|
Leeward
In geography and seamanship, windward () and leeward () are directions relative to the wind. Windward is ''upwind'' from the point of reference, i.e., towards the direction from which the wind is coming; leeward is ''downwind'' from the point of reference, i.e., along the direction towards which the wind is going. The side of a ship that is towards the leeward is its "lee side". If the vessel is heeling under the pressure of crosswind, the lee side will be the "lower side". During the Age of Sail, the term ''weather'' was used as a synonym for ''windward'' in some contexts, as in the '' weather gage''. Since it captures rainfall, the windward side of a mountain tends to be wetter than the leeward side it blocks. The drier leeward area is said to be in a rain shadow. Origin The term "windward" has roots in both Low German and Old English. The word "lee", which means a place without wind, comes from the Old Norse "hle" for "cover" and has been used in marine navigation in G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
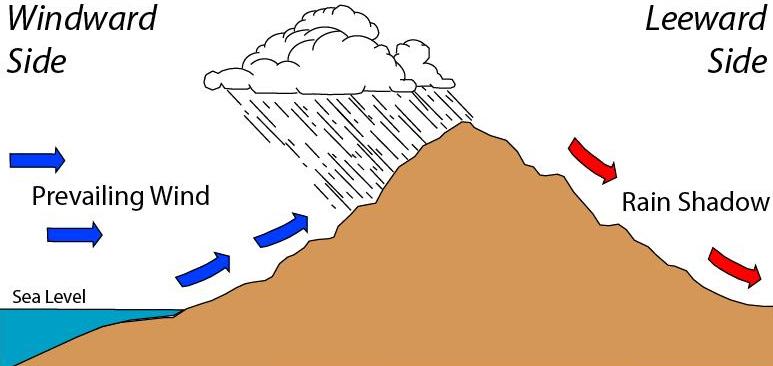
Rain Shadow
A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side. Evaporated moisture from body of water, bodies of water (such as oceans and large lakes) is carried by the prevailing sea breeze, onshore breezes towards the drier and hotter inland areas. When encountering elevated landforms, the moist air is orographic lift, driven upslope towards the summit, peak, where it expands, cools, and its moisture condenses and starts to Precipitation, precipitate. If the landforms are tall and wide enough, most of the humidity will be lost to precipitation over the windward side (also known as the ''rainward'' side) before ever making it past the top. As the air descends the leeward side of the landforms, it is compressed and heated, producing Foehn winds that ''absorb'' moisture downslope and cast a broad "shadow" of arid, dry climate region behind the ridge, mountain crests. This climate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
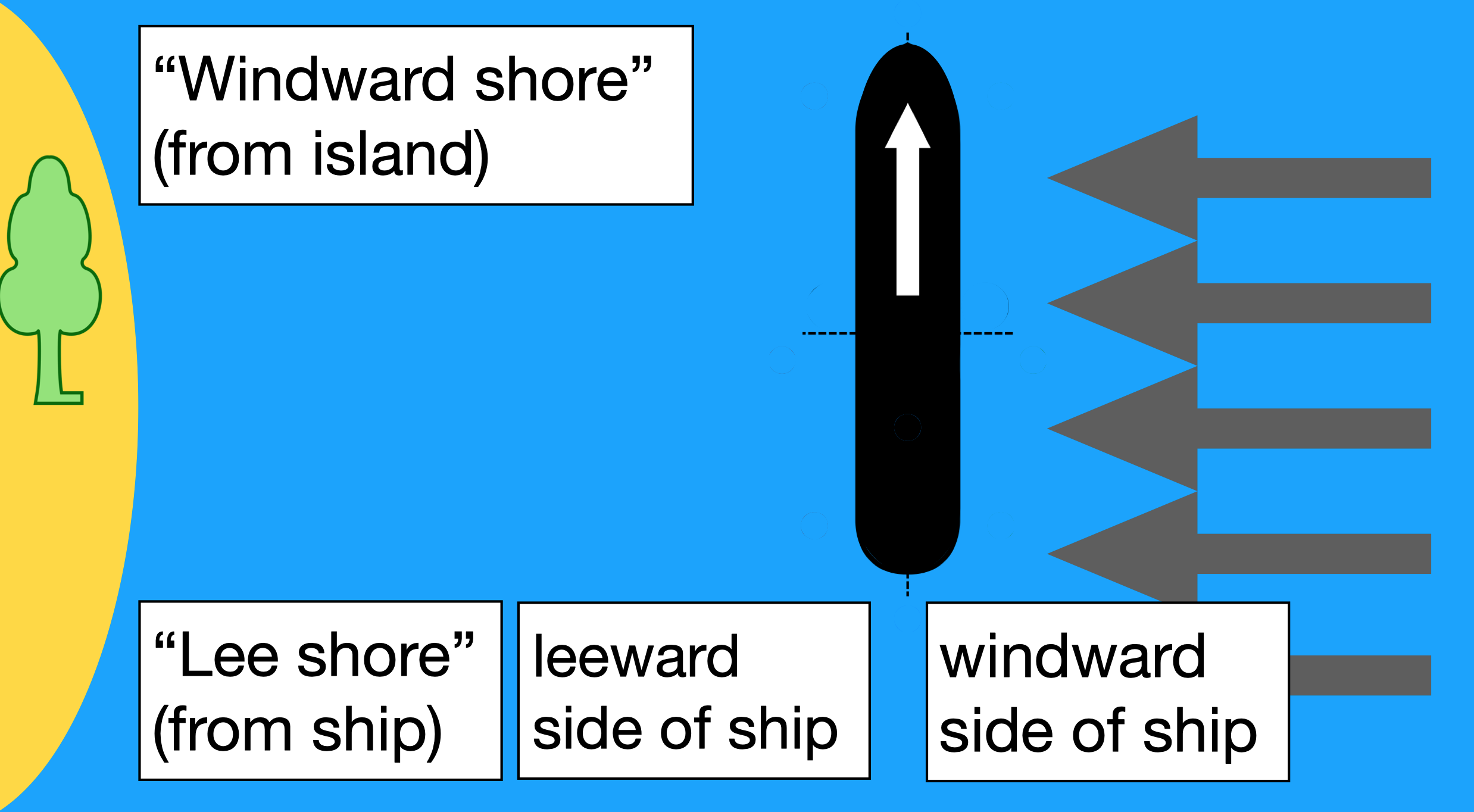
Lee Shore
A lee shore, sometimes also called a leeward ( shore, or more commonly ), is a nautical term to describe a stretch of shoreline that is to the Windward and leeward, lee side of a vessel—meaning the wind is blowing towards land. Its opposite, the shore on the windward side of the vessel, is called the weather or windward shore ( or, more commonly, ). Because of the danger of being driven aground on a lee shore it is essential seamanship to treat one with caution. This is particularly the case with sailing vessels, but a lee shore is an issue for powered vessels as well. Use of the terms "windward", "leeward", and "lee" Usage of the terms to describe shores in relation to an arbitrary point of view, including on land, can lead to ambiguity. The windward shore of an island is a lee shore from the perspective of a vessel travelling offshore. Although the terms are often confused, "the lee shore" is different from "a leeward shore" based on the reference point from which the sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heeling (sailing)
Sailing employs the wind—acting on sails, wingsails or kites—to propel a craft on the surface of the ''water'' (sailing ship, sailboat, raft, windsurfer, or kitesurfer), on ''ice'' (iceboat) or on ''land'' ( land yacht) over a chosen course, which is often part of a larger plan of navigation. From prehistory until the second half of the 19th century, sailing craft were the primary means of maritime trade and transportation; exploration across the seas and oceans was reliant on sail for anything other than the shortest distances. Naval power in this period used sail to varying degrees depending on the current technology, culminating in the gun-armed sailing warships of the Age of Sail. Sail was slowly replaced by steam as the method of propulsion for ships over the latter part of the 19th century – seeing a gradual improvement in the technology of steam through a number of developmental steps. Steam allowed scheduled services that ran at higher average speeds than sailin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
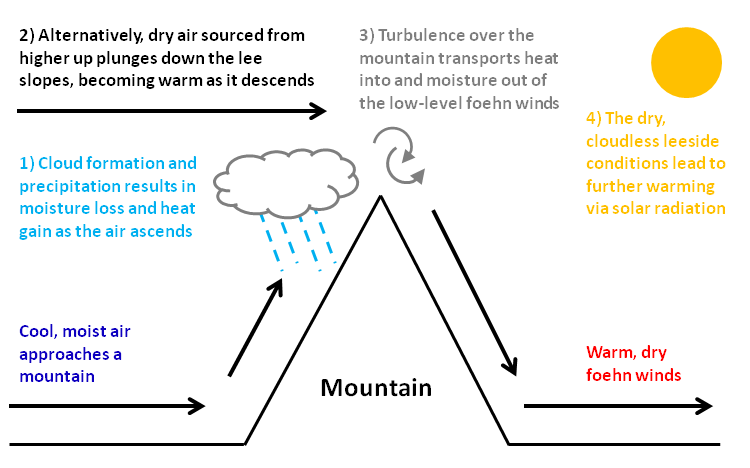
Foehn Wind
A Foehn, or Föhn (, , , ), is a type of dry, relatively warm downslope wind in the lee of a mountain range. It is a rain shadow wind that results from the subsequent adiabatic warming of air that has dropped most of its moisture on windward slopes (see orographic lift). As a consequence of the different adiabatic lapse rates of moist and dry air, the air on the leeward slopes becomes warmer than equivalent elevations on the windward slopes. Foehn winds can raise temperatures by as much as in just a matter of hours. Switzerland, southern Germany, and Austria have a warmer climate due to the Foehn, as moist winds off the Mediterranean Sea blow over the Alps. Etymology The name ''Foehn'' (, ) arose in the Alpine region. Originating from Latin , a mild west wind of which Favonius was the Roman personification and probably transmitted by or just , the term was adopted as . In the Southern Alps, the phenomenon is known as but also and in Serbo-Croatian and Slovene. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weather Gage
The weather gage (sometimes spelled weather gauge or known as nautical gauge) is the advantageous position of a fighting sailing vessel relative to another. The concept is from the Age of Sail and is now antique. A ship at sea is said to possess the weather gage if it is in any position upwind of the other vessel -- having the wind at their back, speeding progress, when sailing towards the other ship. Proximity with the land, tidal and stream effects and wind variability due to geography (hills, cliffs, etc.) may also come into play. * An upwind vessel is able to manoeuvre at will toward any downwind point, since the relative wind then moves aft. * The fastest point of sail for a frigate typically have the wind blowing in the direction of travel, allowing that ship greater choice in the distance of separation. They could more easily disengage if damaged, and could more easily optimize for the range of their gunnery. * However, in sailing warfare, the leeward ship gained a point ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sailing
Sailing employs the wind—acting on sails, wingsails or kites—to propel a craft on the surface of the ''water'' (sailing ship, sailboat, raft, Windsurfing, windsurfer, or Kitesurfing, kitesurfer), on ''ice'' (iceboat) or on ''land'' (Land sailing, land yacht) over a chosen Course (navigation), course, which is often part of a larger plan of navigation. From prehistory until the second half of the 19th century, sailing craft were the primary means of maritime trade and transportation; exploration across the seas and oceans was reliant on sail for anything other than the shortest distances. Naval power in this period used sail to varying degrees depending on the current technology, culminating in the gun-armed sailing warships of the Age of Sail. Sail was slowly replaced by steam as the method of propulsion for ships over the latter part of the 19th century – seeing a gradual improvement in the technology of steam through a number of developmental steps. Steam allowed schedul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precipitation (meteorology)
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls from clouds due to gravitational pull. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, rain and snow mixed ("sleet" in Commonwealth usage), snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. Precipitation occurs when a portion of the atmosphere becomes saturated with water vapor (reaching 100% relative humidity), so that the water condenses and "precipitates" or falls. Thus, fog and mist are not precipitation; their water vapor does not condense sufficiently to precipitate, so fog and mist do not fall. (Such a non-precipitating combination is a colloid.) Two processes, possibly acting together, can lead to air becoming saturated with water vapor: cooling the air or adding water vapor to the air. Precipitation forms as smaller droplets coalesce via collision with other rain drops or ice crystals within a cloud. Short, intense periods of rain in scattered locations are called shower (p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rain
Rain is a form of precipitation where water drop (liquid), droplets that have condensation, condensed from Water vapor#In Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric water vapor fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water on the Earth. It provides water for hydroelectricity, hydroelectric power plants, crop irrigation, and suitable conditions for many types of ecosystems. The major cause of rain production is moisture moving along three-dimensional zones of temperature and moisture contrasts known as weather fronts. If enough moisture and upward motion is present, precipitation falls from convection, convective clouds (those with strong upward vertical motion) such as cumulonimbus (thunder clouds) which can organize into narrow rainbands. In mountainous areas, heavy precipitation is possible where upslope flow is maximized within windward sides of the terrain at elevation which forces moist air to condense and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind
Wind is the natural movement of atmosphere of Earth, air or other gases relative to a planetary surface, planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few hours, to global winds resulting from the difference in absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption of solar energy between the climate zones on Earth. The study of wind is called anemology. The two main causes of large-scale atmospheric circulation are the differential heating between the equator and the poles, and the rotation of the planet (Coriolis effect). Within the tropics and subtropics, thermal low circulations over terrain and high plateaus can drive monsoon circulations. In coastal areas the sea breeze/land breeze cycle can define local winds; in areas that have variable terrain, mountain and valley breezes can prevail. Winds are commonly classified by their scale (spatial), spatial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Verde Islands
Cape Verde or Cabo Verde, officially the Republic of Cabo Verde, is an island country and archipelagic state of West Africa in the central Atlantic Ocean, consisting of ten volcanic islands with a combined land area of about . These islands lie between west of Cap-Vert, the westernmost point of continental Africa. The Cape Verde islands form part of the Macaronesia ecoregion, along with the Azores, the Canary Islands, Madeira and the Savage Isles. The Cape Verde archipelago was uninhabited until the 15th century, when Portuguese explorers colonized the islands, establishing one of the first European settlements in the tropics. Due to its strategic position, Cape Verde became a significant location in the transatlantic slave trade during the 16th and 17th centuries. The islands experienced economic growth during this period, driven by their role by the rapid emergence of merchants, privateers, and pirates. It declined economically in the 19th century, and many of its inh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prevailing Wind
In meteorology, prevailing wind in a region of the Earth's surface is a surface wind that blows predominantly from a particular direction. The dominant winds are the trends in direction of wind with the highest speed over a particular point on the Earth's surface at any given time. A region's prevailing and dominant winds are the result of global patterns of movement in the Earth's atmosphere. In general, winds are predominantly easterly at low latitudes globally. In the mid-latitudes, westerly winds are dominant, and their strength is largely determined by the polar cyclone. In areas where winds tend to be light, the sea breeze-land breeze cycle (powered by differential solar heating and night cooling of sea and land) is the most important cause of the prevailing wind. In areas which have variable terrain, mountain and valley breezes dominate the wind pattern. Highly elevated surfaces can induce a thermal low, which then augments the environmental wind flow. Wind direction a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |