An enclave is a territory (or a small territory apart of a larger one) that is entirely surrounded by the territory of one other state or entity.
Enclaves may also exist within territorial waters.
''Enclave'' is sometimes used improperly to denote a territory that is only partly surrounded by another state.
The
Vatican City
Vatican City (), officially the Vatican City State ( it, Stato della Città del Vaticano; la, Status Civitatis Vaticanae),—'
* german: Vatikanstadt, cf. '—' (in Austria: ')
* pl, Miasto Watykańskie, cf. '—'
* pt, Cidade do Vati ...
and
San Marino
San Marino (, ), officially the Republic of San Marino ( it, Repubblica di San Marino; ), also known as the Most Serene Republic of San Marino ( it, Serenissima Repubblica di San Marino, links=no), is the fifth-smallest country in the world an ...
, both enclaved by
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, and
Lesotho
Lesotho ( ), officially the Kingdom of Lesotho, is a country landlocked as an enclave in South Africa. It is situated in the Maloti Mountains and contains the highest mountains in Southern Africa. It has an area of over and has a populatio ...
, enclaved by
South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring count ...
, are completely enclaved sovereign states.
An exclave is a portion of a state or district geographically separated from the main part by surrounding alien territory (of one or more states or districts etc).
Many exclaves are also enclaves, but not all: an exclave can be surrounded by the territory of more than one state.
The
Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
i exclave of
Nakhchivan is an example of an exclave that is not an enclave, as it borders
Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ...
,
Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
and
Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkm ...
.
Semi-enclaves and semi-exclaves are areas that, except for possessing an unsurrounded sea border (a coastline contiguous with
international waters
The terms international waters or transboundary waters apply where any of the following types of bodies of water (or their drainage basins) transcend international boundaries: oceans, large marine ecosystems, enclosed or semi-enclosed region ...
), would otherwise be enclaves or exclaves.
Enclaves and semi-enclaves can exist as independent states (
Monaco
Monaco (; ), officially the Principality of Monaco (french: Principauté de Monaco; Ligurian: ; oc, Principat de Mónegue), is a sovereign
''Sovereign'' is a title which can be applied to the highest leader in various categories. The word ...
,
The Gambia
The Gambia,, ff, Gammbi, ar, غامبيا officially the Republic of The Gambia, is a country in West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 c ...
and
Brunei
Brunei ( , ), formally Brunei Darussalam ( ms, Negara Brunei Darussalam, Jawi alphabet, Jawi: , ), is a country located on the north coast of the island of Borneo in Southeast Asia. Apart from its South China Sea coast, it is completely sur ...
are semi-enclaves), while exclaves and semi-exclaves proper always constitute just a part of a sovereign state (like the
Kaliningrad Oblast).
A pene-exclave is a part of the territory of one country that can be conveniently approached—in particular, by wheeled traffic—only through the territory of another country.
Pene-exclaves are also called functional exclaves or practical exclaves.
Many pene-exclaves partially border their own territorial waters (i.e., they are not surrounded by other nations' territorial waters), such as
Point Roberts, Washington and Minnesota's
Northwest Angle. A pene-exclave can also exist entirely on land, such as when intervening mountains render a territory inaccessible from other parts of a country except through alien territory. A commonly cited example is the
Kleinwalsertal, a valley part of
Vorarlberg
Vorarlberg ( , ; gsw, label= Vorarlbergisch, Vorarlbearg, , or ) is the westernmost state () of Austria. It has the second-smallest geographical area after Vienna and, although it also has the second-smallest population, it is the state with the ...
, Austria, that is accessible only from Germany to the north.
Origin and usage
The word ''enclave'' is French and first appeared in the mid-15th century as a derivative of the verb (1283), from the colloquial Latin (to close with a key).
[Le Grand Robert, ''Dictionnaire de la Langue Française'', 2001, vol. III, p. 946.] Originally, it was a term of property law that denoted the situation of a land or parcel of land surrounded by land owned by a different owner, and that could not be reached for its exploitation in a practical and sufficient manner without crossing the surrounding land.
In law, this created a ''servitude'' of passage for the benefit of the owner of the surrounded land. The first diplomatic document to contain the word ''enclave'' was the
Treaty of Madrid, signed in 1526.
Later, the term enclave began to be used also to refer to parcels of countries, counties, fiefs, communes, towns, parishes, etc. that were surrounded by alien territory. This French word eventually entered English and other languages to denote the same concept, although local terms have continued to be used. In India, the word "pocket" is often used as a synonym for enclave (such as "the pockets of Puducherry district"). In British administrative history, subnational enclaves were usually called detachments or detached parts, and national enclaves as detached districts or detached dominions. In English
ecclesiastic history, subnational enclaves were known as peculiars (see also
royal peculiar).
The word ''exclave''
[ is a logically extended ]back-formation
In etymology, back-formation is the process or result of creating a new word via inflection, typically by removing or substituting actual or supposed affixes from a lexical item, in a way that expands the number of lexemes associated with the ...
of ''enclave''.
Characteristics
Enclaves exist for a variety of historical, political
Politics (from , ) is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of resources or status. The branch of social science that studi ...
and geographical reasons. For example, in the feudal system in Europe, the ownership of feudal domains was often transferred or partitioned, either through purchase and sale or through inheritance, and often such domains were or came to be surrounded by other domains. In particular, this state of affairs persisted into the 19th century in the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
, and these domains (principalities, etc.) exhibited many of the characteristics of sovereign states. Prior to 1866 Prussia alone consisted of more than 270 discontiguous pieces of territory.India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the ...
and Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million pe ...
implemented a Land Boundary Agreement that exchanged 162 first-order enclaves (111 Indian and 51 Bangladeshi). This exchange thus effectively de-enclaved another two dozen second-order enclaves and one third-order enclave, eliminating 197 of the India–Bangladesh enclaves in all. The residents in these enclaves had complained of being effectively stateless. Only Bangladesh's Dahagram–Angarpota enclave remained.
Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
and Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to ...
decided to keep the enclave and exclave system in Baarle. As both Netherlands and Belgium are members of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been ...
and Schengen Area, people, goods and services flow freely with little or no restrictions.
Enclave versus exclave
For illustration, in the figure (above), A1 is a semi-enclave (attached to C and also bounded by water that only touches C's territorial water). Although A2 is an exclave of A, it cannot be classed as an enclave because it shares borders with B and C. The territory A3 is both an exclave of A and an enclave from the viewpoint of B. The singular territory D, although an enclave, is not an exclave.
True enclaves
An enclave is a part of the territory of a state that is enclosed within the territory of another state. To distinguish the parts of a state entirely enclosed in a single other state, they are called true enclaves.Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
. Since 1945, all of Berlin was ruled ''de jure'' by the four Allied powers. However, the East German government and the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
treated East Berlin as an integral part of East Germany, so West Berlin was a ''de facto'' enclave within East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state ...
. Also, 12 small West Berlin enclaves, such as Steinstücken, were separated from the city, some by only a few meters.
Enclaved countries
 Three nations qualify as completely surrounded by another country's land and/or internal waters:
* The Republic of
Three nations qualify as completely surrounded by another country's land and/or internal waters:
* The Republic of San Marino
San Marino (, ), officially the Republic of San Marino ( it, Repubblica di San Marino; ), also known as the Most Serene Republic of San Marino ( it, Serenissima Repubblica di San Marino, links=no), is the fifth-smallest country in the world an ...
, enclaved within Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
* Vatican City
Vatican City (), officially the Vatican City State ( it, Stato della Città del Vaticano; la, Status Civitatis Vaticanae),—'
* german: Vatikanstadt, cf. '—' (in Austria: ')
* pl, Miasto Watykańskie, cf. '—'
* pt, Cidade do Vati ...
, enclaved within the city of Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
, Italy
* The Kingdom of Lesotho
Lesotho ( ), officially the Kingdom of Lesotho, is a country landlocked as an enclave in South Africa. It is situated in the Maloti Mountains and contains the highest mountains in Southern Africa. It has an area of over and has a populatio ...
, enclaved within South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring count ...
The Republic of Artsakh
Artsakh, officially the Republic of Artsakh () or the Nagorno-Karabakh Republic (),, is a breakaway state in the South Caucasus whose territory is internationally recognised as part of Azerbaijan. Artsakh controls a part of the former ...
, a disputed territory not recognised by any UN member states, controls part of Nagorno-Karabakh, which is an enclave within Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
.
Historically, four Bantustans (or "Black homelands") of South Africa were granted nominal independence, unrecognized internationally, by the Apartheid
Apartheid (, especially South African English: , ; , "aparthood") was a system of institutionalised racial segregation that existed in South Africa and South West Africa (now Namibia) from 1948 to the early 1990s. Apartheid was ...
government from 1976 until their reabsorption in 1994. Others remained under government rule from 1948 to 1994. Being heavily partitioned, various parts of these Bantustans were true enclaves.
The United States' constitutional principle of tribal sovereignty treats federally recognized Indian reservations as quasi-independent enclaves.
True exclaves
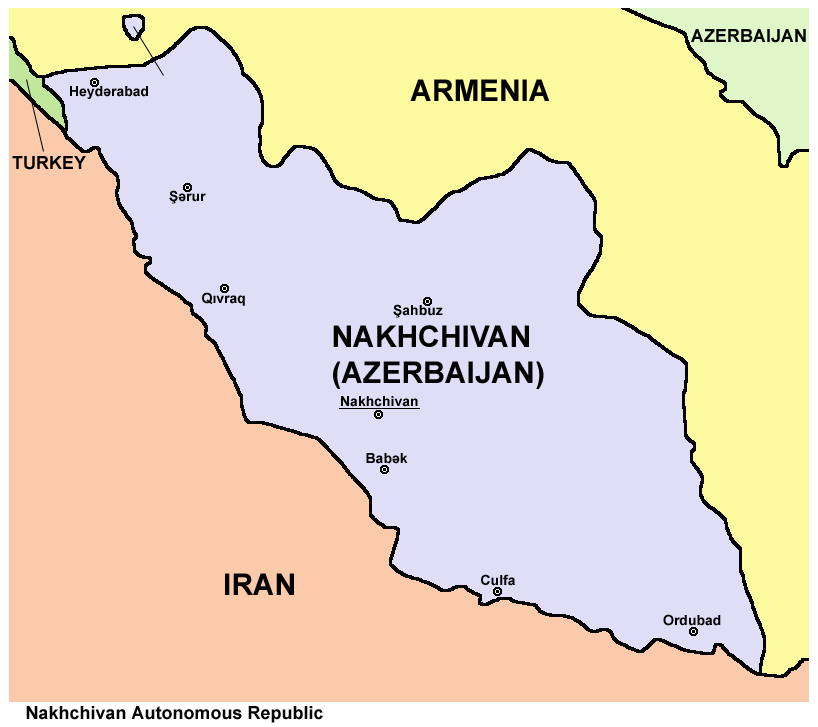 ''True exclave'' is an extension of the concept of ''true enclave''. In order to access a true exclave from the mainland, a traveller must go through the territory of at least one other state. Examples include:
* Nakhchivan, which borders
''True exclave'' is an extension of the concept of ''true enclave''. In order to access a true exclave from the mainland, a traveller must go through the territory of at least one other state. Examples include:
* Nakhchivan, which borders Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
, Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ...
and Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkm ...
, is an exclave of Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
.
* Baarle-Hertog is a collection of Belgian exclaves in the Netherlands.
* In the United Arab Emirates
The United Arab Emirates (UAE; ar, اَلْإِمَارَات الْعَرَبِيَة الْمُتَحِدَة ), or simply the Emirates ( ar, الِْإمَارَات ), is a country in Western Asia ( The Middle East). It is located at ...
, four emirates have five true exclaves: Dubai
Dubai (, ; ar, دبي, translit=Dubayy, , ) is the most populous city in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and the capital of the Emirate of Dubai, the most populated of the 7 emirates of the United Arab Emirates.The Government and Politics ...
( Hatta), Ajmān
Ajman ( ar, عجمان, '; Gulf Arabic: عيمان ʿymān) is the capital of the emirate of Ajman in the United Arab Emirates. It is the fifth-largest city in UAE after Dubai, Abu Dhabi, Sharjah and Al Ain. Located along the Persian Gulf, it is ...
( Masfout and Manama
Manama ( ar, المنامة ', Bahrani pronunciation: ) is the capital and largest city of Bahrain, with an approximate population of 200,000 people as of 2020. Long an important trading center in the Persian Gulf, Manama is home to a very d ...
