|
Simulated Reality
The simulation theory is the hypothesis that reality could be simulated—for example by quantum computer simulation—to a degree indistinguishable from "true" reality. It could contain conscious minds that may or may not know that they live inside a simulation. This is quite different from the current, technologically achievable concept of virtual reality, which is easily distinguished from the experience of actuality. Simulated reality, by contrast, would be hard or impossible to separate from "true" reality. There has been much debate over this topic, ranging from philosophical discourse to practical applications in computing. Arguments Simulation argument A version of the simulation hypothesis was first theorized as a part of a philosophical argument on the part of René Descartes, and later by Hans Moravec. The philosopher Nick Bostrom developed an expanded argument examining the probability of our reality being a simulation. His argument states that at least one of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypothesis
A hypothesis (plural hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. For a hypothesis to be a scientific hypothesis, the scientific method requires that one can testable, test it. Scientists generally base scientific hypotheses on previous observations that cannot satisfactorily be explained with the available scientific theories. Even though the words "hypothesis" and "theory" are often used interchangeably, a scientific hypothesis is not the same as a scientific theory. A working hypothesis is a provisionally accepted hypothesis proposed for further research in a process beginning with an educated guess or thought. A different meaning of the term ''hypothesis'' is used in formal logic, to denote the antecedent (logic), antecedent of a proposition; thus in the proposition "If ''P'', then ''Q''", ''P'' denotes the hypothesis (or antecedent); ''Q'' can be called a consequent. ''P'' is the :wikt:assumption, assumption in a (possibly Counterfactual conditional, counterfac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
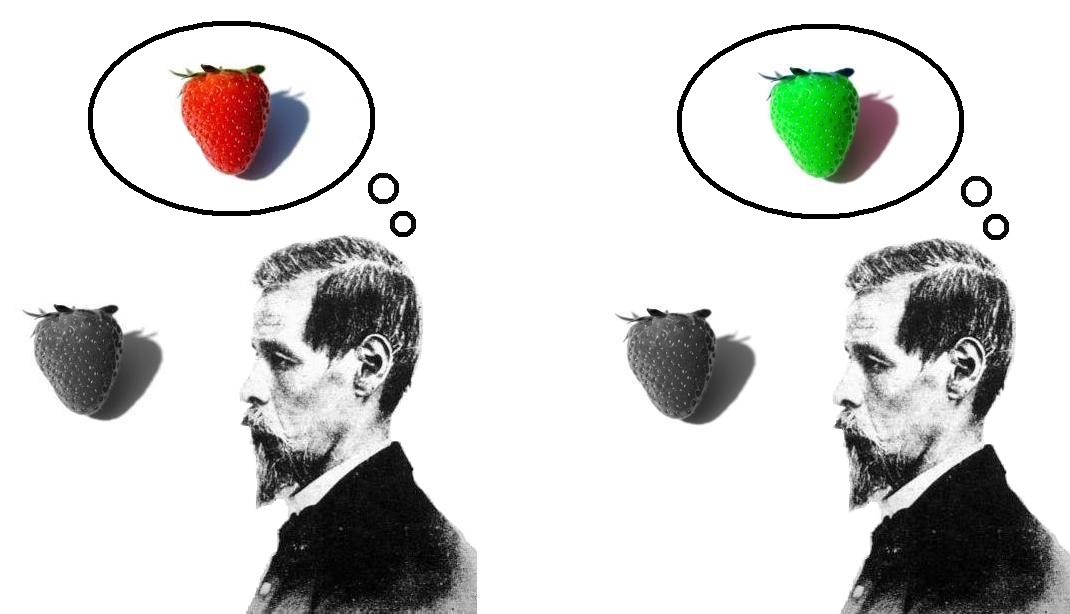
Simulated Consciousness
Artificial consciousness (AC), also known as machine consciousness (MC) or synthetic consciousness (; ), is a field related to artificial intelligence and cognitive robotics. The aim of the theory of artificial consciousness is to "Define that which would have to be synthesized were consciousness to be found in an engineered artifact" . Neuroscience hypothesizes that consciousness is generated by the interoperation of various parts of the brain, called the neural correlates of consciousness or NCC, though there are challenges to that perspective. Proponents of AC believe it is possible to construct systems (e.g., computer systems) that can emulate this NCC interoperation. Artificial consciousness concepts are also pondered in the philosophy of artificial intelligence through questions about mind, consciousness, and mental states. Philosophical views As there are many hypothesized types of consciousness, there are many potential implementations of artificial consciousne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitalism
Vitalism is a belief that starts from the premise that "living organisms are fundamentally different from non-living entities because they contain some non-physical element or are governed by different principles than are inanimate things." Where vitalism explicitly invokes a vital principle, that element is often referred to as the "vital spark," "energy," or "'' élan vital''," which some equate with the soul. In the 18th and 19th centuries vitalism was discussed among biologists, between those who felt that the known mechanics of physics would eventually explain the difference between life and non-life and vitalists who argued that the processes of life could not be reduced to a mechanistic process. Vitalist biologists such as Johannes Reinke proposed testable hypotheses meant to show inadequacies with mechanistic explanations, but their experiments failed to provide support for vitalism. Biologists now consider vitalism in this sense to have been refuted by empirical eviden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consciousness
Consciousness, at its simplest, is sentience and awareness of internal and external existence. However, the lack of definitions has led to millennia of analyses, explanations and debates by philosophers, theologians, linguisticians, and scientists. Opinions differ about what exactly needs to be studied or even considered consciousness. In some explanations, it is synonymous with the mind, and at other times, an aspect of mind. In the past, it was one's "inner life", the world of introspection, of private thought, imagination and volition. Today, it often includes any kind of cognition, experience, feeling or perception. It may be awareness, awareness of awareness, or self-awareness either continuously changing or not. The disparate range of research, notions and speculations raises a curiosity about whether the right questions are being asked. Examples of the range of descriptions, definitions or explanations are: simple wakefulness, one's sense of selfhood or soul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Room
The Chinese room argument holds that a digital computer executing a program cannot have a " mind," "understanding" or "consciousness," regardless of how intelligently or human-like the program may make the computer behave. The argument was presented by philosopher John Searle in his paper, "Minds, Brains, and Programs", published in '' Behavioral and Brain Sciences'' in 1980. Similar arguments were presented by Gottfried Leibniz (1714), Anatoly Dneprov (1961), Lawrence Davis (1974) and Ned Block (1978). Searle's version has been widely discussed in the years since. The centerpiece of Searle's argument is a thought experiment known as the ''Chinese room''. The argument is directed against the philosophical positions of functionalism and computationalism, which hold that the mind may be viewed as an information-processing system operating on formal symbols, and that simulation of a given mental state is sufficient for its presence. Specifically, the argument is intended to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Consciousness
Artificial consciousness (AC), also known as machine consciousness (MC) or synthetic consciousness (; ), is a field related to artificial intelligence and cognitive robotics. The aim of the theory of artificial consciousness is to "Define that which would have to be synthesized were consciousness to be found in an engineered artifact" . Neuroscience hypothesizes that consciousness is generated by the interoperation of various parts of the brain, called the neural correlates of consciousness or NCC, though there are challenges to that perspective. Proponents of AC believe it is possible to construct systems (e.g., computer systems) that can emulate this NCC interoperation. Artificial consciousness concepts are also pondered in the philosophy of artificial intelligence through questions about mind, consciousness, and mental states. Philosophical views As there are many hypothesized types of consciousness, there are many potential implementations of artificial consciousness. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hard Problem Of Consciousness
The hard problem of consciousness is the problem of explaining why and how humans have qualia or phenomenal experiences. This is in contrast to the "easy problems" of explaining the physical systems that give us and other animals the ability to discriminate, integrate information, and so forth. These problems are seen as relatively easy because all that is required for their solution is to specify the mechanisms that perform such functions. Philosopher David Chalmers writes that even once we have solved all such problems about the brain and experience, the hard problem will still persist. The existence of a "hard problem" is controversial. It has been accepted by philosophers of mind such as Joseph Levine, Colin McGinn, and Ned Block and cognitive neuroscientists such as Francisco Varela, Giulio Tononi, and Christof Koch. However, its existence is disputed by philosophers of mind such as Daniel Dennett, Massimo Pigliucci, Thomas Metzinger, Patricia Churchland, and Kei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virtual People
A virtual human, virtual persona, or digital clone is the creation or re-creation of a human being in image and voice using computer-generated imagery and sound, that is often indistinguishable from the real actor. The idea of a virtual actor was first portrayed in the 1981 film '' Looker'', wherein models had their bodies scanned digitally to create 3D computer generated images of the models, and then animating said images for use in TV commercials. Two 1992 books used this concept: ''Fools'' by Pat Cadigan, and ''Et Tu, Babe'' by Mark Leyner. In general, virtual humans employed in movies are known as synthespians, virtual actors, vactors, cyberstars, or "silicentric" actors. There are several legal ramifications for the digital cloning of human actors, relating to copyright and personality rights. People who have already been digitally cloned as simulations include Bill Clinton, Marilyn Monroe, Fred Astaire, Ed Sullivan, Elvis Presley, Bruce Lee, Audrey Hepburn, Ann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simulation Hypothesis
The simulation hypothesis proposes that all of our existence is a simulated reality, such as a computer simulation. The simulation hypothesis bears a close resemblance to various other skeptical scenarios from throughout the history of philosophy. The hypothesis was popularized in its current form by Nick Bostrom. The suggestion that such a hypothesis is compatible with all human perceptual experiences is thought to have significant epistemological consequences in the form of philosophical skepticism. Versions of the hypothesis have also been featured in science fiction, appearing as a central plot device in many stories and films. The hypothesis popularized by Bostrom is very disputed, with, for example, theoretical physicist Sabine Hossenfelder, who called it pseudoscience and cosmologist George F. R. Ellis, who stated that " he hypothesisis totally impracticable from a technical viewpoint" and that "protagonists seem to have confused science fiction with science. Late-night p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computation
Computation is any type of arithmetic or non-arithmetic calculation that follows a well-defined model (e.g., an algorithm). Mechanical or electronic devices (or, historically, people) that perform computations are known as '' computers''. An especially well-known discipline of the study of computation is computer science. Physical process of Computation Computation can be seen as a purely physical process occurring inside a closed physical system called a computer. Examples of such physical systems are digital computers, mechanical computers, quantum computers, DNA computers, molecular computers, microfluidics-based computers, analog computers, and wetware computers. This point of view has been adopted by the physics of computation, a branch of theoretical physics, as well as the field of natural computing. An even more radical point of view, pancomputationalism (inaudible word), is the postulate of digital physics that argues that the evolution of the universe is itself ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognition
Cognition refers to "the mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses". It encompasses all aspects of intellectual functions and processes such as: perception, attention, thought, intelligence, the formation of knowledge, memory and working memory, judgment and evaluation, reasoning and computation, problem solving and decision making, comprehension and production of language. Imagination is also a cognitive process, it is considered as such because it involves thinking about possibilities. Cognitive processes use existing knowledge and discover new knowledge. Cognitive processes are analyzed from different perspectives within different contexts, notably in the fields of linguistics, musicology, anesthesia, neuroscience, psychiatry, psychology, education, philosophy, anthropology, biology, systemics, logic, and computer science. These and other approaches to the analysis of cognition (such as embodie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosophy Of Mind
Philosophy of mind is a branch of philosophy that studies the ontology and nature of the mind and its relationship with the body. The mind–body problem is a paradigmatic issue in philosophy of mind, although a number of other issues are addressed, such as the hard problem of consciousness and the nature of particular mental states.Siegel, S.: ''The Contents of Visual Experience''. New York: Oxford University Press. 2010.Macpherson, F. & Haddock, A., editors, ''Disjunctivism: Perception, Action, Knowledge'', Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2008. Aspects of the mind that are studied include mental events, mental functions, mental properties, consciousness and its neural correlates, the ontology of the mind, the nature of cognition and of thought, and the relationship of the mind to the body. Dualism and monism are the two central schools of thought on the mind–body problem, although nuanced views have arisen that do not fit one or the other category neatly. * Duali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |