New South Wales on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
New South Wales (commonly abbreviated as NSW) is a state on the east coast of :Australia. It borders

 In 1856 New South Wales achieved responsible government with the introduction of a bicameral parliament comprising a directly elected Legislative Assembly and a nominated
In 1856 New South Wales achieved responsible government with the introduction of a bicameral parliament comprising a directly elected Legislative Assembly and a nominated
 Askin's resignation in 1975 was followed by a number of short-lived premierships by Liberal Party leaders. When a general election came in 1976, the ALP under
Askin's resignation in 1975 was followed by a number of short-lived premierships by Liberal Party leaders. When a general election came in 1976, the ALP under
 New South Wales is bordered on the north by Queensland, on the west by South Australia, on the south by Victoria and on the east by the
New South Wales is bordered on the north by Queensland, on the west by South Australia, on the south by Victoria and on the east by the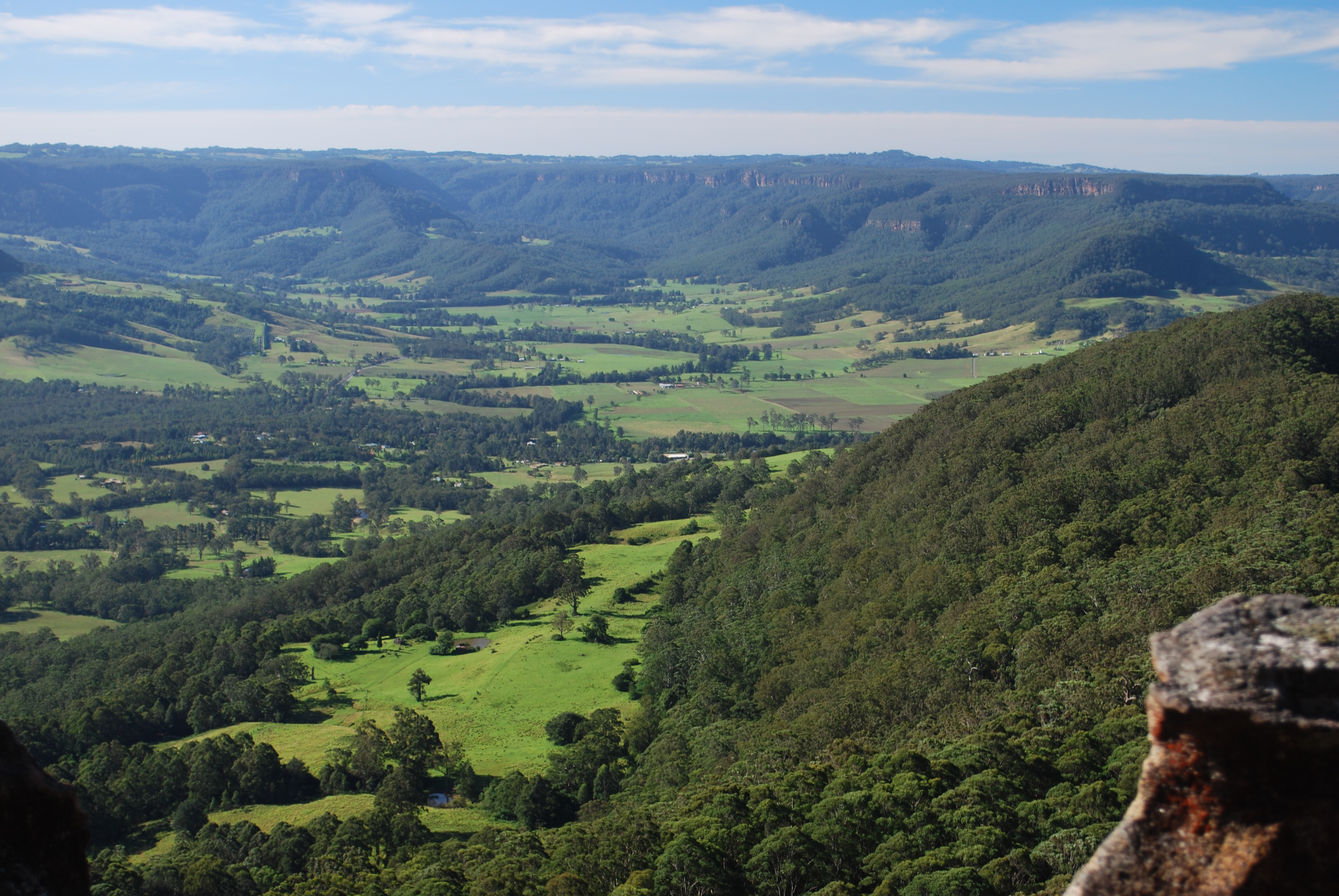  The Great Dividing Range extends from Victoria in the south through New South Wales to Queensland, parallel to the narrow coastal plain. This area includes the Snowy Mountains, the Northern, Central and Southern Tablelands, the Southern Highlands and the South West Slopes. Whilst not particularly steep, many peaks of the range rise above , with the highest Mount Kosciuszko at . Skiing in Australia began in this region at Kiandra around 1861. The relatively short ski season underwrites the tourist industry in the Snowy Mountains. Agriculture, particularly the wool industry, is important throughout the highlands. Major centres include Armidale, Bathurst, Bowral, Goulburn, Inverell, Orange, Queanbeyan and Tamworth.
There are numerous forests in New South Wales, with such tree species as Red Gum
The Great Dividing Range extends from Victoria in the south through New South Wales to Queensland, parallel to the narrow coastal plain. This area includes the Snowy Mountains, the Northern, Central and Southern Tablelands, the Southern Highlands and the South West Slopes. Whilst not particularly steep, many peaks of the range rise above , with the highest Mount Kosciuszko at . Skiing in Australia began in this region at Kiandra around 1861. The relatively short ski season underwrites the tourist industry in the Snowy Mountains. Agriculture, particularly the wool industry, is important throughout the highlands. Major centres include Armidale, Bathurst, Bowral, Goulburn, Inverell, Orange, Queanbeyan and Tamworth.
There are numerous forests in New South Wales, with such tree species as Red Gum
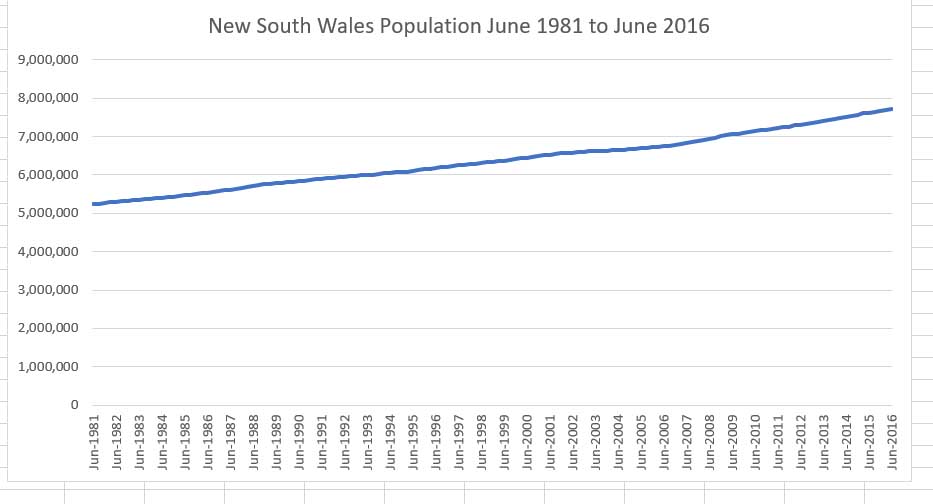 The estimated population of New South Wales at the end of December 2021 was 8,095,430 people, representing approximately 31.42% of nationwide population.
In June 2017 Sydney was home to almost two-thirds (65.3%) of the NSW population. Estimated resident population, 30 June 2017.
The estimated population of New South Wales at the end of December 2021 was 8,095,430 people, representing approximately 31.42% of nationwide population.
In June 2017 Sydney was home to almost two-thirds (65.3%) of the NSW population. Estimated resident population, 30 June 2017.
 Executive power is formally exercised by the Executive Council, which consists of the Governor and senior ministers. The current governor is Margaret Beazley. The governor commissions as premier the leader of the parliamentary political party that can command a simple majority of votes in the Legislative Assembly. The premier then recommends the appointment of other members of the two Houses to the Ministry, under the principle of responsible or Westminster government. As in other Westminster systems, there is no constitutional requirement in New South Wales for the government to be formed from the parliament—merely convention. As of early July 2023, the premier is Chris Minns of the Labor Party.
Executive power is formally exercised by the Executive Council, which consists of the Governor and senior ministers. The current governor is Margaret Beazley. The governor commissions as premier the leader of the parliamentary political party that can command a simple majority of votes in the Legislative Assembly. The premier then recommends the appointment of other members of the two Houses to the Ministry, under the principle of responsible or Westminster government. As in other Westminster systems, there is no constitutional requirement in New South Wales for the government to be formed from the parliament—merely convention. As of early July 2023, the premier is Chris Minns of the Labor Party.
