|
Podiata
Podiates ( Cavalier-Smith, 2012, excl. Ancyromonadida) are a proposed clade containing the Amorphea (incl. Opisthokonta, Amoebozoa, apusomonads and breviates) and the organisms now assigned to the clade CRuMs. Ancyromonadida does not appear to have emerged in this grouping. Sarcomastigota (Cavalier-Smith, 1983) is a proposed subkingdom (currently shown to be paraphyletic) that includes all the podiates that are ''not'' animals or fungi. Sulcozoa ( Cavalier-Smith, 2012) is a proposed phylum (currently shown to be paraphyletic) within Sarcomastigota that does not include the phyla Amoebozoa ( clade) and Choanozoa (paraphyletic), i.e. it includes the proposed subphyla Apusozoa The Apusozoa are an Obazoa phylum comprising several genera of flagellate eukaryotes. They are usually around 5–20 μm in size, and occur in soils and aquatic habitats, where they feed on bacteria. They are grouped together based on the presen ... and Varisulca. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q4899589 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varisulca
Varisulca was a proposed basal Podiate taxon. It encompassed several lineages of heterotrophic protists, most notably the ancyromonads (planomonads), collodictyonids (diphylleids), rigifilids (''Rigifila'', ''Micronuclearia'') and mantamonadids. Recent evidence suggests that the latter three are closely related to each other, forming a clade called CRuMs, but that this is unlikely to be specifically related to ancyromonads Cavalier-Smith had proposed the new subphylum Varisulca which consists of the classes Hilomonadea, Diphyllatea and Glissodiscea. The validity of this proposed taxonomy has yet to ruled upon by the Society of Protistologists. It is unlikely to be widely accepted, since Varisulca appears to be paraphyletic or polyphyletic (ancyromonads are not inferred to be the sister group to CRuMs). Glissodiscea and Multirhiza (a taxon encompassing Diphyllatea and Glissodiscea) also appear paraphyletic or polyphyletic, since ''Mantamonas'' belongs to CRuMs but ancyromo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Podiata
Podiates ( Cavalier-Smith, 2012, excl. Ancyromonadida) are a proposed clade containing the Amorphea (incl. Opisthokonta, Amoebozoa, apusomonads and breviates) and the organisms now assigned to the clade CRuMs. Ancyromonadida does not appear to have emerged in this grouping. Sarcomastigota (Cavalier-Smith, 1983) is a proposed subkingdom (currently shown to be paraphyletic) that includes all the podiates that are ''not'' animals or fungi. Sulcozoa ( Cavalier-Smith, 2012) is a proposed phylum (currently shown to be paraphyletic) within Sarcomastigota that does not include the phyla Amoebozoa ( clade) and Choanozoa (paraphyletic), i.e. it includes the proposed subphyla Apusozoa The Apusozoa are an Obazoa phylum comprising several genera of flagellate eukaryotes. They are usually around 5–20 μm in size, and occur in soils and aquatic habitats, where they feed on bacteria. They are grouped together based on the presen ... and Varisulca. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q4899589 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neozoa
The Scotokaryotes (Cavalier-Smith) is a proposed basal Neokaryote clade as sister of the Diaphoretickes. Basal Scotokaryote groupings are the Metamonads, the Malawimonas and the Podiata. In this phylogeny the Discoba are sometimes seen as paraphyletic and basal Eukaryotes. An alternative to the Unikont–Bikont division was suggested by Derelle ''et al.'' in 2015, where they proposed the acronyms Opimoda–Diphoda respectively, as substitutes to the older terms. The name Opimoda is formed from the letters (shown in capitals) of OPIsthokonta and aMOebozoa. In this phylogeny Discoba belongs to the Diphoda clade. Taxonomy A proposed cladogram is See also *Diphoda A bikont ("two flagella") is any of the eukaryotic organisms classified in the group Bikonta. Many single-celled members of the group, and the presumed ancestor, have two flagella. Enzymes Another shared trait of bikonts is the fusion of two ge ... References {{Taxonbar, from=Q21399998 Eukaryote unrank ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opimoda
The Scotokaryotes (Cavalier-Smith) is a proposed basal Neokaryote clade as sister of the Diaphoretickes. Basal Scotokaryote groupings are the Metamonads, the Malawimonas and the Podiata. In this phylogeny the Discoba are sometimes seen as paraphyletic and basal Eukaryotes. An alternative to the Unikont– Bikont division was suggested by Derelle ''et al.'' in 2015, where they proposed the acronyms Opimoda–Diphoda respectively, as substitutes to the older terms. The name Opimoda is formed from the letters (shown in capitals) of OPIsthokonta and aMOebozoa Amoebozoa is a major taxonomic group containing about 2,400 described species of amoeboid protists, often possessing blunt, fingerlike, lobose pseudopods and tubular mitochondrial cristae. In traditional and currently no longer supported c .... In this phylogeny Discoba belongs to the Diphoda clade. Taxonomy A proposed cladogram is See also * Diphoda References {{Taxonbar, from=Q21399998 Eukaryote un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CRuMs
CRuMs is a proposed clade of microbial eukaryotes, whose name is an acronym of the following constituent groups: i) collodictyonids also known as diphylleids, ii) rigifilids and iii) mantamonadids as sister of the Amorphea. It more or less supersedes Varisulca, as Ancyromonadida Ancyromonadida or Planomonadida is a small group of biflagellated protists found in the soil and in aquatic habitats, where they feed on bacteria.Cavalier-Smith, T. (2013)Early evolution of eukaryote feeding modes, cell structural diversity, an ... are inferred not to be specifically related to the orders Collodictyonida, Rigifilida and Mantamonadida. Phylogeny References {{Taxonbar, from=Q59153571 Eukaryote subphyla Podiata ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancyromonadida
Ancyromonadida or Planomonadida is a small group of biflagellated protists found in the soil and in aquatic habitats, where they feed on bacteria.Cavalier-Smith, T. (2013)Early evolution of eukaryote feeding modes, cell structural diversity, and classification of the protozoan phyla Loukozoa, Sulcozoa, and Choanozoa European journal of protistology, 49(2), 115-178. Includes freshwater or marine organisms, benthic, dorsoventrally compressed and with two unequal flagellae, each emerging from a separate pocket. The apical anterior flagellum can be very thin or end in the cell membrane, while the posterior flagellum is long and is inserted ventrally or laterally. The cell membrane is supported by a thin single layer teak and the mitochondrial crests are discoidal / flat. The group's placement is doubtful, as it seems to fall outside the five supergroups of eukaryotes. Cavalier-Smith considers that they constitute a basal group to Amoebozoa and Opisthokonta and places it together ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malawimonas
''Malawimonas'' is a Loukozoa genus, possible sister of the Podiata. History of the discovery of Malawimonads In 1993, Charles J O’ Kelly studied the jakobid groups flagellates and implications for the early diversification of eukaryotes and recognized that ''Jakoba, Reclimonas,'' and ''Histonia'' or often refer as “core jakobids” were morphologically somewhat similar. Interestingly, they included an unnamed and undescribed free-swimming, flagellate, and also groove- bearing cell. During the early study, these cells were thought to be a member from ''Jakoba'' due to the external morphology features that resembles ''Jakoba libera'' in terms of lack of cell covering, sessile trophic stages, swimming in a similar manner and sharing the tendency for the anterior flagellum to form a “crook. However, later discovery found that this species seems to not fit and can not be assigned to the genus ''Jakoba'', nor to any other genus of Jakobids, because of their discoidal mitochon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amoebozoa
Amoebozoa is a major taxonomic group containing about 2,400 described species of amoeboid protists, often possessing blunt, fingerlike, lobose pseudopods and tubular mitochondrial cristae. In traditional and currently no longer supported classification schemes, Amoebozoa is ranked as a phylum within either the kingdom Protista or the kingdom Protozoa. In the classification favored by the International Society of Protistologists, it is retained as an unranked " supergroup" within Eukaryota. Molecular genetic analysis supports Amoebozoa as a monophyletic clade. Modern studies of eukaryotic phylogenetic trees identify it as the sister group to Opisthokonta, another major clade which contains both fungi and animals as well as several other clades comprising some 300 species of unicellular eukaryotes. Amoebozoa and Opisthokonta are sometimes grouped together in a high-level taxon, variously named Unikonta, Amorphea or Opimoda. Amoebozoa includes many of the best-known a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choanozoa
Choanozoa is a clade of opisthokont eukaryotes consisting of the choanoflagellates (Choanoflagellatea) and the animals (Animalia, Metazoa). The sister-group relationship between the choanoflagellates and animals has important implications for the origin of the animals. The clade was identified in 2015 by Graham Budd and Sören Jensen, who used the name Apoikozoa. The 2018 revision of the classification first proposed by the International Society of Protistologists in 2012 recommends the use of the name Choanozoa. Introduction A close relationship between choanoflagellates and animals has long been recognised, dating back at least to the 1840s. A particularly striking and famous similarity between the single-celled choanoflagellates and multicellular animals is provided by the collar cells of sponges and the overall morphology of the choanoflagellate cell. The relationship has since been confirmed by multiple molecular analyses. This proposed homology was however thrown into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apusomonadida
The Apusomonadida are a group of protozoan zooflagellates that glide on surfaces, and mostly consume prokaryotes. They are of particular evolutionary interest because they appear to be the sister group to the Opisthokonts, the clade that includes both animals and fungi. Together with the Breviatea, these form the Obazoa clade. Taxonomy * Class Apusomonadea Tedersoo 2017 ** Order Apusomonadida Karpov & Mylnikov 1989 hecomonadales Lee 1989*** Family Apusomonadidae Karpov & Mylnikov 1989 **** Genus '' Amastigomonas'' de Saedeleer 1931 ***** Species '' A. caudata'' Mylnikov 1989 'Amastigomonas borokensis'' Hamar 1979***** Species '' A. debruynei'' de Saedeleer 1931 ***** Species '' A. marisrubri'' Mylnikov & Mylnikov 2012 **** Genus '' Multimonas'' Cavalier-Smith 2010 ***** Species '' M. koreensis'' Heiss et al. 2015 ***** Species '' M. marina'' (Mylnikov 1989) Cavalier-Smith 2010 'Cercomonas marina'' Mylnikov 1989; ''Amastigomonas marina'' (Mylnikov 1989) Mylnikov 1999***** ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
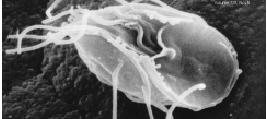
Breviata
''Breviata anathema'' is a single-celled flagellate amoeboid eukaryote, previously studied under the name '' Mastigamoeba invertens''. The cell lacks mitochondria but has remnant mitochondrial genes, and possesses an organelle believed to be a modified anaerobic mitochondrion, similar to the mitosomes and hydrogenosomes found in other eukaryotes that live in low-oxygen environments. Early molecular data placed ''Breviata'' in the Amoebozoa, but without obvious affinity to known amoebozoan groups. More recently, phylogenomic analysis has shown that the class Breviatea is a sister group to the Opisthokonta and Apusomonadida. Together, these three groups form the clade Obazoa (the term Obazoa is based on an acronym of Opisthokonta, Breviatea, and Apusomonadida, plus ‘zóa’ (pertaining to ‘life’ in Greek)). Taxonomy * Class Breviatea ''Breviata anathema'' is a single-celled flagellate amoeboid eukaryote, previously studied under the name '' Mastigamoeba invertens''. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)