), Ras al-Khaimah (the southerly of the emirate's two non-contiguous sections), and Sharjah
Sharjah (; ar, ٱلشَّارقَة ', Gulf Arabic: ''aš-Šārja'') is the third-most populous city in the United Arab Emirates, after Dubai and Abu Dhabi, forming part of the Dubai-Sharjah-Ajman metropolitan area.
Sharjah is the capital ...
( Nahwa, also both a true national-level enclave and a counter-enclave).
* Llívia is an enclave and exclave of Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' ( Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
surrounded by France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
.
* Campione d'Italia is an enclave and exclave of Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
surrounded by Switzerland.
* Büsingen am Hochrhein is an enclave and exclave of Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
surrounded by Switzerland. The shortest distance from Büsingen's borders to the main portion of German territory is only about 700 metres (about 2,300 ft).
* Likoma and Chizumulu Islands in Lake Malawi are lacustrine enclaves and exclaves of Malawi
Malawi (; or aláwi Tumbuka: ''Malaŵi''), officially the Republic of Malawi, is a landlocked country in Southeastern Africa that was formerly known as Nyasaland. It is bordered by Zambia to the west, Tanzania to the north and northe ...
, surrounded by Mozambique
Mozambique (), officially the Republic of Mozambique ( pt, Moçambique or , ; ny, Mozambiki; sw, Msumbiji; ts, Muzambhiki), is a country located in southeastern Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Mala ...
territorial waters.
Related constructs and terms
Semi-enclaves and semi-exclaves
Semi-enclaves and semi-exclaves are areas that, except for possessing an unsurrounded sea border, would otherwise be enclaves or exclaves.Monaco
Monaco (; ), officially the Principality of Monaco (french: Principauté de Monaco; Ligurian: ; oc, Principat de Mónegue), is a sovereign
''Sovereign'' is a title which can be applied to the highest leader in various categories. The word ...
, the Gambia
The Gambia,, ff, Gammbi, ar, غامبيا officially the Republic of The Gambia, is a country in West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 c ...
and Brunei
Brunei ( , ), formally Brunei Darussalam ( ms, Negara Brunei Darussalam, Jawi alphabet, Jawi: , ), is a country located on the north coast of the island of Borneo in Southeast Asia. Apart from its South China Sea coast, it is completely sur ...
. ''Vinokurov (2007)'' declares, "Technically, Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, In recognized minority languages of Portugal:
:* mwl, República Pertuesa is a country located on the Iberian Peninsula, in Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Macaronesian ...
, Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establishe ...
, and Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tota ...
also border only one foreign state, but they are not enclosed in the geographical, political, or economic sense. They have vast access to international waters. At the same time, there are states that, although in possession of sea access, are still enclosed by the territories of a foreign state."Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tota ...
and Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establishe ...
have each gained a second bordering state — each other — with the 2022 division of Hans Island
Hans Island ( Inuktitut and kl, Tartupaluk, ; Inuktitut syllabics: ; da, Hans Ø; french: Île Hans) is an island in the very centre of the Kennedy Channel of Nares Strait in the high Arctic region, split between the Canadian territory of ...
.)
Vinokurov Vinokurov, feminine: Vinokurova, (also Winokurow, Winokurowa) is a Russian occupational surname derived from the word " винокур", which is an archaic name of the profession of spirit distilling. The Ukrainian-language version is Vynokurov, Vy ...
affirms that "no similar quantitative criterion is needed to define the scope of non-sovereign semi-enclaves/exclaves."Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S ...
, one of the states in the United States of America
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territor ...
, is the largest semi-enclave in the world, separated from the US by Canada.
* Oecusse, a district on the northwestern side of the island of Timor, is a semi-enclave of East Timor
East Timor (), also known as Timor-Leste (), officially the Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste, is an island country in Southeast Asia. It comprises the eastern half of the island of Timor, the exclave of Oecusse on the island's north-we ...
separated from the rest of the country by Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
.
* Ceuta
Ceuta (, , ; ar, سَبْتَة, Sabtah) is a Spanish autonomous city on the north coast of Africa.
Bordered by Morocco, it lies along the boundary between the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. It is one of several Spanish territo ...
and Melilla
Melilla ( , ; ; rif, Mřič ; ar, مليلية ) is an autonomous city of Spain located in north Africa. It lies on the eastern side of the Cape Three Forks, bordering Morocco and facing the Mediterranean Sea. It has an area of . It was ...
are Spanish semi-enclaves on the Mediterranean coast of Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria ...
.
* Temburong District is a Bruneian semi-enclave surrounded by Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two r ...
. The Temburong Bridge connects Temburong to the Brunei mainland.
* Kokkina, a village in the ''de facto'' state of Northern Cyprus
Northern Cyprus ( tr, Kuzey Kıbrıs), officially the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus (TRNC; tr, Kuzey Kıbrıs Türk Cumhuriyeti, ''KKTC''), is a ''de facto'' state that comprises the northeastern portion of the Geography of Cyprus, isl ...
, is a semi-enclave situated on the Mediterranean coast. It is separated from the rest of the country by the Republic of Cyprus.
* Kaliningrad Oblast is a federal subject of Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eigh ...
(an oblast), a semi-exclave situated on the Baltic coast and bordering Lithuania and Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, , is a country in Central Europe. Poland is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 mill ...
. Sea access from the Russian mainland is possible from Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
via the Gulf of Finland
The Gulf of Finland ( fi, Suomenlahti; et, Soome laht; rus, Фи́нский зали́в, r=Finskiy zaliv, p=ˈfʲinskʲɪj zɐˈlʲif; sv, Finska viken) is the easternmost arm of the Baltic Sea. It extends between Finland to the north and E ...
without passing through other states' territory.
* Cabinda (also spelled Kabinda, formerly Portuguese Congo) is a semi-exclave and a province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions outsi ...
of Angola
, national_anthem = "Angola Avante"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capital = Luanda
, religion =
, religion_year = 2020
, religion_ref =
, coordina ...
on the Atlantic coast of southwestern Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
, separated by the only sea-access port of the Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (french: République démocratique du Congo (RDC), colloquially "La RDC" ), informally Congo-Kinshasa, DR Congo, the DRC, the DROC, or the Congo, and formerly and also colloquially Zaire, is a country in ...
; also bordered by the Republic of the Congo.
* French Guiana
French Guiana ( or ; french: link=no, Guyane ; gcr, label=French Guianese Creole, Lagwiyann ) is an overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France on the northern Atlantic ...
(a French Overseas Department), in South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the souther ...
, is a semi-exclave that is bounded by Suriname
Suriname (; srn, Sranankondre or ), officially the Republic of Suriname ( nl, Republiek Suriname , srn, Ripolik fu Sranan), is a country on the northeastern Atlantic coast of South America. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north ...
, Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
, and the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Afr ...
.
* The southern part of Dubrovnik-Neretva County in Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
is separated from the rest of the country by Neum in Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and ...
and is also bordered by Montenegro
)
, image_map = Europe-Montenegro.svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Podgorica
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, official_languages = ...
. The Republic of Ragusa once gave the town of Neum to the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
because it did not want to have a land border with Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 bridges. The isla ...
; this small municipality was inherited by Bosnia and Herzegovina. The Pelješac Bridge links the semi-exclave to the rest of country.
Subnational enclaves and exclaves
Sometimes, administrative divisions of a country, for historical or practical reasons, caused some areas to belong to one division while being attached to another. Examples include:
* In India:
** Dadra, enclaved within the state of Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the nin ...
, is part of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu in India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the ...
.
** Puducherry district, of the Union Territory of Puducherry, is made of 12 non-contiguous parts, many of them are true enclaves entirely surrounded by the state of Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is a state in southern India. It is the tenth largest Indian state by area and the sixth largest by population. Its capital and largest city is Chennai. Tamil Nadu is the home of the Tamil people, whose Tamil languag ...
. Before Puducherry, along with the other territories of French India, was absorbed into India in 1954, they were enclaved within the Union of India, and before that the British Raj
The British Raj (; from Hindi language, Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British The Crown, Crown on the Indian subcontinent;
*
* it is also called Crown rule in India,
*
*
*
*
or Direct rule in India,
* Q ...
. Mahe district of Puducherry is made of three non-contiguous parts, two of which are true enclaves within the state of Kerala
Kerala ( ; ) is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South C ...
. Yanam district of Puducherry is an enclave surrounded entirely by the state of Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (, abbr. AP) is a state in the south-eastern coastal region of India. It is the seventh-largest state by area covering an area of and tenth-most populous state with 49,386,799 inhabitants. It is bordered by Telangana to t ...
.
* From 1947 to 1971, Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million pe ...
was a part of Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
as its East Pakistan exclave, separated from West Pakistan by 1,760 kilometers (1,100 miles) of India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the ...
. It eventually gained independence in 1971, during the Bangladesh Liberation War
The Bangladesh Liberation War ( bn, মুক্তিযুদ্ধ, , also known as the Bangladesh War of Independence, or simply the Liberation War in Bangladesh) was a revolution and armed conflict sparked by the rise of the Bengali ...
.
* In the United Kingdom:
** Before 1974, and especially before 1844, there were many exclaves of counties in England and Wales.
** The counties of Scotland before reorganisation in 1889 included dozens of exclaves. This was especially notable in the case of Cromartyshire, which was split into at least nine parts spread across Ross-shire.
* In France:
** The French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
department of Pyrénées-Atlantiques, in the southwest of France, surrounds two enclaves of the neighbouring department of Hautes-Pyrénées.
** The French department of Vaucluse has a rather large exclave to its north that is an enclave within the Drôme
Drôme (; Occitan: ''Droma''; Arpitan: ''Drôma'') is the southernmost department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region of Southeastern France. Named after the river Drôme, it had a population of 516,762 as of 2019. department – the canton
Canton may refer to:
Administrative division terminology
* Canton (administrative division), territorial/administrative division in some countries, notably Switzerland
* Township (Canada), known as ''canton'' in Canadian French
Arts and ent ...
of Valréas (historically known as Enclave des Papes
An enclave is a territory (or a small territory apart of a larger one) that is entirely surrounded by the territory of one other state or entity. Enclaves may also exist within territorial waters. ''Enclave'' is sometimes used improperly to deno ...
).
* San Colombano al Lambro is an exclave of the province of Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard language, Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the List of cities in Italy, second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 ...
at the junction between the Pavia
Pavia (, , , ; la, Ticinum; Medieval Latin: ) is a town and comune of south-western Lombardy in northern Italy, south of Milan on the lower Ticino river near its confluence with the Po. It has a population of c. 73,086. The city was the cap ...
and Lodi provinces. The exclave arose when the province of Lodi was carved out of the province of Milan, but a referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of ...
in San Colombano indicated the locals' wish to stay in Milan. As a result, the commune is the only wine-producing area in the mostly urbanized province of Milan.
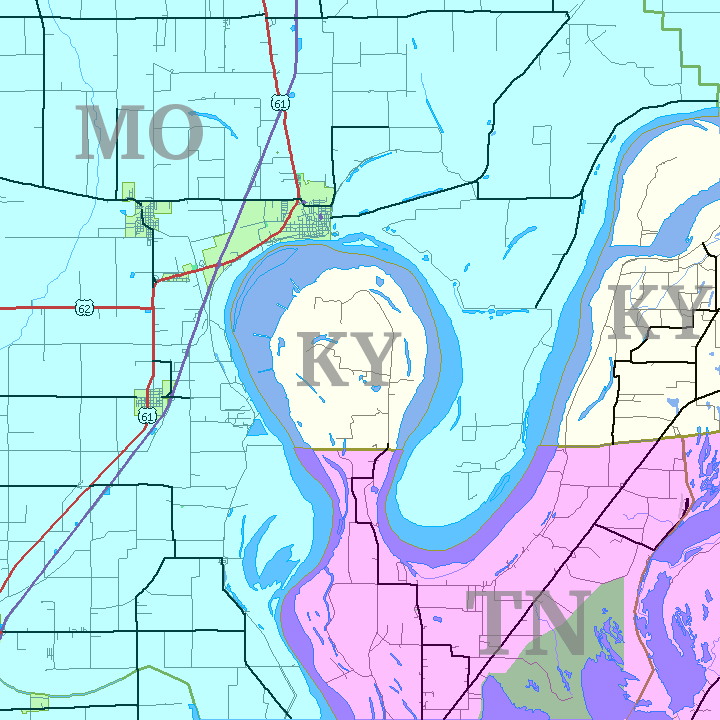 * In the United States:
**A portion of Ellis Island is an exclave of
* In the United States:
**A portion of Ellis Island is an exclave of New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the U ...
within the boundaries of Jersey City, and therefore of New York State within the boundaries of New Jersey
New Jersey is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic States, Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern United States, Northeastern regions of the United States. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York (state), New York; on the ea ...
.
** The Kentucky Bend exists because of a meander
A meander is one of a series of regular sinuous curves in the channel of a river or other watercourse. It is produced as a watercourse erodes the sediments of an outer, concave bank ( cut bank) and deposits sediments on an inner, convex ban ...
of the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it ...
.
** West Hollywood and Beverly Hills, California
Beverly Hills is a city located in Los Angeles County, California. A notable and historic suburb of Greater Los Angeles, it is in a wealthy area immediately southwest of the Hollywood Hills, approximately northwest of downtown Los Angeles. ...
, adjoin one another, but are entirely surrounded by the City of Los Angeles
Los Angeles ( ; es, Los Ángeles, link=no , ), often referred to by its initials L.A., is the largest city in the state of California and the second most populous city in the United States after New York City, as well as one of the wor ...
. San Fernando, California is entirely surrounded by the City of Los Angeles.
** Jeddito, Arizona, lies within a exclave of the Navajo Nation. This exclave is surrounded by territory of the Hopi Reservation, which is itself surrounded by the Navajo Nation.
"Practical" enclaves, exclaves and inaccessible districts
The term pene-exclave was defined in ''Robinson (1959)'' as "parts of the territory of one country that can be approached conveniently – in particular by wheeled traffic – only through the territory of another country."Vorarlberg
Vorarlberg ( , ; gsw, label= Vorarlbergisch, Vorarlbearg, , or ) is the westernmost state () of Austria. It has the second-smallest geographical area after Vienna and, although it also has the second-smallest population, it is the state with the ...
, Austria, that is only accessible from Germany to the north, being separated from the rest of Austria by high mountains traversed by no roads. Another example is the Spanish village of Os de Civís
Os de Civís () is a village in the central Pyrenees mountains, in the municipality of Les Valls de Valira in Catalonia, Spain, and is located to the west of Andorra, near the villages of Aixàs and Bixessarri. Civís is the nearest Spanish ...
, accessible from Andorra.
Hence, such areas are enclaves or exclaves ''for practical purposes'', without meeting the strict definition. Many pene-exclaves partially border the sea or another body of water, which comprises their own territorial waters (i.e., they are not surrounded by other nations' territorial waters). They border their own territorial waters in addition to a land border with another country, and hence they are not true exclaves. Still, one cannot travel to them on land without going through another country. Attribution of a pene-enclave status to a territory can sometimes be disputed, depending on whether the territory is considered to be practically inaccessible from the mainland or not.Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ga, Tuaisceart Éireann ; sco, label=Ulster-Scots, Norlin Airlann) is a part of the United Kingdom, situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, that is variously described as a country, province or region. North ...
, an area of the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, is bounded by the Republic of Ireland
Ireland ( ga, Éire ), also known as the Republic of Ireland (), is a country in north-western Europe consisting of 26 of the 32 Counties of Ireland, counties of the island of Ireland. The capital and largest city is Dublin, on the eastern ...
, the Irish Sea
The Irish Sea or , gv, Y Keayn Yernagh, sco, Erse Sie, gd, Muir Èireann , Ulster-Scots: ''Airish Sea'', cy, Môr Iwerddon . is an extensive body of water that separates the islands of Ireland and Great Britain. It is linked to the Ce ...
and the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Afr ...
.
* Equatorial Guinea's continental portion, Río Muni
Río Muni (called ''Mbini'' in Fang) is the Continental Region (called ''Región Continental'' in Spanish) of Equatorial Guinea, and comprises the mainland geographical region, covering . The name is derived from the Muni River, along whic ...
, is a semi-exclave surrounded by Gabon
Gabon (; ; snq, Ngabu), officially the Gabonese Republic (french: République gabonaise), is a country on the west coast of Central Africa. Located on the equator, it is bordered by Equatorial Guinea to the northwest, Cameroon to the north ...
, Cameroon
Cameroon (; french: Cameroun, ff, Kamerun), officially the Republic of Cameroon (french: République du Cameroun, links=no), is a country in west- central Africa. It is bordered by Nigeria to the west and north; Chad to the northeast; th ...
and the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Afr ...
.
* The Northwest Angle in the U.S. state of Minnesota
Minnesota () is a state in the upper midwestern region of the United States. It is the 12th largest U.S. state in area and the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 22nd most populous, with over 5.75 million residents. Minne ...
is geographically separated from the rest of the state (and United States) by the Lake of the Woods and is accessible on land only through the Canadian province of Manitoba
, image_map = Manitoba in Canada 2.svg
, map_alt = Map showing Manitoba's location in the centre of Southern Canada
, Label_map = yes
, coordinates =
, capital = Win ...
. Additionally, Elm Point, south of the town of Buffalo Point in Manitoba, is separated from the rest of Minnesota by Lake of the Woods.
* Point Roberts, Washington, United States, is an unincorporated community in Whatcom County—located on the southernmost tip of the Tsawwassen Peninsula, south of Delta, British Columbia, Canada—that can be reached by land from the rest of the United States only by traveling through Canada.
* The U.S. state of Vermont
Vermont () is a state in the northeast New England region of the United States. Vermont is bordered by the states of Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, and New York to the west, and the Canadian province of Quebec to the ...
has two pene-enclaves with the Canadian province of Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Government of Canada, Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is ...
. Province Point, a few kilometres to the northeast of the town of East Alburgh, Vermont, is the southernmost tip of a small promontory approximately in size (). The promontory is cut through by the U.S./Canadian border; as such the area is a practical enclave of the United States contiguous with Canada. Similarly, the southern point of Province Island (), a small island mostly in Quebec, crosses into Vermont. It is situated in Lake Memphremagog, near Newport, Vermont.
* Walvis Bay, now part of Namibia
Namibia (, ), officially the Republic of Namibia, is a country in Southern Africa. Its western border is the Atlantic Ocean. It shares land borders with Zambia and Angola to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south and e ...
, was a pene-exclave of the Cape Colony in German South-West Africa, created in 1878. It became part of the Cape Province of the Union of South Africa
The Union of South Africa ( nl, Unie van Zuid-Afrika; af, Unie van Suid-Afrika; ) was the historical predecessor to the present-day Republic of South Africa. It came into existence on 31 May 1910 with the unification of the Cape, Natal, Tran ...
in 1910, but from 1922, it was administered as a ''de facto'' part of South-West Africa, a League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide Intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by ...
Mandate
Mandate most often refers to:
* League of Nations mandates, quasi-colonial territories established under Article 22 of the Covenant of the League of Nations, 28 June 1919
* Mandate (politics), the power granted by an electorate
Mandate may also ...
. In 1977, it was separated from that territory and re-integrated into the Cape Province. South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring count ...
did not relinquish sovereignty over Walvis Bay until 1994, nearly four years after Namibia's independence.
* Baritú National Park in Argentina can only be accessed by road through Bolivia
, image_flag = Bandera de Bolivia (Estado).svg
, flag_alt = Horizontal tricolor (red, yellow, and green from top to bottom) with the coat of arms of Bolivia in the center
, flag_alt2 = 7 × 7 square p ...
, as it is separated from the nearest Argentinian roads by vast stretches of uninhabited rainforest.
Subnational "practical" enclaves, exclaves, and inaccessible districts
* Although the Jervis Bay Territory, which occupies a coastal peninsula in Australia, is not part of the Australian Capital Territory
The Australian Capital Territory (commonly abbreviated as ACT), known as the Federal Capital Territory (FCT) until 1938, is a landlocked federal territory of Australia containing the national capital Canberra and some surrounding townships. ...
, the laws of the ACT apply to it. This was to give the ACT coastal access, which it did not have as it was entirely surrounded by the state of New South Wales
)
, nickname =
, image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, es ...
.
* The Romanian village of Nămoloasa ( Galați County) can be accessed only through Vrancea County (where there is a bridge over the Siret), because it is separated by the Siret from the rest of Galați County.
* The southern part of the Province of Venice, Veneto, can be reached directly from the rest of the province only by boat. By land it can be reached only by traveling through the Province of Padua because territorial continuity with the main part of the province exists only through some unconnected islands and islets.
* It is not possible to drive from the northern half of County Leitrim in the Republic of Ireland
Ireland ( ga, Éire ), also known as the Republic of Ireland (), is a country in north-western Europe consisting of 26 of the 32 Counties of Ireland, counties of the island of Ireland. The capital and largest city is Dublin, on the eastern ...
to the southern half without leaving the county; Lough Allen and the River Shannon
The River Shannon ( ga, Abhainn na Sionainne, ', '), at in length, is the longest river in the British Isles. It drains the Shannon River Basin, which has an area of , – approximately one fifth of the area of the island of Ireland.
The Sha ...
present a water barrier requiring one to drive through County Cavan to the east or County Roscommon to the west.
* The community of East Kemptville, Nova Scotia
Argyle, officially named the Municipality of the District of Argyle, is a district municipality in Yarmouth County, Nova Scotia. Statistics Canada classifies the district municipality as a municipal district.
The district municipality occupies th ...
, Canada, is part of the Municipality of Argyle, but it can only be reached by road from the rest of the municipality by travelling through the Municipality of Yarmouth or the Municipality of Shelburne. The latter route also requires travelling through the Municipality of Barrington.
* The southeastern part of the Tai Po District (northern part of the Sai Kung Peninsula), Hong Kong
Hong Kong ( (US) or (UK); , ), officially the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (abbr. Hong Kong SAR or HKSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China on the eastern Pearl River Delta i ...
, can be reached directly from the rest of the district only by boat. By land it can be reached only by traveling through the Sha Tin District because territorial continuity with the main part of the district is cut off by the Tolo Harbour. In the past, when there was no road network serving the region, the residents commonly travelled by boat to Tai Po Market for their daily lives, hence the districts were drawn this way, but now most of the ferries no longer exist, and residents travel by road to markets in Sha Tin District (Ma On Shan or Sha Tin) instead.
* Within the United States:
** Several portions of land, including parts of Finns Point and Artificial Island, on the New Jersey
New Jersey is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic States, Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern United States, Northeastern regions of the United States. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York (state), New York; on the ea ...
side of the Delaware River are Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Maryland to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and New Jersey and the Atlantic Ocean to its east. The state takes its name from the adjacen ...
territory. Within the Twelve-Mile Circle, Delaware's border extends to the low-water mark across the river. Outside of the Circle, the Delaware – New Jersey border follows the middle of the river and Delaware Bay.
** The Eastern Shore of Virginia on the southern portion of the Delmarva Peninsula shares a border with Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It shares borders with Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; ...
but is only connected to the rest of Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the East Coast of the United States, Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography an ...
by the Chesapeake Bay Bridge-Tunnel, which is part of U.S. Route 13.
** The city of Carter Lake, Iowa is separated from the rest of the state of Iowa
Iowa () is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States, bordered by the Mississippi River to the east and the Missouri River and Big Sioux River to the west. It is bordered by six states: Wiscon ...
by the Missouri River, which changed course during a flood in 1877, cutting the city off from the rest of the state. It is now only accessible through Omaha, Nebraska
Nebraska () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. It is bordered by South Dakota to the north; Iowa to the east and Missouri to the southeast, both across the Missouri River; Kansas to the south; Colorado to the so ...
.
** The village of Kaskaskia, Illinois, the state's first capital, is separated from the rest of Illinois by the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it ...
due to a flood in 1881, which shifted the river to flow east of the town, rather than west. This resulted in the only access to the town being from Missouri
Missouri is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking List of U.S. states and territories by area, 21st in land area, it is bordered by eight states (tied for the most with Tennessee ...
.
** The Upper Peninsula of Michigan
Michigan () is a U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest, upper Midwestern United States. With a population of nearly 10.12 million and an area of nearly , Michigan is the List of U.S. states and ...
is separated from the Lower Peninsula by the Straits of Mackinac, so until the Mackinac Bridge was completed in 1957, the only land routes between them were through the states of Wisconsin
Wisconsin () is a state in the upper Midwestern United States. Wisconsin is the 25th-largest state by total area and the 20th-most populous. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake M ...
, Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolitan areas include, Peoria and Roc ...
, and Indiana
Indiana () is a U.S. state in the Midwestern United States. It is the 38th-largest by area and the 17th-most populous of the 50 States. Its capital and largest city is Indianapolis. Indiana was admitted to the United States as the 19th ...
, or through the Canadian province of Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central C ...
.
** The Marble Hill neighborhood of Manhattan
Manhattan (), known regionally as the City, is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the five Boroughs of New York City, boroughs of New York City. The borough is also coextensive with New York County, one of the List of co ...
was separated from the rest of the borough by the construction of the Harlem Ship Canal in 1895 and then connected to the North American mainland and the Bronx
The Bronx () is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Bronx County, in the state of New York. It is south of Westchester County; north and east of the New York City borough of Manhattan, across the Harlem River; and north of the New ...
when the Harlem River was filled in on its north side in 1914.
** Although O'Hare International Airport is located in Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = List of sovereign states, Count ...
, it can only be reached directly from the rest of the city by passing through the suburban edge city of Rosemont Rosemont may refer to:
* Rosemont (horse), an American Thoroughbred racehorse
* ''Rosemont'', a 2015 film Places
In Australia
* Rosemont (Woollahra), located in the Sydney suburb of Woollahra and listed on the NSW State Heritage Register
In Canada ...
.
Enclaves within enclaves

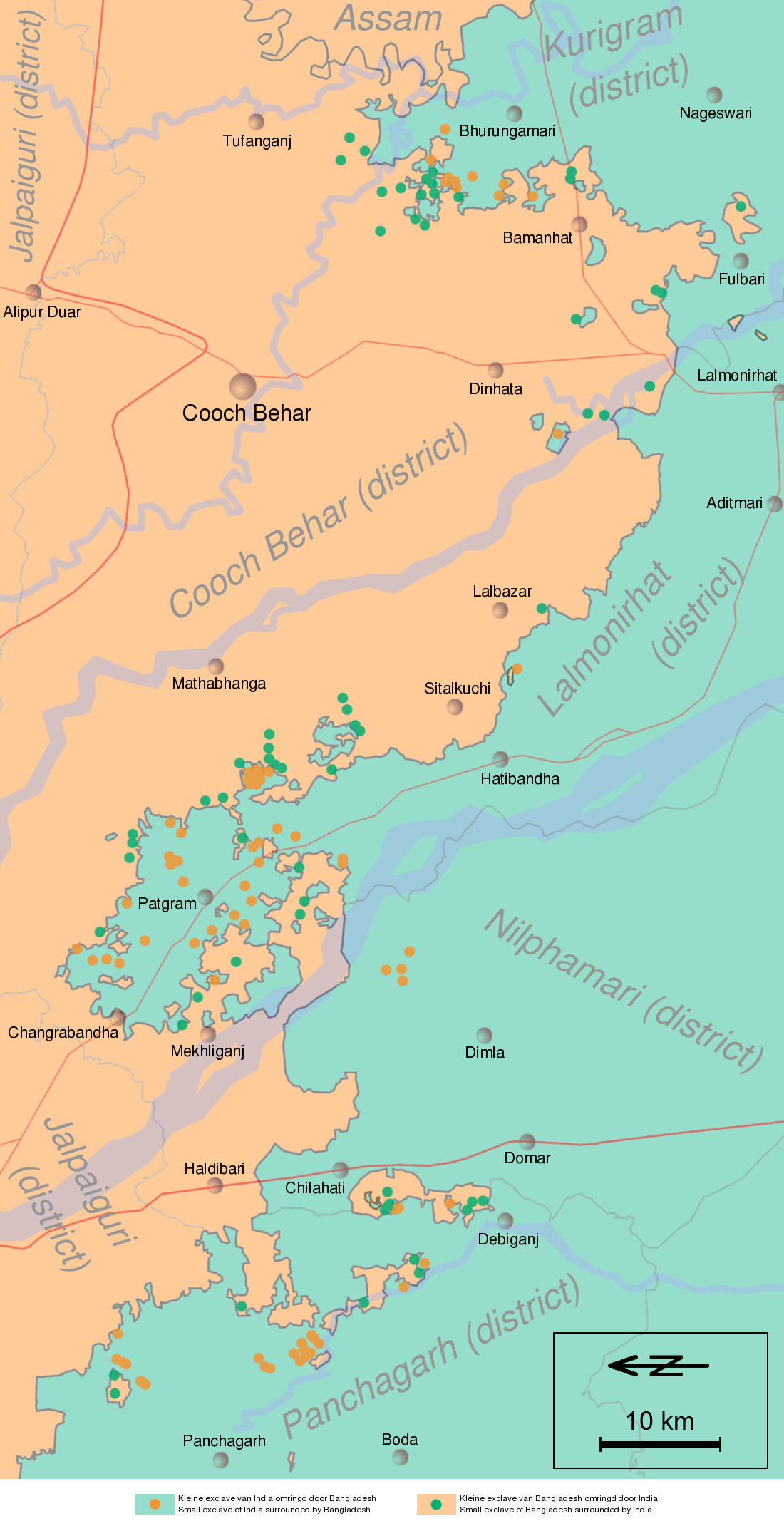 It is possible for an enclave of one country to be completely surrounded by a part of another country that is itself an enclave of the first country. These enclaves are sometimes called ''counter-enclaves''. Two such complexes containing them exist currently:
*The Dutch municipality of Baarle-Nassau has seven exclaves in two exclaves of the Belgian municipality of Baarle-Hertog.
* Nahwa of the
It is possible for an enclave of one country to be completely surrounded by a part of another country that is itself an enclave of the first country. These enclaves are sometimes called ''counter-enclaves''. Two such complexes containing them exist currently:
*The Dutch municipality of Baarle-Nassau has seven exclaves in two exclaves of the Belgian municipality of Baarle-Hertog.
* Nahwa of the United Arab Emirates
The United Arab Emirates (UAE; ar, اَلْإِمَارَات الْعَرَبِيَة الْمُتَحِدَة ), or simply the Emirates ( ar, الِْإمَارَات ), is a country in Western Asia ( The Middle East). It is located at ...
is surrounded by Madha, an exclave of Oman
Oman ( ; ar, عُمَان ' ), officially the Sultanate of Oman ( ar, سلْطنةُ عُمان ), is an Arabian country located in southwestern Asia. It is situated on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula, and spans the mouth of ...
within the U.A.E.
The former complex of enclaves at Cooch Behar district included 24 second-order enclaves and one small third-order enclave called '' Dahala Khagrabari #51'': a piece of India within a part of Bangladesh, within a part of India, within Bangladesh. The Indo-Bangladesh enclaves were exchanged on 31 July 2015 by the ratified Land Boundary Agreement, and Dahala Khagrabari was ceded to Bangladesh.
The border arrangements concerning the Vennbahn meant that, from 1922 to 1949, a Belgian counter-enclave existed within a German enclave.
Ethnic enclaves
An ethnic enclave is a community of an ethnic group inside an area in which another ethnic group predominates. Ghettos, Little Italys, barrios and Chinatowns are examples. These areas may have a separate language, culture and economic system.
* Székely Land is a Hungarian ethnic enclave within Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, a ...
, with its people calling themselves Székely Székely may refer to:
*Székelys, Hungarian people from the historical region of Transylvania, Romania
**Székely Land, historic and ethnographic area in Transylvania, Romania
* Székely (village), a village in northeastern Hungary
*Székely (sur ...
. Originally, the name ''Székely Land'' denoted an autonomous region within Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the ...
. It existed as a legal entity from medieval times until the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867, when the Székely and Saxon
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country ( Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the No ...
seats were dissolved and replaced by the county system. Along with Transylvania, it became a part of Romania in 1920, according with the Treaty of Trianon signed on 4 June 1920 at the Grand Trianon Palace in Versailles, France. In 1938–1940, during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, post-Trianon Hungary temporarily expanded its territory and included some additional territories that were formerly part of the pre-war Kingdom of Hungary, under Third Reich auspices, the Second Vienna Award. It was later reduced to boundaries approximating those of 1920 by the peace treaties signed after World War II at Paris, in 1947. The area was called Magyar Autonomous Region between September 8, 1952 and February 16, 1968, a Hungarian autonomous region within Romania, and today there are territorial autonomy initiatives to reach a higher level of self-governance for this region within Romania.
* There are several Serb enclaves in Kosovo where the institutions of Kosovo
Kosovo ( sq, Kosova or ; sr-Cyrl, Косово ), officially the Republic of Kosovo ( sq, Republika e Kosovës, links=no; sr, Република Косово, Republika Kosovo, links=no), is a partially recognised state in Southeast Eur ...
are not fully operational due to disputes.
Extraterritoriality
Diplomatic missions, such as embassies and consulates, as well as military bases, are usually exempted from the jurisdiction of the host country, i.e., the laws of the host nation in which an embassy is located do not typically apply to the land of the embassy or base itself. This exemption from the jurisdiction of the host country is defined as extraterritoriality
In international law, extraterritoriality is the state of being exempted from the jurisdiction of local law, usually as the result of diplomatic negotiations.
Historically, this primarily applied to individuals, as jurisdiction was usually cl ...
. Areas and buildings enjoying some forms of extraterritoriality are not true enclaves since, in all cases, the host country retains full sovereignty. In addition to embassies, some other areas enjoy a limited form of extraterritoriality.
Examples of this include:
* Pavillon de Breteuil
The Pavillon de Breteuil is the headquarters of the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM). The building lies in the southeastern section of the Parc de Saint-Cloud in Saint-Cloud, France, to the west of Paris. It is listed in Fran ...
in France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
, used by the General Conference on Weights and Measures.
* United Nations headquarters in the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
, used by the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmonizi ...
.
* United Nations Office at Geneva in Switzerland, used by the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmonizi ...
.
* INTERPOL
The International Criminal Police Organization (ICPO; french: link=no, Organisation internationale de police criminelle), commonly known as Interpol ( , ), is an international organization that facilitates worldwide police cooperation and cr ...
headquarters in Lyon
Lyon,, ; Occitan: ''Lion'', hist. ''Lionés'' also spelled in English as Lyons, is the third-largest city and second-largest metropolitan area of France. It is located at the confluence of the rivers Rhône and Saône, to the northwest of ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
, used by INTERPOL
The International Criminal Police Organization (ICPO; french: link=no, Organisation internationale de police criminelle), commonly known as Interpol ( , ), is an international organization that facilitates worldwide police cooperation and cr ...
.
* NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
(political) headquarters near Evere in Haren, a part of the City of Brussels, Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to ...
.
* Headquarters of Allied Command Operations
Allied Command Operations (ACO) is one of the two strategic commands of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), the other being Allied Command Transformation (ACT). The headquarters and commander of ACO is Supreme Headquarters Allied Po ...
(NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
) at the area designated as Supreme Headquarters Allied Powers Europe
Supreme Headquarters Allied Powers Europe (SHAPE) is the military headquarters of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization's (NATO) Allied Command Operations (ACO) that commands all NATO operations worldwide. ACO's and SHAPE's commander is t ...
(SHAPE), north of Mons, Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to ...
.
* Palazzo Malta and the Villa del Priorato di Malta, the headquarters of Sovereign Military Order of Malta in Rome. In addition to extraterritoriality, Italy recognizes the exercise by SMOM of all the prerogatives of sovereignty in its headquarters. Therefore, Italian sovereignty and SMOM sovereignty uniquely coexist without overlapping.
* Extraterritorial properties of the Holy See in Rome and surroundings.
* By treaty of 2 November 1929, Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918–19391945–1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
obtained the lease for 99 years of two plots of land (in the Moldauhafen and in the Saalehafen
Moldauhafen is a lot in the port of Hamburg, Germany that Czechoslovakia acquired on a 99-year lease in 1929 pursuant to the Treaty of Versailles. In 1993, the Czech Republic succeeded to the rights of Czechoslovakia. The lease will expire in 202 ...
), both within the perimeter of the free port of Hamburg
Hamburg (, ; nds, label=Hamburg German, Low Saxon, Hamborg ), officially the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg (german: Freie und Hansestadt Hamburg; nds, label=Low Saxon, Friee un Hansestadt Hamborg),. is the List of cities in Germany by popul ...
. Another plot, in the Peutehafen
Moldauhafen is a lot in the port of Hamburg, Germany that Czechoslovakia acquired on a 99-year lease in 1929 pursuant to the Treaty of Versailles. In 1993, the Czech Republic succeeded to the rights of Czechoslovakia. The lease will expire in 202 ...
, was purchased by the Czechoslovak government in 1929; this plot lies just outside the free-port perimeter.
** Saalehafen – approximately 2 ha of land on Hallesches Ufer, on the southeastern bank of the Saalehafen.
** Moldauhafen – approximately 0.5 ha of land on Dresdener Ufer, on the southeastern bank of the Moldauhafen.
** Peutehafen – the narrow peninsula between the Peutekanal and the Peutehafen dock, comprising 8.054 ha of land and 0.5 ha of water surface.
* In Szczecin, Poland, a similar provision existed following the Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles (french: Traité de Versailles; german: Versailler Vertrag, ) was the most important of the peace treaties of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June 1 ...
for Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918–19391945–1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
to have access to the harbor, which until the end of World War II was located in Germany. From 1945, when Szczecin became part of Poland, Czechoslovakia possessed no extraterritorial rights there. It appears that the German concession ceased at the end of the war and that no successor paid attention to the pre-war rights that Czechoslovakia had under the Versailles Treaty. Neither the Polish nor the occupying Russians appear to have assumed any of Germany's pre-war liabilities. Czechoslovakia gave up the rights to its territory in Szczecin under an agreement signed on 13 January 1956.
* Saimaa Canal: the longitudinal half of the canal in Russia is leased by Finland until 2063. Russian law is in principle valid, but in reality, Finland maintains the area.
* Under a treaty between the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
and the Kingdom of the Netherlands
, national_anthem = )
, image_map = Kingdom of the Netherlands (orthographic projection).svg
, map_width = 250px
, image_map2 = File:KonDerNed-10-10-10.png
, map_caption2 = Map of the four constituent countries shown to scale
, capital = ...
, a Scottish Court was established at Camp Zeist near Utrecht for the trial of those accused in the Lockerbie bombing. The premises were under the authority of the court and immune from external interference for the duration of the trial and subsequent appeal, which lasted from 1999 to 2002. Dutch law continued to apply there in principle but the court was allowed to enact superseding regulations, and court officials enjoyed diplomatic immunity. Contrary to a popular misconception, the area did not become territory of the United Kingdom and the Netherlands retained sovereignty over it as the host country, similar to the status of diplomatic missions.
Land owned by a foreign country
 One or more parcels/holdings of land in most countries is owned by other countries. Most instances are exempt from taxes. In the special case of embassies/consulates these enjoy special privileges driven by international consensus particularly the mutual wish to ensure free
One or more parcels/holdings of land in most countries is owned by other countries. Most instances are exempt from taxes. In the special case of embassies/consulates these enjoy special privileges driven by international consensus particularly the mutual wish to ensure free diplomatic mission
A diplomatic mission or foreign mission is a group of people from a state or organization present in another state to represent the sending state or organization officially in the receiving or host state. In practice, the phrase usually den ...
s, such as being exempt from major hindrances and host-country arrests in ordinary times on the premises. Most non-embassy lands in such ownership are also not enclaves as they fall legally short of ''extraterritoriality'', they are subject to alike court jurisdiction as before their grant/sale in most matters. Nonetheless, for a person's offence against the property itself, equally valid jurisdiction in criminal matters is more likely than elsewhere, assuming the perpetrator is found in the prosecuting authority's homeland. Devoid of permanent residents, formally defined new sovereignty
Sovereignty is the defining authority within individual consciousness, social construct, or territory. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within the state, as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the perso ...
is not warranted or asserted in the examples below. Nonetheless, minor laws, especially on flag flying, are sometimes relaxed to accommodate the needs of the accommodated nation's monument.
Embassies enjoy many different legal statuses approaching quasi-sovereignty, depending on the agreements reached and in practice upheld from time-to-time by host nations. Subject to hosts adhering to basic due process of international law
International law (also known as public international law and the law of nations) is the set of rules, norms, and standards generally recognized as binding between states. It establishes normative guidelines and a common conceptual framework for ...
, including giving warnings, the enforced reduction of scope of a foreign embassy has always been a possibility, even to the point of expelling the foreign embassy entirely, usually on a breakdown of relations, in reaction to extreme actions such as espionage
Espionage, spying, or intelligence gathering is the act of obtaining secret or confidential information ( intelligence) from non-disclosed sources or divulging of the same without the permission of the holder of the information for a tang ...
, or as another form of sanction. The same seems to be possible in profit-driven moving or drilling under any of the sites below, providing safeguards as the structure or a new replacement site. The same possible curtailments and alterations never apply to proper exclaves.
Examples of such land other than for diplomatic missions are:
* Napoleon's original grave in Longwood, Saint Helena, owned by France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
.
* Victor Hugo
Victor-Marie Hugo (; 26 February 1802 – 22 May 1885) was a French Romantic writer and politician. During a literary career that spanned more than sixty years, he wrote in a variety of genres and forms. He is considered to be one of the great ...
's house in Saint Peter Port (Saint-Pierre-Port), Guernsey, owned by the city of Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. ...
.
* The Brest memorial in Brest, France
Brest (; ) is a port city in the Finistère department, Brittany. Located in a sheltered bay not far from the western tip of the peninsula, and the western extremity of metropolitan France, Brest is an important harbour and the second French ...
is owned by the U.S. It commemorates World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
.
* The Normandy American Cemetery and Memorial in Normandy, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
, which contains the graves of 9,386 American military dead, most of whom died during the landings and ensuing operations of World War II, owned by the United States of America
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territor ...
.[Sourc]
American Battle Monument Commission
* Pointe du Hoc, the 13-hectare site of a memorial and museum dedicated to the World War II Normandy landing
The Normandy landings were the landing operations and associated airborne operations on Tuesday, 6 June 1944 of the Allied invasion of Normandy in Operation Overlord during World War II. Codenamed Operation Neptune and often referred to as ...
at Omaha Beach, France, transferred to the U.S. on 11 January 1979.
* The to Russia's final Generalissimo Alexander Suvorov
Alexander Vasilyevich Suvorov (russian: Алекса́ндр Васи́льевич Суво́ров, Aleksándr Vasíl'yevich Suvórov; or 1730) was a Russian general in service of the Russian Empire. He was Count of Rymnik, Count of the Holy ...
near Göschenen in central Switzerland, was erected 99 years after his death by the Russian Empire.
* The Vimy Memorial in France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
, which commemorates the Battle of Vimy Ridge. The French government permanently granted the about to Canada as a war memorial in 1922 in recognition of Canada's military contributions in World War I in general and at Vimy Ridge in particular.
* Two cemeteries on the Outer Banks
The Outer Banks (frequently abbreviated OBX) are a string of barrier islands and spits off the coast of North Carolina and southeastern Virginia, on the east coast of the United States. They line most of the North Carolina coastline, separating ...
of North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia a ...
, United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
: one on Ocracoke Island and one on Hatteras Island in the town of Buxton
Buxton is a spa town in the High Peak, Derbyshire, Borough of High Peak, Derbyshire, England. It is England's highest market town, sited at some above sea level.[United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...]
hosting the British seamen washed ashore after World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
U-boat
U-boats were naval submarines operated by Germany, particularly in the First and Second World Wars. Although at times they were efficient fleet weapons against enemy naval warships, they were most effectively used in an economic warfare ro ...
attacks of 10 April (one from the ''San Delfino'') and 11 May 1942 (five from HMT ''Bedfordshire''). Four graves are at Ocracoke and two at Buxton; three of the bodies were never identified; one of them could be that of a Canadian seaman.Commonwealth War Graves Commission
The Commonwealth War Graves Commission (CWGC) is an intergovernmental organisation of six independent member states whose principal function is to mark, record and maintain the graves and places of commemoration of Commonwealth of Nations mi ...
for as long as the land remained a cemetery.Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only ...
, United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
, the place where James Cook was killed in 1779, is owned by the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
. An historian on the occasion of the monument's 50th anniversary recorded in 1928 that the white stone "obelisk monument aserected to the memory of Captain Cook, about 1876, and on land deeded outright to the British Government by Princess Likelike, sister of King Kalakaua
King is the title given to a male monarch in a variety of contexts. The female equivalent is queen, which title is also given to the consort of a king.
*In the context of prehistory, antiquity and contemporary indigenous peoples, the tit ...
, about the same year, so that that square is absolute British Territory." Hawaii was a sovereign nation at the time. According to MacFarlane, "The land under the monument was deeded to the United Kingdom in 1877 and is considered as sovereign non-embassy land owned by the British Embassy in Washington DC. ... the Hawaiian State Parks agency maintained that as sovereign British territory it was the responsibility of the UK to maintain the site."
* Tiwinza in Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = Seal (emblem), National seal
, national_motto = "Fi ...
: In the 1998 peace agreement following the 1995 Cenepa War, Peru ceded to Ecuador the property, but not the sovereignty, of one square kilometre within Tiwinza (where 14 Ecuadorian soldiers were buried). Ecuador had established a frontier military outpost in Tiwinza, an area that was specified in the agreement as belonging to Peru.
 * The land under the John F. Kennedy memorial at Runnymede,
* The land under the John F. Kennedy memorial at Runnymede, United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
was transferred from the Crown Estates to the United States of America
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territor ...
by the John F. Kennedy Memorial Act 1964 (an Act of the U.K. Parliament
The Parliament of the United Kingdom is the supreme legislative body of the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories. It meets at the Palace of Westminster, London. It alone possesses legislative supremacy ...
); however, it is in the care of the U.K.-based Kennedy Memorial Trust.
* The Tomb of Suleyman Shah (of Suleyman Shah, the grandfather of Osman I, the founder of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
) in Aleppo Governorate
Aleppo Governorate ( ar, محافظة حلب / ALA-LC: ''Muḥāfaẓat Ḥalab'' / ) is one of the fourteen governorates of Syria. It is the most populous governorate in Syria with a population of more than 4,867,000 (2011 Est.), almost 23% of ...
, Syria, is the property of Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
. Article 9 of the Treaty of Ankara Treaty of Ankara may refer to:
*Treaty of Ankara (1921)
*Treaty of Ankara (1926)
The Treaty of Ankara (1926), also known as The Frontier Treaty of 1926 ( tr, Ankara Anlaşması), was signed 5 June 1926 in Ankara by Turkey, United Kingdom and M ...
signed between France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
and Turkey in 1921, provides that the tomb "shall remain, with its appurtenances, the property of Turkey, who may appoint guardians for it and may hoist the Turkish flag there".
* Property and land owned by Sultan of Johor in Singapore, due to historical tie between the two. Notably the Temenggong Daeng Ibrahim Mosque in Singapore is administered by Majlis Agama Islam Johor instead of Islamic Religious Council of Singapore
Unusual cross-border transport channels
National railway passing through another state's territory
Changes in borders can make a railway that was previously located solely within a country traverse the new borders. Since diverting a railway is expensive, this arrangement may last a long time. This may mean that doors on passenger trains are locked and guarded to prevent illicit entry and exit while the train is temporarily in another country. Borders can also be in the "wrong" place, forcing railways into difficult terrain. In large parts of Europe, where the Schengen Area has eliminated border controls when travelling between its 27 member countries, this problem no longer exists, and railways can criss-cross borders with no need for border controls or locked trains.
Examples include:
Africa
 * Due to inability to agree in 1963 on a shorter route through easy terrain, the iron ore railway in Mauritania originally had to use a longer route through a tunnel (built through 2 km of solid
* Due to inability to agree in 1963 on a shorter route through easy terrain, the iron ore railway in Mauritania originally had to use a longer route through a tunnel (built through 2 km of solid granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies und ...
) near Choum to avoid the territory of Spanish Sahara. The tunnel is no longer in use and trains now use the shorter route through 5 km of Western Saharan territory controlled by the Polisario Front.
* In 2013, in Mozambique
Mozambique (), officially the Republic of Mozambique ( pt, Moçambique or , ; ny, Mozambiki; sw, Msumbiji; ts, Muzambhiki), is a country located in southeastern Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Mala ...
, the shortest railway route from coal mines at Tete to a port at Nacala passes through Malawi
Malawi (; or aláwi Tumbuka: ''Malaŵi''), officially the Republic of Malawi, is a landlocked country in Southeastern Africa that was formerly known as Nyasaland. It is bordered by Zambia to the west, Tanzania to the north and northe ...
. A route through solely Mozambican territory is circuitous.
* In 1928, Congo (Belgium) and Angola (Portugal) exchanged some land to facilitate the new route of the railway to Congo-Kinshasa.
Americas
* Bolivia
, image_flag = Bandera de Bolivia (Estado).svg
, flag_alt = Horizontal tricolor (red, yellow, and green from top to bottom) with the coat of arms of Bolivia in the center
, flag_alt2 = 7 × 7 square p ...
is landlocked and has no access to the sea, but a rail route runs through Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the eas ...
from La Paz to the port of Arica on the Pacific Ocean. The rail route was built by Chile under the , with the Bolivian section transferred to Bolivia after 15 years. Bolivia enjoyed duty-free use of the railway and the ports connected.
* The International Railway of Maine was a railroad constructed by the Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR) between Lac-Mégantic, Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Government of Canada, Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is ...
, and Mattawamkeag
Mattawamkeag is a town in Penobscot County, Maine, United States, located where the Mattawamkeag River joins the Penobscot River. The population was 596 at the 2020 census. The village of Mattawamkeag is in the southwest part of the town.
Railr ...
, Maine
Maine () is a U.S. state, state in the New England and Northeastern United States, Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Provinces and territories of Canad ...
, closing a key gap in the railway's transcontinental main line to the port of Saint John, New Brunswick
New Brunswick (french: Nouveau-Brunswick, , locally ) is one of the thirteen Provinces and territories of Canada, provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime Canada, Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic Canad ...
.United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
made the Gadsden Purchase
The Gadsden Purchase ( es, region=MX, la Venta de La Mesilla "The Sale of La Mesilla") is a region of present-day southern Arizona and southwestern New Mexico that the United States acquired from Mexico by the Treaty of Mesilla, which took effe ...
of land from Mexico
Mexico ( Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guate ...
, on which it was planned to build a southern route for the transcontinental railroad. Owing to the topography of the area, acquisition of the land was the only feasible way to construct such a railroad through the southern New Mexico Territory.
* The former San Diego and Arizona Railway, completed in 1919, ran between the California cities of San Diego and El Centro with 71 km of track in Mexico between Tijuana and Tecate. The Mexican segment is now operated as the short line Baja California Railroad.
Europe
= Current
=
* Salzburg
Salzburg (, ; literally "Salt-Castle"; bar, Soizbuag, label=Austro-Bavarian) is the fourth-largest city in Austria. In 2020, it had a population of 156,872.
The town is on the site of the Roman settlement of ''Iuvavum''. Salzburg was founded ...
to Innsbruck (Austria) passes through Rosenheim, Germany. A railway line within Austria exists as well, but trains take about 1.5 hours longer than across German territory.
* Trains on the Birsig Valley Line from Basel
, french: link=no, Bâlois(e), it, Basilese
, neighboring_municipalities= Allschwil (BL), Hégenheim (FR-68), Binningen (BL), Birsfelden (BL), Bottmingen (BL), Huningue (FR-68), Münchenstein (BL), Muttenz (BL), Reinach (BL), Riehen (BS) ...
to Rodersdorf, Switzerland, which passes through Leymen, France. It is operated by Baselland Transport and serviced by line no. 10, which continues into the Basel tram network.
* The Hochrheinbahn
The High Rhine Railway (german: Hochrheinbahn) is the Deutsche Bahn railway line from Basel to Singen. It is also part of the tri-national S-Bahn Basel and referenced as . It was built by the Grand Duchy of Baden State Railways as part of the B ...
(High Rhine Railway) from Basel
, french: link=no, Bâlois(e), it, Basilese
, neighboring_municipalities= Allschwil (BL), Hégenheim (FR-68), Binningen (BL), Birsfelden (BL), Bottmingen (BL), Huningue (FR-68), Münchenstein (BL), Muttenz (BL), Reinach (BL), Riehen (BS) ...
via Waldshut to Schaffhausen
Schaffhausen (; gsw, Schafuuse; french: Schaffhouse; it, Sciaffusa; rm, Schaffusa; en, Shaffhouse) is a town with historic roots, a municipality in northern Switzerland, and the capital of the canton of the same name; it has an estimat ...
is part of the Deutsche Bahn
The (; abbreviated as DB or DB AG) is the national railway company of Germany. Headquartered in the Bahntower in Berlin, it is a joint-stock company ( AG). The Federal Republic of Germany is its single shareholder.
describes itself as the ...
network, and is mostly in Germany, but the two ends are in Switzerland and it is only connected with the rest of the German railway network via Switzerland. At both Basel and Schaffhausen the railway has extraterritorial status: one can travel by train to and from the rest of Germany without going through Swiss customs, despite travelling over territory of the Swiss Customs Area. See Basel Badischer Bahnhof.
* Trains from Neugersdorf, Saxony to Zittau
Zittau ( hsb, Žitawa, dsb, Žytawa, pl, Żytawa, cs, Žitava, Upper Lusatian Dialect: ''Sitte''; from Slavic "''rye''" (Upper Sorbian and Czech: ''žito'', Lower Sorbian: ''žyto'', Polish: ''żyto'')) is the southeasternmost city in the Ger ...
pass Czech territory at Varnsdorf, while Czech trains from Varnsdorf to Chrastava
Chrastava (; german: Kratzau) is a town in Liberec District in the Liberec Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 6,300 inhabitants.
Administrative parts
Chrastava is made up of town parts of Chrastava, Dolní Chrastava and Horní Chrastava, ...
pass through German territory at Zittau, and then a small part of Polish territory near the village of Porajów
Porajów (german: Großporitsch) is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Bogatynia, within Zgorzelec County, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, in south-western Poland, close to the Czech and German borders.
Location
It lies approximatel ...
.
* Trains from Görlitz to Zittau
Zittau ( hsb, Žitawa, dsb, Žytawa, pl, Żytawa, cs, Žitava, Upper Lusatian Dialect: ''Sitte''; from Slavic "''rye''" (Upper Sorbian and Czech: ''žito'', Lower Sorbian: ''žyto'', Polish: ''żyto'')) is the southeasternmost city in the Ger ...
, Germany, pass the border river Neisse several times (see Oder–Neisse line
The Oder–Neisse line (german: Oder-Neiße-Grenze, pl, granica na Odrze i Nysie Łużyckiej) is the basis of most of the international border between Germany and Poland from 1990. It runs mainly along the Oder and Lusatian Neisse rivers ...
); the railway station for Ostritz
Ostritz (, hsb, Wostrowc) is a town in the district Görlitz, in Saxony, Germany. It is situated on the border with Poland, on the left bank of the Lusatian Neisse, 16 km south of Görlitz.
It was the scene of a small battle in the Se ...
, Germany, lies in Krzewina Zgorzelecka, Poland.
* Belgrade–Bar railway crosses into Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and ...
for , between stations Zlatibor and Priboj (both in Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hung ...
). There is one station, Štrpci, but there are no border-crossing facilities, and trains do not call at the station.
* The Knin – Bihać railway between Croatia and Bosnia is split by the Croatian–Bosnian border several times. Similarly, the Savski Marof – Imeno railway was split by the Slovenian–Croatian border several times.
* Lučenec – Veľký Krtíš
Veľký Krtíš (before 1927 ''Veľký Krtýš'', hu, Nagykürtös) is a town in middle Slovakia, situated in the historical Novohrad region. The town's most important economic sectors are mining and agriculture.
Etymology
The name is of Hunga ...
line in Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the ...
passes through Hungary from Ipolytarnóc to Nógrádszakál.
* The local trains on the Burgenlandbahn in Austria cross the area of Hungary at Sopron. During the era of the Iron Curtain, the trains had their doors locked as they traversed Hungarian territory.
* The line from Ventimiglia to Limone Piemonte, Italy, via Breil-sur-Roya, France.
* The railway between France and Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
briefly leaves France to enter Monaco
Monaco (; ), officially the Principality of Monaco (french: Principauté de Monaco; Ligurian: ; oc, Principat de Mónegue), is a sovereign
''Sovereign'' is a title which can be applied to the highest leader in various categories. The word ...
before entering France once more. The railway has a 5300-metre tunnel that goes through Monaco and further, and has an underground station in Monaco.
* For the Belgian Vennbahn (now a cycleway) narrow strips of Belgian territory were created running through Germany, creating five German exclaves.
* The former Soviet republics have numerous examples:
** Semikhody – Chernihiv-Ovruch railway of Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian invas ...
passes through Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...
territory.[ Railway Gazette International April 2008 p 240]
** Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...
/ Lithuania: Adutiškis railway station straddles the Lithuania/Belarus border. Trains pass through Lithuanian territory while traveling to and from Belarus, and platforms are in both Belarus and Lithuania. The station is now mainly used for freight.
** Druzhba – Vorozhba
Vorozhba (, ) is a city in Bilopillia Raion, Sumy Oblast
Sumy Oblast ( uk, Сумська́ о́бласть, translit=Sumska oblast; also referred to as Sumshchyna – uk, Су́мщина) is an oblast (province) in the northeastern part o ...
line of Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian invas ...
passes through Russian territory.Schaffhausen
Schaffhausen (; gsw, Schafuuse; french: Schaffhouse; it, Sciaffusa; rm, Schaffusa; en, Shaffhouse) is a town with historic roots, a municipality in northern Switzerland, and the capital of the canton of the same name; it has an estimat ...
and Rafz pass through the German towns of Jestetten and Lottstetten.
= Historical
=
* During the Cold War, underground lines in West Berlin ran under parts of East Berlin. Ghost stations (german: Geisterbahnhöfe) were stations on Berlin's U-Bahn and S-Bahn metro networks that were closed during this period of Berlin's division.
* In Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bo ...
, Porkkala was leased to the Soviet Union as a Soviet naval base between 1944 and 1956. Porkkala is located on the Rantarata, the main railway line between Helsinki
Helsinki ( or ; ; sv, Helsingfors, ) is the Capital city, capital, primate city, primate, and List of cities and towns in Finland, most populous city of Finland. Located on the shore of the Gulf of Finland, it is the seat of the region of U ...
and Turku. Initially, only Soviet traffic was permitted through, forcing Finnish State Railways to reroute the trains through a circuitous route via Toijala. However, in 1947, the Soviets agreed to let Finnish trains through. At the border, Finnish trains were shunted to a Soviet locomotive, windows were shuttered, guards were posted to the doors, and the Soviet locomotive would pull the train through the base area, to be shunted back to a Finnish locomotive at the opposite border.
= Proposals
=
* The shortest and straightest route for a proposed east–west high-speed railway in Austria through Linz
Linz ( , ; cs, Linec) is the capital of Upper Austria and third-largest city in Austria. In the north of the country, it is on the Danube south of the Czech border. In 2018, the population was 204,846.
In 2009, it was a European Capital ...
, Salzburg
Salzburg (, ; literally "Salt-Castle"; bar, Soizbuag, label=Austro-Bavarian) is the fourth-largest city in Austria. In 2020, it had a population of 156,872.
The town is on the site of the Roman settlement of ''Iuvavum''. Salzburg was founded ...
and Innsbruck would pass under some mountains belonging to Germany.
* In 2012, a railway route was proposed from Angola proper to the enclave of Cabinda crossing not only the Congo River but also about 40 km of territory of the Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (french: République démocratique du Congo (RDC), colloquially "La RDC" ), informally Congo-Kinshasa, DR Congo, the DRC, the DROC, or the Congo, and formerly and also colloquially Zaire, is a country in ...
.
Highway of one state passing through another state's territory
This arrangement is less common as highways are more easily re-aligned. Some examples are:
Africa
* Congo Pedicle road: built to provide access for Zambia
Zambia (), officially the Republic of Zambia, is a landlocked country at the crossroads of Central, Southern and East Africa, although it is typically referred to as being in Southern Africa at its most central point. Its neighbours are ...
's Luapula Province to the Copperbelt through of territory of the DR Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (french: République démocratique du Congo (RDC), colloquially "La RDC" ), informally Congo-Kinshasa, DR Congo, the DRC, the DROC, or the Congo, and formerly and also colloquially Zaire, is a country in ...
, requiring a change from driving on the left to driving on the right.
* In Guinea, where 20 km long tunnel(s) through a hillspur at Naigaya
Naigaya is a village in southwest Guinea. It is near the border with Sierra Leone. Its elevation . It is in the Prefecture of Kindia.
Transport
Naigaya is near a proposed railway to a new port at Matakong for iron-ore traffic from mines at ...
(elevation ), Sicourou, Bokariadi Bokariadi is one of a number of towns in Guinea with this name. This is the one in the south east of the country near the border with Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone,)]. officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country on the southwest coas ...
and Feraya might be avoided by crossing the border into Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone,)]. officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country on the southwest coast of West Africa. It is bordered by Liberia to the southeast and Guinea surrounds the northern half of the nation. Covering a total area of , Sierra ...
at Yana, Sierra Leone, Yana (elevation ).
* Senegal
Senegal,; Wolof: ''Senegaal''; Pulaar: 𞤅𞤫𞤲𞤫𞤺𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭 (Senegaali); Arabic: السنغال ''As-Sinighal'') officially the Republic of Senegal,; Wolof: ''Réewum Senegaal''; Pulaar : 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣� ...
is practically and inconveniently divided almost in two by the sovereign territory of The Gambia
The Gambia,, ff, Gammbi, ar, غامبيا officially the Republic of The Gambia, is a country in West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 c ...
