|
BRCA Mutation
A ''BRCA'' mutation is a mutation in either of the ''BRCA1'' and ''BRCA2'' genes, which are tumour suppressor genes. Hundreds of different types of mutations in these genes have been identified, some of which have been determined to be harmful, while others have no proven impact. Harmful mutations in these genes may produce a hereditary breast–ovarian cancer syndrome in affected persons. Only 5–10% of breast cancer cases in women are attributed to ''BRCA1'' and ''BRCA2'' mutations (with ''BRCA1'' mutations being slightly more common than ''BRCA2'' mutations), but the impact on women with the gene mutation is more profound. Women with harmful mutations in either ''BRCA1'' or ''BRCA2'' have a risk of breast cancer that is about five times the normal risk, and a risk of ovarian cancer that is about ten to thirty times normal. The risk of breast and ovarian cancer is higher for women with a high-risk ''BRCA1'' mutation than with a ''BRCA2'' mutation. Having a high-risk mutation doe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
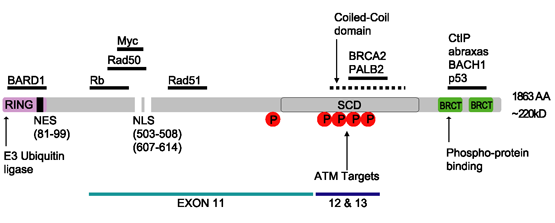
BRCA1
Breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BRCA1'' () gene. Orthologs are common in other vertebrate species, whereas invertebrate genomes may encode a more distantly related gene. ''BRCA1'' is a human tumor suppressor gene (also known as a caretaker gene) and is responsible for repairing DNA. ''BRCA1'' and '' BRCA2'' are unrelated proteins, but both are normally expressed in the cells of breast and other tissue, where they help repair damaged DNA, or destroy cells if DNA cannot be repaired. They are involved in the repair of chromosomal damage with an important role in the error-free repair of DNA double-strand breaks. If ''BRCA1'' or ''BRCA2'' itself is damaged by a BRCA mutation, damaged DNA is not repaired properly, and this increases the risk for breast cancer. ''BRCA1'' and ''BRCA2'' have been described as "breast cancer susceptibility genes" and "breast cancer susceptibility proteins". The predominant allele has a normal, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fanconi Anemia
Fanconi anaemia (FA) is a rare genetic disease resulting in impaired response to DNA damage. Although it is a very rare disorder, study of this and other bone marrow failure syndromes has improved scientific understanding of the mechanisms of normal bone marrow function and development of cancer. Among those affected, the majority develop cancer, most often acute myelogenous leukemia (AML), and 90% develop aplastic anemia (the inability to produce blood cells) by age 40. About 60–75% have congenital defects, commonly short stature, abnormalities of the skin, arms, head, eyes, kidneys, and ears, and developmental disabilities. Around 75% have some form of endocrine problem, with varying degrees of severity. FA is the result of a genetic defect in a cluster of proteins responsible for DNA repair via homologous recombination. Treatment with androgens and hematopoietic (blood cell) growth factors can help bone marrow failure temporarily, but the long-term treatment is bone marrow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
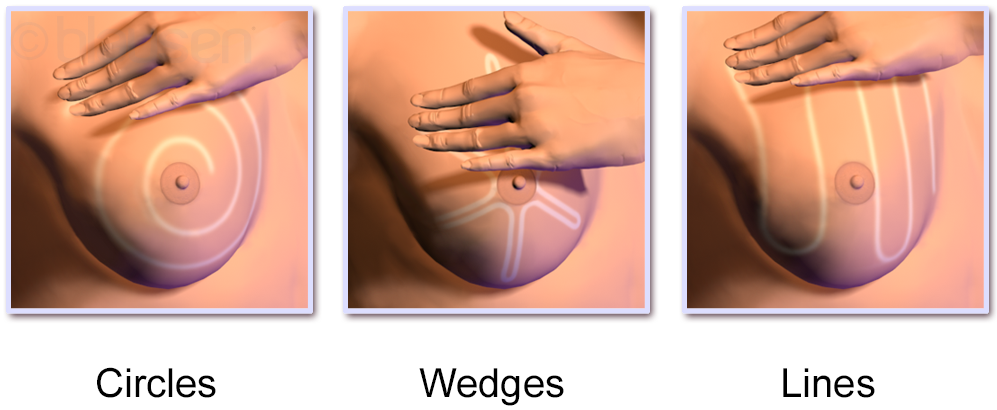
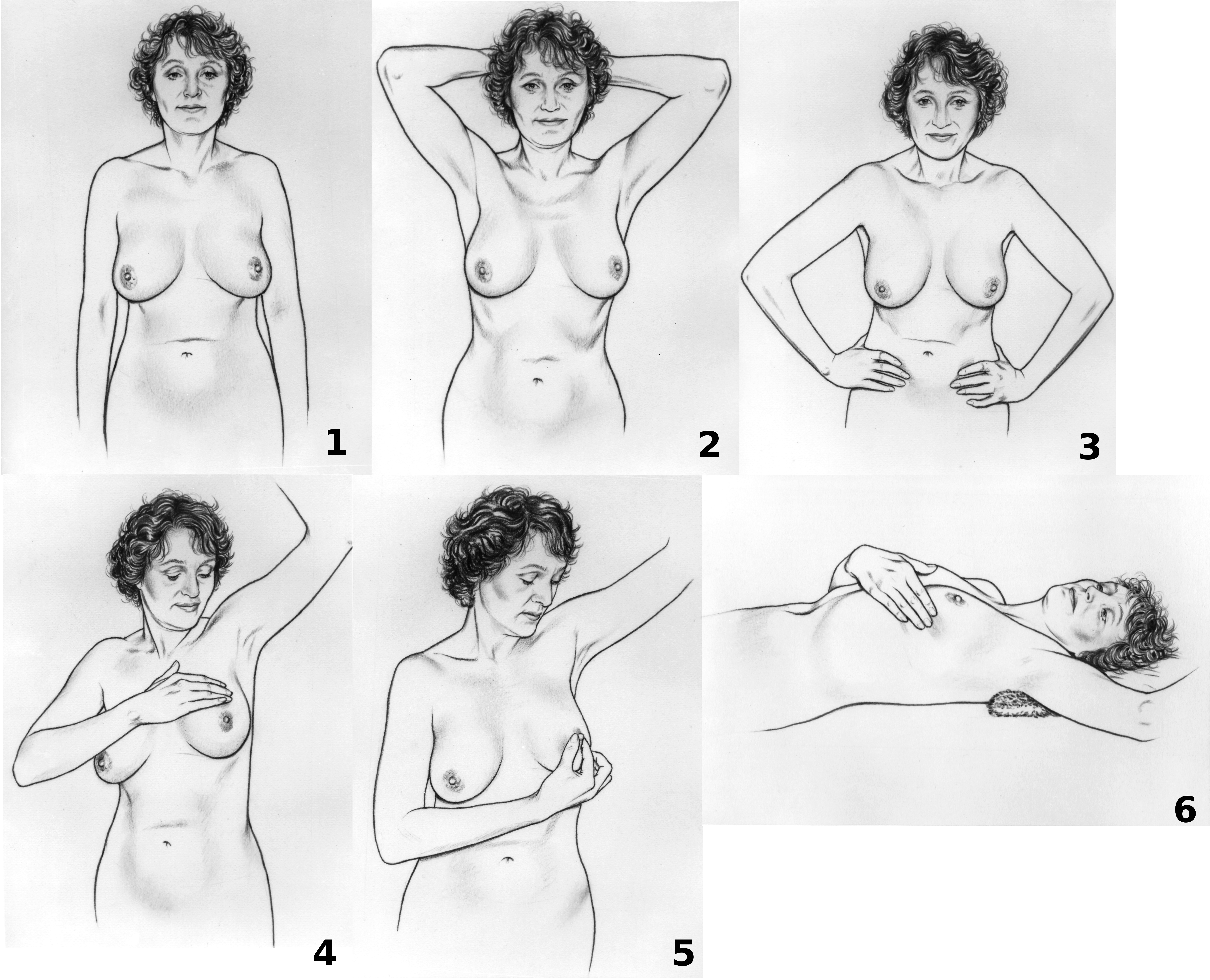
Breast Exam
