Nissan, Nissan Motors began offering a lane-keeping support system on the Nissan Cima#Fourth generation (F50; 2001), Cima 450XV Limited (F500).
** Parking sensor — Toyota introduced ultrasonic Back Sonar on the 1982 Toyota Corona, offering it until 1988.
** Voice command — In 1982, the Nissan Silvia (S110), Nissan Silvia S110 introduced speech recognition, voice recognition for operating the power windows.
** Voice warning system — In 1980, the Toyota Mark II was the first car with a voice warning system.
** Windshield wiper sensor — In 1983, the Nissan Cedric, Nissan Cedric Y30 and Nissan Gloria, Gloria Y30 introduced the world's first windshield wipers that adjust to changes in rain and snow levels.
* Automotive microcomputer — The earliest microcomputer designed for an automobile was developed by Toshiba for Ford's Electronic Engine Control (EEC) in the early 1970s.
** Automotive engine microcomputer — Toshiba developed a close relationship with Ford for the supply of rectifier diodes for automobile AC alternators. In March 1971, Ford unexpectedly sent a set bulky specifications asking Toshiba to join a project to make an Electronic Engine Control in response to US Clean Air Act (sometimes known as the Muskie Act). The system began production in 1974.
** Fiber-optic communication — Introduced in 1982 with the Toyota Century. It was the first application of fiber-optic communication in an automobile, with optical fibers used to transmit fast signals between microcomputer components.
** Carputer — By 1987, Toyota's Electro Multi Vision for the Toyota Crown was an integrated car computer system with a wide range of features. Clarion (company), Clarion is credited with introducing the first carputer in December 1998.
* Car audio features
** Vehicle audio, Component car stereo — In 1975, Pioneer Corporation released the first component car stereo.
** Remote control, Audio control on steering wheel — In 1984, the Nissan 300ZX introduced car radio controls on the steering wheel.
** CD player — In 1984, Pioneer introduced the CDX-1, the first car CD player.
** MP3 player — In 2001, the Mazda Protegé, Mazda Protegé MP3 was the first vehicle to play MP3 files from the CD player.
** 5.1 surround sound — In 2003, Honda's Acura TL was the first car with 5.1 surround sound.
** Active noise cancellation (ANC) — In 2004, Honda's Acura RL was the first car with active noise cancellation.
* Collision avoidance system (CAS) — In 2000, Toyota's laser adaptive cruise control (ACC) system added brake control, which applies brakes. In February 2003, Toyota launched the Pre-Collision System (PCS) with radar technology in the Toyota Harrier, Harrier.
** Driver monitoring system (DMS) — It was first introduced by Toyota in 2006 for its Lexus models. It was first offered in Japan on the Lexus GS (S190)#GWS191 .282007.29, GS 450h. The system's functions co-operate with the pre-collision system (PCS).
** Eye tracking, Driver eyelid Driver monitoring system, monitoring system — Introduced in 2008 on the Toyota Crown's Driver Monitoring System.
* Electro Multi Vision — Toyota's Electro Multi Vision system was an integrated computer system introduced for the Toyota Soarer in 1985 and then further developed for the Toyota Crown in 1987. Electro Multi Vision introduced new features including:
** Cathode-ray tube, CRT Electronic instrument cluster, digital display panel (1985)
** High resolution user interface with on-board diagnostics (1985)
** Television receiver (1985)
** Video tape recorder (1985)
** CD-ROM drive (1987)
** Hands free car phone (1987)
** Touchscreen interface (1987)
* Electronically adjustable damper, Electronically adjustable suspension dampers — In 1981, the Nissan Skyline (R30), Nissan Skyline Turbo GT-ES introduced the first Active suspension, electronically adjustable suspension shock absorbers.
** Electronically controlled suspension (ECS) — In 1983, the Toyota Soarer introduced the Toyota Electronic Modulated Suspension (TEMS), the first Electronic control unit, electronically controlled car suspension, using a shock absorber control actuator.
** Semi-active suspension (SAS) — The first production car was the Toyota Soarer with the semi-active Toyota Electronic Modulated Suspension, TEMS, from 1983. In 1985, Nissan introduced ultrasound "Super Sonic Suspension" optionally on the Nissan Cedric#Y30, Cedric, Gloria and Nissan Laurel#C32, Laurel.
** Active suspension, Active air suspension — Introduced in 1984 with the Mitsubishi Galant's CECS (Chassis Electronic Control Systems).
** Electronic Air Suspension, Electronically controlled air suspension (ECAS) — In 1986, the Toyota Soarer had the first electronically controlled full air suspension (spring constant, variable attenuation force) installed.
** Active suspension, Fully active suspension without anti-roll bars: Introduced in 1989 on the Toyota Celica, with the Toyota Active Control Suspension.
* Electronic control unit (ECU) — In the early 1970s, the Electronics industry in Japan, Japanese electronics industry began producing  *Air bag vest — Honda introduced the first motorcycle airbag system in 2005.
*Motorcycle frame, Double cradle frame — The Honda CB750, released in 1969, was the first mass-production motorcycle with a double cradle motorcycle frame.
**Muffler, Four mufflers — The Honda CB750 (1969) was the first mass-production motorcycle with four Muffler, mufflers.
**Straight-four SOHC — The Honda CB750 (1969) was the first mass-produced motorcycle with a Straight-four engine, parallel four-cylinder single overhead camshaft (SOHC) motorcycle engine.
** Superbike — The Honda CB750, released in 1969, was the original superbike.
*Disc brake, Front disc brake — The Honda CB750 (1969) was the first mass-production motorcycle with front disc brake.
**Motorcycle braking systems, Hydraulic disc brakes — Honda CB750 (1969) was the first production motorcycle with hydraulic disc brakes.
**Combined braking system (CBS) — The first CBS was introduced with the Honda RC series, Honda RCB1000 in 1976.
*Motorcycle dual-clutch transmission (DCT) — The 2009 Honda VFR1200F is the first motorcycle to use DCT.
*Motorcycle traction control system (TCS) — Introduced with the Honda ST1100 in 1992.
*Oval piston engine — A piston engine utilizing oval Cylinder (engine), cylinders, it was developed by Honda and introduced with the Honda NR500 in 1979.
**Multi-valve, 8-valve engine — Introduced with Honda's oval piston engine for the Honda NR500 in 1979.
* Universal Japanese Motorcycle (UJM) — The term was coined in the 1970s to describe a proliferation of similar Japanese Types of motorcycles#Standard, standard Motorcycle, motorcycles that became commonplace following Honda's 1969 introduction of its successful Honda CB750, CB750.
*Air bag vest — Honda introduced the first motorcycle airbag system in 2005.
*Motorcycle frame, Double cradle frame — The Honda CB750, released in 1969, was the first mass-production motorcycle with a double cradle motorcycle frame.
**Muffler, Four mufflers — The Honda CB750 (1969) was the first mass-production motorcycle with four Muffler, mufflers.
**Straight-four SOHC — The Honda CB750 (1969) was the first mass-produced motorcycle with a Straight-four engine, parallel four-cylinder single overhead camshaft (SOHC) motorcycle engine.
** Superbike — The Honda CB750, released in 1969, was the original superbike.
*Disc brake, Front disc brake — The Honda CB750 (1969) was the first mass-production motorcycle with front disc brake.
**Motorcycle braking systems, Hydraulic disc brakes — Honda CB750 (1969) was the first production motorcycle with hydraulic disc brakes.
**Combined braking system (CBS) — The first CBS was introduced with the Honda RC series, Honda RCB1000 in 1976.
*Motorcycle dual-clutch transmission (DCT) — The 2009 Honda VFR1200F is the first motorcycle to use DCT.
*Motorcycle traction control system (TCS) — Introduced with the Honda ST1100 in 1992.
*Oval piston engine — A piston engine utilizing oval Cylinder (engine), cylinders, it was developed by Honda and introduced with the Honda NR500 in 1979.
**Multi-valve, 8-valve engine — Introduced with Honda's oval piston engine for the Honda NR500 in 1979.
* Universal Japanese Motorcycle (UJM) — The term was coined in the 1970s to describe a proliferation of similar Japanese Types of motorcycles#Standard, standard Motorcycle, motorcycles that became commonplace following Honda's 1969 introduction of its successful Honda CB750, CB750.
 * Automotive navigation system — In 1973, Ministry of International Trade and Industry, MITI and Fuji Heavy Industries, Fuji sponsored CATC (Comprehensive Automobile Traffic Control).''Cartographies of Travel and Navigation'', James R. Akerman
* Automotive navigation system — In 1973, Ministry of International Trade and Industry, MITI and Fuji Heavy Industries, Fuji sponsored CATC (Comprehensive Automobile Traffic Control).''Cartographies of Travel and Navigation'', James R. Akerman