. Until the completion of the Senegambia bridge in 2019, the easiest way to travel from northern Senegal to the southern Casamance
, settlement_type = Geographical region
, image_skyline = Senegal Casamance.png
, image_caption = Casamance in Senegal
, image_flag = Flag of Casamance.svg
, image_shield =
, motto ...
region was through Gambia via the Trans-Gambia Highway, with a connecting ferry being the only way to cross the Gambia River. The fare for the ferry crossing is a source of contention between the two countries.
Americas
* East Richford Slide Road in the U.S. state of Vermont
Vermont () is a state in the northeast New England region of the United States. Vermont is bordered by the states of Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, and New York to the west, and the Canadian province of Quebec to the ...
crosses into the Canadian
Canadians (french: Canadiens) are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of ...
province of Québec for a distance of approximately 100 metres (300 feet) before returning to the United States. A cemetery lies directly on the border vista.
Asia
* The road from Dubai
Dubai (, ; ar, دبي, translit=Dubayy, , ) is the most populous city in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and the capital of the Emirate of Dubai, the most populated of the 7 emirates of the United Arab Emirates.The Government and Politics ...
to the tourist spot of Hatta, an exclave of the emirate of Dubai, passes through a small stretch of Oman
Oman ( ; ar, عُمَان ' ), officially the Sultanate of Oman ( ar, سلْطنةُ عُمان ), is an Arabian country located in southwestern Asia. It is situated on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula, and spans the mouth of ...
i territory.
* The highway between Bishkek
Bishkek ( ky, Бишкек), ), formerly Pishpek and Frunze, is the capital and largest city of Kyrgyzstan. Bishkek is also the administrative centre of the Chüy Region. The region surrounds the city, although the city itself is not part of ...
and Issyk Kul, both in Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan,, pronounced or the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Kyrgyzstan is bordered by Kazakhstan to the north, Uzbekistan to the west, Tajikistan to the south, and the People's Republic of China to the ea ...
, skirts the border with Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental coun ...
, with the highway and the border crossing each other for short distances at various points.
Europe
* Various roads cross the Republic of Ireland–United Kingdom border, back and forth between the Republic of Ireland
Ireland ( ga, Éire ), also known as the Republic of Ireland (), is a country in north-western Europe consisting of 26 of the 32 Counties of Ireland, counties of the island of Ireland. The capital and largest city is Dublin, on the eastern ...
and Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ga, Tuaisceart Éireann ; sco, label=Ulster-Scots, Norlin Airlann) is a part of the United Kingdom, situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, that is variously described as a country, province or region. North ...
. The N54 in County Monaghan (RoI) twice becomes the A3 in County Fermanagh (NI), before continuing as the N54. Similarly, the N53 in Monaghan passes through County Armagh (NI) as the A37, before resuming as the N53 at a point where County Armagh, County Monaghan and County Louth (RoI) all meet. , no national or border signs are present: the only indication is the change in margin markings and signs to indicate a change in speed limits between mph and km/h. It remains to be seen whether Brexit
Brexit (; a portmanteau of "British exit") was the withdrawal of the United Kingdom (UK) from the European Union (EU) at 23:00 GMT on 31 January 2020 (00:00 1 February 2020 CET).The UK also left the European Atomic Energy Community (EAE ...
will change this friendly arrangement, which has persisted since the Good Friday Agreement
The Good Friday Agreement (GFA), or Belfast Agreement ( ga, Comhaontú Aoine an Chéasta or ; Ulster-Scots: or ), is a pair of agreements signed on 10 April 1998 that ended most of the violence of The Troubles, a political conflict in Nor ...
of 1998.
* Between 1963 and 2002 the N274 road from Roermond to Heerlen, part of Dutch territory, passed through the German Selfkant, which had been annexed by the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
after the Second World War but returned to Germany in 1963.
* Close to Narvik, a road from Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and t ...
twice enters and leaves Swedish
Swedish or ' may refer to:
Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically:
* Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland
** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ...
territory, following the southern shore of the Kjårdavatnet lake. It does not connect with any other Swedish road in either location before it enters Norwegian land once more. It is private and built for hydropower plants but usable for public.
* Norwegian road 92 continues in Finland as road 92 before it continues as road 92 again in Norway. Norwegian road 7012 continues as road Z821 in Sweden before continuing as road 7012 in Norway again. Road Z821 (near Gäddede) had right-hand driving also before 1967 when the rest of Sweden had left-hand driving. These roads are mostly number construction and do not have special privileges.
* Road 402 between Podsabotin and Solkan in Slovenia
Slovenia ( ; sl, Slovenija ), officially the Republic of Slovenia (Slovene: , abbr.: ''RS''), is a country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, and ...
, built when Slovenia was a state of Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label= Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavij ...
, passes through Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
for 1.5 kilometres. This section of the road does not intersect any other roads and is confined by high concrete walls topped by fences. As Slovenia and Italy are now both signatories to the Schengen Agreement, the barriers are little more than historical curiosities, although there is modern signage indicating that photography is forbidden along the Italian part of the road and that stopping is prohibited.
* The Saatse Boot Road in Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and t ...
, between the villages of Lutepää
Lutepää is a small village on the Värska-to-Saatse road in southeast Estonia. (retrieved 28 July 2021)
Lutepää is one of the few villages in the European Union that can only be reached by travelling through Russia. The one and only road thr ...
and Sesniki, passes through Russian territory. The stretch of road passing through Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eigh ...
is flanked by barbed wire fences and guard towers. Stopping and/or getting out of one's vehicle on the stretch of road is forbidden; the rule is enforced by Russian border guards.
* The D8 coastal highway of Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
passes through a small section of Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and ...
territory, at the town of Neum, as it heads south from Split, Croatia to Dubrovnik.
* Geneva Airport in Switzerland has a ''French Sector'', which, while legally and geographically in Switzerland, is a ''de facto'' French domestic terminal used solely for flights to and from destinations in metropolitan France, and staffed by French officials. Thus, prior to Switzerland's accession to the Schengen Area (which entered into force for air travel in March 2009), the French Sector saved the need for border controls for flights between France and Geneva Airport. The French Sector is only accessible by a road connecting it directly to France, which passes through Swiss territory but has no junctions or other physical access to Switzerland. This road leads to a turn-off on the French side of the Ferney-Voltaire border crossing, thus bypassing Swiss passport controls when they were operational before 2009. While Switzerland's membership of the Schengen Area now renders the convenience of avoiding passport controls obsolete, there is still a small advantage gained in using the French Sector: Switzerland is not in the EU Customs Union, so customs (but not passport) checks are still carried out at Switzerland's border posts. The French Sector, with its road that leads directly to France without access to Switzerland, bypasses this requirement.
**EuroAirport
EuroAirport Basel Mulhouse Freiburg IATA airport 3-letter codes for the French area, the Swiss area, and the metropolitan area, french: Aéroport de Bâle-Mulhouse-Fribourg, it, Aeroporto di Basilea-Mulhouse-Friburgo, rm, Eroport da Basilea-Mu ...
on French territory near Basel
, french: link=no, Bâlois(e), it, Basilese
, neighboring_municipalities= Allschwil (BL), Hégenheim (FR-68), Binningen (BL), Birsfelden (BL), Bottmingen (BL), Huningue (FR-68), Münchenstein (BL), Muttenz (BL), Reinach (BL), Riehen (BS) ...
/Mulhouse
Mulhouse (; Alsatian: or , ; ; meaning ''mill house'') is a city of the Haut-Rhin department, in the Grand Est region, eastern France, close to the Swiss and German borders. It is the largest city in Haut-Rhin and second largest in Alsace af ...
is similar. It has a Swiss section with a customs-free road to Switzerland.
**Basel (Badischer) and Geneva railway stations also have similar foreign areas.
Subnational highway passing through other internal territory
Americas
* United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
:
** Interstate 684, connecting various points in New York State
New York, officially the State of New York, is a U.S. state, state in the Northeastern United States. It is often called New York State to distinguish it from its largest city, New York City. With a total area of , New York is the List of U.S. ...
, passes through Connecticut
Connecticut () is the southernmost state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is bordered by Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. Its cap ...
near Kensico Reservoir and Westchester County Airport but is maintained entirely by New York State. Motor vehicles cannot enter from nor exit to Connecticut roads, even though a portion of the highway is owned by Connecticut.
** A portion of New York State Route 17/ Interstate 86 passes through South Waverly, Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; (Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, Ma ...
but is maintained entirely by New York State. This includes the roadway and traffic lights at the interchange with US Route 220 and a short portion of Pennsylvania Route 199
Pennsylvania Route 199 (PA 199) is a state highway located in Bradford County in Pennsylvania. The southern terminus is at U.S. Route 220 (US 220) near Athens. The northern terminus is the New York state line in Sayre, where it connects to ...
. Nevertheless, Pennsylvania police enforce traffic laws on this short stretch, where there is one overpass built and owned by Pennsylvania.
** A portion of New Hampshire Route 153 runs along the border with and briefly passes through Parsonsfield, Maine as it sweeps around the eastern shore of Province Lake.
** Minnesota State Highway 23 passes through about of Wisconsin
Wisconsin () is a state in the upper Midwestern United States. Wisconsin is the 25th-largest state by total area and the 20th-most populous. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake M ...
just west of Duluth, Minnesota
, settlement_type = City
, nicknames = Twin Ports (with Superior), Zenith City
, motto =
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top: urban Duluth skyline; Minnesota ...
.Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; (Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, Ma ...
where the Twelve-Mile Circle meets the Mason–Dixon Line. The road is maintained by Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Maryland to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and New Jersey and the Atlantic Ocean to its east. The state takes its name from the adjacen ...
, and it appears that at one time Arc Corner Road in Pennsylvania may have intersected here. Further east, Beaver Dam Road enters Chadds Ford Township, Pennsylvania at the intersection of Beaver Valley Road and re-enters Delaware about 0.5 miles later. It is unclear who is supposed to maintain the section in Pennsylvania.
** Wyoming Highway 70 enters Moffat County, Colorado for approximately . The route through Colorado is maintained by the Wyoming Department of Transportation.
** Arizona State Route 101 enters the sovereign Salt River Pima–Maricopa Indian Community for approximately as it skirts the eastern edge of Scottsdale, Arizona
, settlement_type = City
, named_for = Winfield Scott
, image_skyline =
, image_seal = Seal of Scottsdale (Arizona).svg
, image_blank_emblem = City of Scottsdale Script Logo.svg
, nick ...
, whose neighborhoods were built out to the reservation boundary prior to construction. Use of the land for the freeway on Tribal land is under a lease agreement. The route is maintained by the Arizona Department of Transportation.
Asia
* India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the ...
** The highway connecting Guwahati
Guwahati (, ; formerly rendered Gauhati, ) is the biggest city of the Indian state of Assam and also the largest metropolis in northeastern India. Dispur, the capital of Assam, is in the circuit city region located within Guwahati and is the ...
(capital of Assam
Assam (; ) is a state in northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of . The state is bordered by Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh to the north; Nagaland and Manipur ...
state) to Silchar (a city in Barak valley of Assam) passes through Meghalaya
Meghalaya (, or , meaning "abode of clouds"; from Sanskrit , "cloud" + , "abode") is a state in northeastern India. Meghalaya was formed on 21 January 1972 by carving out two districts from the state of Assam: (a) the United Khasi Hills and Jai ...
state.
** One has to travel through part of West Bengal
West Bengal (, Bengali: ''Poshchim Bongo'', , abbr. WB) is a state in the eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabitants within an area of . West Bengal is the four ...
while travelling from Jamshedpur (Tatanagar), Jharkhand
Jharkhand (; ; ) is a state in eastern India. The state shares its border with the states of West Bengal to the east, Chhattisgarh to the west, Uttar Pradesh to the northwest, Bihar to the north and Odisha to the south. It has an area of . ...
to a few other cities of Jharkhand like Ranchi
Ranchi (, ) is the capital of the Indian state of Jharkhand. Ranchi was the centre of the Jharkhand movement, which called for a separate state for the tribal regions of South Bihar, northern Odisha, western West Bengal and the eastern area ...
or Dhanbad.
** Kota
Kota or KOTA may refer to:
People and languages
*Kōta (given name), a masculine Japanese given name
*Kota Brahmin, a sub-caste of Brahmins in Karnataka
*Kota people (India), a tribe in the Nilgiri hills of Tamil Nadu, South India
**Kota language ...
, a city in Rajasthan
Rajasthan (; lit. 'Land of Kings') is a state in northern India. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the largest Indian state by area and the seventh largest by population. It is on India's northwestern s ...
surrounded by territory of Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh (, ; meaning 'central province') is a state in central India. Its capital city, capital is Bhopal, and the largest city is Indore, with Jabalpur, Ujjain, Gwalior, Sagar, Madhya Pradesh, Sagar, and Rewa, India, Rewa being the othe ...
, is connected to other parts of Rajasthan by roads passing through Madhya Pradesh.
** Gwalior
Gwalior() is a major city in the central Indian state of Madhya Pradesh; it lies in northern part of Madhya Pradesh and is one of the Counter-magnet cities. Located south of Delhi, the capital city of India, from Agra and from Bhopal, the ...
(Madhya Pradesh) is connected to few other cities of Madhya Pradesh by highways passing through Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh (; , 'Northern Province') is a state in northern India. With over 200 million inhabitants, it is the most populated state in India as well as the most populous country subdivision in the world. It was established in 1950 ...
, covering the city of Jhansi
Jhansi (; Hindi: झांसी, Urdu: ) is a historic city in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It lies in the region of Bundelkhand on the banks of the Pahuj River, in the extreme south of Uttar Pradesh. Jhansi is the administrative ...
.
* Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
:
** The main road for travel to Bartın
Bartın is a city in northern Turkey and the central district of the province of Bartın.
Formerly a district of Zonguldak Province, Bartın was made into a province seat in 1991 with the constitution of its province, including four districts: ...
via Zonguldak actually crosses Bartın first, traverses Zonguldak a short distance, then returns to Bartın.
Border transport infrastructure
Africa
* The Kazungula Bridge connects Zambia
Zambia (), officially the Republic of Zambia, is a landlocked country at the crossroads of Central, Southern and East Africa, although it is typically referred to as being in Southern Africa at its most central point. Its neighbours are ...
and Botswana
Botswana (, ), officially the Republic of Botswana ( tn, Lefatshe la Botswana, label= Setswana, ), is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. Botswana is topographically flat, with approximately 70 percent of its territory being the Kal ...
in Southern Africa
Southern Africa is the southernmost subregion of the African continent, south of the Congo and Tanzania. The physical location is the large part of Africa to the south of the extensive Congo River basin. Southern Africa is home to a number ...
. The shared border between the two countries is approximately 150 m long, in the middle of the Zambezi River
The Zambezi River (also spelled Zambeze and Zambesi) is the fourth-longest river in Africa, the longest east-flowing river in Africa and the largest flowing into the Indian Ocean from Africa. Its drainage basin covers , slightly less than hal ...
, and thus very nearly forms a quadripoint between Zambia, Botswana, Namibia
Namibia (, ), officially the Republic of Namibia, is a country in Southern Africa. Its western border is the Atlantic Ocean. It shares land borders with Zambia and Angola to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south and e ...
, and Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe (), officially the Republic of Zimbabwe, is a landlocked country located in Southeast Africa, between the Zambezi and Limpopo Rivers, bordered by South Africa to the south, Botswana to the south-west, Zambia to the north, and Mozam ...
. Because the border between Zambia and Botswana is so short and because of the orientation of the river banks, the span of the bridge curves to avoid crossing the adjacent territory of Namibia or Zimbabwe.
Americas
* In 2009, the Canada Border Services Agency
The Canada Border Services Agency (CBSA; french: Agence des services frontaliers du Canada, ''ASFC'') is a federal law enforcement agency that is responsible for border control (i.e. protection and surveillance), immigration enforcement, and c ...
relocated its border inspection post from Cornwall Island, Ontario, a border region with the United States, to Cornwall, Ontario, across from the island and thus further inland, after protests erupted over the CBSA's firearm policy on Mohawk Nation
The Mohawk people ( moh, Kanienʼkehá꞉ka) are the most easterly section of the Haudenosaunee, or Iroquois Confederacy. They are an Iroquoian-speaking Indigenous people of North America, with communities in southeastern Canada and northern N ...
’s sovereign land. To avoid severe penalty, people entering from the United States who are destined for the island are required to proceed across the island to report to the new CBSA post in Cornwall before making a U-turn to return to the island. Residents of the island visiting Cornwall or beyond must also report to the CBSA. Those returning to the island from Cornwall are the only group not required to go through any border inspection.
Asia
* The Hong Kong–Shenzhen Western Corridor on the Hong Kong
Hong Kong ( (US) or (UK); , ), officially the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (abbr. Hong Kong SAR or HKSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China on the eastern Pearl River Delta i ...
–mainland China
"Mainland China" is a geopolitical term defined as the territory governed by the People's Republic of China (including islands like Hainan or Chongming), excluding dependent territories of the PRC, and other territories within Greater Chin ...
border: the immigration control points for Hong Kong ( Shenzhen Bay Control Point) and mainland China ( Shenzhen Bay Port) are co-located in the same building on the Shenzhen
Shenzhen (; ; ; ), also historically known as Sham Chun, is a major Sub-provincial division, sub-provincial city and one of the Special economic zones of China, special economic zones of China. The city is located on the east bank of the Pea ...
side of the bridge in an effective pene-exclave. The Hong Kong portion of the service building and the adjoining bridge are leased to Hong Kong, and are under Hong Kong's jurisdiction for an initial period until 30 June 2047.
* The Mainland Port Area in Kowloon High Speed Railway Station in downtown Hong Kong
Hong Kong ( (US) or (UK); , ), officially the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (abbr. Hong Kong SAR or HKSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China on the eastern Pearl River Delta i ...
is under the jurisdiction of the Mainland Chinese authorities and courts. The 30 km long tunnel to the border is under Hong Kong jurisdiction, however, the train compartments of any train in operation (that is carrying passengers to or from the Mainland) are subject to Mainland Laws and jurisdiction. This arrangement was created to allow for immigration clearance to occur in Hong Kong for all trains travelling to and from the Mainland of China. This has stirred much controversy and multiple protests in Hong Kong.
* As a legacy of British Malaya
The term "British Malaya" (; ms, Tanah Melayu British) loosely describes a set of states on the Malay Peninsula and the island of Singapore that were brought under British hegemony or control between the late 18th and the mid-20th century. ...
, the Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two r ...
n rail network had its southern terminus at Tanjong Pagar railway station in central Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, borde ...
. The land on which the station and the rail tracks stood was leased to Keretapi Tanah Melayu, the Malaysian state railway operator. Consequently, Malaysia had partial sovereignty over the railway land.
Europe
* Several bridges cross the rivers Oder and Neisse between Germany and Poland. To avoid needing to coordinate their efforts on a single bridge, the two riparian
A riparian zone or riparian area is the interface between land and a river or stream. Riparian is also the proper nomenclature for one of the terrestrial biomes of the Earth. Plant habitats and communities along the river margins and banks a ...
states assign each bridge to one or the other; thus Poland is responsible for ''all'' maintenance on some of the bridges, including the German side, and vice versa.
* The Hallein Salt Mine crosses from Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
into Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
. Under an 1829 treaty Austria can dig under the then-Kingdom of Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total l ...
. In return some salt has to be given to Bavaria, and up to 99 of its citizens can be hired to work in the Austrian mine.
* The twin town of TornioHaparanda or HaparandaTornio lies at the mouth of river Tornio, Tornio on the Finnish side and Haparanda on the Swedish
Swedish or ' may refer to:
Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically:
* Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland
** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ...
side. The two towns have a common public transportation, as well as cultural services, fire brigade, sports facilities etc.
* The Basel Badischer Bahnhof is a railway station in the Swiss city of Basel. Although situated on Swiss soil, because of the 1852 treaty between the Swiss Confederation and the state of Baden (one of the predecessors of today's Germany), the largest part of the station (the platforms and the parts of the passenger tunnel that lead to the German/Swiss checkpoint) is treated administratively as an inner-German railway station operated by the Deutsche Bahn
The (; abbreviated as DB or DB AG) is the national railway company of Germany. Headquartered in the Bahntower in Berlin, it is a joint-stock company ( AG). The Federal Republic of Germany is its single shareholder.
describes itself as the ...
. The shops in the station hall, however, are Swiss, and the Swiss franc is used as the official currency there (although the euro is universally accepted). The Swiss post office, car rental office, restaurant and a cluster of shops are each separately located wholly within a surrounding station area that is administered by the German railway. The customs controls are located in a tunnel between the platforms and the station hall; international trains that continue to Basel SBB usually had on-board border controls, until they were abolished in 2008 when Switzerland joined the Schengen Area.
* The tram network in the French city of Strasbourg was extended into the neighbouring German city of Kehl in 2017.France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
but are owned, operated and maintained by the Luxembourg National Railway Company, as are the short stretches of railway between the stations and the Luxembourg border. Thus, holders of a Luxembourg railway pass can travel to these stations without requiring a French ticket. The stations are both end stations on different lines and are not physically connected to any French railway. There are no border issues, as both France and Luxembourg are in the Schengen Area. Likewise, a short stretch of narrow-gauge railway line connects Hendaye in south-western France to the rest of the San Sebastián Metro
Euskotren operates frequent commuter rail services in the city of San Sebastián and the surrounding Donostialdea area, in the Basque Country, Spain. The infrastructure is gradually being upgraded to rapid transit standards, in order to creat ...
network over the border in Spain.
* The bus network of Bratislava, the capital of Slovakia, extends to the nearby Austrian village Wolfsthal where the train S7 (Schnellbahn) from Vienna has its terminal station. After the fall of the Iron Curtain, the abandoned rail road track from Wolfsthal to Bratislava could not be reinstalled because the land had been sold for housing projects.
See also
* Baarle
* Baarle-Hertog
* Baarle-Nassau
* Flagpole annexation
Municipal annexation is a process by which a municipality expands its boundaries into nearby, usually adjacent, unincorporated areas. This has been a common response of cities to urbanization in neighboring areas. It may be done because the neighbo ...
* Landlocked country
* Panhandle
A salient (also known as a panhandle or bootheel) is an elongated protrusion of a geopolitical entity, such as a subnational entity or a sovereign state.
While similar to a peninsula in shape, a salient is most often not surrounded by water on ...
* Polynesian outlier
Lists
* List of countries that border only one other country
* List of enclaves and exclaves
* List of ethnic enclaves in North American cities
* List of former foreign enclaves in China
Notes
Bibliography
*
*
External links
Rolf Palmberg's Enclaves of the world
Jan S. Krogh's Geosite
"Tangled Territories" 2005 review article on exclaves and enclaves in Europe published in ''Hidden Europe'' magazine
Evgeny Vinokurov's Theory of Enclaves - a comprehensive economic and political treatment of enclaves and exclaves
{{Terms for types of country subdivisions
Border-related lists
 ''True exclave'' is an extension of the concept of ''true enclave''. In order to access a true exclave from the mainland, a traveller must go through the territory of at least one other state. Examples include:
* Nakhchivan, which borders
''True exclave'' is an extension of the concept of ''true enclave''. In order to access a true exclave from the mainland, a traveller must go through the territory of at least one other state. Examples include:
* Nakhchivan, which borders  * In the United States:
**A portion of Ellis Island is an exclave of
* In the United States:
**A portion of Ellis Island is an exclave of  It is possible for an enclave of one country to be completely surrounded by a part of another country that is itself an enclave of the first country. These enclaves are sometimes called ''counter-enclaves''. Two such complexes containing them exist currently:
*The Dutch municipality of Baarle-Nassau has seven exclaves in two exclaves of the Belgian municipality of Baarle-Hertog.
* Nahwa of the
It is possible for an enclave of one country to be completely surrounded by a part of another country that is itself an enclave of the first country. These enclaves are sometimes called ''counter-enclaves''. Two such complexes containing them exist currently:
*The Dutch municipality of Baarle-Nassau has seven exclaves in two exclaves of the Belgian municipality of Baarle-Hertog.
* Nahwa of the  One or more parcels/holdings of land in most countries is owned by other countries. Most instances are exempt from taxes. In the special case of embassies/consulates these enjoy special privileges driven by international consensus particularly the mutual wish to ensure free
One or more parcels/holdings of land in most countries is owned by other countries. Most instances are exempt from taxes. In the special case of embassies/consulates these enjoy special privileges driven by international consensus particularly the mutual wish to ensure free  * The land under the John F. Kennedy memorial at Runnymede,
* The land under the John F. Kennedy memorial at Runnymede,  * Due to inability to agree in 1963 on a shorter route through easy terrain, the iron ore railway in Mauritania originally had to use a longer route through a tunnel (built through 2 km of solid
* Due to inability to agree in 1963 on a shorter route through easy terrain, the iron ore railway in Mauritania originally had to use a longer route through a tunnel (built through 2 km of solid