Breast self-examination (BSE) is a screening method used in an attempt to detect early breast cancer. The method involves the woman herself looking at and feeling each breast for possible lumps, distortions or swelling. BSE was once promoted heavily as a means of finding cancer at a more curable stage, but large randomized controlled studies found that it was not effective in preventing death, and actually caused harm through needless biopsies, surgery, and anxiety. The World Health Organization and other organizations recommend against BSE. Other organizations take a neutral stance, and do not recommend for or against BSE. Breast awareness is an informal alternative to breast self-examinations. Limitations According to a meta-analysis in the Cochrane Collaboration, two large trials in Russia and Shanghai found no beneficial effects of screening by breast self-examination "but do suggest increased harm in terms of increased numbers of benign lesions identified and an increa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima ''Oryza glaberrima'', commonly known as African rice, is one of the two domesticated rice species. It was first domesticated and grown in West Africa around 3,000 years ago. In agriculture, it has largely been replaced by higher-yielding Asian r ...'' (African rice). The name wild rice is usually used for species of the genera ''Zizania (genus), Zizania'' and ''Porteresia'', both wild and domesticated, although the term may also be used for primitive or uncultivated varieties of ''Oryza''. As a cereal, cereal grain, domesticated rice is the most widely consumed staple food for over half of the world's World population, human population,Abstract, "Rice feeds more than half the world's population." especially in Asia and Africa. It is the agricultural commodity with the third-highest worldwide production, after sugarcane and maize. Since sizable portions of sugarcane and ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absolute Risk
Absolute risk (or AR) is the probability or chance of an event. It is usually used for the number of events (such as a disease) that occurred in a group, divided by the number of people in that group. Absolute risk is one of the most understandable ways of communicating health risks to the general public. See also * Absolute risk reduction * Relative risk * Relative risk reduction In epidemiology, the relative risk reduction (RRR) or efficacy is the relative decrease in the risk of an adverse event in the exposed group compared to an unexposed group. It is computed as (I_u - I_e) / I_u, where I_e is the incidence in the expo ... External links Know Your Chances: Understanding Health Statistics References {{Reflist, 30em Medical terminology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relative Risk
The relative risk (RR) or risk ratio is the ratio of the probability of an outcome in an exposed group to the probability of an outcome in an unexposed group. Together with risk difference and odds ratio, relative risk measures the association between the exposure and the outcome. Statistical use and meaning Relative risk is used in the statistical analysis of the data of ecological, cohort, medical and intervention studies, to estimate the strength of the association between exposures (treatments or risk factors) and outcomes. Mathematically, it is the incidence rate of the outcome in the exposed group, I_e, divided by the rate of the unexposed group, I_u. As such, it is used to compare the risk of an adverse outcome when receiving a medical treatment versus no treatment (or placebo), or for environmental risk factors. For example, in a study examining the effect of the drug apixaban on the occurrence of thromboembolism, 8.8% of placebo-treated patients experienced the disease, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast Cancer Screening
Breast cancer screening is the medical screening of asymptomatic, apparently healthy women for breast cancer in an attempt to achieve an earlier diagnosis. The assumption is that early detection will improve outcomes. A number of screening tests have been employed, including clinical and self breast exams, mammography, genetic screening, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging. A clinical or self breast exam involves feeling the breast for breast lump, lumps or other abnormalities. Medical evidence, however, does not support its use in women with a typical risk for breast cancer. Universal screening with mammography is controversial as it may not reduce all-cause mortality and may cause harms through unnecessary treatments and medical procedures. Many national organizations recommend it for most older women. The United States Preventive Services Task Force recommends screening mammography in women at normal risk for breast cancer, every two years between the ages of 50 and 74 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cisplatin
Cisplatin is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of cancers. These include testicular cancer, ovarian cancer, cervical cancer, breast cancer, bladder cancer, head and neck cancer, esophageal cancer, lung cancer, mesothelioma, brain tumors and neuroblastoma. It is given by injection into a vein. Common side effects include bone marrow suppression, hearing problems, including total irreversible hearing loss, usually restricted to one ear, kidney damage, and vomiting. Other serious side effects include numbness, trouble walking, allergic reactions, electrolyte problems, and heart disease. Use during pregnancy can cause harm to the developing fetus. Cisplatin is in the platinum-based antineoplastic family of medications. It works in part by binding to DNA and inhibiting its replication. Cisplatin was discovered in 1845 and licensed for medical use in 1978 and 1979. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Medical use Cisplatin is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trastuzumab
Trastuzumab, sold under the brand name Herceptin among others, is a monoclonal antibody used to treat breast cancer and stomach cancer. It is specifically used for cancer that is HER2 receptor positive. It may be used by itself or together with other chemotherapy medication. Trastuzumab is given by slow injection into a vein and injection just under the skin. Common side effects include fever, infection, cough, headache, trouble sleeping, and rash. Other severe side effects include heart failure, allergic reactions, and lung disease. Use during pregnancy may harm the baby. Trastuzumab works by binding to the HER2 receptor and slowing down cell replication. Trastuzumab was approved for medical use in the United States in September 1998, and in the European Union in August 2000. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. A biosimilar was approved in the European Union in November 2017, and in the United States in December 2018. Medical uses The sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triple-negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is any breast cancer that lacks or show low levels of estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR) and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) overexpression and/or gene amplification (i.e. the tumor is negative on all three tests giving the name ''triple-negative''). Triple-negative is sometimes used as a surrogate term for basal-like. Triple-negative breast cancer comprises 15–20% of all breast cancer cases and affects more young women or women with a mutation in the BRCA1 gene than other breast cancers. Triple-negative breast cancers comprise a very heterogeneous group of cancers. TNBC is the most challenging breast cancer type to treat. Hormone therapy that is used for other breast cancers does not work for TNBC. In its early stages, the cancer is typically treated through surgery, radiation and chemotherapy. In later stages where surgery is not possible or the cancer has spread from the initial localised area, treatment i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fallopian Tube
The fallopian tubes, also known as uterine tubes, oviducts or salpinges (singular salpinx), are paired tubes in the human female that stretch from the uterus to the ovaries. The fallopian tubes are part of the female reproductive system. In other mammals they are only called oviducts. Each tube is a muscular hollow organ that is on average between 10 and 14 cm in length, with an external diameter of 1 cm. It has four described parts: the intramural part, isthmus, ampulla, and infundibulum with associated fimbriae. Each tube has two openings a proximal opening nearest and opening to the uterus, and a distal opening furthest and opening to the abdomen. The fallopian tubes are held in place by the mesosalpinx, a part of the broad ligament mesentery that wraps around the tubes. Another part of the broad ligament, the mesovarium suspends the ovaries in place. An egg cell is transported from an ovary to a fallopian tube where it may be fertilized in the ampulla of the tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peritoneal Cancer
Primary peritoneal cancer or carcinoma is also known as serous surface papillary carcinoma, primary peritoneal carcinoma, extra-ovarian serous carcinoma, primary serous papillary carcinoma, and psammomacarcinoma. It was historically classified under "carcinoma of unknown primary" (CUP). Primary peritoneal cancer (PPC, or PPCa) is a cancer of the cells lining the peritoneum, or abdominal cavity. Histomorphological and molecular biological characteristics suggest that serous carcinomas, which include ovarian serous carcinoma, uterine serous carcinoma, Fallopian tube serous carcinoma, cervical serous carcinoma, and primary peritoneal serous carcinoma really represent one entity. Genetic causes Although the precise causes are not known, a link with certain variants of BRCA1/2 has been described. Furthermore, women with BRCA1/2 mutation have a 5% risk of developing primary peritoneal cancer even after prophylactic oophorectomy. Primary peritoneal carcinoma shows similar rates of tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |