BRCA1 protein on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein is a
accessed October 2012 it also led to controversy over high prices and the inability to obtain second opinions from other diagnostic labs, which in turn led to the landmark ''
(map)
''BRCA1''
 Certain variations of the ''BRCA1'' gene lead to an increased risk for
Certain variations of the ''BRCA1'' gene lead to an increased risk for
PDBe-KB
provides an overview of all the structure information available in the PDB for Human BRCA1. {{Medicine Breast cancer Genes on human chromosome 17 Tumor markers Tumor suppressor genes
protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
that in humans is encoded by the ''BRCA1'' () gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
. Ortholog
Sequence homology is the biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences, defined in terms of shared ancestry in the evolutionary history of life. Two segments of DNA can have shared ancestry because of three phenomena: either a s ...
s are common in other vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with c ...
species, whereas invertebrate
Invertebrates are a paraphyletic group of animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''backbone'' or ''spine''), derived from the notochord. This is a grouping including all animals apart from the chordate ...
genomes may encode a more distantly related gene. ''BRCA1'' is a human tumor suppressor gene
A tumor suppressor gene (TSG), or anti-oncogene, is a gene that regulates a cell during cell division and replication. If the cell grows uncontrollably, it will result in cancer. When a tumor suppressor gene is mutated, it results in a loss or re ...
(also known as a caretaker gene) and is responsible for repairing DNA.
''BRCA1'' and '' BRCA2'' are unrelated proteins, but both are normally expressed in the cells of breast
The breast is one of two prominences located on the upper ventral region of a primate's torso. Both females and males develop breasts from the same embryological tissues.
In females, it serves as the mammary gland, which produces and sec ...
and other tissue, where they help repair damaged DNA, or destroy cells if DNA cannot be repaired. They are involved in the repair of chromosomal
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins are ...
damage with an important role in the error-free repair
The technical meaning of maintenance involves functional checks, servicing, repairing or replacing of necessary devices, equipment, machinery, building infrastructure, and supporting utilities in industrial, business, and residential installa ...
of DNA double-strand breaks. If ''BRCA1'' or ''BRCA2'' itself is damaged by a BRCA mutation
A ''BRCA'' mutation is a mutation in either of the ''BRCA1'' and ''BRCA2'' genes, which are tumour suppressor genes. Hundreds of different types of mutations in these genes have been identified, some of which have been determined to be harmful, ...
, damaged DNA is not repaired properly, and this increases the risk for breast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or a r ...
. ''BRCA1'' and ''BRCA2'' have been described as "breast cancer susceptibility genes" and "breast cancer susceptibility proteins". The predominant allele has a normal, tumor suppressive function whereas high penetrance
Penetrance in genetics is the proportion of individuals carrying a particular variant (or allele) of a gene (the genotype) that also express an associated trait (the phenotype). In medical genetics, the penetrance of a disease-causing mutation is t ...
mutations in these genes cause a loss of tumor suppressive function which correlates with an increased risk of breast cancer.
''BRCA1'' combines with other tumor suppressors, DNA damage sensors and signal transducers to form a large multi-subunit protein complex known as the ''BRCA1''-associated genome surveillance complex (BASC). The ''BRCA1'' protein associates with RNA polymerase II
RNA polymerase II (RNAP II and Pol II) is a multiprotein complex that transcribes DNA into precursors of messenger RNA (mRNA) and most small nuclear RNA (snRNA) and microRNA. It is one of the three RNAP enzymes found in the nucleus of eukaryo ...
, and through the C-terminal
The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein or polypeptide), terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH). When the protein is ...
domain, also interacts with histone deacetylase complexes. Thus, this protein plays a role in transcription, and DNA repair
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA da ...
of double-strand DNA breaks ubiquitin
Ubiquitin is a small (8.6 kDa) regulatory protein found in most tissues of eukaryotic organisms, i.e., it is found ''ubiquitously''. It was discovered in 1975 by Gideon Goldstein and further characterized throughout the late 1970s and 1980s. Fo ...
ation, transcriptional regulation
In molecular biology and genetics, transcriptional regulation is the means by which a cell regulates the conversion of DNA to RNA (transcription), thereby orchestrating gene activity. A single gene can be regulated in a range of ways, from al ...
as well as other functions.
Methods to test for the likelihood of a patient with mutations in ''BRCA1'' and '' BRCA2'' developing cancer were covered by patents owned or controlled by Myriad Genetics
Myriad Genetics, Inc. is an American genetic testing and precision medicine company based in Salt Lake City, Utah, United States. Myriad employs a number of proprietary technologies that permit doctors and patients to understand the genetic bas ...
. Myriad's business model of offering the diagnostic test exclusively led from Myriad being a startup in 1994 to being a publicly traded company with 1200 employees and about $500M in annual revenue in 2012;Myriad Investor Page—see "Myriad at a glance"accessed October 2012 it also led to controversy over high prices and the inability to obtain second opinions from other diagnostic labs, which in turn led to the landmark ''
Association for Molecular Pathology v. Myriad Genetics
''Association for Molecular Pathology v. Myriad Genetics, Inc.'', 569 U.S. 576 (2013), was a Supreme Court case that challenged the validity of gene patents in the United States, specifically questioning certain claims in issued patents owned or ...
'' lawsuit.
Discovery
The first evidence for the existence of a gene encoding a DNA repair enzyme involved in breast cancer susceptibility was provided byMary-Claire King
Mary-Claire King (born February 27, 1946) is an American geneticist. She was the first to show that breast cancer can be inherited due to mutations in the gene she called ''BRCA1''. She studies human genetics and is particularly interested in g ...
's laboratory at UC Berkeley
The University of California, Berkeley (UC Berkeley, Berkeley, Cal, or California) is a public land-grant research university in Berkeley, California. Established in 1868 as the University of California, it is the state's first land-grant uni ...
in 1990. Four years later, after an international race to find it, the gene was cloned in 1994 by scientists at University of Utah, National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS) and Myriad Genetics
Myriad Genetics, Inc. is an American genetic testing and precision medicine company based in Salt Lake City, Utah, United States. Myriad employs a number of proprietary technologies that permit doctors and patients to understand the genetic bas ...
.
Gene location
The human ''BRCA1'' gene is located on the long (q) arm ofchromosome 17
Chromosome 17 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 17 spans more than 83 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents between 2.5 and 3% of the total D ...
at region 2 band 1, from base pair 41,196,312 to base pair 41,277,500 (Build GRCh37/hg19(map)
''BRCA1''
orthologs
Sequence homology is the biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences, defined in terms of shared ancestry in the evolutionary history of life. Two segments of DNA can have shared ancestry because of three phenomena: either a sp ...
have been identified in most vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with c ...
s for which complete genome data are available.
Protein structure
The BRCA1protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
contains the following domains:
* Zinc finger, C3HC4 type (RING finger
The ring finger, third finger, fourth finger, leech finger, or annulary is the fourth digit of the human hand, located between the middle finger and the little finger.
Sometimes the term ring finger only refers to the fourth digit of a left-han ...
)
* BRCA1 C Terminus ( BRCT) domain
This protein also contains nuclear localization signal A nuclear localization signal ''or'' sequence (NLS) is an amino acid sequence that 'tags' a protein for import into the cell nucleus by nuclear transport. Typically, this signal consists of one or more short sequences of positively charged lysines o ...
s and nuclear export signal motifs.
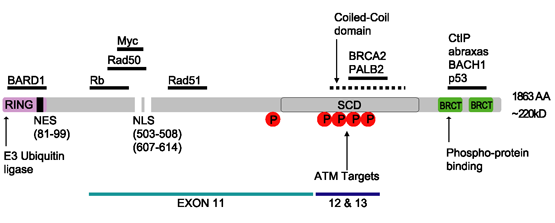
The human BRCA1 protein consists of four major protein domains; the Znf C3HC4- RING domain, the BRCA1 serine domain and two BRCT domains. These domains encode approximately 27% of BRCA1 protein. There are six known isoforms of BRCA1, with isoforms 1 and 2 comprising 1863 amino acids each.
BRCA1 is unrelated to BRCA2, i.e. they are not homologs
A couple of homologous chromosomes, or homologs, are a set of one maternal and one paternal chromosome that pair up with each other inside a cell during fertilization. Homologs have the same genes in the same loci where they provide points alon ...
or paralogs
Sequence homology is the biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences, defined in terms of shared ancestry in the evolutionary history of life. Two segments of DNA can have shared ancestry because of three phenomena: either a sp ...
.

Zinc ring finger domain
The RING motif, a Zn finger found in eukaryotic peptides, is 40–60 amino acids long and consists of eight conserved metal-binding residues, two quartets of cysteine orhistidine
Histidine (symbol His or H) is an essential amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated –NH3+ form under biological conditions), a carboxylic acid group (which is in the d ...
residues that coordinate two zinc atoms. This motif contains a short anti-parallel beta-sheet
The beta sheet, (β-sheet) (also β-pleated sheet) is a common motif of the regular protein secondary structure. Beta sheets consist of beta strands (β-strands) connected laterally by at least two or three backbone hydrogen bonds, forming a ge ...
, two zinc-binding loops and a central alpha helix in a small domain. This RING domain interacts with associated proteins, including BARD1
BRCA1-associated RING domain protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BARD1'' gene. The human BARD1 protein is 777 amino acids long and contains a RING finger domain (residues 46-90), four ankyrin repeats (residues 420-555), and ...
, which also contains a RING motif, to form a heterodimer. The BRCA1 RING motif is flanked by alpha helices formed by residues 8–22 and 81–96 of the BRCA1 protein. It interacts with a homologous region in BARD1 also consisting of a RING finger flanked by two alpha-helices
The alpha helix (α-helix) is a common motif in the secondary structure of proteins and is a right hand-helix conformation in which every backbone N−H group hydrogen bonds to the backbone C=O group of the amino acid located four residues ear ...
formed from residues 36–48 and 101–116. These four helices combine to form a heterodimerization
In biochemistry, a protein dimer is a macromolecular complex formed by two protein monomers, or single proteins, which are usually non-covalently bound. Many macromolecules, such as proteins or nucleic acids, form dimers. The word ''dimer'' has ...
interface and stabilize the BRCA1-BARD1 heterodimer complex. Additional stabilization is achieved by interactions between adjacent residues in the flanking region and hydrophobic interactions. The BARD1/BRCA1 interaction is disrupted by tumorigenic amino acid substitutions in BRCA1, implying that the formation of a stable complex between these proteins may be an essential aspect of BRCA1 tumor suppression.
The ring domain is an important element of ubiquitin E3 ligases, which catalyze protein ubiquitination. Ubiquitin
Ubiquitin is a small (8.6 kDa) regulatory protein found in most tissues of eukaryotic organisms, i.e., it is found ''ubiquitously''. It was discovered in 1975 by Gideon Goldstein and further characterized throughout the late 1970s and 1980s. Fo ...
is a small regulatory protein found in all tissues that direct proteins to compartments within the cell. BRCA1 polypeptides, in particular, Lys-48-linked polyubiquitin chains are dispersed throughout the resting cell nucleus, but at the start of DNA replication
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all living organisms acting as the most essential part for biological inheritanc ...
, they gather in restrained groups that also contain BRCA2 and BARD1. BARD1 is thought to be involved in the recognition and binding of protein targets for ubiquitination. It attaches to proteins and labels them for destruction. Ubiquitination occurs via the BRCA1 fusion protein and is abolished by zinc chelation
Chelation is a type of bonding of ions and molecules to metal ions. It involves the formation or presence of two or more separate coordinate bonds between a polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand and a single central metal atom. These ligands are ...
. The enzyme activity of the fusion protein is dependent on the proper folding of the ring domain.
Serine cluster domain
BRCA1 serine cluster domain (SCD) spans amino acids 1280–1524. A portion of the domain is located in exons 11–13. High rates of mutation occur in exons 11–13. Reported phosphorylation sites of BRCA1 are concentrated in the SCD, where they are phosphorylated by ATM/ATR kinases bothin vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called " test-tube experiments", these studies in biology ...
and in vivo
Studies that are ''in vivo'' (Latin for "within the living"; often not italicized in English) are those in which the effects of various biological entities are tested on whole, living organisms or cells, usually animals, including humans, and ...
. ATM/ATR are kinases activated by DNA damage
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA d ...
. Mutation of serine residues may affect localization of BRCA1 to sites of DNA damage and DNA damage response function.
BRCT domains
The dual repeatBRCT domain
BRCA1 C Terminus (BRCT) domain is a family of evolutionarily related proteins. It is named after the C-terminal domain of BRCA1, a DNA-repair protein that serves as a marker of breast cancer susceptibility.
The BRCT domain is found predominant ...
of the BRCA1 protein is an elongated structure approximately 70 Å long and 30–35 Å wide. The 85–95 amino acid domains in BRCT can be found as single modules or as multiple tandem repeats containing two domains. Both of these possibilities can occur in a single protein in a variety of different conformations. The C-terminal BRCT region of the BRCA1 protein is essential for repair of DNA, transcription regulation and tumor suppressor function. In BRCA1 the dual tandem repeat
Tandem repeats occur in DNA when a pattern of one or more nucleotides is repeated and the repetitions are directly adjacent to each other. Several protein domains also form tandem repeats within their amino acid primary structure, such as armadil ...
BRCT domains are arranged in a head-to-tail-fashion in the three-dimensional structure, burying 1600 Å of hydrophobic, solvent-accessible surface area in the interface. These all contribute to the tightly packed knob-in-hole structure that comprises the interface. These homologous domains interact to control cellular responses to DNA damage
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA d ...
. A missense mutation
In genetics, a missense mutation is a point mutation in which a single nucleotide change results in a codon that codes for a different amino acid. It is a type of nonsynonymous substitution.
Substitution of protein from DNA mutations
Missense m ...
at the interface of these two proteins can perturb the cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a cell that cause it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the duplication of its DNA (DNA replication) and some of its organelles, and sub ...
, resulting a greater risk of developing cancer.
Function and mechanism
BRCA1 is part of a complex that repairsdouble-strand breaks
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA dama ...
in DNA. The strands of the DNA double helix are continuously breaking as they become damaged. Sometimes only one strand is broken, sometimes both strands are broken simultaneously. DNA cross-linking agents are an important source of chromosome/DNA damage. Double-strand breaks occur as intermediates after the crosslinks are removed, and indeed, biallelic mutations in ''BRCA1'' have been identified to be responsible for Fanconi Anemia
Fanconi anaemia (FA) is a rare genetic disease resulting in impaired response to DNA damage. Although it is a very rare disorder, study of this and other bone marrow failure syndromes has improved scientific understanding of the mechanisms of no ...
, Complementation Group S, a genetic disease associated with hypersensitivity to DNA crosslinking agents. BRCA1 is part of a protein complex that repairs DNA when both strands are broken. When this happens, it is difficult for the repair mechanism to "know" how to replace the correct DNA sequence, and there are multiple ways to attempt the repair. The double-strand repair mechanism in which BRCA1 participates is homology-directed repair
Homology-directed repair (HDR) is a mechanism in cells to repair double-strand DNA lesions. The most common form of HDR is homologous recombination. The HDR mechanism can only be used by the cell when there is a homologous piece of DNA present ...
, where the repair proteins copy the identical sequence from the intact sister chromatid
A sister chromatid refers to the identical copies (chromatids) formed by the DNA replication of a chromosome, with both copies joined together by a common centromere. In other words, a sister chromatid may also be said to be 'one-half' of the dup ...
. FANCS is usually a lethal condition in utero; only a handful cases of biallelic BRCA1 mutations have been reported in literature despite the high carrier frequencies in the Ashkenazim, and none since 2013.
In the nucleus of many types of normal cells, the BRCA1 protein interacts with RAD51 during repair of DNA double-strand breaks. These breaks can be caused by natural radiation or other exposures, but also occur when chromosome
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins are ...
s exchange genetic material (homologous recombination, e.g., "crossing over" during meiosis). The BRCA2 protein, which has a function similar to that of BRCA1, also interacts with the RAD51 protein. By influencing DNA damage repair, these three proteins play a role in maintaining the stability of the human genome.
BRCA1 is also involved in another type of DNA repair, termed mismatch repair
DNA mismatch repair (MMR) is a system for recognizing and repairing erroneous insertion, deletion, and mis-incorporation of bases that can arise during DNA replication and recombination, as well as repairing some forms of DNA damage.
Mismatch ...
. BRCA1 interacts with the DNA mismatch repair protein MSH2
DNA mismatch repair protein Msh2 also known as MutS homolog 2 or MSH2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MSH2'' gene, which is located on chromosome 2. MSH2 is a tumor suppressor gene and more specifically a caretaker gene that codes ...
. MSH2, MSH6
MSH6 or mutS homolog 6 is a gene that codes for DNA mismatch repair protein Msh6 in the budding yeast ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae''. It is the homologue of the human "G/T binding protein," (GTBP) also called p160 or hMSH6 (human MSH6). The MSH6 prot ...
, PARP and some other proteins involved in single-strand repair are reported to be elevated in BRCA1-deficient mammary tumors.
A protein called valosin-containing protein
Valosin-containing protein (VCP) or transitional endoplasmic reticulum ATPase (TER ATPase) also known as p97 in mammals and CDC48 in ''S. cerevisiae,'' is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''VCP'' gene. The TER ATPase is an ATPase enzyme ...
(VCP, also known as p97) plays a role to recruit BRCA1 to the damaged DNA sites. After ionizing radiation, VCP is recruited to DNA lesions and cooperates with the ubiquitin ligase RNF8 to orchestrate assembly of signaling complexes for efficient DSB repair. BRCA1 interacts with VCP. BRCA1 also interacts with c-Myc
''Myc'' is a family of regulator genes and proto-oncogenes that code for transcription factors. The ''Myc'' family consists of three related human genes: ''c-myc'' ( MYC), ''l-myc'' ( MYCL), and ''n-myc'' ( MYCN). ''c-myc'' (also sometimes re ...
, and other proteins that are critical to maintain genome stability.
BRCA1 directly binds to DNA, with higher affinity for branched DNA structures. This ability to bind to DNA contributes to its ability to inhibit the nuclease activity of the MRN complex as well as the nuclease activity of Mre11 alone. This may explain a role for BRCA1 to promote lower fidelity DNA repair by non-homologous end joining
Non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) is a pathway that repairs double-strand breaks in DNA. NHEJ is referred to as "non-homologous" because the break ends are directly ligated without the need for a homologous template, in contrast to homology direc ...
(NHEJ). BRCA1 also colocalizes with γ-H2AX (histone H2AX phosphorylated on serine-139) in DNA double-strand break repair foci, indicating it may play a role in recruiting repair factors.
Formaldehyde
Formaldehyde ( , ) (systematic name methanal) is a naturally occurring organic compound with the formula and structure . The pure compound is a pungent, colourless gas that polymerises spontaneously into paraformaldehyde (refer to section ...
and acetaldehyde are common environmental sources of DNA cross links that often require repairs mediated by BRCA1 containing pathways.
This DNA repair function is essential; mice with loss-of-function mutations in both BRCA1 alleles are not viable, and as of 2015 only two adults were known to have loss-of-function mutations in both alleles; both had congenital or developmental issues, and both had cancer. One was presumed to have survived to adulthood because one of the BRCA1 mutations was hypomorphic.
Transcription
BRCA1 was shown to co-purify with the human RNA Polymerase II holoenzyme in HeLa extracts, implying it is a component of the holoenzyme. Later research, however, contradicted this assumption, instead showing that the predominant complex including BRCA1 in HeLa cells is a 2 megadalton complex containing SWI/SNF. SWI/SNF is a chromatin remodeling complex. Artificial tethering of BRCA1 to chromatin was shown to decondense heterochromatin, though the SWI/SNF interacting domain was not necessary for this role. BRCA1 interacts with the NELF-B ( COBRA1) subunit of the NELF complex.Mutations and cancer risk
 Certain variations of the ''BRCA1'' gene lead to an increased risk for
Certain variations of the ''BRCA1'' gene lead to an increased risk for breast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or a r ...
as part of a hereditary breast–ovarian cancer syndrome
Hereditary breast–ovarian cancer syndromes (HBOC) are cancer syndromes that produce higher than normal levels of breast cancer, ovarian cancer and additional cancers in genetically related families (either one individual had both, or several in ...
. Researchers have identified hundreds of mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA replication, DNA or viral repl ...
s in the ''BRCA1'' gene, many of which are associated with an increased risk of cancer. Females with an abnormal BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene have up to an 80% risk of developing breast cancer by age 90; increased risk of developing ovarian cancer is about 55% for females with BRCA1 mutations and about 25% for females with BRCA2 mutations.
These mutations can be changes in one or a small number of DNA base pairs (the building-blocks of DNA), and can be identified with PCR and DNA sequencing.
In some cases, large segments of DNA are rearranged. Those large segments, also called large rearrangements, can be a deletion or a duplication of one or several exons in the gene. Classical methods for mutation detection (sequencing) are unable to reveal these types of mutation. Other methods have been proposed: traditional quantitative PCR
A real-time polymerase chain reaction (real-time PCR, or qPCR) is a laboratory technique of molecular biology based on the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). It monitors the amplification of a targeted DNA molecule during the PCR (i.e., in real ...
, multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification
Multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA) is a variation of the multiplex polymerase chain reaction that permits amplification of multiple targets with only a single primer pair. It detects copy number changes at the molecular level, ...
(MLPA), and Quantitative Multiplex PCR of Short Fluorescent Fragments (QMPSF). Newer methods have also been recently proposed: heteroduplex analysis (HDA) by multi-capillary electrophoresis or also dedicated oligonucleotides array based on comparative genomic hybridization Comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) is a molecular cytogenetic method for analysing copy number variations (CNVs) relative to ploidy level in the DNA of a test sample compared to a reference sample, without the need for culturing cells. The ...
(array-CGH).
Some results suggest that hypermethylation
In the chemical sciences, methylation denotes the addition of a methyl group on a substrate, or the substitution of an atom (or group) by a methyl group. Methylation is a form of alkylation, with a methyl group replacing a hydrogen atom. These t ...
of the BRCA1 promoter, which has been reported in some cancers, could be considered as an inactivating mechanism for BRCA1 expression.
A mutated ''BRCA1'' gene usually makes a protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
that does not function properly. Researchers believe that the defective BRCA1 protein is unable to help fix DNA damage leading to mutations in other genes. These mutations can accumulate and may allow cells to grow and divide uncontrollably to form a tumor. Thus, BRCA1 inactivating mutations lead to a predisposition for cancer.
BRCA1 mRNA 3' UTR
In molecular genetics, the three prime untranslated region (3′-UTR) is the section of messenger RNA (mRNA) that immediately follows the translation termination codon. The 3′-UTR often contains regulatory regions that post-transcriptionally ...
can be bound by an miRNA
MicroRNA (miRNA) are small, single-stranded, non-coding RNA molecules containing 21 to 23 nucleotides. Found in plants, animals and some viruses, miRNAs are involved in RNA silencing and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. miR ...
, Mir-17 microRNA. It has been suggested that variations in this miRNA along with Mir-30 microRNA could confer susceptibility to breast cancer.
In addition to breast cancer, mutations in the ''BRCA1'' gene also increase the risk of ovarian
The ovary is an organ in the female reproductive system that produces an ovum. When released, this travels down the fallopian tube into the uterus, where it may become fertilized by a sperm. There is an ovary () found on each side of the body ...
and prostate cancers. Moreover, precancerous lesions (dysplasia
Dysplasia is any of various types of abnormal growth or development of cells (microscopic scale) or organs ( macroscopic scale), and the abnormal histology or anatomical structure(s) resulting from such growth. Dysplasias on a mainly microscopi ...
) within the Fallopian tube have been linked to ''BRCA1'' gene mutations. Pathogenic mutations anywhere in a model pathway containing BRCA1 and BRCA2 greatly increase risks for a subset of leukemias and lymphomas.
Women who have inherited a defective BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene are at a greatly elevated risk to develop breast and ovarian cancer. Their risk of developing breast and/or ovarian cancer is so high, and so specific to those cancers, that many mutation carriers choose to have prophylactic surgery. There has been much conjecture to explain such apparently striking tissue specificity. Major determinants of where BRCA1/2 hereditary cancers occur are related to tissue specificity of the cancer pathogen, the agent that causes chronic inflammation or the carcinogen. The target tissue may have receptors for the pathogen, may become selectively exposed to an inflammatory process or to a carcinogen. An innate genomic deficit in a tumor suppressor gene impairs normal responses and exacerbates the susceptibility to disease in organ targets. This theory also fits data for several tumor suppressors beyond BRCA1 or BRCA2. A major advantage of this model is that it suggests there may be some options in addition to prophylactic surgery.
Biallelic and homozygous inheritance of the BRCA1 gene leads to FANCS, a severe form of Fanconi anemia
Fanconi anaemia (FA) is a rare genetic disease resulting in impaired response to DNA damage. Although it is a very rare disorder, study of this and other bone marrow failure syndromes has improved scientific understanding of the mechanisms of no ...
, and is usually an embryonically lethal condition.
Low expression of ''BRCA1'' in breast and ovarian cancers
BRCA1 expression is reduced or undetectable in the majority of high grade, ductal breast cancers. It has long been noted that loss of BRCA1 activity, either by germ-line mutations or by down-regulation of gene expression, leads to tumor formation in specific target tissues. In particular, decreased BRCA1 expression contributes to both sporadic and inherited breast tumor progression. Reduced expression of BRCA1 is tumorigenic because it plays an important role in the repair of DNA damages, especially double-strand breaks, by the potentially error-free pathway of homologous recombination. Since cells that lack the BRCA1 protein tend to repair DNA damages by alternative more error-prone mechanisms, the reduction or silencing of this protein generates mutations and gross chromosomal rearrangements that can lead to progression to breast cancer. Similarly, BRCA1 expression is low in the majority (55%) of sporadic epithelial ovarian cancers (EOCs) where EOCs are the most common type of ovarian cancer, representing approximately 90% of ovarian cancers. In serous ovarian carcinomas, a sub-category constituting about 2/3 of EOCs, low BRCA1 expression occurs in more than 50% of cases. Bowtell reviewed the literature indicating that deficient homologous recombination repair caused by BRCA1 deficiency is tumorigenic. In particular this deficiency initiates a cascade of molecular events that sculpt the evolution of high-grade serous ovarian cancer and dictate its response to therapy. Especially noted was that BRCA1 deficiency could be the cause of tumorigenesis whether due to BRCA1 mutation or any other event that causes a deficiency of BRCA1 expression.Mutation of ''BRCA1'' in breast and ovarian cancer
Only about 3%–8% of all women with breast cancer carry a mutation in BRCA1 or BRCA2. Similarly, ''BRCA1'' mutations are only seen in about 18% of ovarian cancers (13% germline mutations and 5% somatic mutations). Thus, while BRCA1 expression is low in the majority of these cancers, ''BRCA1'' mutation is not a major cause of reduced expression. Certain latent viruses, which are frequently detected in breast cancer tumors, can decrease the expression of the BRCA1 gene and cause the development of breast tumors.''BRCA1'' promoter hypermethylation in breast and ovarian cancer
''BRCA1'' promoter hypermethylation was present in only 13% of unselected primary breast carcinomas. Similarly, ''BRCA1'' promoter hypermethylation was present in only 5% to 15% of EOC cases. Thus, while BRCA1 expression is low in these cancers, ''BRCA1'' promoter methylation is only a minor cause of reduced expression.MicroRNA repression of BRCA1 in breast cancers
There are a number of specificmicroRNAs
MicroRNA (miRNA) are small, single-stranded, non-coding RNA molecules containing 21 to 23 nucleotides. Found in plants, animals and some viruses, miRNAs are involved in RNA silencing and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. miR ...
, when overexpressed, that directly reduce expression of specific DNA repair proteins (see MicroRNA section DNA repair and cancer) In the case of breast cancer, microRNA-182 (miR-182) specifically targets BRCA1. Breast cancers can be classified based on receptor status or histology, with triple-negative breast cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is any breast cancer that lacks or show low levels of estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR) and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) overexpression and/or gene amplification (i.e. the t ...
(15%–25% of breast cancers), HER2+ (15%–30% of breast cancers), ER+/ PR+ (about 70% of breast cancers), and Invasive lobular carcinoma (about 5%–10% of invasive breast cancer). All four types of breast cancer were found to have an average of about 100-fold increase in miR-182, compared to normal breast tissue. In breast cancer cell lines, there is an inverse correlation of BRCA1 protein levels with miR-182 expression. Thus it appears that much of the reduction or absence of BRCA1 in high grade ductal breast cancers may be due to over-expressed miR-182.
In addition to miR-182, a pair of almost identical microRNAs, miR-146a and miR-146b-5p, also repress BRCA1 expression. These two microRNAs are over-expressed in triple-negative tumors and their over-expression results in BRCA1 inactivation. Thus, miR-146a and/or miR-146b-5p may also contribute to reduced expression of BRCA1 in these triple-negative breast cancers.
MicroRNA repression of BRCA1 in ovarian cancers
In both serous tubal intraepithelial carcinoma (the precursor lesion to high grade serous ovarian carcinoma (HG-SOC)), and in HG-SOC itself, miR-182 is overexpressed in about 70% of cases. In cells with over-expressed miR-182, BRCA1 remained low, even after exposure to ionizing radiation (which normally raises BRCA1 expression). Thus much of the reduced or absent BRCA1 in HG-SOC may be due to over-expressed miR-182. Another microRNA known to reduce expression of BRCA1 in ovarian cancer cells is miR-9. Among 58 tumors from patients with stage IIIC or stage IV serous ovarian cancers (HG-SOG), an inverse correlation was found between expressions of miR-9 and BRCA1, so that increased miR-9 may also contribute to reduced expression of BRCA1 in these ovarian cancers.Deficiency of ''BRCA1'' expression is likely tumorigenic
DNA damage appears to be the primary underlying cause of cancer, and deficiencies in DNA repair appears to underlie many forms of cancer. If DNA repair is deficient, DNA damage tends to accumulate. Such excess DNA damage may increasemutational
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mi ...
errors during DNA replication
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all living organisms acting as the most essential part for biological inheritanc ...
due to error-prone translesion synthesis
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA dama ...
. Excess DNA damage may also increase epigenetic alterations due to errors during DNA repair. Such mutations and epigenetic alterations may give rise to cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
. The frequent microRNA-induced deficiency of ''BRCA1'' in breast and ovarian cancers likely contribute to the progression of those cancers.
Germ-line mutations and founder effect
All germ-line BRCA1 mutations identified to date have been inherited, suggesting the possibility of a large "founder" effect in which a certain mutation is common to a well-defined population group and can, in theory, be traced back to a common ancestor. Given the complexity of mutation screening for BRCA1, these common mutations may simplify the methods required for mutation screening in certain populations. Analysis of mutations that occur with high frequency also permits the study of their clinical expression. Examples of manifestations of a founder effect are seen amongAshkenazi Jews
Ashkenazi Jews ( ; he, יְהוּדֵי אַשְׁכְּנַז, translit=Yehudei Ashkenaz, ; yi, אַשכּנזישע ייִדן, Ashkenazishe Yidn), also known as Ashkenazic Jews or ''Ashkenazim'',, Ashkenazi Hebrew pronunciation: , singu ...
. Three mutations in BRCA1 have been reported to account for the majority of Ashkenazi Jewish patients with inherited BRCA1-related breast and/or ovarian cancer: 185delAG, 188del11 and 5382insC in the BRCA1 gene. In fact, it has been shown that if a Jewish woman does not carry a BRCA1 185delAG, BRCA1 5382insC founder mutation, it is highly unlikely that a different BRCA1 mutation will be found. Additional examples of founder mutations in BRCA1 are given in Table 1 (mainly derived from).
Female fertility
As women age, reproductive performance declines, leading to menopause. This decline is tied to a reduction in the number of ovarian follicles. Although about 1 million oocytes are present at birth in the human ovary, only about 500 (about 0.05%) of these ovulate. The decline in ovarian reserve appears to occur at a constantly increasing rate with age, and leads to nearly complete exhaustion of the reserve by about age 52. As ovarian reserve and fertility decline with age, there is also a parallel increase in pregnancy failure and meiotic errors, resulting in chromosomally abnormal conceptions. Women with a germ-line ''BRCA1'' mutation appear to have a diminished oocyte reserve and decreased fertility compared to normally aging women. Furthermore, women with an inherited ''BRCA1'' mutation undergo menopause prematurely. Since BRCA1 is a key DNA repair protein, these findings suggest that naturally occurring DNA damages in oocytes are repaired less efficiently in women with a ''BRCA1'' defect, and that this repair inefficiency leads to early reproductive failure. As noted above, the BRCA1 protein plays a key role in homologous recombinational repair. This is the only known cellular process that can accurately repair DNA double-strand breaks. DNA double-strand breaks accumulate with age in humans and mice in primordial follicles. Primordial follicles contain oocytes that are at an intermediate (prophase I) stage of meiosis. Meiosis is the general process in eukaryotic organisms by which germ cells are formed, and it is likely an adaptation for removing DNA damages, especially double-strand breaks, from germ line DNA. (Also see articleMeiosis
Meiosis (; , since it is a reductional division) is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, such as sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately r ...
). Homologous recombinational repair employing BRCA1 is especially promoted during meiosis. It was found that expression of four key genes necessary for homologous recombinational repair of DNA double-strand breaks (''BRCA1, MRE11, RAD51'' and ''ATM'') decline with age in the oocytes of humans and mice, leading to the hypothesis that DNA double-strand break repair is necessary for the maintenance of oocyte reserve and that a decline in efficiency of repair with age plays a role in ovarian aging.
Cancer chemotherapy
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the leading cause of cancer deaths worldwide. At diagnosis, almost 70% of persons with NSCLC have locally advanced or metastatic disease. Persons with NSCLC are often treated with therapeutic platinum compounds (e.g. cisplatin, carboplatin or oxaliplatin) that cause inter-strand cross-links in DNA. Among individuals with NSCLC, low expression of ''BRCA1'' in the primary tumor correlated with improved survival after platinum-containing chemotherapy. This correlation implies that low BRCA1 in cancer, and the consequent low level of DNA repair, causes vulnerability of cancer to treatment by the DNA cross-linking agents. High BRCA1 may protect cancer cells by acting in a pathway that removes the damages in DNA introduced by the platinum drugs. Thus the level of ''BRCA1'' expression is a potentially important tool for tailoring chemotherapy in lung cancer management. Level of ''BRCA1'' expression is also relevant to ovarian cancer treatment. Patients having sporadic ovarian cancer who were treated with platinum drugs had longer median survival times if their ''BRCA1'' expression was low compared to patients with higher ''BRCA1'' expression (46 compared to 33 months).Patents, enforcement, litigation, and controversy
A patent application for the isolated BRCA1 gene and cancer promoting mutations discussed above, as well as methods to diagnose the likelihood of getting breast cancer, was filed by the University of Utah, National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS) andMyriad Genetics
Myriad Genetics, Inc. is an American genetic testing and precision medicine company based in Salt Lake City, Utah, United States. Myriad employs a number of proprietary technologies that permit doctors and patients to understand the genetic bas ...
in 1994; over the next year, Myriad, (in collaboration with investigators at Endo Recherche, Inc., HSC Research & Development Limited Partnership, and University of Pennsylvania), isolated and sequenced the BRCA2 gene and identified key mutations, and the first BRCA2 patent was filed in the U.S. by Myriad and other institutions in 1995. Myriad is the exclusive licensee of these patents and has enforced them in the US against clinical diagnostic labs. This business model led from Myriad being a startup in 1994 to being a publicly traded company with 1200 employees and about $500M in annual revenue in 2012; it also led to controversy over high prices and the inability to get second opinions from other diagnostic labs, which in turn led to the landmark ''Association for Molecular Pathology v. Myriad Genetics
''Association for Molecular Pathology v. Myriad Genetics, Inc.'', 569 U.S. 576 (2013), was a Supreme Court case that challenged the validity of gene patents in the United States, specifically questioning certain claims in issued patents owned or ...
'' lawsuit. The patents began to expire in 2014.
According to an article published in the journal, ''Genetic Medicine'', in 2010, "The patent story outside the United States is more complicated.... For example, patents have been obtained but the patents are being ignored by provincial health systems in Canada. In Australia and the UK, Myriad's licensee permitted use by health systems but announced a change of plans in August 2008. Only a single mutation has been patented in Myriad's lone European-wide patent, although some patents remain under review of an opposition proceeding. In effect, the United States is the only jurisdiction where Myriad's strong patent position has conferred sole-provider status." Peter Meldrum, CEO of Myriad Genetics, has acknowledged that Myriad has "other competitive advantages that may make such atentenforcement unnecessary" in Europe.
As with any gene, finding variation in BRCA1 is not hard. The real value comes from understanding what the clinical consequences of any particular variant are. Myriad has a large, proprietary database of such genotype-phenotype correlations. In response, parallel open-source databases are being developed.
Legal decisions surrounding the BRCA1 and BRCA2 patents will affect the field of genetic testing in general. A June 2013 article, in ''Association for Molecular Pathology v. Myriad Genetics'' (No. 12-398), quoted the US Supreme Court
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all U.S. federal court cases, and over state court cases that involve a point of ...
's unanimous ruling that, "A naturally occurring DNA segment is a product of nature and not patent eligible merely because it has been isolated," invalidating Myriad's patents on the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes. However, the Court also held that manipulation of a gene to create something not found in nature could still be eligible for patent protection. The Federal Court of Australia came to the opposite conclusion, upholding the validity of an Australian Myriad Genetics patent over the BRCA1 gene in February 2013. The Federal Court also rejected an appeal in September 2014. Yvonne D'Arcy won her case against US-based biotech company Myriad Genetics in the High Court of Australia. In their unanimous decision on October 7, 2015, the "high court found that an isolated nucleic acid, coding for a BRCA1 protein, with specific variations from the norm that are indicative of susceptibility to breast cancer and ovarian cancer was not a 'patentable invention.'"
Interactions
BRCA1 has been shown to interact with the following proteins: * ABL1 *AKT1
RAC(Rho family)-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''AKT1'' gene. This enzyme belongs to the AKT subfamily of serine/threonine kinases that contain SH2 (Src homology 2-like) protein domains. It ...
* AR
* ATR
* ATM
* ATF1
Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ATF1'' gene.
This gene encodes an activating transcription factor, which belongs to the ATF subfamily and bZIP (basic-region leucine zipper) family. ...
* BACH1
Transcription regulator protein BACH1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BACH1'' gene.
Function
This gene encodes a transcription factor that belongs to the cap'n'collar type of basic region leucine zipper factor family (CNC-bZip) ...
* BARD1
BRCA1-associated RING domain protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BARD1'' gene. The human BARD1 protein is 777 amino acids long and contains a RING finger domain (residues 46-90), four ankyrin repeats (residues 420-555), and ...
* BRCA2
* BRCC3
Lys-63-specific deubiquitinase BRCC36 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''BRCC3'' gene.
Function
This gene encodes a subunit of the BRCA1-BRCA2-containing complex (BRCC), which is an E3 ubiquitin ligase. This protein is also though ...
* BRE
British English (BrE, en-GB, or BE) is, according to Oxford Dictionaries, "English as used in Great Britain, as distinct from that used elsewhere". More narrowly, it can refer specifically to the English language in England, or, more broadly, ...
* BRIP1
* C-jun
* CHEK2
* CLSPN
* COBRA1
* CREBBP
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate Response Element Binding protein Binding Protein (CREB-binding protein), also known as CREBBP or CBP or KAT3A, is a coactivator encoded by the ''CREBBP'' gene in humans, located on chromosome 16p13.3. CBP has intri ...
* CSNK2B
* CSTF2
Cleavage stimulation factor 64 kDa subunit is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CSTF2'' gene.
This gene encodes a nuclear protein with an RRM (RNA recognition motif) domain. The protein is a member of the cleavage stimulation factor ( ...
* CDK2
Cyclin-dependent kinase 2, also known as cell division protein kinase 2, or Cdk2, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''CDK2'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the cyclin-dependent kinase family of Ser/Thr protein ...
* DHX9
ATP-dependent RNA helicase A (RHA; also known as DHX9, LKP, and NDHI) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''DHX9'' gene.
Function
DEAD/DEAH box helicases are proteins, and are putative RNA helicases. They are implicated in a number o ...
* ELK4
* EP300
* ESR1
Estrogen receptor alpha (ERα), also known as NR3A1 (nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group A, member 1), is one of two main types of estrogen receptor, a nuclear receptor (mainly found as a chromatin-binding protein)
that is activated by the sex ...
* FANCA
Fanconi anaemia, complementation group A, also known as FAA, FACA and FANCA, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''FANCA'' gene. It belongs to the Fanconi anaemia complementation group (FANC) family of genes of which 12 complementatio ...
* FANCD2
Fanconi anemia group D2 protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''FANCD2'' gene. The Fanconi anemia complementation group ( FANC) currently includes FANCA, FANCB, FANCC, FANCD1 (also called BRCA2), FANCD2 (this gene), FANCE, FANCF, F ...
* FHL2
Four and a half LIM domains protein 2 also known as FHL-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''FHL2'' gene. LIM proteins contain a highly conserved double zinc finger motif called the LIM domain.
Function
FHL-2 is thought to have ...
* H2AFX
H2A histone family member X (usually abbreviated as H2AX) is a type of histone protein from the H2A family encoded by the ''H2AFX'' gene. An important phosphorylated form is γH2AX (S139), which forms when double-strand breaks appear.
In humans ...
* JUNB
* JunD
Under the early Caliphates, a ''jund'' ( ar, جند; plural ''ajnad'', اجناد) was a military division, which became applied to Arab military colonies in the conquered lands and, most notably, to the provinces into which Greater Syria (the Le ...
* LMO4
LIM domain transcription factor LMO4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LMO4'' gene.
LIM domain only 4 is a cysteine-rich, two LIM domain-containing protein that may play a role as a transcriptional regulator or possibly an oncogene. ...
* MAP3K3
Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MAP3K3'' gene, which is located on the long arm of chromosome 17 (17q23.3).MAP3K3 in GeneCards – The Human Gene Compendium. https://www.genecards. ...
* MED1
Mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit 1 also known as DRIP205 or Trap220 is a subunit of the Mediator complex and is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MED1'' gene. MED1 functions as a nuclear receptor coactivator.
Fun ...
* MED17
* MED21
Mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit 21 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MED21'' gene.
Interactions
MED21 has been shown to interact with:
* BRCA1,
* CDK8,
* GTF2F1,
* GTF2H4,
* MED6, and
* POLR2A
DNA-directed ...
* MED24
Mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit 24 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MED24'' gene.
Function
This gene encodes a component of the mediator complex (also known as TRAP, SMCC, DRIP, or ARC), a transcriptional coa ...
* MRE11A
Double-strand break repair protein MRE11 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MRE11'' gene. The gene has been designated ''MRE11A'' to distinguish it from the pseudogene ''MRE11B'' that is nowadays named ''MRE11P1''.
Function
This ge ...
* MSH2
DNA mismatch repair protein Msh2 also known as MutS homolog 2 or MSH2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MSH2'' gene, which is located on chromosome 2. MSH2 is a tumor suppressor gene and more specifically a caretaker gene that codes ...
* MSH3
DNA mismatch repair protein, MutS Homolog 3 (MSH3) is a human homologue of the bacterial mismatch repair protein MutS that participates in the mismatch repair (MMR) system. MSH3 typically forms the heterodimer MutSβ with MSH2 in order to correc ...
* MSH6
MSH6 or mutS homolog 6 is a gene that codes for DNA mismatch repair protein Msh6 in the budding yeast ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae''. It is the homologue of the human "G/T binding protein," (GTBP) also called p160 or hMSH6 (human MSH6). The MSH6 prot ...
* Myc
''Myc'' is a family of regulator genes and proto-oncogenes that code for transcription factors. The ''Myc'' family consists of three related human genes: ''c-myc'' (MYC), ''l-myc'' ( MYCL), and ''n-myc'' (MYCN). ''c-myc'' (also sometimes refe ...
* NBN
* NMI
* NPM1
Nucleophosmin (NPM), also known as nucleolar phosphoprotein B23 or numatrin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NPM1'' gene.
Function
NPM1 is associated with nucleolar ribonucleoprotein structures and binds single-stranded and ...
* NCOA2
* NUFIP1
Nuclear fragile X mental retardation-interacting protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NUFIP1'' gene.
Interactions
NUFIP1 has been shown to interact with:
* BRCA1,
* Cyclin T1, and
* FMR1
''FMR1'' (Fragile X Messenger ...
* P53
p53, also known as Tumor protein P53, cellular tumor antigen p53 (UniProt name), or transformation-related protein 53 (TRP53) is a regulatory protein that is often mutated in human cancers. The p53 proteins (originally thought to be, and often s ...
* PALB2
Partner and localizer of BRCA2, also known as PALB2 or FANCN, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''PALB2'' gene.
Function
This gene encodes a protein that functions in genome maintenance ( double strand break repair). This prote ...
* POLR2A
DNA-directed RNA polymerase II subunit RPB1, also known as RPB1, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''POLR2A'' gene.
Function
This gene encodes the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II, the polymerase responsible for synthesizing m ...
* PPP1CA
Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase PP1-alpha catalytic subunit is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PPP1CA'' gene.
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is one of the three catalytic subunits of protein phosphatase 1 (PP1). PP ...
* Rad50
DNA repair protein RAD50, also known as RAD50, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''RAD50'' gene.
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is highly similar to ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' Rad50, a protein involved in DNA double- ...
* RAD51
* RBBP4 #REDIRECT RBBP4
{{R from other capitalization
...
* RBBP7
* RBBP8
* RELA
Transcription factor p65 also known as nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p65 subunit is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''RELA'' gene.
RELA, also known as p65, is a REL-associated protein involved in NF-κB heterodimer formation, nuclear tra ...
* RB1
* RBL1
* RBL2
* RPL31
* SMARCA4
Transcription activator BRG1 also known as ATP-dependent chromatin remodeler SMARCA4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SMARCA4'' gene.
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the SWI/SNF family of proteins and i ...
* SMARCB1
SWI/SNF-related matrix-associated actin-dependent regulator of chromatin subfamily B member 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SMARCB1'' gene.
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is part of a complex that relieves repressiv ...
* STAT1
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1) is a transcription factor which in humans is encoded by the ''STAT1'' gene. It is a member of the STAT protein family.
Function
All STAT molecules are phosphorylated by receptor associ ...
* TOPBP1
DNA topoisomerase 2-binding protein 1 (TOPBP1) is a scaffold protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TOPBP1'' gene.
TOPBP1 was first identified as a protein binding partner of DNA topoisomerase-IIβ by a yeast 2-hybrid screen, giving it its ...
* UBE2D1
Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 D1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''UBE2D1'' gene.
Function
The modification of proteins with ubiquitin is an important cellular mechanism for targeting abnormal or short-lived proteins for degrad ...
* USF2
* VCP
* XIST
* ZNF350
References
External links
* *PDBe-KB
provides an overview of all the structure information available in the PDB for Human BRCA1. {{Medicine Breast cancer Genes on human chromosome 17 Tumor markers Tumor suppressor genes