Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek
philosopher
A philosopher is a person who practices or investigates philosophy. The term ''philosopher'' comes from the grc, φιλόσοφος, , translit=philosophos, meaning 'lover of wisdom'. The coining of the term has been attributed to the Greek th ...
and
polymath during the
Classical period in
Ancient Greece. Taught by
Plato, he was the founder of the
Peripatetic school of philosophy within the
Lyceum and the wider
Aristotelian tradition. His writings cover many subjects including
physics,
biology,
zoology,
metaphysics,
logic,
ethics,
aesthetics,
poetry,
theatre,
music,
rhetoric
Rhetoric () is the art of persuasion, which along with grammar and logic (or dialectic), is one of the three ancient arts of discourse. Rhetoric aims to study the techniques writers or speakers utilize to inform, persuade, or motivate parti ...
,
psychology,
linguistics,
economics,
politics,
meteorology,
geology, and
government. Aristotle provided a complex synthesis of the various philosophies existing prior to him. It was above all from his teachings that
the West inherited its intellectual
lexicon
A lexicon is the vocabulary of a language or branch of knowledge (such as nautical or medical). In linguistics, a lexicon is a language's inventory of lexemes. The word ''lexicon'' derives from Koine Greek language, Greek word (), neuter of () ...
, as well as problems and methods of inquiry. As a result, his philosophy has exerted a unique influence on almost every form of knowledge in the West and it continues to be a subject of contemporary philosophical discussion.
Little is known about his life. Aristotle was born in the city of
Stagira in
Northern Greece. His father,
Nicomachus
Nicomachus of Gerasa ( grc-gre, Νικόμαχος; c. 60 – c. 120 AD) was an important ancient mathematician and music theorist, best known for his works ''Introduction to Arithmetic'' and ''Manual of Harmonics'' in Greek. He was born in ...
, died when Aristotle was a child, and he was brought up by a guardian. At seventeen or eighteen years of age he joined
Plato's Academy in
Athens and remained there until the age of thirty-seven (). Shortly after Plato died, Aristotle left Athens and, at the request of
Philip II of Macedon, tutored his son
Alexander the Great beginning in 343 BC. He established a library in the
Lyceum which helped him to produce many of his hundreds of books on
papyrus scrolls. Though Aristotle wrote many elegant treatises and dialogues for publication, only around
a third of his original output has survived, none of it intended for publication.
Aristotle's views profoundly shaped
medieval scholarship. The influence of
physical science extended from
Late Antiquity and the
Early Middle Ages into the
Renaissance, and were not replaced systematically until
the Enlightenment and theories such as
classical mechanics were developed. Some of Aristotle's zoological observations found in
his biology, such as on the
hectocotyl (reproductive) arm of the
octopus
An octopus ( : octopuses or octopodes, see below for variants) is a soft-bodied, eight- limbed mollusc of the order Octopoda (, ). The order consists of some 300 species and is grouped within the class Cephalopoda with squids, cuttle ...
, were disbelieved until the 19th century. He also influenced
Judeo-Islamic philosophies during the Middle Ages, as well as
Christian theology
Christian theology is the theology of Christianity, Christian belief and practice. Such study concentrates primarily upon the texts of the Old Testament and of the New Testament, as well as on Christian tradition. Christian theology, theologian ...
, especially the
Neoplatonism of the
Early Church
Early Christianity (up to the First Council of Nicaea in 325) spread from the Levant, across the Roman Empire, and beyond. Originally, this progression was closely connected to already established Jewish centers in the Holy Land and the Jewish ...
and the
scholastic tradition of the
Catholic Church. Aristotle was revered among medieval Muslim scholars as "The First Teacher", and among medieval Christians like
Thomas Aquinas as simply "The Philosopher", while the poet
Dante called him "the master of those who know". His works contain the earliest known formal study of logic, and were studied by medieval scholars such as
Peter Abelard
Peter Abelard (; french: link=no, Pierre Abélard; la, Petrus Abaelardus or ''Abailardus''; 21 April 1142) was a medieval French scholastic philosopher, leading logician, theologian, poet, composer and musician. This source has a detailed desc ...
and
John Buridan
Jean Buridan (; Latin: ''Johannes Buridanus''; – ) was an influential 14th-century French philosopher.
Buridan was a teacher in the faculty of arts at the University of Paris for his entire career who focused in particular on logic and the wo ...
.
Aristotle's influence on logic continued well into the 19th century. In addition, his
ethics, though always influential, gained renewed interest with the modern advent of
virtue ethics. Aristotle has been called the father of logic, biology, political science, zoology, embryology, natural law, scientific method, rhetoric, psychology, realism, criticism, individualism, teleology, and meteorology.
Life

In general, the details of Aristotle's life are not well-established. The biographies written in ancient times are often speculative and historians only agree on a few salient points.
Aristotle was born in 384 BC in
Stagira,
Chalcidice
Chalkidiki (; el, Χαλκιδική , also spelled Halkidiki, is a peninsula and regional unit of Greece, part of the region of Central Macedonia, in the geographic region of Macedonia in Northern Greece. The autonomous Mount Athos region c ...
, about 55 km (34 miles) east of modern-day
Thessaloniki. His father,
Nicomachus
Nicomachus of Gerasa ( grc-gre, Νικόμαχος; c. 60 – c. 120 AD) was an important ancient mathematician and music theorist, best known for his works ''Introduction to Arithmetic'' and ''Manual of Harmonics'' in Greek. He was born in ...
, was the personal physician to
King Amyntas of Macedon. While he was young, Aristotle learned about biology and medical information, which was taught by his father. Both of Aristotle's parents died when he was about thirteen, and
Proxenus of Atarneus Proxenus of Atarneus ( el, Πρόξενος ὁ Ἀταρνεύς) is most famous for being Aristotle's guardian after the death of his parents. Proxenus educated Aristotle for a couple of years before sending him to Athens to Plato's Academy. He ...
became his guardian. Although little information about Aristotle's childhood has survived, he probably spent some time within the Macedonian palace, making his first connections with the
Macedonian monarchy.
At the age of seventeen or eighteen, Aristotle moved to Athens to continue his education at
Plato's Academy. He probably experienced the
Eleusinian Mysteries as he wrote when describing the sights one viewed at the Eleusinian Mysteries, "to experience is to learn"
�αθείν μαθεĩν Aristotle remained in Athens for nearly twenty years before leaving in 348/47 BC. The traditional story about his departure records that he was disappointed with the Academy's direction after control passed to Plato's nephew
Speusippus, although it is possible that he feared the anti-Macedonian sentiments in Athens at that time and left before Plato died. Aristotle then accompanied
Xenocrates to the court of his friend
Hermias of Atarneus in
Asia Minor. After the death of Hermias, Aristotle travelled with his pupil
Theophrastus to the island of
Lesbos, where together they researched the
botany and zoology of the island and its sheltered lagoon. While in Lesbos, Aristotle married
Pythias, either Hermias's adoptive daughter or niece. She bore him a daughter, whom they also named Pythias. In 343 BC, Aristotle was invited by
Philip II of Macedon to become the tutor to his son
Alexander.

Aristotle was appointed as the head of the royal academy of
Macedon. During Aristotle's time in the Macedonian court, he gave lessons not only to Alexander but also to two other future kings:
Ptolemy and
Cassander. Aristotle encouraged Alexander toward eastern conquest, and Aristotle's own attitude towards
Persia was unabashedly
ethnocentric. In one famous example, he counsels Alexander to be "a leader to the Greeks and a despot to the barbarians, to look after the former as after friends and relatives, and to deal with the latter as with beasts or plants". By 335 BC, Aristotle had returned to Athens, establishing his own school there known as the
Lyceum. Aristotle conducted courses at the school for the next twelve years. While in Athens, his wife Pythias died and Aristotle became involved with
Herpyllis Herpyllis of Stagira ( el, Ἑρπυλλίς) was Aristotle's concubine after his wife, Pythias, died.
Together Aristotle and Herpyllis had a son, named Nicomachus
Nicomachus of Gerasa ( grc-gre, Νικόμαχος; c. 60 – c. 120 AD) wa ...
of Stagira, who bore him a son whom he named after his father,
Nicomachus
Nicomachus of Gerasa ( grc-gre, Νικόμαχος; c. 60 – c. 120 AD) was an important ancient mathematician and music theorist, best known for his works ''Introduction to Arithmetic'' and ''Manual of Harmonics'' in Greek. He was born in ...
. If the ''
Suda
The ''Suda'' or ''Souda'' (; grc-x-medieval, Σοῦδα, Soûda; la, Suidae Lexicon) is a large 10th-century Byzantine encyclopedia of the ancient Mediterranean world, formerly attributed to an author called Soudas (Σούδας) or Souidas ...
'' an uncritical compilation from the Middle Ages is accurate, he may also have had an ''
erômenos'',
Palaephatus of Abydus.
This period in Athens, between 335 and 323 BC, is when Aristotle is believed to have composed many of his works. He wrote many dialogues, of which only fragments have survived. Those works that have survived are in
treatise form and were not, for the most part, intended for widespread publication; they are generally thought to be lecture aids for his students. His most important treatises include ''
Physics'', ''
Metaphysics'', ''
Nicomachean Ethics
The ''Nicomachean Ethics'' (; ; grc, Ἠθικὰ Νικομάχεια, ) is Aristotle's best-known work on ethics, the science of the good for human life, which is the goal or end at which all our actions aim. (I§2) The aim of the inquiry is ...
'', ''
Politics'', ''
On the Soul'' and ''
Poetics
Poetics is the theory of structure, form, and discourse within literature, and, in particular, within poetry.
History
The term ''poetics'' derives from the Ancient Greek ποιητικός ''poietikos'' "pertaining to poetry"; also "creative" an ...
''. Aristotle studied and made significant contributions to "logic, metaphysics, mathematics, physics, biology, botany, ethics, politics, agriculture, medicine, dance, and theatre."
Near the end of his life, Alexander and Aristotle became estranged over Alexander's relationship with Persia and Persians. A widespread tradition in antiquity suspected Aristotle of playing a role in Alexander's death, but the only evidence of this is an
unlikely claim made some six years after the death. Following Alexander's death, anti-Macedonian sentiment in Athens was rekindled. In 322 BC, Demophilus and
Eurymedon the Hierophant reportedly denounced Aristotle for impiety, prompting him to flee to his mother's family estate in
Chalcis, on Euboea, at which occasion he was said to have stated: "I will not allow the Athenians to sin twice against philosophy" – a reference to Athens's
trial and execution of Socrates. He died on Euboea of natural causes later that same year, having named his student
Antipater
Antipater (; grc, , translit=Antipatros, lit=like the father; c. 400 BC319 BC) was a Macedonian general and statesman under the subsequent kingships of Philip II of Macedon and his son, Alexander the Great. In the wake of the collaps ...
as his chief
executor
An executor is someone who is responsible for executing, or following through on, an assigned task or duty. The feminine form, executrix, may sometimes be used.
Overview
An executor is a legal term referring to a person named by the maker of a ...
and leaving a
will
Will may refer to:
Common meanings
* Will and testament, instructions for the disposition of one's property after death
* Will (philosophy), or willpower
* Will (sociology)
* Will, volition (psychology)
* Will, a modal verb - see Shall and will
...
in which he asked to be buried next to his wife.
Speculative philosophy
Logic
With the ''
Prior Analytics
The ''Prior Analytics'' ( grc-gre, Ἀναλυτικὰ Πρότερα; la, Analytica Priora) is a work by Aristotle on reasoning, known as his syllogistic, composed around 350 BCE. Being one of the six extant Aristotelian writings on logic ...
'', Aristotle is credited with the earliest study of formal logic, and his conception of it was the dominant form of Western logic until 19th-century advances in
mathematical logic.
Kant stated in the ''
Critique of Pure Reason'' that with Aristotle logic reached its completion.
''Organon''
What is today called ''Aristotelian logic'' with its
types of syllogism (methods of logical argument), Aristotle himself would have labelled "analytics". The term "logic" he reserved to mean ''dialectics''. Most of Aristotle's work is probably not in its original form, because it was most likely edited by students and later lecturers. The logical works of Aristotle were compiled into a set of six books called the ''
Organon'' around 40 BC by
Andronicus of Rhodes
Andronicoos of Rhodes ( grc, Ἀνδρόνικος ὁ Ῥόδιος, translit=Andrónikos ho Rhódios; la, Andronicus Rhodius; ) was a Greek philosophy, Greek philosopher from Rhodes who was also the scholarch (head) of the Peripatetic school. He ...
or others among his followers. The books are:
# ''
Categories''
# ''
On Interpretation''
# ''
Prior Analytics
The ''Prior Analytics'' ( grc-gre, Ἀναλυτικὰ Πρότερα; la, Analytica Priora) is a work by Aristotle on reasoning, known as his syllogistic, composed around 350 BCE. Being one of the six extant Aristotelian writings on logic ...
''
# ''
Posterior Analytics
The ''Posterior Analytics'' ( grc-gre, Ἀναλυτικὰ Ὕστερα; la, Analytica Posteriora) is a text from Aristotle's ''Organon'' that deals with demonstration, definition, and scientific knowledge. The demonstration is distinguished ...
''
# ''
Topics
Topic, topics, TOPIC, topical, or topicality may refer to:
Topic / Topics
* Topić, a Slavic surname
* ''Topics'' (Aristotle), a work by Aristotle
* Topic (chocolate bar), a brand of confectionery bar
* Topic (DJ), German musician
* Topic (g ...
''
# ''
On Sophistical Refutations''

The order of the books (or the teachings from which they are composed) is not certain, but this list was derived from analysis of Aristotle's writings. It goes from the basics, the analysis of simple terms in the ''Categories,'' the analysis of propositions and their elementary relations in ''On Interpretation'', to the study of more complex forms, namely, syllogisms (in the ''Analytics'') and dialectics (in the ''Topics'' and ''Sophistical Refutations''). The first three treatises form the core of the logical theory ''stricto sensu'': the grammar of the language of logic and the correct rules of reasoning. The ''Rhetoric'' is not conventionally included, but it states that it relies on the ''Topics''.
Metaphysics
The word "metaphysics" appears to have been coined by the first century AD editor who assembled various small selections of Aristotle's works to the treatise we know by the name ''Metaphysics''. Aristotle called it "first philosophy", and distinguished it from mathematics and natural science (physics) as the contemplative (''theoretikē'') philosophy which is "theological" and studies the divine. He wrote in his ''Metaphysics'' (1026a16):
Substance
Aristotle examines the concepts of
substance
Substance may refer to:
* Matter, anything that has mass and takes up space
Chemistry
* Chemical substance, a material with a definite chemical composition
* Drug substance
** Substance abuse, drug-related healthcare and social policy diagnosis ...
(''ousia'') and
essence (''to ti ên einai'', "the what it was to be") in his ''Metaphysics'' (Book VII), and he concludes that a particular substance is a combination of both matter and form, a philosophical theory called
hylomorphism. In Book VIII, he distinguishes the matter of the substance as the
substratum
In linguistics, a stratum (Latin for "layer") or strate is a language that influences or is influenced by another through contact. A substratum or substrate is a language that has lower power or prestige than another, while a superstratum or sup ...
, or the stuff of which it is composed. For example, the matter of a house is the bricks, stones, timbers, etc., or whatever constitutes the ''potential'' house, while the form of the substance is the ''actual'' house, namely 'covering for bodies and chattels' or any other
differentia that let us define something as a house. The formula that gives the components is the account of the matter, and the formula that gives the differentia is the account of the form.
= Immanent realism
=

Like his teacher Plato, Aristotle's philosophy aims at the
universal
Universal is the adjective for universe.
Universal may also refer to:
Companies
* NBCUniversal, a media and entertainment company
** Universal Animation Studios, an American Animation studio, and a subsidiary of NBCUniversal
** Universal TV, a t ...
. Aristotle's
ontology places the universal (''katholou'') in
particulars (''kath' hekaston''), things in the world, whereas for Plato the universal is a separately existing form which actual things imitate. For Aristotle, "form" is still what
phenomena
A phenomenon ( : phenomena) is an observable event. The term came into its modern philosophical usage through Immanuel Kant, who contrasted it with the noumenon, which ''cannot'' be directly observed. Kant was heavily influenced by Gottfried W ...
are based on, but is "instantiated" in a particular substance.
Plato argued that all things have a
universal form, which could be either a property or a relation to other things. When one looks at an apple, for example, one sees an apple, and one can also analyse a form of an apple. In this distinction, there is a particular apple and a universal form of an apple. Moreover, one can place an apple next to a book, so that one can speak of both the book and apple as being next to each other. Plato argued that there are some universal forms that are not a part of particular things. For example, it is possible that there is no particular good in existence, but "good" is still a proper universal form. Aristotle disagreed with Plato on this point, arguing that all universals are instantiated at some period of time, and that there are no universals that are unattached to existing things. In addition, Aristotle disagreed with Plato about the location of universals. Where Plato spoke of the forms as existing separately from the things that participate in them, Aristotle maintained that universals exist within each thing on which each universal is predicated. So, according to Aristotle, the form of apple exists within each apple, rather than in the world of the forms.
= Potentiality and actuality
=
Concerning the nature of change (''
kinesis'') and its causes, as he outlines in his ''
Physics'' and ''
On Generation and Corruption (''319b–320a), he distinguishes coming-to-be (''genesis'', also translated as 'generation') from:
# growth and diminution, which is change in quantity;
# locomotion, which is change in space; and
# alteration, which is change in quality.

Coming-to-be is a change where the substrate of the thing that has undergone the change has itself changed. In that particular change he introduces the concept of potentiality (''
dynamis
Dunamis (Ancient Greek: δύναμις) is a Greek philosophical concept meaning "power", "potential" or "ability", and is central to the Aristotelian idea of ''potentiality and actuality''.
Dunamis or Dynamis may also refer to:
* Dynamis (Bosp ...
'') and actuality (''
entelecheia'') in association with the matter and the form. Referring to potentiality, this is what a thing is capable of doing or being acted upon if the conditions are right and it is not prevented by something else. For example, the seed of a plant in the soil is potentially (''dynamei'') a plant, and if it is not prevented by something, it will become a plant. Potentially beings can either 'act' (''poiein'') or 'be acted upon' (''paschein''), which can be either innate or learned. For example, the eyes possess the potentiality of sight (innate – being acted upon), while the capability of playing the flute can be possessed by learning (exercise – acting). Actuality is the fulfilment of the end of the potentiality. Because the end (''telos'') is the principle of every change, and potentiality exists for the sake of the end, actuality, accordingly, is the end. Referring then to the previous example, it can be said that an actuality is when a plant does one of the activities that plants do.
In summary, the matter used to make a house has potentiality to be a house and both the activity of building and the form of the final house are actualities, which is also a
final cause or end. Then Aristotle proceeds and concludes that the actuality is prior to potentiality in formula, in time and in substantiality. With this definition of the particular substance (i.e., matter and form), Aristotle tries to solve the problem of the unity of the beings, for example, "what is it that makes a man one"? Since, according to
Plato there are two Ideas: animal and biped, how then is man a unity? However, according to Aristotle, the potential being (matter) and the actual one (form) are one and the same.
Epistemology
Aristotle's immanent realism means his
epistemology is based on the study of things that exist or happen in the world, and rises to knowledge of the universal, whereas for Plato epistemology begins with knowledge of universal
Forms (or ideas) and descends to knowledge of particular imitations of these. Aristotle uses
induction
Induction, Inducible or Inductive may refer to:
Biology and medicine
* Labor induction (birth/pregnancy)
* Induction chemotherapy, in medicine
* Induced stem cells, stem cells derived from somatic, reproductive, pluripotent or other cell t ...
from examples alongside
deduction, whereas Plato relies on deduction from ''
a priori'' principles.
Natural philosophy
Aristotle's "natural philosophy" spans a wide range of natural phenomena including those now covered by physics, biology and other natural sciences. In Aristotle's terminology, "natural philosophy" is a branch of philosophy examining the phenomena of the natural world, and includes fields that would be regarded today as physics, biology and other natural sciences. Aristotle's work encompassed virtually all facets of intellectual inquiry. Aristotle makes philosophy in the broad sense coextensive with reasoning, which he also would describe as "science". However, his use of the term ''science'' carries a different meaning than that covered by the term "scientific method". For Aristotle, "all science (''dianoia'') is either practical, poetical or theoretical" (''Metaphysics'' 1025b25). His practical science includes ethics and politics; his poetical science means the study of fine arts including poetry; his theoretical science covers physics, mathematics and metaphysics.
Physics

Five elements
In his ''
On Generation and Corruption'', Aristotle related each of the four elements proposed earlier by
Empedocles,
earth,
water,
air, and
fire, to two of the four sensible qualities, hot, cold, wet, and dry. In the Empedoclean scheme, all matter was made of the four elements, in differing proportions. Aristotle's scheme added the heavenly
aether Aether, æther or ether may refer to:
Metaphysics and mythology
* Aether (classical element), the material supposed to fill the region of the universe above the terrestrial sphere
* Aether (mythology), the personification of the "upper sky", sp ...
, the divine substance of the
heavenly spheres
''Heavenly Spheres'' (L'Harmonie des Sphères) is an a cappella choral album by the Studio de musique ancienne de Montréal under the direction of Christopher Jackson. Recorded in 1998, it features songs from the late 15th to early 16th centu ...
, stars and planets.
Motion
Aristotle describes two kinds of motion: "violent" or "unnatural motion", such as that of a thrown stone, in the ''Physics'' (254b10), and "natural motion", such as of a falling object, in ''On the Heavens'' (300a20). In violent motion, as soon as the agent stops causing it, the motion stops also: in other words, the natural state of an object is to be at rest, since Aristotle does not address
friction. With this understanding, it can be observed that, as Aristotle stated, heavy objects (on the ground, say) require more force to make them move; and objects pushed with greater force move faster. This would imply the equation
::
,
incorrect in modern physics.
Natural motion depends on the element concerned: the aether naturally moves in a circle around the heavens, while the 4 Empedoclean elements move vertically up (like fire, as is observed) or down (like earth) towards their natural resting places.

In the ''Physics'' (215a25), Aristotle effectively states a quantitative law, that the speed, v, of a falling body is proportional (say, with constant c) to its weight, W, and inversely proportional to the density, ρ, of the fluid in which it is falling:;
::
Aristotle implies that in a
vacuum the speed of fall would become infinite, and concludes from this apparent absurdity that a vacuum is not possible. Opinions have varied on whether Aristotle intended to state quantitative laws. Henri Carteron held the "extreme view" that Aristotle's concept of force was basically qualitative, but other authors reject this.
Archimedes
Archimedes of Syracuse (;; ) was a Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor from the ancient city of Syracuse in Sicily. Although few details of his life are known, he is regarded as one of the leading scientists ...
corrected Aristotle's theory that bodies move towards their natural resting places; metal boats can float if they
displace enough water; floating depends in Archimedes' scheme on the mass and volume of the object, not, as Aristotle thought, its elementary composition.
Aristotle's writings on motion remained influential until the
Early Modern period.
John Philoponus (in the
Middle Ages) and
Galileo
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642) was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a polymath. Commonly referred to as Galileo, his name was pronounced (, ). He was ...
are said to have shown by experiment that Aristotle's claim that a heavier object falls faster than a lighter object is incorrect. A contrary opinion is given by
Carlo Rovelli
Carlo Rovelli (born May 3, 1956) is an Italian theoretical physicist and writer who has worked in Italy, the United States and, since 2000, in France. He is also currently a Distinguished Visiting Research Chair at the Perimeter Institute, and c ...
, who argues that Aristotle's physics of motion is correct within its domain of validity, that of objects in the
Earth's gravitational field immersed in a fluid such as air. In this system, heavy bodies in steady fall indeed travel faster than light ones (whether friction is ignored, or not), and they do fall more slowly in a denser medium.
Newton's "forced" motion corresponds to Aristotle's "violent" motion with its external agent, but Aristotle's assumption that the agent's effect stops immediately it stops acting (e.g., the ball leaves the thrower's hand) has awkward consequences: he has to suppose that surrounding fluid helps to push the ball along to make it continue to rise even though the hand is no longer acting on it, resulting in the Medieval
theory of impetus.
Four causes

Aristotle suggested that the reason for anything coming about can be attributed to four different types of simultaneously active factors. His term ''aitia'' is traditionally translated as "cause", but it does not always refer to temporal sequence; it might be better translated as "explanation", but the traditional rendering will be employed here.
*
Material cause describes the material out of which something is composed. Thus the material cause of a table is wood. It is not about action. It does not mean that one domino knocks over another domino.
* The
formal cause
The four causes or four explanations are, in Aristotelian thought, four fundamental types of answer to the question "why?", in analysis of change or movement in nature: the material, the formal, the efficient, and the final. Aristotle wrote th ...
is its form, i.e., the arrangement of that matter. It tells one what a thing is, that a thing is determined by the definition, form, pattern, essence, whole, synthesis or archetype. It embraces the account of causes in terms of fundamental principles or general laws, as the whole (i.e., macrostructure) is the cause of its parts, a relationship known as the whole-part causation. Plainly put, the formal cause is the idea in the mind of the sculptor that brings the sculpture into being. A simple example of the formal cause is the mental image or idea that allows an artist, architect, or engineer to create a drawing.
* The
efficient cause is "the primary source", or that from which the change under consideration proceeds. It identifies 'what makes of what is made and what causes change of what is changed' and so suggests all sorts of agents, non-living or living, acting as the sources of change or movement or rest. Representing the current understanding of causality as the relation of cause and effect, this covers the modern definitions of "cause" as either the agent or agency or particular events or states of affairs. In the case of two dominoes, when the first is knocked over it causes the second also to fall over. In the case of animals, this agency is a combination of
how it develops from the egg, and
how its body functions.
* The
final cause (''telos'') is its purpose, the reason why a thing exists or is done, including both purposeful and instrumental actions and activities. The final cause is the purpose or function that something is supposed to serve. This covers modern ideas of motivating causes, such as volition. In the case of living things, it implies
adaptation
In biology, adaptation has three related meanings. Firstly, it is the dynamic evolutionary process of natural selection that fits organisms to their environment, enhancing their evolutionary fitness. Secondly, it is a state reached by the po ...
to a particular way of life.
Optics
Aristotle describes experiments in
optics using a
camera obscura in ''
Problems'', book 15. The apparatus consisted of a dark chamber with a small
aperture that let light in. With it, he saw that whatever shape he made the hole, the sun's image always remained circular. He also noted that increasing the distance between the aperture and the image surface magnified the image.
Chance and spontaneity
According to Aristotle, spontaneity and chance are causes of some things, distinguishable from other types of cause such as simple necessity. Chance as an incidental cause lies in the realm of
accidental things, "from what is spontaneous". There is also more a specific kind of chance, which Aristotle names "luck", that only applies to people's moral choices.
Astronomy
In
astronomy, Aristotle refuted
Democritus's claim that the
Milky Way was made up of "those stars which are shaded by the earth from the sun's rays," pointing out correctly that if "the size of the sun is greater than that of the earth and the distance of the stars from the earth many times greater than that of the sun, then... the sun shines on all the stars and the earth screens none of them."
Geology and natural sciences

Aristotle was one of the first people to record any
geological observations. He stated that
geological change was too slow to be observed in one person's lifetime.
The geologist
Charles Lyell
Sir Charles Lyell, 1st Baronet, (14 November 1797 – 22 February 1875) was a Scottish geologist who demonstrated the power of known natural causes in explaining the earth's history. He is best known as the author of ''Principles of Geolo ...
noted that Aristotle described such change, including "lakes that had dried up" and "deserts that had become watered by rivers", giving as examples the growth of the
Nile delta
The Nile Delta ( ar, دلتا النيل, or simply , is the delta formed in Lower Egypt where the Nile River spreads out and drains into the Mediterranean Sea. It is one of the world's largest river deltas—from Alexandria in the west to Po ...
since the time of
Homer, and "the upheaving of one of the
Aeolian islands
The Aeolian Islands ( ; it, Isole Eolie ; scn, Ìsuli Eoli), sometimes referred to as the Lipari Islands or Lipari group ( , ) after their largest island, are a volcanic archipelago in the Tyrrhenian Sea north of Sicily, said to be named after ...
, previous to a
volcanic eruption."'
Aristotle also made many observations about the hydrologic cycle and meteorology (including his major writings "Meteorologica"). For example, he made some of the earliest observations about desalination: he observed early – and correctly – that when seawater is heated, freshwater evaporates and that the oceans are then replenished by the cycle of rainfall and river runoff ("I have proved by experiment that salt water evaporated forms fresh and the vapor does not when it condenses condense into sea water again.")
Biology

Empirical research
Aristotle was the first person to study biology systematically, and biology forms a large part of his writings. He spent two years observing and describing the zoology of
Lesbos and the surrounding seas, including in particular the Pyrrha lagoon in the centre of Lesbos. His data in ''
History of Animals'', ''
Generation of Animals'', ''
Movement of Animals'', and ''
Parts of Animals'' are assembled from his own observations, statements given by people with specialized knowledge such as beekeepers and fishermen, and less accurate accounts provided by travellers from overseas. His apparent emphasis on animals rather than plants is a historical accident: his works on
botany have been lost, but two books on plants by his pupil Theophrastus have survived.
Aristotle reports on the sea-life visible from observation on Lesbos and the catches of fishermen. He describes the
catfish,
electric ray, and
frogfish in detail, as well as
cephalopod
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan class Cephalopoda (Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head ...
s such as the
octopus
An octopus ( : octopuses or octopodes, see below for variants) is a soft-bodied, eight- limbed mollusc of the order Octopoda (, ). The order consists of some 300 species and is grouped within the class Cephalopoda with squids, cuttle ...
and
paper nautilus
The argonauts (genus ''Argonauta'', the only extant genus in the family Argonautidae) are a group of pelagic octopuses. They are also called paper nautili, referring to the paper-thin eggcase that females secrete. This structure lacks the gas-fi ...
. His description of the
hectocotyl arm of cephalopods, used in sexual reproduction, was widely disbelieved until the 19th century. He gives accurate descriptions of the four-chambered fore-stomachs of
ruminants, and of the
ovoviviparous embryological development of the
hound shark.
He notes that an animal's structure is well matched to function, so, among birds, the
heron
The herons are long-legged, long-necked, freshwater and coastal birds in the family Ardeidae, with 72 recognised species, some of which are referred to as egrets or bitterns rather than herons. Members of the genera ''Botaurus'' and ''Ixobrychus ...
, which lives in marshes with soft mud and lives by catching fish, has a long neck and long legs, and a sharp spear-like beak, whereas
ducks that swim have short legs and webbed feet.
Darwin
Darwin may refer to:
Common meanings
* Charles Darwin (1809–1882), English naturalist and writer, best known as the originator of the theory of biological evolution by natural selection
* Darwin, Northern Territory, a territorial capital city i ...
, too, noted these sorts of differences between similar kinds of animal, but unlike Aristotle used the data to come to the theory of
evolution. Aristotle's writings can seem to modern readers close to implying evolution, but while Aristotle was aware that new mutations or
hybridizations could occur, he saw these as rare accidents. For Aristotle, accidents, like heat waves in winter, must be considered distinct from natural causes. He was thus critical of Empedocles's materialist theory of a "survival of the fittest" origin of living things and their organs, and ridiculed the idea that accidents could lead to orderly results. To put his views into modern terms, he nowhere says that different species can have a
common ancestor, or that one kind can
change into another, or that kinds can become
extinct
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and ...
.
Scientific style

Aristotle did not do experiments in the modern sense. He used the ancient Greek term ''pepeiramenoi'' to mean observations, or at most investigative procedures like dissection. In ''Generation of Animals'', he finds a fertilized hen's egg of a suitable stage and opens it to see the embryo's heart beating inside.
Instead, he practiced a different style of science: systematically gathering data, discovering patterns common to whole groups of animals, and inferring possible causal explanations from these.; This style is common in modern biology when large amounts of data become available in a new field, such as
genomics
Genomics is an interdisciplinary field of biology focusing on the structure, function, evolution, mapping, and editing of genomes. A genome is an organism's complete set of DNA, including all of its genes as well as its hierarchical, three-dim ...
. It does not result in the same certainty as experimental science, but it sets out testable hypotheses and constructs a narrative explanation of what is observed. In this sense,
Aristotle's biology is scientific.
From the data he collected and documented, Aristotle inferred quite a number of
rules relating the life-history features of the live-bearing tetrapods (terrestrial placental mammals) that he studied. Among these correct predictions are the following. Brood size decreases with (adult) body mass, so that an elephant has fewer young (usually just one) per brood than a mouse.
Lifespan increases with
gestation period
In mammals, pregnancy is the period of reproduction during which a female carries one or more live offspring from implantation in the uterus through gestation. It begins when a fertilized zygote implants in the female's uterus, and ends once it ...
, and also with body mass, so that elephants live longer than mice, have a longer period of gestation, and are heavier. As a final example,
fecundity decreases with lifespan, so long-lived kinds like elephants have fewer young in total than short-lived kinds like mice.
Classification of living things

Aristotle distinguished about 500 species of
animals, arranging these in the ''History of Animals'' in a graded scale of perfection, a nonreligious version of the ''
scala naturae
The great chain of being is a hierarchical structure of all matter and life, thought by medieval Christianity to have been decreed by God. The chain begins with God and descends through angels, humans, animals and plants to minerals.
The great c ...
'', with man at the top. His system had eleven grades of animal, from highest potential to lowest, expressed in their form at birth: the highest gave
live birth to hot and wet creatures, the lowest laid cold, dry mineral-like eggs. Animals came above
plants, and these in turn were above minerals. He grouped what the modern zoologist would call
vertebrates as the hotter "animals with blood", and below them the colder
invertebrates as "animals without blood". Those with blood were divided into the live-bearing (
mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or ...
s), and the egg-laying (
birds,
reptile
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians ( ...
s,
fish). Those without blood were insects, crustacea (non-shelled – cephalopods, and
shelled) and the hard-shelled
mollusc
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is esti ...
s (
bivalve
Bivalvia (), in previous centuries referred to as the Lamellibranchiata and Pelecypoda, is a class of marine and freshwater molluscs that have laterally compressed bodies enclosed by a shell consisting of two hinged parts. As a group, bival ...
s and
gastropod
The gastropods (), commonly known as snails and slugs, belong to a large taxonomic class of invertebrates within the phylum Mollusca called Gastropoda ().
This class comprises snails and slugs from saltwater, from freshwater, and from land. T ...
s). He recognised that animals did not exactly fit into a linear scale, and noted various exceptions, such as that sharks had a
placenta like the tetrapods. To a modern biologist, the explanation, not available to Aristotle, is
convergent evolution. Philosophers of science have generally concluded that Aristotle was not interested in taxonomy, but zoologists who studied this question recently think otherwise. He believed that purposive final causes guided all natural processes; this
teleological view justified his observed data as an expression of formal design.
Psychology
Soul

Aristotle's
psychology, given in his treatise ''
On the Soul'' (''peri psychēs''), posits three kinds of
soul ("psyches"): the vegetative soul, the sensitive soul, and the rational soul. Humans have a rational soul. The human soul incorporates the powers of the other kinds: Like the vegetative soul it can grow and nourish itself; like the sensitive soul it can experience sensations and move locally. The unique part of the human, rational soul is its ability to receive forms of other things and to compare them using the ''
nous
''Nous'', or Greek νοῦς (, ), sometimes equated to intellect or intelligence, is a concept from classical philosophy for the faculty of the human mind necessary for understanding what is true or real.
Alternative English terms used in p ...
'' (intellect) and ''logos'' (reason).
For Aristotle, the soul is the
form
Form is the shape, visual appearance, or configuration of an object. In a wider sense, the form is the way something happens.
Form also refers to:
*Form (document), a document (printed or electronic) with spaces in which to write or enter data
...
of a living being. Because all beings are composites of form and matter, the form of living beings is that which endows them with what is specific to living beings, e.g. the ability to initiate movement (or in the case of plants, growth and chemical transformations, which Aristotle considers types of movement). In contrast to earlier philosophers, but in accordance with the Egyptians, he placed the rational soul in the heart, rather than the brain. Notable is Aristotle's division of sensation and thought, which generally differed from the concepts of previous philosophers, with the exception of
Alcmaeon.
In ''On the Soul'', Aristotle famously criticizes Plato's theory of the soul and develops his own in response to Plato's. The first criticism is against Plato's view of the soul in the ''Timaeus'' that the soul takes up space and is able to come into physical contact with bodies. 20th-century scholarship overwhelmingly opposed Aristotle's interpretation of Plato and maintained that he had misunderstood Plato. Today's scholars have tended to re-assess Aristotle's interpretation and have warmed up to it. Aristotle's other criticism is that Plato's view of reincarnation entails that it is possible for a soul and its body to be mis-matched; in principle, Aristotle alleges, any soul can go with any body, according to Plato's theory. Aristotle's claim that the soul is the form of a living being is meant to eliminate that possibility and thus rule out reincarnation.
Memory
According to Aristotle in ''On the Soul'', memory is the ability to hold a perceived experience in the mind and to distinguish between the internal "appearance" and an occurrence in the past. In other words, a memory is a mental picture (
phantasm) that can be recovered. Aristotle believed an impression is left on a semi-fluid bodily organ that undergoes several changes in order to make a memory. A memory occurs when
stimuli such as sights or sounds are so complex that the nervous system cannot receive all the impressions at once. These changes are the same as those involved in the operations of sensation, Aristotelian , and thinking.
Aristotle uses the term 'memory' for the actual retaining of an experience in the impression that can develop from sensation, and for the intellectual anxiety that comes with the impression because it is formed at a particular time and processing specific contents. Memory is of the past, prediction is of the future, and sensation is of the present. Retrieval of impressions cannot be performed suddenly. A transitional channel is needed and located in past experiences, both for previous experience and present experience.
Because Aristotle believes people receive all kinds of sense perceptions and perceive them as impressions, people are continually weaving together new impressions of experiences. To search for these impressions, people search the memory itself. Within the memory, if one experience is offered instead of a specific memory, that person will reject this experience until they find what they are looking for. Recollection occurs when one retrieved experience naturally follows another. If the chain of "images" is needed, one memory will stimulate the next. When people recall experiences, they stimulate certain previous experiences until they reach the one that is needed. Recollection is thus the self-directed activity of retrieving the information stored in a memory impression. Only humans can remember impressions of intellectual activity, such as numbers and words. Animals that have perception of time can retrieve memories of their past observations. Remembering involves only perception of the things remembered and of the time passed.

Aristotle believed the chain of thought, which ends in recollection of certain impressions, was connected systematically in relationships such as similarity, contrast, and
contiguity, described in his
laws of association
In psychology, the principal laws of association are contiguity, repetition, attention, pleasure-pain, and similarity. The basic laws were formulated by Aristotle in approximately 300 B.C. and by John Locke
John Locke (; 29 August 16 ...
. Aristotle believed that past experiences are hidden within the mind. A force operates to awaken the hidden material to bring up the actual experience. According to Aristotle, association is the power innate in a mental state, which operates upon the unexpressed remains of former experiences, allowing them to rise and be recalled.
Dreams
Aristotle describes sleep in ''On Sleep and Wakefulness''. Sleep takes place as a result of overuse of the senses or of digestion, so it is vital to the body. While a person is asleep, the critical activities, which include thinking, sensing, recalling and remembering, do not function as they do during wakefulness. Since a person cannot sense during sleep they cannot have desire, which is the result of sensation. However, the senses are able to work during sleep, albeit differently, unless they are weary.
Dreams do not involve actually sensing a stimulus. In dreams, sensation is still involved, but in an altered manner. Aristotle explains that when a person stares at a moving stimulus such as the waves in a body of water, and then looks away, the next thing they look at appears to have a wavelike motion. When a person perceives a stimulus and the stimulus is no longer the focus of their attention, it leaves an impression. When the body is awake and the senses are functioning properly, a person constantly encounters new stimuli to sense and so the impressions of previously perceived stimuli are ignored. However, during sleep the impressions made throughout the day are noticed as there are no new distracting sensory experiences. So, dreams result from these lasting impressions. Since impressions are all that are left and not the exact stimuli, dreams do not resemble the actual waking experience. During sleep, a person is in an altered state of mind. Aristotle compares a sleeping person to a person who is overtaken by strong feelings toward a stimulus. For example, a person who has a strong infatuation with someone may begin to think they see that person everywhere because they are so overtaken by their feelings. Since a person sleeping is in a suggestible state and unable to make judgements, they become easily deceived by what appears in their dreams, like the infatuated person. This leads the person to believe the dream is real, even when the dreams are absurd in nature. In ''De Anima'' iii 3, Aristotle ascribes the ability to create, to store, and to recall images in the absence of perception to the faculty of imagination, ''phantasia''.
One component of Aristotle's theory of dreams disagrees with previously held beliefs. He claimed that dreams are not foretelling and not sent by a divine being. Aristotle reasoned naturalistically that instances in which dreams do resemble future events are simply coincidences. Aristotle claimed that a dream is first established by the fact that the person is asleep when they experience it. If a person had an image appear for a moment after waking up or if they see something in the dark it is not considered a dream because they were awake when it occurred. Secondly, any sensory experience that is perceived while a person is asleep does not qualify as part of a dream. For example, if, while a person is sleeping, a door shuts and in their dream they hear a door is shut, this sensory experience is not part of the dream. Lastly, the images of dreams must be a result of lasting impressions of waking sensory experiences.
Practical philosophy
Aristotle's practical philosophy covers areas such as
ethics,
politics,
economics, and
rhetoric
Rhetoric () is the art of persuasion, which along with grammar and logic (or dialectic), is one of the three ancient arts of discourse. Rhetoric aims to study the techniques writers or speakers utilize to inform, persuade, or motivate parti ...
.
Ethics
Aristotle considered ethics to be a practical rather than theoretical study, i.e., one aimed at becoming good and doing good rather than knowing for its own sake. He wrote several treatises on ethics, most notably including the ''
Nicomachean Ethics
The ''Nicomachean Ethics'' (; ; grc, Ἠθικὰ Νικομάχεια, ) is Aristotle's best-known work on ethics, the science of the good for human life, which is the goal or end at which all our actions aim. (I§2) The aim of the inquiry is ...
''.
Aristotle taught that virtue has to do with the proper function (''ergon'') of a thing. An eye is only a good eye in so much as it can see, because the proper function of an eye is sight. Aristotle reasoned that humans must have a function specific to humans, and that this function must be an activity of the ''
psuchē'' (''soul'') in accordance with reason (''
logos''). Aristotle identified such an optimum activity (the virtuous mean, between the accompanying vices of excess or deficiency) of the soul as the aim of all human deliberate action, ''
eudaimonia
Eudaimonia (Greek: εὐδαιμονία ; sometimes anglicized as eudaemonia or eudemonia, ) is a Greek word literally translating to the state or condition of 'good spirit', and which is commonly translated as 'happiness' or 'welfare'.
In wor ...
'', generally translated as "happiness" or sometimes "well-being". To have the potential of ever being happy in this way necessarily requires a good character (''ēthikē'' ''
aretē''), often translated as moral or ethical virtue or excellence.
Aristotle taught that to achieve a virtuous and potentially happy character requires a first stage of having the fortune to be habituated not deliberately, but by teachers, and experience, leading to a later stage in which one consciously chooses to do the best things. When the best people come to live life this way their practical wisdom (''
phronesis
''Phronesis'' ( grc, φρόνησῐς, phrónēsis), translated into English by terms such as prudence, practical virtue and practical wisdom, or, colloquially, sense (as in "good sense", "horse sense") is an ancient Greek word for a type of w ...
'') and their intellect (''
nous
''Nous'', or Greek νοῦς (, ), sometimes equated to intellect or intelligence, is a concept from classical philosophy for the faculty of the human mind necessary for understanding what is true or real.
Alternative English terms used in p ...
'') can develop with each other towards the highest possible human virtue, the wisdom of an accomplished theoretical or speculative thinker, or in other words, a philosopher.
Politics
In addition to his works on ethics, which address the individual, Aristotle addressed the city in his work titled ''
Politics''. Aristotle considered the city to be a natural community. Moreover, he considered the city to be prior in importance to the family, which in turn is prior to the individual, "for the whole must of necessity be prior to the part". He famously stated that "man is by nature a political animal" and argued that humanity's defining factor among others in the animal kingdom is its rationality. Aristotle conceived of politics as being like an organism rather than like a machine, and as a collection of parts none of which can exist without the others. Aristotle's conception of the city is organic, and he is considered one of the first to conceive of the city in this manner.

The common modern understanding of a political community as a modern state is quite different from Aristotle's understanding. Although he was aware of the existence and potential of larger empires, the natural community according to Aristotle was the city (''
polis'') which functions as a political "community" or "partnership" (''koinōnia''). The aim of the city is not just to avoid injustice or for economic stability, but rather to allow at least some citizens the possibility to live a good life, and to perform beautiful acts: "The political partnership must be regarded, therefore, as being for the sake of noble actions, not for the sake of living together." This is distinguished from modern approaches, beginning with
social contract
In moral and political philosophy
Political philosophy or political theory is the philosophical study of government, addressing questions about the nature, scope, and legitimacy of public agents and institutions and the relationships betw ...
theory, according to which individuals leave the
state of nature
The state of nature, in moral and political philosophy, religion, social contract theories and international law, is the hypothetical life of people before societies came into existence. Philosophers of the state of nature theory deduce that ther ...
because of "fear of violent death" or its "inconveniences".
In ''
Protrepticus'', the character 'Aristotle' states:
As Plato's disciple Aristotle was rather critical concerning democracy and, following the outline of certain ideas from Plato's ''
Statesman
A statesman or stateswoman typically is a politician who has had a long and respected political career at the national or international level.
Statesman or Statesmen may also refer to:
Newspapers United States
* ''The Statesman'' (Oregon), a n ...
'', he developed a coherent theory of integrating various forms of power into a so-called mixed state:
To illustrate this approach, Aristotle proposed a first-of-its-kind mathematical model of voting, albeit textually described, where the democratic principle of "one voter–one vote" is combined with the oligarchic "merit-weighted voting"; for relevant quotes and their translation into mathematical formulas see.
Economics
Aristotle made substantial contributions to
economic thought
Economics () is the social science that studies the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services.
Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Microeconomics analyzes w ...
, especially to thought in the Middle Ages. In ''
Politics'', Aristotle addresses the city,
property, and
trade. His response to criticisms of
private property
Private property is a legal designation for the ownership of property by non-governmental legal entities. Private property is distinguishable from public property and personal property, which is owned by a state entity, and from collective or ...
, in
Lionel Robbins's view, anticipated later proponents of private property among philosophers and economists, as it related to the overall
utility of social arrangements. Aristotle believed that although communal arrangements may seem beneficial to society, and that although private property is often blamed for social strife, such evils in fact come from
human nature. In ''Politics'', Aristotle offers one of the earliest accounts of the origin of
money. Money came into use because people became dependent on one another, importing what they needed and exporting the surplus. For the sake of convenience, people then agreed to deal in something that is intrinsically useful and easily applicable, such as iron or
silver.
Aristotle's discussions on
retail and
interest was a major influence on economic thought in the Middle Ages. He had a low opinion of retail, believing that contrary to using money to procure things one needs in managing the household, retail trade seeks to make a
profit
Profit may refer to:
Business and law
* Profit (accounting), the difference between the purchase price and the costs of bringing to market
* Profit (economics), normal profit and economic profit
* Profit (real property), a nonpossessory intere ...
. It thus uses goods as a means to an end, rather than as an end unto itself. He believed that retail trade was in this way unnatural. Similarly, Aristotle considered making a profit through interest unnatural, as it makes a gain out of the money itself, and not from its use.
Aristotle gave a summary of the function of money that was perhaps remarkably precocious for his time. He wrote that because it is impossible to determine the value of every good through a count of the number of other goods it is worth, the necessity arises of a single universal standard of measurement. Money thus allows for the association of different goods and makes them "commensurable". He goes on to state that money is also useful for future exchange, making it a sort of security. That is, "if we do not want a thing now, we shall be able to get it when we do want it".
Rhetoric and poetics
Aristotle's ''Rhetoric'' proposes that a speaker can use three basic kinds of appeals to persuade his audience: ''
ethos'' (an appeal to the speaker's character), ''
pathos
Pathos (, ; plural: ''pathea'' or ''pathê''; , for "suffering" or "experience") appeals to the emotions and ideals of the audience and elicits feelings that already reside in them. Pathos is a term used most often in rhetoric (in which it is c ...
'' (an appeal to the audience's emotion), and ''
logos'' (an appeal to logical reasoning). He also categorizes rhetoric into three genres:
epideictic
The epideictic oratory, also called ceremonial oratory, or praise-and-blame rhetoric, is one of the three branches, or "species" (eidē), of rhetoric as outlined in Aristotle's '' Rhetoric'', to be used to praise or blame during ceremonies.
Orig ...
(ceremonial speeches dealing with praise or blame),
forensic (judicial speeches over guilt or innocence), and
deliberative Deliberative rhetoric (Greek: ''genos'' ''symbouleutikon;'' Latin: ''genus deliberativum,'' sometimes called legislative oratory) is one of the three kinds of rhetoric described by Aristotle. Deliberative rhetoric juxtaposes potential future outcome ...
(speeches calling on an audience to make a decision on an issue). Aristotle also outlines two kinds of rhetorical
proofs
Proof most often refers to:
* Proof (truth), argument or sufficient evidence for the truth of a proposition
* Alcohol proof, a measure of an alcoholic drink's strength
Proof may also refer to:
Mathematics and formal logic
* Formal proof, a co ...
: ''
enthymeme
An enthymeme ( el, ἐνθύμημα, ''enthýmēma'') is a form of rational appeal, or deductive argument. It is also known as a rhetorical syllogism and is used in oratorical practice. While the syllogism is used in dialectic, or the art of logi ...
'' (proof by
syllogism
A syllogism ( grc-gre, συλλογισμός, ''syllogismos'', 'conclusion, inference') is a kind of logical argument that applies deductive reasoning to arrive at a conclusion based on two propositions that are asserted or assumed to be true.
...
) and ''
paradeigma'' (proof by example).
Aristotle writes in his ''Poetics'' that
epic poetry, tragedy, comedy,
dithyrambic poetry, painting, sculpture, music, and dance are all fundamentally acts of ''
mimesis
Mimesis (; grc, μίμησις, ''mīmēsis'') is a term used in literary criticism and philosophy that carries a wide range of meanings, including ''imitatio'', imitation, nonsensuous similarity, receptivity, representation, mimicry, the act ...
'' ("imitation"), each varying in imitation by medium, object, and manner. He applies the term ''mimesis'' both as a property of a work of art and also as the product of the artist's intention and contends that the audience's realisation of the ''mimesis'' is vital to understanding the work itself. Aristotle states that ''mimesis'' is a natural instinct of humanity that separates humans from animals and that all human artistry "follows the pattern of nature". Because of this, Aristotle believed that each of the mimetic arts possesses what
Stephen Halliwell calls "highly structured procedures for the achievement of their purposes." For example, music imitates with the media of rhythm and harmony, whereas dance imitates with rhythm alone, and poetry with language. The forms also differ in their object of imitation. Comedy, for instance, is a dramatic imitation of men worse than average; whereas tragedy imitates men slightly better than average. Lastly, the forms differ in their manner of imitation – through narrative or character, through change or no change, and through drama or no drama.
While it is believed that Aristotle's ''Poetics'' originally comprised two books – one on comedy and one on tragedy – only the portion that focuses on tragedy has survived. Aristotle taught that tragedy is composed of six elements: plot-structure, character, style, thought, spectacle, and lyric poetry. The characters in a tragedy are merely a means of driving the story; and the plot, not the characters, is the chief focus of tragedy. Tragedy is the imitation of action arousing pity and fear, and is meant to effect the
catharsis of those same emotions. Aristotle concludes ''Poetics'' with a discussion on which, if either, is superior: epic or tragic mimesis. He suggests that because tragedy possesses all the attributes of an epic, possibly possesses additional attributes such as spectacle and music, is more unified, and achieves the aim of its mimesis in shorter scope, it can be considered superior to epic. Aristotle was a keen systematic collector of riddles, folklore, and proverbs; he and his school had a special interest in the riddles of the
Delphic Oracle
Pythia (; grc, Πυθία ) was the name of the high priestess of the Temple of Apollo at Delphi. She specifically served as its oracle and was known as the Oracle of Delphi. Her title was also historically glossed in English as the Pythoness ...
and studied the fables of
Aesop.
Views on women
Aristotle's analysis of procreation describes an active, ensouling masculine element bringing life to an inert, passive female element. The biological differences are a result of the fact that the female body is well-suited for reproduction, which changes her body temperature, which in turn makes her, in Aristotle's view, incapable of participating in political life. On this ground, proponents of
feminist metaphysics have accused Aristotle of
misogyny and
sexism. However, Aristotle gave equal weight to women's happiness as he did to men's, and commented in his ''Rhetoric'' that the things that lead to happiness need to be in women as well as men.
Influence
More than 2300 years after his death, Aristotle remains one of the most influential people who ever lived. He contributed to almost every field of human knowledge then in existence, and he was the founder of many new fields. According to the philosopher
Bryan Magee, "it is doubtful whether any human being has ever known as much as he did". Among countless other achievements, Aristotle was the founder of
formal logic, pioneered the study of
zoology, and left every future scientist and philosopher in his debt through his contributions to the scientific method. Taneli Kukkonen, writing in ''The Classical Tradition'', observes that his achievement in founding two sciences is unmatched, and his reach in influencing "every branch of intellectual enterprise" including Western ethical and political theory, theology, rhetoric and literary analysis is equally long. As a result, Kukkonen argues, any analysis of reality today "will almost certainly carry Aristotelian overtones ... evidence of an exceptionally forceful mind."
Jonathan Barnes wrote that "an account of Aristotle's intellectual afterlife would be little less than a history of European thought".
On his successor, Theophrastus

Aristotle's pupil and successor,
Theophrastus, wrote the ''
History of Plants'', a pioneering work in botany. Some of his technical terms remain in use, such as
carpel from ''carpos'', fruit, and
pericarp, from ''pericarpion'', seed chamber.
Theophrastus was much less concerned with formal causes than Aristotle was, instead pragmatically describing how plants functioned.
On later Greek philosophers
The immediate influence of Aristotle's work was felt as the
Lyceum grew into the
Peripatetic school. Aristotle's students included
Aristoxenus,
Dicaearchus,
Demetrius of Phalerum
Demetrius of Phalerum (also Demetrius of Phaleron or Demetrius Phalereus; grc-gre, Δημήτριος ὁ Φαληρεύς; c. 350 – c. 280 BC) was an Athenian orator originally from Phalerum, an ancient port of Athens. A student of Theophrast ...
,
Eudemos of Rhodes,
Harpalus,
Hephaestion
Hephaestion ( grc, Ἡφαιστίων ''Hephaistíon''; c. 356 BC – October 324 BC), son of Amyntor, was an ancient Macedonian nobleman and a general in the army of Alexander the Great. He was "by far the dearest of all the ...
,
Mnason of Phocis,
Nicomachus
Nicomachus of Gerasa ( grc-gre, Νικόμαχος; c. 60 – c. 120 AD) was an important ancient mathematician and music theorist, best known for his works ''Introduction to Arithmetic'' and ''Manual of Harmonics'' in Greek. He was born in ...
, and Theophrastus. Aristotle's influence over
Alexander the Great is seen in the latter's bringing with him on his expedition a host of zoologists, botanists, and researchers. He had also learned a great deal about
Persian customs and traditions from his teacher. Although his respect for Aristotle was diminished as his travels made it clear that much of Aristotle's geography was clearly wrong, when the old philosopher released his works to the public, Alexander complained "Thou hast not done well to publish thy acroamatic doctrines; for in what shall I surpass other men if those doctrines wherein I have been trained are to be all men's common property?"
On Hellenistic science
After Theophrastus, the Lyceum failed to produce any original work. Though interest in Aristotle's ideas survived, they were generally taken unquestioningly. It is not until the age of
Alexandria under the
Ptolemies
The Ptolemaic dynasty (; grc, Πτολεμαῖοι, ''Ptolemaioi''), sometimes referred to as the Lagid dynasty (Λαγίδαι, ''Lagidae;'' after Ptolemy I's father, Lagus), was a Macedonian Greek royal dynasty which ruled the Ptolemaic K ...
that advances in biology can be again found.
The first medical teacher at Alexandria,
Herophilus of Chalcedon
Herophilos (; grc-gre, Ἡρόφιλος; 335–280 BC), sometimes Latinised Herophilus, was a Greek physician regarded as one of the earliest anatomists. Born in Chalcedon, he spent the majority of his life in Alexandria. He was the first sci ...
, corrected Aristotle, placing intelligence in the brain, and connected the nervous system to motion and sensation. Herophilus also distinguished between
veins and
arteries, noting that the latter
pulse while the former do not. Though a few ancient
atomists such as
Lucretius challenged the
teleological viewpoint of Aristotelian ideas about life,
teleology (and after the rise of Christianity,
natural theology
Natural theology, once also termed physico-theology, is a type of theology that seeks to provide arguments for theological topics (such as the existence of a deity) based on reason and the discoveries of science.
This distinguishes it from ...
) would remain central to biological thought essentially until the 18th and 19th centuries.
Ernst Mayr
Ernst Walter Mayr (; 5 July 1904 – 3 February 2005) was one of the 20th century's leading evolutionary biologists. He was also a renowned Taxonomy (biology), taxonomist, tropical explorer, ornithologist, Philosophy of biology, philosopher o ...
states that there was "nothing of any real consequence in biology after Lucretius and
Galen until the Renaissance."
On Byzantine scholars
Greek Christian scribes played a crucial role in the preservation of Aristotle by copying all the extant Greek language manuscripts of the corpus. The first Greek Christians to comment extensively on Aristotle were Philoponus, Elias, and David in the sixth century, and
Stephen of Alexandria
Stephanus of Alexandria (; fl. c. 580 – c. 640) was a Byzantine philosopher and teacher who, besides philosophy in the Neo-Platonic tradition, also wrote on alchemy, astrology and astronomy. He was one of the last exponents of the Alexandrian aca ...
in the early seventh century.
John Philoponus stands out for having attempted a fundamental critique of Aristotle's views on the eternity of the world, movement, and other elements of Aristotelian thought. Philoponus questioned Aristotle's teaching of physics, noting its flaws and introducing the
theory of impetus to explain his observations.
After a hiatus of several centuries, formal commentary by Eustratius and
Michael of Ephesus
Michael of Ephesus or Michael Ephesius ( grc-gre, Μιχαήλ Ἐφέσιος; fl. early or mid-12th century AD) wrote important commentaries on Aristotle, including the first full commentary on the ''Sophistical Refutations'', which established ...
reappeared in the late eleventh and early twelfth centuries, apparently sponsored by
Anna Comnena.
On the medieval Islamic world

Aristotle was one of the most revered Western thinkers in early
Islamic theology. Most of the still extant works of Aristotle, as well as a number of the original Greek commentaries, were translated into Arabic and studied by Muslim philosophers, scientists and scholars.
Averroes,
Avicenna
Ibn Sina ( fa, ابن سینا; 980 – June 1037 CE), commonly known in the West as Avicenna (), was a Persian polymath who is regarded as one of the most significant physicians, astronomers, philosophers, and writers of the Islamic G ...
and
Alpharabius
Abu Nasr Muhammad Al-Farabi ( fa, ابونصر محمد فارابی), ( ar, أبو نصر محمد الفارابي), known in the West as Alpharabius; (c. 872 – between 14 December, 950 and 12 January, 951)PDF version was a renowned early Isla ...
, who wrote on Aristotle in great depth, also influenced
Thomas Aquinas and other Western Christian scholastic philosophers.
Alkindus
Abū Yūsuf Yaʻqūb ibn ʼIsḥāq aṣ-Ṣabbāḥ al-Kindī (; ar, أبو يوسف يعقوب بن إسحاق الصبّاح الكندي; la, Alkindus; c. 801–873 AD) was an Arab Muslim philosopher, polymath, mathematician, physicia ...
greatly admired Aristotle's philosophy, and Averroes spoke of Aristotle as the "exemplar" for all future philosophers. Medieval Muslim scholars regularly described Aristotle as the "First Teacher". The title was later used by Western philosophers (as in the famous poem of
Dante) who were influenced by the tradition of
Islamic philosophy.
On medieval Europe
With the loss of the study of ancient Greek in the early
medieval Latin West, Aristotle was practically unknown there from c. AD 600 to c. 1100 except through the Latin translation of the ''Organon'' made by
Boethius. In the twelfth and thirteenth centuries, interest in Aristotle revived and Latin Christians had translations made, both from Arabic translations, such as those by
Gerard of Cremona, and from the original Greek, such as those by
James of Venice James of Venice was a Catholic cleric and significant translator of Aristotle of the twelfth century. He has been called "the first systematic translator of Aristotle since Boethius." Not much is otherwise known about him.
He was active in particul ...
and
William of Moerbeke. After the
Scholastic Thomas Aquinas wrote his ''
Summa Theologica'', working from Moerbeke's translations and calling Aristotle "The Philosopher", the demand for Aristotle's writings grew, and the
Greek manuscripts returned to the West, stimulating a revival of Aristotelianism in Europe that continued into the
Renaissance. These thinkers blended Aristotelian philosophy with Christianity, bringing the thought of Ancient Greece into the Middle Ages. Scholars such as Boethius,
Peter Abelard
Peter Abelard (; french: link=no, Pierre Abélard; la, Petrus Abaelardus or ''Abailardus''; 21 April 1142) was a medieval French scholastic philosopher, leading logician, theologian, poet, composer and musician. This source has a detailed desc ...
, and
John Buridan
Jean Buridan (; Latin: ''Johannes Buridanus''; – ) was an influential 14th-century French philosopher.
Buridan was a teacher in the faculty of arts at the University of Paris for his entire career who focused in particular on logic and the wo ...
worked on Aristotelian logic.
The medieval English poet
Chaucer describes his student as being happy by having
A
cautionary medieval tale held that Aristotle advised his pupil Alexander to avoid the king's seductive mistress, Phyllis, but was himself captivated by her, and allowed her to ride him. Phyllis had secretly told Alexander what to expect, and he witnessed Phyllis proving that a woman's charms could overcome even the greatest philosopher's male intellect. Artists such as
Hans Baldung produced a series of illustrations of the popular theme.
The Italian poet Dante says of Aristotle in ''
The Divine Comedy'':
Besides Dante's fellow poets, the classical figure that most influenced the
''Comedy'' is Aristotle. Dante built up the philosophy of the ''Comedy'' with the works of Aristotle as a foundation, just as the scholastics used Aristotle as the basis for their thinking. Dante knew Aristotle directly from Latin translations of his works and indirectly through quotations in the works of
Albert Magnus. Dante even acknowledges Aristotle's influence explicitly in the poem, specifically when Virgil justifies the Inferno's structure by citing the ''
Nicomachean Ethics
The ''Nicomachean Ethics'' (; ; grc, Ἠθικὰ Νικομάχεια, ) is Aristotle's best-known work on ethics, the science of the good for human life, which is the goal or end at which all our actions aim. (I§2) The aim of the inquiry is ...
''.
On medieval Judaism
Moses Maimonides (considered to be the foremost intellectual figure of medieval Judaism) adopted Aristotelianism from the Islamic scholars and based his ''
Guide for the Perplexed'' on it and that became the basis of Jewish
scholastic philosophy
Scholasticism was a medieval school of philosophy that employed a critical organic method of philosophical analysis predicated upon the Aristotelian 10 Categories. Christian scholasticism emerged within the monastic schools that translate ...
. Maimonides also considered Aristotle to be the greatest philosopher that ever lived, and styled him as the "chief of the philosophers". Also, in his letter to
Samuel ibn Tibbon, Maimonides observes that there is no need for Samuel to study the writings of philosophers who preceded Aristotle because the works of the latter are "sufficient by themselves and
uperiorto all that were written before them. His intellect, Aristotle's is the extreme limit of human intellect, apart from him upon whom the divine emanation has flowed forth to such an extent that they reach the level of prophecy, there being no level higher".
On Early Modern scientists

In the
Early Modern period, scientists such as
William Harvey in England and
Galileo Galilei in Italy reacted against the theories of Aristotle and other classical era thinkers like
Galen, establishing new theories based to some degree on observation and experiment. Harvey demonstrated the
circulation of the blood, establishing that the heart functioned as a pump rather than being the seat of the soul and the controller of the body's heat, as Aristotle thought. Galileo used more doubtful arguments to displace Aristotle's physics, proposing that bodies all fall at the same speed whatever their weight.
On 18th/19th-century thinkers
The 19th-century German philosopher
Friedrich Nietzsche has been said to have taken nearly all of his political philosophy from Aristotle. Aristotle rigidly separated action from production, and argued for the deserved subservience of some people ("natural slaves"), and the natural superiority (virtue, ''arete'') of others. It was
Martin Heidegger
Martin Heidegger (; ; 26 September 188926 May 1976) was a German philosopher who is best known for contributions to phenomenology, hermeneutics, and existentialism. He is among the most important and influential philosophers of the 20th centur ...
, not Nietzsche, who elaborated a new interpretation of Aristotle, intended to warrant his deconstruction of scholastic and philosophical tradition.
The English mathematician
George Boole fully accepted Aristotle's logic, but decided "to go under, over, and beyond" it with his system of
algebraic logic
In mathematical logic, algebraic logic is the reasoning obtained by manipulating equations with free variables.
What is now usually called classical algebraic logic focuses on the identification and algebraic description of models appropriate for ...
in his 1854 book ''
The Laws of Thought''. This gives logic a mathematical foundation with equations, enables it to solve equations as well as check
validity
Validity or Valid may refer to:
Science/mathematics/statistics:
* Validity (logic), a property of a logical argument
* Scientific:
** Internal validity, the validity of causal inferences within scientific studies, usually based on experiments
** ...
, and allows it to handle a wider class of problems by expanding propositions of any number of terms, not just two.
Charles Darwin regarded Aristotle as the most important contributor to the subject of biology. In an 1882 letter he wrote that "Linnaeus and Cuvier have been my two gods, though in very different ways, but they were mere schoolboys to old Aristotle".
Also, in later editions of the book "
On the Origin of Species', Darwin traced evolutionary ideas as far back as Aristotle; the text he cites is a summary by Aristotle of the ideas of the earlier Greek philosopher
Empedocles.
James Joyce's favoured philosopher was Aristotle, whom he considered to be "the greatest thinker of all times".
Samuel Taylor Coleridge said: Everybody is born either a Platonist or an Aristotelian.
Ayn Rand
Alice O'Connor (born Alisa Zinovyevna Rosenbaum;, . Most sources transliterate her given name as either ''Alisa'' or ''Alissa''. , 1905 – March 6, 1982), better known by her pen name Ayn Rand (), was a Russian-born American writer and p ...
acknowledged Aristotle as her greatest influence and remarked that in the
history of philosophy
Philosophy (from , ) is the systematized study of general and fundamental questions, such as those about existence, reason, knowledge, values, mind, and language. Such questions are often posed as problems to be studied or resolved. Some ...
she could only recommend "three A's"—Aristotle, Aquinas, and Ayn Rand. She also regarded Aristotle as the greatest of all philosophers.
Karl Marx considered Aristotle to be the "greatest thinker of antiquity", and called him a "giant thinker", a "genius", and "the great scholar".
[Judith A. Swanson, C. David Corbin, Aristotle's 'Politics': A Reader's Guide, p. 146.]
Modern rejection and rehabilitation
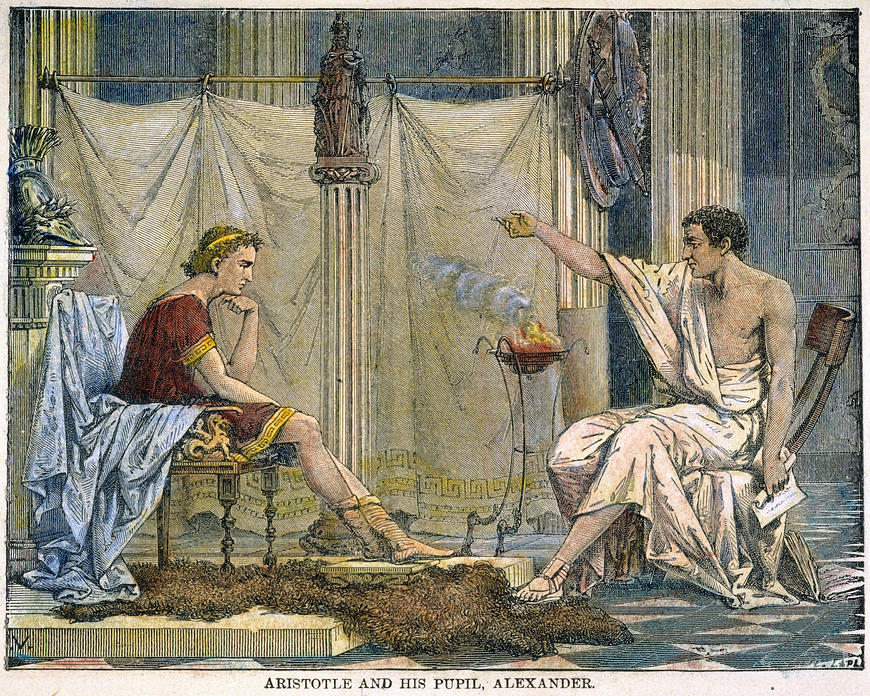
During the 20th century, Aristotle's work was widely criticized. The philosopher
Bertrand Russell
argued that "almost every serious intellectual advance has had to begin with an attack on some Aristotelian doctrine". Russell called Aristotle's ethics "repulsive", and labelled his logic "as definitely antiquated as Ptolemaic astronomy". Russell stated that these errors made it difficult to do historical justice to Aristotle, until one remembered what an advance he made upon all of his predecessors.
The Dutch historian of science
Eduard Jan Dijksterhuis
Eduard Jan Dijksterhuis (28 October 1892, in Tilburg – 18 May 1965, in De Bilt) was a Dutch historian of science.
Career
Dijksterhuis studied mathematics at the University of Groningen from 1911 to 1918. His Ph.d. thesis was entitled "A Contrib ...
wrote that Aristotle and his predecessors showed the difficulty of science by "proceed
ngso readily to frame a theory of such a general character" on limited evidence from their senses. In 1985, the biologist
Peter Medawar could still state in "pure seventeenth century" tones that Aristotle had assembled "a strange and generally speaking rather tiresome farrago of hearsay, imperfect observation, wishful thinking and credulity amounting to downright gullibility".
By the start of the 21st century, however, Aristotle was taken more seriously: Kukkonen noted that "In the best 20th-century scholarship Aristotle comes alive as a thinker wrestling with the full weight of the Greek philosophical tradition."
Alasdair MacIntyre
Alasdair Chalmers MacIntyre (; born 12 January 1929) is a Scottish-American philosopher who has contributed to moral and political philosophy as well as history of philosophy and theology. MacIntyre's '' After Virtue'' (1981) is one of the most ...
has attempted to reform what he calls the Aristotelian tradition in a way that is anti-elitist and capable of disputing the claims of both liberals and Nietzscheans. Kukkonen observed, too, that "that most enduring of romantic images, Aristotle tutoring the future conqueror Alexander" remained current, as in the 2004 film ''
Alexander'', while the "firm rules" of Aristotle's theory of drama have ensured a role for the ''Poetics'' in
Hollywood
Hollywood usually refers to:
* Hollywood, Los Angeles, a neighborhood in California
* Hollywood, a metonym for the cinema of the United States
Hollywood may also refer to:
Places United States
* Hollywood District (disambiguation)
* Hollywood, ...
.
Biologists continue to be interested in Aristotle's thinking.
Armand Marie Leroi
Armand Marie Leroi (born 16 July 1964) is a New Zealand-born Dutch author, broadcaster, and professor of evolutionary developmental biology at Imperial College in London. He received the Guardian First Book Award in 2004 for his book ''Mutant ...
has reconstructed Aristotle's biology, while
Niko Tinbergen's four questions, based on Aristotle's four causes, are used to analyse
animal behaviour
Ethology is the scientific study of animal behaviour, usually with a focus on behaviour under natural conditions, and viewing behaviour as an evolutionarily adaptive trait. Behaviourism as a term also describes the scientific and objectiv ...
; they examine
function,
phylogeny,
mechanism
Mechanism may refer to:
*Mechanism (engineering), rigid bodies connected by joints in order to accomplish a desired force and/or motion transmission
*Mechanism (biology), explaining how a feature is created
*Mechanism (philosophy), a theory that a ...
, and
ontogeny.
Surviving works
Corpus Aristotelicum

The works of Aristotle that have survived from antiquity through medieval manuscript transmission are collected in the Corpus Aristotelicum. These texts, as opposed to Aristotle's lost works, are technical philosophical treatises from within Aristotle's school. Reference to them is made according to the organization of
Immanuel Bekker's Royal Prussian Academy edition (''Aristotelis Opera edidit Academia Regia Borussica'', Berlin, 1831–1870), which in turn is based on ancient classifications of these works.
Loss and preservation
Aristotle wrote his works on papyrus scrolls, the common writing medium of that era. His writings are divisible into two groups: the "
exoteric
Exoteric refers to knowledge that is outside and independent from a person's experience and can be ascertained by anyone (related to common sense).
The word is derived from the comparative form of Greek ἔξω ''eksô'', "from, out of, outside". ...
", intended for the public, and the "
esoteric", for use within the
Lyceum school. Aristotle's "lost" works stray considerably in characterization from the surviving Aristotelian corpus. Whereas the lost works appear to have been originally written with a view to subsequent publication, the surviving works mostly resemble lecture notes not intended for publication.
Cicero's description of Aristotle's literary style as "a river of gold" must have applied to the published works, not the surviving notes. A major question in the history of Aristotle's works is how the exoteric writings were all lost, and how the ones now possessed came to be found. The consensus is that Andronicus of Rhodes collected the esoteric works of Aristotle's school which existed in the form of smaller, separate works, distinguished them from those of Theophrastus and other Peripatetics, edited them, and finally compiled them into the more cohesive, larger works as they are known today.
Legacy
Depictions
;Paintings
Aristotle has been depicted by major artists including
Lucas Cranach the Elder
Lucas Cranach the Elder (german: Lucas Cranach der Ältere ; – 16 October 1553) was a German Renaissance painter and printmaker in woodcut and engraving. He was court painter to the Electors of Saxony for most of his career, and is know ...
,
Justus van Gent,
Raphael,
Paolo Veronese
Paolo Caliari (152819 April 1588), known as Paolo Veronese ( , also , ), was an Italian Renaissance painter based in Venice, known for extremely large history paintings of religion and mythology, such as ''The Wedding at Cana'' (1563) and ''The ...
,
Jusepe de Ribera,
Rembrandt
Rembrandt Harmenszoon van Rijn (, ; 15 July 1606 – 4 October 1669), usually simply known as Rembrandt, was a Dutch Golden Age painter, printmaker and draughtsman. An innovative and prolific master in three media, he is generally consid ...
, and
Francesco Hayez over the centuries. Among the best-known depictions is Raphael's
fresco
Fresco (plural ''frescos'' or ''frescoes'') is a technique of mural painting executed upon freshly laid ("wet") lime plaster. Water is used as the vehicle for the dry-powder pigment to merge with the plaster, and with the setting of the plaste ...
''
The School of Athens'', in the
Vatican's Apostolic Palace, where the figures of Plato and Aristotle are central to the image, at the architectural
vanishing point, reflecting their importance. Rembrandt's ''
Aristotle with a Bust of Homer
''Aristotle with a Bust of Homer'' ( nl, Aristoteles bij de buste van Homerus), also known as ''Aristotle Contemplating a Bust of Homer'', is an oil-on-canvas painting by Rembrandt that depicts Aristotle wearing a gold chain and contemplating a ...
'', too, is a celebrated work, showing the knowing philosopher and the blind Homer from an earlier age: as the art critic
Jonathan Jones writes, "this painting will remain one of the greatest and most mysterious in the world, ensnaring us in its musty, glowing, pitch-black, terrible knowledge of time."
File:Aristotle in Nuremberg Chronicle.jpg, ''Nuremberg Chronicle
The ''Nuremberg Chronicle'' is an illustrated encyclopedia consisting of world historical accounts, as well as accounts told through biblical paraphrase. Subjects include human history in relation to the Bible, illustrated mythological creatures, ...
'' anachronistically
An anachronism (from the Greek , 'against' and , 'time') is a chronological inconsistency in some arrangement, especially a juxtaposition of people, events, objects, language terms and customs from different time periods. The most common type ...
shows Aristotle in a medieval scholar's clothing. Ink and watercolour on paper, 1493
File:Gent, Justus van - Aristotle - c. 1476.jpg, ''Aristotle'' by Justus van Gent. Oil on panel, c. 1476
File:Lucas Cranach d.Ä. - Phyllis und Aristotle (1530).jpg, ''Phyllis and Aristotle'' by Lucas Cranach the Elder
Lucas Cranach the Elder (german: Lucas Cranach der Ältere ; – 16 October 1553) was a German Renaissance painter and printmaker in woodcut and engraving. He was court painter to the Electors of Saxony for most of his career, and is know ...
. Oil on panel, 1530
File:Biblioteka Marciana, Aristotel.jpg, ''Aristotle'' by Paolo Veronese
Paolo Caliari (152819 April 1588), known as Paolo Veronese ( , also , ), was an Italian Renaissance painter based in Venice, known for extremely large history paintings of religion and mythology, such as ''The Wedding at Cana'' (1563) and ''The ...
, Biblioteka Marciana. Oil on canvas, 1560s
File:Turchi-AristoteIMG 1713.JPG, ''Aristotle and Campaspe'', Alessandro Turchi
Alessandro Turchi (1578 – 22 January 1649) was an Italian painter of the early Baroque, born and active mainly in Verona, and moving late in life to Rome. He also went by the name Alessandro Veronese or the nickname ''L'Orbetto''. His style ...
(attrib.) Oil on canvas, 1713
File:Aristotle by Jusepe de Ribera.jpg, '' Aristotle'' by Jusepe de Ribera. Oil on canvas, 1637
File:Rembrandt - Aristotle with a Bust of Homer - WGA19232.jpg, ''Aristotle with a Bust of Homer'' by Rembrandt
Rembrandt Harmenszoon van Rijn (, ; 15 July 1606 – 4 October 1669), usually simply known as Rembrandt, was a Dutch Golden Age painter, printmaker and draughtsman. An innovative and prolific master in three media, he is generally consid ...
. Oil on canvas, 1653
File:Johann Jakob Dorner d Ä (attr) Aristoteles.jpg, ''Aristotle'' by Johann Jakob Dorner the Elder. Oil on canvas, by 1813
File:Francesco Hayez 001.jpg, ''Aristotle'' by Francesco Hayez. Oil on canvas, 1811
;Sculptures
File:Aristoteles Louvre.jpg, Roman copy of 1st or 2nd century from original bronze by Lysippos
Lysippos (; grc-gre, Λύσιππος) was a Ancient Greek sculpture, Greek sculptor of the 4th century BC. Together with Scopas and Praxiteles, he is considered one of the three greatest sculptors of the Ancient Greece, Classical Greek era, bri ...
. Louvre Museum
File:DSC00218 - Aristotele - Copia romana del 117-138 dC. - Foto di G. Dall'Orto.jpg, Roman copy of 117-138 AD of Greek original. Palermo Regional Archeology Museum
File:Formella 21, platone e aristotele o la filosofia, luca della robbia, 1437-1439.JPG, Relief of Aristotle and Plato by Luca della Robbia, Florence Cathedral
Florence Cathedral, formally the (; in English Cathedral of Saint Mary of the Flower), is the cathedral of Florence, Italy ( it, Duomo di Firenze). It was begun in 1296 in the Gothic style to a design of Arnolfo di Cambio and was structurally c ...
, 1437–1439
File:Llyfrgell Sant Deiniol and Gladstone's Library Hawarden Penarlâg 05.JPG, Stone statue in niche, Gladstone's Library
Gladstone's Library, known until 2010 as St Deiniol's Library ( cy, Llyfrgell Deiniol Sant), is a residential library in Hawarden, Flintshire, Wales. It is a Grade I listed building and a registered charity.
Gladstone's Library is Britain' ...
, Hawarden
Hawarden (; cy, Penarlâg) is a village, community (Wales), community and Wards and electoral divisions of the United Kingdom, electoral ward in Flintshire, Wales. It is part of the Deeside conurbation on the Wales-England border and is home ...
, Wales, 1899
File:Uni Freiburg - Philosophen 4.jpg, Bronze statue, University of Freiburg, Germany, 1915
Eponyms
The
Aristotle Mountains
Aristotle Mountains is the fan-shaped sequence of ridges spreading east-northeastwards from its summit Madrid Dome (1647 m) on Oscar II Coast in Graham Land on the Antarctic Peninsula. The feature is named after the ancient Greek scientist Aristotl ...
in
Antarctica are named after Aristotle. He was the first person known to conjecture, in his book ''
Meteorology'', the existence of a landmass in the southern high-latitude region and called it ''Antarctica''.
Aristoteles
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of phi ...
is a crater on the
Moon bearing the classical form of Aristotle's name.
See also
*
Aristotelian Society
The Aristotelian Society for the Systematic Study of Philosophy, more generally known as the Aristotelian Society, is a philosophical society in London.
History
Aristotelian Society was founded at a meeting on 19 April 1880, at 17 Bloomsbury Squar ...
*
Aristotle's Biology
*
Conimbricenses
*
Perfectionism
References
Notes
Citations
Sources
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
The secondary literature on Aristotle is vast. The following is only a small selection.
*
Ackrill, J. L. (1997). ''Essays on Plato and Aristotle'', Oxford University Press.
*
*
*
* These translations are available in several places online; see External links.
* Bakalis, Nikolaos. (2005). ''Handbook of Greek Philosophy: From Thales to the Stoics Analysis and Fragments'', Trafford Publishing, .
*
* Bolotin, David (1998). ''An Approach to Aristotle's Physics: With Particular Attention to the Role of His Manner of Writing.'' Albany: SUNY Press. A contribution to our understanding of how to read Aristotle's scientific works.
*
Burnyeat, Myles F. ''et al.'' (1979). ''Notes on Book Zeta of Aristotle's Metaphysics''. Oxford: Sub-faculty of Philosophy.
*
*
* Code, Alan (1995). Potentiality in Aristotle's Science and Metaphysics, Pacific Philosophical Quarterly 76.
*
*
* De Groot, Jean (2014). ''Aristotle's Empiricism: Experience and Mechanics in the 4th century BC'', Parmenides Publishing, .
* Frede, Michael (1987). ''Essays in Ancient Philosophy''. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press.
*
*
Gendlin, Eugene T. (2012).
Line by Line Commentary on Aristotle's De Anima'', Volume 1: Books I & II; Volume 2: Book III. The Focusing Institute.
* Gill, Mary Louise (1989). ''Aristotle on Substance: The Paradox of Unity''. Princeton University Press.
*
*
*
*
*
*
Jori, Alberto (2003). ''Aristotele'', Bruno Mondadori (Prize 2003 of the "
International Academy of the History of Science"), .
*
* Knight, Kelvin (2007). ''Aristotelian Philosophy: Ethics and Politics from Aristotle to MacIntyre'', Polity Press.
* Lewis, Frank A. (1991). ''Substance and Predication in Aristotle''. Cambridge University Press.
* Lord, Carnes (1984). ''Introduction to ''The Politics'', by Aristotle''. Chicago University Press.
* Loux, Michael J. (1991). Primary Ousia: An Essay on Aristotle's Metaphysics Ζ and Η. Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press.
* Maso, Stefano (Ed.), Natali, Carlo (Ed.), Seel, Gerhard (Ed.) (2012) ''Reading Aristotle: Physics'' VII. 3: ''What is Alteration?'' ''Proceedings of the International ESAP-HYELE Conference'', Parmenides Publishing. .
*
*
eprinted in J. Barnes, M. Schofield, and R.R.K. Sorabji, eds.(1975). ''Articles on Aristotle'' Vol 1. Science. London: Duckworth 14–34.*
*
* Reeve, C. D. C. (2000). ''Substantial Knowledge: Aristotle's Metaphysics''. Hackett.
*
*
* Scaltsas, T. (1994). ''Substances and Universals in Aristotle's Metaphysics''. Cornell University Press.
* Strauss, Leo (1964). "On Aristotle's ''Politics''", in ''The City and Man'', Rand McNally.
*
*
*
External links
*
*
* At the
Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy
The ''Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy'' (''IEP'') is a scholarly online encyclopedia, dealing with philosophy, philosophical topics, and philosophers. The IEP combines open access publication with peer reviewed publication of original pape ...
:
*:
* At th
Internet Classics Archive* From the
Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy
The ''Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy'' (''SEP'') combines an online encyclopedia of philosophy with peer-reviewed publication of original papers in philosophy, freely accessible to Internet users. It is maintained by Stanford University. Eac ...
:
*:
*
*
;Collections of works
*
* A
Massachusetts Institute of Technology*
*
*
*
*
Perseus Projectat
Tufts University
* At th
University of Adelaide
*
* The 11-volume 1837 Bekker edition of ''Aristotle's Works'' in Greek
PDFhttps://web.archive.org/web/20050816192647/http://grid.ceth.rutgers.edu/ancient/greek/aristotle_greek/ DJVU])
{{Authority control
Aristotle,
*
384 BC births
322 BC deaths
4th-century BC mathematicians
4th-century BC philosophers
4th-century BC writers
Academic philosophers
Acting theorists
Ancient Greek biologists
Ancient Greek economists
Ancient Greek epistemologists
Ancient Greek ethicists
Ancient Greek logicians
Ancient Greek mathematicians
Ancient Greek metaphilosophers
Ancient Greek metaphysicians
Ancient Greek philosophers
Ancient Greek philosophers of language
Ancient Greek philosophers of mind
Ancient Greek physicists
Ancient Greek political philosophers
Ancient Greek political refugees
Ancient Greek philosophers of art
Ancient literary critics
Ancient Stagirites
Aphorists
Aristotelian philosophers
Attic Greek writers
Ancient Greek cosmologists
Critical thinking
Cultural critics
Founders of philosophical traditions
Greek male writers
Greek geologists
Greek meteorologists
Greek social commentators
Humor researchers
Irony theorists
Metic philosophers in Classical Athens
Moral philosophers
Natural philosophers
Ontologists
Peripatetic philosophers
Philosophers and tutors of Alexander the Great
Philosophers of ancient Chalcidice
Philosophers of culture
Philosophers of education
Philosophers of ethics and morality
Philosophers of history
Philosophers of law
Philosophers of literature
Philosophers of logic
Philosophers of love
Philosophers of psychology
Philosophers of science
Philosophers of time
Philosophers of sexuality
Philosophers of technology
Philosophical logic
Philosophical theists
Philosophy academics
Philosophy writers
Rhetoric theorists
Social critics
Social philosophers
Students of Plato
Trope theorists
Virtue ethicists
Virtue ethics
Western culture
Western philosophy
Zoologists
Natural law ethicists
 In general, the details of Aristotle's life are not well-established. The biographies written in ancient times are often speculative and historians only agree on a few salient points.
Aristotle was born in 384 BC in Stagira,
In general, the details of Aristotle's life are not well-established. The biographies written in ancient times are often speculative and historians only agree on a few salient points.
Aristotle was born in 384 BC in Stagira,  Aristotle was appointed as the head of the royal academy of Macedon. During Aristotle's time in the Macedonian court, he gave lessons not only to Alexander but also to two other future kings: Ptolemy and Cassander. Aristotle encouraged Alexander toward eastern conquest, and Aristotle's own attitude towards Persia was unabashedly ethnocentric. In one famous example, he counsels Alexander to be "a leader to the Greeks and a despot to the barbarians, to look after the former as after friends and relatives, and to deal with the latter as with beasts or plants". By 335 BC, Aristotle had returned to Athens, establishing his own school there known as the Lyceum. Aristotle conducted courses at the school for the next twelve years. While in Athens, his wife Pythias died and Aristotle became involved with
Aristotle was appointed as the head of the royal academy of Macedon. During Aristotle's time in the Macedonian court, he gave lessons not only to Alexander but also to two other future kings: Ptolemy and Cassander. Aristotle encouraged Alexander toward eastern conquest, and Aristotle's own attitude towards Persia was unabashedly ethnocentric. In one famous example, he counsels Alexander to be "a leader to the Greeks and a despot to the barbarians, to look after the former as after friends and relatives, and to deal with the latter as with beasts or plants". By 335 BC, Aristotle had returned to Athens, establishing his own school there known as the Lyceum. Aristotle conducted courses at the school for the next twelve years. While in Athens, his wife Pythias died and Aristotle became involved with  The order of the books (or the teachings from which they are composed) is not certain, but this list was derived from analysis of Aristotle's writings. It goes from the basics, the analysis of simple terms in the ''Categories,'' the analysis of propositions and their elementary relations in ''On Interpretation'', to the study of more complex forms, namely, syllogisms (in the ''Analytics'') and dialectics (in the ''Topics'' and ''Sophistical Refutations''). The first three treatises form the core of the logical theory ''stricto sensu'': the grammar of the language of logic and the correct rules of reasoning. The ''Rhetoric'' is not conventionally included, but it states that it relies on the ''Topics''.
The order of the books (or the teachings from which they are composed) is not certain, but this list was derived from analysis of Aristotle's writings. It goes from the basics, the analysis of simple terms in the ''Categories,'' the analysis of propositions and their elementary relations in ''On Interpretation'', to the study of more complex forms, namely, syllogisms (in the ''Analytics'') and dialectics (in the ''Topics'' and ''Sophistical Refutations''). The first three treatises form the core of the logical theory ''stricto sensu'': the grammar of the language of logic and the correct rules of reasoning. The ''Rhetoric'' is not conventionally included, but it states that it relies on the ''Topics''.
 Coming-to-be is a change where the substrate of the thing that has undergone the change has itself changed. In that particular change he introduces the concept of potentiality (''
Coming-to-be is a change where the substrate of the thing that has undergone the change has itself changed. In that particular change he introduces the concept of potentiality ('' Aristotle was one of the first people to record any geological observations. He stated that geological change was too slow to be observed in one person's lifetime.
The geologist
Aristotle was one of the first people to record any geological observations. He stated that geological change was too slow to be observed in one person's lifetime.
The geologist 
 Aristotle's psychology, given in his treatise '' On the Soul'' (''peri psychēs''), posits three kinds of soul ("psyches"): the vegetative soul, the sensitive soul, and the rational soul. Humans have a rational soul. The human soul incorporates the powers of the other kinds: Like the vegetative soul it can grow and nourish itself; like the sensitive soul it can experience sensations and move locally. The unique part of the human, rational soul is its ability to receive forms of other things and to compare them using the ''
Aristotle's psychology, given in his treatise '' On the Soul'' (''peri psychēs''), posits three kinds of soul ("psyches"): the vegetative soul, the sensitive soul, and the rational soul. Humans have a rational soul. The human soul incorporates the powers of the other kinds: Like the vegetative soul it can grow and nourish itself; like the sensitive soul it can experience sensations and move locally. The unique part of the human, rational soul is its ability to receive forms of other things and to compare them using the '' Aristotle's pupil and successor, Theophrastus, wrote the '' History of Plants'', a pioneering work in botany. Some of his technical terms remain in use, such as carpel from ''carpos'', fruit, and pericarp, from ''pericarpion'', seed chamber.
Theophrastus was much less concerned with formal causes than Aristotle was, instead pragmatically describing how plants functioned.
Aristotle's pupil and successor, Theophrastus, wrote the '' History of Plants'', a pioneering work in botany. Some of his technical terms remain in use, such as carpel from ''carpos'', fruit, and pericarp, from ''pericarpion'', seed chamber.
Theophrastus was much less concerned with formal causes than Aristotle was, instead pragmatically describing how plants functioned.
 Aristotle was one of the most revered Western thinkers in early Islamic theology. Most of the still extant works of Aristotle, as well as a number of the original Greek commentaries, were translated into Arabic and studied by Muslim philosophers, scientists and scholars. Averroes,
Aristotle was one of the most revered Western thinkers in early Islamic theology. Most of the still extant works of Aristotle, as well as a number of the original Greek commentaries, were translated into Arabic and studied by Muslim philosophers, scientists and scholars. Averroes,  With the loss of the study of ancient Greek in the early medieval Latin West, Aristotle was practically unknown there from c. AD 600 to c. 1100 except through the Latin translation of the ''Organon'' made by Boethius. In the twelfth and thirteenth centuries, interest in Aristotle revived and Latin Christians had translations made, both from Arabic translations, such as those by Gerard of Cremona, and from the original Greek, such as those by
With the loss of the study of ancient Greek in the early medieval Latin West, Aristotle was practically unknown there from c. AD 600 to c. 1100 except through the Latin translation of the ''Organon'' made by Boethius. In the twelfth and thirteenth centuries, interest in Aristotle revived and Latin Christians had translations made, both from Arabic translations, such as those by Gerard of Cremona, and from the original Greek, such as those by  In the Early Modern period, scientists such as William Harvey in England and Galileo Galilei in Italy reacted against the theories of Aristotle and other classical era thinkers like Galen, establishing new theories based to some degree on observation and experiment. Harvey demonstrated the circulation of the blood, establishing that the heart functioned as a pump rather than being the seat of the soul and the controller of the body's heat, as Aristotle thought. Galileo used more doubtful arguments to displace Aristotle's physics, proposing that bodies all fall at the same speed whatever their weight.
In the Early Modern period, scientists such as William Harvey in England and Galileo Galilei in Italy reacted against the theories of Aristotle and other classical era thinkers like Galen, establishing new theories based to some degree on observation and experiment. Harvey demonstrated the circulation of the blood, establishing that the heart functioned as a pump rather than being the seat of the soul and the controller of the body's heat, as Aristotle thought. Galileo used more doubtful arguments to displace Aristotle's physics, proposing that bodies all fall at the same speed whatever their weight.
 During the 20th century, Aristotle's work was widely criticized. The philosopher Bertrand Russell
argued that "almost every serious intellectual advance has had to begin with an attack on some Aristotelian doctrine". Russell called Aristotle's ethics "repulsive", and labelled his logic "as definitely antiquated as Ptolemaic astronomy". Russell stated that these errors made it difficult to do historical justice to Aristotle, until one remembered what an advance he made upon all of his predecessors.
The Dutch historian of science
During the 20th century, Aristotle's work was widely criticized. The philosopher Bertrand Russell
argued that "almost every serious intellectual advance has had to begin with an attack on some Aristotelian doctrine". Russell called Aristotle's ethics "repulsive", and labelled his logic "as definitely antiquated as Ptolemaic astronomy". Russell stated that these errors made it difficult to do historical justice to Aristotle, until one remembered what an advance he made upon all of his predecessors.
The Dutch historian of science  The works of Aristotle that have survived from antiquity through medieval manuscript transmission are collected in the Corpus Aristotelicum. These texts, as opposed to Aristotle's lost works, are technical philosophical treatises from within Aristotle's school. Reference to them is made according to the organization of Immanuel Bekker's Royal Prussian Academy edition (''Aristotelis Opera edidit Academia Regia Borussica'', Berlin, 1831–1870), which in turn is based on ancient classifications of these works.
The works of Aristotle that have survived from antiquity through medieval manuscript transmission are collected in the Corpus Aristotelicum. These texts, as opposed to Aristotle's lost works, are technical philosophical treatises from within Aristotle's school. Reference to them is made according to the organization of Immanuel Bekker's Royal Prussian Academy edition (''Aristotelis Opera edidit Academia Regia Borussica'', Berlin, 1831–1870), which in turn is based on ancient classifications of these works.