 Eleven universities primarily operate in New South Wales. Sydney is home to Australia's first university, the
Eleven universities primarily operate in New South Wales. Sydney is home to Australia's first university, the
 NSW is the largest state economy in Australia, with service industries contributing almost 80% of the state's economic activity and 90% of its employment. Business services which includes financial services; professional, scientific and technical services; property services; information media; and telecommunications, account for nearly a third of the state economy. Major merchandise exports include coal, copper, beef and aluminium. In recent years there has been strong growth in exports of education, tourism, and financial and business services.
Construction accounted for 8% of the NSW economy in 2020–21, while manufacturing contributed 6%, mining 2%, and agriculture, forestry and fishing just under 2%.
Coal and related products are the state's biggest merchandise export. Its value to the state's economy is over A$5 billion, accounting for about 19% of all merchandise exports from NSW. Tourism is worth over $18.1 billion to the New South Wales economy and employs 3.1% of the workforce.
NSW is the largest state economy in Australia, with service industries contributing almost 80% of the state's economic activity and 90% of its employment. Business services which includes financial services; professional, scientific and technical services; property services; information media; and telecommunications, account for nearly a third of the state economy. Major merchandise exports include coal, copper, beef and aluminium. In recent years there has been strong growth in exports of education, tourism, and financial and business services.
Construction accounted for 8% of the NSW economy in 2020–21, while manufacturing contributed 6%, mining 2%, and agriculture, forestry and fishing just under 2%.
Coal and related products are the state's biggest merchandise export. Its value to the state's economy is over A$5 billion, accounting for about 19% of all merchandise exports from NSW. Tourism is worth over $18.1 billion to the New South Wales economy and employs 3.1% of the workforce.
 Sydney Airport located in the Sydney suburb of Mascot is the principal airport for not just the state but the whole nation. It is a hub for Australia's national airline
Sydney Airport located in the Sydney suburb of Mascot is the principal airport for not just the state but the whole nation. It is a hub for Australia's national airline
 The most popular sports by participation in the state are
The most popular sports by participation in the state are  The state is represented in the
The state is represented in the
 Sydney is home to five Arts teaching organisations, which have all produced world-famous students: The National Art School, The College of Fine Arts, the National Institute of Dramatic Art (NIDA), the Australian Film, Television & Radio School and the Conservatorium of Music (now part of the University of Sydney).
New South Wales is the setting and shooting location of many Australian films, including '' Mad Max 2'', which was shot near the mining town of Broken Hill. The state has also attracted international productions, both as a setting, such as in '' Mission: Impossible 2'', and as a stand-in for other locations, as seen in '' The Matrix'' franchise, '' The Great Gatsby'' and '' Unbroken''.
Sydney is home to five Arts teaching organisations, which have all produced world-famous students: The National Art School, The College of Fine Arts, the National Institute of Dramatic Art (NIDA), the Australian Film, Television & Radio School and the Conservatorium of Music (now part of the University of Sydney).
New South Wales is the setting and shooting location of many Australian films, including '' Mad Max 2'', which was shot near the mining town of Broken Hill. The state has also attracted international productions, both as a setting, such as in '' Mission: Impossible 2'', and as a stand-in for other locations, as seen in '' The Matrix'' franchise, '' The Great Gatsby'' and '' Unbroken''.
NSW Parliament
Official NSW Tourism website
* * {{Authority control States and territories of Australia States and territories established in 1788 1788 establishments in Australia
Queensland
Queensland ( , commonly abbreviated as Qld) is a States and territories of Australia, state in northeastern Australia, and is the second-largest and third-most populous state in Australia. It is bordered by the Northern Territory, South Austr ...
to the north, Victoria to the south, and South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a States and territories of Australia, state in the southern central part of Australia. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest of Australia's states and territories by area, which in ...
to the west. Its coast borders the Coral
Corals are colonial marine invertebrates within the subphylum Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact Colony (biology), colonies of many identical individual polyp (zoology), polyps. Coral species include the important Coral ...
and Tasman Sea
The Tasman Sea is a marginal sea of the South Pacific Ocean, situated between Australia and New Zealand. It measures about across and about from north to south. The sea was named after the Dutch explorer Abel Janszoon Tasman, who in 1642 wa ...
s to the east. The Australian Capital Territory
The Australian Capital Territory (ACT), known as the Federal Capital Territory until 1938, is an internal States and territories of Australia, territory of Australia. Canberra, the capital city of Australia, is situated within the territory, an ...
and Jervis Bay Territory are enclaves within the state. New South Wales' state capital is Sydney
Sydney is the capital city of the States and territories of Australia, state of New South Wales and the List of cities in Australia by population, most populous city in Australia. Located on Australia's east coast, the metropolis surrounds Syd ...
, which is also Australia's most populous city. , the population of New South Wales was over 8.3 million, making it Australia's most populous state. Almost two-thirds of the state's population, 5.3 million, live in the Greater Sydney area.
The Colony of New South Wales was founded as a British penal colony in 1788. It originally comprised more than half of the Australian mainland with its western boundary set at 129th meridian east in 1825. The colony then also included the island territories of Van Diemen's Land
Van Diemen's Land was the colonial name of the island of Tasmania during the European exploration of Australia, European exploration and colonisation of Australia in the 19th century. The Aboriginal Tasmanians, Aboriginal-inhabited island wa ...
, Lord Howe Island
Lord Howe Island (; formerly Lord Howe's Island) is an irregularly crescent-shaped volcanic remnant in the Tasman Sea between Australia and New Zealand, part of the Australian state of New South Wales. It lies directly east of mainland Port ...
, and Norfolk Island
Norfolk Island ( , ; ) is an States and territories of Australia, external territory of Australia located in the Pacific Ocean between New Zealand and New Caledonia, directly east of Australia's Evans Head, New South Wales, Evans Head and a ...
. During the 19th century, most of the colony's area was detached to form separate British colonies that eventually became the various states and territories of Australia
The states and territories are the national subdivisions and second level of government of Australia. The states are partially sovereignty, sovereign, administrative divisions that are autonomous administrative division, self-governing polity, ...
. The Swan River Colony (later called the Colony of Western Australia) was never administered as part of New South Wales.
Lord Howe Island remains part of New South Wales, while Norfolk Island became a federal territory, as have the areas now known as the Australian Capital Territory and the Jervis Bay Territory.
History
Aboriginal Australians
The original inhabitants of New South Wales were the Aboriginal tribes who arrived in Australia about 40,000 to 60,000 years ago. Before European settlement there were an estimated 250,000 Aboriginal people in the region. The Wodi wodi people, who spoke a variant of the Dharawal language, are the original custodians of an area south of Sydney which was approximately bounded by modern Campbelltown, Shoalhaven River and Moss Vale and included the Illawarra. The Bundjalung people are the original custodians of parts of the northern coastal areas. There are other Aboriginal peoples whose traditional lands are within what is now New South Wales, including the Wiradjuri, Gamilaray, Yuin, Ngarigo, Gweagal, and Ngiyampaa peoples.1788: British settlement
In 1825 Van Diemen's Land (now Tasmania) became a separate colony and the western border of New South Wales was extended to the 129th meridian east (now the West Australian border). In 1770,James Cook
Captain (Royal Navy), Captain James Cook (7 November 1728 – 14 February 1779) was a British Royal Navy officer, explorer, and cartographer famous for his three voyages of exploration to the Pacific and Southern Oceans, conducted between 176 ...
charted the unmapped eastern coast of the continent of New Holland, now Australia, and claimed the entire coastline that he had just explored as British territory. Contrary to his instructions, Cook did not gain the consent of the Aboriginal inhabitants. Cook originally named the land ''New Wales'', but on his return voyage to Britain he settled on the name ''New South Wales''.
In January 1788 Arthur Phillip arrived in Botany Bay with the First Fleet
The First Fleet were eleven British ships which transported a group of settlers to mainland Australia, marking the beginning of the History of Australia (1788–1850), European colonisation of Australia. It consisted of two Royal Navy vessel ...
of 11 vessels, which carried over a thousand settlers, including 736 convicts. A few days after arrival at Botany Bay
Botany Bay (Dharawal language, Dharawal: ''Kamay'') is an open oceanic embayment, located in Sydney, New South Wales, Australia, south of the Sydney central business district. Its source is the confluence of the Georges River at Taren Point a ...
, the fleet moved to the more suitable Port Jackson
Port Jackson, commonly known as Sydney Harbour, is a natural harbour on the east coast of Australia, around which Sydney was built. It consists of the waters of Sydney Harbour, Middle Harbour, North Harbour and the Lane Cove and Parramatta ...
, where Phillip established a settlement at the place he named Sydney Cove (in honour of the Secretary of State, Lord Sydney) on 26 January 1788. This date later became Australia's national day, Australia Day
Australia Day is the official national day of Australia. Observed annually on 26 January, it marks the 1788 landing of the First Fleet and raising of the Flag of Great Britain, Union Flag of Great Britain by Arthur Phillip at Sydney Cove, a ...
. Governor Phillip formally proclaimed the colony on 7 February 1788 at Sydney. Phillip, as Governor of New South Wales
The governor of New South Wales is the representative of the monarch, King Charles III, in the state of New South Wales. In an analogous way to the governor-general of Australia, Governor-General of Australia at the national level, the governor ...
, exercised nominal authority over all of Australia east of the 135th meridian east between the latitudes of 10°37'S and 43°39'S, and "all the islands adjacent in the Pacific Ocean". The area included modern New South Wales, Queensland, Victoria, Tasmania. Robert J. King, "Terra Australis, New Holland, and New South Wales: the Treaty of Tordesillas and Australia", ''The Globe'', no.47, 1998, pp.35–55. He remained as governor until 1792.
The settlement was initially planned to be a self-sufficient penal colony based on subsistence agriculture. Trade and shipbuilding were banned to keep the convicts isolated. However, after the departure of Governor Phillip, the colony's military officers began acquiring land and importing consumer goods obtained from visiting ships. Former convicts also farmed land granted to them and engaged in trade. Farms spread to the more fertile lands surrounding Paramatta, Windsor and Camden, and by 1803 the colony was self-sufficient in grain. Boat building was developed to make travel easier and exploit the marine resources of the coastal settlements. Sealing and whaling became important industries.
In March 1804, Irish convicts led around 300 rebels in the Castle Hill Rebellion, an attempt to march on Sydney, commandeer a ship, and sail to freedom. Poorly armed, and with their leader Philip Cunningham captured, about 100 troops and volunteers routed the main body of insurgents at Rouse Hill. At least 39 convicts were killed in the uprising and subsequent executions.


Lachlan Macquarie
Major-general (United Kingdom), Major General Lachlan Macquarie, Companion of the Order of the Bath, CB (; ; 31 January 1762 – 1 July 1824) was a British Army officer and colonial administrator from Scotland. Macquarie served as the fifth Gove ...
(governor 1810–1821) commissioned the construction of roads, wharves, churches and public buildings, sent explorers out from Sydney, and employed a planner to design the street layout of Sydney. A road across the Blue Mountains was completed in 1815, opening the way for large scale farming and grazing in the lightly wooded pastures west of the Great Dividing Range.
New South Wales established a military outpost on King George Sound in Western Australia in 1826 which was later transferred to the Swan River colony.
In 1839, the UK decided to formally annex at least part of New Zealand to New South Wales. It was administered as a dependency until becoming the separate Colony of New Zealand on 3 May 1841.
From the 1820s, squatters increasingly established unauthorised cattle and sheep runs beyond the official limits of the settled colony. In 1836, an annual licence was introduced in an attempt to control the pastoral industry, but booming wool prices and the high cost of land in the settled areas encouraged further squatting. The expansion of the pastoral industry led to violent episodes of conflict between settlers and traditional Aboriginal landowners, such as the Myall Creek massacre of 1838. By 1844 wool accounted for half of the colony's exports and by 1850 most of the eastern third of New South Wales was controlled by fewer than 2,000 pastoralists.
The transportation of convicts to New South Wales ended in 1840, and in 1842 a Legislative Council was introduced, with two-thirds of its members elected and one-third appointed by the governor. Former convicts were granted the vote, but a property qualification meant that only one in five adult males were enfranchised.
By 1850 the settler population of New South Wales had grown to 180,000, not including the 70,000 living in the area which became the separate colony of Victoria in 1851.
1850s to 1890s
 In 1856 New South Wales achieved responsible government with the introduction of a bicameral parliament comprising a directly elected Legislative Assembly and a nominated
In 1856 New South Wales achieved responsible government with the introduction of a bicameral parliament comprising a directly elected Legislative Assembly and a nominated Legislative Council
A legislative council is the legislature, or one of the legislative chambers, of a nation, colony, or subnational division such as a province or state. It was commonly used to label unicameral or upper house legislative bodies in the Brit ...
. William Charles Wentworth was prominent in this process, but his proposal for a hereditary upper house was widely ridiculed and subsequently dropped.
The property qualification for voters had been reduced in 1851, and by 1856 95 per cent of adult males in Sydney, and 55 per cent in the colony as a whole, were eligible to vote. Full adult male suffrage was introduced in 1858. In 1859 Queensland became a separate colony.
In 1861 the NSW parliament legislated land reforms intended to encourage family farms and mixed farming and grazing ventures. The amount of land under cultivation subsequently increased from 246,000 acres in 1861 to 800,000 acres in the 1880s. Wool production also continued to grow, and by the 1880s New South Wales produced almost half of Australia's wool. Coal had been discovered in the early years of settlement and gold in 1851, and by the 1890s wool, gold and coal were the main exports of the colony.
The NSW economy also became more diversified. From the 1860s, New South Wales had more people employed in manufacturing than any other Australian colony. The NSW government also invested strongly in infrastructure such as railways, telegraph, roads, ports, water and sewerage. By 1889 it was possible to travel by train from Brisbane to Adelaide via Sydney and Melbourne. The extension of the rail network inland also encouraged regional industries and the development of the wheat belt.
In the 1880s trade unions grew and were extended to lower skilled workers. In 1890 a strike in the shipping industry spread to wharves, railways, mines, and shearing sheds. The defeat of the strike was one of the factors leading the Trades and Labor Council to form a political party. The Labor Electoral League won a quarter of seats in the NSW elections of 1891 and held the balance of power between the Free Trade Party and the Protectionist Party
The Protectionist Party, also known as the Protectionist Liberal Party or Liberal Protectionist Party, was an Politics of Australia, Australian political party, formally organised from 1887 until 1909, with policies centred on protectionism. T ...
.
The suffragette
A suffragette was a member of an activist women's organisation in the early 20th century who, under the banner "Votes for Women", fought for the right to vote in public elections in the United Kingdom. The term refers in particular to members ...
movement was developing at this time. The Womanhood Suffrage League of New South Wales was founded in 1891.
1901: Federation of Australia
AFederal Council of Australasia
The Federal Council of Australasia was a forerunner to the current Commonwealth of Australia, though its structure and members were different.
The final (and successful) push for the Federal Council came at a "Convention" on 28 November 1883, wh ...
was formed in 1885 but New South Wales declined to join. A major obstacle to the federation of the Australian colonies was the protectionist policies of Victoria which conflicted with the free trade policies dominant in New South Wales. Nevertheless, the NSW premier Henry Parkes
Sir Henry Parkes, (27 May 1815 – 27 April 1896) was a colonial Australian politician and the longest-serving non-consecutive Premier of New South Wales, premier of the Colony of New South Wales, the present-day state of New South Wales in ...
was a strong advocate of federation
A federation (also called a federal state) is an entity characterized by a political union, union of partially federated state, self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a #Federal governments, federal government (federalism) ...
and his Tenterfield Oration in 1889 was pivotal in gathering support for the cause. Parkes also struck a deal with Edmund Barton, leader of the NSW Protectionist Party, whereby they would work together for federation and leave the question of a protective tariff for a future Australian government to decide.
In early 1893 the first citizens' Federation League was established in the Riverina region of New South Wales and many other leagues were soon formed in the colony. The leagues organised a conference in Corowa in July 1893 which developed a plan for federation. The new NSW premier, George Reid, endorsed the "Corowa plan" and in 1895 convinced the majority of other premiers to adopt it. A constitutional convention held sessions in 1897 and 1898 which resulted in a proposed constitution for a Commonwealth of federated states. However, a referendum on the constitution failed to gain the required majority in New South Wales after that colony's Labor party campaigned against it and premier Reid gave it such qualified support that he earned the nickname "yes-no Reid".
The premiers of the other colonies agreed to a number of concessions to New South Wales (particularly that the future Commonwealth capital would be located in NSW), and in 1899 further referendums were held in all the colonies except Western Australia. All resulted in yes votes, with the yes vote in New South Wales meeting the required majority. The Imperial Parliament passed the necessary enabling legislation in 1900 and Western Australia subsequently voted to join the new federation. The Commonwealth of Australia was inaugurated on 1 January 1901, and Barton was sworn in as Australia's first prime minister.
1901 to 1945
The first post-federation NSW governments were Progressive or Liberal Reform and implemented a range of social reforms with Labor support. Women won the right to vote in NSW elections in 1902, but were ineligible to stand for parliament until 1918. Labor increased its parliamentary representation in every election from 1904 before coming to power in 1910 with a majority of one seat. The outbreak of the First World War in 1914 saw more NSW volunteers for service than the federal authorities could handle, leading to unrest in camps as recruits waited for transfer overseas. In 1916 NSW premier William Holman and a number of his supporters were expelled from the Labor party over their support for military conscription. Holman subsequently formed aNationalist
Nationalism is an idea or movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the State (polity), state. As a movement, it presupposes the existence and tends to promote the interests of a particular nation,Anthony D. Smith, Smith, A ...
government which remained in power until 1920. Despite a huge victory for Holman's pro-conscription Nationalists in the elections of March 1917, a second referendum on conscription held in December that year was defeated in New South Wales and nationally.
Following the war, NSW governments embarked on large public works programs including road building, the extension and electrification of the rail network and the construction of the Sydney Harbour Bridge. The works were largely funded by loans from London, leading to a debt crisis after the onset of the Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe global economic downturn from 1929 to 1939. The period was characterized by high rates of unemployment and poverty, drastic reductions in industrial production and international trade, and widespread bank and ...
in 1929. New South Wales was hit harder by the depression than other states, and by 1932 one third of union members in the state were unemployed, compared with 20 per cent nationally.
Labor won the November 1930 NSW elections and Jack Lang became premier for the second time. In 1931 Lang proposed a plan to deal with the depression which included a suspension of interest payments to British creditors, diverting the money to unemployment relief. The Commonwealth and state premiers rejected the plan and later that year Lang's supporters in the Commonwealth parliament brought down James Scullin's federal Labor government. The NSW Lang government subsequently defaulted on overseas interest payments and was dismissed from office in May 1932 by the governor, Sir Phillip Game.
The following elections were won comfortably by the United Australia Party in coalition with the Country Party. Bertram Stevens became premier, remaining in office until 1939, when he was replaced by Alexander Mair.
A contemporary study by sociologist A. P. Elkin found that the population of New South Wales responded to the outbreak of war in 1939 with pessimism and apathy. This changed with the threat of invasion by Japan, which entered the war in December 1941. In May 1942 three Japanese midget submarines entered Sydney harbour and sank a naval ship, killing 29 men aboard. The following month Sydney and Newcastle were shelled by Japanese warships. American troops began arriving in the state in large numbers. Manufacturing, steelmaking, shipbuilding and rail transport all grew with the war effort and unemployment virtually disappeared.
A Labor government led by William McKell was elected in May 1941. The McKell government benefited from full employment, budget surpluses, and a co-operative relationship with John Curtin's federal Labor government. McKell became the first Labor leader to serve a full term and to be re-elected for a second. The Labor party was to govern New South Wales until 1965.
Post-war period
The Labor government introduced two weeks of annual paid leave for most NSW workers in 1944, and the 40-hour working week was implemented by 1947. The post-war economic boom brought near-full employment and rising living standards, and the government engaged in large spending programs on housing, dams, electricity generation and other infrastructure. In 1954 the government announced a plan for the construction of an opera house on Bennelong Point. The design competition was won by Jørn Utzon. Controversy over the cost of theSydney Opera House
The Sydney Opera House is a multi-venue Performing arts center, performing arts centre in Sydney, New South Wales, Australia. Located on the foreshore of Sydney Harbour, it is widely regarded as one of the world's most famous and distinctive b ...
and construction delays became a political issue and was a factor in the eventual defeat of Labor in 1965 by the conservative Liberal Party
The Liberal Party is any of many political parties around the world.
The meaning of ''liberal'' varies around the world, ranging from liberal conservatism on the right to social liberalism on the left. For example, while the political systems ...
and Country Party coalition led by Robert Askin.
The Askin government promoted private development, law and order issues and greater state support for non-government schools. However, Askin, a former bookmaker, became increasingly associated with illegal bookmaking, gambling and police corruption.
In the late 1960s, a secessionist movement in the New England
New England is a region consisting of six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the ...
region of the state led to a 1967 referendum on the issue which was narrowly defeated. The new state would have consisted of much of northern NSW including Newcastle.
 Askin's resignation in 1975 was followed by a number of short-lived premierships by Liberal Party leaders. When a general election came in 1976, the ALP under
Askin's resignation in 1975 was followed by a number of short-lived premierships by Liberal Party leaders. When a general election came in 1976, the ALP under Neville Wran
Neville Kenneth Wran, (11 October 1926 – 20 April 2014) was an Australian politician who was the Premier of New South Wales from 1976 to 1986. He was the national president of the Australian Labor Party (ALP) from 1980 to 1986 and chairman o ...
came to power. Wran was able to transform this narrow one seat victory into landslide wins (known as Wranslides) in 1978 and 1981.
After winning a comfortable though reduced majority in 1984, Wran resigned as premier and left parliament. His replacement Barrie Unsworth
Barrie John Unsworth (born 16 April 1934) is an Australian former politician, representing the Labor Party in the Parliament of New South Wales from 1978 to 1991. He served as the 36th Premier from July 1986 to March 1988. Since the death o ...
struggled to emerge from Wran's shadow and lost a 1988 election against a resurgent Liberal Party led by Nick Greiner. The Greiner government embarked on an efficiency program involving public sector cost-cutting, the corporatisation of government agencies and the privatisation of some government services. An Independent Commission Against Corruption (ICAC) was created. Greiner called a snap election in 1991 which the Liberals were expected to win. However, the ALP polled extremely well and the Liberals lost their majority and needed the support of independents to retain power.
In 1992, Greiner was investigated by ICAC for possible corruption over the offer of a public service position to a former Liberal MP. Greiner resigned but was later cleared of corruption. His replacement as Liberal leader and Premier was John Fahey, whose government narrowly lost the 1995 election to the ALP under Bob Carr
Robert John Carr (born 28 September 1947) is an Australian retired politician and journalist who served as the 39th Premier of New South Wales from 1995 to 2005, as the leader of the New South Wales Labor Party, New South Wales branch of the A ...
, who was to become the longest serving premier of the state.
The Carr government (1995–2005) largely continued its predecessors' focus on the efficient delivery of government services such as health, education, transport and electricity. There was an increasing emphasis on public-private partnerships to deliver infrastructure such as freeways, tunnels and rail links. The Carr government gained popularity for its successful organisation of international events, especially the 2000 Sydney Olympics, but Carr himself was critical of the federal government over its high immigration intake, arguing that a disproportionate number of new migrants were settling in Sydney, putting undue pressure on state infrastructure.
Carr unexpectedly resigned from office in 2005 and was replaced by Morris Iemma, who remained premier after being re-elected in the March 2007 state election, until he was replaced by Nathan Rees in September 2008. Rees was subsequently replaced by Kristina Keneally in December 2009, who became the first female premier of New South Wales. Keneally's government was defeated at the 2011 state election and Barry O'Farrell
Barry Robert O'Farrell (born 24 May 1959) is an Australian former politician who was Australia's List of Australian High Commissioners to India, High Commissioner to India and non-resident Ambassador to Bhutan from February 2020 to 30 June 202 ...
became Premier on 28 March. On 17 April 2014 O'Farrell stood down as Premier after misleading an ICAC investigation concerning a gift of a bottle of wine. The Liberal Party then elected Treasurer Mike Baird
Michael Bruce Baird (born 1 April 1968) is an Australian investment banker and former politician who was the 44th Premier of New South Wales, the Minister for Infrastructure, the Minister for Jobs, Investment, Tourism and Western Sydney, Mini ...
as party leader and Premier. Baird resigned as Premier on 23 January 2017, and was replaced by Gladys Berejiklian.
On 23 March 2019, Berejiklian led the Coalition to a third term in office. She maintained high personal approval ratings for her management of a bushfire crisis and the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic (also known as the coronavirus pandemic and COVID pandemic), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), began with an disease outbreak, outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, in December ...
. However, Berejiklian resigned as premier on 5 October 2021, following the opening of an ICAC investigation into her actions between 2012 and 2018. She was replaced by Dominic Perrottet.
Geography
 New South Wales is bordered on the north by Queensland, on the west by South Australia, on the south by Victoria and on the east by the
New South Wales is bordered on the north by Queensland, on the west by South Australia, on the south by Victoria and on the east by the Coral
Corals are colonial marine invertebrates within the subphylum Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact Colony (biology), colonies of many identical individual polyp (zoology), polyps. Coral species include the important Coral ...
and Tasman Sea
The Tasman Sea is a marginal sea of the South Pacific Ocean, situated between Australia and New Zealand. It measures about across and about from north to south. The sea was named after the Dutch explorer Abel Janszoon Tasman, who in 1642 wa ...
s. The Australian Capital Territory
The Australian Capital Territory (ACT), known as the Federal Capital Territory until 1938, is an internal States and territories of Australia, territory of Australia. Canberra, the capital city of Australia, is situated within the territory, an ...
and the Jervis Bay Territory form a separately administered entity that is bordered entirely by New South Wales. The state can be divided geographically into four areas. New South Wales's three largest cities, Sydney
Sydney is the capital city of the States and territories of Australia, state of New South Wales and the List of cities in Australia by population, most populous city in Australia. Located on Australia's east coast, the metropolis surrounds Syd ...
, Newcastle and Wollongong
Wollongong ( ; Dharawal: ''Woolyungah'') is a city located in the Illawarra region of New South Wales, Australia. The name is believed to originate from the Dharawal language, meaning either 'five islands/clouds', 'ground near water' or 'sound ...
, lie near the centre of a narrow coastal strip extending from cool temperate areas on the far south coast to subtropical
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical zone, geographical and Köppen climate classification, climate zones immediately to the Northern Hemisphere, north and Southern Hemisphere, south of the tropics. Geographically part of the Ge ...
areas near the Queensland border. Gulaga National Park in the South Coast features the southernmost subtropical rainforest in the state.
The Illawarra region is centred on the city of Wollongong, with the Shoalhaven, Eurobodalla and the Sapphire Coast to the south. The Central Coast lies between Sydney and Newcastle, with the Mid North Coast and Northern Rivers
Northern Rivers is the most northeasterly Regions of New South Wales, region of the Australian state of New South Wales, located between north of the state capital, Sydney, and encompasses the catchments and fertile valleys of the Clarence Ri ...
regions reaching northwards to the Queensland border. Tourism is important to the economies of coastal towns such as Coffs Harbour
Coffs Harbour, locally nicknamed Coffs, is a coastal city on the Mid North Coast of New South Wales, Australia, north of Sydney, and south of Brisbane. It is one of the largest urban centres on the North Coast, with a population of 78,759 a ...
, Lismore, Nowra and Port Macquarie, but the region also produces seafood, beef, dairy, fruit, sugar cane and timber.
 The Great Dividing Range extends from Victoria in the south through New South Wales to Queensland, parallel to the narrow coastal plain. This area includes the Snowy Mountains, the Northern, Central and Southern Tablelands, the Southern Highlands and the South West Slopes. Whilst not particularly steep, many peaks of the range rise above , with the highest Mount Kosciuszko at . Skiing in Australia began in this region at Kiandra around 1861. The relatively short ski season underwrites the tourist industry in the Snowy Mountains. Agriculture, particularly the wool industry, is important throughout the highlands. Major centres include Armidale, Bathurst, Bowral, Goulburn, Inverell, Orange, Queanbeyan and Tamworth.
There are numerous forests in New South Wales, with such tree species as Red Gum
The Great Dividing Range extends from Victoria in the south through New South Wales to Queensland, parallel to the narrow coastal plain. This area includes the Snowy Mountains, the Northern, Central and Southern Tablelands, the Southern Highlands and the South West Slopes. Whilst not particularly steep, many peaks of the range rise above , with the highest Mount Kosciuszko at . Skiing in Australia began in this region at Kiandra around 1861. The relatively short ski season underwrites the tourist industry in the Snowy Mountains. Agriculture, particularly the wool industry, is important throughout the highlands. Major centres include Armidale, Bathurst, Bowral, Goulburn, Inverell, Orange, Queanbeyan and Tamworth.
There are numerous forests in New South Wales, with such tree species as Red Gum Eucalyptus
''Eucalyptus'' () is a genus of more than 700 species of flowering plants in the family Myrtaceae. Most species of ''Eucalyptus'' are trees, often Mallee (habit), mallees, and a few are shrubs. Along with several other genera in the tribe Eucalyp ...
and Crow Ash ('' Flindersia australis''), being represented. Forest floors have a diverse set of understory shrubs and fungi. One of the widespread fungi is Witch's Butter ('' Tremella mesenterica'').
The western slopes and plains fill a significant portion of the state's area and have a much sparser population than areas nearer the coast. Agriculture is central to the economy of the western slopes, particularly the Riverina region and Murrumbidgee Irrigation Area in the state's south-west. Regional cities such as Albury, Dubbo, Griffith and Wagga Wagga and towns such as Deniliquin, Leeton and Parkes exist primarily to service these agricultural regions. The western slopes descend slowly to the western plains that comprise almost two-thirds of the state and are largely arid or semi-arid. The mining town of Broken Hill is the largest centre in this area.
One possible definition of the centre for New South Wales is located west-north-west of Tottenham
Tottenham (, , , ) is a district in north London, England, within the London Borough of Haringey. It is located in the Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county of Greater London. Tottenham is centred north-northeast of Charing Cross, ...
.
Climate
A little more than half of the state has an arid to semi arid climate, where the rainfall averages from a year throughout most of this climate zone. Summer temperatures can be very hot, while winter nights can be quite cold in this region. Rainfall varies throughout the state. The far north-west receives the least, less than annually, while the east receives between of rain. The climate along the flat, coastal plain east of the range varies from oceanic in the south to humid subtropical in the northern half of the state, right aboveWollongong
Wollongong ( ; Dharawal: ''Woolyungah'') is a city located in the Illawarra region of New South Wales, Australia. The name is believed to originate from the Dharawal language, meaning either 'five islands/clouds', 'ground near water' or 'sound ...
. Rainfall is highest in this area; however, it still varies from around to as high as in the wettest areas, for example Dorrigo. In the state's south, on the westward side of the Great Dividing Range, rainfall is heaviest in winter due to cold front
A cold front is the leading edge of a cooler mass of air at ground level that replaces a warmer mass of air and lies within a pronounced surface Trough (meteorology), trough of Low-pressure area, low pressure. It often forms behind an extratropica ...
s which move across southern Australia, while in the north, around Lismore, rain is heaviest in summer from tropical systems and occasionally even cyclones. During late winter, the coastal plain is relatively dry due to foehn winds that originate from the Great Dividing Range; the mountain range block the moist, westerly cold fronts that arrive from the Southern Ocean
The Southern Ocean, also known as the Antarctic Ocean, comprises the southernmost waters of the world ocean, generally taken to be south of 60th parallel south, 60° S latitude and encircling Antarctica. With a size of , it is the seco ...
, whereby providing generally clear conditions on the leeward side.
The climate in the southern half of the state is generally warm to hot in summer and cool in the winter. The seasons are more defined in the southern half of the state, especially as one moves inland towards South West Slopes, Central West and the Riverina region. The climate in the northeast region of the state, or the North Coast, bordering Queensland
Queensland ( , commonly abbreviated as Qld) is a States and territories of Australia, state in northeastern Australia, and is the second-largest and third-most populous state in Australia. It is bordered by the Northern Territory, South Austr ...
, is hot and humid in the summer and mild in winter. The Northern Tablelands, which are also on the North coast, have relatively mild summers and cold winters, due to their high elevation on the Great Dividing Range.
Peaks along the Great Dividing Range vary from to over above sea level. Temperatures can be cool to cold in winter with frequent frosts and snowfall
Snow consists of individual ice crystals that grow while suspended in the atmosphere—usually within clouds—and then fall, accumulating on the ground where they undergo further changes.
It consists of frozen crystalline water througho ...
, and are rarely hot in summer due to the elevation. Lithgow has a climate typical of the range, as do the regional cities of Orange, Cooma, Oberon and Armidale. Such places fall within the subtropical highland (''Cwb'') variety. Rainfall is moderate in this area, ranging from .
Snowfall is common in the higher parts of the range, sometimes occurring as far north as the Queensland
Queensland ( , commonly abbreviated as Qld) is a States and territories of Australia, state in northeastern Australia, and is the second-largest and third-most populous state in Australia. It is bordered by the Northern Territory, South Austr ...
border. On the highest peaks of the Snowy Mountains, the climate can be subpolar oceanic and even alpine on the higher peaks with very cold temperatures and heavy snow. The Blue Mountains, Southern Tablelands and Central Tablelands, which are situated on the Great Dividing Range, have mild to warm summers and cold winters, although not as severe as those in the Snowy Mountains.
The highest maximum temperature recorded was at Menindee in the west of the state on 10 January 1939. The lowest minimum temperature was at Charlotte Pass in the Snowy Mountains on 29 June 1994. This is also the lowest temperature recorded in the whole of Australia excluding the Antarctic Territory.
Demographics
 The estimated population of New South Wales at the end of December 2021 was 8,095,430 people, representing approximately 31.42% of nationwide population.
In June 2017 Sydney was home to almost two-thirds (65.3%) of the NSW population. Estimated resident population, 30 June 2017.
The estimated population of New South Wales at the end of December 2021 was 8,095,430 people, representing approximately 31.42% of nationwide population.
In June 2017 Sydney was home to almost two-thirds (65.3%) of the NSW population. Estimated resident population, 30 June 2017.
Cities and towns
Ancestry and immigration
At the , the most commonly nominated ancestries were: At the , there were 2,794,666 people living in New South Wales that were born overseas, accounting for 34.6% of the population. Only 43.7% of the population had both parents born in Australia. 3.4% of the population, or 278,043 people, identified asIndigenous Australians
Indigenous Australians are people with familial heritage from, or recognised membership of, the various ethnic groups living within the territory of contemporary Australia prior to History of Australia (1788–1850), British colonisation. The ...
(Aboriginal Australians
Aboriginal Australians are the various indigenous peoples of the Mainland Australia, Australian mainland and many of its islands, excluding the ethnically distinct people of the Torres Strait Islands.
Humans first migrated to Australia (co ...
and Torres Strait Islanders
Torres Strait Islanders ( ) are the Indigenous Melanesians, Melanesian people of the Torres Strait Islands, which are part of the state of Queensland, Australia. Ethnically distinct from the Aboriginal Australians, Aboriginal peoples of the res ...
) in 2021.
Language
According to the , 29.5% of people in New South Wales speak a language other than English at home with Mandarin (3.4%),Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
(2.8%), Cantonese
Cantonese is the traditional prestige variety of Yue Chinese, a Sinitic language belonging to the Sino-Tibetan language family. It originated in the city of Guangzhou (formerly known as Canton) and its surrounding Pearl River Delta. While th ...
(1.8%), Vietnamese (1.5%) and Hindi
Modern Standard Hindi (, ), commonly referred to as Hindi, is the Standard language, standardised variety of the Hindustani language written in the Devanagari script. It is an official language of India, official language of the Government ...
(1.0%) being the most popular.
Religion
In the , Christianity was the primary religious affiliation in New South Wales (NSW), comprising 47.6% of the population, mostlyRoman Catholicism
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
(22.4%) and Anglicanism
Anglicanism, also known as Episcopalianism in some countries, is a Western Christianity, Western Christian tradition which developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the ...
(11.9%). This percentage has declined over time, while the number of people identifying with no religious affiliation has risen. In 2016, the Christian affiliation rate was 55.2%, and in 1971 it was 88.4%. About 33.2% of people in NSW reported having no religious affiliation in 2021.
About 12.1% of the population in 2021 identified with a non-Christian religion, with Islam (4.3%), Hinduism (3.4%), and Buddhism (2.8%) being the most common.
Government
 Executive power is formally exercised by the Executive Council, which consists of the Governor and senior ministers. The current governor is Margaret Beazley. The governor commissions as premier the leader of the parliamentary political party that can command a simple majority of votes in the Legislative Assembly. The premier then recommends the appointment of other members of the two Houses to the Ministry, under the principle of responsible or Westminster government. As in other Westminster systems, there is no constitutional requirement in New South Wales for the government to be formed from the parliament—merely convention. As of early July 2023, the premier is Chris Minns of the Labor Party.
Executive power is formally exercised by the Executive Council, which consists of the Governor and senior ministers. The current governor is Margaret Beazley. The governor commissions as premier the leader of the parliamentary political party that can command a simple majority of votes in the Legislative Assembly. The premier then recommends the appointment of other members of the two Houses to the Ministry, under the principle of responsible or Westminster government. As in other Westminster systems, there is no constitutional requirement in New South Wales for the government to be formed from the parliament—merely convention. As of early July 2023, the premier is Chris Minns of the Labor Party.
Constitution
The form of the Government of New South Wales is prescribed in its Constitution, dating from 1856 and currently the '' Constitution Act 1902'' (NSW). Since 1901 New South Wales has been a state of the Commonwealth of Australia, and the Australian Constitution regulates its relationship with the Commonwealth. In 2006, the Constitution Amendment Pledge of Loyalty Act 2006 No 6, was enacted to amend the NSW Constitution Act 1902 to require Members of the New South Wales Parliament and its Ministers to take a pledge of loyalty to Australia and to the people of New South Wales instead of swearing allegiance toElizabeth II
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; 21 April 19268 September 2022) was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until Death and state funeral of Elizabeth II, her death in 2022. ...
her heirs and successors, and to revise the oaths taken by Executive Councillors. The Pledge of Loyalty Act was officially assented to by the Queen on 3 April 2006. The option to swear allegiance to the Queen was restored as an alternative option in June 2012.
Under the Australian Constitution, New South Wales ceded certain legislative and judicial powers to the Commonwealth, but retained independence in all other areas. The New South Wales Constitution says: "The Legislature shall, subject to the provisions of the Commonwealth of Australia Constitution Act, have power to make laws for the peace, welfare, and good government of New South Wales in all cases whatsoever".
Parliament
The first responsible self-government of New South Wales was formed on 6 June 1856 with Sir Stuart Alexander Donaldson appointed by Governor Sir William Denison as its first Colonial Secretary which in those days accounted also as thePremier
Premier is a title for the head of government in central governments, state governments and local governments of some countries. A second in command to a premier is designated as a deputy premier.
A premier will normally be a head of govern ...
. The Parliament of New South Wales
The Parliament of New South Wales, formally the Legislature of New South Wales, (definition of "The Legislature") is the bicameral legislative body of the Australian state of New South Wales (NSW). It consists of the Monarch, the New South Wa ...
is composed of the Sovereign and two houses: the Legislative Assembly (lower house), and the Legislative Council
A legislative council is the legislature, or one of the legislative chambers, of a nation, colony, or subnational division such as a province or state. It was commonly used to label unicameral or upper house legislative bodies in the Brit ...
(upper house). Elections are held every four years on the fourth Saturday of March, the most recent being on 23 March 2019. At each election one member is elected to the Legislative Assembly from each of 93 electoral districts and half of the 42 members of the Legislative Council are elected by a statewide electorate.
Local government
New South Wales is divided into 128local government areas
A local government area (LGA) is an administrative division of a country that a local government is responsible for. The size of an LGA varies by country but it is generally a subdivision of a state, province, division, or territory.
The ph ...
. There is also the Unincorporated Far West Region which is not part of any local government area, in the sparsely inhabited Far West, and Lord Howe Island
Lord Howe Island (; formerly Lord Howe's Island) is an irregularly crescent-shaped volcanic remnant in the Tasman Sea between Australia and New Zealand, part of the Australian state of New South Wales. It lies directly east of mainland Port ...
, which is also unincorporated but self-governed by the Lord Howe Island Board.
Emergency services
New South Wales is policed by theNew South Wales Police Force
The New South Wales Police Force is a law enforcement agency of the state of New South Wales, Australia, established in 1862. With more than 17,000 police officers, it is the largest police organisation in Australia, policing an area of 801,60 ...
, a statutory authority. Established in 1862, the New South Wales Police Force investigates Summary and Indictable offences throughout the State of New South Wales. The state has two fire services: the volunteer based New South Wales Rural Fire Service, which is responsible for the majority of the state, and the Fire and Rescue NSW, a government agency responsible for protecting urban areas. There is some overlap in due to suburbanisation. Ambulance services are provided through the New South Wales Ambulance. Rescue services (i.e. vertical, road crash, confinement) are a joint effort by all emergency services, with Ambulance Rescue, Police Rescue Squad and Fire Rescue Units contributing. Volunteer rescue organisations include Marine Rescue New South Wales, State Emergency Service (SES), Surf Life Saving NSW and Volunteer Rescue Association (VRA).
Education
Primary and secondary
The NSW school system comprises a kindergarten to year 12 system with primary schooling up to year 6 and secondary schooling between years 7 and 12. Schooling is compulsory from before 6 years old until the age of 17 (unless Year 10 is completed earlier). Between 1943 and 2009, schooling was only compulsory in NSW until age 15. Primary and secondary schools include government and non-government schools. Government schools are further classified as comprehensive and selective schools. Non-government schools include Catholic schools, other denominational schools, and non-denominational independent schools. Typically, a primary school provides education from kindergarten level to year 6. A secondary school, usually called a "high school", provides education from years 7 to 12. Secondary colleges are secondary schools which only cater for years 11 and 12. The NSW Education Standards Authority classifies the 13 years of primary and secondary schooling into six stages, beginning with Early Stage 1 (Kindergarten) and ending with Stage 6 (years 11 and 12).Record of School Achievement
A Record of School Achievement (RoSA) is awarded by the NSW Education Standards Authority to students who have completed at least Year 10 but leave school without completing the Higher School Certificate. The RoSA was introduced in 2012 to replace the former School Certificate.Higher School Certificate
The Higher School Certificate (HSC) is the usual Year 12 leaving certificate in NSW. The HSC is the most popular high school credential in Australia with 75,493 students studying one or more HSC courses in 2022. Most students complete the HSC prior to entering the workforce or going on to study at university or TAFE (although the HSC itself can be completed at TAFE). The HSC must be completed for a student to get an Australian Tertiary Admission Rank (formerly Universities Admission Index), which determines the student's rank against fellow students who completed the Higher School Certificate.Tertiary
 Eleven universities primarily operate in New South Wales. Sydney is home to Australia's first university, the
Eleven universities primarily operate in New South Wales. Sydney is home to Australia's first university, the University of Sydney
The University of Sydney (USYD) is a public university, public research university in Sydney, Australia. Founded in 1850, it is the oldest university in both Australia and Oceania. One of Australia's six sandstone universities, it was one of the ...
founded in 1850. Other universities include the University of New South Wales, Macquarie University
Macquarie University ( ) is a Public university, public research university in Sydney, New South Wales, Australia. Founded in 1964 by the New South Wales Government, it was the third university to be established in the Sydney metropolitan area. ...
, University of Technology, Sydney and Western Sydney University. The Australian Catholic University has three of its seven campuses in Sydney, and the private University of Notre Dame Australia also operates a secondary campus in the city.
Outside Sydney, the leading universities are the University of Newcastle and the University of Wollongong
The University of Wollongong (UOW) is an Australian public university, public research university located in the coastal city of Wollongong, New South Wales, approximately south of Sydney. , the university had an enrolment of more than 33,000 s ...
. Armidale is home to the University of New England, and Charles Sturt University. Southern Cross University has campuses spread across cities in the state's north coast.
The public universities are state government agencies; however, they are largely regulated by the federal government, which also administers their public funding. Admission to NSW universities is arranged together with universities in the Australian Capital Territory
The Australian Capital Territory (ACT), known as the Federal Capital Territory until 1938, is an internal States and territories of Australia, territory of Australia. Canberra, the capital city of Australia, is situated within the territory, an ...
by another organisation, the Universities Admission Centre.
Primarily vocational training is provided up the level of advanced diplomas is provided by the state government's ten Technical and Further Education (TAFE) institutes. These institutes run courses in 138 campuses throughout the state.
Economy
 NSW is the largest state economy in Australia, with service industries contributing almost 80% of the state's economic activity and 90% of its employment. Business services which includes financial services; professional, scientific and technical services; property services; information media; and telecommunications, account for nearly a third of the state economy. Major merchandise exports include coal, copper, beef and aluminium. In recent years there has been strong growth in exports of education, tourism, and financial and business services.
Construction accounted for 8% of the NSW economy in 2020–21, while manufacturing contributed 6%, mining 2%, and agriculture, forestry and fishing just under 2%.
Coal and related products are the state's biggest merchandise export. Its value to the state's economy is over A$5 billion, accounting for about 19% of all merchandise exports from NSW. Tourism is worth over $18.1 billion to the New South Wales economy and employs 3.1% of the workforce.
NSW is the largest state economy in Australia, with service industries contributing almost 80% of the state's economic activity and 90% of its employment. Business services which includes financial services; professional, scientific and technical services; property services; information media; and telecommunications, account for nearly a third of the state economy. Major merchandise exports include coal, copper, beef and aluminium. In recent years there has been strong growth in exports of education, tourism, and financial and business services.
Construction accounted for 8% of the NSW economy in 2020–21, while manufacturing contributed 6%, mining 2%, and agriculture, forestry and fishing just under 2%.
Coal and related products are the state's biggest merchandise export. Its value to the state's economy is over A$5 billion, accounting for about 19% of all merchandise exports from NSW. Tourism is worth over $18.1 billion to the New South Wales economy and employs 3.1% of the workforce.
Agriculture
Agriculture accounts for just under 2% of the NSW economy. NSW has the second-highest value of agricultural production of the Australian states. is the most extensive crop in the state by hectare amounting to 39% of the continent's harvest. The most important wheat-growing areas are the Central West, Orana,New England
New England is a region consisting of six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the ...
, North-West and Riverina.
Barley, cotton and canola are also important broadacre crops. Most cotton production is in the New England, Orana, North West and Far West regions. However, the southern regions of the state now produce almost one-third of the state's crop by value.NSW produces about 20% of Australia's fruit and nuts, and about 12% of its vegetables by value. The major regions for fruit and nut production are the Riverina, Coffs Harbour-Grafton and the Murray. About of vineyards lie across the eastern region of the state, with the Hunter Valley and the Riverina being major wine producing regions.
Cattle, sheep and pigs are the predominant livestock of NSW. The state has over one-third of the country's sheep, and one-fifth of its cattle and pigs. Australia's largest and most valuable Thoroughbred
The Thoroughbred is a list of horse breeds, horse breed developed for Thoroughbred racing, horse racing. Although the word ''thoroughbred'' is sometimes used to refer to any breed of purebred horse, it technically refers only to the Thorough ...
horse breeding area is centred on Scone
A scone ( or ) is a traditional British and Irish baked good, popular in the United Kingdom and Ireland. It is usually made of either wheat flour or oatmeal, with baking powder as a leavening agent, and baked on sheet pans. A scone is often ...
in the Hunter Valley.
Transport
Passage through New South Wales is vital for cross-continent transport. Rail and road traffic from Brisbane (Queensland) toPerth
Perth () is the list of Australian capital cities, capital city of Western Australia. It is the list of cities in Australia by population, fourth-most-populous city in Australia, with a population of over 2.3 million within Greater Perth . The ...
(Western Australia), or to Melbourne (Victoria) must pass through New South Wales.
Railways
The majority of railways in New South Wales are currently operated by the state government. Some lines began as branch-lines of railways starting in other states. For instance, Balranald near the Victorian border was connected by a rail line coming up from Victoria and into New South Wales. Another line beginning in Adelaide crossed over the border and stopped at Broken Hill. Railways management are conducted by Sydney Trains and NSW TrainLink which maintain rolling stock. Sydney Trains operates trains within Sydney while NSW TrainLink operates outside Sydney, intercity, country and interstate services. Both Sydney Trains and NSW TrainLink have their main terminus at Sydney's Central station. NSW TrainLink regional and long-distance services consist of XPT services to Grafton,Casino
A casino is a facility for gambling. Casinos are often built near or combined with hotels, resorts, restaurants, retail shops, cruise ships, and other tourist attractions. Some casinos also host live entertainment, such as stand-up comedy, conce ...
, Brisbane
Brisbane ( ; ) is the List of Australian capital cities, capital and largest city of the States and territories of Australia, state of Queensland and the list of cities in Australia by population, third-most populous city in Australia, with a ...
, Melbourne
Melbourne ( , ; Boonwurrung language, Boonwurrung/ or ) is the List of Australian capital cities, capital and List of cities in Australia by population, most populous city of the States and territories of Australia, Australian state of Victori ...
and Dubbo, as well as Xplorer services to Canberra
Canberra ( ; ) is the capital city of Australia. Founded following the Federation of Australia, federation of the colonies of Australia as the seat of government for the new nation, it is Australia's list of cities in Australia, largest in ...
, Griffith, Broken Hill, Armidale and Moree. NSW TrainLink intercity trains operate on the Blue Mountains Line, Central Coast & Newcastle Line, South Coast Line, Southern Highlands Line and Hunter Line.
Roads
Major roads are the concern of both federal and state governments. The latter maintains these through the Transport for NSW agency. The main roads in New South Wales are * Hume Highway linking Sydney toMelbourne
Melbourne ( , ; Boonwurrung language, Boonwurrung/ or ) is the List of Australian capital cities, capital and List of cities in Australia by population, most populous city of the States and territories of Australia, Australian state of Victori ...
, Victoria
* Princes Highway
Princes Highway is a major road in Australia, extending from Sydney via Melbourne to Adelaide through the states of New South Wales, Victoria (Australia), Victoria and South Australia. It has a length of (along Highway 1) or via the former ...
linking Sydney to Melbourne via the Tasman Sea coast
* Pacific Highway linking Sydney to Brisbane
Brisbane ( ; ) is the List of Australian capital cities, capital and largest city of the States and territories of Australia, state of Queensland and the list of cities in Australia by population, third-most populous city in Australia, with a ...
, Queensland via the Pacific coast
* New England Highway running from the Pacific Highway, at Newcastle to Brisbane by an inland route
* Federal Highway running from the Hume Highway south of Goulburn to Canberra
Canberra ( ; ) is the capital city of Australia. Founded following the Federation of Australia, federation of the colonies of Australia as the seat of government for the new nation, it is Australia's list of cities in Australia, largest in ...
, Australian Capital Territory
* Sturt Highway running from the Hume Highway near Gundagai to Adelaide
Adelaide ( , ; ) is the list of Australian capital cities, capital and most populous city of South Australia, as well as the list of cities in Australia by population, fifth-most populous city in Australia. The name "Adelaide" may refer to ei ...
, South Australia
* Newell Highway linking rural Victoria with Queensland, passing through the centre of New South Wales
* Great Western Highway
Great Western Highway is a state highway in New South Wales, Australia. From east to west, the highway links Sydney with Bathurst, New South Wales, Bathurst, on the state's Central Tablelands. The highway also has local road names between the ...
linking Sydney with Bathurst, as Route 32 it continues west as the Mitchell Highway then as the Barrier Highway to Adelaide via Broken Hill
Other roads are usually the concern of the TfNSW or the local government authority.
Air
 Sydney Airport located in the Sydney suburb of Mascot is the principal airport for not just the state but the whole nation. It is a hub for Australia's national airline
Sydney Airport located in the Sydney suburb of Mascot is the principal airport for not just the state but the whole nation. It is a hub for Australia's national airline Qantas
Qantas ( ), formally Qantas Airways Limited, is the flag carrier of Australia, and the largest airline by fleet size, international flights, and international destinations in Australia and List of largest airlines in Oceania, Oceania. A foundi ...
.
Other airlines serving regional New South Wales include: NSW Rural and Regional Air Transport Operators
* FlyPelican
* Jetstar
* Rex Airlines
* Virgin Australia
* Corporate Air
Ferries
Transdev Sydney Ferries operates Sydney Ferries services within Sydney Harbour and the Parramatta River, while Newcastle Transport has a ferry service within Newcastle. All other ferry services are privately operated. Spirit of Tasmania ran a commercial ferry service between Sydney and Devonport, Tasmania. This service was terminated in 2006. Private boat services operated between South Australia, Victoria and New South Wales along the Murray and Darling Rivers but these only exist now as the occasional tourist paddle-wheeler service.National parks
New South Wales has more than 780 national parks and reserves covering more than 8% of the state. These parks range from rainforests, waterfalls, rugged bush to marine wonderlands and outback deserts, including World Heritage sites. The Royal National Park on the southern outskirts of Sydney became Australia's first national park when proclaimed on 26 April 1879. Originally named simply 'National Park' until 1955, this park was the second national park to be established in the world after Yellowstone National Park in the U.S.Kosciuszko National Park
The Kosciuszko National Park ( ) is a national park and contains mainland Australia's highest peak, Mount Kosciuszko, for which it is named, and Cabramurra, New South Wales, Cabramurra, the highest town in Australia. Its borders contain a mix o ...
is the largest park in state encompassing New South Wales' alpine region.
The National Parks Association was formed in 1957 to create a system of national parks all over New South Wales which led to the formation of the National Parks and Wildlife Service in 1967. This government agency is responsible for developing and maintaining the parks and reserve system, and conserving natural and cultural heritage, in the state of New South Wales. These parks preserve special habitats, plants and wildlife, such as the Wollemi National Park where the Wollemi Pine grows and areas sacred to Australian Aboriginals such as Mutawintji National Park in western New South Wales.
Sport
 The most popular sports by participation in the state are
The most popular sports by participation in the state are soccer
Association football, more commonly known as football or soccer, is a team sport played between two teams of 11 Football player, players who almost exclusively use their feet to propel a Ball (association football), ball around a rectangular f ...
and tennis. The National Rugby League, which is based in Sydney, is the dominant professional spectator sport. In rugby league, the state is represented by the New South Wales Blues in the State of Origin series. The state hosts 10 of the 17 NRL teams: the Canterbury-Bankstown Bulldogs, Cronulla-Sutherland Sharks, Manly-Warringah Sea Eagles
The Manly Warringah Sea Eagles are an Australian professional rugby league club based in Sydney's Northern Beaches. They compete in the National Rugby League (NRL). The Manly club debuted in the 1947 New South Wales Rugby Football League sea ...
, Newcastle Knights, Parramatta Eels, Penrith Panthers
The Penrith Panthers are an Australian professional rugby league football club based in the Greater Western Sydney suburb of Penrith, New South Wales, Penrith that competes in the National Rugby League (NRL). The team is based west of the cen ...
, St George Illawarra Dragons, South Sydney Rabbitohs, Sydney Roosters
Eastern Suburbs District Rugby League Football Club, known as the Sydney Roosters are an Australian professional rugby league football club based in Sydney's Eastern Suburbs (Sydney), Eastern Suburbs. The club competes in the National Rugby Lea ...
, and Wests Tigers. Other rugby league competitions in the state include the NSW Cup, the Sydney A-Grade, and regional competitions administered by the NSWRL's Country Rugby League division.
The main summer sport is cricket and the Sydney Cricket Ground hosts the 'New Year' cricket Test match in January each year. The NSW Blues play in the One-Day Cup and Sheffield Shield
The Sheffield Shield is the domestic first-class cricket competition of Australia. The tournament is contested between teams representing the six states of Australia. The Sheffield Shield is named after Henry Holroyd, 3rd Earl of Sheffield, Lor ...
competitions. Sydney Sixers
The Sydney Sixers is an Australian professional franchise men's cricket team, competing in Australia's domestic Twenty20 cricket competition, the Big Bash League (BBL). Along with the Sydney Thunder, the Sixers are the successors of the Spee ...
and Sydney Thunder
The Sydney Thunder is an Australian franchise professional cricket team, competing in Australia's domestic Twenty20 cricket competition, the Big Bash League. Along with the Sydney Sixers, the Thunder is the successor to the Speed Blitz Blues, ...
both play in the Big Bash League.
 The state is represented in the
The state is represented in the Australian Football League
The Australian Football League (AFL) is the pre-eminent professional sports, professional competition of Australian rules football. It was originally named the Victorian Football League (VFL) and was founded in 1896 as a breakaway competition ...
by the Sydney Swans, who won the AFL premiership in 2005, and the Greater Western Sydney Giants who entered the competition in 2012.
The state is represented by five teams in soccer
Association football, more commonly known as football or soccer, is a team sport played between two teams of 11 Football player, players who almost exclusively use their feet to propel a Ball (association football), ball around a rectangular f ...
's A-League: Sydney FC, Western Sydney Wanderers ( 2014 Asian champions), Central Coast Mariners, Newcastle Jets and Macarthur FC.
Other teams in major national competitions include the Sydney Kings and Illawarra Hawks in the National Basketball League, Sydney Uni Flames in the Women's National Basketball League
The Women's National Basketball League (WNBL) is a professional women's basketball list of basketball leagues, league in Australia composed of eight teams. The league was founded in 1981 and is the Women's sports, women's counterpart to the Na ...
, New South Wales Waratahs
The New South Wales Waratahs ( or ;), often referred to as the Waratahs, are an Australian professional rugby union team based in Sydney that represents the majority of New South Wales in the Super Rugby Pacific competition. The Waratahs play t ...
in Super Rugby
Super Rugby is a men's professional rugby union club competition involving teams from Australia, Fiji, New Zealand, and the Pacific Islands. It has previously included teams from Argentina, Japan, and South Africa. Super Rugby started as the S ...
and New South Wales Swifts in Super Netball.
Sydney was the host of the 1938 British Empire Games and 2000 Summer Olympics
The 2000 Summer Olympics, officially the Games of the XXVII Olympiad, officially branded as Sydney 2000, and also known as the Games of the New Millennium, were an international multi-sport event held from 15 September to 1 October ...
. The Stadium Australia hosts major events including the NRL Grand Final, State of Origin, rugby union and soccer internationals.
The annual Sydney to Hobart Yacht Race begins in Sydney Harbour on Boxing Day. Bathurst hosts the annual Bathurst 1000 as part of the Supercars Championship at Mount Panorama Circuit.
The equine sports of campdrafting
Campdrafting is a unique Australian sport involving a horse and equestrianism, rider working cattle. The riding style is Australian stock saddle, Australian stock, somewhat akin to American Western riding and the event is similar to the Americ ...
and polocrosse were developed in New South Wales and competitions are now held across Australia. Polocrosse is now played in many overseas countries.
Other professional teams include:
* Baseball
Baseball is a bat-and-ball games, bat-and-ball sport played between two team sport, teams of nine players each, taking turns batting (baseball), batting and Fielding (baseball), fielding. The game occurs over the course of several Pitch ...
: Sydney Blue Sox
* Ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey in North America) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an Ice rink, ice skating rink with Ice hockey rink, lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. Tw ...
: Newcastle Northstars, Sydney Bears, Sydney Ice Dogs
* Motor racing: Brad Jones Racing, Team Sydney
Culture
As Australia's most populous state, New South Wales is home to a number of cultural institutions of importance to the nation. In music, New South Wales is home to the Sydney Symphony Orchestra, Australia's busiest and largest orchestra. Australia's largest opera company, Opera Australia, is headquartered in Sydney. Both of these organisations perform a subscription series at the Sydney Opera House. Other major musical bodies include the Australian Chamber Orchestra. Sydney is host to the Australian Ballet for its Sydney season (the ballet is headquartered in Melbourne). Apart from theSydney Opera House
The Sydney Opera House is a multi-venue Performing arts center, performing arts centre in Sydney, New South Wales, Australia. Located on the foreshore of Sydney Harbour, it is widely regarded as one of the world's most famous and distinctive b ...
, major musical performance venues include the City Recital Hall and the Sydney Town Hall.
New South Wales is home to several major museums and art galleries, including the Australian Museum, the Powerhouse Museum
The Powerhouse Museum, formerly known as the Museum of Applied Arts & Sciences (MAAS), is a collection of 4 museums in Sydney, owned by the Government of New South Wales. Powerhouse is a contemporary museum of applied arts and sciences, explori ...
, the Museum of Sydney, the Art Gallery of New South Wales
The Art Gallery of New South Wales (AGNSW), founded as the New South Wales Academy of Art in 1872 and known as the National Art Gallery of New South Wales between 1883 and 1958, is located in The Domain, Sydney, Australia. It is the most import ...
and the Museum of Contemporary Art.
 Sydney is home to five Arts teaching organisations, which have all produced world-famous students: The National Art School, The College of Fine Arts, the National Institute of Dramatic Art (NIDA), the Australian Film, Television & Radio School and the Conservatorium of Music (now part of the University of Sydney).
New South Wales is the setting and shooting location of many Australian films, including '' Mad Max 2'', which was shot near the mining town of Broken Hill. The state has also attracted international productions, both as a setting, such as in '' Mission: Impossible 2'', and as a stand-in for other locations, as seen in '' The Matrix'' franchise, '' The Great Gatsby'' and '' Unbroken''.
Sydney is home to five Arts teaching organisations, which have all produced world-famous students: The National Art School, The College of Fine Arts, the National Institute of Dramatic Art (NIDA), the Australian Film, Television & Radio School and the Conservatorium of Music (now part of the University of Sydney).
New South Wales is the setting and shooting location of many Australian films, including '' Mad Max 2'', which was shot near the mining town of Broken Hill. The state has also attracted international productions, both as a setting, such as in '' Mission: Impossible 2'', and as a stand-in for other locations, as seen in '' The Matrix'' franchise, '' The Great Gatsby'' and '' Unbroken''. 20th Century Fox
20th Century Studios, Inc., formerly 20th Century Fox, is an American film studio, film production and Film distributor, distribution company owned by the Walt Disney Studios (division), Walt Disney Studios, the film studios division of the ...
operates Fox Studios Australia in Sydney. Screen NSW, which controls the state film industry, generates approximately $100 million into the New South Wales economy each year.
Sister states
New South Wales in recent history has pursued bilateral partnerships with other federated states/provinces and metropolises through establishing a network of sister state relationships. The state currently has 7 sister states: *Guangdong
) means "wide" or "vast", and has been associated with the region since the creation of Guang Prefecture in AD 226. The name "''Guang''" ultimately came from Guangxin ( zh, labels=no, first=t, t= , s=广信), an outpost established in Han dynasty ...
, China (since 1979)
* Tokyo
Tokyo, officially the Tokyo Metropolis, is the capital of Japan, capital and List of cities in Japan, most populous city in Japan. With a population of over 14 million in the city proper in 2023, it is List of largest cities, one of the most ...
, Japan (since 1984)
* Ehime, Japan (since 1999)
* North Rhine-Westphalia
North Rhine-Westphalia or North-Rhine/Westphalia, commonly shortened to NRW, is a States of Germany, state () in Old states of Germany, Western Germany. With more than 18 million inhabitants, it is the List of German states by population, most ...
, Germany (since 1989)
* Seoul
Seoul, officially Seoul Special Metropolitan City, is the capital city, capital and largest city of South Korea. The broader Seoul Metropolitan Area, encompassing Seoul, Gyeonggi Province and Incheon, emerged as the world's List of cities b ...
, South Korea (since 1991)
* Jakarta
Jakarta (; , Betawi language, Betawi: ''Jakartè''), officially the Special Capital Region of Jakarta (; ''DKI Jakarta'') and formerly known as Batavia, Dutch East Indies, Batavia until 1949, is the capital and largest city of Indonesia and ...
, Indonesia (since 1994)
* California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
, United States (since 1997)
See also
* Geology of New South Wales * Index of Australia-related articles * Outline of Australia * Outline of New South Wales * Postage stamps and postal history of New South Wales * Selection (Australian history) * SquattocracyNotes
References
External links
*NSW Parliament
Official NSW Tourism website
* * {{Authority control States and territories of Australia States and territories established in 1788 1788 establishments in Australia